Bactericidal Efficacy of the Combination of Maresin-like Proresolving Mediators and Carbenicillin Action on Biofilm-Forming Burn Trauma Infection-Related Bacteria
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
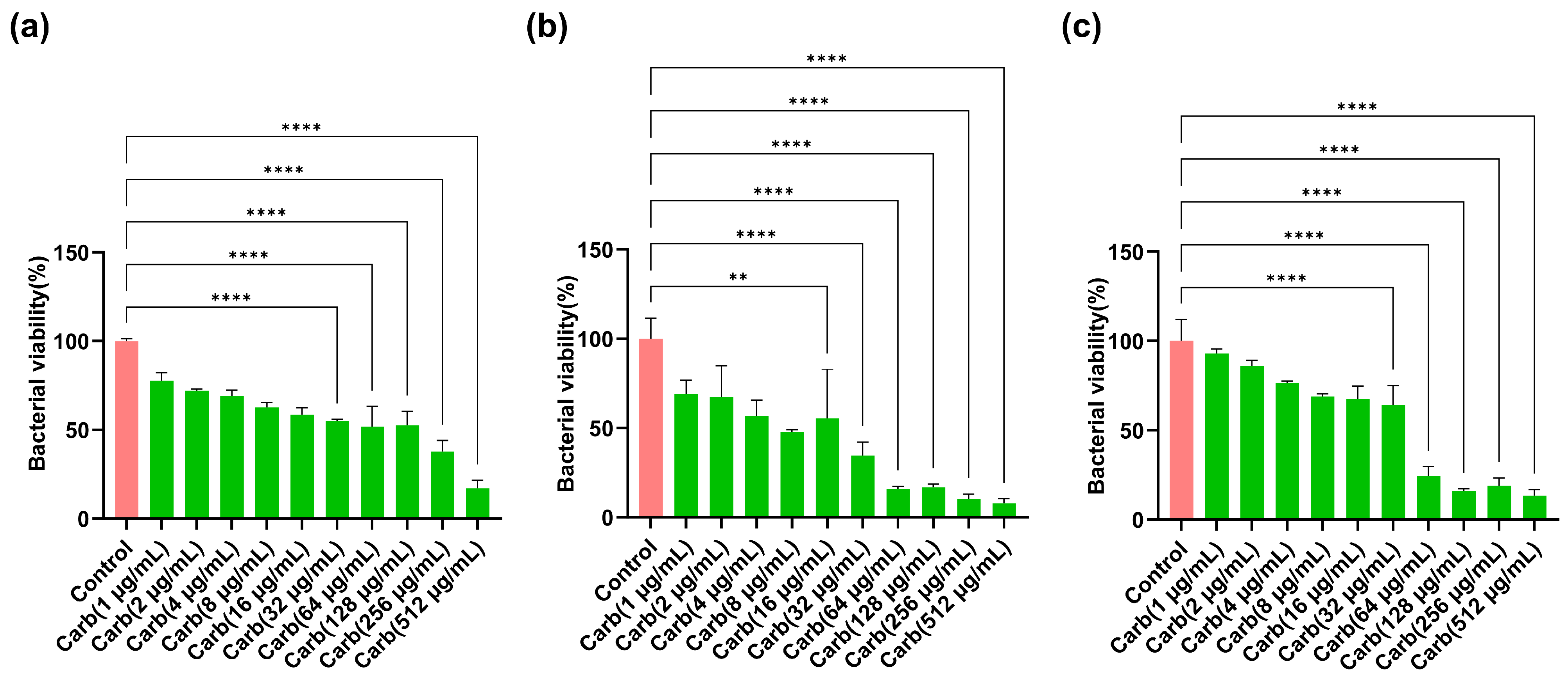
2.1. Determination of Concentration-Dependent Bactericidal Actions of Carbenicillin
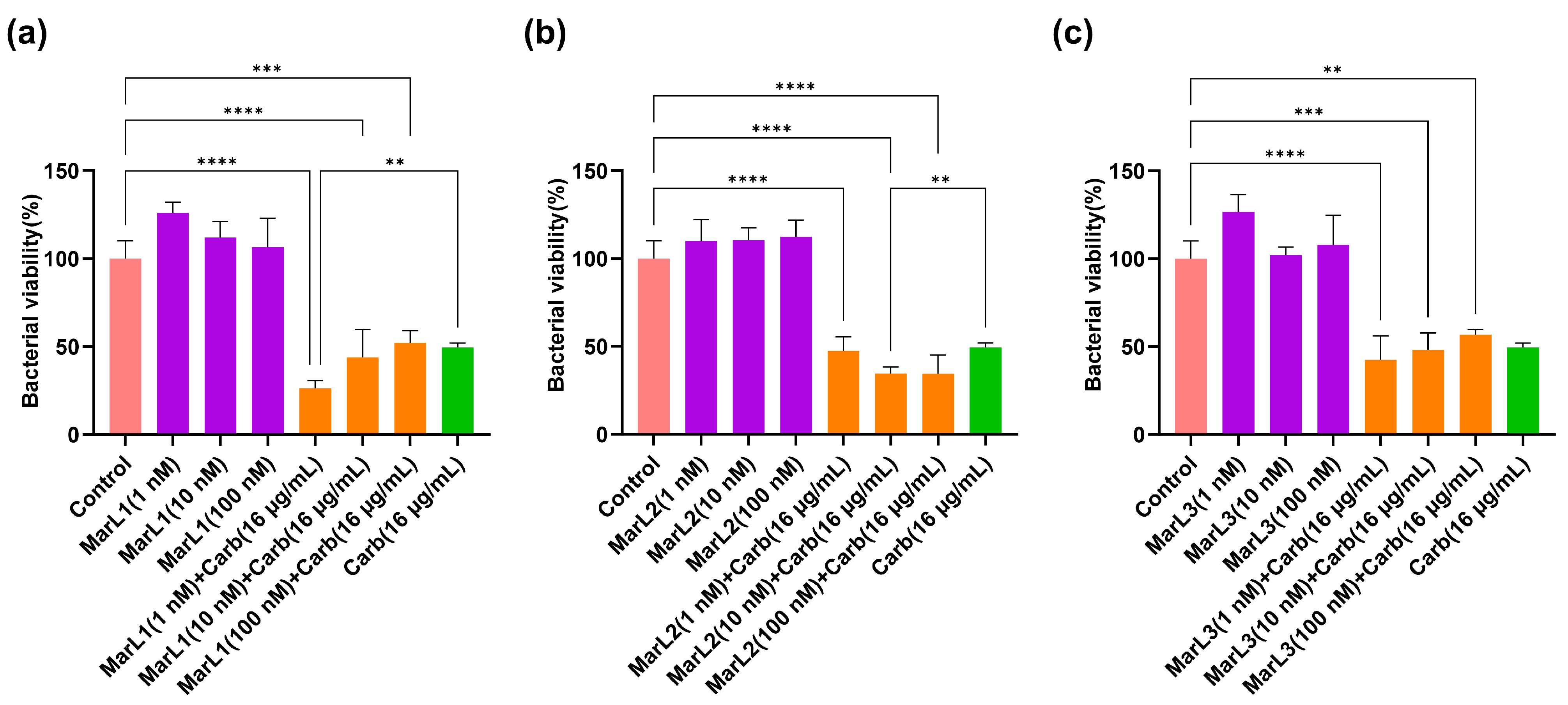
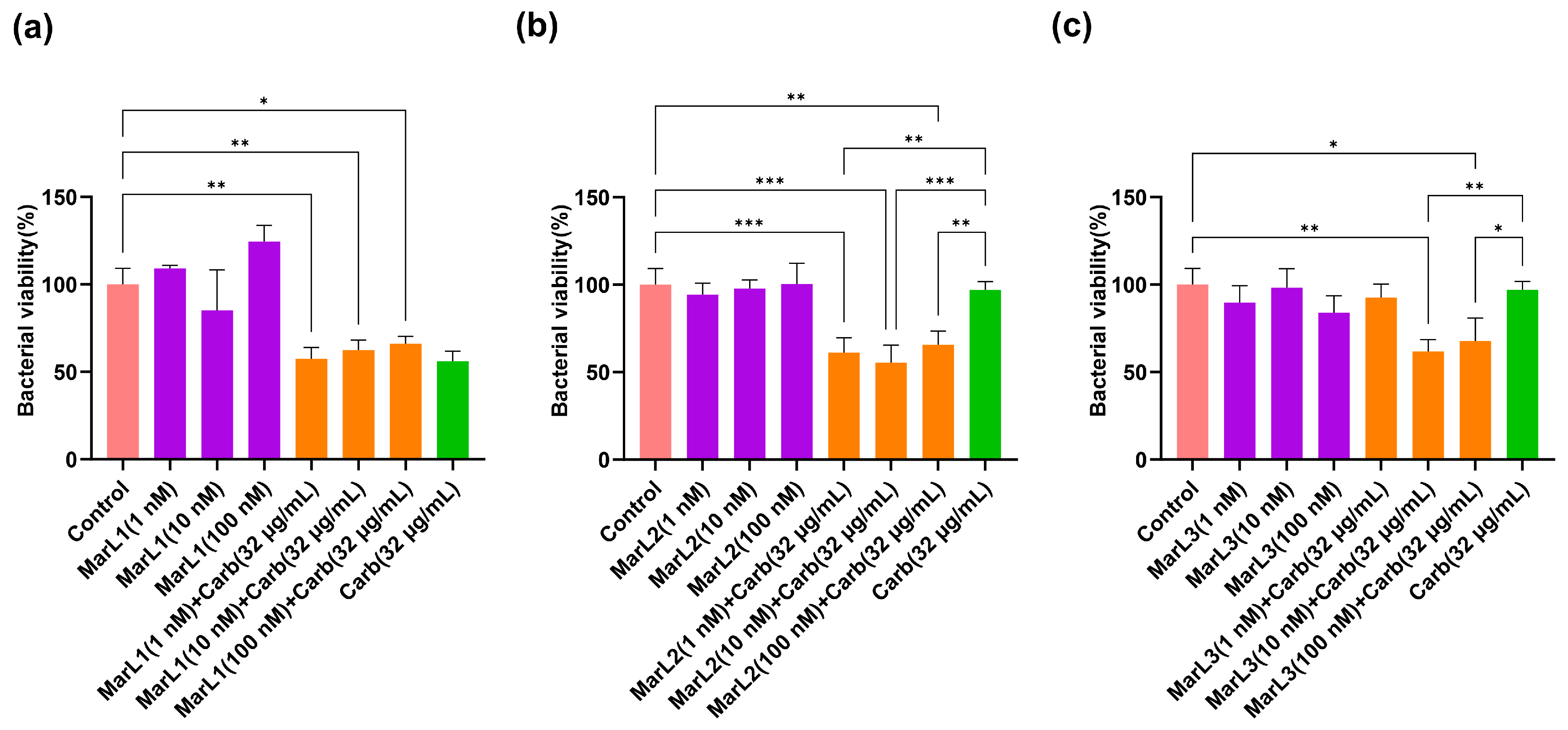
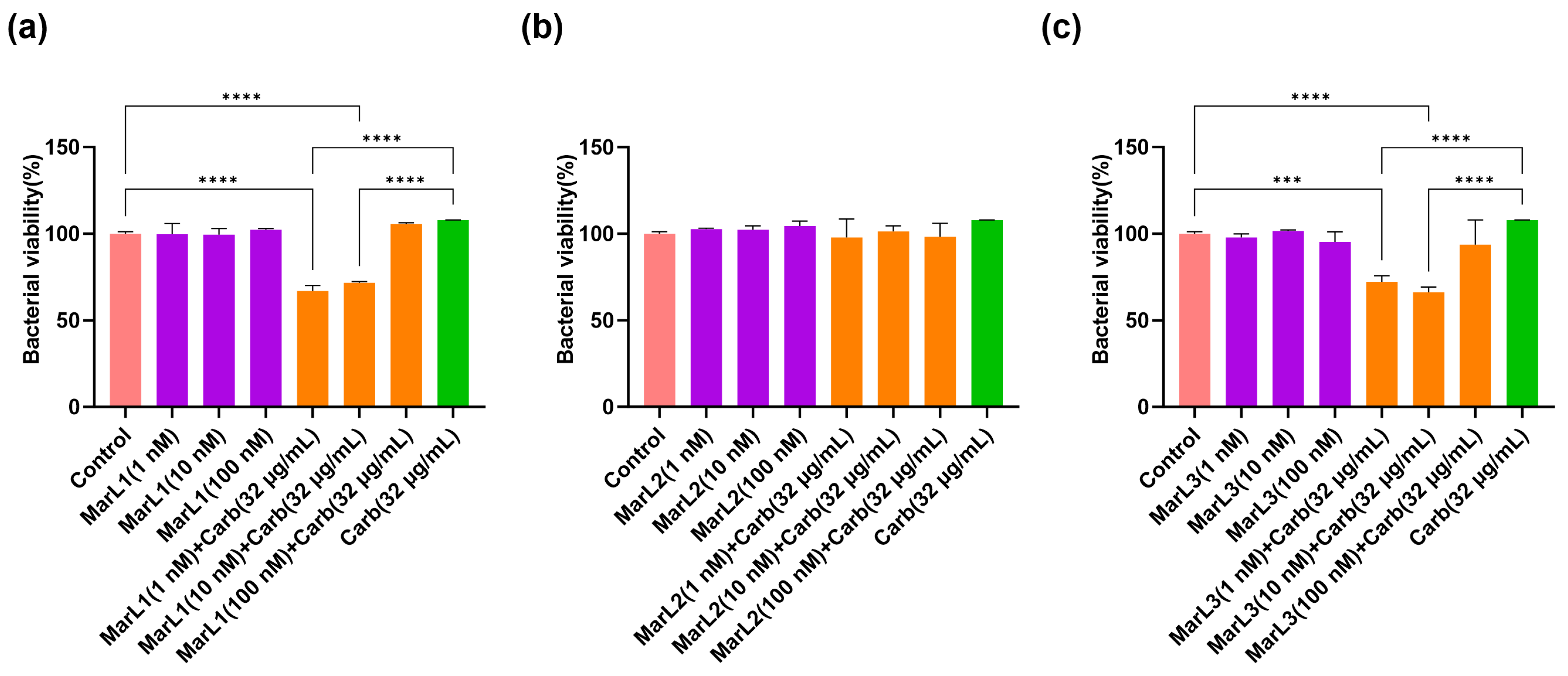
2.2. Combined Effect of a Maresin-like Mediator and Carbenicillin on Bacterial Viabilities in Their Biofilms
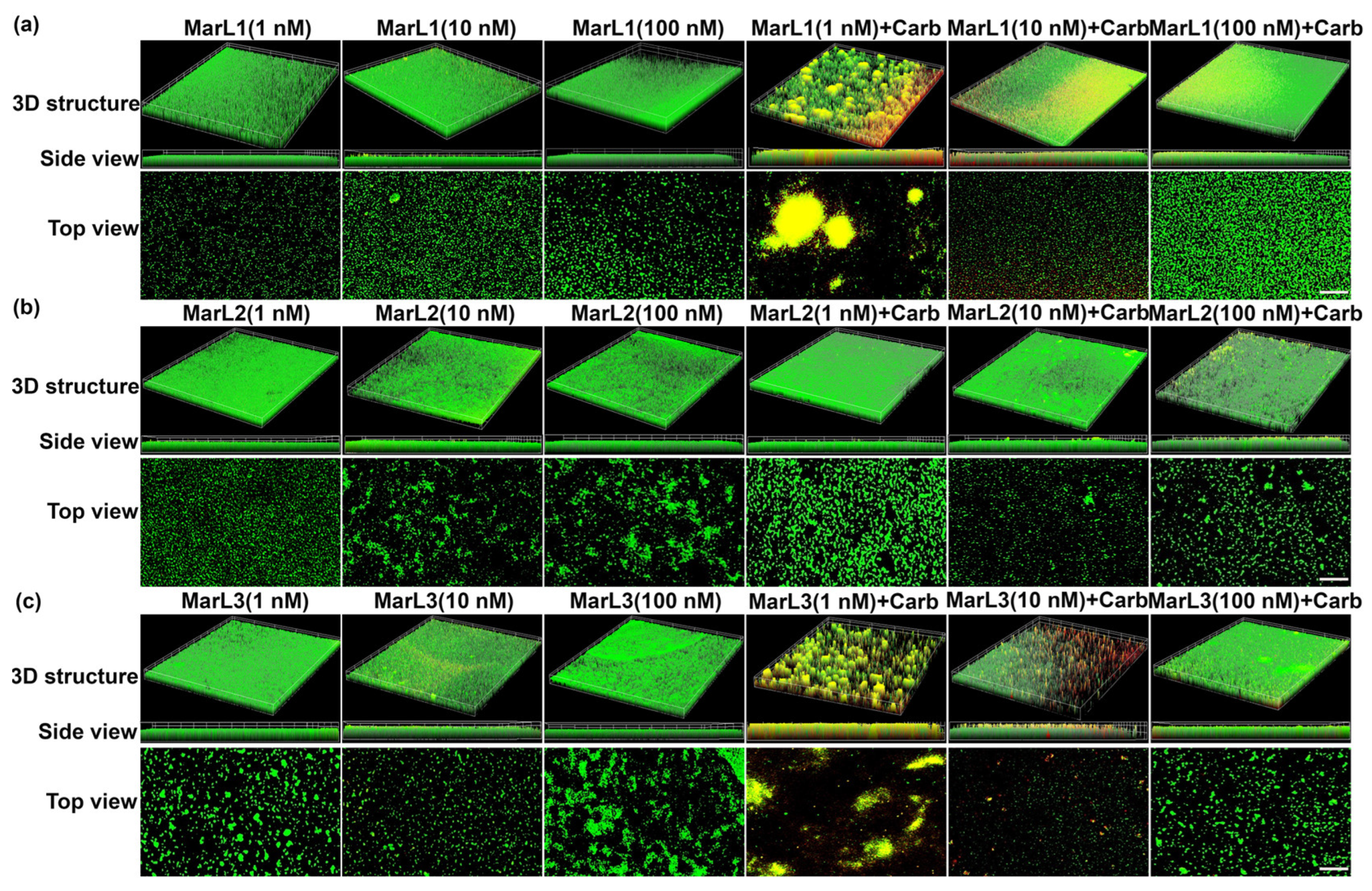
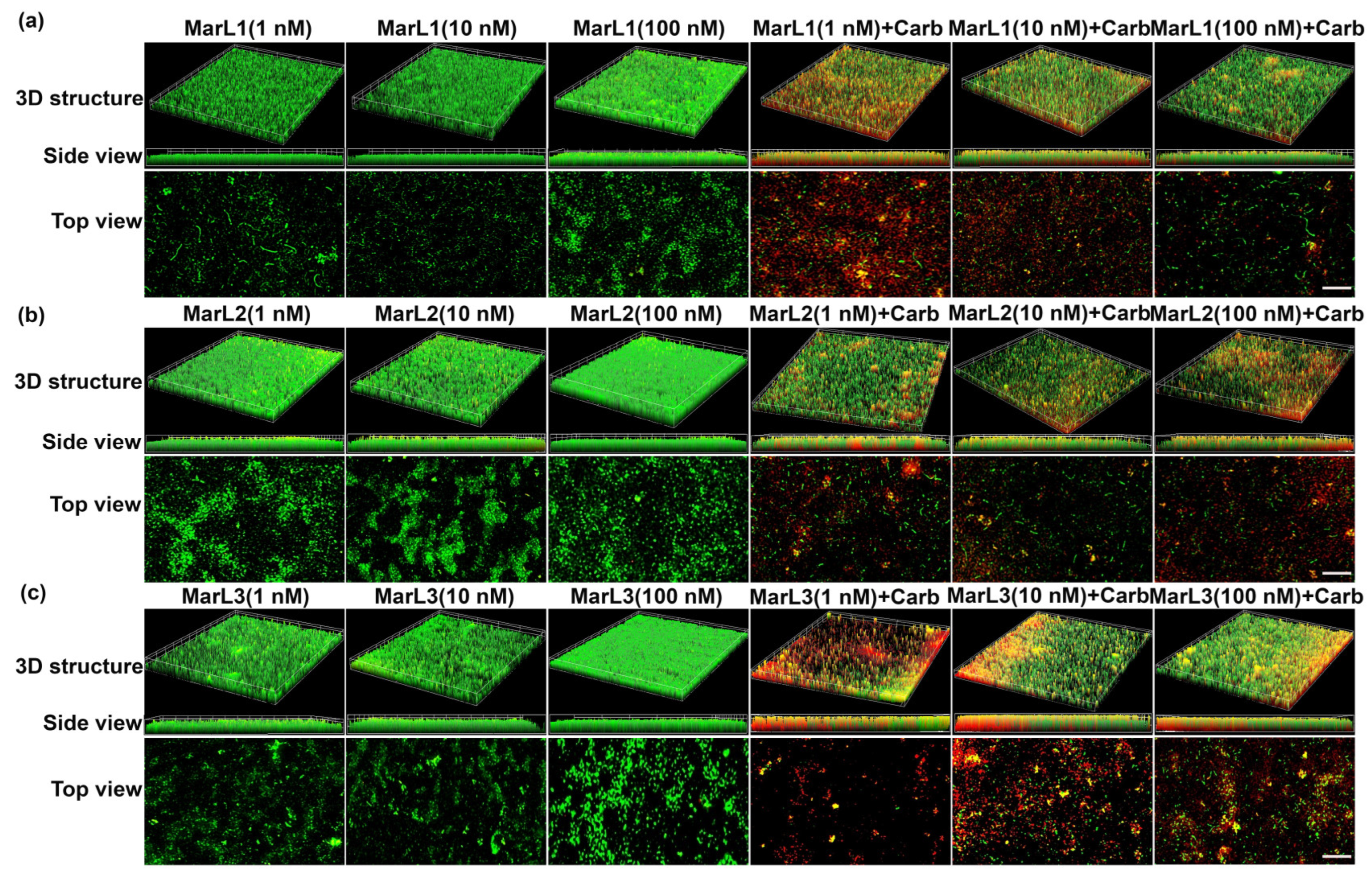
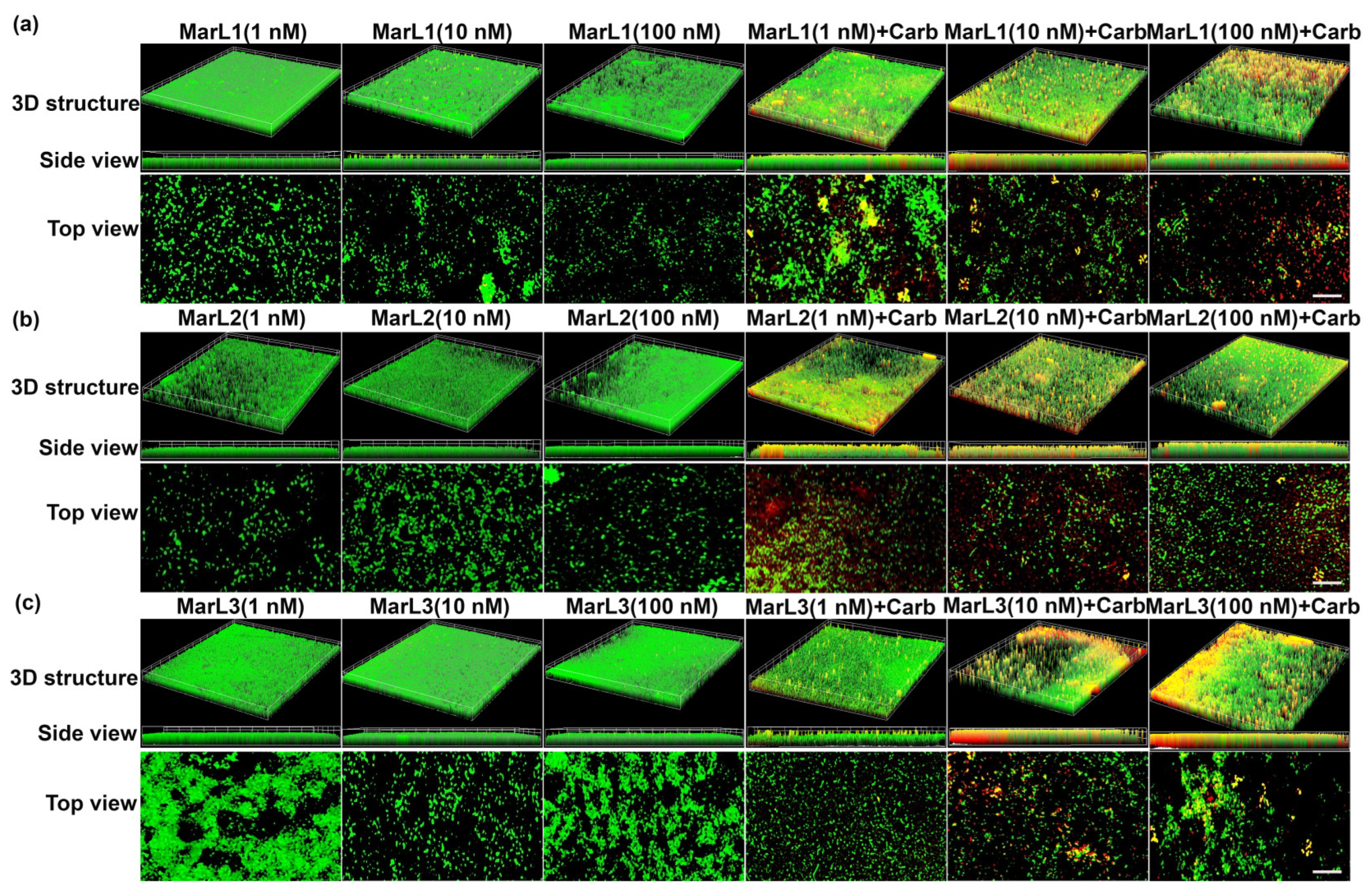
2.3. Live/Dead Assay Imaging Revealed Combined Effects of a Maresin-like Mediator and Carbenicillin on Bacterial Survival in Their Biofilms
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Biofilm Formation
4.3. Determination of Concentration-Dependent Bactericidal Actions of Carbenicillin
4.4. Determination of Bacterial Viability with the MTT Assay
4.5. Live/Dead Assay
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Antimicrobial Resistance, C. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: A systematic analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shineh, G.; Mobaraki, M.; Bappy, M.J.P.; Mills, D.K. Biofilm Formation, and Related Impacts on Healthcare, Food Processing and Packaging, Industrial Manufacturing, Marine Industries, and Sanitation—A Review. Appl. Microbiol. 2023, 3, 629–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, O.Y.A.; Raaijmakers, J.M.; Kuramae, E.E. Microbial Extracellular Polymeric Substances: Ecological Function and Impact on Soil Aggregation. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, D.N.; Wysocki, A.; Specht-Glick, D.D.; Rooney, A.; Feldman, R.A.; St Amand, A.L.; Pace, N.R.; Trent, J.D. Microbial diversity in chronic open wounds. Wound Repair Regen. 2009, 17, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomic-Canic, M.; Burgess, J.L.; O’Neill, K.E.; Strbo, N.; Pastar, I. Skin Microbiota and its Interplay with Wound Healing. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2020, 21, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemmati, J.; Azizi, M.; Asghari, B.; Arabestani, M.R. Multidrug-Resistant Pathogens in Burn Wound, Prevention, Diagnosis, and Therapeutic Approaches (Conventional Antimicrobials and Nanoparticles). Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol. = J. Can. Des Mal. Infect. Microbiol. Medicale 2023, 2023, 8854311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinaik, R.; Barayan, D.; Shahrokhi, S.; Jeschke, M.G. Management and prevention of drug resistant infections in burn patients. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2019, 17, 607–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halstead, F.D.; Rauf, M.; Moiemen, N.S.; Bamford, A.; Wearn, C.M.; Fraise, A.P.; Lund, P.A.; Oppenheim, B.A.; Webber, M.A. The Antibacterial Activity of Acetic Acid against Biofilm-Producing Pathogens of Relevance to Burns Patients. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luck, M.E.; Herrnreiter, C.J.; Choudhry, M.A. Gut Microbial Changes and their Contribution to Post-Burn Pathology. Shock 2021, 56, 329–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Lu, Y.; Shah, S.P.; Hong, S. 14S,21R-Dihydroxydocosahexaenoic Acid Remedies Impaired Healing and Mesenchymal Stem Cell Functions in Diabetic Wounds. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 4443–4453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Tian, H.; Hong, S. Novel 14,21-dihydroxy-docosahexaenoic acids: Structures, formation pathways, and enhancement of wound healing. J. Lipid Res. 2010, 51, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, H.; Lu, Y.; Shah, S.P.; Wang, Q.; Hong, S. 14S,21R-dihydroxy-docosahexaenoic acid treatment enhances mesenchymal stem cell amelioration of renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. Stem Cells Dev. 2012, 21, 1187–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Lu, Y.; Tian, H.; Alapure, B.V.; Wang, Q.; Bunnell, B.A.; Laborde, J.M. Maresin-like lipid mediators are produced by leukocytes and platelets and rescue reparative function of diabetes-impaired macrophages. Chem. Biol. 2014, 21, 1318–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Lu, Y.; Morita, M.; Saito, S.; Kobayashi, Y.; Jun, B.; Bazan, N.G.; Xu, X.; Wang, Y. Stereoselective Synthesis of Maresin-like Lipid Mediators. Synlett 2019, 30, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, K.; Sakaguchi, T.; Nanba, Y.; Suganuma, Y.; Morita, M.; Hong, S.; Lu, Y.; Jun, B.; Bazan, N.G.; Arita, M.; et al. Stereoselective Total Synthesis of Macrophage-Produced Prohealing 14,21-Dihydroxy Docosahexaenoic Acids. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 83, 154–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serhan, C.N.; Yang, R.; Martinod, K.; Kasuga, K.; Pillai, P.S.; Porter, T.F.; Oh, S.F.; Spite, M. Maresins: Novel macrophage mediators with potent antiinflammatory and proresolving actions. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, N.; Tojo, T.; Kobayashi, Y. Synthesis of maresin 1 and (7S)-isomer. Tetrahedron Lett. 2014, 55, 2738–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, N.; Amano, T.; Kobayashi, Y. Synthesis of Optically Active Maresin 2 and Maresin 2n-3 DPA. Synlett 2021, 32, 295–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serhan, C.N.; Sulciner, M.L. Resolution medicine in cancer, infection, pain and inflammation: Are we on track to address the next Pandemic? Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2023, 42, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serhan, C.N.; Chiang, N. Resolvins and cysteinyl-containing pro-resolving mediators activate resolution of infectious inflammation and tissue regeneration. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2023, 166, 106718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, N.; Libreros, S.; Norris, P.C.; de la Rosa, X.; Serhan, C.N. Maresin 1 activates LGR6 receptor promoting phagocyte immunoresolvent functions. J. Clin. Investig. 2023, 133, e168084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serhan, C.N.; de la Rosa, X.; Jouvene, C. Novel mediators and mechanisms in the resolution of infectious inflammation: Evidence for vagus regulation. J. Intern. Med. 2019, 286, 240–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serhan, C.N. Treating inflammation and infection in the 21st century: New hints from decoding resolution mediators and mechanisms. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 1273–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colas, R.A.; Dalli, J.; Chiang, N.; Vlasakov, I.; Sanger, J.M.; Riley, I.R.; Serhan, C.N. Identification and Actions of the Maresin 1 Metabolome in Infectious Inflammation. J. Immunol. 2016, 197, 4444–4452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, X.; Hao, Y.; Wu, C.; Fu, Y.; Su, N.; Chen, H.; Ying, B.; Wang, H.; Su, L.; et al. Maresin 1 intervention reverses experimental pulmonary arterial hypertension in mice. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 179, 5132–5147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, N.; Serhan, C.N. Specialized pro-resolving me-diator network: An update on production and ac-tions. Essays Biochem. 2020, 64, 443–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, P.C.; Libreros, S.; Serhan, C.N. Resolution metabolomes activated by hypoxic en-vironment. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaax4895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, M.J.; Sabaj, M.; Tolosa, G.; Herrera Vielma, F.; Zuniga, M.J.; Gonzalez, D.R.; Zuniga-Hernandez, J. Maresin-1 Prevents Liver Fibrosis by Targeting Nrf2 and NF-κB, Reducing Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. Cells 2021, 10, 3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, A.; Sarabia, C.; Torres, M.; Juarez, E. Resolvin D1 (RvD1) and maresin 1 (Mar1) contribute to human macrophage control of M. tuberculosis infection while resolving inflammation. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 74, 105694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, S.; Mena, H.A.; Sansbury, B.E.; Kobayashi, S.; Tsuji, T.; Wang, C.H.; Yin, X.; Huang, T.L.; Kusuyama, J.; Kodani, S.D.; et al. Brown adipose tissue-derived MaR2 contributes to cold-induced resolution of inflammation. Nat. Metab. 2022, 4, 775–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emre, C.; Arroyo-Garcia, L.E.; Do, K.V.; Jun, B.; Ohshima, M.; Alcalde, S.G.; Cothern, M.L.; Maioli, S.; Nilsson, P.; Hjorth, E.; et al. Intranasal delivery of pro-resolving lipid mediators rescues memory and gamma oscillation impairment in App(NL-G-F/NL-G-F) mice. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Fernandez, A.; Zandee, S.; Mastrogiovanni, M.; Charabati, M.; Rubbo, H.; Prat, A.; Lopez-Vales, R. Administration of Maresin-1 ameliorates the physiopathology of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Neuroinflamm. 2022, 19, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, J.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Yang, L.; Chen, H.; Su, N.; Wu, C.; Hao, Y.; Jin, S.; Li, H. MCTR1 Intervention Reverses Experimental Lung Fibrosis in Mice. J. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 14, 1873–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falsetta, M.L.; Wood, R.W.; Linder, M.A.; Bonham, A.D.; Honn, K.V.; Maddipati, K.R.; Phipps, R.P.; Haidaris, C.G.; Foster, D.C. Specialized Pro-Resolving Mediators Reduce Pro-Nociceptive Inflammatory Mediator Production in Models of Localized Provoked Vulvodynia. J. Pain 2021, 22, 1195–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Vi, L.; Zong, X.; Baht, G.S. Maresin 1 resolves aged-associated macrophage inflammation to improve bone regeneration. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 13521–13532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, K.; English, A.R.; Ray, V.A.; Timreck, A.E. Carbenicillin: Chemistry and mode of action. J. Infect. Dis. 1970, 122 (Suppl. S1), S1–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castle, S.S. Carbenicillin. In xPharm: The Comprehensive Pharmacology Reference; Enna, S.J., Bylund, D.B., Eds.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernier, S.P.; Surette, M.G. Concentration-dependent activity of antibiotics in natural environments. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Technical Data Sheet, Light Producing Microorganisms—Staphylococcus aureus: S. aureus ATCC 12600 (Xen29); Product No.: 119240; PerkinElmer, Inc.: Waltham, MA, USA, 2015; Available online: https://www.summitpharma.co.jp/japanese/service/products/pdf/_light_producing_microorganisms/tec_sheet/119240-Xen29.pdf (accessed on 1 January 2024).
- Caliper LifeSciences. Bioware™ Microorganism—Pseudomonas aeruginosa Xen41-In Vitro Characteristics; Caliper Life Sciences, Inc.: Hopkinton, MA, USA, 2008; Available online: https://www.caliperls.com/assets/017/7488.pdf (accessed on 1 January 2024).
- Technical Data Sheet, Light Producing Microorganisms—Escherichia coli, E. coli WS2572 (Xen14); Product Number: 119223; Revvity, Inc.: Waltham, MA, USA, 2023; Available online: https://www.revvity.com/product/ivisbrite-escherichia-coli-xen14-119223 (accessed on 1 January 2024).
- Donlan, R.M. Biofilm formation: A clinically relevant microbiological process. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 33, 1387–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rather, M.A.; Gupta, K.; Mandal, M. Microbial biofilm: Formation, architecture, antibiotic resistance, and control strategies. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2021, 52, 1701–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoiby, N.; Bjarnsholt, T.; Givskov, M.; Molin, S.; Ciofu, O. Antibiotic resistance of bacterial biofilms. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2010, 35, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, G.D. Bacterial resistance to antibiotics: Enzymatic degradation and modification. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2005, 57, 1451–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, M.; Brooks, B.D.; Brooks, A.E. The Complex Relationship between Virulence and Antibiotic Resistance. Genes 2017, 8, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, N.; Dalli, J.; Colas, R.A.; Serhan, C.N. Identification of resolvin D2 receptor mediating resolution of infections and organ protection. J. Exp. Med. 2015, 212, 1203–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, J.; Dichter, E.; Lacorte, G.; Kerner, D.; Spur, B.; Rodriguez, A.; Yin, K. Lipoxin a4 increases survival by decreasing systemic inflammation and bacterial load in sepsis. Shock 2011, 36, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musken, M.; Di Fiore, S.; Dotsch, A.; Fischer, R.; Haussler, S. Genetic determinants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm establishment. Microbiology 2010, 156, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, D.; Turner, K.E.; Kirienko, N.V. PqsA Promotes Pyoverdine Production via Biofilm Formation. Pathogens 2017, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thornton, J.M.; Walker, J.M.; Sundarasivarao, P.Y.K.; Spur, B.W.; Rodriguez, A.; Yin, K. Lipoxin A4 promotes reduction and antibiotic efficacy against Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2021, 152, 106505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibeaux, R.; Kainiu, M.; Goarant, C. Biofilm Formation and Quantification Using the 96-Microtiter Plate. Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2134, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.A.; Nasr, M.; Elkhatib, W.F.; Eltayeb, W.N. In Vitro Evaluation of Antimicrobial Activity and Cytotoxicity of Different Nanobiotics Targeting Multidrug Resistant and Biofilm Forming Staphylococci. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 7658238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grela, E.; Kozlowska, J.; Grabowiecka, A. Current methodology of MTT assay in bacteria—A review. Acta Histochem. 2018, 120, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thamizhchelvan, A.M.; Masoud, A.-R.; Su, S.; Lu, Y.; Peng, H.; Kobayashi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Archer, N.K.; Hong, S. Bactericidal Efficacy of the Combination of Maresin-like Proresolving Mediators and Carbenicillin Action on Biofilm-Forming Burn Trauma Infection-Related Bacteria. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2792. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25052792
Thamizhchelvan AM, Masoud A-R, Su S, Lu Y, Peng H, Kobayashi Y, Wang Y, Archer NK, Hong S. Bactericidal Efficacy of the Combination of Maresin-like Proresolving Mediators and Carbenicillin Action on Biofilm-Forming Burn Trauma Infection-Related Bacteria. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(5):2792. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25052792
Chicago/Turabian StyleThamizhchelvan, Anbu Mozhi, Abdul-Razak Masoud, Shanchun Su, Yan Lu, Hongying Peng, Yuichi Kobayashi, Yu Wang, Nathan K. Archer, and Song Hong. 2024. "Bactericidal Efficacy of the Combination of Maresin-like Proresolving Mediators and Carbenicillin Action on Biofilm-Forming Burn Trauma Infection-Related Bacteria" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 5: 2792. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25052792
APA StyleThamizhchelvan, A. M., Masoud, A.-R., Su, S., Lu, Y., Peng, H., Kobayashi, Y., Wang, Y., Archer, N. K., & Hong, S. (2024). Bactericidal Efficacy of the Combination of Maresin-like Proresolving Mediators and Carbenicillin Action on Biofilm-Forming Burn Trauma Infection-Related Bacteria. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(5), 2792. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25052792








