Analysis of Whole-Genome as a Novel Strategy for Animal Species Identification
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
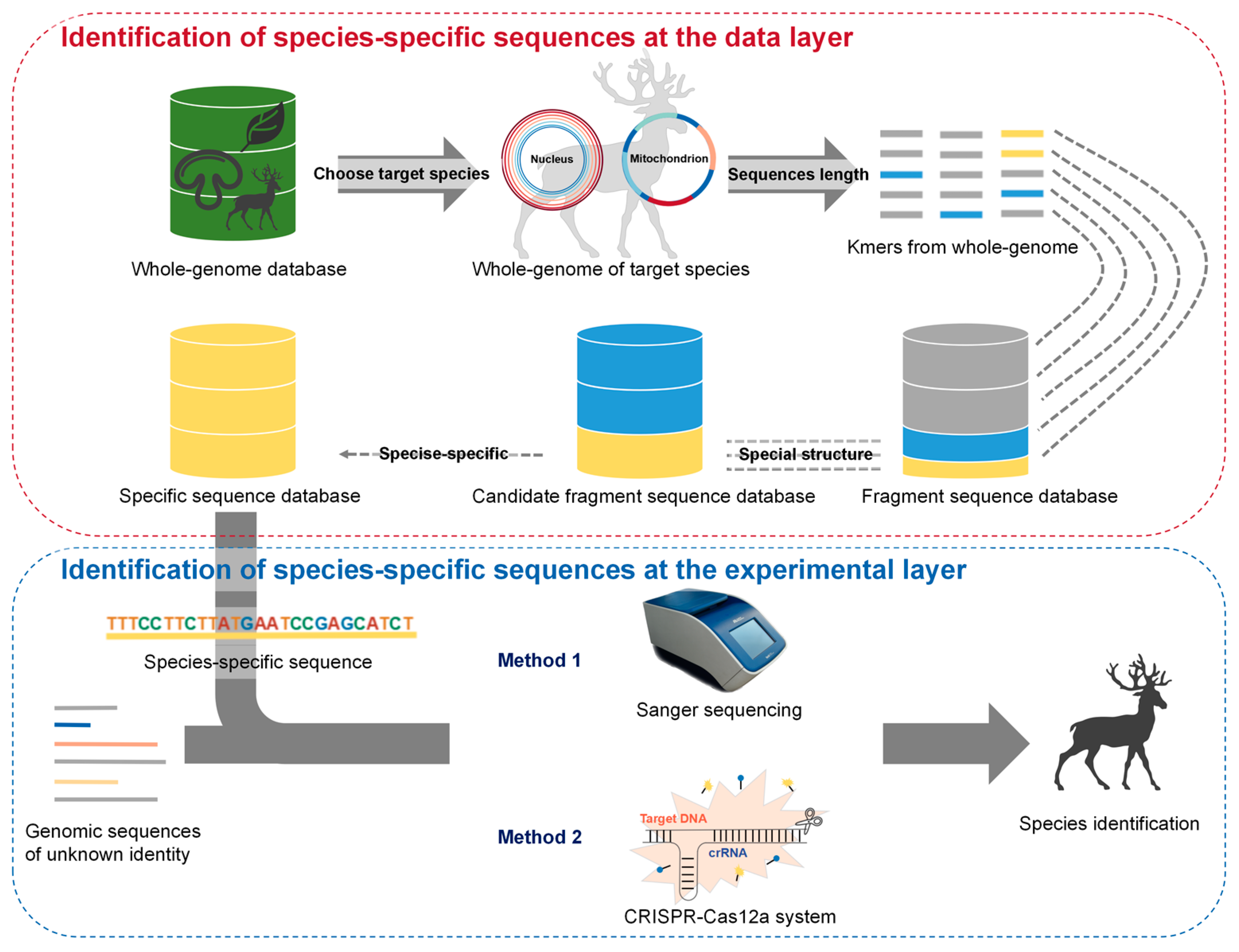
2.1. Screening for Species-Specific Sequences through Bioinformatics Analysis of the Whole Genome
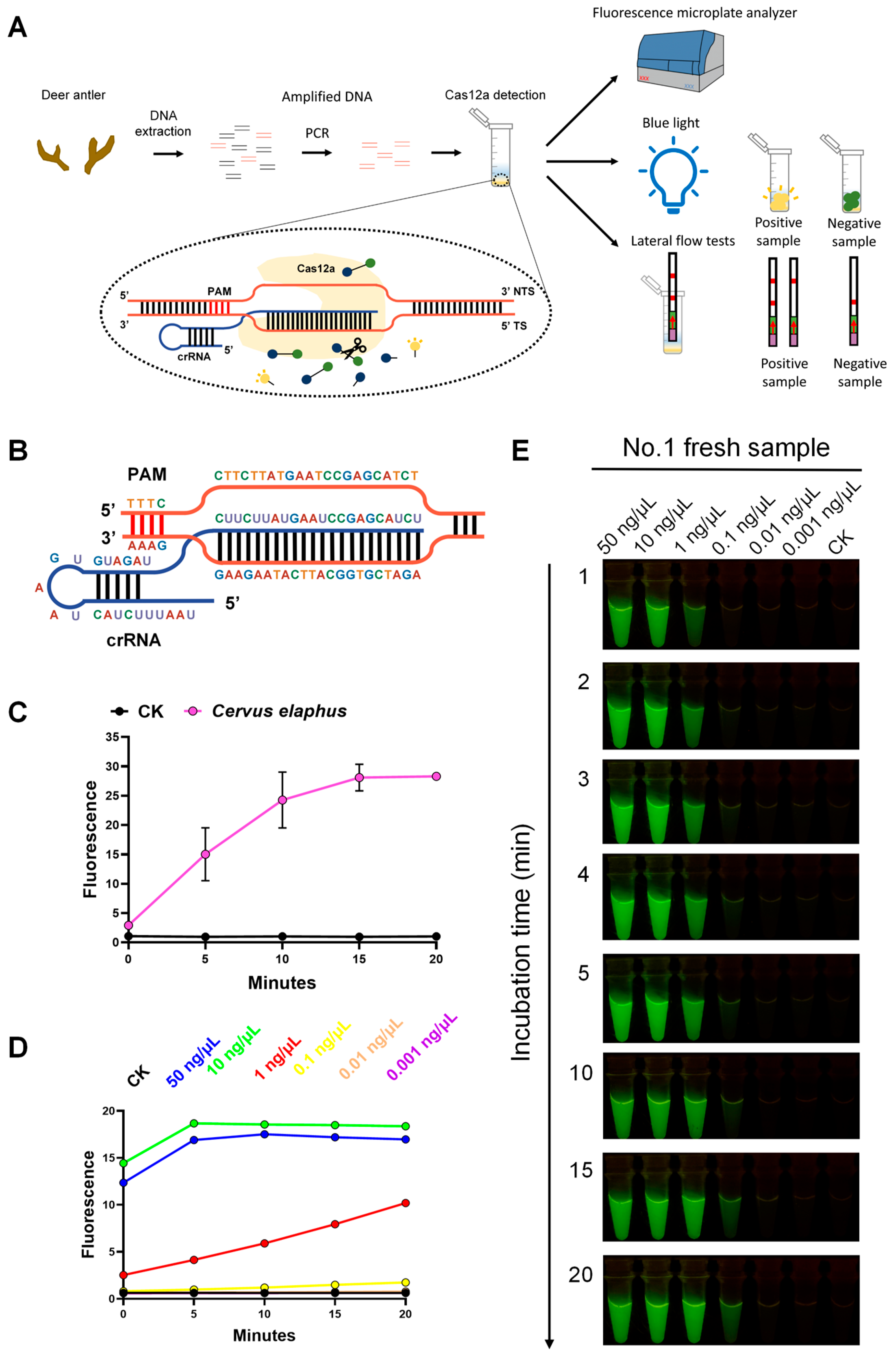
2.2. Species Identification by Discerning Species-Specific Sequences Using Different Experimental Technologies
2.3. Animal Species Identification of Fresh Samples and Commercially Available Products Based on Analysis of Whole-Genome (AGE)
2.4. Generating Species Identification from Mixtures
3. Discussion
3.1. Analysis of Whole-Genome (AGE) Identification System Developed via Whole Genome Analysis in the Animal Kingdom
3.2. Species Identification via Analysis of Whole-Genome (AGE) in Two Layers: Research and Application
3.3. Compatibility of Analysis of Whole-Genome (AGE) with Multiple Molecular Technologies Enhances Its Versatility
3.4. Analysis of Whole-Genome (AGE) Performs Well When Identifying Mixed DNA Samples
3.5. Factors That May Affect Species Identification by Analysis of Whole-Genome (AGE)
3.6. Potential of Analysis of Whole-Genome (AGE) to Tackle Identification Challenges
3.7. Analysis of Whole-Genome (AGE) Helps Protect Biodiversity
3.8. Analysis of Whole-Genome (AGE) as a Powerful Tool for the Regulation of Commercial Products
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials’ Preparation
4.2. Bioinformatics Analysis of Target Species’ Genomes
4.3. DNA Extraction, Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Amplification, and Purification
4.4. Species-Specific Target Sequence Acquisition
4.5. CRISPR-Cas12a System
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dirzo, R.; Young, H.S.; Galetti, M.; Ceballos, G.; Isaac, N.J.B.; Collen, B. Defaunation in the Anthropocene. Science 2014, 345, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, U.G.; Wolfenbarger, L.L. AFLP genotyping and fingerprinting. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1999, 14, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, C.; Burgener, M.; Hübner, P.; Lüthy, J. PCR-RFLP Analysis of Mitochondrial DNA: Differentiation of Fish Species. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2000, 33, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, X.; Liu, G.-Q.; Luo, J.-X.; Guo, Y.-S.; Qian, J.-P.; Ya, M.; Guo, L. Triplex real-time PCR assay for the authentication of camel-derived dairy and meat products. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 9841–9850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebert, P.D.N.; Cywinska, A.; Ball, S.L.; deWaard, J.R. Biological identifications through DNA barcodes. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2003, 270, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Yin, X.; Han, J.; Sun, W.; Yao, H.; Song, J.; Li, X. DNA barcoding in herbal medicine: Retrospective and prospective. J. Pharm. Anal. 2023, 13, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, T.; Xu, Z.; Jia, J.; Leon, C.; Hu, S.; Lin, Y.; Ragupathy, S.; Song, J.; Newmaster, S.G. Biomonitoring for traditional herbal medicinal products using DNA metabarcoding and single molecule, real-time sequencing. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2018, 8, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Xu, Z.; Xin, T.; Shi, L.; Song, J. Quality Control of the Traditional Patent Medicine Yimu Wan Based on SMRT Sequencing and DNA Barcoding. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xiang, L.; Shi, L.; Li, G.; Yao, H.; Han, J.; Lin, Y.; Song, J.; Chen, S. Identification of crude drugs in the Japanese pharmacopoeia using a DNA barcoding system. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.; Xu, W.; Qi, G.; Xin, T.; Xu, Z.; Lei, H.; Song, J. GAGE is a method for identification of plant species based on whole genome analysis and genome editing. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Y.; Xin, T.; Xu, W.; Hao, L.; Qi, G.; Lou, Q.; Song, J. Principles and strategies for species identification based on analysis of whole-genome. Acta Pharm. Sin. 2023, 58, 2364–2374. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, G.; Hao, L.; Gan, Y.; Xin, T.; Lou, Q.; Xu, W.; Song, J. Identification of closely related species in Aspergillus through Analysis of Whole-Genome. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1323572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanger, F.; Air, G.M.; Barrell, B.G.; Brown, N.L.; Coulson, A.R.; Fiddes, J.C.; Hutchison, C.A.; Slocombe, P.M.; Smith, M. Nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage φX174 DNA. Nature 1977, 265, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Xu, W.; Xin, T.; Song, J. Application of third-generation sequencing to herbal genomics. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1124536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewin, H.A.; Robinson, G.E.; Kress, W.J.; Baker, W.J.; Coddington, J.; Crandall, K.A.; Durbin, R.; Edwards, S.V.; Forest, F.; Gilbert, M.T.P.; et al. Earth BioGenome Project: Sequencing life for the future of life. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 4325–4333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, C.; Tittensor, D.P.; Adl, S.; Simpson, A.G.B.; Worm, B. How Many Species Are There on Earth and in the Ocean? PLoS Biol. 2011, 9, e1001127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunn, H.T. Archaeological evidence for meat-eating by Plio-Pleistocene hominids from Koobi Fora and Olduvai Gorge. Nature 1981, 291, 574–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S. Animal research and the search for understanding. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, T.; Tao, J.; Yang, M.; He, C.; Tian, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Deng, S.; Feng, J.; Zhang, Z.; et al. An AANAT/ASMT transgenic animal model constructed with CRISPR/Cas9 system serving as the mammary gland bioreactor to produce melatonin-enrich milk in sheep. J. Pineal Res. 2017, 63, e12406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.; Han, L.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Q.; Xia, Y.; Li, H. Haplotype-resolved Genome of Sika Deer Reveals Allele-specific Gene Expression and Chromosome Evolution. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2023, 21, 470–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.; Ai, C.; Wang, T.; Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Hu, P.; Wang, G.; Liu, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, R.; et al. The First High-quality Reference Genome of Sika Deer Provides Insights into High-tannin Adaptation. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2023, 21, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Peña, R.; Hodgson, H.; Liu, J.C.-T.; Stephenson, M.J.; Martin, A.C.; Owen, C.; Harkess, A.; Leebens-Mack, J.; Jimenez, L.E.; Osbourn, A.; et al. Complex scaffold remodeling in plant triterpene biosynthesis. Science 2023, 379, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobe, S.S.; Kitchener, A.C.; Linacre, A.M.T. Reconstructing Mammalian Phylogenies: A Detailed Comparison of the Cytochrome b and Cytochrome Oxidase Subunit I Mitochondrial Genes. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e14156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, B.; Meganathan, P.R.; Haque, I. DNA mini-barcoding: An approach for forensic identification of some endangered Indian snake species. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2011, 5, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, M.H.S.; Aragão, D.G.; Silva, J.L.N.; Lima, R.C.; Birindelli, J.L.O.; Fraga, E.C.; Barros, M.C. The DNA barcode reveals cryptic diversity and a new record for the genus Leporinus (Characiformes, Anostomidae) in the hydrographic basins of central northern Brazil. PeerJ 2023, 11, e15184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva De Souza, C.; Mattox, G.; Vita, G.; Orrego, L.; Melo, B.F.; Oliveira, C.D. Molecular species delimitation and description of a new species of Phenacogaster (Teleostei, Characidae) from the southern Amazon basin. ZooKeys 2023, 1164, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, R.D.; Zemlak, T.S.; Innes, B.H.; Last, P.R.; Hebert, P.D.N. DNA barcoding Australia’s fish species. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2005, 360, 1847–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, K.F.; Ball, S.L. DNA barcodes for biosecurity: Invasive species identification. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2005, 360, 1813–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, J.; Wu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Feng, C.; Yuan, X.; Jia, G.; Deng, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, Q.; et al. Assessment of four DNA fragments (COI, 16S rDNA, ITS2, 12S rDNA) for species identification of the Ixodida (Acari: Ixodida). Parasites Vectors 2014, 7, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebert, P.D.N.; deWaard, J.R.; Landry, J.-F. DNA barcodes for 1/1000 of the animal kingdom. Biol. Lett. 2010, 6, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebert, P.D.N.; Penton, E.H.; Burns, J.M.; Janzen, D.H.; Hallwachs, W. Ten species in one: DNA barcoding reveals cryptic species in the neotropical skipper butterfly Astraptes fulgerator. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 14812–14817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, T.; Zhang, J.-M.; Ouyang, J.; Leung, W.; Simoneau, A.; Zou, L. TERRA and RAD51AP1 promote alternative lengthening of telomeres through an R- to D-loop switch. Mol. Cell 2022, 82, 3985–4000.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, J.; Yadav, T.; Zhang, J.-M.; Yang, H.; Rheinbay, E.; Guo, H.; Haber, D.A.; Lan, L.; Zou, L. RNA transcripts stimulate homologous recombination by forming DR-loops. Nature 2021, 594, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharawat, S.K.; Bakhshi, R.; Vishnubhatla, S.; Bakhshi, S. Mitochondrial D-loop variations in paediatric acute myeloid leukaemia: A potential prognostic marker. Br. J. Haematol. 2010, 149, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Komiyama, T.; Nitta, M.; Kawamura, Y.; Hasegawa, M.; Shoji, S.; Orihashi, Y.; Inomoto, C.; Kajiwara, H.; Nakamura, N.; et al. D-loop Mutations in Renal Cell Carcinoma Improve Predictive Accuracy for Cancer-Related Death by Integrating with Mutations in the NADH Dehydrogenase Subunit 1 Gene. Genes 2019, 10, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Shang, J.; Wang, F.; Huo, X.; Sun, R.; Ren, Z.; Wang, W.; Yang, M.; Li, G.; Gao, D.; et al. Decreased mitochondrial D-loop region methylation mediates an increase in mitochondrial DNA copy number in CADASIL. Clin. Epigenet. 2022, 14, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, Y.; Peng, C.; Dong, Y.; Wang, J.; Kong, F.; Yang, X.; Wang, Y.; Gao, H. NADH dehydrogenase subunit 1/4/5 promotes survival of acute myeloid leukemia by mediating specific oxidative phosphorylation. Mol. Med. Rep. 2022, 25, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velazquez-Villarreal, E.I.; Maheshwari, S.; Sorenson, J.; Fiddes, I.T.; Kumar, V.; Yin, Y.; Webb, M.G.; Catalanotti, C.; Grigorova, M.; Edwards, P.A.; et al. Single-cell sequencing of genomic DNA resolves sub-clonal heterogeneity in a melanoma cell line. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, C.; Sun, S.; Liu, K.; Wang, J.; Li, S.; Liu, Q.; Deagle, B.E.; Seim, I.; Biscontin, A.; Wang, Q.; et al. The enormous repetitive Antarctic krill genome reveals environmental adaptations and population insights. Cell 2023, 186, 1279–1294.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, F.; Guerrero, R.J.; Sánchez-Restrepo, A.F. Systematics and diversity of Neotropical ants. Rev. Colomb. De Entomol. 2021, 47, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, F.M.; Csősz, S.; Markó, B.; Gamisch, A.; Rinnhofer, L.; Folterbauer, C.; Hammerle, S.; Stauffer, C.; Arthofer, W.; Schlick-Steiner, B.C. Turning one into five: Integrative taxonomy uncovers complex evolution of cryptic species in the harvester ant Messor “structor”. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2018, 127, 387–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delsinne, T.; Mackay, W.; Wild, A.; Roisin, Y.; Leponce, M. Distribution and Diversity of the Cryptic Ant Genus Oxyepoecus (Hymenoptera: Formicidae: Myrmicinae) in Paraguay with Descriptions of Two New Species. Psyche 2012, 2012, 594302. [Google Scholar]
- Gaikwad, S.S.; Ghate, H.V.; Ghaskadbi, S.S.; Patole, M.S.; Shouche, Y.S. DNA barcoding of nymphalid butterflies (Nymphalidae: Lepidoptera) from Western Ghats of India. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2012, 39, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyata, M.N.; Kageyama, D.; Nomura, M. Multiplex PCR for identification of two butterfly sister species: Eurema mandarina and Eurema hecabe. BMC Res. Notes 2020, 13, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalta, I.; Ledet, R.; Baude, M.; Genoud, D.; Bouget, C.; Cornillon, M.; Moreau, S.; Courtial, B.; Lopez-Vaamonde, C. A DNA barcode-based survey of wild urban bees in the Loire Valley, France. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, K.; Kumar, V.; Kundu, S.; Pakrashi, A.; Prasad, P.; Caleb, J.T.D.; Chandra, K. Identification of Indian Spiders through DNA barcoding: Cryptic species and species complex. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, J.-H.; Kim, S.; Lee, S. DNA barcodes reveal population-dependent cryptic diversity and various cases of sympatry of Korean leptonetid spiders (Araneae: Leptonetidae). Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 15528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bingpeng, X.; Heshan, L.; Zhilan, Z.; Chunguang, W.; Yanguo, W.; Jianjun, W. DNA barcoding for identification of fish species in the Taiwan Strait. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffers, B.R.; Oliveira, B.F.; Lamb, I.; Edwards, D.P. Global wildlife trade across the tree of life. Science 2019, 366, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coghlan, M.L.; Haile, J.; Houston, J.; Murray, D.C.; White, N.E.; Moolhuijzen, P.; Bellgard, M.I.; Bunce, M. Deep Sequencing of Plant and Animal DNA Contained within Traditional Chinese Medicines Reveals Legality Issues and Health Safety Concerns. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newmaster, S.G.; Grguric, M.; Shanmughanandhan, D.; Ramalingam, S.; Ragupathy, S. DNA barcoding detects contamination and substitution in North American herbal products. BMC Med. 2013, 11, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Yang, J.-W.; Liu, B.-S.; Zhang, N.; Guo, L.; Guo, H.-Y.; Zhang, D.-C. Detection and identification of marine fish mislabeling in Guangzhou’s supermarkets and sushi restaurants using DNA barcoding. J. Food Sci. 2022, 87, 2440–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Ruth, S.M.; van der Veeken, J.; Dekker, P.; Luning, P.A.; Huisman, W. Feeding fiction: Fraud vulnerability in the food service industry. Food Res. Int. 2020, 133, 109158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Pang, X.; Song, J.; Shi, L.; Yao, H.; Han, J.; Leon, C. A renaissance in herbal medicine identification: From morphology to DNA. Biotechnol. Adv. 2014, 32, 1237–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marçais, G.; Kingsford, C. A fast, lock-free approach for efficient parallel counting of occurrences of k-mers. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 764–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.-Y.; Cheng, Q.-X.; Liu, J.-K.; Nie, X.-Q.; Zhao, G.-P.; Wang, J. CRISPR-Cas12a has both cis- and trans-cleavage activities on single-stranded DNA. Cell Res. 2018, 28, 491–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, B.; Trapnell, C.; Pop, M.; Salzberg, S.L. Ultrafast and memory-efficient alignment of short DNA sequences to the human genome. Genome Biol. 2009, 10, R25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.; Park, J.; Kim, J.-S. Cas-OFFinder: A fast and versatile algorithm that searches for potential off-target sites of Cas9 RNA-guided endonucleases. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1473–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
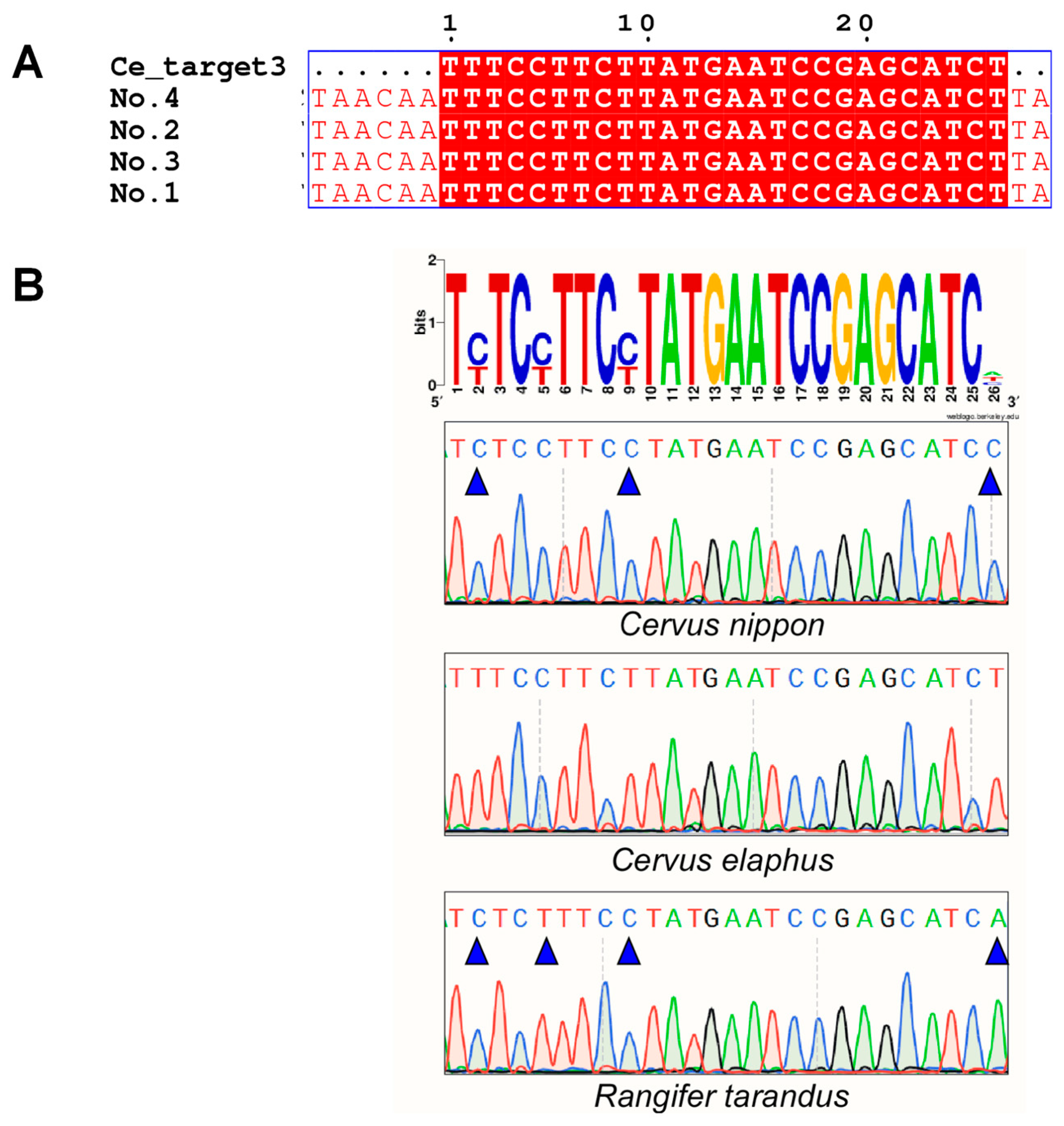



| Species | Sequence Location | No. | Specific Target Sequence (5′→3′) | Annotation | CrRNA (5′→3′) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cervus elaphus | chromosome 29 | Ce_target1 | TTTGGGGAACTTAAGACTTGGGCAT | unannotated | UAAUUUCUACUAAGUGUAGAU GGGAACUUAAGACUUGGGCAU |
| chromosome 29 | Ce_target2 | TTTGGGTCTAGATACTCATCTTCCG | unannotated | UAAUUUCUACUAAGUGUAGAU GGTCTAGATACTCATCTTCCG | |
| mitochondrial genome | Ce_target3 | TTTCCTTCTTATGAATCCGAGCATCT | ND1 | UAAUUUCUACUAAGUGUAGAU CUUCUUAUGAAUCCGAGCAUCU | |
| Cervus nippon | nuclear genome | Cn_target1 | TTTGAATCTGGACGGACATCCAGCC | unannotated | UAAUUUCUACUAAGUGUAGAU AAUCUGGACGGACAUCCAGCC |
| nuclear genome | Cn_target2 | TTTGACACCGGTCTACTGGCCTGCC | unannotated | UAAUUUCUACUAAGUGUAGAU ACACCGGUCUACUGGCCUGCC | |
| mitochondrial genome | Cn_target3 | TTTATGTACCATTGTACATGTGTGC | D-loop | UAAUUUCUACUAAGUGUAGAU UGUACCAUUGUACAUGUGUGC | |
| Rangifer tarandus | chromosome 29 | Rt_target1 | TTTCGTTACCCCTCCGTCGTCGGGA | unannotated | UAAUUUCUACUAAGUGUAGAU GUUACCCCUCCGUCGUCGGGA |
| chromosome12/13 | Rt_target2 | TTTGAGATTGCCAATGTCGCGGTCG | unannotated | UAAUUUCUACUAAGUGUAGAU AGAUUGCCAAUGUCGCGGUCG | |
| mitochondrial genome | Rt_target3 | TTTCTACTTCTTCTAGCATCATCCA | COI | UAAUUUCUACUAAGUGUAGAU UACUUCUUCUAGCAUCAUCCA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gan, Y.; Qi, G.; Hao, L.; Xin, T.; Lou, Q.; Xu, W.; Song, J. Analysis of Whole-Genome as a Novel Strategy for Animal Species Identification. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2955. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25052955
Gan Y, Qi G, Hao L, Xin T, Lou Q, Xu W, Song J. Analysis of Whole-Genome as a Novel Strategy for Animal Species Identification. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(5):2955. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25052955
Chicago/Turabian StyleGan, Yutong, Guihong Qi, Lijun Hao, Tianyi Xin, Qian Lou, Wenjie Xu, and Jingyuan Song. 2024. "Analysis of Whole-Genome as a Novel Strategy for Animal Species Identification" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 5: 2955. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25052955
APA StyleGan, Y., Qi, G., Hao, L., Xin, T., Lou, Q., Xu, W., & Song, J. (2024). Analysis of Whole-Genome as a Novel Strategy for Animal Species Identification. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(5), 2955. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25052955






