Chronic Gut Inflammation and Dysbiosis in IBS: Unraveling Their Contribution to Atopic Dermatitis Progression
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
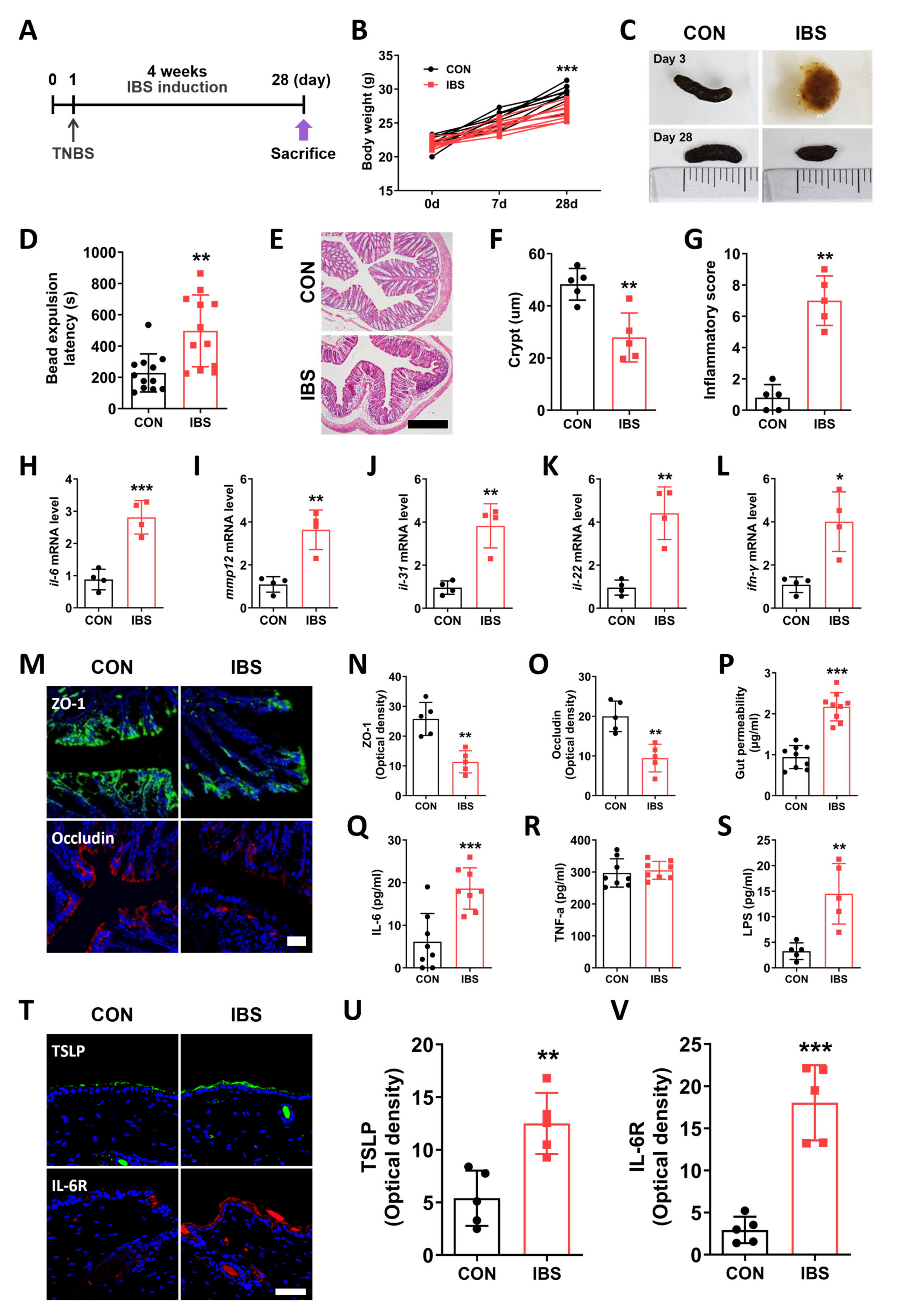
2.1. GI Dysfunction in the TNBS-Induced IBS Model
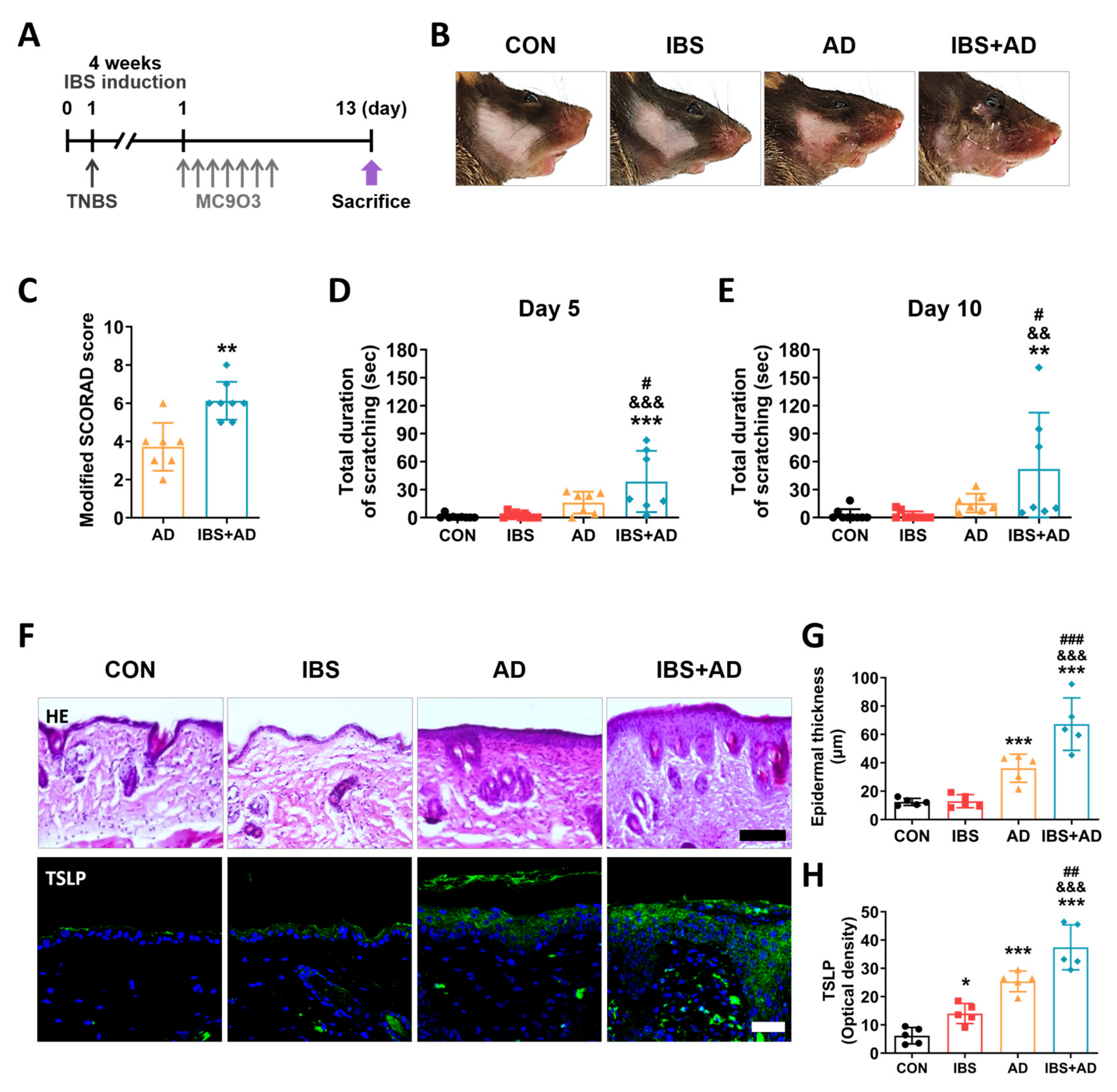
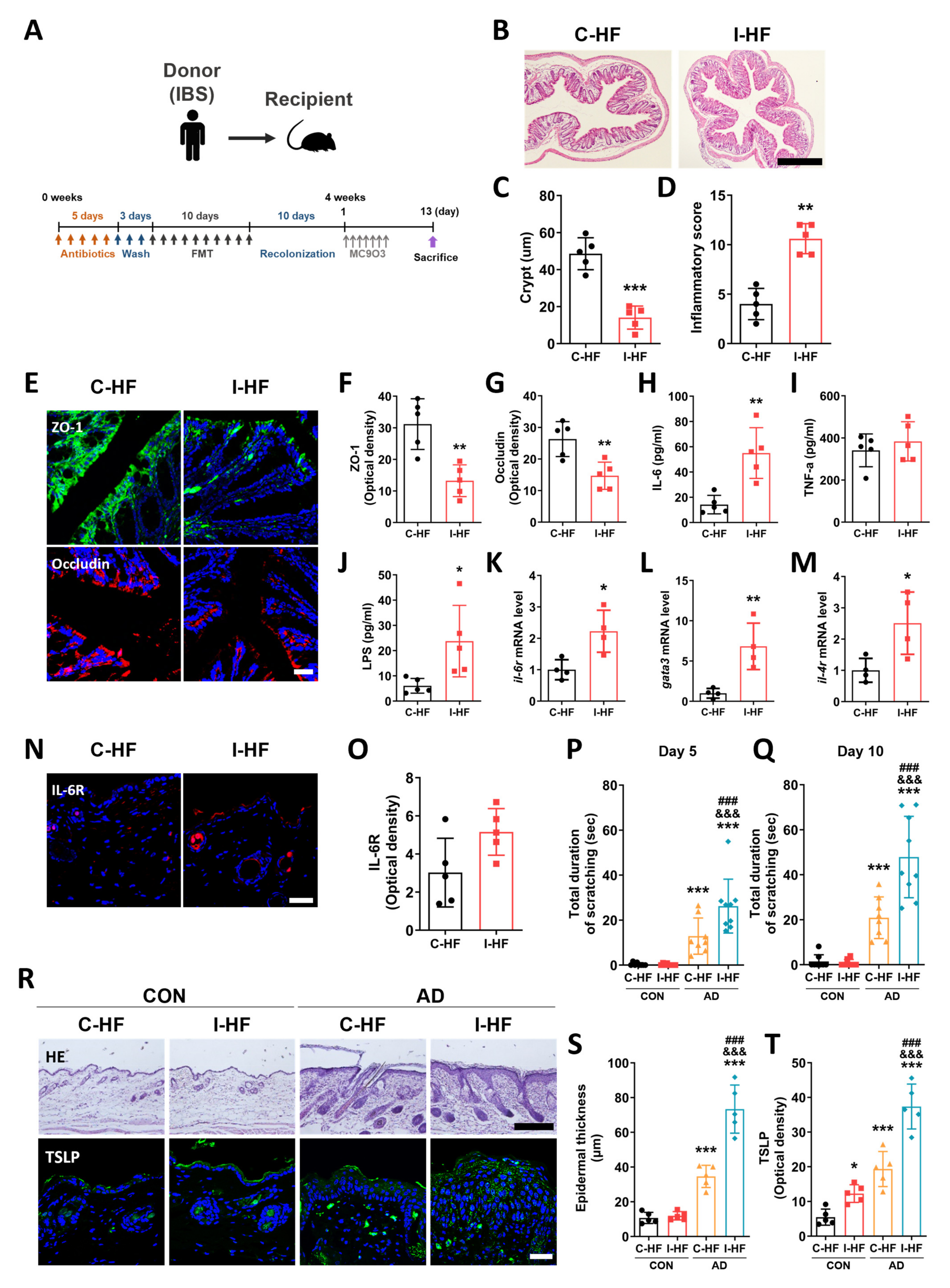
2.2. Leaky Gut and Alterations in the Skin of the IBS Model
2.3. Exacerbation of AD Symptoms by IBS
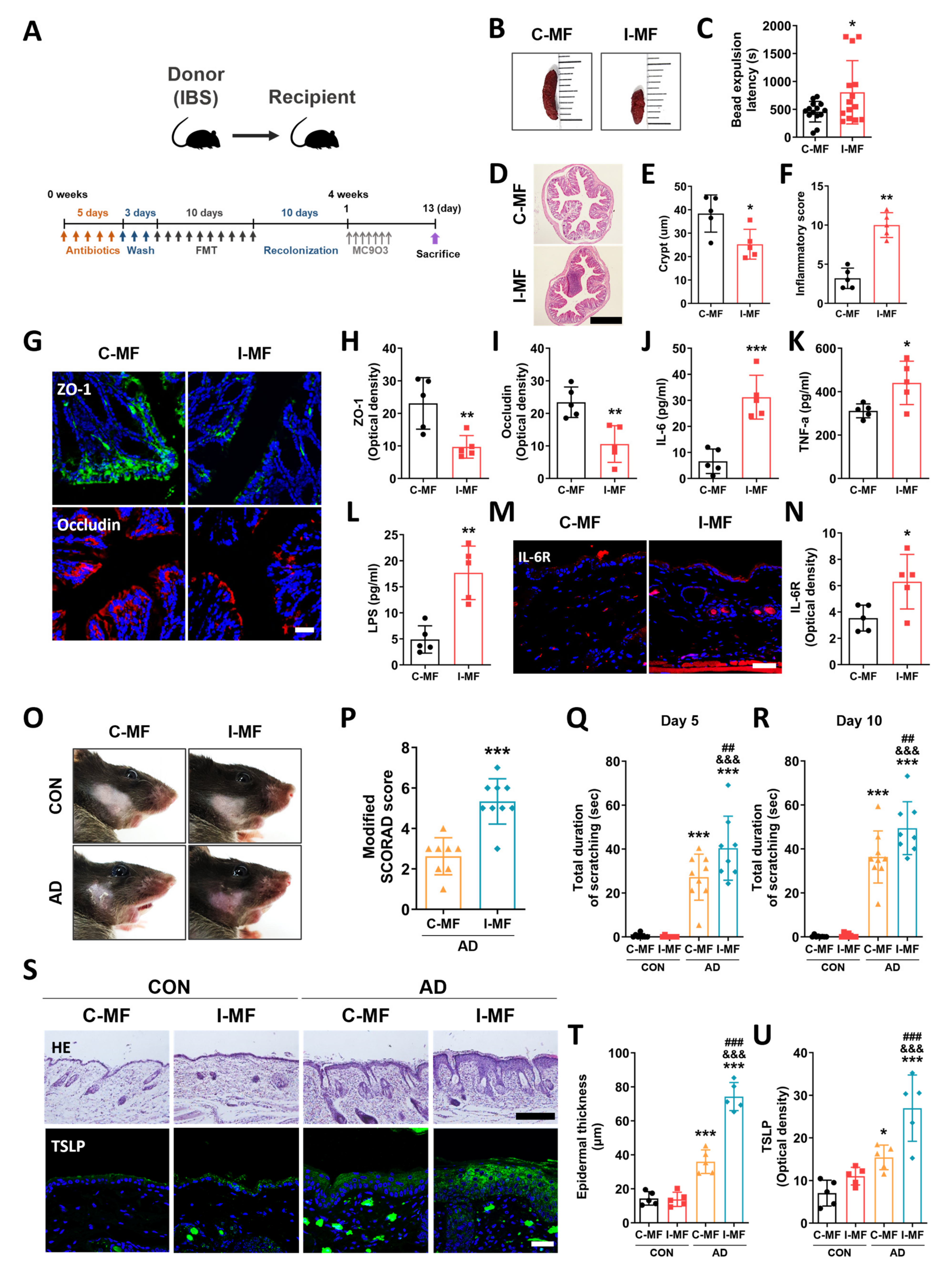
2.4. Exacerbation of AD Symptoms in IBS Mice–Fecal Microbiota-Transplanted Mice
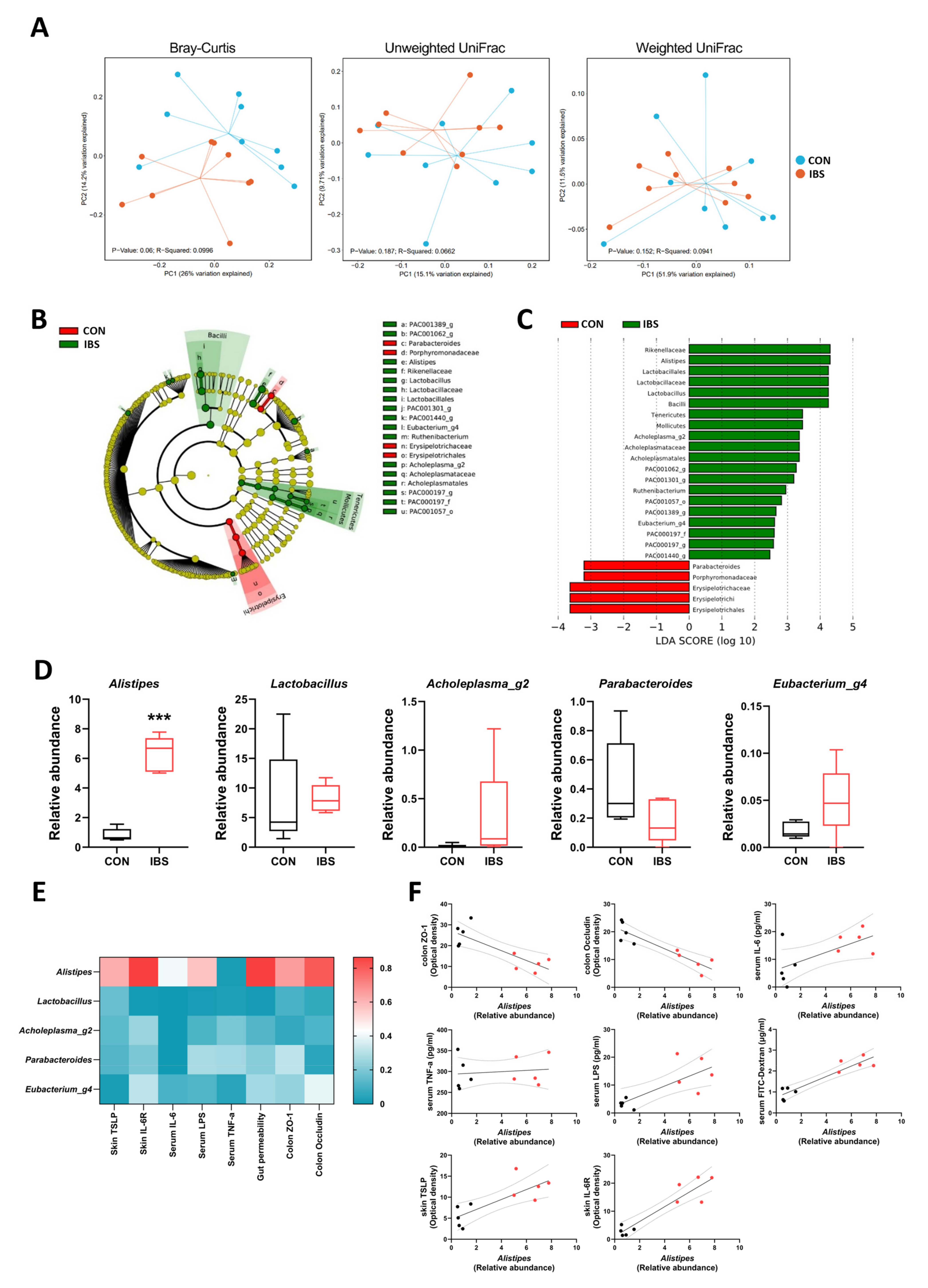
2.5. Gut Microbial Dysbiosis and Its Association with Gut–Blood–Skin Axis Markers in IBS Mice
2.6. Aggravation of AD Symptoms in IBS Patient–Fecal Microbiota-Transplanted Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) Model
4.3. Atopic Dermatitis (AD) Model
4.4. Modified SCORAD Score
4.5. Scratching Behavior
4.6. Stool Collection
4.7. Bead Expulsion Test
4.8. Hematoxylin and Eosin Staining
4.9. Quantitative RT-PCR
4.10. In Vivo Intestinal Permeability Test
4.11. Evaluation of Inflammatory Cytokine Levels
4.12. Endotoxin Assay
4.13. Immunofluorescence Analysis
4.14. 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing
4.15. The IBS Patient and Healthy Control
4.16. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation
4.17. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, G.; Seok, J.K.; Kang, H.C.; Cho, Y.Y.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, J.Y. Skin Barrier Abnormalities and Immune Dysfunction in Atopic Dermatitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nutten, S. Atopic dermatitis: Global epidemiology and risk factors. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2015, 66 (Suppl. S1), 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langan, S.M.; Irvine, A.D.; Weidinger, S. Atopic dermatitis. Lancet 2020, 396, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fyhrquist, N.; Werner, P.; Alenius, H. Host-microbiome interactions in atopic and allergic diseases. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2023, 35, 100420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Wu, L.; Xiao, S.; Ji, Y.; Tan, Y.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, G. Dysregulation of the gut-brain-skin axis and key overlapping inflammatory and immune mechanisms of psoriasis and depression. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 137, 111065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, N.; Li, N.; Duan, X.; Niu, H. Interaction between the gut microbiome and mucosal immune system. Mil. Med. Res. 2017, 4, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungar, B.; Garcet, S.; Gonzalez, J.; Dhingra, N.; Correa da Rosa, J.; Shemer, A.; Krueger, J.G.; Suarez-Farinas, M.; Guttman-Yassky, E. An Integrated Model of Atopic Dermatitis Biomarkers Highlights the Systemic Nature of the Disease. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vich Vila, A.; Imhann, F.; Collij, V.; Jankipersadsing, S.A.; Gurry, T.; Mujagic, Z.; Kurilshikov, A.; Bonder, M.J.; Jiang, X.; Tigchelaar, E.F.; et al. Gut microbiota composition and functional changes in inflammatory bowel disease and irritable bowel syndrome. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaap8914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Feng, S.; Li, Y.; Zhang, C.; Chao, G.; Zhang, S. Gut microbiota and intestinal immunity—A crosstalk in irritable bowel syndrome. Immunology 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiecolt-Glaser, J.K.; Wilson, S.J.; Bailey, M.L.; Andridge, R.; Peng, J.; Jaremka, L.M.; Fagundes, C.P.; Malarkey, W.B.; Laskowski, B.; Belury, M.A. Marital distress, depression, and a leaky gut: Translocation of bacterial endotoxin as a pathway to inflammation. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2018, 98, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passeron, T.; Piche, T. Skin manifestations associated with irritable bowel syndrome. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020, 34, e651–e652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, U.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, H.; Kim, D.Y.; Kang, S.; Koh, S.J.; Park, H. Various skin manifestations related to inflammatory bowel disease: A nationwide cross-sectional study on the Korean population. J. Dermatol. 2021, 48, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Yang, W.R.; Wang, X.H.; Li, G.Q.; Xu, L.Q.; Cui, X.; Liu, Y.; Zuo, X.L. Clostridium butyricum alleviates intestinal low-grade inflammation in TNBS-induced irritable bowel syndrome in mice by regulating functional status of lamina propria dendritic cells. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 5469–5482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, S.; Thiemermann, C. Role of Metabolic Endotoxemia in Systemic Inflammation and Potential Interventions. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 594150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, S.R.; The, L.; Batia, L.M.; Beattie, K.; Katibah, G.E.; McClain, S.P.; Pellegrino, M.; Estandian, D.M.; Bautista, D.M. The epithelial cell-derived atopic dermatitis cytokine TSLP activates neurons to induce itch. Cell 2013, 155, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.P.; Schunck, M.; Kallen, K.J.; Neumann, C.; Trautwein, C.; Rose-John, S.; Proksch, E. The interleukin-6 cytokine system regulates epidermal permeability barrier homeostasis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2004, 123, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, R.; Silverberg, J.I. Assessing the severity of atopic dermatitis in clinical trials and practice. Clin. Dermatol. 2018, 36, 606–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya Islamoglu, Z.G.; Unal, M.; Kucuk, A. Atopic Dermatitis in Adults and Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Cross-sectional Study. Indian J. Dermatol. 2019, 64, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivashkin, V.; Poluektov, Y.; Kogan, E.; Shifrin, O.; Sheptulin, A.; Kovaleva, A.; Kurbatova, A.; Krasnov, G.; Poluektova, E. Disruption of the pro-inflammatory, anti-inflammatory cytokines and tight junction proteins expression, associated with changes of the composition of the gut microbiota in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0252930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Hener, P.; Zhang, Z.; Kato, S.; Metzger, D.; Chambon, P. Topical vitamin D3 and low-calcemic analogs induce thymic stromal lymphopoietin in mouse keratinocytes and trigger an atopic dermatitis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 11736–11741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Lee, J.H.; Koh, S.-J.; Park, H. Bidirectional relationship between atopic dermatitis and inflammatory bowel disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020, 83, 1385–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altomare, A.; Del Chierico, F.; Rocchi, G.; Emerenziani, S.; Nuglio, C.; Putignani, L.; Angeletti, S.; Lo Presti, A.; Ciccozzi, M.; Russo, A.; et al. Association between Dietary Habits and Fecal Microbiota Composition in Irritable Bowel Syndrome Patients: A Pilot Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.F.; Pei, L.X.; Chen, L.; Geng, H.; Yuan, M.Q.; Xu, W.L.; Wu, J.; Zhou, J.Y.; Sun, J.H. Electroacupuncture Relieves Irritable Bowel Syndrome by Regulating IL-18 and Gut Microbial Dysbiosis in a Trinitrobenzene Sulfonic Acid-Induced Post-Inflammatory Animal Model. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2020, 48, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nourrisson, C.; Scanzi, J.; Brunet, J.; Delbac, F.; Dapoigny, M.; Poirier, P. Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Fecal Microbiota in Irritable Bowel Syndrome Patients and Healthy Individuals Colonized With Blastocystis. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 713347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Guo, Q.; Wen, Z.; Tan, S.; Chen, J.; Lin, L.; Chen, P.; He, J.; Wen, J.; Chen, Y. The multiple effects of fecal microbiota transplantation on diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome (IBS-D) patients with anxiety and depression behaviors. Microb. Cell Fact. 2021, 20, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, D.N.; St Amand, A.L.; Feldman, R.A.; Boedeker, E.C.; Harpaz, N.; Pace, N.R. Molecular-phylogenetic characterization of microbial community imbalances in human inflammatory bowel diseases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 13780–13785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Chen, L.; Zhou, R.; Wang, X.; Song, L.; Huang, S.; Wang, G.; Xia, B. Increased proportions of Bifidobacterium and the Lactobacillus group and loss of butyrate-producing bacteria in inflammatory bowel disease. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saulnier, D.M.; Riehle, K.; Mistretta, T.A.; Diaz, M.A.; Mandal, D.; Raza, S.; Weidler, E.M.; Qin, X.; Coarfa, C.; Milosavljevic, A.; et al. Gastrointestinal microbiome signatures of pediatric patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 1782–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thingholm, L.B.; Rühlemann, M.C.; Koch, M.; Fuqua, B.; Laucke, G.; Boehm, R.; Bang, C.; Franzosa, E.A.; Hübenthal, M.; Rahnavard, A.; et al. Obese Individuals with and without Type 2 Diabetes Show Different Gut Microbial Functional Capacity and Composition. Cell Host Microbe 2019, 26, 252–264.e210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escobedo, G.; López-Ortiz, E.; Torres-Castro, I. Gut microbiota as a key player in triggering obesity, systemic inflammation and insulin resistance. Rev. Investig. Clin. 2014, 66, 450–459. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Hu, M.; Kim, J.J.; Lin, R.; Xu, J.; Fan, L.; Qi, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, W.; et al. Dietary type 2 resistant starch improves systemic inflammation and intestinal permeability by modulating microbiota and metabolites in aged mice on high-fat diet. Aging 2020, 12, 9173–9187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobin, M.C.; Moparty, B.; Farhadi, A.; DeMeo, M.T.; Bansal, P.J.; Keshavarzian, A. Atopic irritable bowel syndrome: A novel subgroup of irritable bowel syndrome with allergic manifestations. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2008, 100, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristek, M.; Collins, L.E.; DeCourcey, J.; McEvoy, F.A.; Loscher, C.E. Soluble factors from colonic epithelial cells contribute to gut homeostasis by modulating macrophage phenotype. Innate Immun. 2015, 21, 358–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H.; Erickson, A.; Moreau, R. Divergent regulation of inflammatory cytokines by mTORC1 in THP-1-derived macrophages and intestinal epithelial Caco-2 cells. Life Sci. 2021, 284, 119920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose-John, S. IL-6 trans-signaling via the soluble IL-6 receptor: Importance for the pro-inflammatory activities of IL-6. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2012, 8, 1237–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diehl, S.; Rincon, M. The two faces of IL-6 on Th1/Th2 differentiation. Mol. Immunol. 2002, 39, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doganci, A.; Sauer, K.; Karwot, R.; Finotto, S. Pathological role of IL-6 in the experimental allergic bronchial asthma in mice. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2005, 28, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David Boothe, W.; Tarbox, J.A.; Tarbox, M.B. Atopic Dermatitis: Pathophysiology. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 1027, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.J.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, D.H.; Woo, S.Y.; Lee, K.H.; Yun, S.T.; Kim, J.M.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, J.W. Therapeutic effects and immunomodulation of suanbo mineral water therapy in a murine model of atopic dermatitis. Ann. Dermatol. 2013, 25, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeom, M.; Ahn, S.; Jang, S.-Y.; Jang, J.-H.; Lee, Y.; Hahm, D.-H.; Park, H.-J. Acupuncture attenuates comorbid anxiety- and depressive-like behaviors of atopic dermatitis through modulating neuroadaptation in the brain reward circuit in mice. Biol. Res. 2022, 55, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szymaszkiewicz, A.; Włodarczyk, J.; Wasilewski, A.; Di Marzo, V.; Storr, M.; Fichna, J.; Zielińska, M. Desensitization of transient receptor potential vanilloid type-1 (TRPV1) channel as promising therapy of irritable bowel syndrome: Characterization of the action of palvanil in the mouse gastrointestinal tract. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2020, 393, 1357–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, D.; Sangar, M.; Park, J.L.; Kang, S.G.; Ham, K.S. Roasted garlic protects against leaky gut syndrome in dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis mice. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2022, 31, 1335–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.H.; Song, E.M.; Do, Y.H.; Ahn, S.; Oh, J.Y.; Hwang, T.Y.; Ryu, Y.; Jeon, S.; Song, M.Y.; Park, H.J. Acupuncture alleviates chronic pain and comorbid conditions in a mouse model of neuropathic pain: The involvement of DNA methylation in the prefrontal cortex. Pain 2021, 162, 514–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.-H.; Yeom, M.-J.; Ahn, S.; Oh, J.-Y.; Ji, S.; Kim, T.-H.; Park, H.-J. Acupuncture inhibits neuroinflammation and gut microbial dysbiosis in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 89, 641–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, M.J.; Weingarden, A.R.; Sadowsky, M.J.; Khoruts, A. Standardized frozen preparation for transplantation of fecal microbiota for recurrent Clostridium difficile infection. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 107, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuijt, T.J.; Lankelma, J.M.; Scicluna, B.P.; de Sousa e Melo, F.; Roelofs, J.J.; de Boer, J.D.; Hoogendijk, A.J.; de Beer, R.; de Vos, A.; Belzer, C.; et al. The gut microbiota plays a protective role in the host defence against pneumococcal pneumonia. Gut 2016, 65, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jang, J.-H.; Jang, S.-Y.; Ahn, S.; Oh, J.-Y.; Yeom, M.; Ko, S.-J.; Park, J.-W.; Kwon, S.-K.; Kim, K.; Lee, I.-S.; et al. Chronic Gut Inflammation and Dysbiosis in IBS: Unraveling Their Contribution to Atopic Dermatitis Progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2753. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25052753
Jang J-H, Jang S-Y, Ahn S, Oh J-Y, Yeom M, Ko S-J, Park J-W, Kwon S-K, Kim K, Lee I-S, et al. Chronic Gut Inflammation and Dysbiosis in IBS: Unraveling Their Contribution to Atopic Dermatitis Progression. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(5):2753. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25052753
Chicago/Turabian StyleJang, Jae-Hwan, Sun-Young Jang, Sora Ahn, Ju-Young Oh, Mijung Yeom, Seok-Jae Ko, Jae-Woo Park, Soon-Kyeong Kwon, Kyuseok Kim, In-Seon Lee, and et al. 2024. "Chronic Gut Inflammation and Dysbiosis in IBS: Unraveling Their Contribution to Atopic Dermatitis Progression" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 5: 2753. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25052753
APA StyleJang, J.-H., Jang, S.-Y., Ahn, S., Oh, J.-Y., Yeom, M., Ko, S.-J., Park, J.-W., Kwon, S.-K., Kim, K., Lee, I.-S., Hahm, D.-H., & Park, H.-J. (2024). Chronic Gut Inflammation and Dysbiosis in IBS: Unraveling Their Contribution to Atopic Dermatitis Progression. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(5), 2753. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25052753






