Neuroprotective Effects of Aucubin against Cerebral Ischemia and Ischemia Injury through the Inhibition of the TLR4/NF-κB Inflammatory Signaling Pathway in Gerbils
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
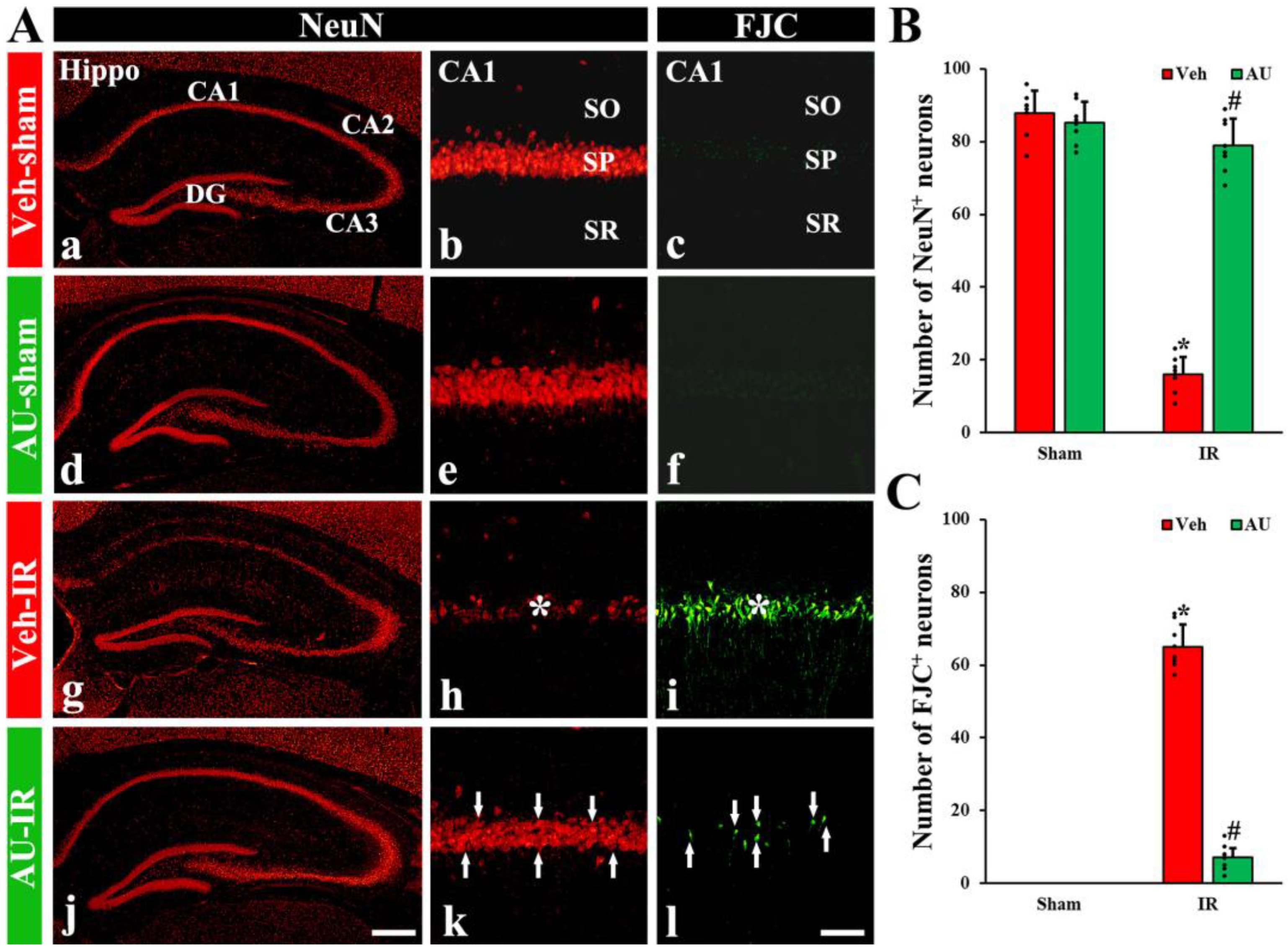
2.1. Protection of Cerebral IR-Induced Neuronal Death by AU
2.1.1. NeuN-Immunoreactive (NeuN+) Neurons
2.1.2. FJC-Positive (FJC+) Neurons
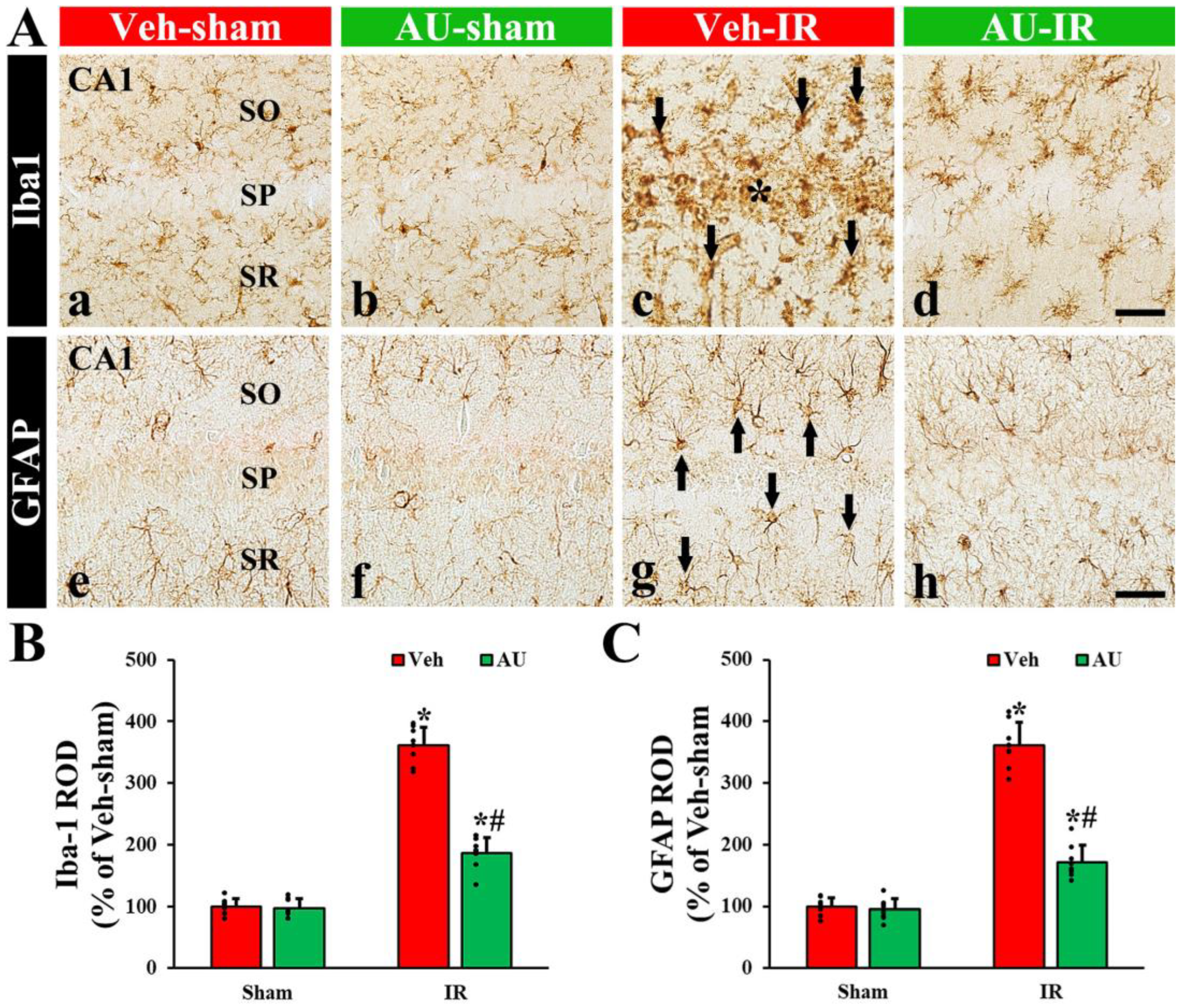
2.2. Attenuation of Cerebral IR-Induced Gliosis by AU
2.2.1. Microgliosis
2.2.2. Astrogliosis
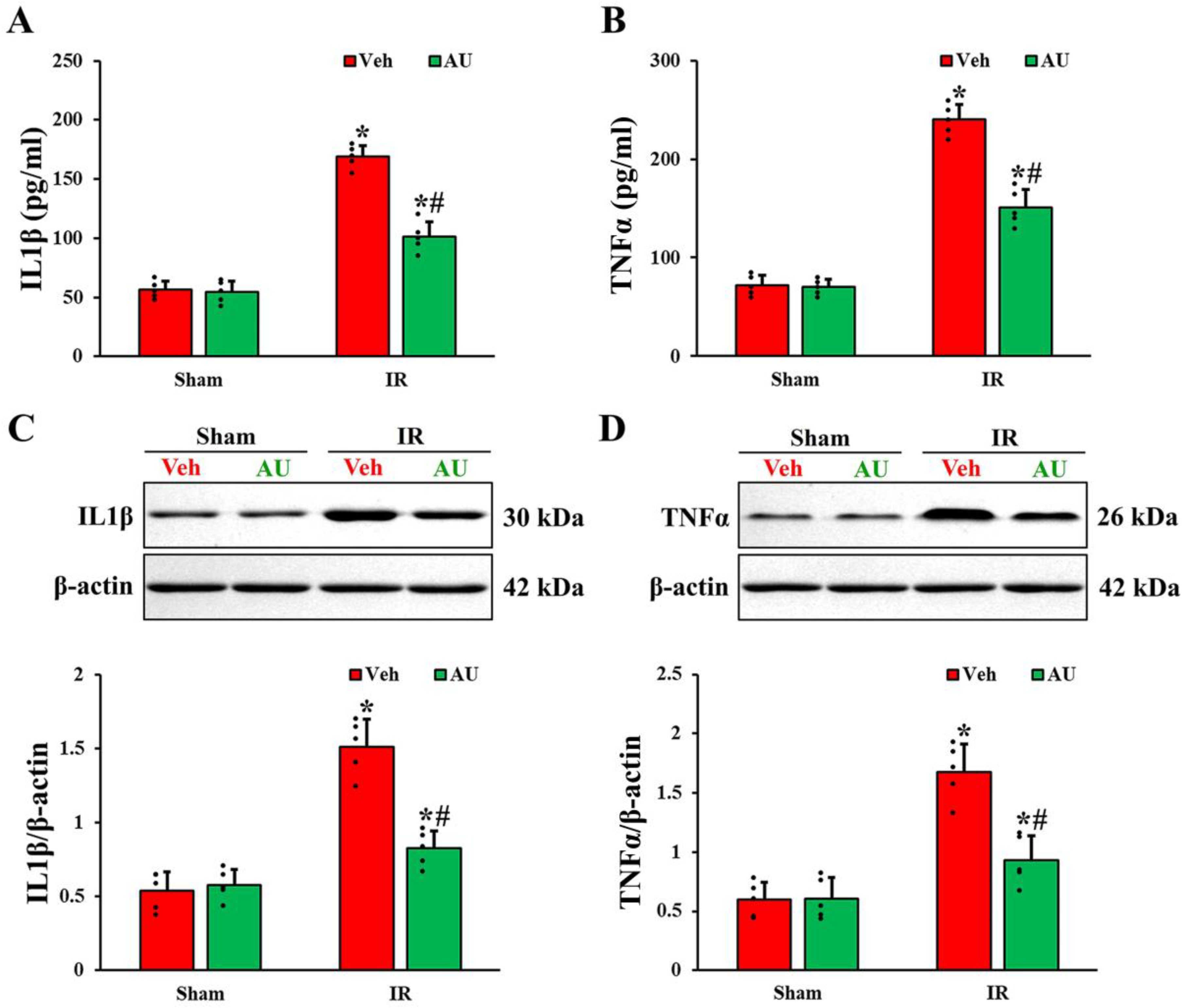
2.3. Attenuation of Cerebral IR-Induced Increases of Proinflammatory Cytokines by AU
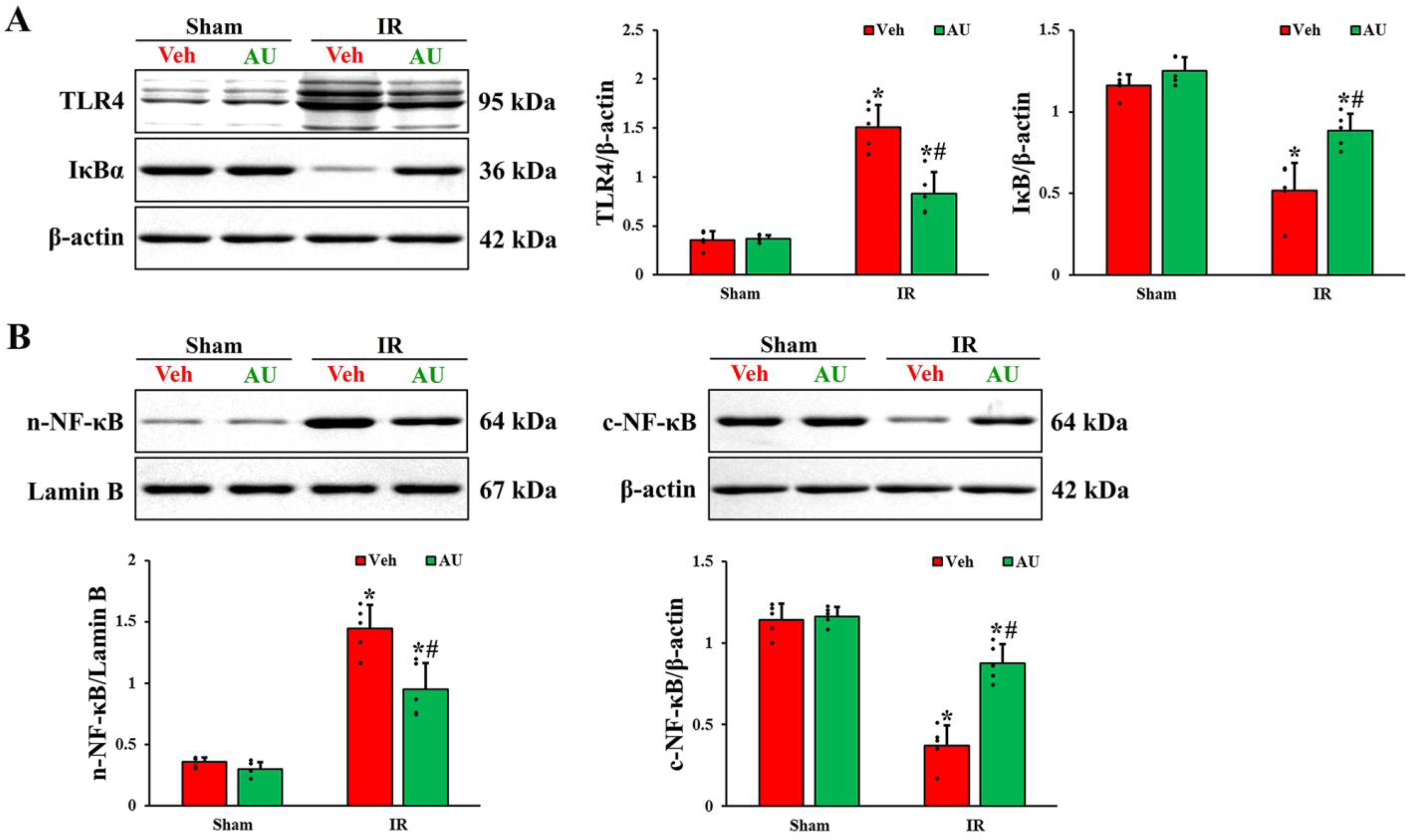
2.4. Inactivation of Transient Global Cerebral IR-Mediated TLR4/NF-κB Signaling Pathway by AU
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethical Statement and Experimental Animals
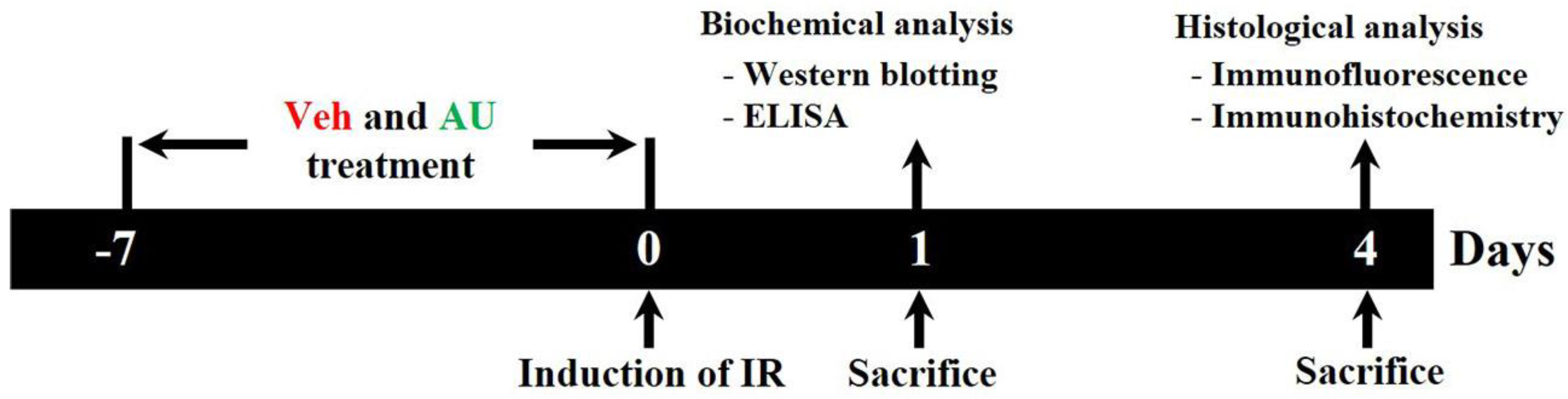
4.2. Experimental Groups, AU Treatment, and Induction of Cerebral IR
4.3. Tissue Preparation for Histological Analysis
4.4. NeuN Immunofluorescence and FJC Histofluorescence Staining
4.5. Immunohistochemistry
4.6. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.7. Western Blotting
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ding, X.D.; Zheng, N.N.; Cao, Y.Y.; Zhao, G.Y.; Zhao, P. Dexmedetomidine preconditioning attenuates global cerebral ischemic injury following asphyxial cardiac arrest. Int. J. Neurosci. 2016, 126, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchino, H.; Ogihara, Y.; Fukui, H.; Chijiiwa, M.; Sekine, S.; Hara, N.; Elmer, E. Brain injury following cardiac arrest: Pathophysiology for neurocritical care. J. Intensive Care 2016, 4, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petito, C.K.; Feldmann, E.; Pulsinelli, W.A.; Plum, F. Delayed hippocampal damage in humans following cardiorespiratory arrest. Neurology 1987, 37, 1281–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahul, A.B.; Joshi, P.C.; Kumar, A.; Chakravarty, S. Transient global cerebral ischemia differentially affects cortex, striatum and hippocampus in bilateral common carotid arterial occlusion (BCCAo) mouse model. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2018, 92, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Globus, M.Y.; Busto, R.; Martinez, E.; Valdes, I.; Dietrich, W.D.; Ginsberg, M.D. Comparative effect of transient global ischemia on extracellular levels of glutamate, glycine, and gamma-aminobutyric acid in vulnerable and nonvulnerable brain regions in the rat. J. Neurochem. 1991, 57, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt-Kastner, R. Genomic approach to selective vulnerability of the hippocampus in brain ischemia-hypoxia. Neuroscience 2015, 309, 259–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirino, T.; Tamura, A.; Sano, K. Delayed neuronal death in the rat hippocampus following transient forebrain ischemia. Acta Neuropathol. 1984, 64, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.C.; Park, J.H.; Ahn, J.H.; Kim, I.H.; Cho, J.H.; Choi, J.H.; Yoo, K.Y.; Lee, C.H.; Hwang, I.K.; Cho, J.H.; et al. New gabaergic neurogenesis in the hippocampal ca1 region of a gerbil model of long-term survival after transient cerebral ischemic injury. Brain Pathol. 2016, 26, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, I.H.; Villa-Gonzalez, M.; Martin, G.; Soto, M.; Perez-Alvarez, M.J. Glial cells as therapeutic approaches in brain ischemia-reperfusion injury. Cells 2021, 10, 1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.W.; Ahn, J.H.; Lee, T.K.; Park, Y.E.; Kim, B.; Lee, J.C.; Kim, D.W.; Shin, M.C.; Park, Y.; Cho, J.H.; et al. Post-treatment with oxcarbazepine confers potent neuroprotection against transient global cerebral ischemic injury by activating nrf2 defense pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 124, 109850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Xu, W.; Chu, K.; Chen, L.; Chen, X. Antioxidant and anti-excitotoxicity effect of gualou guizhi decoction on cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Exp. Ther. Med. 2015, 9, 2121–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Kader, M.S.; Alqasoumi, S.I. In vivo hepatoprotective and nephroprotective activity of acylated iridoid glycosides from Scrophularia hepericifolia. Biology 2021, 10, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Qiu, X.Q.; Shu, Z.H.; Liu, Q.C.; Hu, M.B.; Han, T.; Rahman, K.; Qin, L.P.; Zheng, C.J. Hepatoprotective activity of total iridoid glycosides isolated from Paederia scandens (lour.) Merr. var. tomentosa. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 174, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Gong, X.; Bo, A.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, M.; Zang, E.; Zhang, C.; Li, M. Iridoids: Research advances in their phytochemistry, biological activities, and pharmacokinetics. Molecules 2020, 25, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harput, U.S.; Saracoglu, I.; Inoue, M.; Ogihara, Y. Phenylethanoid and iridoid glycosides from veronica persica. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2002, 50, 869–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, W.S.; Jung, E.; Kim, J. Aucuba japonica extract and aucubin prevent desiccating stress-induced corneal epithelial cell injury and improve tear secretion in a mouse model of dry eye disease. Molecules 2018, 23, 2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.; Jin, L.; Jin, L.; Zhang, P.; Li, D.; Xia, Y.; Lu, Y.; Xu, Y. Neuroprotection of aucubin in primary diabetic encephalopathy. Sci. China C Life Sci. 2008, 51, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.Y.; Jin, L.; Jin, L.J.; Li, X.Y.; Zhang, P.; Ma, Y.S.; Lu, Y.N.; Xia, Y.Q.; Xu, Y.P. Aucubin prevents loss of hippocampal neurons and regulates antioxidative activity in diabetic encephalopathy rats. Phytother. Res. 2009, 23, 980–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Lee, T.K.; Kim, D.W.; Ahn, J.H.; Lee, C.H.; Lim, S.S.; Kim, Y.H.; Cho, J.H.; Kang, I.J.; Won, M.H. Aucubin exerts neuroprotection against forebrain ischemia and reperfusion injury in gerbils through antioxidative and neurotrophic effects. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Ye, T.; Long, T.; Peng, X. Ginkgetin exerts anti-inflammatory effects on cerebral ischemia/reperfusion-induced injury in a rat model via the tlr4/nf-kappab signaling pathway. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2019, 83, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Zheng, Y.; Fan, X. The natural (poly)phenols as modulators of microglia polarization via tlr4/nf-kappab pathway exert anti-inflammatory activity in ischemic stroke. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 914, 174660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Sairazi, N.S.; Sirajudeen, K.N.S. Natural products and their bioactive compounds: Neuroprotective potentials against neurodegenerative diseases. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2020, 2020, 6565396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.D.; Kim, M.; Wu, H.H.; Jin, B.K.; Jeon, M.S.; Song, Y.S. Prunus cerasoides extract and its component compounds upregulate neuronal neuroglobin levels, mediate antioxidant effects, and ameliorate functional losses in the mouse model of cerebral ischemia. Antioxidants 2021, 11, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, P.F.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, F.; Chen, J.G. Natural compounds from traditional medicinal herbs in the treatment of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2010, 31, 1523–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Hua, X.; Niu, H.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, L. Cornel iridoid glycoside protects against white matter lesions induced by cerebral ischemia in rats via activation of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor/neuregulin-1 pathway. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2019, 15, 3327–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, T.; Xu, Y.; Li, S.; Li, N.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, H. Cornin protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by preventing autophagy via the pi3k/akt/mtor pathway. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2022, 23, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedergaard, M.; Dirnagl, U. Role of glial cells in cerebral ischemia. Glia 2005, 50, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moya-Gomez, A.; Font, L.P.; Burlacu, A.; Alpizar, Y.A.; Cardonne, M.M.; Brone, B.; Bronckaers, A. Extremely low-frequency electromagnetic stimulation (elf-ems) improves neurological outcome and reduces microglial reactivity in a rodent model of global transient stroke. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tureckova, J.; Hermanova, Z.; Marchetti, V.; Anderova, M. Astrocytic trpv4 channels and their role in brain ischemia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, K.; Yin, B.; Wang, J.; Peng, G.; Liang, H.; Xu, Z.; Du, Y.; Fang, M.; Xia, Q.; Luo, B. Inhibition of p2x7 receptor ameliorates transient global cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury via modulating inflammatory responses in the rat hippocampus. J. Neuroinflamm. 2012, 9, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Lu, J.; Shao, A.; Zhang, J.H.; Zhang, J. Glial cells: Role of the immune response in ischemic stroke. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hou, J.; Zhang, P.; Li, D.; Zhang, C.; Liu, J. Geniposide reduces inflammatory responses of oxygen-glucose deprived rat microglial cells via inhibition of the tlr4 signaling pathway. Neurochem. Res. 2012, 37, 2235–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambertsen, K.L.; Biber, K.; Finsen, B. Inflammatory cytokines in experimental and human stroke. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2012, 32, 1677–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, I.G.; Jin, J.J.; Hwang, L.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, C.J.; Jeon, J.W.; Chung, J.Y.; Han, J.H. Adenosine a2a receptor agonist polydeoxyribonucleotide ameliorates short-term memory impairment by suppressing cerebral ischemia-induced inflammation via mapk pathway. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0248689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Zhong, Q.; Chen, X.; Wu, X.; Sha, R.; Song, G.; Zhang, C.; Chen, X. Neuroprotective effects of celastrol on transient global cerebral ischemia rats via regulating hmgb1/nf-kappab signaling pathway. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadi Moghadam, B.; Fereidoni, M. Neuroprotective effect of menaquinone-4 (mk-4) on transient global cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rat. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Kim, J.D.; Lee, T.K.; Han, X.; Sim, H.; Kim, B.; Lee, J.C.; Ahn, J.H.; Lee, C.H.; Kim, D.W.; et al. Neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory effects of pinus densiflora bark extract in gerbil hippocampus following transient forebrain ischemia. Molecules 2021, 26, 4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caso, J.R.; Pradillo, J.M.; Hurtado, O.; Leza, J.C.; Moro, M.A.; Lizasoain, I. Toll-like receptor 4 is involved in subacute stress-induced neuroinflammation and in the worsening of experimental stroke. Stroke 2008, 39, 1314–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Xu, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Cao, J.; Fu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Lou, J.; et al. Cottonseed oil alleviates ischemic stroke injury by inhibiting the inflammatory activation of microglia and astrocyte. J. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 17, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ge, P.; Zhu, Y. Tlr2 and tlr4 in the brain injury caused by cerebral ischemia and reperfusion. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 124614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, C.X.; Yang, Q.W.; Lv, F.L.; Cui, J.; Fu, H.B.; Wang, J.Z. Reduced cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in toll-like receptor 4 deficient mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 353, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyakkoku, K.; Hamanaka, J.; Tsuruma, K.; Shimazawa, M.; Tanaka, H.; Uematsu, S.; Akira, S.; Inagaki, N.; Nagai, H.; Hara, H. Toll-like receptor 4 (tlr4), but not tlr3 or tlr9, knock-out mice have neuroprotective effects against focal cerebral ischemia. Neuroscience 2010, 171, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.W.; Jeon, Y.T.; Lim, Y.J.; Park, H.P. Sevoflurane postconditioning-induced anti-inflammation via inhibition of the toll-like receptor-4/nuclear factor kappa b pathway contributes to neuroprotection against transient global cerebral ischemia in rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.; Kim, H.C.; Lee, S.; Ryu, H.G.; Park, Y.H.; Kim, J.H.; Lim, Y.J.; Park, H.P. Dexmedetomidine confers neuroprotection against transient global cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats by inhibiting inflammation through inactivation of the tlr-4/nf-kappab pathway. Neurosci. Lett. 2017, 649, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Feng, Z.; Gao, W.; Duan, Y.; Fan, G.; Geng, X.; Wu, B.; Li, K.; Liu, K.; Peng, C. Aucubin attenuates liver ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting the hmgb1/tlr-4/nf-kappab signaling pathway, oxidative stress, and apoptosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 544124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Lee, T.K.; Kim, D.W.; Ahn, J.H.; Lee, C.H.; Kim, J.D.; Shin, M.C.; Cho, J.H.; Lee, J.C.; Won, M.H.; et al. Astaxanthin confers a significant attenuation of hippocampal neuronal loss induced by severe ischemia-reperfusion injury in gerbils by reducing oxidative stress. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Ahn, J.H.; Song, M.; Kim, D.W.; Lee, T.K.; Lee, J.C.; Kim, Y.M.; Kim, J.D.; Cho, J.H.; Hwang, I.K.; et al. Pretreated fucoidan confers neuroprotection against transient global cerebral ischemic injury in the gerbil hippocampal ca1 area via reducing of glial cell activation and oxidative stress. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 109, 1718–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Park, J.H.; Ahn, J.H.; Won, M.H. Effects of melatonin on cognitive impairment and hippocampal neuronal damage in a rat model of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion. Exp. Ther. Med. 2016, 11, 2240–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, J.H.; Lee, T.-K.; Kim, D.W.; Ahn, J.H.; Shin, M.C.; Cho, J.H.; Won, M.-H.; Kang, I.J. Neuroprotective Effects of Aucubin against Cerebral Ischemia and Ischemia Injury through the Inhibition of the TLR4/NF-κB Inflammatory Signaling Pathway in Gerbils. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3461. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25063461
Park JH, Lee T-K, Kim DW, Ahn JH, Shin MC, Cho JH, Won M-H, Kang IJ. Neuroprotective Effects of Aucubin against Cerebral Ischemia and Ischemia Injury through the Inhibition of the TLR4/NF-κB Inflammatory Signaling Pathway in Gerbils. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(6):3461. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25063461
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Joon Ha, Tae-Kyeong Lee, Dae Won Kim, Ji Hyeon Ahn, Myoung Cheol Shin, Jun Hwi Cho, Moo-Ho Won, and Il Jun Kang. 2024. "Neuroprotective Effects of Aucubin against Cerebral Ischemia and Ischemia Injury through the Inhibition of the TLR4/NF-κB Inflammatory Signaling Pathway in Gerbils" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 6: 3461. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25063461
APA StylePark, J. H., Lee, T.-K., Kim, D. W., Ahn, J. H., Shin, M. C., Cho, J. H., Won, M.-H., & Kang, I. J. (2024). Neuroprotective Effects of Aucubin against Cerebral Ischemia and Ischemia Injury through the Inhibition of the TLR4/NF-κB Inflammatory Signaling Pathway in Gerbils. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(6), 3461. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25063461






