EspP2 Regulates the Adhesion of Glaesserella parasuis via Rap1 Signaling Pathway
Abstract
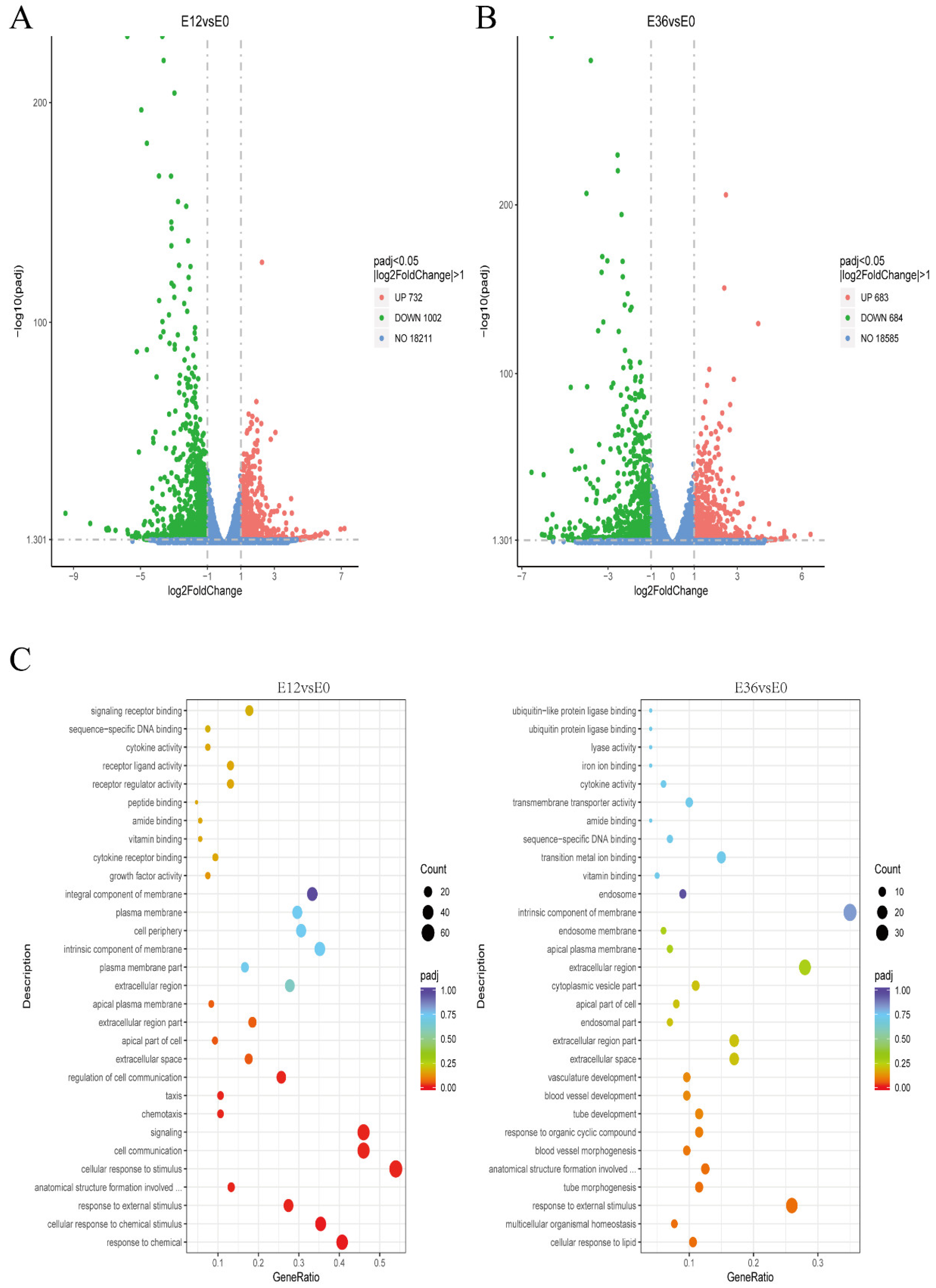
1. Introduction
2. Results
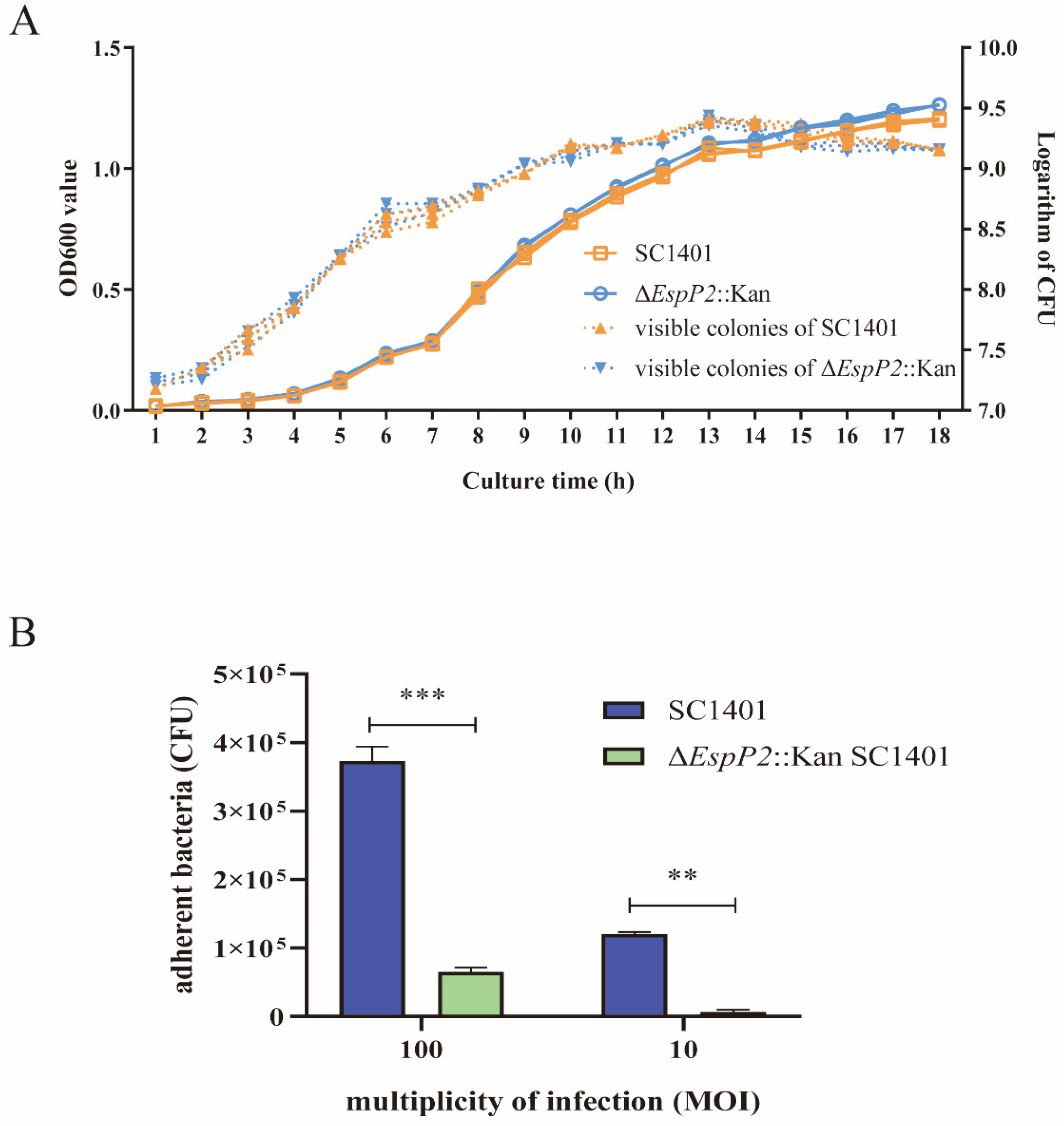
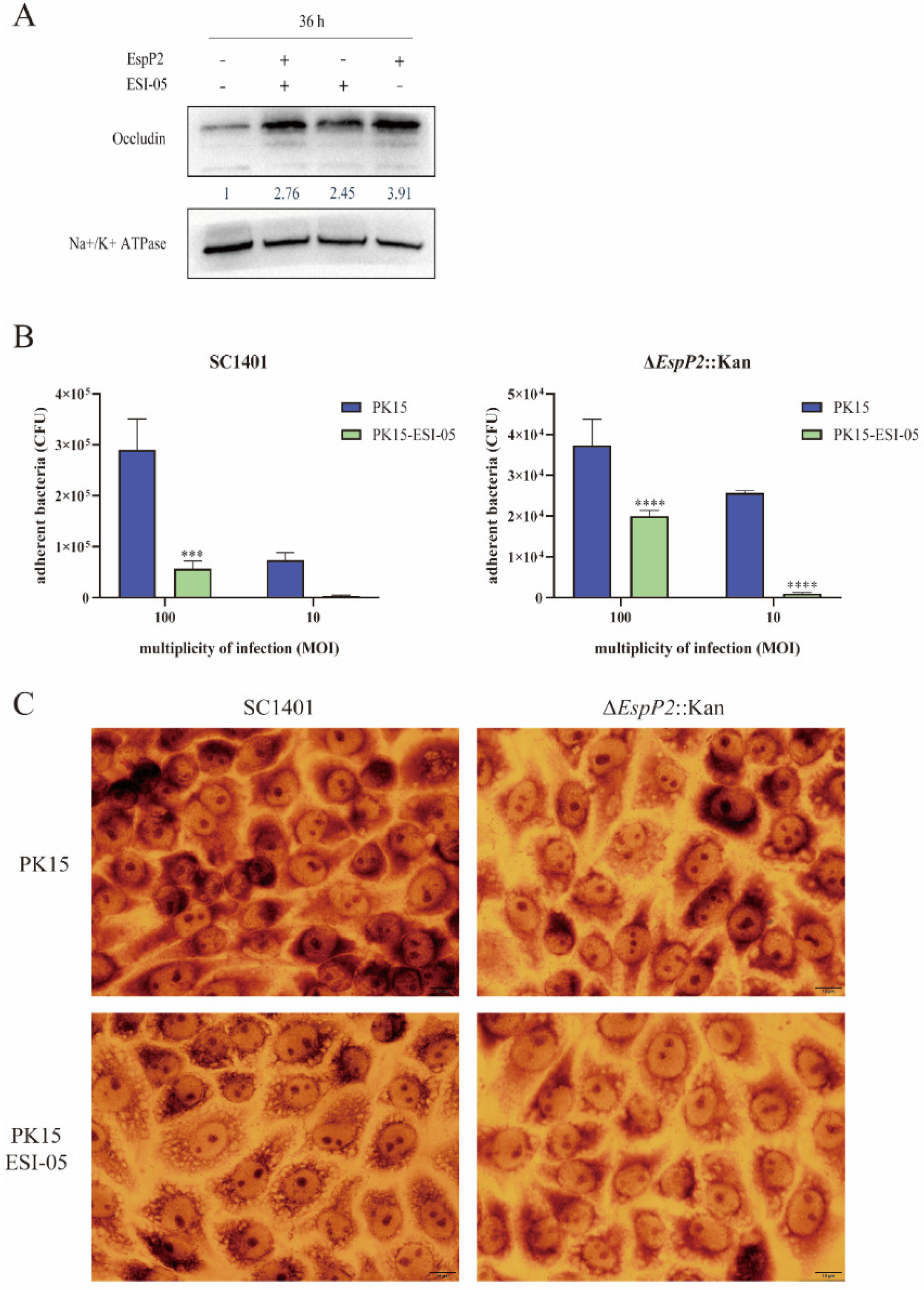
2.1. Deletion of EspP2 Decreases G. parasuis Adherence
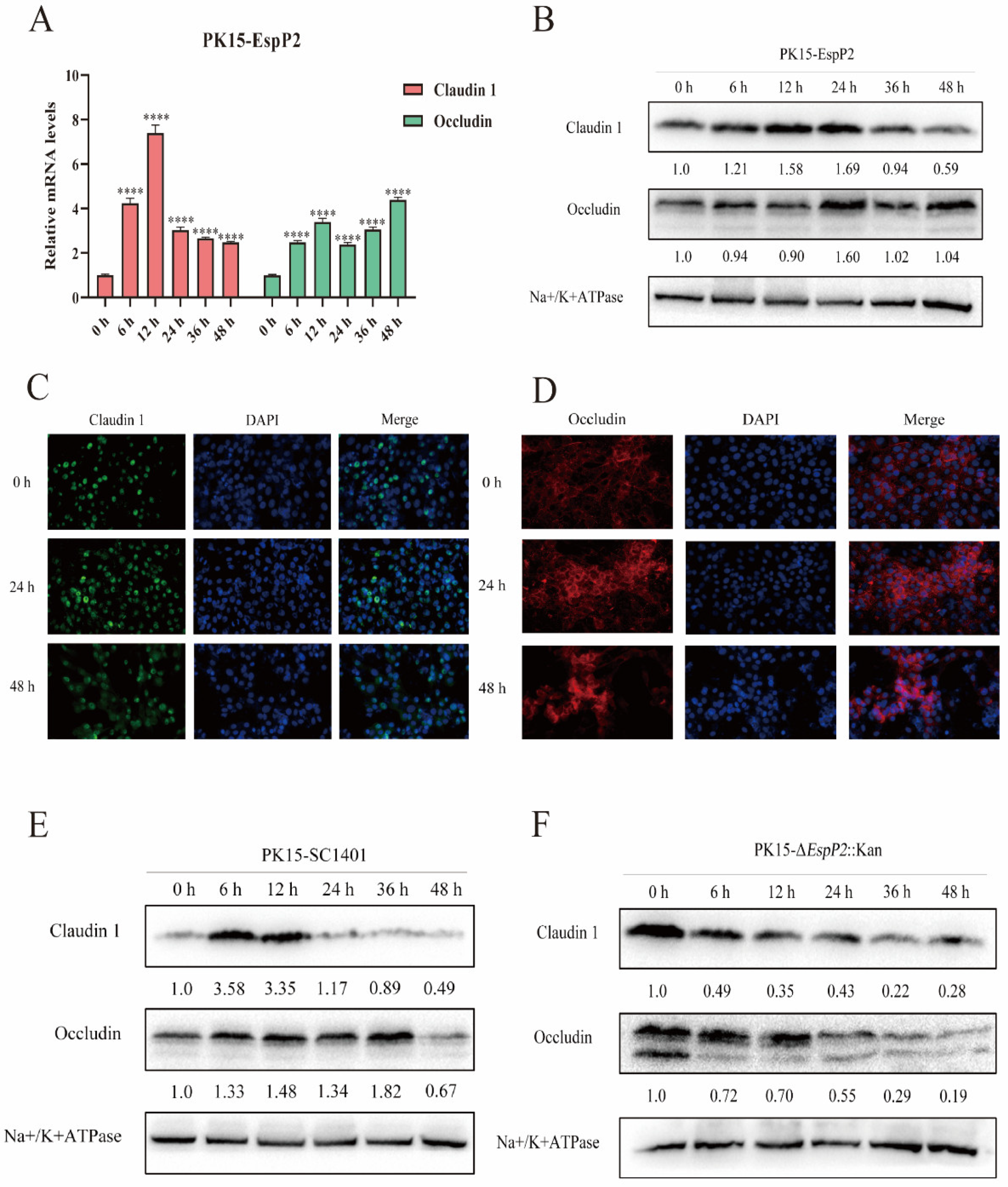
2.2. EspP2 Enhances Expression of Claudin-1 and Occludin
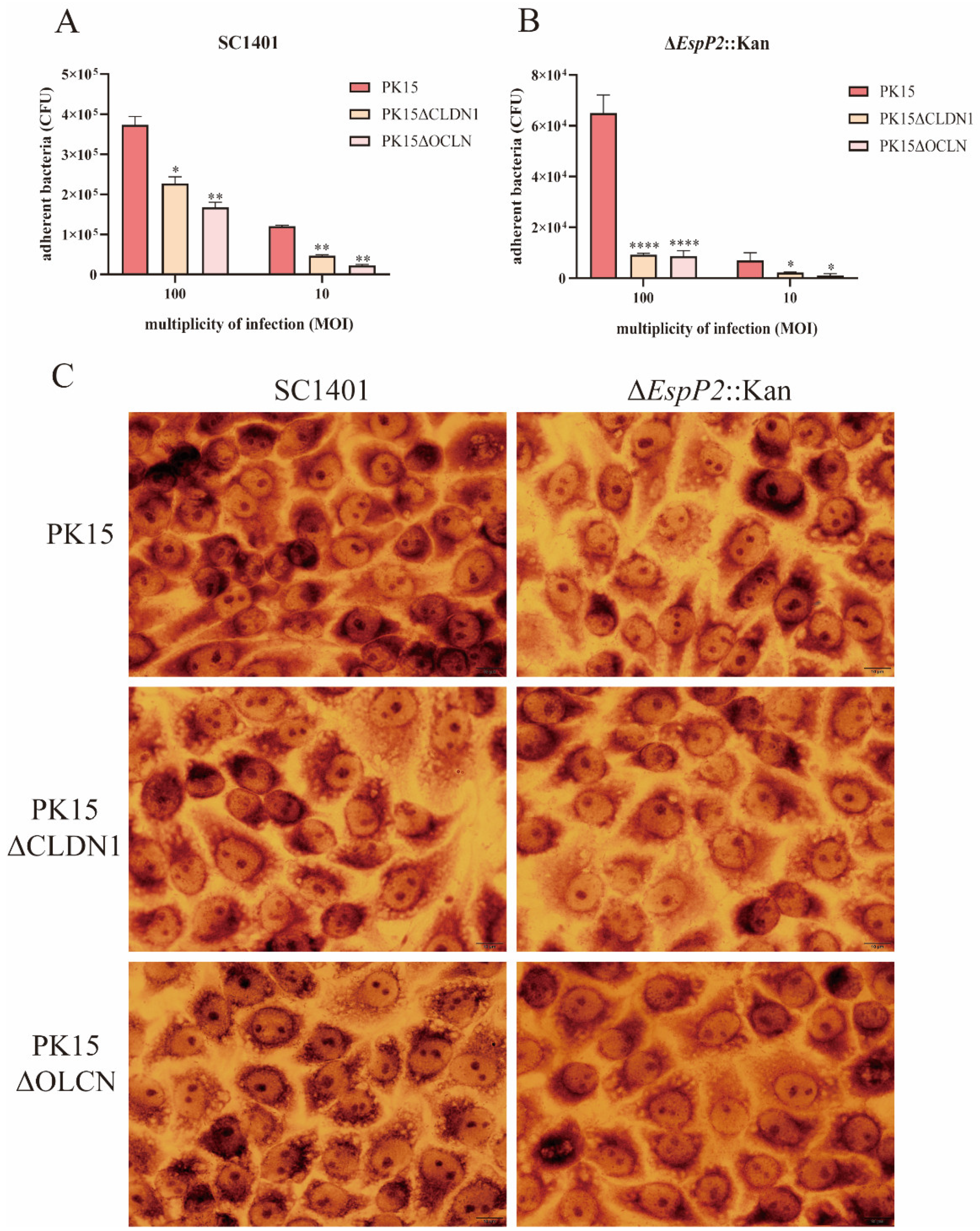
2.3. EspP2 Regulates Adhesion by Affecting Claudin1 and Occludin
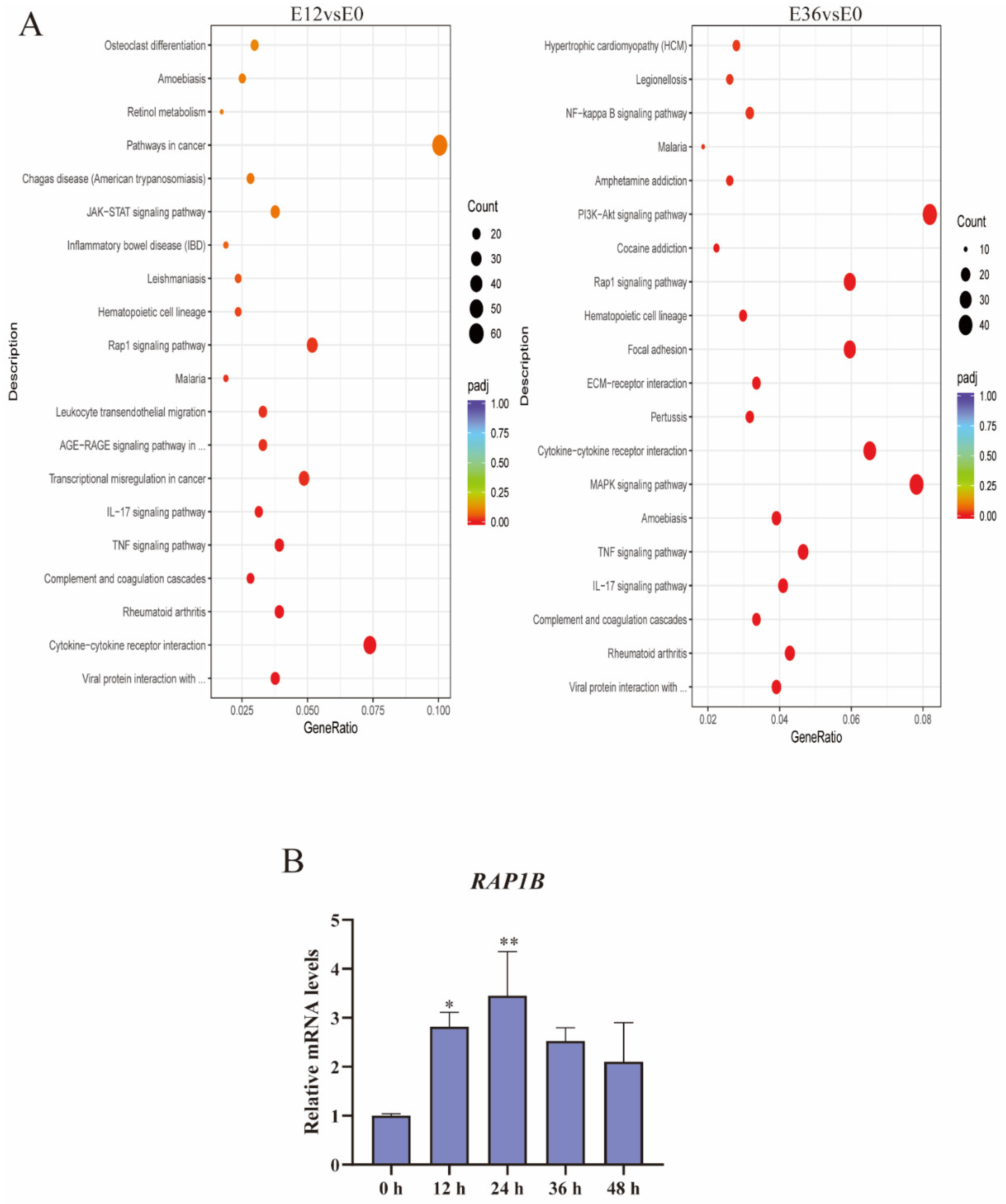
2.4. EspP2 Treatment Activates the Rap1 Signaling Pathway
2.5. Inhibition of the Rap1 Signaling Pathway Reduces Occludin Expression and Inhibits Adhesion
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Strains, Primers, Bacterial and Cell Culture Conditions
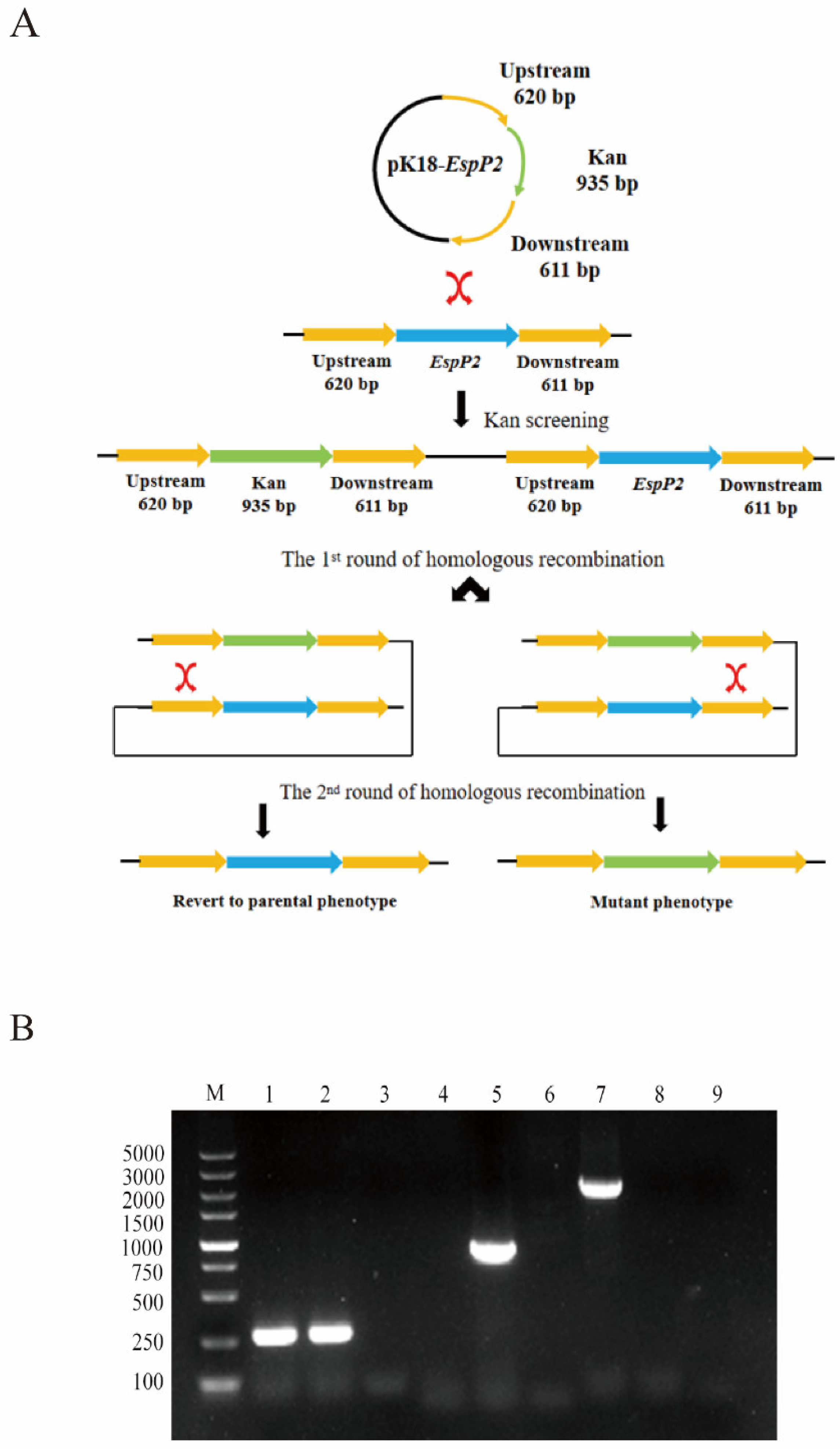
4.2. Construction of EspP2 Deficient Mutants
4.3. Expression of Recombinant EspP2
4.4. Adherence Assay
4.5. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.6. Western Blotting
4.7. Indirect Immunofluorescence
4.8. Giemsa Staining
4.9. Transcriptome Sequencing and Data Analysis
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gong, H.; Chen, L.; He, Y.; Hua, K.; Ma, B.; Gao, Y.; Xu, X.; Hu, X.; Jin, H. Pleural thickening induced by Glaesserella parasuis infection was linked to increased collagen and elastin. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 952377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Chang, X.; Zhou, H.; Lin, H.; Fan, H. Glaesserella parasuis induces inflammatory response in 3D4/21 cells through activation of NLRP3 inflammasome signaling pathway via ROS. Vet. Microbiol. 2021, 256, 109057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Xue, Q.; Zeng, Q.; Zhao, Z. Haemophilus parasuis vaccines. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2016, 180, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Yang, X.; Wang, A.; Huang, C.; Tang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Fang, Q.; Yu, Z.; Liu, X.; Huang, Q.; et al. Pigs Overexpressing Porcine β-Defensin 2 Display Increased Resilience to Glaesserella parasuis Infection. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanier, G.; Szczotka, A.; Friedl, P.; Lacouture, S.; Jacques, M.; Gottschalk, M. Haemophilus parasuis invades porcine brain microvascular endothelial cells. Microbiology 2006, 152 Pt 1, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y.; Hao, C.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Li, G.; Liu, S.; Hua, X. Inhibition of Haemophilus parasuis by berberine and proteomic studies of its mechanism of action. Res. Vet. Sci. 2021, 138, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Xu, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, S.; Feng, S.; He, Y.; Liao, M. Enhanced adherence to and invasion of PUVEC and PK-15 cells due to the overexpression of RfaD, ThyA and Mip in the ΔompP2 mutant of Haemophilus parasuis SC096 strain. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 162, 713–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallen, M.J.; Chaudhuri, R.R.; Henderson, I.R. Genomic analysis of secretion systems. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2003, 6, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desvaux, M.; Parham, N.J.; Henderson, I.R. The autotransporter secretion system. Res. Microbiol. 2004, 155, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigas, A.; Garrido, M.E.; de Rozas, A.M.P.; Badiola, I.; Barbé, J.; Llagostera, M. Development of a genetic manipulation system for Haemophilus parasuis. Vet. Microbiol. 2005, 105, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, Y.T.; Kostakioti, M.; Henderson, I.R.; Stathopoulos, C. Common themes and variations in serine protease autotransporters. Trends Microbiol. 2008, 16, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y. Characterization of porcine AIDA-I adhesin and its receptors. Neuroence Res. Suppl. 2007, 19, 478–491. [Google Scholar]
- Eitel, J.; Dersch, P. The YadA protein of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis mediates high-efficiency uptake into human cells under environmental conditions in which invasin is repressed. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 4880–4891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, H.; Lim, J.Y.; Knecht, H.J.; Li, J.; Hovde, C.J. Role of Escherichia coli O157:H7 virulence factors in colonization at the bovine terminal rectal mucosa. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 4685–4693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, J.Y.; La, H.J.; Sheng, H.; Forney, L.J.; Hovde, C.J. Influence of plasmid pO157 on Escherichia coli O157:H7 Sakai biofilm formation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 963–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otani, T.; Furuse, M. Tight Junction Structure and Function Revisited. Trends Cell Biol. 2020, 30, 805–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aijaz, S.; Balda, M.S.; Matter, K. Tight junctions: Molecular architecture and function. Int. Rev. Cytol. 2006, 248, 261–298. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Guo, L.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Y.; Gu, W.; Feng, L.; Wang, Y. Tight Junction Protein Occludin Is a Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Entry Factor. J. Virol. 2017, 91, 10-1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nehme, Z.; Roehlen, N.; Dhawan, P.; Baumert, T.F. Tight Junction Protein Signaling and Cancer Biology. Cells 2023, 12, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ploss, A.; Evans, M.J.; Gaysinskaya, V.A.; Panis, M.; You, H.; de Jong, Y.P.; Rice, C.M. Human occludin is a hepatitis C virus entry factor required for infection of mouse cells. Nature 2009, 457, 882–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilbi, H.; Kortholt, A. Role of the small GTPase Rap1 in signal transduction, cell dynamics and bacterial infection. Small GTPases 2019, 10, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, S.; Guo, J.; Li, R.; Qiu, Y.; Ye, C.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Guo, L.; Hou, Y.; Hu, C.-A.A. Transcriptional Profiling of Host Cell Responses to Virulent Haemophilus parasuis: New Insights into Pathogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Gao, X.; Hardwidge, P.R. Heat-labile enterotoxin-induced activation of NF-κB and MAPK pathways in intestinal epithelial cells impacts enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) adherence. Cell Microbiol. 2012, 14, 1231–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, C.T.; Le, N.-T.; Tran, T.D.-H.; Kim, E.-H.; Park, S.-S.; Luong, T.T.; Chung, K.-T.; Pyo, S.; Rhee, D.-K. Streptococcus pneumoniae ClpL modulates adherence to A549 human lung cells through Rap1/Rac1 activation. Infect. Immun. 2014, 82, 3802–3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Howell, K.J.; Peters, S.E.; Wang, J.; Hernandez-Garcia, J.; Weinert, L.A.; Luan, S.-L.; Chaudhuri, R.R.; Angen, Ø.; Aragon, V.; Williamson, S.M.; et al. Development of a Multiplex PCR Assay for Rapid Molecular Serotyping of Haemophilus parasuis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 3812–3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Gu, J.; Xiao, K.; Zhu, W.; Lin, Y.; Wen, S.; He, Q.; Xu, X.; Cai, X. Glaesserella parasuis autotransporters EspP1 and EspP2 are novel IgA-specific proteases. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1041774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.-Z.; Chu, Y.-F.; Gao, P.-C.; Zhao, P.; He, Y.; Lu, Z.-X. Immunological identification and characterization of extracellular serine protease-like protein encoded in a putative espP2 gene of Haemophilus parasuis. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2012, 74, 983–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Rose, E.C.; Odle, J.; Blikslager, A.T.; Ziegler, A.L. Probiotics, Prebiotics and Epithelial Tight Junctions: A Promising Approach to Modulate Intestinal Barrier Function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, J.D.; Witt, K.A.; Hom, S.; Egleton, R.D.; Mark, K.S.; Davis, T.P. Inflammatory pain alters blood-brain barrier permeability and tight junctional protein expression. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2001, 280, H1241–H1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradis, T.; Bègue, H.; Basmaciyan, L.; Dalle, F.; Bon, F. Tight Junctions as a Key for Pathogens Invasion in Intestinal Epithelial Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, Y.; Morita, K.; Mizoguchi, A.; Ide, C.; Miyachi, Y. Altered expression of occludin and tight junction formation in psoriasis. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2001, 293, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyauchi, E.; Morita, H.; Tanabe, S. Lactobacillus rhamnosus alleviates intestinal barrier dysfunction in part by increasing expression of zonula occludens-1 and myosin light-chain kinase in vivo. J. Dairy Sci. 2009, 92, 2400–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ukena, S.N.; Singh, A.; Dringenberg, U.; Engelhardt, R.; Seidler, U.; Hansen, W.; Bleich, A.; Bruder, D.; Franzke, A.; Rogler, G.; et al. Probiotic Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 inhibits leaky gut by enhancing mucosal integrity. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roe, K.; Kumar, M.; Lum, S.; Orillo, B.; Nerurkar, V.R.; Verma, S. West Nile virus-induced disruption of the blood-brain barrier in mice is characterized by the degradation of the junctional complex proteins and increase in multiple matrix metalloproteinases. J. Gen. Virol. 2012, 93 Pt 6, 1193–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulnour-Nakhoul, S.M.; Al-Tawil, Y.; Gyftopoulos, A.A.; Brown, K.L.; Hansen, M.; Butcher, K.F.; Eidelwein, A.P.; Noel, R.A.; Rabon, E.; Posta, A.; et al. Alterations in junctional proteins, inflammatory mediators and extracellular matrix molecules in eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin. Immunol. 2013, 148, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lechner, J.; Krall, M.; Netzer, A.; Radmayr, C.; Ryan, M.P.; Pfaller, W. Effects of interferon alpha-2b on barrier function and junctional complexes of renal proximal tubular LLC-PK1 cells. Kidney Int. 1999, 55, 2178–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ulanova, M.; Gravelle, S.; Barnes, R. The role of epithelial integrin receptors in recognition of pulmonary pathogens. J. Innate Immun. 2009, 1, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, R.J.; Koval, M. Above the Matrix: Functional Roles for Apically Localized Integrins. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 699407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kooistra, M.R.H.; Dubé, N.; Bos, J.L. Rap1: A key regulator in cell-cell junction formation. J. Cell Sci. 2007, 120 Pt 1, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonello, T.T.; Perez-Vale, K.Z.; Sumigray, K.D.; Peifer, M. Rap1 acts via multiple mechanisms to position Canoe and adherens junctions and mediate apical-basal polarity establishment. Development 2018, 145, dev157941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannekoek, W.-J.; Post, A.; Bos, J.L. Rap1 signaling in endothelial barrier control. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2014, 8, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartsock, A.; Nelson, W.J. Adherens and tight junctions: Structure, function and connections to the actin cytoskeleton. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1778, 660–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spindler, V.; Schlegel, N.; Waschke, J. Role of GTPases in control of microvascular permeability. Cardiovasc. Res. 2010, 87, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terry, S.; Nie, M.; Matter, K.; Balda, M.S. Rho signaling and tight junction functions. Physiology 2010, 25, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Wang, K.; Yang, Z.; Tang, X.; Chang, Y.-F.; Dai, K.; Tang, X.; Hu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, S.; et al. Identification of a Novel Linear B-Cell Epitope of HbpA Protein from Glaesserella parasuis Using Monoclonal Antibody. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, K.; Yang, Z.; Ma, X.; Chang, Y.-F.; Cao, S.; Zhao, Q.; Huang, X.; Wu, R.; Huang, Y.; Xia, J.; et al. Deletion of Polyamine Transport Protein PotD Exacerbates Virulence in Glaesserella (Haemophilus) parasuis in the Form of Non-biofilm-generated Bacteria in a Murine Acute Infection Model. Virulence 2021, 12, 520–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Dai, K.; Gu, C.; Yu, Z.; He, M.; Xiao, W.; Zhao, M.; He, L. Deletion of two-component system QseBC weakened virulence of Glaesserella parasuis in a murine acute infection model and adhesion to host cells. PeerJ 2022, 10, e13648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Yang, Z.; Dai, K.; Liu, G.; Chang, Y.-F.; Tang, X.; Wang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, B.; Cao, S.; et al. The molecular diversity of transcriptional factor TfoX is a determinant in natural transformation in Glaesserella parasuis. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 948633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Tang, X.; Wang, K.; Dai, K.; Chang, Y.-F.; Du, S.; Zhao, Q.; Huang, X.; Wu, R.; Yan, Q.; et al. Metal Ion Periplasmic-Binding Protein YfeA of Glaesserella parasuis Induces the Secretion of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines of Macrophages via MAPK and NF-κB Signaling through TLR2 and TLR4. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Du, S.; Zhao, Q.; Huang, X.; Wu, R.; Yan, Q.; Han, X.; Cao, S.; Chang, Y.-F.; et al. Upregulation of occludin by cytolethal distending toxin facilitates Glaesserella parasuis adhesion to respiratory tract cells. Infect. Immun. 2023, 91, e0035123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stano, F.; Brindicci, G.; Monno, R.; Rizzo, C.; Ghezzani, F.; Carbonara, S.; Guaglianone, E.; Donelli, G.; Monno, L. Aeromonas sobria sepsis complicated by rhabdomyolysis in an HIV-positive patient: Case report and evaluation of traits associated with bacterial virulence. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 13, e113–e118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dallagassa, C.B.; Surek, M.; Vizzotto, B.S.; Prediger, K.C.; Moriel, B.; Wolf, S.; Weiss, V.; Cruz, L.M.; Assis, F.E.A.; Paludo, K.S.; et al. Characteristics of an Aeromonas trota strain isolated from cerebrospinal fluid. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 116, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anders, S.; Huber, W. Differential expression analysis for sequence count data. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, M.D.; Wakefield, M.J.; Smyth, G.K.; Oshlack, A. Gene ontology analysis for RNA-seq: Accounting for selection bias. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Araki, M.; Goto, S.; Hattori, M.; Hirakawa, M.; Itoh, M.; Katayama, T.; Kawashima, S.; Okuda, S.; Tokimatsu, T.; et al. KEGG for linking genomes to life and the environment. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, D480–D484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, X.; Xu, S.; Yang, Z.; Wang, K.; Dai, K.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, B.; Wang, Y.; Cao, S.; Huang, X.; et al. EspP2 Regulates the Adhesion of Glaesserella parasuis via Rap1 Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4570. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25084570
Tang X, Xu S, Yang Z, Wang K, Dai K, Zhang Y, Hu B, Wang Y, Cao S, Huang X, et al. EspP2 Regulates the Adhesion of Glaesserella parasuis via Rap1 Signaling Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(8):4570. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25084570
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Xinwei, Shiyu Xu, Zhen Yang, Kang Wang, Ke Dai, Yiwen Zhang, Bangdi Hu, Yu Wang, Sanjie Cao, Xiaobo Huang, and et al. 2024. "EspP2 Regulates the Adhesion of Glaesserella parasuis via Rap1 Signaling Pathway" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 8: 4570. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25084570
APA StyleTang, X., Xu, S., Yang, Z., Wang, K., Dai, K., Zhang, Y., Hu, B., Wang, Y., Cao, S., Huang, X., Yan, Q., Wu, R., Zhao, Q., Du, S., Wen, X., & Wen, Y. (2024). EspP2 Regulates the Adhesion of Glaesserella parasuis via Rap1 Signaling Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(8), 4570. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25084570





