An Innovative Probiotic-Based Supplement to Mitigate Molecular Factors Connected to Depression and Anxiety: An In Vitro Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
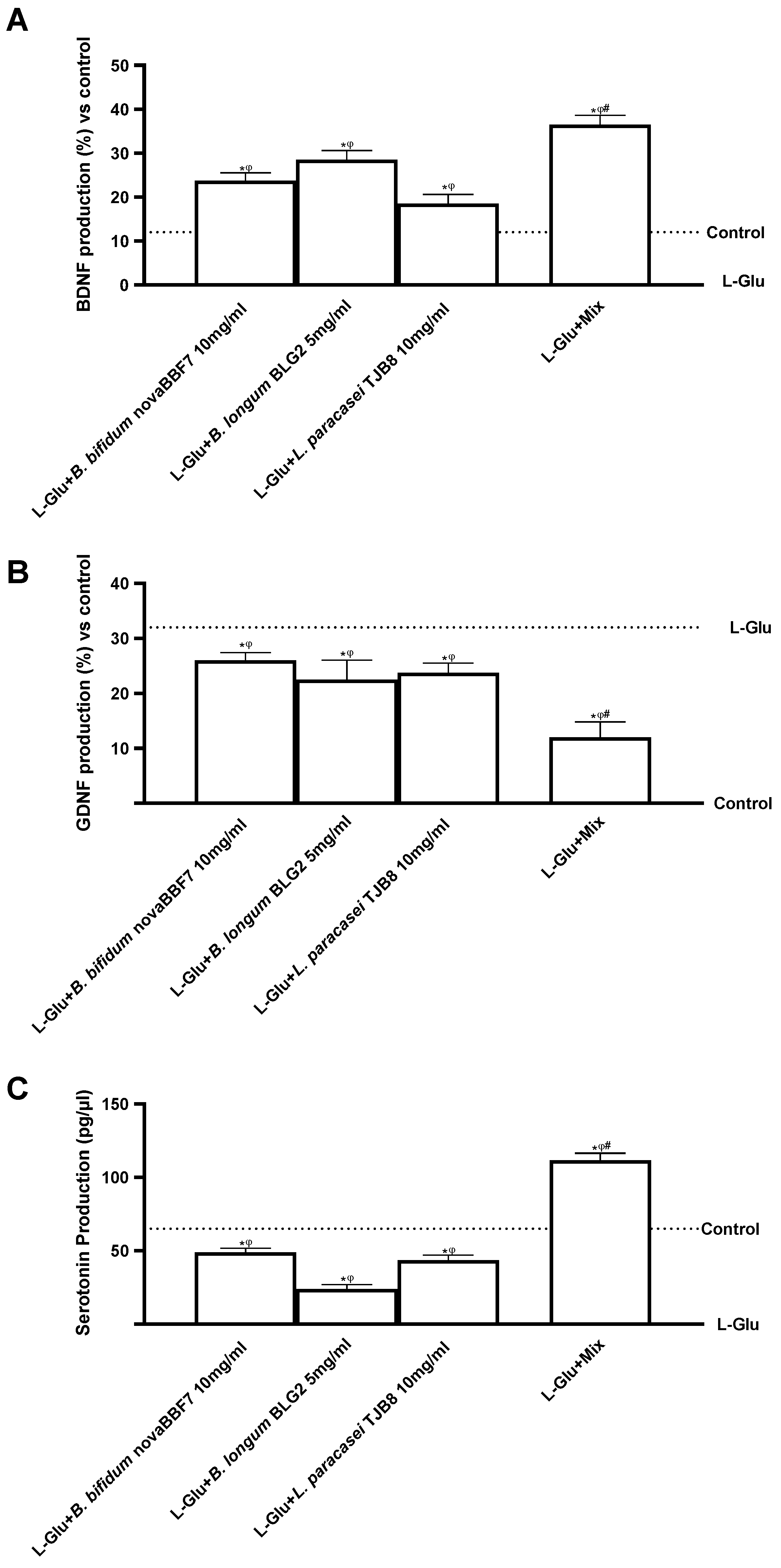
2. Results
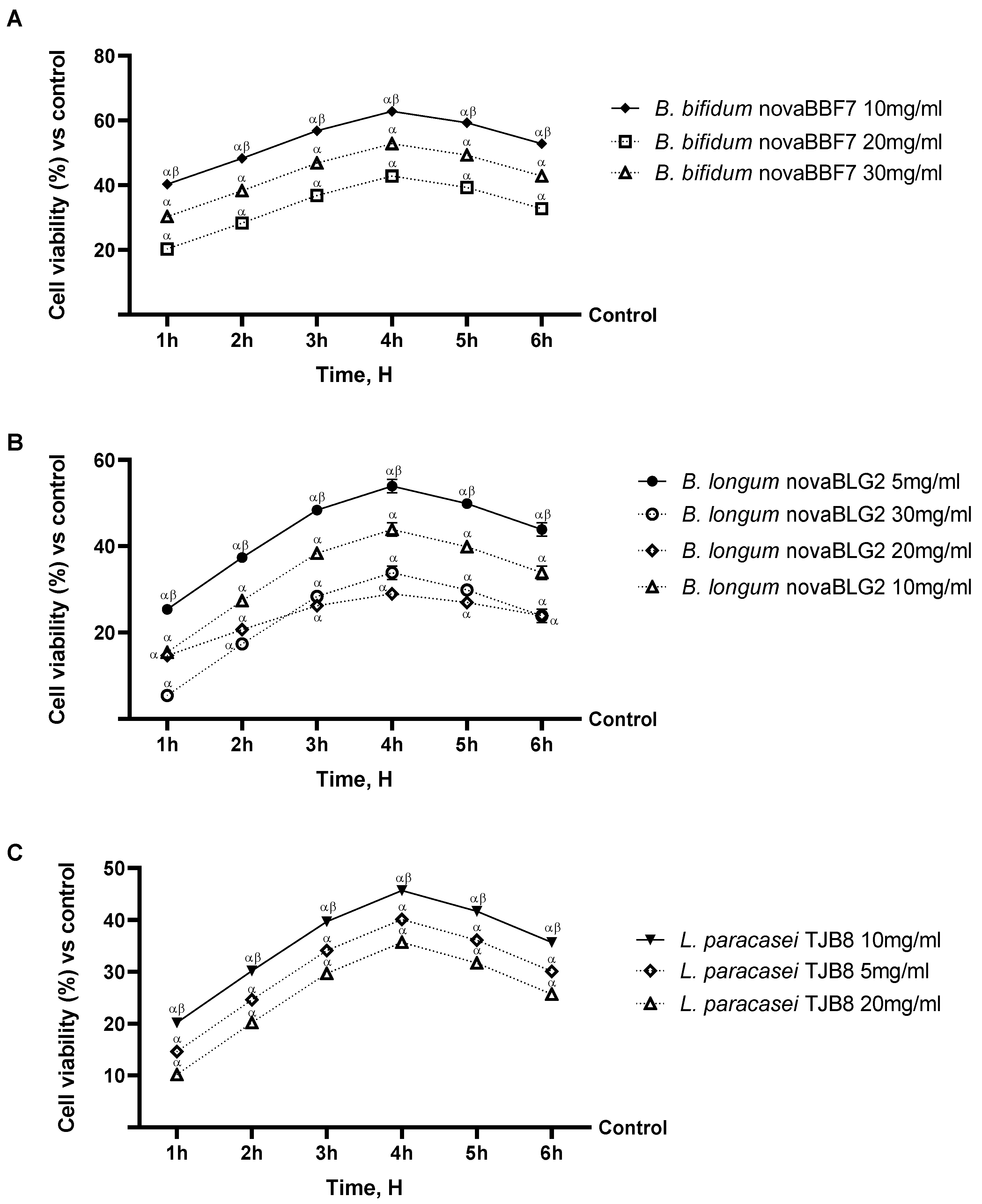
2.1. Probiotic Strain Screening in a Dose–Response Study on CaCo-2
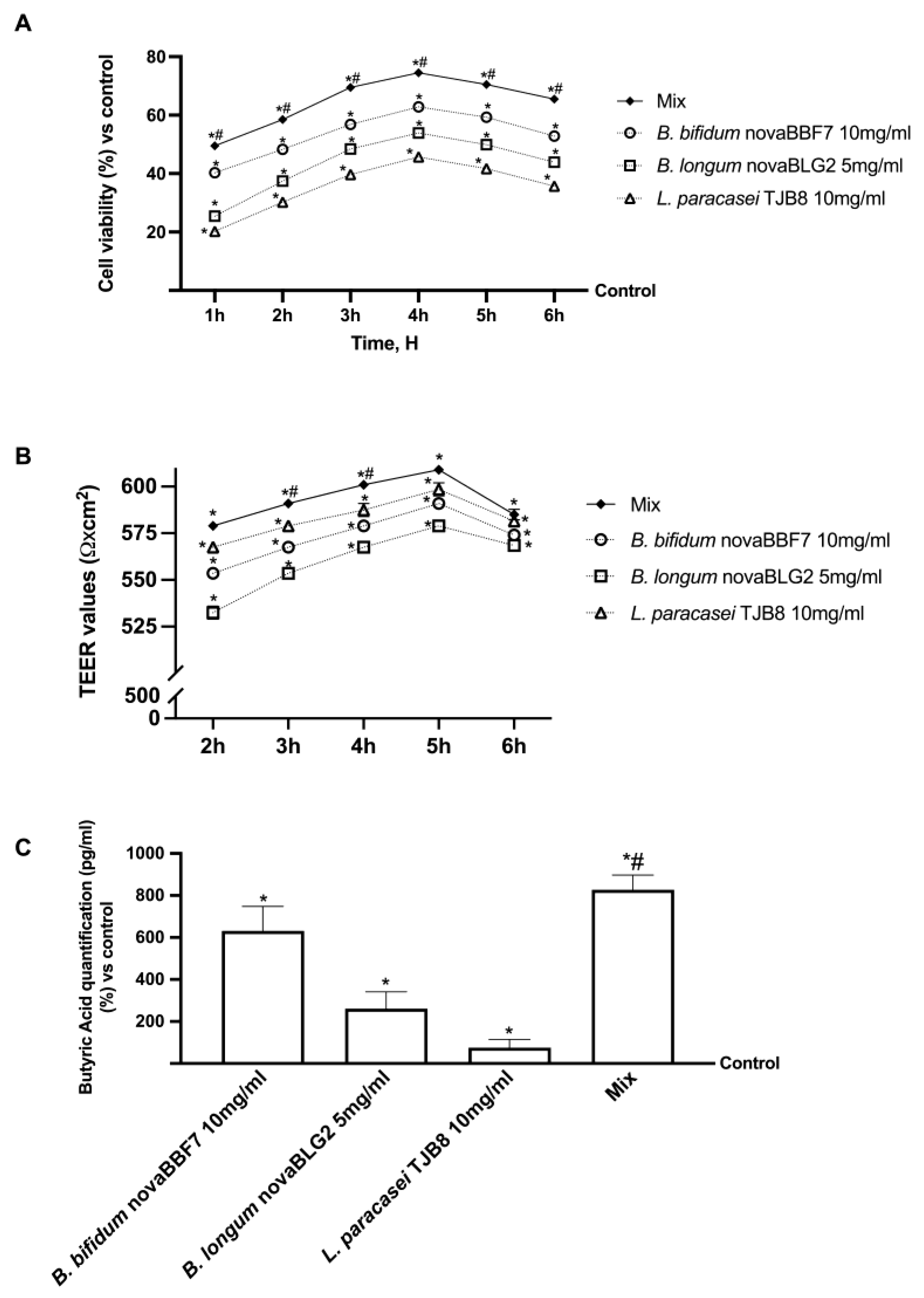
2.2. Effects of Selected Probiotic Strain on Intestinal In Vitro Model
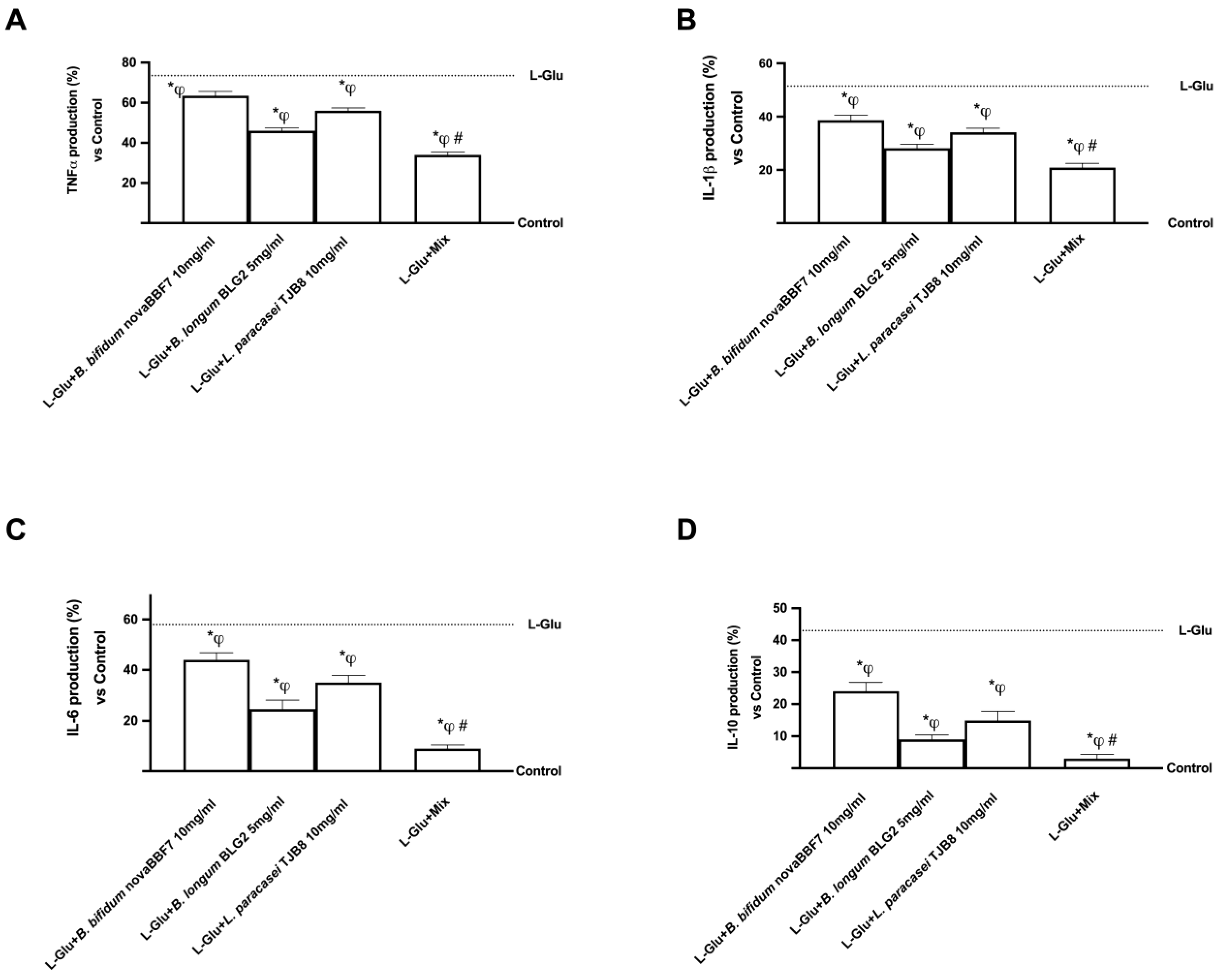
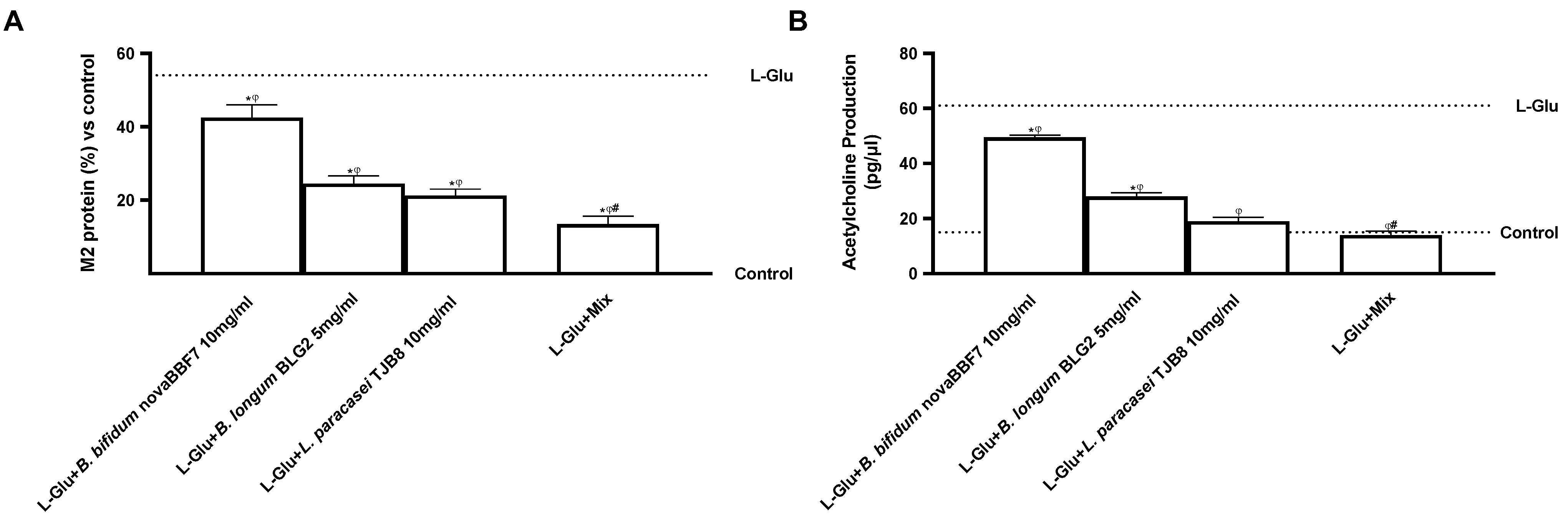
2.3. Biological Effects of Probiotic Metabolites on SHSY-5Y in the Condition of Mood Disorders
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Substances Preparation
4.2. Cell Cultures
4.3. Experimental Protocol
4.4. Gut–Brain Axis
4.5. Cell Viability Test
4.6. Intestinal Integrity Analysis
4.7. Butyric Acid Quantification
4.8. Oxygen Consumption and Mitochondrial Membrane Potential
4.9. Lipid Peroxydation Assay Kit
4.10. BAX ELISA Assay
4.11. Cytochrome C Assay Kit
4.12. TNFα Assay Kit
4.13. IL-1β Assay Kit
4.14. Human IL-6 (Interleukin-6) ELISA Kit
4.15. Interleukin-10 ELISA Kit
4.16. Human Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptor M2/CHRM2 ELISA Kit
4.17. Choline/Ach Quantification Kit
4.18. BDNF ELISA Kit
4.19. GDNF ELISA Kit
4.20. Human HTR1A (5-Hydroxytryptamine Receptor 1A) ELISA Kit
4.21. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 5HT | Serotonin |
| Adv DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium Advance |
| Adv DMEM-F12 | Advanced Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium/Nutrient F-12 Ham |
| AIWG | Antipsychotic-induced weight gain |
| BDNF | Brain-derived neurotrophic factor |
| CFU | Colony-forming unit |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| Cyto-C | Cytochrome C |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium |
| EMA | European Medicines Agency |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| GI | Gastrointestinal tract |
| GMB | Gut microbiota |
| HRP | Horseradish peroxidase |
| HTR1A | 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 1A |
| IBS | Irritable bowel syndrome |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1β |
| IL-10 | Interleukin-10 |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| L-Glu | L-Glutamic acid |
| M2 | Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptor |
| MTT | 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide |
| PS128 | L. plantarum PS128 |
| SCFAs | Short-chain fatty acids |
| SCZ | Schizophrenia |
| TEER | Transepithelial electrical resistance |
| TMB | 3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine |
| TNFα | Tumor Necrosis Factor α |
References
- Accettulli, A.; Corbo, M.R.; Sinigaglia, M.; Speranza, B.; Campaniello, D.; Racioppo, A.; Altieri, C.; Bevilacqua, A. Psycho-Microbiology, a New Frontier for Probiotics: An Exploratory Overview. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petra, A.I.; Panagiotidou, S.; Hatziagelaki, E.; Stewart, J.M.; Conti, P.; Theoharides, T.C. Gut-Microbiota-Brain Axis and Its Effect on Neuropsychiatric Disorders with Suspected Immune Dysregulation. Clin. Ther. 2015, 37, 984–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cryan, J.F.; O’Riordan, K.J.; Cowan, C.S.M.; Sandhu, K.V.; Bastiaanssen, T.F.S.; Boehme, M.; Codagnone, M.G.; Cussotto, S.; Fulling, C.; Golubeva, A.V.; et al. The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 1877–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rea, K.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. The microbiome: A key regulator of stress and neuroinflammation. Neurobiol. Stress. 2016, 4, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Q.; Xing, C.; Long, W.; Wang, H.Y.; Liu, Q.; Wang, R.F. Impact of microbiota on central nervous system and neurological diseases: The gut-brain axis. J. Neuroinflammation 2019, 16, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erny, D.; Hrabě de Angelis, A.L.; Jaitin, D.; Wieghofer, P.; Staszewski, O.; David, E.; Keren-Shaul, H.; Mahlakoiv, T.; Jakobshagen, K.; Buch, T.; et al. Host microbiota constantly control maturation and function of microglia in the CNS. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 965–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.C.W.; Gorbovskaya, I.; Hahn, M.K.; Müller, D.J. The Gut Microbiome in Schizophrenia and the Potential Benefits of Prebiotic and Probiotic Treatment. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Xu, J.; Li, Z.; Huang, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, M.; Hu, S.; Liang, Y. Analysis of gut microbiota diversity and auxiliary diagnosis as a biomarker in patients with schizophrenia: A cross-sectional study. Schizophr. Res. 2018, 197, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Pan, L.Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Jiang, H.Y.; Ruan, B. Analysis of gut mycobiota in first-episode, drug-naïve Chinese patients with schizophrenia: A pilot study. Behav. Brain Res. 2020, 379, 112374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machiels, K.; Joossens, M.; Sabino, J.; De Preter, V.; Arijs, I.; Eeckhaut, V.; Ballet, V.; Claes, K.; Van Immerseel, F.; Verbeke, K.; et al. A decrease of the butyrate-producing species Roseburia hominis and Faecalibacterium prausnitzii defines dysbiosis in patients with ulcerative colitis. Gut 2014, 63, 1275–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, E.; Ross, R.P.; O’Toole, P.W.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Stanton, C. γ-Aminobutyric acid production by culturable bacteria from the human intestine. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 113, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, C.J.K.; Milev, R. The effects of probiotics on depressive symptoms in humans: A systematic review. Ann. Gen. Psychiatry 2017, 16, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishida, K.; Sawada, D.; Kuwano, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Rokutan, K. Health Benefits of Lactobacillus gasseri CP2305 Tablets in Young Adults Exposed to Chronic Stress: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messaoudi, M.; Lalonde, R.; Violle, N.; Javelot, H.; Desor, D.; Nejdi, A.; Bisson, J.F.; Rougeot, C.; Pichelin, M.; Cazaubiel, M.; et al. Assessment of psychotropic-like properties of a probiotic formulation (Lactobacillus helveticus R0052 and Bifidobacterium longum R0175) in rats and human subjects. Br. J. Nutr. 2011, 105, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knuesel, T.; Mohajeri, M.H. The Role of the Gut Microbiota in the Development and Progression of Major Depressive and Bipolar Disorder. Nutrients 2021, 14, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, P.; O’Riordan, K.J.; Lee, Y.K.; Wang, G.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Cryan, J.F.; Chen, W. Towards a psychobiotic therapy for depression. Neurobiol. Stress. 2020, 12, 100216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardsjord, E.S.; Romm, K.L.; Friis, S.; Barder, H.E.; Evensen, J.; Haahr, U.; ten Velden Hegelstad, W.; Joa, I.; Johannessen, J.O.; Langeveld, J.; et al. Subjective quality of life in first-episode psychosis. A ten year follow-up study. Schizophr. Res. 2016, 172, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickerson, F.B.; Stallings, C.; Origoni, A.; Katsafanas, E.; Savage, C.L.; Schweinfurth, L.A.; Goga, J.; Khushalani, S.; Yolken, R.H. Effect of probiotic supplementation on schizophrenia symptoms and association with gastrointestinal functioning: A randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Prim. Care Companion CNS Disord. 2014, 16, PCC.13m01579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomasik, J.; Yolken, R.H.; Bahn, S.; Dickerson, F.B. Immunomodulatory Effects of Probiotic Supplementation in Schizophrenia Patients: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Biomark. Insights 2015, 10, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minichino, A.; Brondino, N.; Solmi, M.; Del Giovane, C.; Fusar-Poli, P.; Burnet, P.; Cipriani, A.; Lennox, B.R. The gut-microbiome as a target for the treatment of schizophrenia: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials of add-on strategies. Schizophr. Res. 2021, 234, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.K.; Shin, C. The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis in Neuropsychiatric Disorders: Pathophysiological Mechanisms and Novel Treatments. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2018, 16, 559–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dealberto, M.J. Clinical symptoms of psychotic episodes and 25-hydroxy vitamin D serum levels in black first-generation immigrants. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2013, 128, 475–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, S.C.; Cryan, J.F.; Dinan, T. The Psychobiotic Revolution: Mood, Food, and the New Science of the Gut-Brain Connection; National Geographic Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Penninx, B.W.J.H.; Lange, S.M.M. Metabolic syndrome in psychiatric patients: Overview, mechanisms, and implications. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2018, 20, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, A.P.; Crowley, J.J.; Nonneman, R.J.; Quackenbush, C.R.; Miller, C.N.; Ryan, A.K.; Bogue, M.A.; Paredes, S.H.; Yourstone, S.; Carroll, I.M.; et al. The antipsychotic olanzapine interacts with the gut microbiome to cause weight gain in mouse. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e115225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davey, K.J.; O’Mahony, S.M.; Schellekens, H.; O’Sullivan, O.; Bienenstock, J.; Cotter, P.D.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Gender-dependent consequences of chronic olanzapine in the rat: Effects on body weight, inflammatory, metabolic and microbiota parameters. Psychopharmacology 2012, 221, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.W.; Liu, W.H.; Wu, C.C.; Juan, Y.C.; Wu, Y.C.; Tsai, H.P.; Wang, S.; Tsai, Y.C. Psychotropic effects of Lactobacillus plantarum PS128 in early life-stressed and naïve adult mice. Brain Res. 2016, 1631, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.T.; Tsai, Y.C.; Kuo, T.B.J.; Yang, C.C.H. Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum PS128 on Depressive Symptoms and Sleep Quality in Self-Reported Insomniacs: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Pilot Trial. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arseneault-Bréard, J.; Rondeau, I.; Gilbert, K.; Girard, S.A.; Tompkins, T.A.; Godbout, R.; Rousseau, G. Combination of Lactobacillus helveticus R0052 and Bifidobacterium longum R0175 reduces post-myocardial infarction depression symptoms and restores intestinal permeability in a rat model. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 107, 1793–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savignac, H.M.; Tramullas, M.; Kiely, B.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Bifidobacteria modulate cognitive processes in an anxious mouse strain. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 287, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, A.; Noorbala, A.A.; Azam, K.; Eskandari, M.H.; Djafarian, K. Effect of probiotic and prebiotic vs placebo on psychological outcomes in patients with major depressive disorder: A randomized clinical trial. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskandarzadeh, S.; Effatpanah, M.; Khosravi-Darani, K.; Askari, R.; Hosseini, A.F.; Reisian, M.; Jazayeri, S. Efficacy of a multispecies probiotic as adjunctive therapy in generalized anxiety disorder: A double blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Nutr. Neurosci. 2021, 24, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perin, S.; Lai, J.; Pase, M.; Bransby, L.; Buckley, R.; Yassi, N.; Pietrzak, R.H.; Maruff, P.; Lim, Y.Y. Elucidating the association between depression, anxiety, and cognition in middle-aged adults: Application of dimensional and categorical approaches. J. Affect. Disord. 2022, 296, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, S.; Galla, R.; Mulè, S.; Rosso, G.; Brovero, A.; Macchi, V.; Ruga, S.; Uberti, F. The Role of Bifidobacterium bifidum novaBBF7, Bifidobacterium longum novaBLG2 and Lactobacillus paracasei TJB8 to Improve Mechanisms Linked to Neuronal Cells Protection against Oxidative Condition in a Gut-Brain Axis Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.B.; Park, D.J.; Shah, M.A.; Koh, P.O. Quercetin ameliorates glutamate toxicity-induced neuronal cell death by controlling calcium-binding protein parvalbumin. J. Vet. Sci. 2022, 23, e26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Povarnina, P.Y.; Kolyasnikova, K.N.; Nikolaev, S.V.; Antipova, T.A.; Gudasheva, T.A. Neuropeptide Cycloprolylglycine Exhibits Neuroprotective Activity after Systemic Administration to Rats with Modeled Incomplete Global Ischemia and in In Vitro Modeled Glutamate Neurotoxicity. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2016, 160, 653–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, A.Q.; Gao, B.; Fan, J.J.; Zhu, Y.J.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Y.L.; Xu, L.Z.; Wu, W.N. NLRP1 inflammasome contributes to chronic stress-induced depressive-like behaviors in mice. J. Neuroinflammation 2020, 17, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Feng, Y.B.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Fan, C.; Song, Q.; Yu, S.Y. Interleukin-6: Its role and mechanisms in rescuing depression-like behaviors in rat models of depression. Brain Behav. Immun. 2019, 82, 106–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, A.; Tam, W.W.; Zhang, M.W.; Ho, C.S.; Husain, S.F.; McIntyre, R.S.; Ho, R.C. IL-1β, IL-6, TNF- α and CRP in Elderly Patients with Depression or Alzheimer’s disease: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.M.; Leal, B.; Ferreira, I.; Brás, S.; Moreira, I.; Samões, R.; Sousa, A.P.; Santos, E.; Silva, B.; Costa, P.P.; et al. Depression and anxiety in multiple sclerosis patients: The role of genetic variability of interleukin 1β. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2021, 52, 102982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eijsbouts, C.; Zheng, T.; Kennedy, N.A.; Bonfiglio, F.; Anderson, C.A.; Moutsianas, L.; Holliday, J.; Shi, J.; Shringarpure, S.; Voda, A.I.; et al. Genome-wide analysis of 53,400 people with irritable bowel syndrome highlights shared genetic pathways with mood and anxiety disorders. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 1543–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhu, G. Gut-Brain Axis and Mood Disorder. Front. Psychiatry 2018, 9, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishuty, N.L.; Khandoker, M.M.H.; Karmoker, J.R.; Ferdous, S.; Shahriar, M.; Qusar, M.M.A.S.; Islam, M.S.; Kadir, M.F.; Islam, M.R. Evaluation of Serum Interleukin-6 and C-reactive Protein Levels in Drug-naïve Major Depressive Disorder Patients. Cureus 2019, 11, e3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.J.; Au, B.; Ollis, L.; Schmitz, N. The association between C-reactive protein, Interleukin-6 and depression among older adults in the community: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Exp. Gerontol. 2018, 102, 109–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roque, S.; Correia-Neves, M.; Mesquita, A.R.; Palha, J.A.; Sousa, N. Interleukin-10: A key cytokine in depression? Cardiovasc. Psychiatry Neurol. 2009, 2009, 187894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesquita, A.R.; Correia-Neves, M.; Roque, S.; Castro, A.G.; Vieira, P.; Pedrosa, J.; Palha, J.A.; Sousa, N. IL-10 modulates depressive-like behavior. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2008, 43, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogłodek, E. Changes in the Serum Levels of Cytokines: IL-1β, IL-4, IL-8 and IL-10 in Depression with and without Posttraumatic Stress Disorder. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheller, J.; Chalaris, A.; Schmidt-Arras, D.; Rose-John, S. The pro- and anti-inflammatory properties of the cytokine interleukin-6. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1813, 878–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Zhang, M.; Hao, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Liu, C. Neuroinflammation mechanisms of neuromodulation therapies for anxiety and depression. Transl. Psychiatry 2023, 13, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiMarco, R.L.; Hunt, D.R.; Dewi, R.E.; Heilshorn, S.C. Improvement of paracellular transport in the Caco-2 drug screening model using protein-engineered substrates. Biomaterials 2017, 129, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galla, R.; Ruga, S.; Aprile, S.; Ferrari, S.; Brovero, A.; Grosa, G.; Molinari, C.; Uberti, F. New Hyaluronic Acid from Plant Origin to Improve Joint Protection-An In Vitro Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uberti, F.; Morsanuto, V.; Ruga, S.; Galla, R.; Farghali, M.; Notte, F.; Bozzo, C.; Magnani, C.; Nardone, A.; Molinari, C. Study of Magnesium Formulations on Intestinal Cells to Influence Myometrium Cell Relaxation. Nutrients 2020, 12, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceriotti, L.; Meloni, M. La valutazione dell’assorbimento intestinale in vitro. L’integratore Nutr. 2014, 17, 62–65. [Google Scholar]
- Uberti, F.; Morsanuto, V.; Ghirlanda, S.; Molinari, C. Iron Absorption from Three Commercially Available Supplements in Gastrointestinal Cell Lines. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubatsch, I.; Ragnarsson, E.G.; Artursson, P. Determination of drug permeability and prediction of drug absorption in Caco-2 monolayers. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 2111–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fda.Gov. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/117974/download (accessed on 3 February 2024).
- Ema.Eu. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-guideline/ich-m9-biopharmaceutics-classification-system-based-biowaivers-step-2b-first-version_en.pdf (accessed on 3 February 2024).
- Wu, H.C.; Hu, Q.L.; Zhang, S.J.; Wang, Y.M.; Jin, Z.K.; Lv, L.F.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Z.L.; Wu, H.L.; Cheng, O.M. Neuroprotective effects of genistein on SH-SY5Y cells overexpressing A53T mutant α-synuclein. Neural Regen. Res. 2018, 13, 1375–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayashree, S.; Karthikeyan, R.; Nithyalakshmi, S.; Ranjani, J.; Gunasekaran, P.; Rajendhran, J. Anti-adhesion Property of the Potential Probiotic Strain. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piletz, J.E.; Cooper, J.; Chidester, K.; Erson, K.; Melton, S.; Osemeka, A.; Patterson, M.; Strickland, K.; Wan, J.X.; Williams, K. Transepithelial Effect of Probiotics in a Novel Model of Gut Lumen to Nerve Signaling. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruga, S.; Galla, R.; Penna, C.; Molinari, C.; Uberti, F. The Activity of Ten Natural Extracts Combined in a Unique Blend to Maintain Cholesterol Homeostasis-In Vitro Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allers, K.; Stahl-Hennig, C.; Fiedler, T.; Wibberg, D.; Hofmann, J.; Kunkel, D.; Moos, V.; Kreikemeyer, B.; Kalinowski, J.; Schneider, T. The colonic mucosa-associated microbiome in SIV infection: Shift towards Bacteroidetes coincides with mucosal CD4. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinari, C.; Morsanuto, V.; Ghirlanda, S.; Ruga, S.; Notte, F.; Gaetano, L.; Uberti, F. Role of Combined Lipoic Acid and Vitamin D3 on Astrocytes as a Way to Prevent Brain Ageing by Induced Oxidative Stress and Iron Accumulation. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 2843121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uberti, F.; Trotta, F.; Pagliaro, P.; Bisericaru, D.M.; Cavalli, R.; Ferrari, S.; Penna, C.; Matencio, A. Developing New Cyclodextrin-Based Nanosponges Complexes to Improve Vitamin D Absorption in an In Vitro Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaaban, I.; Hafez, H.; AlZaim, I.; Tannous, C.; Ragab, H.; Hazzaa, A.; Ketat, S.; Ghoneim, A.; Katary, M.; Abd-Alhaseeb, M.M.; et al. Transforming iodoquinol into broad spectrum anti-tumor leads: Repurposing to modulate redox homeostasis. Bioorg Chem. 2021, 113, 105035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Zhang, P.; Heing-Becker, I.; Zhang, J.; Tang, P.; Bej, R.; Bhatia, S.; Zhong, Y.; Haag, R. Dual tumor- and subcellular-targeted photodynamic therapy using glucose-functionalized MoS. Biomaterials 2022, 290, 121844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uberti, F.; Trotta, F.; Cavalli, R.; Galla, R.; Caldera, F.; Ferrari, S.; Mulè, S.; Brovero, A.; Molinari, C.; Pagliaro, P.; et al. Enhancing Vitamin D3 Efficacy: Insights from Complexation with Cyclodextrin Nanosponges and Its Impact on Gut-Brain Axes in Physiology and IBS Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, A.; Li, N.; Li, P.L.; Zhang, F. Concentration-Dependent Diversifcation Effects of Free Cholesterol Loading on Macrophage Viability and Polarization. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 37, 419–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujimulyani, D.; Yulianto, W.A.; Setyowati, A.; Prastyo, P.; Windrayahya, S.; Maruf, A. White saffron (Curcuma mangga Val.) attenuates diabetes and improves pancreatic β-cell regeneration in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Toxicol. Rep. 2022, 9, 1213–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uberti, F.; Morsanuto, V.; Ghirlanda, S.; Ruga, S.; Clemente, N.; Boieri, C.; Boldorini, R.; Molinari, C. Highly Diluted Acetylcholine Promotes Wound Repair in an In Vivo Model. Adv. Wound Care 2018, 7, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinari, C.; Morsanuto, V.; Ruga, S.; Notte, F.; Farghali, M.; Galla, R.; Uberti, F. The Role of BDNF on Aging-Modulation Markers. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bliźniewska-Kowalska, K.; Gałecki, P.; Szemraj, J.; Talarowska, M. Expression of Selected Genes Involved in Neurogenesis in the Etiopathogenesis of Depressive Disorders. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szurpnicka, A.; Wrońska, A.K.; Bus, K.; Kozińska, A.; Jabłczyńska, R.; Szterk, A.; Lubelska, K. Phytochemical screening and effect of Viscum album L. on monoamine oxidase A and B activity and serotonin, dopamine and serotonin receptor 5-HTR1A levels in Galleria mellonealla (Lepidoptera). J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 298, 115604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ferrari, S.; Mulè, S.; Rosso, G.; Parini, F.; Galla, R.; Molinari, C.; Uberti, F. An Innovative Probiotic-Based Supplement to Mitigate Molecular Factors Connected to Depression and Anxiety: An In Vitro Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4774. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25094774
Ferrari S, Mulè S, Rosso G, Parini F, Galla R, Molinari C, Uberti F. An Innovative Probiotic-Based Supplement to Mitigate Molecular Factors Connected to Depression and Anxiety: An In Vitro Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(9):4774. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25094774
Chicago/Turabian StyleFerrari, Sara, Simone Mulè, Giorgia Rosso, Francesca Parini, Rebecca Galla, Claudio Molinari, and Francesca Uberti. 2024. "An Innovative Probiotic-Based Supplement to Mitigate Molecular Factors Connected to Depression and Anxiety: An In Vitro Study" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 9: 4774. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25094774
APA StyleFerrari, S., Mulè, S., Rosso, G., Parini, F., Galla, R., Molinari, C., & Uberti, F. (2024). An Innovative Probiotic-Based Supplement to Mitigate Molecular Factors Connected to Depression and Anxiety: An In Vitro Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(9), 4774. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25094774





