Conformational Dynamics of Lipoxygenases and Their Interaction with Biological Membranes
Abstract
1. Introduction
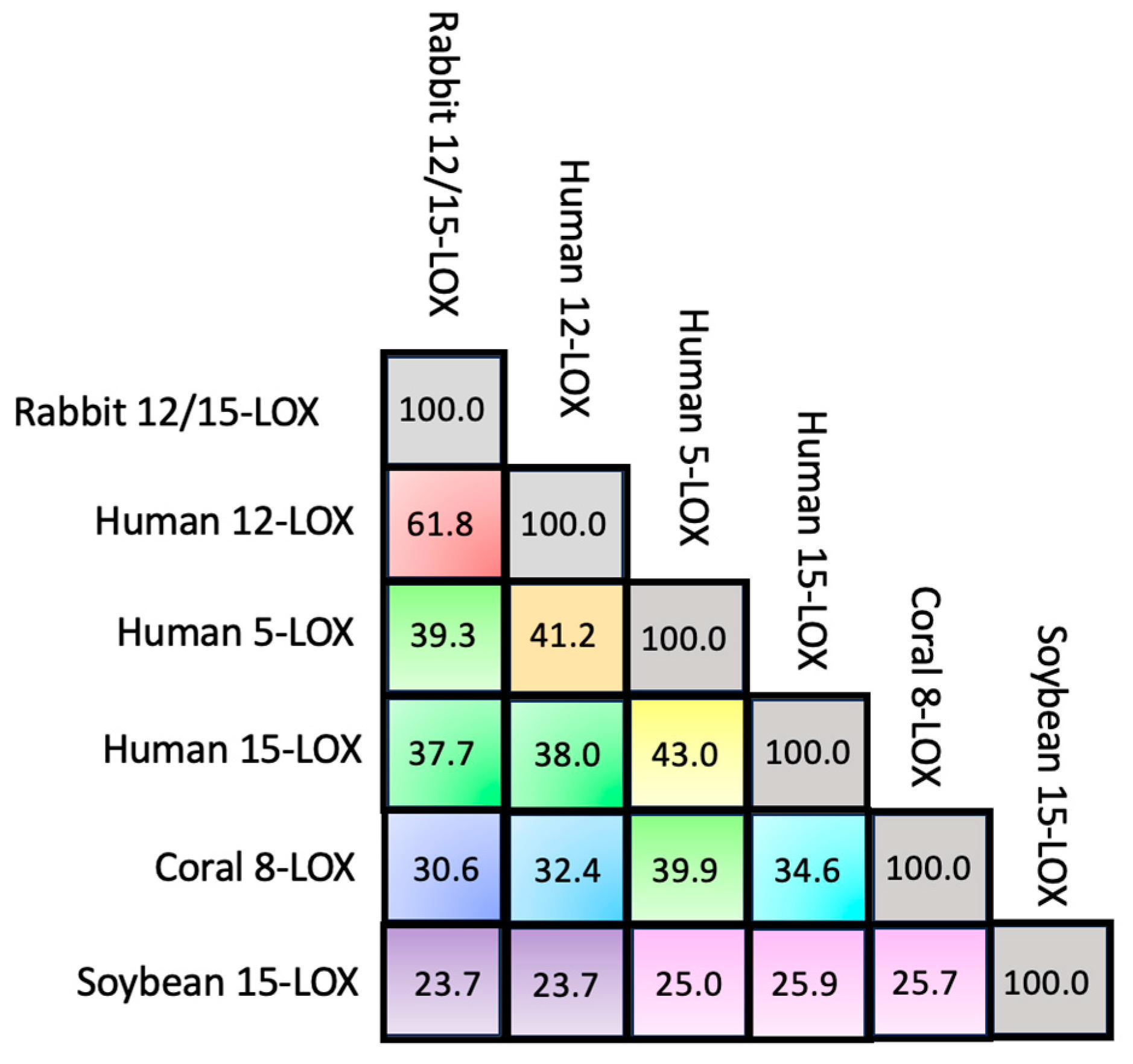
2. Insights into the Architecture of LOXs
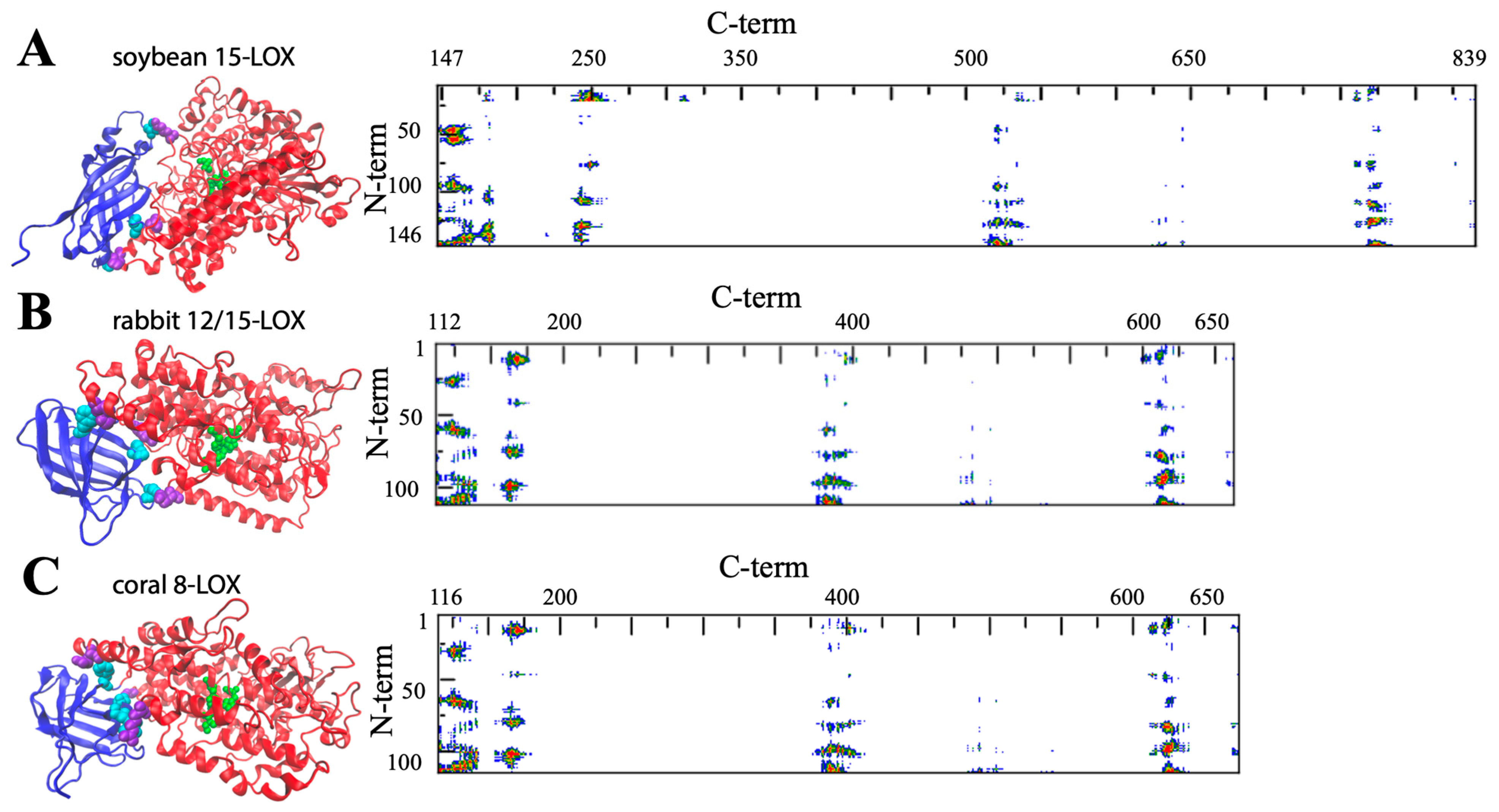
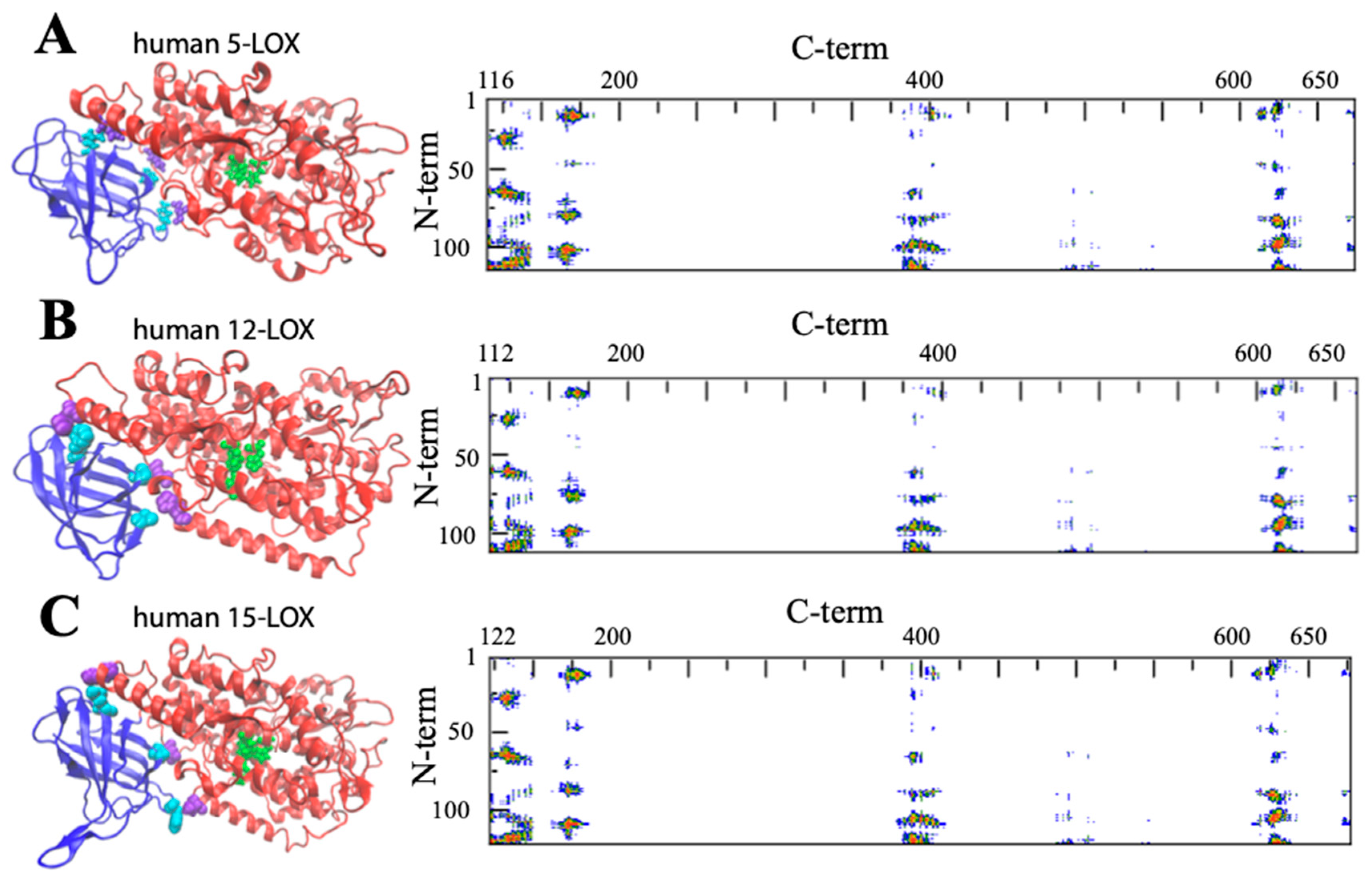
3. Structural Flexibility of LOXs
4. Membrane Binding Ability of LOXs
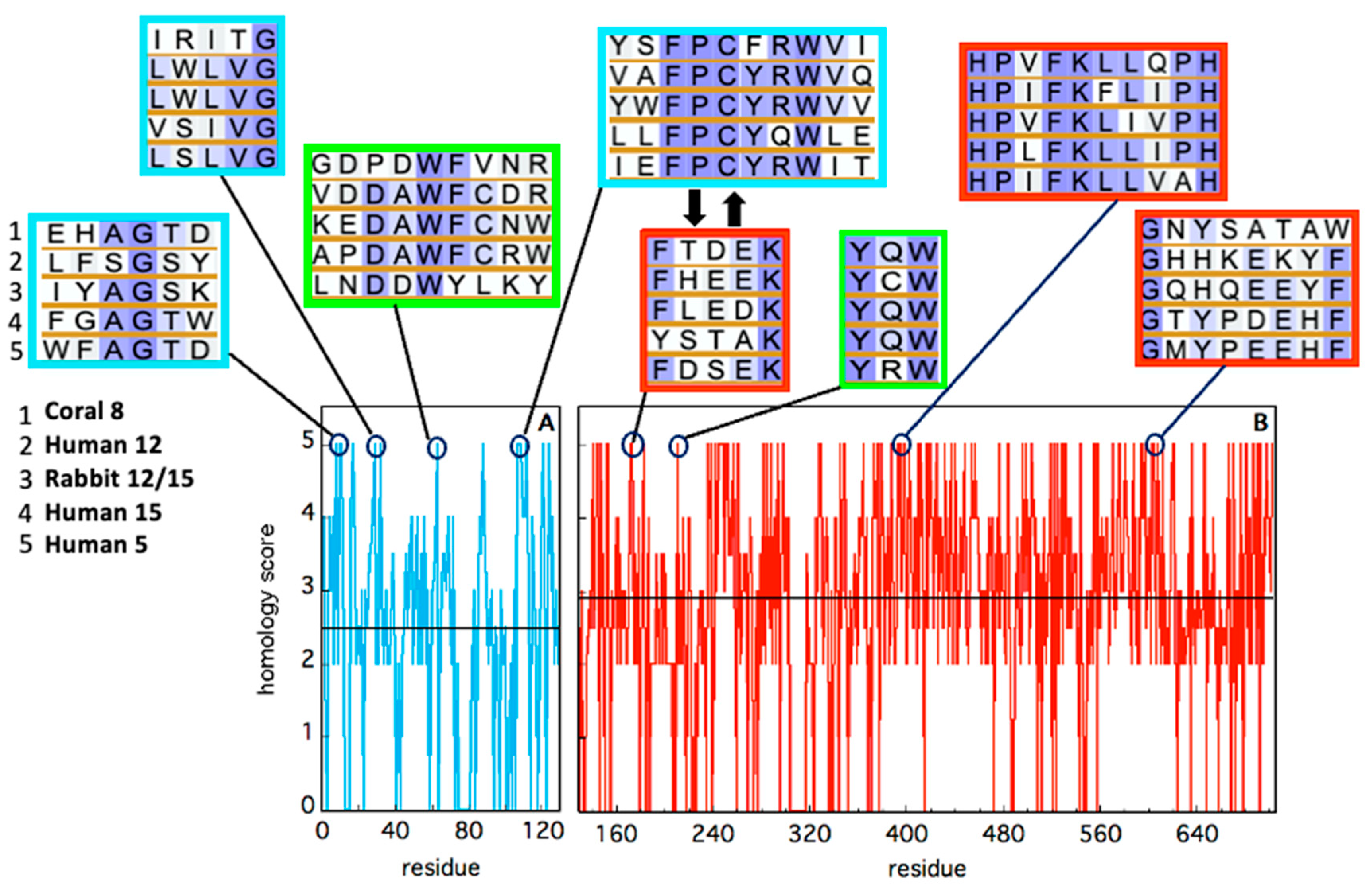
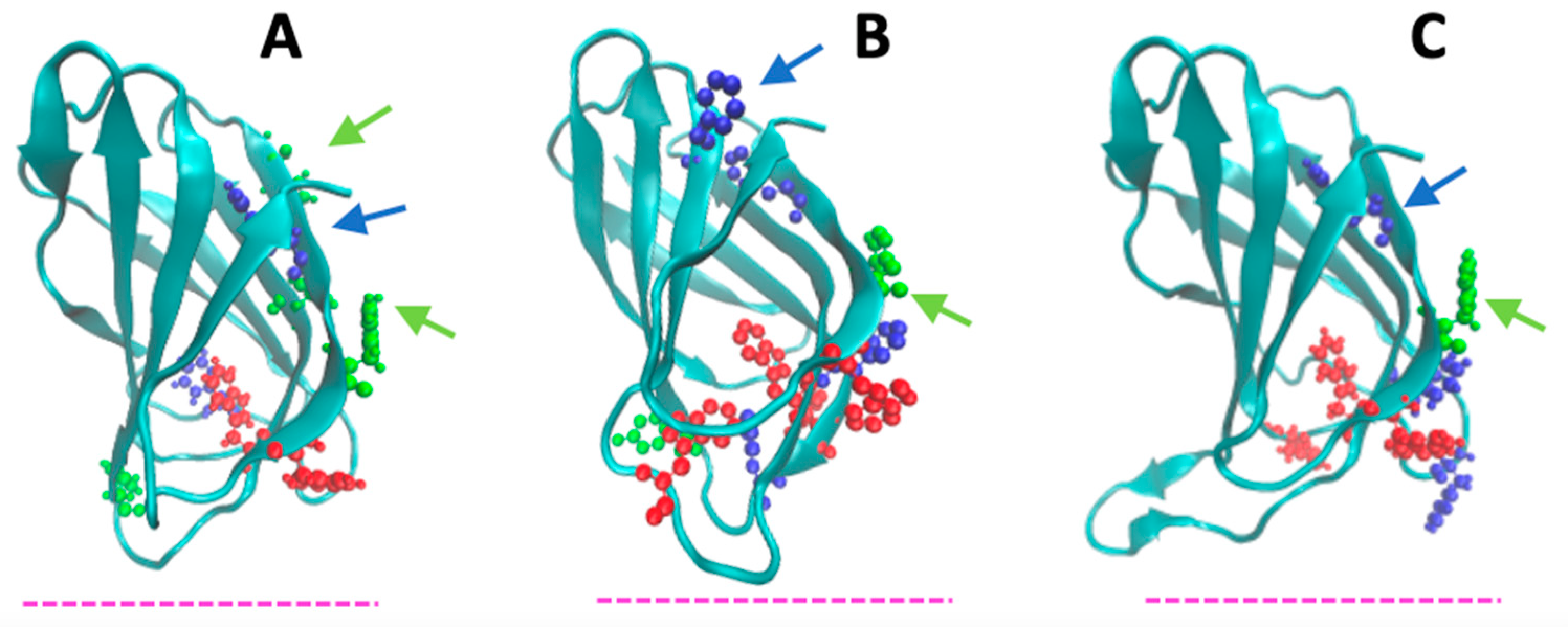
4.1. Peculiar Features of the N-Terminal β-Sandwich Domain
4.2. Membrane-Binding Modeling
4.3. Measure of LOXs Binding to Synthetic Vesicles
4.4. Lessons Learned from Prokaryotic LOXs
4.5. Oligomerization: An Additional Determinant of Membrane Binding by LOXs
5. Future Perspectives
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brash, A.R. Lipoxygenases: Occurrence, functions, catalysis, and acquisition of substrate. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 23679–23682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrisnasari, R.; Hennebelle, M.; Vincken, J.P.; van Berkel, W.J.H.; Ewing, T.A. Bacterial lipoxygenases: Biochemical characteristics, molecular structure and potential applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2022, 61, 108046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanath, K.K.; Varakumar, P.; Pamuru, R.R.; Basha, S.J.; Mehta, S.; Rao, A.D. Plant Lipoxygenases and Their Role in Plant Physiology. J. Plant Biol. 2020, 63, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrzypczak-Jankun, E.; Jankun, J.; Al-Senaidy, A. Human lipoxygenase: Developments in its structure, function, relevance to diseases and challenges in drug development. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 5122–5127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, H.; Banthiya, S.; van Leyen, K. Mammalian lipoxygenases and their biological relevance. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1851, 308–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, T.; Adel, S.; Schumann, R.; Sur, S.; Kakularam, K.R.; Polamarasetty, A.; Redanna, P.; Kuhn, H.; Heydeck, D. Evolutionary aspects of lipoxygenases and genetic diversity of human leukotriene signaling. Prog. Lipid Res. 2015, 57, 13–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, Y.C.; Oh, D.K. Lipoxygenases: Potential starting biocatalysts for the synthesis of signaling compounds. Biotechnol. Adv. 2012, 30, 1524–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuelsson, B.; Dahlén, S.E.; Lindgren, J.A.; Rouzer, C.A.; Serhan, C.N. Leukotrienes and lipoxins: Structures, biosynthesis, and biological effects. Science 1987, 237, 1171–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feinmark, S.J.; Cornicelli, J.A. Is there a role for 15-lipoxygenase in atherogenesis? Biochem. Pharmacol. 1997, 54, 953–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belkner, J.; Wiesner, R.; Rathman, J.; Barnett, J.; Sigal, E.; Kühn, H. Oxygenation of lipoproteins by mammalian lipoxygenases. Eur. J. Biochem. 1993, 213, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapoport, S.M.; Schewe, T.; Wiesner, R.; Halangk, W.; Ludwig, P.; Janicke-Höhne, M.; Tannert, C.; Hiebsch, C.; Klatt, D. The lipoxygenase of reticulocytes. Purification, characterization and biological dynamics of the lipoxygenase; its identity with the respiratory inhibitors of the reticulocyte. Eur. J. Biochem. 1979, 96, 545–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapoport, S.M.; Schewe, T. The maturational breakdown of mitochondria in reticulocytes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1986, 864, 471–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roza, M.; Francke, A. Soyabean lipoxygenase: An iron-containing enzyme. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1973, 327, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, H.W. Soya-bean lipoxygenase: An iron-containing dioxygenase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1973, 327, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siedow, J.N. Plant lipoxygenase: Structure and function. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 1991, 42, 145–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyington, J.C.; Gaffney, B.J.; Amzel, L.M. The three-dimensional structure of an arachidonic acid 15-lipoxygenase. Science 1993, 260, 1482–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyington, J.C.; Gaffney, B.J.; Amzel, L.M. Crystallization and preliminary x-ray analysis of soybean lipoxygenase-1, a non-heme iron-containing dioxygenase. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 12771–12773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prigge, S.T.; Boyington, J.C.; Gaffney, B.J.; Amzel, L.M. Structure conservation in lipoxygenases: Structural analysis of soybean lipoxygenase-1 and modeling of human lipoxygenases. Proteins 1996, 24, 275–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloane, D.L.; Browner, M.F.; Dauter, Z.; Wilson, K.; Fletterick, R.J.; Sigal, E. Purification and crystallization of 15-lipoxygenase from rabbit reticulocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1990, 173, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillmor, S.A.; Villaseñor, A.; Fletterick, R.; Sigal, E.; Browner, M.F. The structure of mammalian 15-lipoxygenase reveals similarity to the lipases and the determinants of substrate specificity. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1997, 4, 1003–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Chon, J.K.; Kim, S.; Shin, W. Conformational flexibility in mammalian 15S-lipoxygenase: Reinterpretation of the crystallographic data. Proteins 2008, 70, 1023–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, N.C.; Bartlett, S.G.; Waight, M.T.; Neau, D.B.; Boeglin, W.E.; Brash, A.R.; Newcomer, M.E. The structure of human 5-lipoxygenase. Science 2011, 331, 217–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobe, M.J.; Neau, D.B.; Mitchell, C.E.; Bartlett, S.G.; Newcomer, M.E. The structure of human 15-lipoxygenase-2 with a substrate mimic. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 8562–8569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Mueser, T.C.; Marnett, L.J.; Funk, M.O., Jr. Crystal structure of 12-lipoxygenase catalytic-domain-inhibitor complex identifies a substrate-binding channel for catalysis. Structure 2012, 20, 1490–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oldham, M.L.; Brash, A.R.; Newcomer, M.E. Insights from the X-ray crystal structure of coral 8R-lipoxygenase: Calcium activation via a C2-like domain and a structural basis of product chirality. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 39545–39552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brock, T.G. Regulating leukotriene synthesis: The role of nuclear 5-lipoxygenase. J. Cell. Biochem. 2005, 96, 1203–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werz, O.; Steinhilber, D. Therapeutic options for 5-lipoxygenase inhibitors. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 112, 701–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werz, O.; Steinhilber, D. Development of 5-lipoxygenase inhibitors--lessons from cellular enzyme regulation. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2005, 70, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rådmark, O.; Werz, O.; Steinhilber, D.; Samuelsson, B. 5-Lipoxygenase, a key enzyme for leukotriene biosynthesis in health and disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1851, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallegos, E.M.; Reed, T.D.; Mathes, F.A.; Guevara, N.V.; Neau, D.B.; Huang, W.; Newcomer, M.E.; Gilbert, N.C. Helical remodeling augments 5-lipoxygenase activity in the synthesis of proinflammatory mediators. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 102282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epand, R.M. Recognition of polyunsaturated acyl chains by enzymes acting on membrane lipids. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1818, 957–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Walther, M.; Hofheinz, K.; Vogel, R.; Roffeis, J.; Kühn, H. The N-terminal β-barrel domain of mammalian lipoxygenases including mouse 5-lipoxygenase is not essential for catalytic activity and membrane binding but exhibits regulatory functions. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2011, 516, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobbs, J.I.; Black, K.A.; Tran, M.; Burger, W.A.C.; Venugopal, H.; Holman, T.R.; Holinstat, M.; Thal, D.M.; Glukhova, A. Cryo-EM structures of human arachidonate 12S-lipoxygenase bound to endogenous and exogenous inhibitors. Blood 2023, 142, 1233–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sievers, F.; Wilm, A.; Dineen, D.G.; Gibson, T.J.; Karplus, K.; Li, W.; Lopez, R.; McWilliam, H.; Remmert, M.; Söding, J.; et al. Fast, scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequence alignments using Clustal Omega. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2011, 7, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, N.C.; Gerstmeier, J.; Schexnaydre, E.E.; Börner, F.; Garscha, U.; Neau, D.B.; Werz, O.; Newcomer, M.E. Structural and mechanistic insights into 5-lipoxygenase inhibition by natural products. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2020, 16, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaffney, B.J. Lipoxygenases: Structural principles and spectroscopy. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 1996, 25, 431–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prigge, S.T.; Boyington, J.C.; Faig, M.; Doctor, K.S.; Gaffney, B.J.; Amzel, L.M. Structure and mechanism of lipoxygenases. Biochimie 1997, 79, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, I.; Heydeck, D.; Hofheinz, K.; Roffeis, J.; O’Donnell, V.B.; Kuhn, H.; Walther, M. Molecular enzymology of lipoxygenases. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2010, 503, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Paola, L.; Mei, G.; Di Venere, A.; Giuliani, A. Exploring the stability of dimers through protein structure topology. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2016, 17, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vangone, A.; Spinelli, R.; Scarano, V.; Cavallo, L.; Oliva, R. COCOMAPS: A web application to analyze and visualize contacts at the interface of biomolecular complexes. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2915–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera--a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Lasker, K.; Schneidman-Duhovny, D.; Webb, B.; Huang, C.C.; Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Meng, E.C.; Sali, A.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera, MODELLER, and IMP: An integrated modeling system. J. Struct. Biol. 2012, 179, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammel, M.; Walther, M.; Prassl, R.; Kuhn, H. Structural flexibility of the N-terminal beta-barrel domain of 15-lipoxygenase-1 probed by small angle X-ray scattering. Functional consequences for activity regulation and membrane binding. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 343, 917–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, W.; Ivanov, I.; Svergun, D.I.; Borbulevych, O.Y.; Aleem, A.M.; Stehling, S.; Jankun, J.; Kühn, H.; Skrzypczak-Jankun, E. Probing dimerization and structural flexibility of mammalian lipoxygenases by small-angle X-ray scattering. J. Mol. Biol. 2011, 409, 654–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, G.; Di Venere, A.; Nicolai, E.; Angelucci, C.B.; Ivanov, I.; Sabatucci, A.; Dainese, E.; Kuhn, H.; Maccarrone, M. Structural properties of plant and mammalian lipoxygenases. Temperature-dependent conformational alterations and membrane binding ability. Biochemistry 2008, 47, 9234–9242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Venere, A.; Nicolai, E.; Ivanov, I.; Dainese, E.; Adel, S.; Angelucci, B.C.; Kuhn, H.; Maccarrone, M.; Mei, G. Probing conformational changes in lipoxygenases upon membrane binding: Fine-tuning by the active site inhibitor ETYA. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1841, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moin, S.T.; Hofer, T.S.; Sattar, R.; Ul-Haq, Z. Molecular dynamics simulation of mammalian 15S-lipoxygenase with AMBER force field. Eur. Biophys. J. 2011, 40, 715–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, I.; Di Venere, A.; Horn, T.; Scheerer, P.; Nicolai, E.; Stehling, S.; Richter, C.; Skrzypczak-Jankun, E.; Mei, G.; Maccarrone, M.; et al. Tight association of N-terminal and catalytic subunits of rabbit 12/15-lipoxygenase is important for protein stability and catalytic activity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1811, 1001–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Droege, K.D.; Keithly, M.E.; Sanders, C.R.; Armstrong, R.N.; Thompson, M.K. Structural Dynamics of 15-Lipoxygenase-2 via Hydrogen-Deuterium Exchange. Biochemistry 2017, 56, 5065–5074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eek, P.; Järving, R.; Järving, I.; Gilbert, N.C.; Newcomer, M.E.; Samel, N. Structure of a calcium-dependent 11R-lipoxygenase suggests a mechanism for Ca2+ regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 22377–22386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammarberg, T.; Provost, P.; Persson, B.; Rådmark, O. The N-terminal domain of 5-lipoxygenase binds calcium and mediates calcium stimulation of enzyme activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 38787–38793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.S.; Funk, C.D. The N-terminal “beta-barrel” domain of 5-lipoxygenase is essential for nuclear membrane translocation. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, F.K.; D’Arcy, A.; Hunziker, W. Structure of human pancreatic lipase. Nature 1990, 343, 771–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chahinian, H.; Sias, B.; Carrière, F. The C-terminal domain of pancreatic lipase: Functional and structural analogies with c2 domains. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2000, 1, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Walther, M.; Anton, M.; Wiedmann, M.; Fletterick, R.; Kuhn, H. The N-terminal domain of the reticulocyte-type 15-lipoxygenase is not essential for enzymatic activity but contains determinants for membrane binding. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 27360–27366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanov, I.; Kuhn, H.; Heydeck, D. Structural and functional biology of arachidonic acid 15-lipoxygenase-1 (ALOX15). Gene 2015, 573, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maccarrone, M.; Salucci, M.L.; van Zadelhoff, G.; Malatesta, F.; Veldink, G.; Vliegenthart, J.F.; Finazzi-Agrò, A. Tryptic digestion of soybean lipoxygenase-1 generates a 60 kDa fragment with improved activity and membrane binding ability. Biochemistry 2001, 40, 6819–6827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Di Venere, A.; Salucci, M.L.; van Zadelhoff, G.; Veldink, G.; Mei, G.; Rosato, N.; Finazzi-Agrò, A.; Maccarrone, M. Structure-to-function relationship of mini-lipoxygenase; a 60-kDa fragment of soybean lipoxygenase-1 with lower stability but higher enzymatic activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 20, 18281–18288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, S.; Das, S.; Funk, C.D.; Murray, D.; Cho, W. Molecular basis of the specific subcellular localization of the C2-like domain of 5-lipoxygenase. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 13167–13174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pande, A.H.; Qin, S.; Tatulian, S.A. Membrane fluidity is a key modulator of membrane binding; insertion; and activity of 5-lipoxygenase. Biophys. J. 2005, 6, 4084–4094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walther, M.; Wiesner, R.; Kuhn, H. Investigations into calcium-dependent membrane association of 15-lipoxygenase-1. Mechanistic roles of surface-exposed hydrophobic amino acids and calcium. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 3717–3725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohlik, D.L.; Patel, E.; Gilbert, N.C.; Offenbacher, A.R.; Garcia, B.L. Investigating membrane-binding properties of lipoxygenases using surface plasmon resonance. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2023, 670, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleem, A.M.; Jankun, J.; Dignam, J.D.; Walther, M.; Kühn, H.; Svergun, D.I.; Skrzypczak-Jankun, E. Human platelet 12-lipoxygenase, new findings about its activity, membrane binding and low-resolution structure. J. Mol. Biol. 2008, 376, 193–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dainese, E.; Sabatucci, A.; Angelucci, C.B.; Barsacchi, D.; Chiarini, M.; Maccarrone, M. Impact of Embedded Endocannabinoids and Their Oxygenation by Lipoxygenase on Membrane Properties. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2012, 3, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maccarrone, M.; Di Marzo, V.; Gertsch, J.; Grether, U.; Howlett, A.C.; Hua, T.; Makriyannis, A.; Piomelli, D.; Ueda, N.; van der Stelt, M. Goods and Bads of the Endocannabinoid System as a Therapeutic Target: Lessons Learned after 30 Years. Pharmacol. Rev. 2023, 75, 885–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomize, M.A.; Pogozheva, I.D.; Joo, H.; Mosberg, H.I.; Lomize, A.L. OPM database and PPM web server: Resources for positioning of proteins in membranes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D370–D376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomize, A.L.; Todd, S.C.; Pogozheva, I.D. Spatial arrangement of proteins in planar and curved membranes by PPM 3.0. Protein Sci. 2022, 31, 930–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werz, O.; Burkert, E.; Samuelsson, B.; Rådmark, O.; Steinhilber, D. Activation of 5-lipoxygenase by cell stress is calcium independent in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Blood 2002, 99, 1044–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.B.; Purhonen, P.; Hebert, H.; Jegerschöld, C. Arachidonic acid promotes the binding of 5-lipoxygenase on nanodiscs containing 5-lipoxygenase activating protein in the absence of calcium-ions. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0228607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garreta, A.; Val-Moraes, S.P.; García-Fernández, Q.; Busquets, M.; Juan, C.; Oliver, A.; Ortiz, A.; Gaffney, B.J.; Fita, I.; Manresa, À.; et al. Structure and interaction with phospholipids of a prokaryotic lipoxygenase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. FASEB J. 2013, 27, 4811–4821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newie, J.; Andreou, A.; Neumann, P.; Einsle, O.; Feussner, I.; Ficner, R.; Crystal structure of a lipoxygenase from Cyanothece, sp. may reveal novel features for substrate acquisition. J. Lipid Res. 2016, 57, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dainese, E.; Angelucci, C.B.; Sabatucci, A.; De Filippis, V.; Mei, G.; Maccarrone, M. A novel role for iron in modulating the activity and membrane-binding ability of a trimmed soybean lipoxygenase-1. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 1725–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banthiya, S.; Kalms, J.; Yoga, E.G.; Ivanov, I.; Carpena, X.; Hamberg, M.; Kuhn, H.; Scheerer, P. Structural and functional basis of phospholipid oxygenase activity of bacterial lipoxygenase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1861, 1681–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Wang, G.; Feng, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhou, X.; Du, G.; Chen, J. The N-Terminal α-Helix Domain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Lipoxygenase Is Required for Its Soluble Expression in Escherichia coli but Not for Catalysis. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 26, 1701–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banthiya, S.; Pekárová, M.; Kuhn, H.; Heydeck, D. Secreted lipoxygenase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa exhibits biomembrane oxygenase activity and induces hemolysis in human red blood cells. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2015, 584, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonhardt, R.H.; Plagemann, I.; Linke, D.; Zelena, K.; Berger, R.G. Orthologous lipoxygenases of Pleurotus spp.—A comparison of substrate specificity and sequence homology. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2013, 97, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dainese, E.; Sabatucci, A.; Van Zadelhoff, G.; Angelucci, C.B.; Vachette, P.; Veldink, G.A.; Agrò, A.F.; Maccarrone, M. Structural Stability of Soybean Lipoxygenase-1 in Solution as Probed by Small Angle x-Ray Scattering. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 349, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Häfner, A.K.; Cernescu, M.; Hofmann, B.; Ermisch, M.; Hörnig, M.; Metzner, J.; Schneider, G.; Brutschy, B.; Steinhilber, D. Dimerization of human 5-lipoxygenase. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 392, 1097–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wecksler, A.T.; Kenyon, V.; Deschamps, J.D.; Holman, T.R. Substrate specificity changes for human reticulocyte and epithelial 15-lipoxygenases reveal allosteric product regulation. Biochemistry 2008, 47, 7364–7375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanov, I.; Shang, W.; Toledo, L.; Masgrau, L.; Svergun, D.I.; Stehling, S.; Gómez, H.; Di Venere, A.; Mei, G.; Lluch, J.M.; et al. Ligand-induced formation of transient dimers of mammalian 12/15-lipoxygenase: A key to allosteric behavior of this class of enzymes? Proteins 2012, 3, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stank, A.; Kokh, D.B.; Fuller, J.C.; Wade, R.C. Protein Binding Pocket Dynamics. Acc. Chem. Res. 2016, 49, 809–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Börner, F.; Pace, S.; Jordan, P.M.; Gerstmeier, J.; Gomez, M.; Rossi, A.; Gilbert, N.C.; Newcomer, M.E.; Werz, O. Allosteric Activation of 15-Lipoxygenase-1 by Boswellic Acid Induces the Lipid Mediator Class Switch to Promote Resolution of Inflammation. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, e2205604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakonjac, M.; Fischer, L.; Provost, P.; Werz, O.; Steinhilber, D.; Samuelsson, B.; Rådmark, O. Coactosin-like protein supports 5-lipoxygenase enzyme activity and up-regulates leukotriene A4 production. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 13150–13155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esser, J.; Rakonjac, M.; Hofmann, B.; Fischer, L.; Provost, P.; Schneider, G.; Steinhilber, D.; Samuelsson, B.; Rådmark, O. Coactosin-like protein functions as a stabilizing chaperone for 5-lipoxygenase: Role of tryptophan 102. Biochem. J. 2009, 425, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torras, J.; Maccarrone, M.; Dainese, E. Molecular dynamics study on the Apo- and Holo-forms of 5-lipoxygenase. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2018, 65, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schewe, T.; Halangk, W.; Hiebsch, C.; Rapoport, S.M. A lipoxygenase in rabbit reticulocytes which attacks phospholipids and intact mitochondria. FEBS Lett. 1975, 60, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroschwald, P.; Kroschwald, A.; Kühn, H.; Ludwig, P.; Thiele, B.J.; Höhne, M.; Schewe, T.; Rapoport, S.M. Occurrence of the erythroid cell specific arachidonate 15-lipoxygenase in human reticulocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1989, 160, 954–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, C.; Höhne, M.; Gnau, P.; Schwennesen, K.; Kindl, H. The N-terminal beta-barrel structure of lipid body lipoxygenase mediates its binding to liposomes and lipid bodies. Eur. J. Biochem. 2000, 267, 1100–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters-Golden, M.; Brock, T.G. 5-lipoxygenase and FLAP. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2003, 69, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häfner, A.K.; Gerstmeier, J.; Hörnig, M.; George, S.; Ball, A.K.; Schröder, M.; Garscha, U.; Werz, O.; Steinhilber, D. Characterization of the interaction of human 5-lipoxygenase with its activating protein FLAP. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1851, 1465–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haeggström, J.Z.; Funk, C.D. Lipoxygenase and leukotriene pathways: Biochemistry, biology, and roles in disease. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 5866–5898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, S.; Doble, M.; Manju, S.L. 5-Lipoxygenase as a drug target: A review on trends in inhibitors structural design, SAR and mechanism based approach. Bioorg Med. Chem. 2019, 27, 3745–3759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scala, A.; Allmann, S.; Mirabella, R.; Haring, M.A.; Schuurink, R.C. Green leaf volatiles: A plant’s multifunctional weapon against herbivores and pathogens. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 17781–17811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, M.; Yan, J.; Khurshid, M.; Weng, W.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, K. Jasmonic Acid Signaling Pathway in Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Mandal, R.; Singh, A.; Singh, A.P. Legume lipoxygenase: Strategies for application in food industry. Legume Sci. 2020, 2, e44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| LOX Isozyme | Kd (μM) | Membrane * | Condition (T, pH, [Salts], [Ions]) | Method ** | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soybean 15-LOX (LOX1) | 17.9 ± 2.0 | DPPC | Tris HCl pH 8 0.2 M 4 mM CaCl2 | FRET | Dainese et al. (2010) [72] |
| Soybean mini-15-LOX | 9.2 ± 1.0 | DPPC | Tris HCl pH 8 0.2 M 4 mM CaCl2 | FRET | Dainese et al. (2010) [72] |
| Soybean mini-15-LOX (Apo form) | 45.4 ± 4.3 | DPPC | Tris HCl pH 8 0.2 M 4 mM CaCl2 | FRET | Dainese et al. (2010) [72] |
| Soybean 15-LOX | 0.35 ± 0.03 | POPC | Tris HCl pH 7.4 50 mM 0.2 mM CaCl2 22 °C | FRET | Mei et al. (2008) [45] |
| Soybean 15-LOX | 0.36 ± 0.03 | DPPC | Tris HCl pH 7.4 50 mM 0.2 mM CaCl2 22 °C | FRET | Mei et al. (2008) [45] |
| Rabbit 12/15 LOX | 0.28 ± 0.02 | POPC | Tris HCl pH 7.4 50 mM 0.2 mM CaCl2 22 °C | FRET | Mei et al. (2008) [45] |
| Rabbit 12/15 LOX | 0.35 ± 0.03 | DPPC | Tris HCl pH 7.4 50 mM 0.2 mM CaCl2 22 °C | FRET | Mei et al. (2008) [45] |
| Human 5-LOX | 1.15 | DPPC | Tris-HCl pH 7.5 50 mM 150 mM NaCl, 0.1 mM EGTA, 0.3 mM CaCl2 22 °C | FRET | Pande et al. (2005) [60] |
| Human 5-LOX | 0.78 | POPC | Tris-HCl pH 7.5 50 mM 150 mM NaCl, 0.1 mM EGTA, 0.3 mM CaCl2 22 °C | FRET | Pande et al. (2005) [60] |
| Human 5-LOX | 0.56 | PLPC | Tris-HCl pH 7.5 50 mM 150 mM NaCl, 0.1 mM EGTA, 0.3 mM CaCl2 22 °C | FRET | Pande et al. (2005) [60] |
| Human 5-LOX | 0.24 | PAPC | Tris-HCl pH 7.5 50 mM 150 mM NaCl, 0.1 mM EGTA, 0.3 mM CaCl2 22 °C | FRET | Pande et al. (2005) [60] |
| Human 5-LOX | 0.32 | PDPC | Tris-HCl pH 7.5 50 mM 150 mM NaCl, 0.1 mM EGTA, 0.3 mM CaCl2 22 °C | FRET | Pande et al. (2005) [60] |
| Human 5-LOX (N-terminal) | ≈0.001 | PC | Hepes pH 7.4 10 mM 0.1 M NaCl 0.1 mM CaCl2 24 °C | SPR | Kulkarni et al. (2002) [59] |
| Human 5-LOX (N-terminal) | 2.5 ± 0.4 | PC | Hepes pH 7.4 10 mM 0.1 M NaCl 0.001 mM CaCl2 24 °C | SPR | Kulkarni et al. (2002) [59] |
| Coral 8R-LOX | 0.28 ± 0.04 | PC:PE | Tris-HCl pH 8.0 50 mM | SPR | Rohlik et al. (2023) [62] |
| Coral 8R-LOX | 0.21 ± 0.02 | PC:PS | Tris-HCl pH 8.0 50 mM | SPR | Rohlik et al. (2023) [62] |
| Human 15-LOX-2 | 0.63 ± 0.02 | PC:PS | Tris-HCl pH 8.0 50 mM | SPR | Rohlik et al. (2023) [62] |
| Coral 8R-LOX | 11.4 ± 2.7 | POPC:POPS (3:1) | Tris-HCl pH 7.5 50 mM, 500 mM NaCl, 2 mM EDTA 4 mM CaCl2 | FRET | Oldham et al. (2005) [25] |
| Coral 11R-LOX | 0.59 ± 0.06 | SUV PC | Tris-HCl pH 8.0 50 mM, 100 mM NaCl 25 °C | SPR | Eek et al. (2012) [50] |
| Coral 11R-LOX | 0.12 ± 0.02 | SUV PC | Tris-HCl pH 8.0 50 mM, 100 mM NaCl 0.4 mM CaCl2 25 °C | SPR | Eek et al. (2012) [50] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Erba, F.; Mei, G.; Minicozzi, V.; Sabatucci, A.; Di Venere, A.; Maccarrone, M. Conformational Dynamics of Lipoxygenases and Their Interaction with Biological Membranes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2241. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25042241
Erba F, Mei G, Minicozzi V, Sabatucci A, Di Venere A, Maccarrone M. Conformational Dynamics of Lipoxygenases and Their Interaction with Biological Membranes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(4):2241. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25042241
Chicago/Turabian StyleErba, Fulvio, Giampiero Mei, Velia Minicozzi, Annalaura Sabatucci, Almerinda Di Venere, and Mauro Maccarrone. 2024. "Conformational Dynamics of Lipoxygenases and Their Interaction with Biological Membranes" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 4: 2241. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25042241
APA StyleErba, F., Mei, G., Minicozzi, V., Sabatucci, A., Di Venere, A., & Maccarrone, M. (2024). Conformational Dynamics of Lipoxygenases and Their Interaction with Biological Membranes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(4), 2241. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25042241








