Cognitive Impairment Related to Chronic Kidney Disease Is Associated with a Decreased Abundance of Membrane-Bound Klotho in the Cerebral Cortex
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
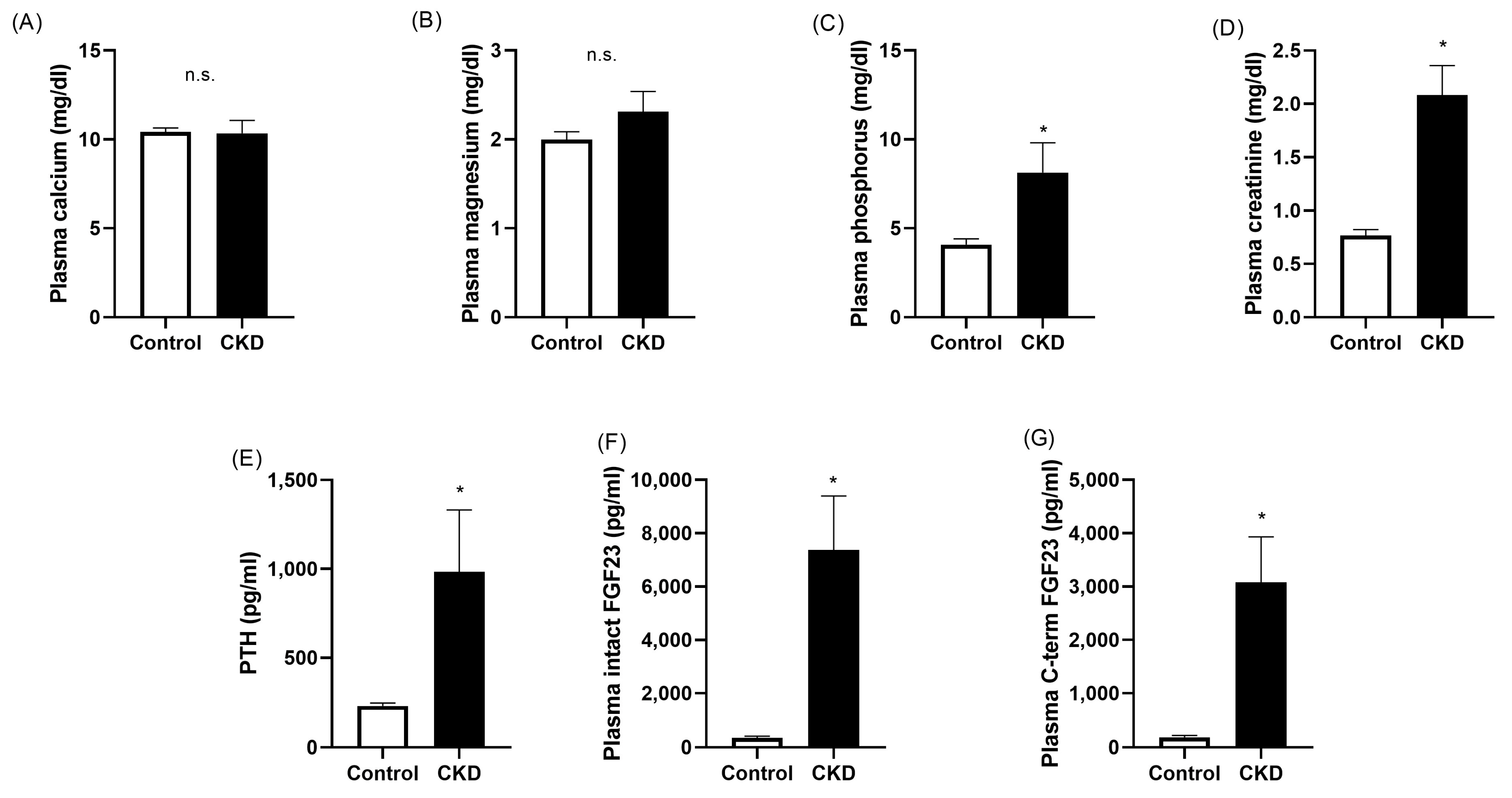
2.1. Plasma Biochemistry
2.2. Urine Biochemistry
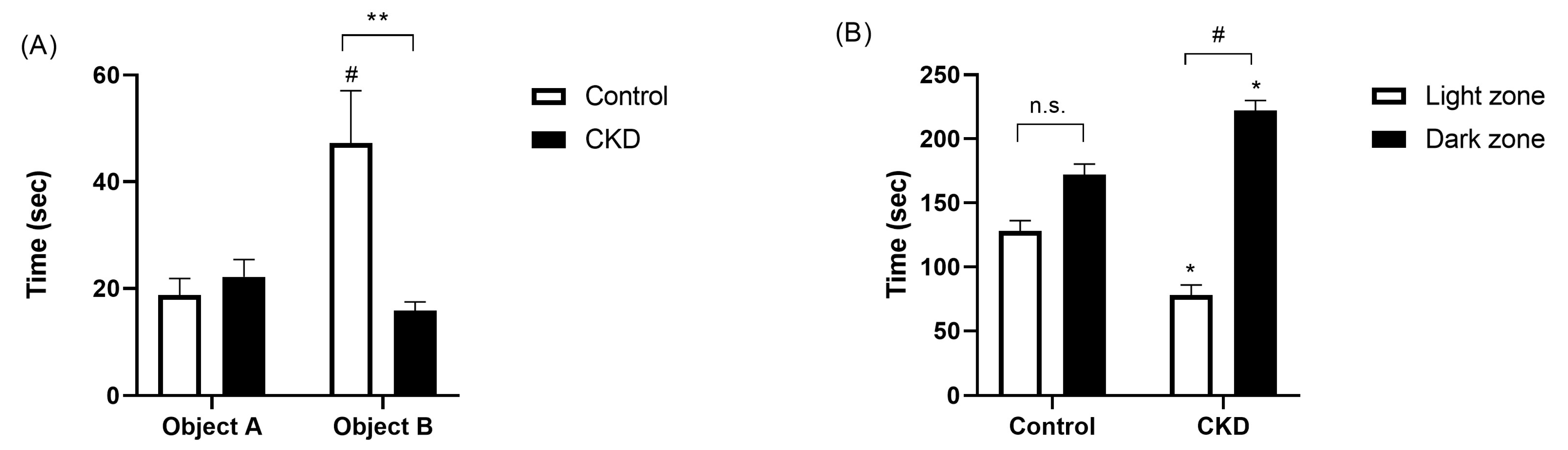
2.3. Neurobehavioral Evaluation
2.4. Assessment of Klotho Abundance
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. CKD Experimental Model
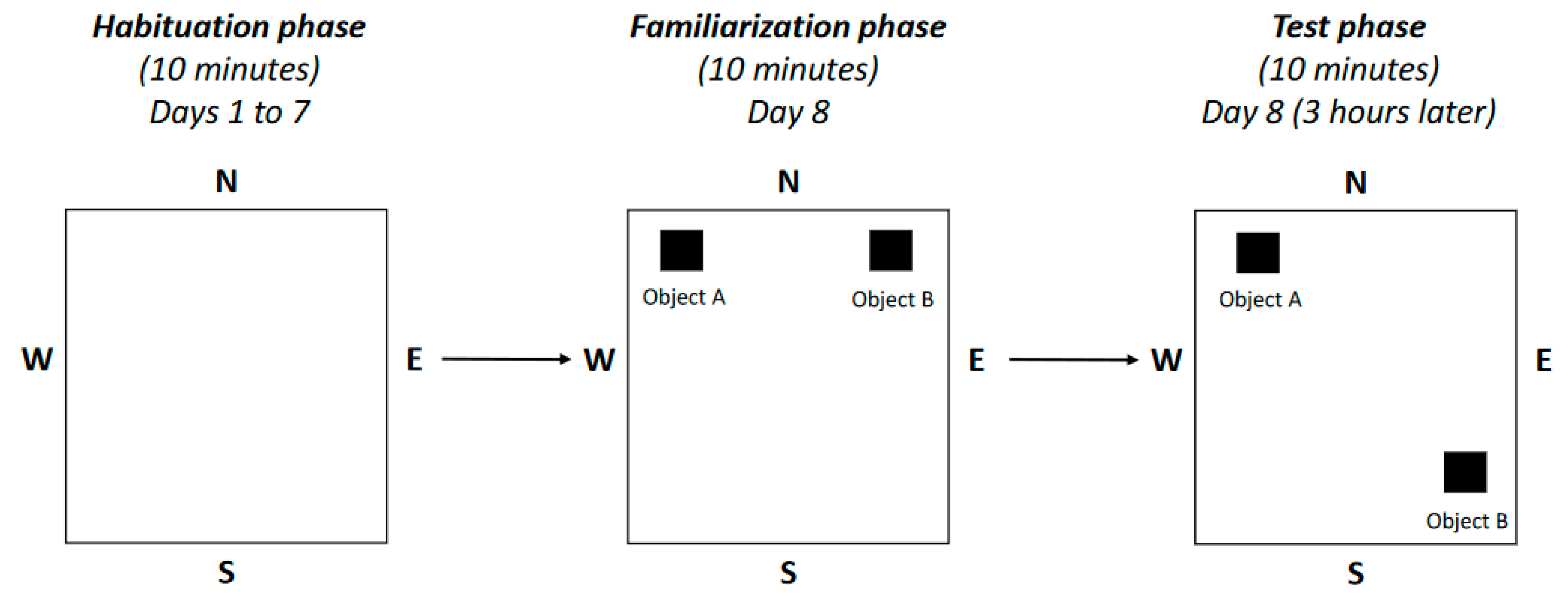
4.3. Neurobehavioral Tests
4.4. Serum and Urine Biochemistries
4.5. Immunohistochemistry
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Foreman, K.J.; Marquez, N.; Dolgert, A.; Fukutaki, K.; Fullman, N.; McGaughey, M.; Pletcher, M.A.; Smith, A.E.; Tang, K.; Yuan, C.W.; et al. Forecasting life expectancy, years of life lost, and all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 250 causes of death: Reference and alternative scenarios for 2016-40 for 195 countries and territories. Lancet 2018, 392, 2052–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, M.; Perera, G.; Ford, L.; Arrighi, H.M.; Foskett, N.; Debove, C.; Novak, G.; Gordon, M.F. Age-Stratified Prevalence of Mild Cognitive Impairment and Dementia in European Populations: A Systematic Review. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2015, 48, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebert, T.; Pawelzik, S.-C.; Witasp, A.; Arefin, S.; Hobson, S.; Kublickiene, K.; Shiels, P.G.; Bäck, M.; Stenvinkel, P. Inflammation and Premature Ageing in Chronic Kidney Disease. Toxins 2020, 12, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arafa, A.; Kawachi, H.; Matsumoto, C.; Teramoto, M.; Yasui, Y.; Kato, Y.; Matsuo, M.; Nakao, Y.M.; Kashima, R.; Kokubo, Y. The association between the estimated glomerular filtration rate and cognitive impairment: The Suita Study. Hypertens. Res. 2023; ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurella Tamura, M.; Xie, D.; Yaffe, K.; Cohen, D.L.; Teal, V.; Kasner, S.E.; Messé, S.R.; Sehgal, A.R.; Kusek, J.; DeSalvo, K.B.; et al. Vascular risk factors and cognitive impairment in chronic kidney disease: The Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort (CRIC) study. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 6, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viggiano, D.; Wagner, C.A.; Martino, G.; Nedergaard, M.; Zoccali, C.; Unwin, R.; Capasso, G. Mechanisms of cognitive dysfunction in CKD. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 452–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuro-o, M.; Matsumura, Y.; Aizawa, H.; Kawaguchi, H.; Suga, T.; Utsugi, T.; Ohyama, Y.; Kurabayashi, M.; Kaname, T.; Kume, E.; et al. Mutation of the mouse klotho gene leads to a syndrome resembling ageing. Nature 1997, 390, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.-S.; Sheng, M.-J.; Sun, Z.-Y.; Liang, Y.; Yu, L.-X.; Liu, Q.-F. Upstream and downstream regulators of Klotho expression in chronic kidney disease. Metabolism 2023, 142, 155530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.C.; Kuro-o, M.; Moe, O.W. Klotho and Chronic Kidney Disease. Contrib. Nephrol. 2013, 180, 47–63. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sanz, B.; Arrieta, H.; Rezola-Pardo, C.; Fernández-Atutxa, A.; Garin-Balerdi, J.; Arizaga, N.; Rodriguez-Larrad, A.; Irazusta, J. Low serum klotho concentration is associated with worse cognition, psychological components of frailty, dependence, and falls in nursing home residents. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuriyama, N.; Ozaki, E.; Mizuno, T.; Ihara, M.; Mizuno, S.; Koyama, T.; Matsui, D.; Watanabe, I.; Akazawa, K.; Takeda, K.; et al. Association between α-Klotho and Deep White Matter Lesions in the Brain: A Pilot Case Control Study Using Brain MRI. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018, 61, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, A. Relationships between serum Klotho concentrations and cognitive performance among older chronic kidney disease patients with albuminuria in NHANES 2011–2014. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1215977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diwan, V.; Mistry, A.; Gobe, G.; Brown, L. Adenine-induced chronic kidney and cardiovascular damage in rats. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2013, 68, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diwan, V.; Brown, L.; Gobe, G.C. Adenine-induced chronic kidney disease in rats. Nephrology 2018, 23, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hobson, P.; Kumwenda, M.; Shrikanth, S.; Nair, H.; Wong, S. Risk and incidence of cognitive impairment in patients with chronic kidney disease and diabetes: The results from a longitudinal study in a community cohort of patients and an age and gender-matched control cohort in North Wales, UK. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e053008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, A.M.; Thao, L.T.P.; Ryan, J.; Wolfe, R.; Wetmore, J.B.; Woods, R.L.; Polkinghorne, K.R. CKD Biomarkers, Cognitive Impairment, and Incident Dementia in an Older Healthy Cohort. Kidney360 2021, 3, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pépin, M.; Levassort, H.; Boucquemont, J.; Lambert, O.; Alencar de Pinho, N.; Turinici, M.; Helmer, C.; Metzger, M.; Cheddani, L.; Frimat, L.; et al. Cognitive performance is associated with glomerular filtration rate in patients with chronic kidney disease: Results from the CKD-REIN cohort. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2023, 94, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhagen, C.; Janssen, J.; Minderhoud, C.A.; van den Berg, E.; Wanner, C.; Passera, A.; Johansen, O.E.; Biessels, G.J. Chronic kidney disease and cognitive decline in patients with type 2 diabetes at elevated cardiovascular risk. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2022, 36, 108303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujisaki, K.; Tsuruya, K.; Yamato, M.; Toyonaga, J.; Noguchi, H.; Nakano, T.; Taniguchi, M.; Hirakata, H.; Kitazono, T. Cerebral oxidative stress induces spatial working memory dysfunction in uremic mice: Neuroprotective effect of tempol. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2014, 29, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.H.; Kim, S.-W.; Park, D.-K.; Song, H.-Y.; Kim, D.-S.; Gil, H.-W. Altered Emotional Phenotypes in Chronic Kidney Disease Following 5/6 Nephrectomy. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamidizad, Z.; Kadkhodaee, M.; Karimian, S.M.; Ranjbaran, M.; Heidari, F.; Bakhshi, E.; Kianian, F.; Zahedi, E.; Seifi, B. Therapeutic effects of CORM3 and NaHS in chronic kidney disease induced cognitive impairment via the interaction between carbon monoxide and hydrogen sulfide on Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway in rats. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2022, 368, 110217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, K.; Qiao, Z.-X.; Bao, X.-R. Chronic Kidney Disease Induces Cognitive Impairment in the Early Stage. Curr. Med. Sci. 2023, 43, 988–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundu, P.; Zimmerman, B.; Quinn, J.F.; Kaye, J.; Mattek, N.; Westaway, S.K.; Raber, J. Serum Levels of α-Klotho Are Correlated with Cerebrospinal Fluid Levels and Predict Measures of Cognitive Function. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2022, 86, 1471–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Yu, R.; Li, Q.; Chen, J.; Wang, W. Exploring the impact of cognitive impairments on treatment compliance and quality of life in patients with Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis (CAPD). Medicine 2023, 102, e35813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klotho, a longevity factor, improves cognitive function in aging nonhuman primates. Nat. Aging 2023, 3, 915–916. [CrossRef]
- Degaspari, S.; Tzanno-Martins, C.B.; Kazue Fujihara, C.; Zatz, R.; Branco-Martins, J.P.; Araujo Viel, T.; Buck, H.d.S.; Orellana, A.M.M.; Böhmer, A.E.; Lima, L.d.S.; et al. Altered KLOTHO and NF-κB-TNF-α Signaling are Correlated with Nephrectomy-Induced Cognitive Impairment in Rats. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Yu, Y.; Li, H.; Wei, Y.; Sun, M. Effect of dietary protein intake on cognitive function in the elderly with chronic kidney disease: Analysis of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2011–2014. Ren. Fail. 2023, 45, 2294147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz-Castañeda, J.R.; Herencia, C.; Pendón-Ruiz de Mier, M.V.; Rodriguez-Ortiz, M.E.; Diaz-Tocados, J.M.; Vergara, N.; Martínez-Moreno, J.M.; Salmerón, M.D.; Richards, W.G.; Felsenfeld, A.; et al. Differential regulation of renal Klotho and FGFR1 in normal and uremic rats. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 3858–3867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.-S.; Liu, C.-K.; Lee, H.-C.; Chou, M.-C.; Ke, L.-Y.; Chen, C.-H.; Chen, S.-L. Electronegative very-low-density lipoprotein induces brain inflammation and cognitive dysfunction in mice. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandeesha, H.; Keshri, N.; Rajappa, M.; Menon, V. Association of hyperglycaemia and hyperlipidaemia with cognitive dysfunction in schizophrenia spectrum disorder. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2023, 129, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, S.; Luo, W.; Lei, L.; Zhang, Q.; Xiu, J. Association between serum Klotho concentration and hyperlipidemia in adults: A cross-sectional study from NHANES 2007–2016. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1280873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.-H.; Park, S.; Choi, J.-S.; Cho, N.-J.; Moon, J.-S.; Gil, H.-W. Indoxyl sulfate induces apoptotic cell death by inhibiting glycolysis in human astrocytes. Kidney Res. Clin. Pract. 2023; ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.-Y.; Chang, S.-C.; Wu, M.-S. Suppression of Klotho expression by protein-bound uremic toxins is associated with increased DNA methyltransferase expression and DNA hypermethylation. Kidney. Int. 2012, 81, 640–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, J.A.; Izquierdo, M.C.; Sanchez-Niño, M.D.; Suárez-Alvarez, B.; Lopez-Larrea, C.; Jakubowski, A.; Blanco, J.; Ramirez, R.; Selgas, R.; Ruiz-Ortega, M.; et al. The inflammatory cytokines TWEAK and TNFα reduce renal klotho expression through NFκB. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 22, 1315–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Ortiz, M.E.; Díaz-Tocados, J.M.; Muñoz-Castañeda, J.R.; Herencia, C.; Pineda, C.; Martínez-Moreno, J.M.; Montes de Oca, A.; López-Baltanás, R.; Alcalá-Díaz, J.; Ortiz, A.; et al. Inflammation both increases and causes resistance to FGF23 in normal and uremic rats. Clin. Sci. 2020, 134, 15–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovarova, L.; Valerianova, A.; Kmentova, T.; Lachmanova, J.; Hladinova, Z.; Malik, J. Low Cerebral Oxygenation Is Associated with Cognitive Impairment in Chronic Hemodialysis Patients. Nephron 2018, 139, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polinder-Bos, H.A.; García, D.V.; Kuipers, J.; Elting, J.W.J.; Aries, M.J.H.; Krijnen, W.P.; Groen, H.; Willemsen, A.T.; van Laar, P.J.; Strijkert, F.; et al. Hemodialysis Induces an Acute Decline in Cerebral Blood Flow in Elderly Patients. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 29, 1317–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, C.; Wang, H.; Chu, Z.; Li, J.; Qian, T.; Mark Haacke, E.; Xia, S.; Shen, W. Reduced regional cerebral venous oxygen saturation is a risk factor for the cognitive impairment in hemodialysis patients: A quantitative susceptibility mapping study. Brain Imaging Behav. 2020, 14, 1339–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuki, H.; Mandai, S.; Shiwaku, H.; Koide, T.; Takahashi, N.; Yanagi, T.; Inaba, S.; Ida, S.; Fujiki, T.; Mori, Y.; et al. Chronic kidney disease causes blood-brain barrier breakdown via urea-activated matrix metalloproteinase-2 and insolubility of tau protein. Aging 2023, 15, 10972–10995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stringuetta-Belik, F.; Shiraishi, F.G.; Oliveira e Silva, V.R.; Barretti, P.; Caramori, J.C.T.; Bôas, P.J.F.V.; Martin, L.C.; Franco, R.J.d.S. Greater level of physical activity associated with better cognitive function in hemodialysis in end stage renal disease. J. Bras. Nefrol. 2012, 34, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gesualdo, G.D.; Duarte, J.G.; Zazzetta, M.S.; Kusumota, L.; Say, K.G.; Pavarini, S.C.I.; Orlandi, F. de S. Cognitive impairment of patients with chronic renal disease on hemodialysis and its relationship with sociodemographic and clinical characteristics. Dement. Neuropsychol. 2017, 11, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, R.; Xu, C.; Li, Y.; Yu, L.; Shao, X.; Xie, K.; Gu, J.; Yu, Z.; Yan, Y.; Guan, Y.; et al. The Incidence Prognosis and Risk Factors of Cognitive Impairment in Maintenance Haemodialysis Patients. Blood Purif. 2019, 47, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheets, K.M.; Davey, C.S.; St Peter, W.L.; Reule, S.A.; Murray, A.M. Cognitive impairment, perceived medication adherence, and high-risk medication use in patients with reduced kidney function: A cross-sectional analysis. Health Sci. Rep. 2022, 5, e697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voorend, C.G.N.; van Buren, M.; Berkhout-Byrne, N.C.; Kerckhoffs, A.P.M.; van Oevelen, M.; Gussekloo, J.; Richard, E.; Bos, W.J.W.; Mooijaart, S.P. Apathy Symptoms, Physical and Cognitive Function, Health-Related Quality of Life, and Mortality in Older Patients With CKD: A Longitudinal Observational Study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2024, 83, 162–172.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diwan, V.; Small, D.; Kauter, K.; Cobe, G.C.; Brown, L. Gender differences in adenine-induced chronic kidney disease and cardiovascular complications in rats. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 2014, 307, F1168–F1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Control (n = 5) | CKD (n = 5) | |
|---|---|---|
| Calcium/creatinine ratio | 0.025 ± 0.002 | 0.106 ± 0.030 * |
| Phosphorus/creatinine ratio | 0.22 ± 0.01 | 0.24 ± 0.03 |
| Magnesium/creatinine ratio | 0.018 ± 0.004 | 0.019 ± 0.005 |
| Sodium/creatinine ratio | 0.17 ± 0.04 | 0.24 ± 0.02 |
| Potassium/creatinine ratio | 0.53 ± 0.10 | 0.52 ± 0.06 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodríguez-Ortiz, M.E.; Jurado-Montoya, D.; Valdés-Díaz, K.; García-Sáez, R.M.; Torralbo, A.I.; Obrero, T.; Vidal-Jiménez, V.; Jiménez, M.J.; Carmona, A.; Guerrero, F.; et al. Cognitive Impairment Related to Chronic Kidney Disease Is Associated with a Decreased Abundance of Membrane-Bound Klotho in the Cerebral Cortex. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4194. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25084194
Rodríguez-Ortiz ME, Jurado-Montoya D, Valdés-Díaz K, García-Sáez RM, Torralbo AI, Obrero T, Vidal-Jiménez V, Jiménez MJ, Carmona A, Guerrero F, et al. Cognitive Impairment Related to Chronic Kidney Disease Is Associated with a Decreased Abundance of Membrane-Bound Klotho in the Cerebral Cortex. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(8):4194. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25084194
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodríguez-Ortiz, María E., Daniel Jurado-Montoya, Karen Valdés-Díaz, Raquel M. García-Sáez, Ana I. Torralbo, Teresa Obrero, Victoria Vidal-Jiménez, María J. Jiménez, Andrés Carmona, Fátima Guerrero, and et al. 2024. "Cognitive Impairment Related to Chronic Kidney Disease Is Associated with a Decreased Abundance of Membrane-Bound Klotho in the Cerebral Cortex" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 8: 4194. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25084194
APA StyleRodríguez-Ortiz, M. E., Jurado-Montoya, D., Valdés-Díaz, K., García-Sáez, R. M., Torralbo, A. I., Obrero, T., Vidal-Jiménez, V., Jiménez, M. J., Carmona, A., Guerrero, F., Pendón-Ruiz de Mier, M. V., Rodelo-Haad, C., Canalejo, A., Rodríguez, M., Soriano-Cabrera, S., & Muñoz-Castañeda, J. R. (2024). Cognitive Impairment Related to Chronic Kidney Disease Is Associated with a Decreased Abundance of Membrane-Bound Klotho in the Cerebral Cortex. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(8), 4194. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25084194






