Early Movement Restriction Affects FNDC5/Irisin and BDNF Levels in Rat Muscle and Brain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Impact of SMR on Hindlimb Muscle Weight
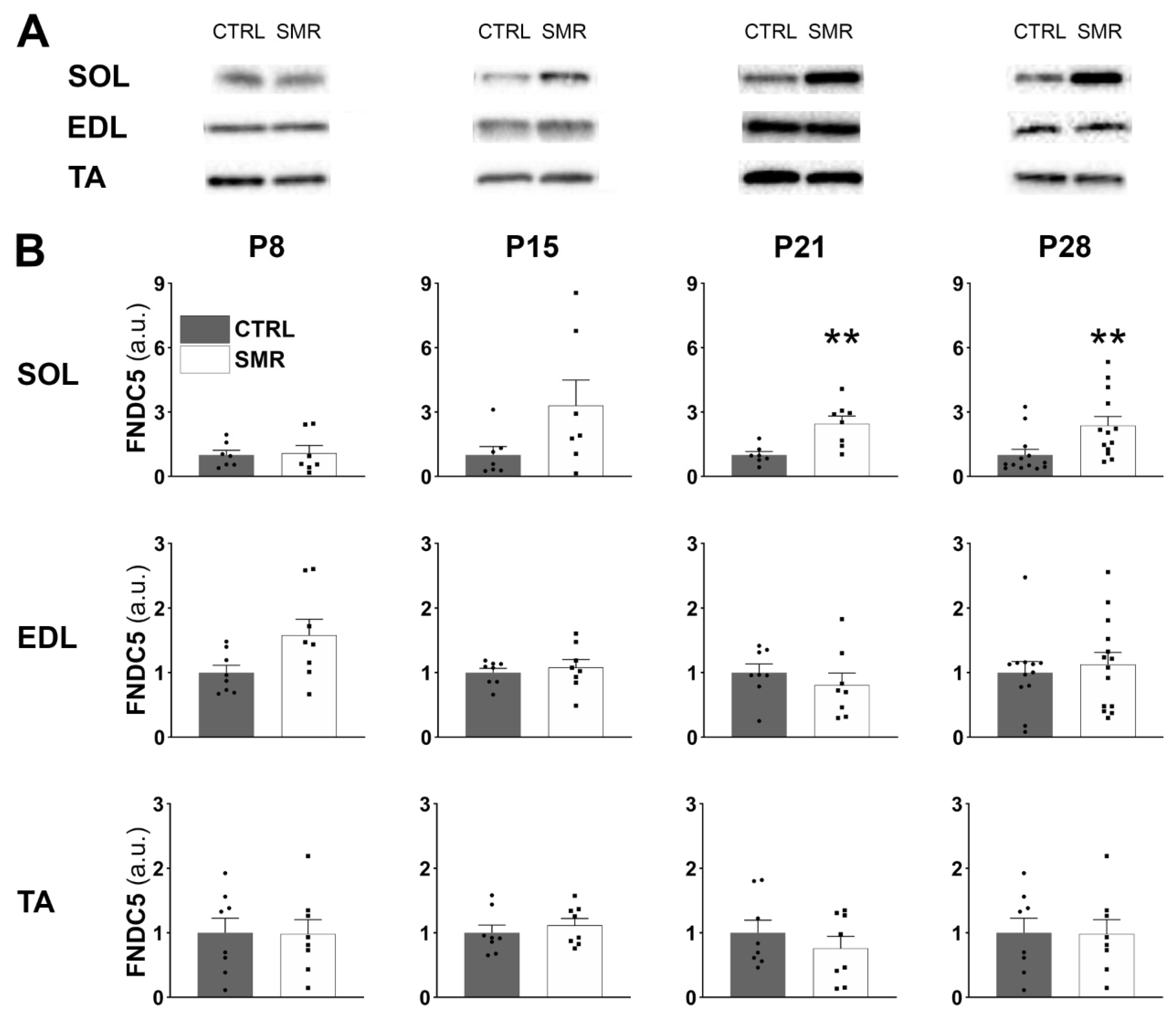
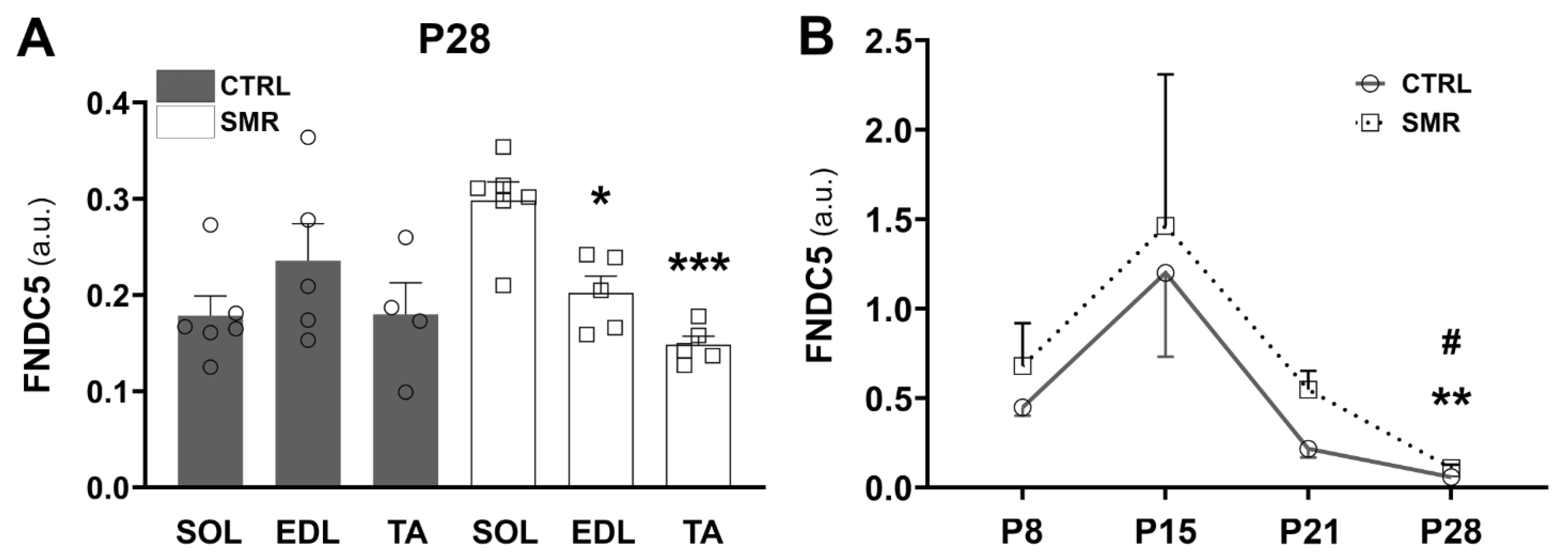
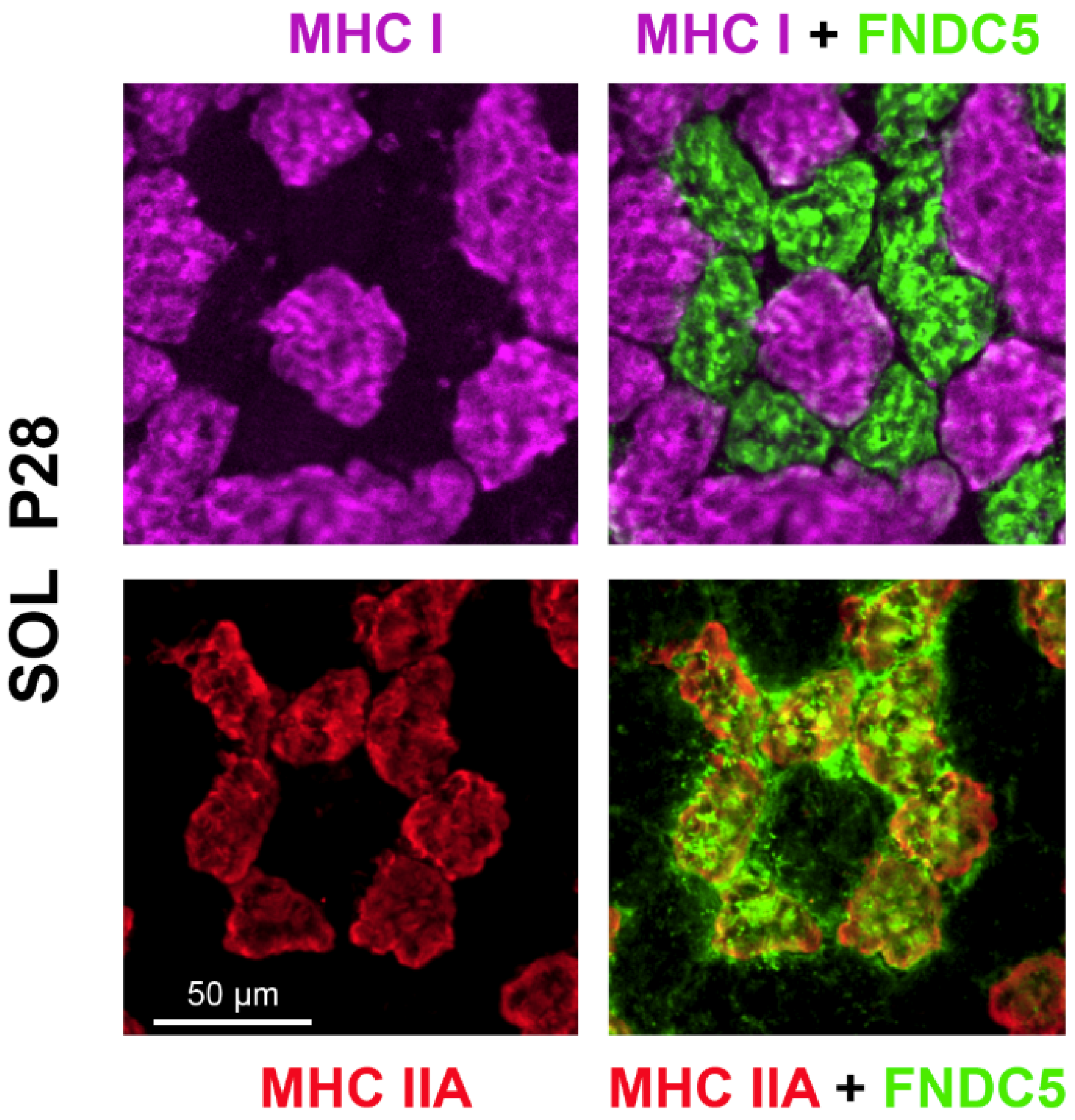
2.2. Differential Impact of SMR on FNDC5/Irisin Levels in Hindlimb Muscles
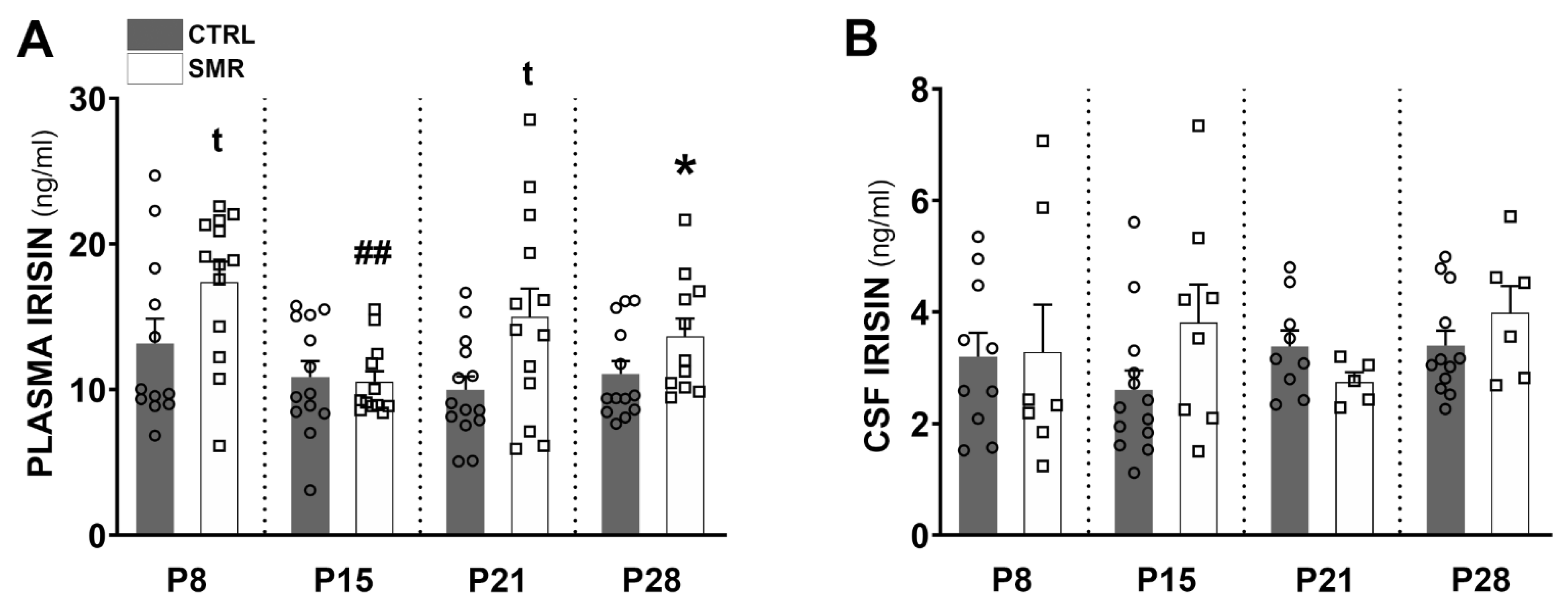
2.3. SMR Increased Irisin Levels in Plasma and CSF
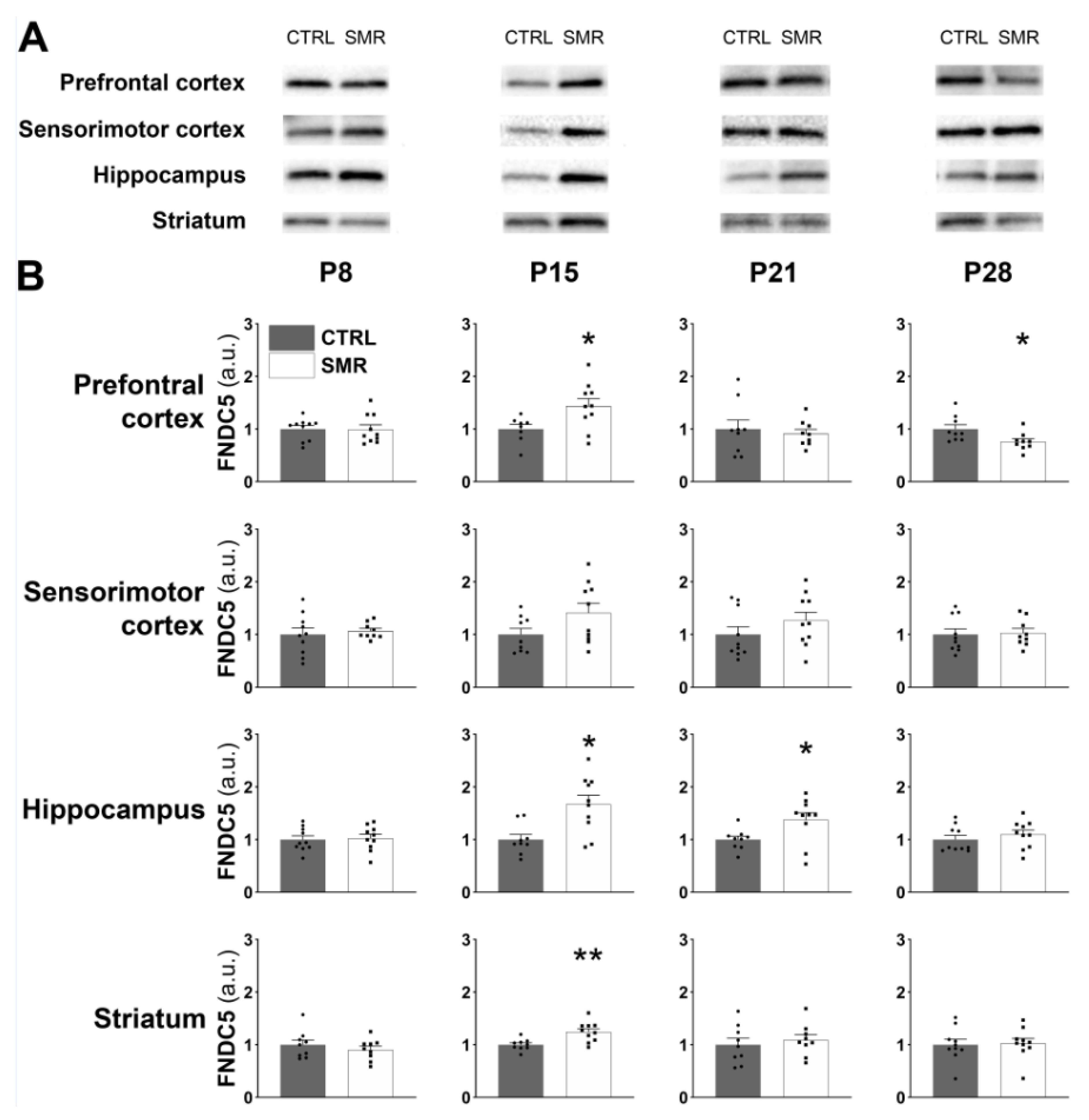
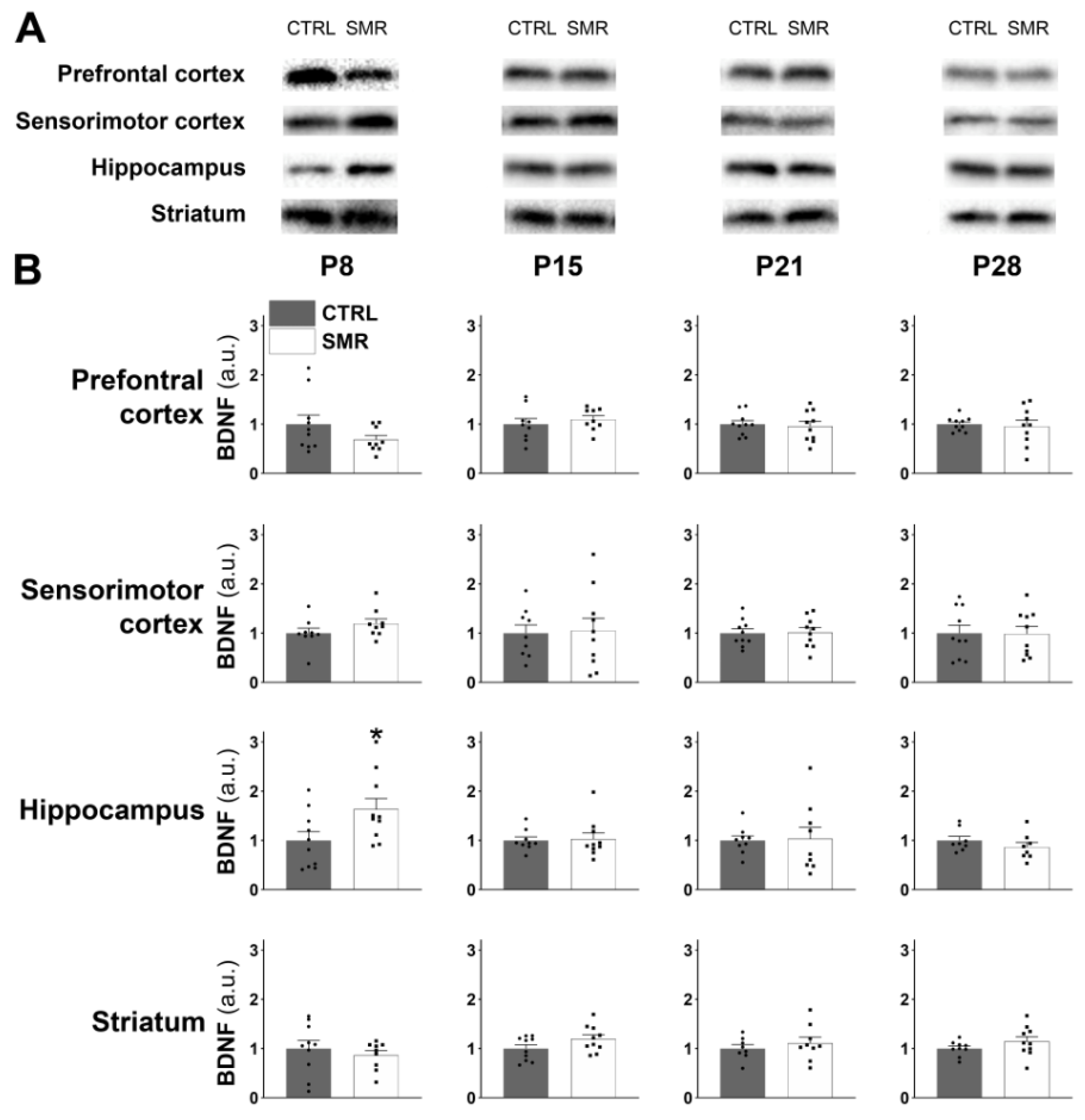
2.4. SMR Had a Differential Impact on FNDC5/Irisin and BDNF Levels Depending on the Cerebral Structures
3. Discussion
3.1. Methodological Considerations
3.2. FNDC5/Irisin Levels Are Increased in SMR Pups
3.3. Kinetics of FNDC5/Irisin Expression Level
3.4. Muscle–Brain Dialogue
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. HindLimb Immobilization
4.3. Tissue Sampling
4.4. Protein Isolation
4.5. SDS-PAGE and Western Blotting
4.6. ELISA Assay
4.7. Immunohistochemistry
4.8. Data Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sale, A.; Berardi, N.; Maffei, L. Environment and brain plasticity: Towards an endogenous pharmacotherapy. Physiol. Rev. 2014, 94, 189–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paquet, A.; Olliac, B.; Golse, B.; Vaivre-Douret, L. Nature of motor impairments in autism spectrum disorder: A comparison with developmental coordination disorder. J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 2019, 41, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaivre-Douret, L.; Lalanne, C.; Golse, B. Developmental Coordination Disorder, An Umbrella Term for Motor Impairments in Children: Nature and Co-Morbid Disorders. Front. Psychol. 2016, 7, 178215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwicker, J.G.; Missiuna, C.; Harris, S.R.; Boyd, L.A. Developmental coordination disorder: A review and update. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. EJPN Off. J. Eur. Paediatr. Neurol. Soc. 2012, 16, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antolini, G.; Colizzi, M. Where Do Neurodevelopmental Disorders Go? Casting the Eye Away from Childhood towards Adulthood. Healthcare 2023, 11, 1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, V.; Zhang, Z.; Predy, M.; Pritchard, L.; Hesketh, K.D. Adherence to Canadian 24-Hour Movement Guidelines among infants and associations with development: A longitudinal study. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2022, 19, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canu, M.H.; Montel, V.; Dereumetz, J.; Marqueste, T.; Decherchi, P.; Coq, J.O.; Dupont, E.; Bastide, B. Early movement restriction deteriorates motor function and soleus muscle physiology. Exp. Neurol. 2022, 347, 113886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delcour, M.; Massicotte, V.S.; Russier, M.; Bras, H.; Peyronnet, J.; Canu, M.H.; Cayetanot, F.; Barbe, M.F.; Coq, J.O. Early movement restriction leads to enduring disorders in muscle and locomotion. Brain Pathol. 2018, 28, 889–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delcour, M.; Russier, M.; Castets, F.; Turle-Lorenzo, N.; Canu, M.H.; Cayetanot, F.; Barbe, M.F.; Coq, J.O. Early movement restriction leads to maladaptive plasticity in the sensorimotor cortex and to movement disorders. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canu, M.H.; Fourneau, J.; Coq, J.O.; Dannhoffer, L.; Cieniewski-Bernard, C.; Stevens, L.; Bastide, B.; Dupont, E. Interplay between hypoactivity, muscle properties and motor command: How to escape the vicious deconditioning circle? Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2019, 62, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, B.K.; Febbraio, M.A. Muscles, exercise and obesity: Skeletal muscle as a secretory organ. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2012, 8, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bostrom, P.; Wu, J.; Jedrychowski, M.P.; Korde, A.; Ye, L.; Lo, J.C.; Rasbach, K.A.; Bostrom, E.A.; Choi, J.H.; Long, J.Z.; et al. A PGC1-alpha-dependent myokine that drives brown-fat-like development of white fat and thermogenesis. Nature 2012, 481, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waseem, R.; Shamsi, A.; Mohammad, T.; Hassan, M.I.; Kazim, S.N.; Chaudhary, A.A.; Rudayni, H.A.; Al-Zharani, M.; Ahmad, F.; Islam, A. FNDC5/Irisin: Physiology and Pathophysiology. Molecules 2022, 27, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazeminasab, F.; Sadeghi, E.; Afshari-Safavi, A. Comparative Impact of Various Exercises on Circulating Irisin in Healthy Subjects: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 8235809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, R. Irisin at the crossroads of inter-organ communications: Challenge and implications. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 989135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.R.; Valaris, S.; Young, M.F.; Haley, E.B.; Luo, R.; Bond, S.F.; Mazuera, S.; Kitchen, R.R.; Caldarone, B.J.; Bettio, L.E.B.; et al. Exercise hormone irisin is a critical regulator of cognitive function. Nat. Metab. 2021, 3, 1058–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lourenco, M.V.; Frozza, R.L.; de Freitas, G.B.; Zhang, H.; Kincheski, G.C.; Ribeiro, F.C.; Goncalves, R.A.; Clarke, J.R.; Beckman, D.; Staniszewski, A.; et al. Exercise-linked FNDC5/irisin rescues synaptic plasticity and memory defects in Alzheimer’s models. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siteneski, A.; Cunha, M.P.; Lieberknecht, V.; Pazini, F.L.; Gruhn, K.; Brocardo, P.S.; Rodrigues, A.L.S. Central irisin administration affords antidepressant-like effect and modulates neuroplasticity-related genes in the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex of mice. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 84 Pt A, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.J.; Li, Y.H.; Yuan, H.B.; Qu, L.F.; Wang, P. The novel exercise-induced hormone irisin protects against neuronal injury via activation of the Akt and ERK1/2 signaling pathways and contributes to the neuroprotection of physical exercise in cerebral ischemia. Metab. Clin. Exp. 2017, 68, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrann, C.D.; White, J.P.; Salogiannnis, J.; Laznik-Bogoslavski, D.; Wu, J.; Ma, D.; Lin, J.D.; Greenberg, M.E.; Spiegelman, B.M. Exercise induces hippocampal BDNF through a PGC-1alpha/FNDC5 pathway. Cell Metab. 2013, 18, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Li, H.; Shen, S.W.; Shen, Z.H.; Xu, M.; Yang, C.J.; Li, F.; Feng, Y.B.; Yun, J.T.; Wang, L.; et al. Swimming exercise increases serum irisin level and reduces body fat mass in high-fat-diet fed Wistar rats. Lipids Health Dis. 2016, 15, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morton, T.L.; Galior, K.; McGrath, C.; Wu, X.; Uzer, G.; Uzer, G.B.; Sen, B.; Xie, Z.; Tyson, D.; Rubin, J.; et al. Exercise Increases and Browns Muscle Lipid in High-Fat Diet-Fed Mice. Front. Endocrinol. 2016, 7, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawao, N.; Moritake, A.; Tatsumi, K.; Kaji, H. Roles of Irisin in the Linkage from Muscle to Bone During Mechanical Unloading in Mice. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2018, 103, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuchiya, Y.; Mizuno, S.; Goto, K. Irisin response to downhill running exercise in humans. J. Exerc. Nutr. Biochem. 2018, 22, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Amuri, A.; Sanz, J.M.; Lazzer, S.; Pišot, R.; Šimunič, B.; Biolo, G.; Zuliani, G.; Gasparini, M.; Narici, M.; Grassi, B.; et al. Irisin Attenuates Muscle Impairment during Bed Rest through Muscle-Adipose Tissue Crosstalk. Biology 2022, 11, 999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furino, V.O.; Alves, J.M.; Marine, D.A.; Sene-Fiorese, M.; Rodrigues, C.; Arrais-Lima, C.; Mattiello, S.M.; de Castro, C.A.; Borra, R.C.; Rocha, M.C.; et al. Dietary Intervention, When Not Associated With Exercise, Upregulates Irisin/FNDC5 While Reducing Visceral Adiposity Markers in Obese Rats. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 564963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavi, G.; Horwitz, A.; Einstein, O.; Zipori, R.; Gross, O.; Birk, R. Fndc5/irisin is regulated by myogenesis stage, irisin, muscle type and training. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2022, 14, 7063–7079. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Buroker, N.E.; Ning, X.H.; Portman, M. Cardiac PPARalpha Protein Expression is Constant as Alternate Nuclear Receptors and PGC-1 Coordinately Increase During the Postnatal Metabolic Transition. PPAR Res. 2008, 2008, 279531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walton, K.D.; Lieberman, D.; Llinas, A.; Begin, M.; Llinas, R.R. Identification of a critical period for motor development in neonatal rats. Neuroscience 1992, 51, 763–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloch-Gallego, E. Mechanisms controlling neuromuscular junction stability. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2015, 72, 1029–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, J.K.; Fladby, T. The perinatal reorganization of the innervation of skeletal muscle in mammals. Prog. Neurobiol. 1990, 34, 39–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geisler, H.C.; Westerga, J.; Gramsbergen, A. Development of posture in the rat. Acta Neurobiol. Exp. 1993, 53, 517–523. [Google Scholar]
- Dupuis, O.; Van Gaever, M.; Montel, V.; Dereumetz, J.; Coq, J.O.; Canu, M.H.; Dupont, E. Early movement restriction affects the acquisition of neurodevelopmental reflexes in rat pups. Brain Res. 2024, 1828, 148773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, D.; Sanches, E.F.; Sizonenko, S.V. Early neurodevelopmental reflex impairments in a rodent model of cerebral palsy. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2022, 82, 815–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouspillou, G.; Sgarioto, N.; Norris, B.; Barbat-Artigas, S.; Aubertin-Leheudre, M.; Morais, J.A.; Burelle, Y.; Taivassalo, T.; Hepple, R.T. The relationship between muscle fiber type-specific PGC-1α content and mitochondrial content varies between rodent models and humans. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.Y.; Tse, M.C.L.; Hu, X.; Jia, W.H.; Du, G.H.; Chan, C.B. Interaction of CREB and PGC-1alpha Induces Fibronectin Type III Domain-Containing Protein 5 Expression in C2C12 Myotubes. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 50, 1574–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, G.R.; McCue, S.A.; Zeng, M.; Baldwin, K.M. Time course of myosin heavy chain transitions in neonatal rats: Importance of innervation and thyroid state. Am. J. Physiol. 1999, 276 Pt 2, R954–R961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picquet, F.; Stevens, L.; Butler-Browne, G.S.; Mounier, Y. Contractile properties and myosin heavy chain composition of newborn rat soleus muscles at different stages of postnatal development. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 1997, 18, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punkt, K.; Naupert, A.; Asmussen, G. Differentiation of rat skeletal muscle fibres during development and ageing. Acta Histochem. 2004, 106, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, X.M.; Xu, Z.W.; Tao, X.; Deng, B.; Qi, K.K. FNDC5 expression closely correlates with muscle fiber types in porcine longissimus dorsi muscle and regulates myosin heavy chains (MyHCs) mRNA expression in C2C12 cells. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vints, W.A.J.; Levin, O.; Fujiyama, H.; Verbunt, J.; Masiulis, N. Exerkines and long-term synaptic potentiation: Mechanisms of exercise-induced neuroplasticity. Front. Neuroendocr. 2022, 66, 100993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cefis, M.; Chaney, R.; Wirtz, J.; Méloux, A.; Quirié, A.; Leger, C.; Prigent-Tessier, A.; Garnier, P. Molecular mechanisms underlying physical exercise-induced brain BDNF overproduction. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2023, 16, 1275924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mysoet, J.; Canu, M.H.; Cieniewski-Bernard, C.; Bastide, B.; Dupont, E. Hypoactivity affects IGF-1 level and PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in cerebral structures implied in motor control. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Q.; Vaynman, S.; Akhavan, M.; Ying, Z.; Gomez-Pinilla, F. Insulin-like growth factor I interfaces with brain-derived neurotrophic factor-mediated synaptic plasticity to modulate aspects of exercise-induced cognitive function. Neuroscience 2006, 140, 823–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Kim, J.; Mikami, T. Exercise-Induced Lactate Release Mediates Mitochondrial Biogenesis in the Hippocampus of Mice via Monocarboxylate Transporters. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 736905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reza, M.M.; Subramaniyam, N.; Sim, C.M.; Ge, X.; Sathiakumar, D.; McFarlane, C.; Sharma, M.; Kambadur, R. Irisin is a pro-myogenic factor that induces skeletal muscle hypertrophy and rescues denervation-induced atrophy. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrash, W.; Brook, M.; Crossland, H.; Phillips, B.E.; Cegielski, J.; Wilkinson, D.J.; Constantin-Teodosiu, D.; Greenhaff, P.L.; Smith, K.; Cleasby, M.; et al. Impacts of rat hindlimb Fndc5/irisin overexpression on muscle and adipose tissue metabolism. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 318, E943–E955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dupuis, O.; Girardie, J.; Van Gaever, M.; Garnier, P.; Coq, J.-O.; Canu, M.-H.; Dupont, E. Early Movement Restriction Affects FNDC5/Irisin and BDNF Levels in Rat Muscle and Brain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3918. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25073918
Dupuis O, Girardie J, Van Gaever M, Garnier P, Coq J-O, Canu M-H, Dupont E. Early Movement Restriction Affects FNDC5/Irisin and BDNF Levels in Rat Muscle and Brain. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(7):3918. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25073918
Chicago/Turabian StyleDupuis, Orlane, Julien Girardie, Mélanie Van Gaever, Philippe Garnier, Jacques-Olivier Coq, Marie-Hélène Canu, and Erwan Dupont. 2024. "Early Movement Restriction Affects FNDC5/Irisin and BDNF Levels in Rat Muscle and Brain" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 7: 3918. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25073918
APA StyleDupuis, O., Girardie, J., Van Gaever, M., Garnier, P., Coq, J.-O., Canu, M.-H., & Dupont, E. (2024). Early Movement Restriction Affects FNDC5/Irisin and BDNF Levels in Rat Muscle and Brain. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(7), 3918. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25073918





