Association between RMTg Neuropeptide Genes and Negative Effect during Alcohol Withdrawal in Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
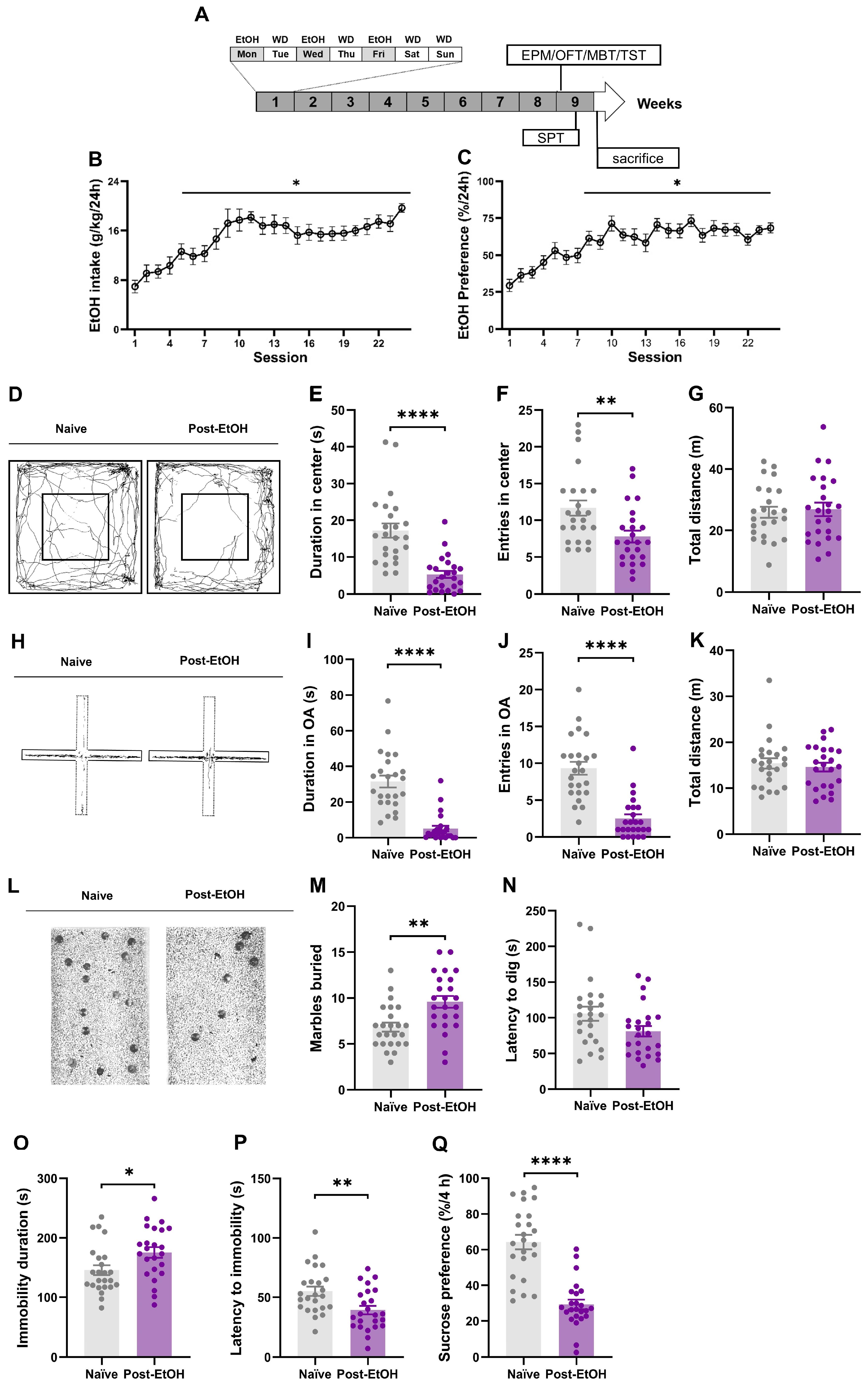
2.1. Expression of Anxiety- and Depression-like Behaviors after Alcohol Withdrawal
2.2. Chronic Alcohol Consumption and Withdrawal Impair the Gene Expression of Stress-Related Neuropeptides in the RMTg
2.3. Chronic Alcohol Consumption and Withdrawal Impair the Gene Expression of Stress-Related Neuropeptides in the VTA-Projecting RMTg Neurons
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Drugs
4.3. Intermittent Access to 20% Ethanol in the Two-Bottle Free-Choice (IA2BC) Drinking Procedure
4.4. Open Field Test (OFT)
4.5. Elevated Plus Maze (EPM)
4.6. Marble-Burying Test (MBT)
4.7. Tail Suspension Test (TST)
4.8. Sucrose Preference Test (SPT)
4.9. Stereotaxic Surgery and Microinjection Procedure
4.10. Complete Laser Capture Microdissection Process
4.11. RNA Extraction and Real-Time Quantitative PCR
4.12. Statistical Methods
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carvalho, A.F.; Heilig, M.; Perez, A.; Probst, C.; Rehm, J. Alcohol use disorders. Lancet 2019, 394, 781–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuckit, M.A. Alcohol-use disorders. Lancet 2009, 373, 492–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luderer, M.; Ramos Quiroga, J.A.; Faraone, S.V.; Zhang James, Y.; Reif, A. Alcohol use disorders and ADHD. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2021, 128, 648–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehm, J.; Shield, K.D. Global Burden of Disease and the Impact of Mental and Addictive Disorders. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2019, 21, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koob, G.F. Alcoholism: Allostasis and beyond. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2003, 27, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, H.C. Influence of stress associated with chronic alcohol exposure on drinking. Neuropharmacology 2017, 122, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouza, C.; Angeles, M.; Munoz, A.; Amate, J.M. Efficacy and safety of naltrexone and acamprosate in the treatment of alcohol dependence: A systematic review. Addiction 2004, 99, 811–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, A.S.; Askgaard, G.; Thiele, M. Treatment of alcohol use disorder in patients with liver disease. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2022, 62, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowen, M.S.; Chen, F.; Lawrence, A.J. Neuropeptides: Implications for alcoholism. J. Neurochem. 2004, 89, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilpin, N.W.; Misra, K.; Herman, M.A.; Cruz, M.T.; Koob, G.F.; Roberto, M. Neuropeptide Y opposes alcohol effects on gamma-aminobutyric acid release in amygdala and blocks the transition to alcohol dependence. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 69, 1091–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdez, G.R.; Koob, G.F. Allostasis and dysregulation of corticotropin-releasing factor and neuropeptide Y systems: Implications for the development of alcoholism. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2004, 79, 671–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccocioppo, R.; Gehlert, D.R.; Ryabinin, A.; Kaur, S.; Cippitelli, A.; Thorsell, A.; Le, A.D.; Hipskind, P.A.; Hamdouchi, C.; Lu, J.; et al. Stress-related neuropeptides and alcoholism: CRH, NPY, and beyond. Alcohol 2009, 43, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberto, M.; Gilpin, N.W.; Siggins, G.R. The central amygdala and alcohol: Role of gamma-aminobutyric acid, glutamate, and neuropeptides. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a012195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schank, J.R.; Ryabinin, A.E.; Giardino, W.J.; Ciccocioppo, R.; Heilig, M. Stress-related neuropeptides and addictive behaviors: Beyond the usual suspects. Neuron 2012, 76, 192–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, M.; Shizunaga, H.; Harada, H.; Tajiri, Y.; Murata, Y.; Terada, K.; Ohe, K.; Enjoji, M. Oxytocin treatment improves dexamethasone-induced depression-like symptoms associated with enhancement of hippocampal CREB-BDNF signaling in female mice. Neuropsychopharmacol. Rep. 2022, 42, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Ding, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Zhou, L.; Tian, G.; Qin, J. Enhancement of Oxytocin in the Medial Prefrontal Cortex Reverses Behavioral Deficits Induced by Repeated Ketamine Administration in Mice. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 723064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiozaki, K.; Kawabe, M.; Karasuyama, K.; Kurachi, T.; Hayashi, A.; Ataka, K.; Iwai, H.; Takeno, H.; Hayasaka, O.; Kotani, T.; et al. Neuropeptide Y deficiency induces anxiety-like behaviours in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funk, C.K.; O’Dell, L.E.; Crawford, E.F.; Koob, G.F. Corticotropin-releasing factor within the central nucleus of the amygdala mediates enhanced ethanol self-administration in withdrawn, ethanol-dependent rats. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 11324–11332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ungless, M.A.; Singh, V.; Crowder, T.L.; Yaka, R.; Ron, D.; Bonci, A. Corticotropin-releasing factor requires CRF binding protein to potentiate NMDA receptors via CRF receptor 2 in dopamine neurons. Neuron 2003, 39, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby, L.G.; Rice, K.C.; Valentino, R.J. Effects of corticotropin-releasing factor on neuronal activity in the serotonergic dorsal raphe nucleus. Neuropsychopharmacology 2000, 22, 148–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.J.; van den Pol, A.N.; Aghajanian, G.K. Hypocretins (orexins) regulate serotonin neurons in the dorsal raphe nucleus by excitatory direct and inhibitory indirect actions. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 9453–9464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Wang, Q.; Ji, B.; Pan, Y.; Xu, C.; Cheng, B.; Bai, B.; Chen, J. The Orexin/Receptor System: Molecular Mechanism and Therapeutic Potential for Neurological Diseases. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nestler, E.J.; Carlezon, W.A., Jr. The mesolimbic dopamine reward circuit in depression. Biol. Psychiatry 2006, 59, 1151–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Ren, Z.; Tang, Y.; Fu, Y.; Sun, S.; Ding, R.; Hou, J.; Mai, Y.; Zhan, B.; Zhu, Y.; et al. Rostromedial tegmental nucleus nociceptin/orphanin FQ (N/OFQ) signaling regulates anxiety- and depression-like behaviors in alcohol withdrawn rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 2023, 48, 908–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhou, T.C.; Fields, H.L.; Baxter, M.G.; Saper, C.B.; Holland, P.C. The rostromedial tegmental nucleus (RMTg), a GABAergic afferent to midbrain dopamine neurons, encodes aversive stimuli and inhibits motor responses. Neuron 2009, 61, 786–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhou, T.C. The rostromedial tegmental (RMTg) “brake” on dopamine and behavior: A decade of progress but also much unfinished work. Neuropharmacology 2021, 198, 108763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, R.; Zuo, W.; Shiwalkar, N.; Mei, Q.; Fan, Q.; Chen, X.; Li, J.; Bekker, A.; Ye, J.H. Alcohol withdrawal drives depressive behaviors by activating neurons in the rostromedial tegmental nucleus. Neuropsychopharmacology 2019, 44, 1464–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glover, E.J.; Starr, E.M.; Chao, Y.; Jhou, T.C.; Chandler, L.J. Inhibition of the rostromedial tegmental nucleus reverses alcohol withdrawal-induced anxiety-like behavior. Neuropsychopharmacology 2019, 44, 1896–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.J.; Vento, P.J.; Chao, Y.S.; Good, C.H.; Jhou, T.C. Gene expression and neurochemical characterization of the rostromedial tegmental nucleus (RMTg) in rats and mice. Brain Struct. Funct. 2019, 224, 219–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quijano Carde, N.A.; De Biasi, M. Behavioral characterization of withdrawal following chronic voluntary ethanol consumption via intermittent two-bottle choice points to different susceptibility categories. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2022, 46, 614–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morisot, N.; Novotny, C.J.; Shokat, K.M.; Ron, D. A new generation of mTORC1 inhibitor attenuates alcohol intake and reward in mice. Addict. Biol. 2018, 23, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koob, G.F.; Volkow, N.D. Neurobiology of addiction: A neurocircuitry analysis. Lancet Psychiatry 2016, 3, 760–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwako, L.E.; Koob, G.F. Neuroclinical Framework for the Role of Stress in Addiction. Chronic Stress 2017, 1, 2470547017698140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tizabi, Y.; Getachew, B.; Rezvani, A.H.; Hauser, S.R.; Overstreet, D.H. Antidepressant-like effects of nicotine and reduced nicotinic receptor binding in the Fawn-Hooded rat, an animal model of co-morbid depression and alcoholism. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2009, 33, 398–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Hou, J.; Li, W.; Tang, Y.; Wang, M.; Ding, R.; Liu, S.; Fu, Y.; Mai, Y.; Xia, J.; et al. LPA1 receptors in the lateral habenula regulate negative affective states associated with alcohol withdrawal. Neuropsychopharmacology 2023, 48, 1567–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, R.; Mei, Q.; Shiwalkar, N.; Zuo, W.; Zhang, H.; Gregor, D.; Patel, S.; Ye, J.H. Anxiety during alcohol withdrawal involves 5-HT2C receptors and M-channels in the lateral habenula. Neuropharmacology 2020, 163, 107863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, R.; Tang, Y.; Li, W.; Ren, Z.; Li, D.; Zheng, J.; Zuo, W.; Chen, X.; Zuo, Q.K.; Tam, K.L.; et al. Endocannabinoid signaling in the lateral habenula regulates pain and alcohol consumption. Transl. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, R.; Zuo, W.; Gregor, D.; Li, J.; Grech, D.; Ye, J.H. Pharmacological Manipulation of the Rostromedial Tegmental Nucleus Changes Voluntary and Operant Ethanol Self-Administration in Rats. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2016, 40, 572–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, R.; Chen, X.; Zuo, W.; Li, J.; Kang, S.; Zhou, L.H.; Siegel, A.; Bekker, A.; Ye, J.H. Ablation of mu opioid receptor-expressing GABA neurons in rostromedial tegmental nucleus increases ethanol consumption and regulates ethanol-related behaviors. Neuropharmacology 2016, 107, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, R.; Gregor, D.; Peng, Z.; Li, J.; Bekker, A.; Ye, J. Chronic intermittent voluntary alcohol drinking induces hyperalgesia in Sprague-Dawley rats. Int. J. Physiol. Pathophysiol. Pharmacol. 2015, 7, 136–144. [Google Scholar]
- Griffin, W.C., 3rd. Alcohol dependence and free-choice drinking in mice. Alcohol 2014, 48, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juarez, B.; Morel, C.; Ku, S.M.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Montgomery, S.; Gregoire, H.; Ribeiro, E.; Crumiller, M.; Roman-Ortiz, C.; et al. Midbrain circuit regulation of individual alcohol drinking behaviors in mice. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, O.B.; Skelly, M.J.; Miller, J.D.; Rivera-Irizarry, J.K.; Rowson, S.A.; DiBerto, J.F.; Rinker, J.A.; Thiele, T.E.; Kash, T.L.; Pleil, K.E. The paraventricular thalamus provides a polysynaptic brake on limbic CRF neurons to sex-dependently blunt binge alcohol drinking and avoidance behavior in mice. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloch, S.; Rinker, J.A.; Marcus, M.M.; Mulholland, P.J. Absence of effects of intermittent access to alcohol on negative affective and anxiety-like behaviors in male and female C57BL/6J mice. Alcohol 2020, 88, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwa, L.S.; Chu, A.; Levinson, S.A.; Kayyali, T.M.; DeBold, J.F.; Miczek, K.A. Persistent escalation of alcohol drinking in C57BL/6J mice with intermittent access to 20% ethanol. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2011, 35, 1938–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dao, N.C.; Suresh Nair, M.; Magee, S.N.; Moyer, J.B.; Sendao, V.; Brockway, D.F.; Crowley, N.A. Forced Abstinence From Alcohol Induces Sex-Specific Depression-Like Behavioral and Neural Adaptations in Somatostatin Neurons in Cortical and Amygdalar Regions. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boschloo, L.; Vogelzangs, N.; van den Brink, W.; Smit, J.H.; Veltman, D.J.; Beekman, A.T.; Penninx, B.W. Alcohol use disorders and the course of depressive and anxiety disorders. Br. J. Psychiatry 2012, 200, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McHugh, R.K.; Weiss, R.D. Alcohol Use Disorder and Depressive Disorders. Alcohol Res. 2019, 40, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.M.; Coelho, M.A.; Class, M.A.; Szumlinski, K.K. mGlu5-dependent modulation of anxiety during early withdrawal from binge-drinking in adult and adolescent male mice. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2018, 184, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillmer, A.T.; Angarita, G.A.; Esterlis, I.; Anderson, J.M.; Nabulsi, N.; Lim, K.; Ropchan, J.; Carson, R.E.; Krystal, J.H.; Malley, S.S.O.; et al. Longitudinal imaging of metabotropic glutamate 5 receptors during early and extended alcohol abstinence. Neuropsychopharmacology 2021, 46, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlmann, A.; Bandelow, B.; Stein, D.J.; Bloch, S.; Engel, K.R.; Havemann-Reinecke, U.; Wedekind, D. Grey matter structural differences in alcohol-dependent individuals with and without comorbid depression/anxiety-an MRI study. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2019, 269, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peregud, D.; Kvichansky, A.; Shirobokova, N.; Stepanichev, M.; Gulyaeva, N. 7,8-DHF enhances SHH in the hippocampus and striatum during early abstinence but has minor effects on alcohol intake in IA2BC paradigm and abstinence-related anxiety-like behavior in rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2022, 781, 136671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Jhou, T.C.; Smith, M.; Saleem, K.S.; Hikosaka, O. Negative reward signals from the lateral habenula to dopamine neurons are mediated by rostromedial tegmental nucleus in primates. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 11457–11471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrot, M.; Sesack, S.R.; Georges, F.; Pistis, M.; Hong, S.; Jhou, T.C. Braking dopamine systems: A new GABA master structure for mesolimbic and nigrostriatal functions. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 14094–14101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufling, J.; Veinante, P.; Pawlowski, S.A.; Freund-Mercier, M.J.; Barrot, M. Afferents to the GABAergic tail of the ventral tegmental area in the rat. J. Comp. Neurol. 2009, 513, 597–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jhou, T.C.; Geisler, S.; Marinelli, M.; Degarmo, B.A.; Zahm, D.S. The mesopontine rostromedial tegmental nucleus: A structure targeted by the lateral habenula that projects to the ventral tegmental area of Tsai and substantia nigra compacta. J. Comp. Neurol. 2009, 513, 566–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Pullmann, D.; Cho, J.Y.; Eid, M.; Jhou, T.C. Generality and opponency of rostromedial tegmental (RMTg) roles in valence processing. elife 2019, 8, e41542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisz, H.A.; Boone, D.R.; Sell, S.L.; Hellmich, H.L. Stereotactic Atlas-Guided Laser Capture Microdissection of Brain Regions Affected by Traumatic Injury. J. Vis. Exp. 2017, 127, e56134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, L.C. A balancing act: The role of pro- and anti-stress peptides within the central amygdala in anxiety and alcohol use disorders. J. Neurochem. 2021, 157, 1615–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koob, G.F. Addiction is a Reward Deficit and Stress Surfeit Disorder. Front. Psychiatry 2013, 4, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heilig, M.; Egli, M.; Crabbe, J.C.; Becker, H.C. Acute withdrawal, protracted abstinence and negative affect in alcoholism: Are they linked? Addict. Biol. 2010, 15, 169–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, M.T.; Herman, M.A.; Kallupi, M.; Roberto, M. Nociceptin/orphanin FQ blockade of corticotropin-releasing factor-induced gamma-aminobutyric acid release in central amygdala is enhanced after chronic ethanol exposure. Biol. Psychiatry 2012, 71, 666–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Economidou, D.; Hansson, A.C.; Weiss, F.; Terasmaa, A.; Sommer, W.H.; Cippitelli, A.; Fedeli, A.; Martin-Fardon, R.; Massi, M.; Ciccocioppo, R.; et al. Dysregulation of nociceptin/orphanin FQ activity in the amygdala is linked to excessive alcohol drinking in the rat. Biol. Psychiatry 2008, 64, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, Y.S.; Adrian, T.E.; Allen, J.M.; Tatemoto, K.; Crow, T.J.; Bloom, S.R.; Polak, J.M. Neuropeptide Y distribution in the rat brain. Science 1983, 221, 877–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilpin, N.W. Neuropeptide Y (NPY) in the extended amygdala is recruited during the transition to alcohol dependence. Neuropeptides 2012, 46, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caberlotto, L.; Thorsell, A.; Rimondini, R.; Sommer, W.; Hyytia, P.; Heilig, M. Differential expression of NPY and its receptors in alcohol-preferring AA and alcohol-avoiding ANA rats. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2001, 25, 1564–1569. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thiele, T.E.; Marsh, D.J.; Ste Marie, L.; Bernstein, I.L.; Palmiter, R.D. Ethanol consumption and resistance are inversely related to neuropeptide Y levels. Nature 1998, 396, 366–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, B.H.; Suzuki, R.; Lumeng, L.; Li, T.K.; McBride, W.J. Innate differences in neuropeptide Y (NPY) mRNA expression in discrete brain regions between alcohol-preferring (P) and -nonpreferring (NP) rats: A significantly low level of NPY mRNA in dentate gyrus of the hippocampus and absence of NPY mRNA in the medial habenular nucleus of P rats. Neuropeptides 2004, 38, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korotkova, T.M.; Brown, R.E.; Sergeeva, O.A.; Ponomarenko, A.A.; Haas, H.L. Effects of arousal- and feeding-related neuropeptides on dopaminergic and GABAergic neurons in the ventral tegmental area of the rat. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2006, 23, 2677–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, S.L.; Bendrath, S.C.; Yates, E.M.; Thiele, T.E. Basolateral amygdala neuropeptide Y system modulates binge ethanol consumption. Neuropsychopharmacology 2023, 49, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, L.W.; Neuner, S.; Polepalli, J.S.; Beier, K.T.; Wright, M.; Walsh, J.J.; Lewis, E.M.; Luo, L.; Deisseroth, K.; Dolen, G.; et al. Gating of social reward by oxytocin in the ventral tegmental area. Science 2017, 357, 1406–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.R.; Weerts, E.M. Oxytocin for the treatment of drug and alcohol use disorders. Behav. Pharmacol. 2016, 27, 640–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peris, J.; MacFadyen, K.; Smith, J.A.; de Kloet, A.D.; Wang, L.; Krause, E.G. Oxytocin receptors are expressed on dopamine and glutamate neurons in the mouse ventral tegmental area that project to nucleus accumbens and other mesolimbic targets. J. Comp. Neurol. 2017, 525, 1094–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lammel, S.; Lim, B.K.; Ran, C.; Huang, K.W.; Betley, M.J.; Tye, K.M.; Deisseroth, K.; Malenka, R.C. Input-specific control of reward and aversion in the ventral tegmental area. Nature 2012, 491, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, A.; Zuo, W.; Kang, S.; Li, J.; Fu, R.; Zhang, H.; Bekker, A.; Ye, J.H. The lateral habenula and alcohol: Role of glutamate and M-type potassium channels. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2017, 162, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimbrough, A.; de Guglielmo, G.; Kononoff, J.; Kallupi, M.; Zorrilla, E.P.; George, O. CRF(1) Receptor-Dependent Increases in Irritability-Like Behavior During Abstinence from Chronic Intermittent Ethanol Vapor Exposure. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2017, 41, 1886–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scammell, T.E.; Saper, C.B. Orexin, drugs and motivated behaviors. Nat. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 1286–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sargin, D. The role of the orexin system in stress response. Neuropharmacology 2019, 154, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, R.M.; Lawrence, A.J. Ascending orexinergic pathways and alcohol-seeking. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2013, 23, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karkhanis, A.N.; Al-Hasani, R. Dynorphin and its role in alcohol use disorder. Brain Res. 2020, 1735, 146742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Kreek, M.J. Involvement of Activated Brain Stress Responsive Systems in Excessive and “Relapse” Alcohol Drinking in Rodent Models: Implications for Therapeutics. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2018, 366, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunstall, B.J.; Carmack, S.A.; Koob, G.F.; Vendruscolo, L.F. Dysregulation of Brain Stress Systems Mediates Compulsive Alcohol Drinking. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 2017, 13, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Addario, C.; Caputi, F.F.; Rimondini, R.; Gandolfi, O.; Del Borrello, E.; Candeletti, S.; Romualdi, P. Different alcohol exposures induce selective alterations on the expression of dynorphin and nociceptin systems related genes in rat brain. Addict. Biol. 2013, 18, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruchas, M.R.; Land, B.B.; Chavkin, C. The dynorphin/kappa opioid system as a modulator of stress-induced and pro-addictive behaviors. Brain Res. 2010, 1314, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Land, B.B.; Bruchas, M.R.; Lemos, J.C.; Xu, M.; Melief, E.J.; Chavkin, C. The dysphoric component of stress is encoded by activation of the dynorphin kappa-opioid system. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, S.P.; Montalvo-Ortiz, J.L.; Csernansky, J.G.; Eiger, R.I.; Herrold, A.A.; Koola, M.M.; Dong, H. Early Life Stress as a Risk Factor for Substance use Disorders: Clinical and Neurobiological Substrates. Indian. J. Psychol. Med. 2015, 37, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Przewlocka, B.; Lason, W.; Przewlocki, R. Repeated ethanol differently affects opioid peptide biosynthesis in the rat pituitary. Neuroendocrinology 1994, 60, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du Preez, A.; Law, T.; Onorato, D.; Lim, Y.M.; Eiben, P.; Musaelyan, K.; Egeland, M.; Hye, A.; Zunszain, P.A.; Thuret, S.; et al. The type of stress matters: Repeated injection and permanent social isolation stress in male mice have a differential effect on anxiety- and depressive-like behaviours, and associated biological alterations. Transl. Psychiatry 2020, 10, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krimberg, J.S.; Lumertz, F.S.; Orso, R.; Viola, T.W.; de Almeida, R.M.M. Impact of social isolation on the oxytocinergic system: A systematic review and meta-analysis of rodent data. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2022, 134, 104549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabbaa, M.; Paedae, B.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z. Neuropeptide Regulation of Social Attachment: The Prairie Vole Model. Compr. Physiol. 2016, 7, 81–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziv, Y.; Rahamim, N.; Lezmy, N.; Even-Chen, O.; Shaham, O.; Malishkevich, A.; Giladi, E.; Elkon, R.; Gozes, I.; Barak, S. Activity-dependent neuroprotective protein (ADNP) is an alcohol-responsive gene and negative regulator of alcohol consumption in female mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 2019, 44, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ron, D.; Barak, S. Molecular mechanisms underlying alcohol-drinking behaviours. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2016, 17, 576–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraeuter, A.K.; Guest, P.C.; Sarnyai, Z. The Open Field Test for Measuring Locomotor Activity and Anxiety-Like Behavior. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1916, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pentkowski, N.S.; Rogge-Obando, K.K.; Donaldson, T.N.; Bouquin, S.J.; Clark, B.J. Anxiety and Alzheimer’s disease: Behavioral analysis and neural basis in rodent models of Alzheimer’s-related neuropathology. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2021, 127, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunstall, B.J.; Kirson, D.; Zallar, L.J.; McConnell, S.A.; Vendruscolo, J.C.M.; Ho, C.P.; Oleata, C.S.; Khom, S.; Manning, M.; Lee, M.R.; et al. Oxytocin blocks enhanced motivation for alcohol in alcohol dependence and blocks alcohol effects on GABAergic transmission in the central amygdala. PLoS Biol. 2019, 17, e2006421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabris, D.; Carvalho, M.C.; Brandao, M.L.; Prado, W.A.; Zuardi, A.W.; Crippa, J.A.; de Oliveira, A.R.; Lovick, T.A.; Genaro, K. Sex-dependent differences in the anxiolytic-like effect of cannabidiol in the elevated plus-maze. J. Psychopharmacol. 2022, 36, 1371–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rath, M.; Guergues, J.; Pinho, J.P.C.; Zhang, P.; Nguyen, T.G.; MacFadyen, K.A.; Peris, J.; McLaughlin, J.P.; Stevens, S.M., Jr.; Liu, B. Chronic Voluntary Binge Ethanol Consumption Causes Sex-Specific Differences in Microglial Signaling Pathways and Withdrawal-associated Behaviors in Mice. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2020, 44, 1791–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cryan, J.F.; Mombereau, C.; Vassout, A. The tail suspension test as a model for assessing antidepressant activity: Review of pharmacological and genetic studies in mice. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2005, 29, 571–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrocoso, E.; Ikeda, K.; Sora, I.; Uhl, G.R.; Sanchez-Blazquez, P.; Mico, J.A. Active behaviours produced by antidepressants and opioids in the mouse tail suspension test. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2013, 16, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro-Carvalho, A.; Lima, C.S.; Nunes-Freitas, A.L.; Filgueiras, C.C.; Manhaes, A.C.; Abreu-Villaca, Y. Exposure to nicotine and ethanol in adolescent mice: Effects on depressive-like behavior during exposure and withdrawal. Behav. Brain Res. 2011, 221, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.H.; Yang, E.; Lee, J.; Kim, J.Y.; Yoo, H.; Park, H.S.; Jung, J.T.; Lee, D.; Chun, S.; Jo, Y.S.; et al. Neural mechanism of acute stress regulation by trace aminergic signalling in the lateral habenula in male mice. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Total RMTg | Anti-Stress Neuropeptide mRNA Levels | Pro-Stress Neuropeptide mRNA Levels | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pnoc | Oxt | Npy | Crf | Pomc | Avp | Orx | Pdyn | |||||||||
| Behaviors | r | p | r | p | r | p | r | p | r | p | r | p | r | p | r | p |
| EtOH intake | −0.8855 | 0.0189 | 0.3069 | 0.5540 | −0.9689 | 0.0014 | 0.8711 | 0.0238 | 0.7642 | 0.0769 | 0.7253 | 0.1029 | −0.7784 | 0.0682 | −0.4168 | 0.4111 |
| Entries in center | 0.5582 | 0.3116 | 0.8050 | 0.0534 | 0.4370 | 0.3862 | −0.6882 | 0.1307 | −0.1290 | 0.8075 | 0.5765 | 0.2310 | 0.4752 | 0.3409 | 0.0611 | 0.9084 |
| Duration in center | 0.6286 | 0.1813 | 0.8066 | 0.0525 | 0.8160 | 0.0477 | −0.8177 | 0.0468 | −0.6013 | 0.2067 | 0.7035 | 0.1188 | 0.7859 | 0.0638 | −0.3824 | 0.4545 |
| Entries in OA | 0.4740 | 0.3422 | 0.7771 | 0.0690 | 0.7145 | 0.1106 | −0.5067 | 0.3050 | −0.2983 | 0.5658 | 0.5771 | 0.2304 | 0.0874 | 0.8693 | −0.1422 | 0.7881 |
| Duration in OA | 0.8340 | 0.0390 | 0.5078 | 0.3037 | 0.8063 | 0.0526 | −0.5295 | 0.2800 | −0.7931 | 0.0598 | 0.4970 | 0.3159 | 0.7530 | 0.0840 | −0.6402 | 0.1708 |
| Latancy to dig | −0.1576 | 0.7656 | −0.5225 | 0.2876 | 0.1247 | 0.8139 | −0.4761 | 0.3398 | −0.1350 | 0.7987 | −0.1258 | 0.8123 | −0.3784 | 0.4595 | −0.1595 | 0.7628 |
| Marbles buried | −0.2683 | 0.6072 | 0.2963 | 0.5685 | −0.3715 | 0.4684 | 0.5186 | 0.2919 | −0.0570 | 0.9145 | 0.8611 | 0.0276 | 0.8678 | 0.0251 | −0.2506 | 0.6319 |
| Latancy to immobility | 0.2406 | 0.6460 | 0.0650 | 0.9026 | 0.1752 | 0.7400 | 0.1718 | 0.7449 | 0.3270 | 0.5271 | 0.1102 | 0.8354 | −0.0964 | 0.8559 | −0.3205 | 0.5357 |
| Immobility time | −0.9316 | 0.0069 | −0.8550 | 0.0300 | −0.8134 | 0.0490 | 0.8101 | 0.0507 | −0.6996 | 0.1218 | −0.6946 | 0.1256 | −0.7543 | 0.0832 | 0.1751 | 0.7400 |
| Sucrose preference | 0.5900 | 0.2177 | 0.5128 | 0.2982 | 0.6518 | 0.1607 | −0.4827 | 0.3322 | 0.8105 | 0.0505 | 0.5854 | 0.2222 | 0.7429 | 0.0906 | −0.5752 | 0.2323 |
| VTA−Projecting RMTg | Anti-Stress Neuropeptide mRNA Levels | Pro-Stress Neuropeptide mRNA Levels | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pnoc | Oxt | Npy | Crf | Pomc | Avp | Orx | ||||||||
| Behaviors | r | p | r | p | r | p | r | p | r | p | r | p | r | p |
| EtOH intake | −0.8463 | 0.0336 | −0.6530 | 0.1597 | −0.8243 | 0.0436 | −0.4623 | 0.3560 | −0.9032 | 0.0136 | 0.8968 | 0.0154 | −0.8050 | 0.0533 |
| Entries in center | 0.5180 | 0.2925 | −0.0312 | 0.9532 | −0.1481 | 0.7795 | 0.3088 | 0.5515 | −0.1333 | 0.8013 | 0.8078 | 0.0519 | 0.0052 | 0.9922 |
| Duration in center | −0.3873 | 0.4481 | 0.7353 | 0.0959 | 0.8134 | 0.0490 | −0.9891 | 0.0002 | 0.9591 | 0.0025 | −0.5840 | 0.2237 | 0.6864 | 0.1321 |
| Entries in OA | 0.4082 | 0.4218 | −0.1236 | 0.8155 | −0.0155 | 0.9768 | 0.1324 | 0.8026 | 0.3716 | 0.4682 | 0.3270 | 0.5270 | −0.1397 | 0.7919 |
| Duration in OA | 0.6803 | 0.1370 | 0.5808 | 0.2268 | 0.8388 | 0.0369 | −0.6253 | 0.1843 | 0.7641 | 0.0769 | −0.5007 | 0.3117 | 0.6527 | 0.1600 |
| Latancy to dig | 0.1659 | 0.7534 | −0.2498 | 0.6331 | −0.3339 | 0.5178 | 0.3138 | 0.5448 | −0.4438 | 0.3780 | 0.2948 | 0.5706 | −0.7710 | 0.0726 |
| Marbles buried | −0.6355 | 0.1750 | −0.8786 | 0.0212 | −0.7239 | 0.1038 | 0.9468 | 0.0042 | 0.4012 | 0.4304 | 0.2859 | 0.5828 | −0.3468 | 0.5006 |
| Latancy to immobility | 0.5892 | 0.2185 | −0.4074 | 0.4226 | 0.4999 | 0.3126 | −0.8361 | 0.0381 | 0.1284 | 0.8084 | −0.5644 | 0.2433 | 0.7258 | 0.1025 |
| Immobility time | −0.8463 | 0.0336 | 0.7636 | 0.0772 | −0.9209 | 0.0091 | 0.9420 | 0.0049 | −0.7224 | 0.1049 | 0.8606 | 0.0278 | −0.5411 | 0.2676 |
| Sucrose preference | 0.7685 | 0.0742 | 0.1918 | 0.7158 | 0.6888 | 0.1302 | −0.7763 | 0.0694 | 0.2172 | 0.6794 | −0.7885 | 0.0623 | 0.7496 | 0.0862 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, Y.; Li, W.; Mai, Y.; Guan, J.; Ding, R.; Hou, J.; Chen, B.; Cao, G.; Sun, S.; Tang, Y.; et al. Association between RMTg Neuropeptide Genes and Negative Effect during Alcohol Withdrawal in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2933. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25052933
Fu Y, Li W, Mai Y, Guan J, Ding R, Hou J, Chen B, Cao G, Sun S, Tang Y, et al. Association between RMTg Neuropeptide Genes and Negative Effect during Alcohol Withdrawal in Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(5):2933. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25052933
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Yixin, Wenfu Li, Yunlin Mai, Junhao Guan, Ruxuan Ding, Jiawei Hou, Bingqing Chen, Guoxin Cao, Shizhu Sun, Ying Tang, and et al. 2024. "Association between RMTg Neuropeptide Genes and Negative Effect during Alcohol Withdrawal in Mice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 5: 2933. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25052933
APA StyleFu, Y., Li, W., Mai, Y., Guan, J., Ding, R., Hou, J., Chen, B., Cao, G., Sun, S., Tang, Y., & Fu, R. (2024). Association between RMTg Neuropeptide Genes and Negative Effect during Alcohol Withdrawal in Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(5), 2933. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25052933






