Therapeutic Effect of Natural Products and Dietary Supplements on Aflatoxin-Induced Nephropathy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
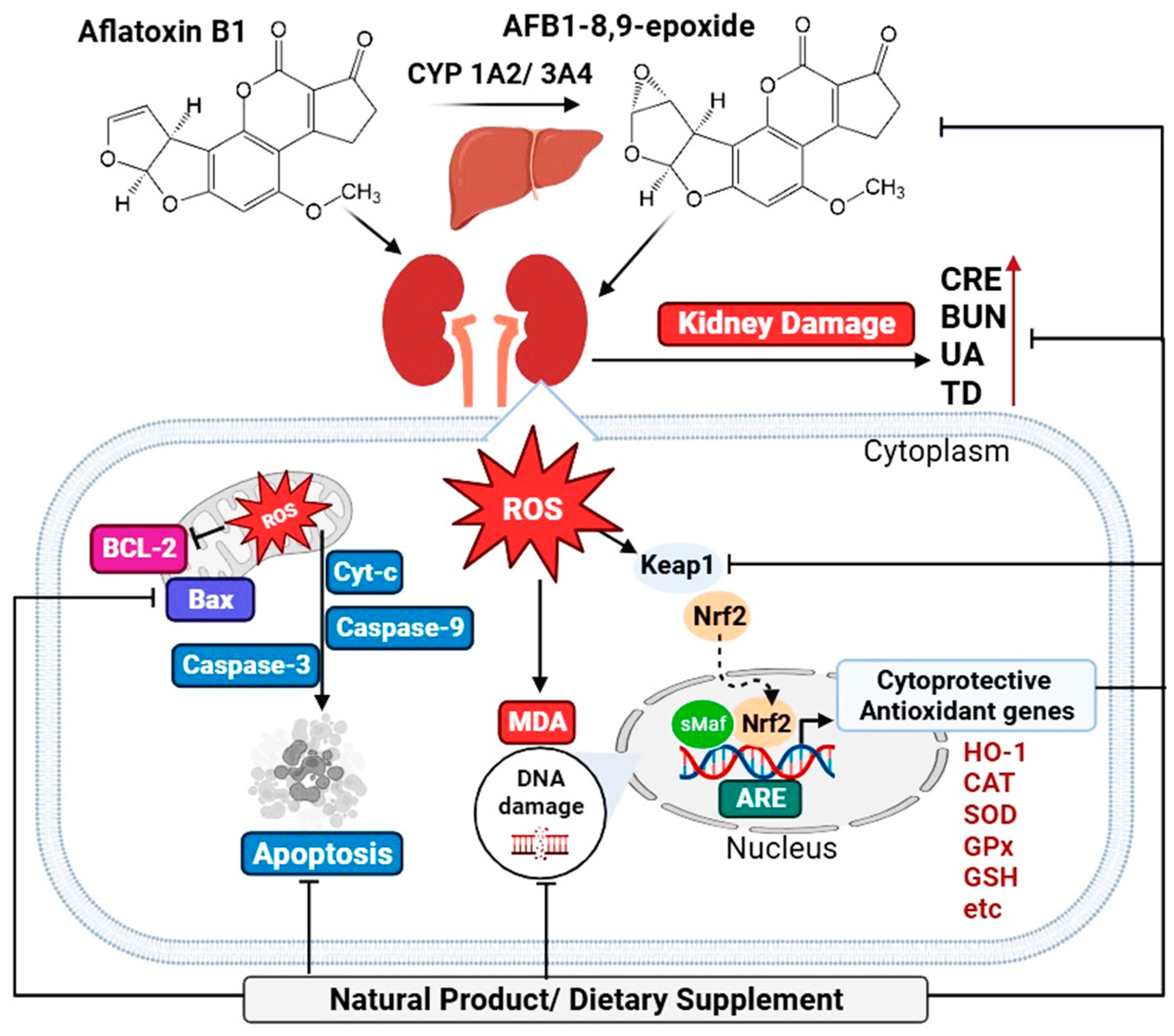
3. Aflatoxin Metabolism and Toxicity
3.1. Aflatoxin and Renal Dysfunction
3.2. Aflatoxin Induces Oxidative Stress in the Kidney
4. Natural Products and Dietary Supplements for AFB1-Induced Kidney Damage
4.1. Curcumin
4.2. Resveratrol
4.3. Gallic Acid
4.4. Caffeic Acid
4.5. Diosmin
4.6. Apigenin
4.7. Morin
4.8. Esculin
4.9. Fucoidans
4.10. Selenium
4.11. Vitamin E
4.12. 3-Indole Propionic Acid
4.13. Lycopene
5. Herbal Product
5.1. Kalpaamruthaa
5.2. Fenugreek
6. Probiotics
7. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lizárraga-Paulín, E.G.; Miranda-Castro, S.P.; Moreno-Martínez, E.; Torres-Pacheco, I.; Lara-Sagahón, A.V.; Prospects, F. Novel methods for preventing and controlling aflatoxins in food: A worldwide daily challenge. In Aflatoxins-Recent Advances and Future Prospects; Razzaghi-Abyaneh, M., Ed.; InTech Open: London, UK, 2013; pp. 93–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Stoev, S.D. Foodborne mycotoxicosis, risk assessment and underestimated hazard of masked mycotoxins and joint mycotoxin effects or interaction. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 39, 794–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskola, M.; Kos, G.; Elliott, C.T.; Hajšlová, J.; Mayar, S.; Krska, R. Worldwide contamination of food-crops with mycotoxins: Validity of the widely cited ‘FAO estimate’ of 25%. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 2773–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumi, J.; Mitchell, N.; Asare, G.; Dotse, E.; Kwaa, F.; Phillips, T.; Ankrah, N.A. Aflatoxins and fumonisins contamination of home-made food (weanimix) from cereal-legume blends for children. Ghana Med. J. 2014, 48, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.-H.; Lei, M.-y.; Zhang, N.-Y.; Gao, X.; Li, C.; Krumm, C.S.; Qi, D.-S. Individual and combined cytotoxic effects of aflatoxin B1, zearalenone, deoxynivalenol and fumonisin B1 on BRL 3A rat liver cells. Toxicon 2015, 95, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo, A.; Giuberti, G.; Frisvad, J.C.; Bertuzzi, T.; Nielsen, K.F. Review on mycotoxin issues in ruminants: Occurrence in forages, effects of mycotoxin ingestion on health status and animal performance and practical strategies to counteract their negative effects. Toxins 2015, 7, 3057–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofori-Attah, E.; Aning, A.; Ofosuhene, M.; Kumi, J.; Appiah-Opong, R. Determination of aflatoxin levels in bokina beverage. Ghana Med. J. 2021, 55, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Hamid, A.A.; Firgany, A.E.-D.L. Vitamin E supplementation ameliorates aflatoxin B1-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Acta Histochem. 2015, 117, 767–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, T.; Li, P.; Chen, J.; Nepovimova, E.; Long, M.; Wu, W.; Kuca, K. Bacillus amyloliquefaciens B10 can alleviate aflatoxin B1-induced kidney oxidative stress and apoptosis in mice. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 218, 112286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chhonker, S.; Rawat, D.; Naik, R.; Koiri, R. An overview of mycotoxins in human health with emphasis on development and progression of liver cancer. Clin. Oncol 2018, 3, 1408. [Google Scholar]
- Qing, H.; Huang, S.; Zhan, K.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, J.; Ji, C.; Ma, Q. Combined toxicity evaluation of ochratoxin A and aflatoxin B1 on kidney and liver injury, immune inflammation, and gut microbiota alteration through pair-feeding pullet model. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bbosa, G.S.; Kitya, D.; Lubega, A.; Ogwal-Okeng, J.; Anokbonggo, W.W.; Kyegombe, D.B. Review of the biological and health effects of aflatoxins on body organs and body systems. Aflatoxins-Recent Adv. Future Prospect. 2013, 12, 239–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Song, M.; Wang, Q.; Guo, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Cui, Y.; Cao, Z.; Li, Y. PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy is activated to protect against AFB1-induced kidney damage in mice. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2022, 358, 109884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R.; Sharma, V. Ameliorative effects of Tinospora cordifolia root extract on histopathological and biochemical changes induced by aflatoxin-B1 in mice kidney. Toxicol. Int. 2011, 18, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, S.; Kaya, E.; Kisacam, M.A. The effect on oxidative stress of aflatoxin and protective effect of lycopene on aflatoxin damage. Aflatoxin-Control Anal. Detect. Health Risks 2017, 30, 67–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrar, M.; Anjum, F.M.; Butt, M.S.; Pasha, I.; Randhawa, M.A.; Saeed, F.; Waqas, K. Aflatoxins: Biosynthesis, occurrence, toxicity, and remedies. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 53, 862–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eftekhari, A.; Ahmadian, E.; Panahi-Azar, V.; Hosseini, H.; Tabibiazar, M.; Maleki Dizaj, S. Hepatoprotective and free radical scavenging actions of quercetin nanoparticles on aflatoxin B1-induced liver damage: In vitro/in vivo studies. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solcan, C.; Gogu, M.; Floristean, V.; Oprisan, B.; Solcan, G. The hepatoprotective effect of sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides) berries on induced aflatoxin B1 poisoning in chickens. Poult. Sci. 2013, 92, 966–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, F.; Zhou, X.; Liu, M.; Zang, H.; Liu, X.; Shan, A.; Feng, X. Alleviation of Oral Exposure to Aflatoxin B1-Induced Renal Dysfunction, Oxidative Stress, and Cell Apoptosis in Mice Kidney by Curcumin. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owumi, S.; Najophe, E.S.; Farombi, E.O.; Oyelere, A. Gallic acid protects against Aflatoxin B1-induced oxidative and inflammatory stress damage in rats’ kidneys and liver. J. Food Biochem. 2020, 44, e13316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owumi, S.E.; Irozuru, C.E.; Arunsi, U.O.; Oyelere, A.K. Caffeic acid protects against DNA damage, oxidative and inflammatory mediated toxicities, and upregulated caspases activation in the hepatorenal system of rats treated with aflatoxin B1. Toxicon 2022, 207, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owumi, S.E.; Kazeem, A.I.; Wu, B.; Ishokare, L.O.; Arunsi, U.O.; Oyelere, A.K. Apigeninidin-rich Sorghum bicolor (L. Moench) extracts suppress A549 cells proliferation and ameliorate toxicity of aflatoxin B1-mediated liver and kidney derangement in rats. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 7438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owumi, S.E.; Arunsi, U.O.; Oyelere, A.K. The protective effect of 3-indolepropanoic acid on aflatoxin B1-induced systemic perturbation of the liver and kidney function in rats. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2023, 37, 369–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popolo, A.; Autore, G.; Pinto, A.; Marzocco, S. Oxidative stress in patients with cardiovascular disease and chronic renal failure. Free Radic. Res. 2013, 47, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umaya, S.R.; Vijayalakshmi, Y.; Sejian, V. Exploration of plant products and phytochemicals against aflatoxin toxicity in broiler chicken production: Present status. Toxicon 2021, 200, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, S.; Shi, D.; Clemons-Chevis, C.L.; Guo, S.; Su, R.; Qiang, P.; Tang, Z. Protective role of selenium on aflatoxin B 1-induced hepatic dysfunction and apoptosis of liver in ducklings. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2014, 162, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daenen, K.; Andries, A.; Mekahli, D.; Van Schepdael, A.; Jouret, F.; Bammens, B. Oxidative stress in chronic kidney disease. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2019, 34, 975–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Yu, P.; Yang, K.; Cao, D. Aflatoxin B1: Metabolism, toxicology, and its involvement in oxidative stress and cancer development. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2022, 32, 395–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz de León-Martínez, L.; Díaz-Barriga, F.; Barbier, O.; Ortíz, D.L.G.; Ortega-Romero, M.; Pérez-Vázquez, F.; Flores-Ramírez, R. Evaluation of emerging biomarkers of renal damage and exposure to aflatoxin-B1 in Mexican indigenous women: A pilot study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 12205–12216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanchana, K.; Hedhayathullahkhan, H.B.; Vedagiri, A.; Palanivelu, S.; Panchanatham, S. Pharmacological effect of Kalpaamruthaa on renal and cardiac damage induced by ingestion of aflatoxin B1 studied in wistar rats. Biomed. Prev. Nutr. 2013, 3, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.Y.; Chiu, Y.W.; Chang, J.S.; Lin, H.L.; Lee, C.T.C.; Chiu, G.F.; Kuo, M.C.; Wu, M.T.; Chen, H.C.; Hwang, S.J. Association of prescribed Chinese herbal medicine use with risk of end-stage renal disease in patients with chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2015, 88, 1365–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Yao, G.-M.; Luo, C.; Zhang, C. Natural product therapies in chronic kidney diseases: An update. Nephrol. Ther. 2021, 18, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Sun, F.; Lin, H.; Fan, Y.; Wang, C.; Yu, D.; Liu, N.; Wu, A. Food bioactive compounds with prevention functionalities against fungi and mycotoxins: Developments and challenges. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2022, 2022, 100916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; El-Rayes, S.M.; Khalil, W.F.; Abdeen, A.; Abdelkader, A.; Youssef, M.; Maher, Z.M.; Ibrahim, A.N.; Abdelrahman, S.M.; Ibrahim, S.F. Arabic Gum Could Alleviate the Aflatoxin B1-Provoked Hepatic Injury in Rat: The Involvement of Oxidative Stress, Inflammatory, and Apoptotic Pathways. Toxins 2022, 14, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, D.; Li, C.; Cui, S.; Yun, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wei, Y.; Sun, F. Chromatographic methods for rapid aflatoxin B1 analysis in food: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci Nutr. 2022, 2022, 2155107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gündüz, A.; Yalçın, E.; Çavuşoğlu, K. Combined toxic effects of aflatoxin B2 and the protective role of resveratrol in Swiss albino mice. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 18081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rushing, B.R.; Selim, M.I. Aflatoxin B1: A review on metabolism, toxicity, occurrence in food, occupational exposure, and detoxification methods. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 124, 81–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkerroum, N. Chronic and acute toxicities of aflatoxins: Mechanisms of action. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchese, S.; Polo, A.; Ariano, A.; Velotto, S.; Costantini, S.; Severino, L. Aflatoxin B1 and M1: Biological properties and their involvement in cancer development. Toxins 2018, 10, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damiano, S.; Jarriyawattanachaikul, W.; Girolami, F.; Longobardi, C.; Nebbia, C.; Andretta, E.; Lauritano, C.; Dabbou, S.; Avantaggiato, G.; Schiavone, A. Curcumin supplementation protects broiler chickens against the renal oxidative stress induced by the dietary exposure to low levels of aflatoxin B1. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 8, 1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveed, M.; Haleem, K.S.; Ghazanfar, S.; Tauseef, I.; Bano, N.; Adetunji, C.O.; Saleem, M.H.; Alshaya, H.; Paray, B.A. Quantitative estimation of aflatoxin level in poultry feed in selected poultry farms. Biomed. Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IARC (International Agency for Research on Cancer). Agents Classified by the IARC Monographs. Volume 1–113. 2014. Available online: http://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php (accessed on 25 January 2024).
- Lin, H.; Liu, W.; Zeng, H.; Pu, C.; Zhang, R.; Qiu, Z.; Chen, J.-a.; Wang, L.; Tan, Y.; Zheng, C.; et al. Determination of environmental exposure to microcystin and aflatoxin as a risk for renal function based on 5493 rural people in southwest China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 5346–5356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.; Li, L.P.; Zeng, Z.; Mu, J.X.; Yang, X.; Zhou, C.; Wang, L.Z.; Zhang, H. Value of urinary KIM-1 and NGAL combined with serum Cys-C for predicting acute kidney injury secondary to decompensated cirrhosis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xing, L.; Zhang, M.; Wang, J.; Zheng, N. The toxic effects of aflatoxin B1 and aflatoxin M1 on kidney through regulating L-proline and downstream apoptosis. Biomed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 9074861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Li, X.; Gao, Y.; Wang, J.; Zheng, N. Integrated Metabolomics and Lipidomics Analysis Reveals Lipid Metabolic Disorder in NCM460 Cells Caused by Aflatoxin B1 and Aflatoxin M1 Alone and in Combination. Toxins 2023, 15, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Barbary, M.I. Detoxification and antioxidant effects of garlic and curcumin in Oreochromis niloticus injected with aflatoxin B 1 with reference to gene expression of glutathione peroxidase (GPx) by RT-PCR. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 42, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appiah-Opong, R.; Ankrah, N.A.; Nyarko, A.K.; Ofori-Attah, E.; Agordzo, E. Inhibition of aflatoxin B1-8, 9-epoxide formation by selected Ghanaian vegetables. J. Ghana Sci. Assoc. 2016, 16, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, M.; Kensler, T.W.; Motohashi, H. The KEAP1-NRF2 system: A thiol-based sensor-effector apparatus for maintaining redox homeostasis. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 1169–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Feng, X.; Hu, X.; Sha, J.; Li, B.; Zhang, H.; Fan, H. Dexmedetomidine ameliorates acute stress-induced kidney injury by attenuating oxidative stress and apoptosis through inhibition of the ROS/JNK signaling pathway. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2018, 2018, 4035310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, K.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, J.; He, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, T. Supplemental effects of probiotic Bacillus subtilis fmbJ on growth performance, antioxidant capacity, and meat quality of broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2017, 96, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravinayagam, V.; Jaganathan, R.; Panchanadham, S.; Palanivelu, S. Potential antioxidant role of tridham in managing oxidative stress against aflatoxin-B1-induced experimental hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Hepatol. 2012, 2012, 428373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ren, R.; Yang, Z.; Cai, J.; Du, S.; Shen, X. The COL11A1/Akt/CREB signaling axis enables mitochondrial-mediated apoptotic evasion to promote chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer cells through modulating BAX/BCL-2 function. J. Cancer 2021, 12, 1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; Liu, M.; Huang, W.; Zhang, J.; Song, M.; Shao, B.; Li, Y. The nephrotoxicity of T-2 toxin in mice caused by oxidative stress-mediated apoptosis is related to Nrf2 pathway. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 149, 112027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lv, Z.; Chen, J.; Nepovimova, E.; Long, M.; Wu, W.; Kuca, K. Bacillus amyloliquefaciens B10 can alleviate liver apoptosis and oxidative stress induced by aflatoxin B1. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 151, 112124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, X.; Ou, Y.; Zhu, X.; Cheng, Z.; Zhang, P.; Wu, X.; Meng, Y.; Zhang, L. The relationship between the Bcl-2/Bax proteins and the mitochondria-mediated apoptosis pathway in the differentiation of adipose-derived stromal cells into neurons. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Feng, L.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, H.; Shi, Y.; Liang, S.; Zhao, T.; Fu, Y.; Duan, J.; Sun, Z. Cytotoxicity induced by fine particulate matter (PM2. 5) via mitochondria-mediated apoptosis pathway in human cardiomyocytes. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 161, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paunkov, A.; Chartoumpekis, D.V.; Ziros, P.G.; Sykiotis, G.P. A bibliometric review of the Keap1/Nrf2 pathway and its related antioxidant compounds. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.-H.; Huo, L.-J.; Li, T.-T. Antioxidant axis Nrf2-keap1-ARE in inhibition of alcoholic liver fibrosis by IL-22. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sureshbabu, A.; Ryter, S.W.; Choi, M.E. Oxidative stress and autophagy: Crucial modulators of kidney injury. Redox Biol. 2015, 4, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, S.; Hu, J.; Song, S.; Huang, D.; Xu, H.; Qian, G.; Gan, F.; Huang, K. Selenium alleviates aflatoxin B1-induced immune toxicity through improving glutathione peroxidase 1 and selenoprotein S expression in primary porcine splenocytes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 1385–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, P.; Yang, S.-H.; Zhang, W.-K.; Han, J.-X.; Wang, Y.; He, J.-B. Intervention of grape seed proanthocyanidin extract on the subchronic immune injury in mice induced by aflatoxin B1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wang, Y.; Jin, S.; Pang, Q.; Shan, A.; Feng, X. Dietary resveratrol alleviated lipopolysaccharide-induced ileitis through Nrf2 and NF-κB signalling pathways in ducks (Anas platyrhynchos). J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2022, 106, 1306–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Daim, M.M.; Abdeen, A.; Jalouli, M.; Abdelkader, A.; Megahed, A.; Alkahtane, A.; Almeer, R.; Alhoshani, N.M.; Al-Johani, N.S.; Alkahtani, S. Fucoidan supplementation modulates hepato-renal oxidative stress and DNA damage induced by aflatoxin B1 intoxication in rats. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 768, 144781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural products as sources of new drugs over the nearly four decades from 01/1981 to 09/2019. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 770–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.; Egbuna, C.; Tijjani, H.; Ifemeje, J.C.; Olisah, M.C.; Patrick-Iwuanyanwu, K.C.; Onyeike, P.C.; Ephraim-Emmanuel, B.C. Dietary supplements: Types, health benefits, industry, and regulation. In Functional Foods and Nutraceuticals: Bioactive Components, Formulations and Innovations; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Hamidu, S.; Yang, X.; Yan, Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, L.; Oduro, P.K.; Li, Y. Dietary supplements, and natural products: An update on their clinical effectiveness and molecular mechanisms of action during accelerated biological aging. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 880421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, R.L. Current regulatory guidelines and resources to support research of dietary supplements in the United States. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 298–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wruck, W.; Genfi, A.K.A.; Adjaye, J. Natural Products in Renal-Associated Drug Discovery. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Liang, Y.; Zhou, L. Natural products for kidney disease treatment: Focus on targeting mitochondrial dysfunction. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mahalaway, A.M. Protective effect of curcumin against experimentally induced aflatoxicosis on the renal cortex of adult male albino rats: A histological and immunohisochemical study. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 6019. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- El-Mekkawy, H.I.; Al-Kahtani, M.A.; Shati, A.A.; Alshehri, M.A.; Al-Doaiss, A.A.; Elmansi, A.A.; Ahmed, A.E. Black tea and curcumin synergistically mitigate the hepatotoxicity and nephropathic changes induced by chronic exposure to aflatoxin-B1 in Sprague–Dawley rats. J. Food Biochem. 2020, 44, e13346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawat, D.; Shrivastava, S.; Naik, R.A.; Chhonker, S.K.; Koiri, R.K. SIRT1-mediated amelioration of oxidative stress in kidney of alcohol-aflatoxin-B1-induced hepatocellular carcinoma by resveratrol is catalase dependent and GPx independent. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2020, 34, e22576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, M.; Suganthi, R.; Thammiaha, V. Effect of dietary resveratrol in ameliorating aflatoxin B1-induced changes in broiler birds. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2015, 99, 1094–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eraslan, G.; Sarıca, Z.S.; Bayram, L.Ç.; Tekeli, M.Y.; Kanbur, M.; Karabacak, M. The effects of diosmin on aflatoxin-induced liver and kidney damage. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 27931–27941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Xu, J.; Jiang, L.; Liu, W.; Hong, H.; Qian, Y.; Li, S.; Huang, W.; Zhao, H.; Yang, Z. Morin alleviates aflatoxin B1-induced liver and kidney injury by inhibiting heterophil extracellular traps release, oxidative stress and inflammatory responses in chicks. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 101513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naaz, F.; Abdin, M.; Javed, S. Protective effect of esculin against prooxidant aflatoxin B 1-induced nephrotoxicity in mice. Mycotoxin Res. 2014, 30, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Daim, M.M.; Dawood, M.A.; Aleya, L.; Alkahtani, S. Effects of fucoidan on the hematic indicators and antioxidative responses of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) fed diets contaminated with aflatoxin B1. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 12579–12586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleissa, M.S.; Alkahtani, S.; Abd Eldaim, M.A.; Ahmed, A.M.; Bungău, S.G.; Almutairi, B.; Bin-Jumah, M.; AlKahtane, A.A.; Alyousif, M.S.; Abdel-Daim, M.M. Fucoidan ameliorates oxidative stress, inflammation, DNA damage, and hepatorenal injuries in diabetic rats intoxicated with aflatoxin B1. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2020, 2020, 9316751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Shu, G.; Peng, X.; Fang, J.; Chen, K.; Cui, H.; Chen, Z.; Zuo, Z.; Deng, J.; Geng, Y. Protective effects of sodium selenite against aflatoxin B1-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in broiler spleen. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 2834–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parveen, F.; Nizamani, Z.A.; Gan, F.; Chen, X.; Shi, X.; Kumbhar, S.; Zeb, A.; Huang, K. Protective effect of selenomethionine on aflatoxin B1-induced oxidative stress in MDCK cells. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2014, 157, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, S.; Kaya, E.; Karaca, A.; Karatas, O. Aflatoxin B1 induced renal and cardiac damage in rats: Protective effect of lycopene. Res. Vet. Sci. 2018, 119, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sheshtawy, S.M.; El-Zoghby, A.F.; Shawky, N.A.; Samak, D.H. Aflatoxicosis in Pekin duckling and the effects of treatments with lycopene and silymarin. Vet. World 2021, 14, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EL Hak, H.N.G.; Metawea, S.I.; Nabil, Z.I. Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum graecum L.) supplementation safeguards male mice from aflatoxin B1-induced liver and kidney damage. Comp. Clin. Pathol. 2022, 31, 925–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Śliżewska, K.; Cukrowska, B.; Smulikowska, S.; Cielecka-Kuszyk, J. The effect of probiotic supplementation on performance and the histopathological changes in liver and kidneys in broiler chickens fed diets with aflatoxin B1. Toxins 2019, 11, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.-W.; Chang, J.; Wang, P.; Yin, Q.-Q.; Liu, C.-Q.; Xu, X.-X.; Dang, X.-W.; Hu, X.-F.; Wang, Q.-L. Effects of compound probiotics and aflatoxin-degradation enzyme on alleviating aflatoxin-induced cytotoxicity in chicken embryo primary intestinal epithelium, liver and kidney cells. AMB Express 2021, 11, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrami, A.; Sathyapalan, T.; Moallem, S.A.; Sahebkar, A. Counteracting arsenic toxicity: Curcumin to the rescue? J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 400, 123160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillo, J.; Chirino, Y.I.; Molina-Jijón, E.; Andérica-Romero, A.C.; Tapia, E.; Pedraza-Chaverrí, J. Renoprotective effect of the antioxidant curcumin: Recent findings. Redox Biol. 2013, 1, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, S.; Yang, H.; Jiao, Y.; Pang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Shan, A.; Feng, X. Dietary curcumin alleviated acute ileum damage of ducks (Anas platyrhynchos) induced by AFB1 through regulating Nrf2-ARE and NF-κB signaling pathways. Foods 2021, 10, 1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimiya, Y.; Wang, W.; Du, Z.; Sukamtoh, E.; Zhu, J.; Decker, E.; Zhang, G. Redox modulation of curcumin stability: Redox active antioxidants increase chemical stability of curcumin. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2016, 60, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.; Tian, E.; Hao, Z.; Tang, S.; Wang, Z.; Sharma, G.; Jiang, H.; Shen, J. Aflatoxin B1 Toxicity and Protective Effects of Curcumin: Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Implications. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunnumakkara, A.B.; Bordoloi, D.; Padmavathi, G.; Monisha, J.; Roy, N.K.; Prasad, S.; Aggarwal, B.B. Curcumin, the golden nutraceutical: Multitargeting for multiple chronic diseases. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 1325–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Wahhab, M.A.; Salman, A.S.; Ibrahim, M.I.; El-Kady, A.A.; Abdel-Aziem, S.H.; Hassan, N.S.; Waly, A.I. Curcumin nanoparticles loaded hydrogels protects against aflatoxin B1-induced genotoxicity in rat liver. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 94, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Rizvi, S.I. Black tea supplementation improves antioxidant status in rats subjected to oxidative stress. Z. Naturforsch. C J. Biosci. 2013, 68, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.-M.; Cao, S.-Y.; Wei, X.-L.; Gan, R.-Y.; Wang, Y.-F.; Cai, S.-X.; Xu, X.-Y.; Zhang, P.-Z.; Li, H.-B. Effects and mechanisms of tea for the prevention and management of diabetes mellitus and diabetic complications: An updated review. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limaye, A.; Yu, R.-C.; Chou, C.-C.; Liu, J.-R.; Cheng, K.-C. Protective and detoxifying effects conferred by dietary selenium and curcumin against AFB1-mediated toxicity in livestock: A review. Toxins 2018, 10, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, I.; Wang, H.; Sun, X.; Wang, X.; Han, M.; Lu, Z.; Cheng, P.; Hussain, M.A.; Zhang, X. Dual role of dietary curcumin through attenuating AFB1-induced oxidative stress and liver injury via modulating liver phase-I and phase-II enzymes involved in AFB1 bioactivation and detoxification. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malaguarnera, L. Influence of resveratrol on the immune response. Nutrients 2019, 11, 946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saldanha, J.F.; Leal, V.d.O.; Stenvinkel, P.; Carraro-Eduardo, J.C.; Mafra, D. Resveratrol: Why is it a promising therapy for chronic kidney disease patients? Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2013, 2013, 963217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.-N.; Hou, C.-Y.; Tain, Y.-L. Preventive aspects of early resveratrol supplementation in cardiovascular and kidney disease of developmental origins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grujić-Milanović, J.; Jaćević, V.; Miloradović, Z.; Milanović, S.D.; Jovović, D.; Ivanov, M.; Karanović, D.; Vajić, U.-J.; Mihailović-Stanojević, N. Pharmacotherapy, Resveratrol improved kidney function and structure in malignantly hypertensive rats by restoration of antioxidant capacity and nitric oxide bioavailability. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 154, 113642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santini, A.; Ritieni, A. Aflatoxins: Risk, exposure and remediation. In Aflatoxins-Recent Advances and Future Prospects; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 343–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badhani, B.; Sharma, N.; Kakkar, R. Gallic acid: A versatile antioxidant with promising therapeutic and industrial applications. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 27540–27557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asci, H.; Ozmen, O.; Ellidag, H.Y.; Aydin, B.; Bas, E.; Yilmaz, N. The impact of gallic acid on the methotrexate-induced kidney damage in rats. J. Food. Drug. Anal. 2017, 25, 890–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garud, M.S.; Kulkarni, Y.A. Gallic acid attenuates type I diabetic nephropathy in rats. Chem. Biol. Interac. 2018, 282, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matboli, M.; Eissa, S.; Ibrahim, D.; Hegazy, M.G.; Imam, S.S.; Habib, E.K. Caffeic acid attenuates diabetic kidney disease via modulation of autophagy in a high-fat diet/streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinhart, A.D.; Damin, F.M.; Caldeirao, L.; de Jesus Filho, M.; da Silva, L.C.; da Silva Constant, L.; Filho, J.T.; Wagner, R.; Godoy, H.T. Chlorogenic and caffeic acids in 64 fruits consumed in Brazil. Food Chem. 2019, 286, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, R.; Singh, S.V.; Jaiswal, K.; Kumar, R.; Pandey, A.K. Modulatory effect of caffeic acid in alleviating diabetes and associated complications. World J. Diabetes 2023, 14, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nur, G.; Caylak, E.; Deveci, H.A.; Kılıcle, P.A.; Deveci, A. The protective effect of caffeic acid phenethyl ester in the nephrotoxicity induced by α-cypermethrin. Open Med. 2023, 18, 20230781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senthamizhselvan, O.; Manivannan, J.; Silambarasan, T.; Raja, B. Diosmin pretreatment improves cardiac function and suppresses oxidative stress in rat heart after ischemia/reperfusion. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 736, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, D.; Bansal, M.K.; Dalvi, R.; Upganlawar, A.; Somani, R. Protective effect of diosmin against diabetic neuropathy in experimental rats. J. Integr. Med. 2014, 12, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silambarasan, T.; Raja, B. Diosmin, a bioflavonoid reverses alterations in blood pressure, nitric oxide, lipid peroxides and antioxidant status in DOCA-salt induced hypertensive rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 679, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanrikulu, Y.; Şahin, M.; Kismet, K.; Kilicoglu, S.S.; Devrim, E.; Tanrikulu, C.S.; Erdemli, E.; Erel, S.; Bayraktar, K.; Akkus, M.A. The protective effect of diosmin on hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury: An experimental study. Bosn. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2013, 13, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, S.; Pari, L. Ameliorative effect of diosmin, a citrus flavonoid against streptozotocin-nicotinamide generated oxidative stress induced diabetic rats. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2012, 195, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, M.U.; Tahir, M.; Khan, A.Q.; Khan, R.; Lateef, A.; Hamiza, O.O.; Ali, F.; Sultana, S. Diosmin protects against trichloroethylene-induced renal injury in Wistar rats: Plausible role of p53, Bax and caspases. Br. J. Nutr. 2013, 110, 699–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arab, H.H.; Salama, S.A.; Omar, H.A.; Arafa, E.-S.A.; Maghrabi, I.A. Diosmin protects against ethanol-induced gastric injury in rats: Novel anti-ulcer actions. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, G.; Riahi, Y.; Sunda, V.; Deplano, S.; Chatgilialoglu, C.; Ferreri, C.; Kaiser, N.; Sasson, S.J. Signaling properties of 4-hydroxyalkenals formed by lipid peroxidation in diabetes. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 65, 978–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hostetler, G.L.; Ralston, R.A.; Schwartz, S.J. Flavones: Food sources, bioavailability, metabolism, and bioactivity. Adv. Nutr. 2017, 8, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salehi, B.; Venditti, A.; Sharifi-Rad, M.; Kręgiel, D.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Durazzo, A.; Lucarini, M.; Santini, A.; Souto, E.B.; Novellino, E. The therapeutic potential of apigenin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.A.; Parama, D.; Daimari, E.; Girisa, S.; Banik, K.; Harsha, C.; Dutta, U.; Kunnumakkara, A.B. Rationalizing the therapeutic potential of apigenin against cancer. Life Sci. 2021, 267, 118814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makanjuola, S.B.; Ogundaini, A.O.; Ajonuma, L.C.; Dosunmu, A. Apigenin and apigeninidin isolates from the Sorghum bicolor leaf targets inflammation via cyclo-oxygenase-2 and prostaglandin-E2 blockade. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 21, 1487–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caselli, A.; Cirri, P.; Santi, A.; Paoli, P. Morin: A promising natural drug. Curr. Med. Chem. 2016, 23, 774–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, K.; Ghosh, J.; Sil, P.C. Morin and its role in chronic diseases. In Anti-Inflammatory Nutraceuticals and Chronic Diseases; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 453–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, K.; Sadhukhan, P.; Saha, S.; Pal, P.B.; Sil, P.C. Morin protects gastric mucosa from nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug, indomethacin induced inflammatory damage and apoptosis by modulating NF-κB pathway. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. 2015, 1850, 769–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopal, J.V. Morin hydrate: Botanical origin, pharmacological activity and its applications: A mini review. Pharmacogn. J. 2013, 5, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Yang, H.; Hu, R.; Liang, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, W.; Fan, X.; Liu, Y. Comparing the interaction of four structurally similar coumarins from Fraxinus Chinensis Roxb. with HSA through multi-spectroscopic and docking studies. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 340, 117234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Xin, X.; Lai, F.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Wu, H. Cellular transport of esculin and its acylated derivatives in Caco-2 cell monolayers and their antioxidant properties in vitro. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 7424–7432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Kar, S.; Basu Ball, W.; Ghosh, K.; Das, P.K. The curative effect of fucoidan on visceral leishmaniasis is mediated by activation of MAP kinases through specific protein kinase C isoforms. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2014, 11, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luthuli, S.; Wu, S.; Cheng, Y.; Zheng, X.; Wu, M.; Tong, H. Therapeutic effects of fucoidan: A review on recent studies. Mar. Drugs. 2019, 17, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xing, M.; Cao, Q.; Ji, A.; Liang, H.; Song, S. Biological activities of fucoidan and the factors mediating its therapeutic effects: A review of recent studies. Mar. Drugs. 2019, 17, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahan, M.S.; Hasan, A.; Rahman, M.H.; Meem, K.N.; Moni, A.; Hannan, M.A.; Uddin, M.J. Protective effects of fucoidan against kidney diseases: Pharmacological insights and future perspectives. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 209, 2119–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.-C.; Huang, R.-Y.; Chou, T.-C. Oligo-fucoidan improves diabetes-induced renal fibrosis via activation of Sirt-1, GLP-1R, and Nrf2/HO-1: An in vitro and in vivo study. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agar, G.; Alpsoy, L.; Bozari, S.; Erturk, F.A.; Yildirim, N. Determination of protective role of selenium against aflatoxin B1-induced DNA damage. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2013, 29, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Shu, G.; Peng, X.; Fang, J.; Cui, H.; Chen, J.; Wang, F.; Chen, Z.; Zuo, Z.; Deng, J. Protective role of sodium selenite on histopathological lesions, decreased T-cell subsets and increased apoptosis of thymus in broilers intoxicated with aflatoxin B1. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 59, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zachara, B.A. Selenium and selenium-dependent antioxidants in chronic kidney disease. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2015, 68, 131–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salehi, M.; Sohrabi, Z.; Ekramzadeh, M.; Fallahzadeh, M.K.; Ayatollahi, M.; Geramizadeh, B.; Hassanzadeh, J.; Sagheb, M.M. Selenium supplementation improves the nutritional status of hemodialysis patients: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2013, 28, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, P.; Selgas, R.; Romero, S.; Díez, J.J. Selenium and kidney disease. J. Nephrol. 2012, 26, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mughal, M.J.; Peng, X.; Kamboh, A.A.; Zhou, Y.; Fang, J. Aflatoxin B 1 induced systemic toxicity in poultry and rescue effects of Selenium and Zinc. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2017, 178, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galli, F.; Azzi, A.; Birringer, M.; Cook-Mills, J.M.; Eggersdorfer, M.; Frank, J.; Cruciani, G.; Lorkowski, S.; Özer, N.K. Vitamin E: Emerging aspects and new directions. Free Radic. Biol. 2017, 102, 16–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Kim, H.D.; Ryu, D. Protective Effect of alpha-Tocopherol Against Ochratoxin A in Kidney Cell Line HK-2. J. Food Prot. 2023, 86, 100082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizvi, S.; Raza, S.T.; Ahmed, F.; Ahmad, A.; Abbas, S.; Mahdi, F.J. The role of vitamin E in human health and some diseases. Sultan Qaboos Univ. Med. J. 2014, 14, e157. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Galli, F.; Bonomini, M.; Bartolini, D.; Zatini, L.; Reboldi, G.; Marcantonini, G.; Gentile, G.; Sirolli, V.; Di Pietro, N.J.A. Vitamin E (Alpha-Tocopherol) Metabolism and Nutrition in Chronic Kidney Disease. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koay, Y.Y.; Tan, G.C.J.; Phang, S.C.W.; Ho, J.-I.; Chuar, P.F.; Ho, L.S.; Ahmad, B.; Abdul Kadir, K. A phase IIb randomized controlled trial investigating the effects of tocotrienol-rich vitamin E on diabetic kidney disease. Nutrients 2021, 13, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.Y.; Lin, C.J.; Pan, H.C.; Lee, C.C.; Lu, S.C.; Hsieh, Y.T.; Huang, S.Y.; Huang, H.Y. Clinical association between the metabolite of healthy gut microbiota, 3-indolepropionic acid and chronic kidney disease. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 2945–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.; Chen, X.; Yu, C.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, S.; Chen, X.; Chen, K.; Yang, Y.; Ling, W. Gut microbially produced indole-3-propionic acid inhibits atherosclerosis by promoting reverse cholesterol transport and its deficiency is causally related to atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Circ. Res. 2022, 131, 404–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meléndez-Martínez, A.J.; Mapelli-Brahm, P.; Benítez-González, A.; Stinco, C.M. A comprehensive review on the colorless carotenoids phytoene and phytofluene. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2015, 572, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-H.; Zhang, R.-R.; Yin, Y.; Tan, G.-F.; Wang, G.-L.; Liu, H.; Zhuang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhuang, F.-Y.; Xiong, A.-S. Advances in engineering the production of the natural red pigment lycopene: A systematic review from a biotechnology perspective. J. Adv. Res. 2023, 46, 31–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Rahman, H.G.; Abdelrazek, H.; Zeidan, D.W.; Mohamed, R.M.; Abdelazim, A.M. Lycopene: Hepatoprotective and antioxidant effects toward bisphenol A-induced toxicity in female Wistar rats. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2018, 2018, 5167524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedir, F.; Kocaturk, H.; Turangezli, O.; Sener, E.; Akyuz, S.; Ozgeris, F.; Dabanlioglu, B.; Suleyman, H.; Altuner, D.; Suleyman, B. The protective effect of lycopene against oxidative kidney damage associated with combined use of isoniazid and rifampicin in rats. Braz. J. Med. Biol. 2021, 54, 10660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeira, S.P.; Borges Filho, C.; Del’Fabbro, L.; Roman, S.S.; Royes, L.F.F.; Fighera, M.R.; Jessé, C.R.; Oliveira, M.S.; Furian, A.F. Lycopene treatment prevents hematological, reproductive and histopathological damage induced by acute zearalenone administration in male Swiss mice. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2014, 66, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaca, A.; Yilmaz, S.; Kaya, E.; Altun, S. The effect of lycopene on hepatotoxicity of aflatoxin B1 in rats. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 127, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taheri, Z.; Ghafari, M.; Amiri, M. Lycopene and kidney; future potential application. J. Nephropharmacol. 2015, 4, 49. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Q.; Piao, Y.; Yin, S.; Zhang, K. Association of serum lycopene concentrations with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality among individuals with chronic kidney disease: A cohort study. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1048884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, S.; Pergola, P.E.; Zager, R.A.; Vaziri, N.D. Targeting the transcription factor Nrf2 to ameliorate oxidative stress and inflammation in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2013, 83, 1029–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, C.; Tang, S.; Deng, S.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Velkov, T.; Li, J.; Xiao, X. Lycopene attenuates colistin-induced nephrotoxicity in mice via activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matzinger, M.; Fischhuber, K.; Heiss, E.H. Activation of Nrf2 signaling by natural products-can it alleviate diabetes? Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 1738–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelton, L.M.; Park, B.K.; Copple, I.M. Role of Nrf2 in protection against acute kidney injury. Kidney Int. 2013, 84, 1090–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadhwa, K.; Pahwa, R.; Kumar, M.; Kumar, S.; Sharma, P.C.; Singh, G.; Verma, R.; Mittal, V.; Singh, I.; Kaushik, D.; et al. Mechanistic insights into the pharmacological significance of silymarin. Molecules 2022, 27, 5327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedayati, N.; Naeini, M.B.; Nezami, A.; Hosseinzadeh, H.; Wallace Hayes, A.; Hosseini, S.; Imenshahidi, M.; Karimi, G. Protective effect of lycopene against chemical and natural toxins: A review. BioFactors 2019, 45, 5–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyene, B.; Beyene, B.; Deribe, H. Review on application and management of medicinal plants for the livelihood of the local community. J. Manag. Dev. 2016, 22, 33–39. [Google Scholar]
- Saad, B.; Zaid, H.; Shanak, S.; Kadan, S.; Saad, B.; Zaid, H.; Shanak, S.; Kadan, S. Introduction to Medicinal Plant Safety and Efficacy; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 21–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, M.; Ye, C.; Bayliss, G.; Zhuang, S. New Insights into the Effects of Individual Chinese Herbal Medicines on Chronic Kidney Disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 774414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, P.; Sharma, H. A potential ethnomedicinal plant Semecarpus anacardium Linn. A review. Int. J. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 3, 564–572. [Google Scholar]
- Selvam, C.; Jachak, S.M. A cyclooxygenase (COX) inhibitory biflavonoid from the seeds of Semecarpus anacardium. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2004, 95, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scartezzini, P.; Antognoni, F.; Raggi, M.A.; Poli, F.; Sabbioni, C. Vitamin C content and antioxidant activity of the fruit and of the Ayurvedic preparation of Emblica officinalis Gaertn. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2006, 104, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljadi, A.M.; Kamaruddin, M.Y. Evaluation of the phenolic contents and antioxidant capacities of two Malaysian floral honeys. Food Chem. 2004, 85, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laila, O.; Murtaza, I.; Muzamil, S.; Ali, S.I.; Ali, S.A.; Paray, B.A.; Aneela Gulnaz, A.; Carmen Vladulescu, C.; Mansoor, S. Enhancement of nutraceutical and anti-diabetic potential of fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum). Sprouts with natural elicitors. Saudi Pharm. J. 2023, 31, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baset, M.E.; Ali, T.I.; Elshamy, H.; El Sadek, A.M.; Sami, D.G.; Badawy, M.T.; Abou-Zekry, S.S.; Heiba, H.H.; Saadeldin, M.K.; Abdellatif, A. Anti-diabetic effects of fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum): A comparison between oral and intraperitoneal administration-an animal study. Int. J. Funct. Nutr. 2020, 1, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farouk, S.M.; Abdel-Rahman, H.G.; Abdallah, O.A.; El-Behidy, N.G. Comparative immunomodulatory efficacy of rosemary and fenugreek against Escherichia coli infection via suppression of inflammation and oxidative stress in broilers. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 40053–40067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.-F.; Wang, R.-N.; Zhang, L.-L.; Wang, Y.; Lin, P.-C. Extraction technology, composition analysis and antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of volatile oil from fenugreek leaves. China J. Chin. Mater. Medica 2020, 45, 3161–3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roohbakhsh, E.; Barari, A.; Abbaszadeh, H. The effect of interval training and consuming fenugreek seed extract on FGF-21 and VEGF gene expression in patients with coronary artery diseases. Intern. Med. 2021, 27, 130–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamit, U.; Adali, Y. Hepatoprotective and nephroprotective effects of Trigonella foenum-graecum L. (Fenugreek) seed extract against sodium nitrite toxicity in rats. Biomed. Res. Ther. 2019, 6, 3142–3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belguithhadriche, O.; Bouaziz, M.; Jamoussi, K.; Elfeki, A.; Makniayedi, F. Renoprotective effects of fenugreek seeds against oxidative stress in hypercholesterolemic fed Rats. Her. J. Agric. Food Sci. Res. 2014, 8, 382–385. [Google Scholar]
- Das, S. Hepatoprotective activity of methanol extract of fenugreek seeds on rats. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 5, 1506–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaldiz, G.; Camlica, M. Assessment of Secondary Metabolites with Different Uses of Fenugreek. Legum. Res. 2021, 2, 99479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tang, H.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Derrien, M.; Rocher, E.; van-Hylckama Vlieg, J.E.; Strissel, K.; Zhao, L.; Obin, M. Modulation of gut microbiota during probiotic-mediated attenuation of metabolic syndrome in high fat diet-fed mice. ISME J. 2015, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, A.C.; Bueno, A.A.; de Souza, R.G.M.; Mota, J.F. Gut microbiota, probiotics and diabetes. Nutr. J. 2014, 13, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, H.; Mei, X.; Yu, D.; Wang, Y.; Li, W. Antioxidant properties of probiotic bacteria. Nutrients 2017, 9, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motawe, H.; Salam, A.A.; El Meleigy, K.M. Reducing the toxicity of aflatoxin in broiler chickens’ diet by using probiotic and yeast. Int. J. Poult. Sci. 2014, 13, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimbalo, A.; Alonso-Garrido, M.; Font, G.; Manyes, L. Toxicity of mycotoxins in vivo on vertebrate organisms: A review. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 137, 111161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Natural Products/Dietary Supplements | Model | Effect/Mechanism | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Curcumin | Reduces renal function markers: | ||
| Mice | ↓ Urea, CREA, UA | ||
| Gene and protein expression associated with the Keap1/Nrf2 pathway: | |||
| ↑ SOD1, CAT, NQO1, GSH, GCLC, GCLM, Nrf2 | [19] | ||
| ↓ Keap1 | |||
| Kidney antioxidant capacity: | |||
| ↑ SOD, CAT, H2O2, GSH, T-AOC | |||
| ↓ MDA | |||
| Renal Apoptosis: ↓ Bax, Cyt-c, Caspase-3, Caspase-9, TUNEL-positive cells | |||
| ↑ BCl-2 | |||
| Restored pathological structure of kidney. | |||
| Rat | Reduction in glomeruli enlargement and histological improvement. | [71] | |
| ↑ Bcl-2 | |||
| Poultry | ↑ SOD, CAT, GPx | [39] | |
| ↓ MDA, 8-OHdG, NOX4 | |||
| Curcumin and black tea | Rat | ↓ MDA | [72] |
| ↑ GSH and Bcl-2 in kidney tissue | |||
| Anti-tumor p53 | |||
| Resveratrol | Reduces renal function markers and excessive oxidative damage. | ||
| Mice | ↑ GSH | [36] | |
| ↓ MDA | |||
| ↓ Urea, CREA | |||
| Rat | ↑ SOD, CAT, GPx | [73] | |
| ↓ SIRT1, | |||
| ↓ MDA | |||
| ↓ UA | |||
| Poultry | ↓ Fatty kidney | [74] | |
| ↓ Interstitial spaces of kidney | |||
| Gallic Acid | Rat | Improves renal in kidney cytoarchitecture, such as glomerular mesangialization and inflammatory cell infiltration. | [20] |
| ↑ CAT, SOD, GPx, GST, GSH | |||
| ↓ RONs, LPO, NO, MPO, | |||
| ↓ Renal caspase 3, TNF-α, | |||
| ↓ Urea, CREA | |||
| Caffeic acid | Rat | Improvements kidney cytoarchitecture, such as glomerular mesangialization and inflammatory cell infiltration. | [21] |
| ↑ Kidney weight | |||
| ↓ Urea, CREA | |||
| ↑ SOD, CAT, GPx, GST | |||
| ↑ GSH, TSH and Trx l | |||
| ↓ XO, RONS, LPO | |||
| ↓ NO, MPO, IL-1β, IL-10 | |||
| ↓ 8-OHdG, caspase-3, caspase-9 | |||
| Diosmin | Rat | Reduces renal function markers, and renal oxidative stress. | [75] |
| ↓ MDA, 4-HNE, NO | |||
| ↑ SOD, CAT, GPx | |||
| ↓ BUN, CREA, UA | |||
| Apigenin | Rat | Anti-inflammatory, reduces renal function markers, and preserves the histoarchitectural network of kidney. | [22] |
| ↓ Urea, CREA | |||
| ↑ SOD, CAT, GPx, GST | |||
| ↑ GSH, TSH and Trx l | |||
| ↓ XO, RONS, LPO | |||
| ↓ NO, MPO, IL-1β, IL-10 | |||
| ↓ caspase-3, caspase-9 | |||
| Morin | Poultry | Effectively relieved kidney damage; Renal cell necrosis, exfoliation, and vacuolization. | [76] |
| ↓ BUN, CREA | |||
| ↑ SOD, GPx, CAT | |||
| ↓ MDA | |||
| ↓ TNF-α, IL-6 IL-1β iNOS COX-2 | |||
| ↓ caspase 1, 3 and 11 | |||
| Esculin | Mice | Exhibits regenerative activity in renal tubules and antioxidant activity. | [77] |
| ↑ GST, GSH, GPx, GR, CAT, SOD | |||
| ↓ MDA | |||
| Fucoidan | Rat/Nile Tilapia | Improves renal function markers and tissue damage. | [64,78] |
| ↑ Nrf2, HO-1, CAT, SOD, GPx, GST | |||
| ↓ MDA, NO, DNA Damage (PCNA) | |||
| ↓ BUN, CREA | |||
| Diabetic Rat | ↑ SOD, CAT, GSH, GPx | [79] | |
| ↓ MDA | |||
| ↓ BUN, CREA | |||
| ↓ 8-OHdG | |||
| ↓ IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α | |||
| Selenium | Poultry | Improves renal apoptosis and DNA damage. | [80] |
| ↑ Bcl-2 | |||
| ↓ Cell cycle blockage in renal cell | |||
| ↓ DNA damage (PCNA), Caspase-3 | |||
| MDCK cells | ↓ Cytotoxicity | [81] | |
| ↓ MDA | |||
| ↑ mRNA GPx, GSH | |||
| Vitamin E | Rat | Reduces glomerular architectural impairment and blood renal barriers in the renal cortex. | [8] |
| ↓ Renal caspase 3 | |||
| ↑ GSH, GPx, GR, GST | |||
| ↓ MDA | |||
| ↓ Urea, CREA | |||
| 3-indole propionic acid | Rat | Moderate glomerular atrophy | [23] |
| ↑ GST, GSH, SOD, CAT, GPx, TSH | |||
| ↓ XO, RONS, LPO | |||
| ↓ MDA, 8-OHdG | |||
| ↓ Caspase-9, and 3 | |||
| ↓ CREA, BUN | |||
| ↓ NO, IL-1β | |||
| ↑ IL-10 | |||
| Lycopene | Rat | Improves intertubular hemorrhage and dilatation in tubules. | [82] |
| ↑ GSH, GST, GPx, CAT, SOD, G6PD | |||
| ↓ BUN, CREA, UA | |||
| ↓ MDA | |||
| Lycopene or silymarin | Ducklings | ↑ SOD, CAT, TAC, GST | [83] |
| ↓ MDA | |||
| ↓ Urea, CREA | |||
| Kalpaamruthaa (S. anacardium and E. officinalis) | Rat | ↑ CAT, SOD, GR, GPx, GSH | [30] |
| ↓ MDA | |||
| ↓ BUN, CREA | |||
| Fenugreek | Mice | Improvement of kidney histological and cellular structure. | [84] |
| ↑ GSH | |||
| ↓ CREA, Urea, UA | |||
| ↓ MDA | |||
| Probiotic | Mice | Activates antioxidant response element and inhibits renal apoptosis. | [9] |
| ↑ Nrf2, HO-1, AKT, P-AKT, BCl-2 | |||
| ↑ SOD, CAT, GPx | |||
| ↓ Keap1, PTEN, Bax, Caspase 9 & 3 | |||
| ↓ UA, CREA, TUNEL positive cells | |||
| ↓ MDA | |||
| Poultry | Reduces aflatoxin levels in kidney. | [85,86] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ofori-Attah, E.; Hashimoto, M.; Oki, M.; Kadowaki, D. Therapeutic Effect of Natural Products and Dietary Supplements on Aflatoxin-Induced Nephropathy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2849. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25052849
Ofori-Attah E, Hashimoto M, Oki M, Kadowaki D. Therapeutic Effect of Natural Products and Dietary Supplements on Aflatoxin-Induced Nephropathy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(5):2849. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25052849
Chicago/Turabian StyleOfori-Attah, Ebenezer, Mai Hashimoto, Mayu Oki, and Daisuke Kadowaki. 2024. "Therapeutic Effect of Natural Products and Dietary Supplements on Aflatoxin-Induced Nephropathy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 5: 2849. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25052849
APA StyleOfori-Attah, E., Hashimoto, M., Oki, M., & Kadowaki, D. (2024). Therapeutic Effect of Natural Products and Dietary Supplements on Aflatoxin-Induced Nephropathy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(5), 2849. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25052849






