Interactions of Highly Diluted Arnica montana Extract with Water Across Glass Interfaces †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
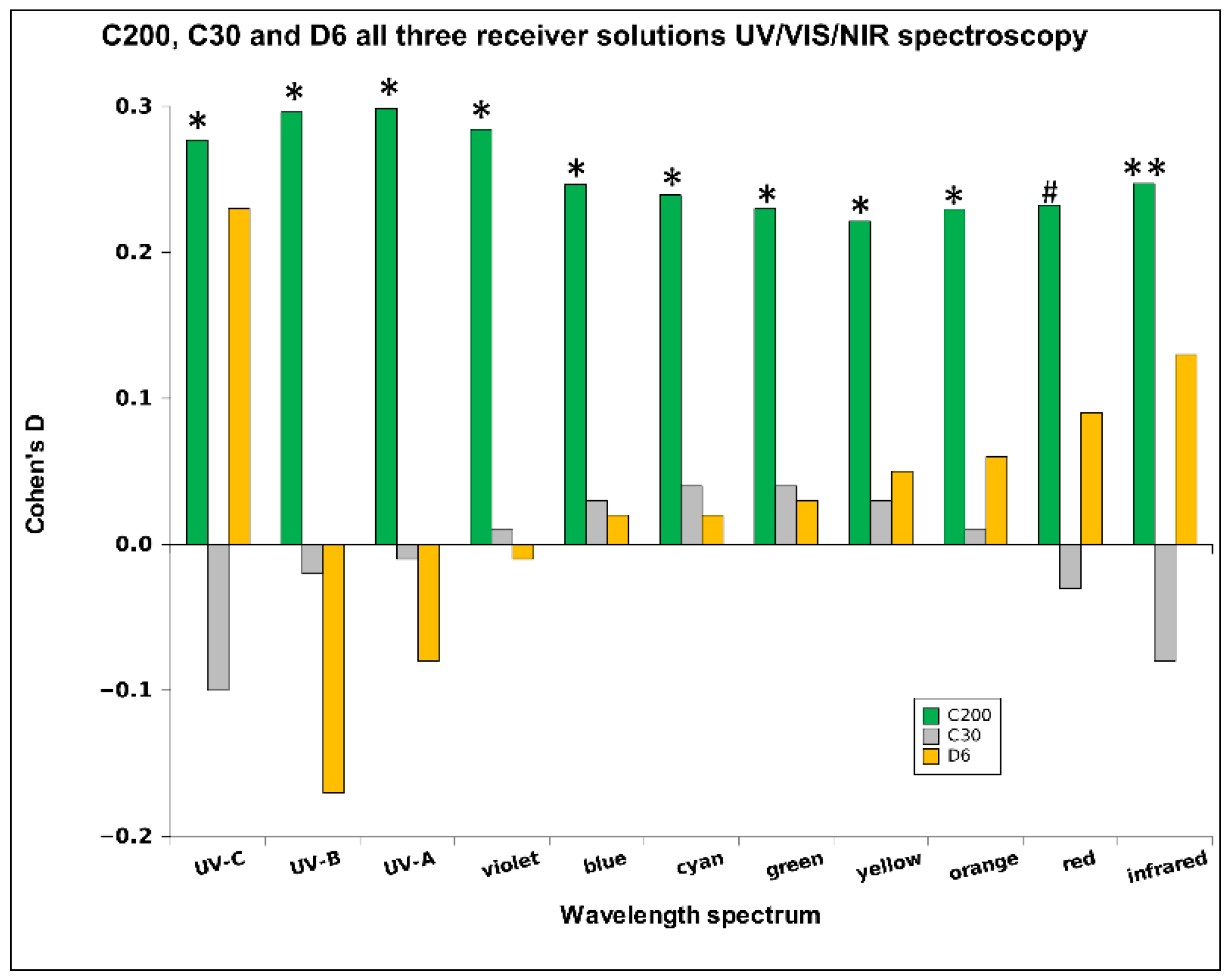
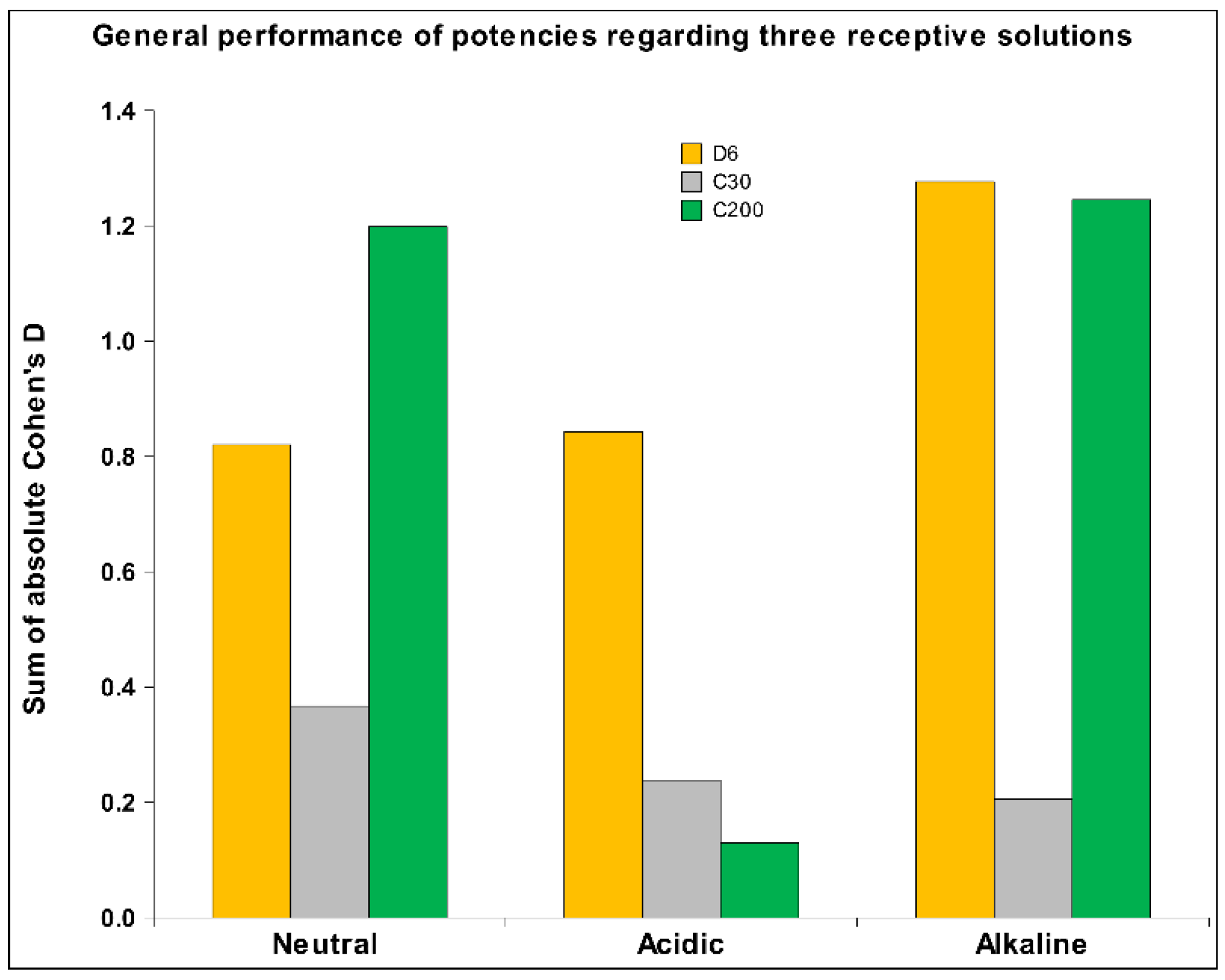
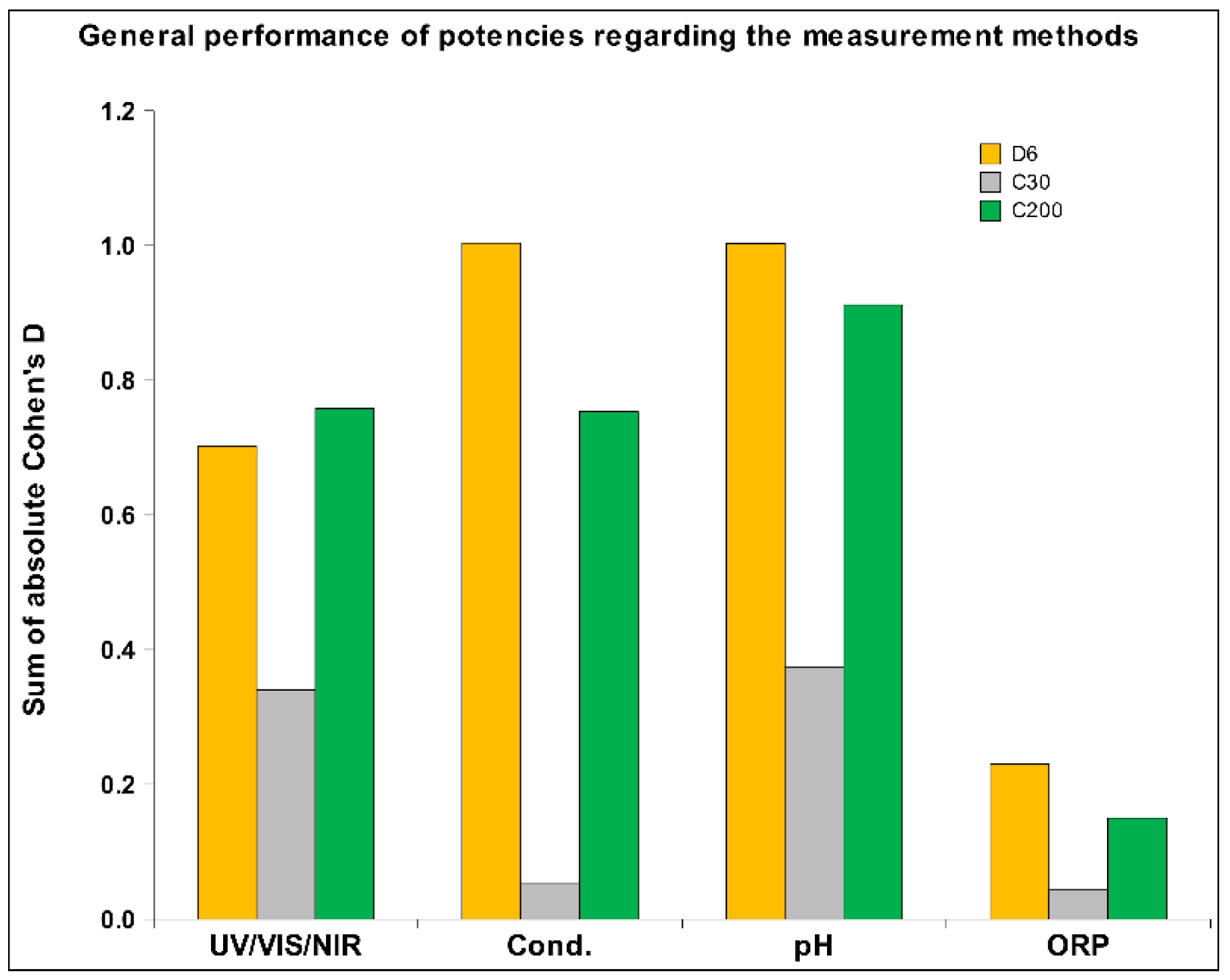
2.1. UHD Signal Transfer Detection in Neutral Receiver Solutions
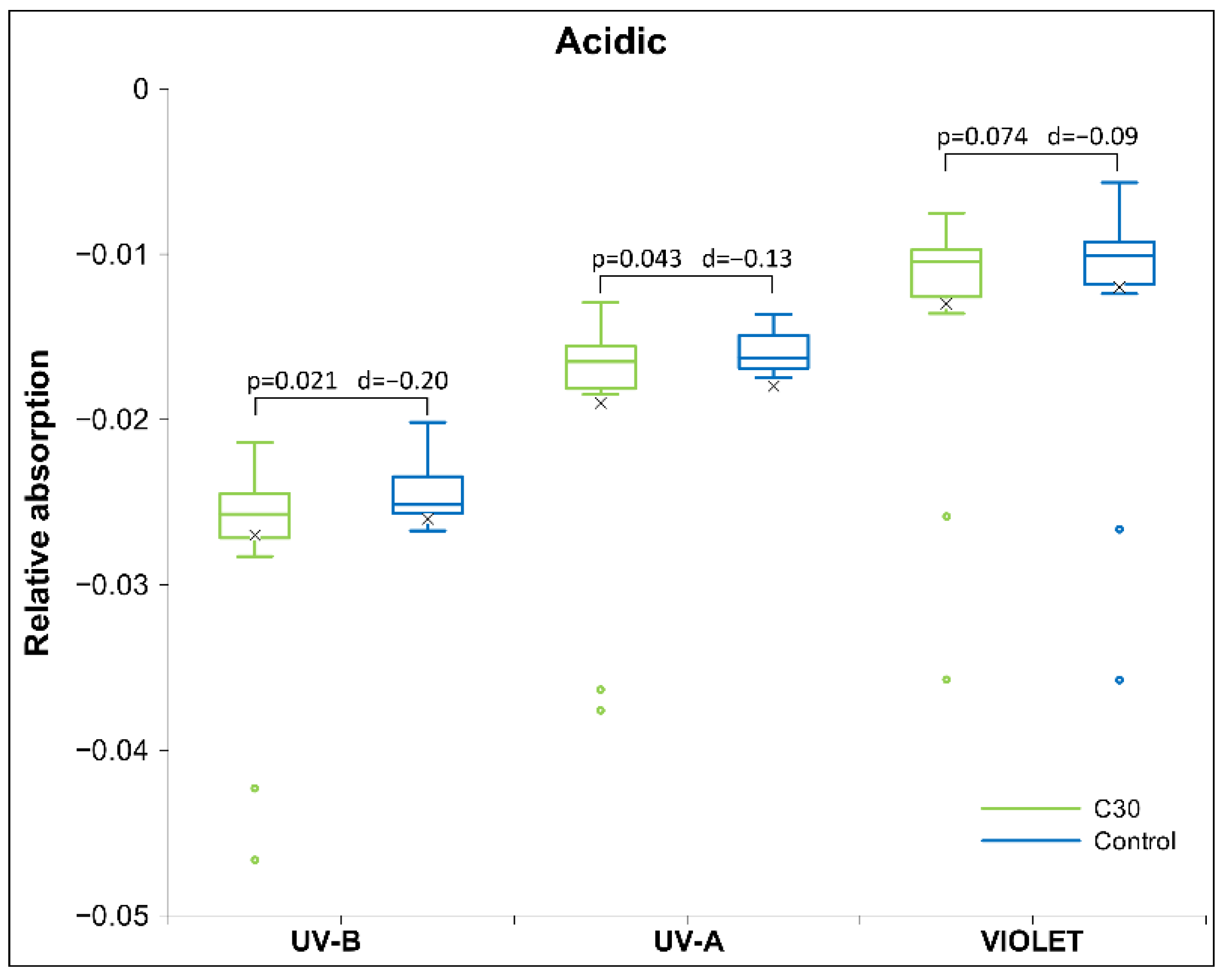
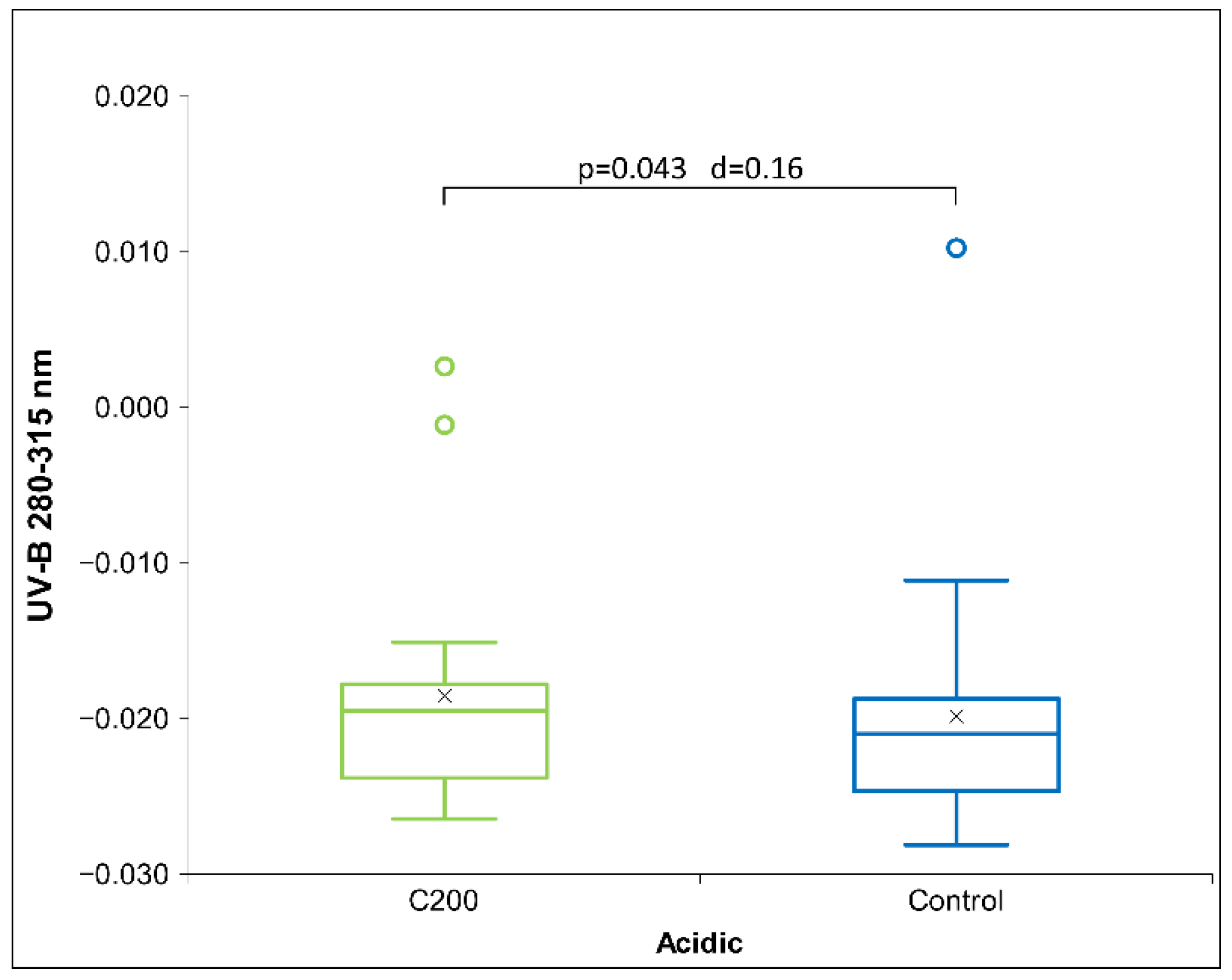
2.2. UHD Signal Transfer Detection in Acidic Receiver Solutions
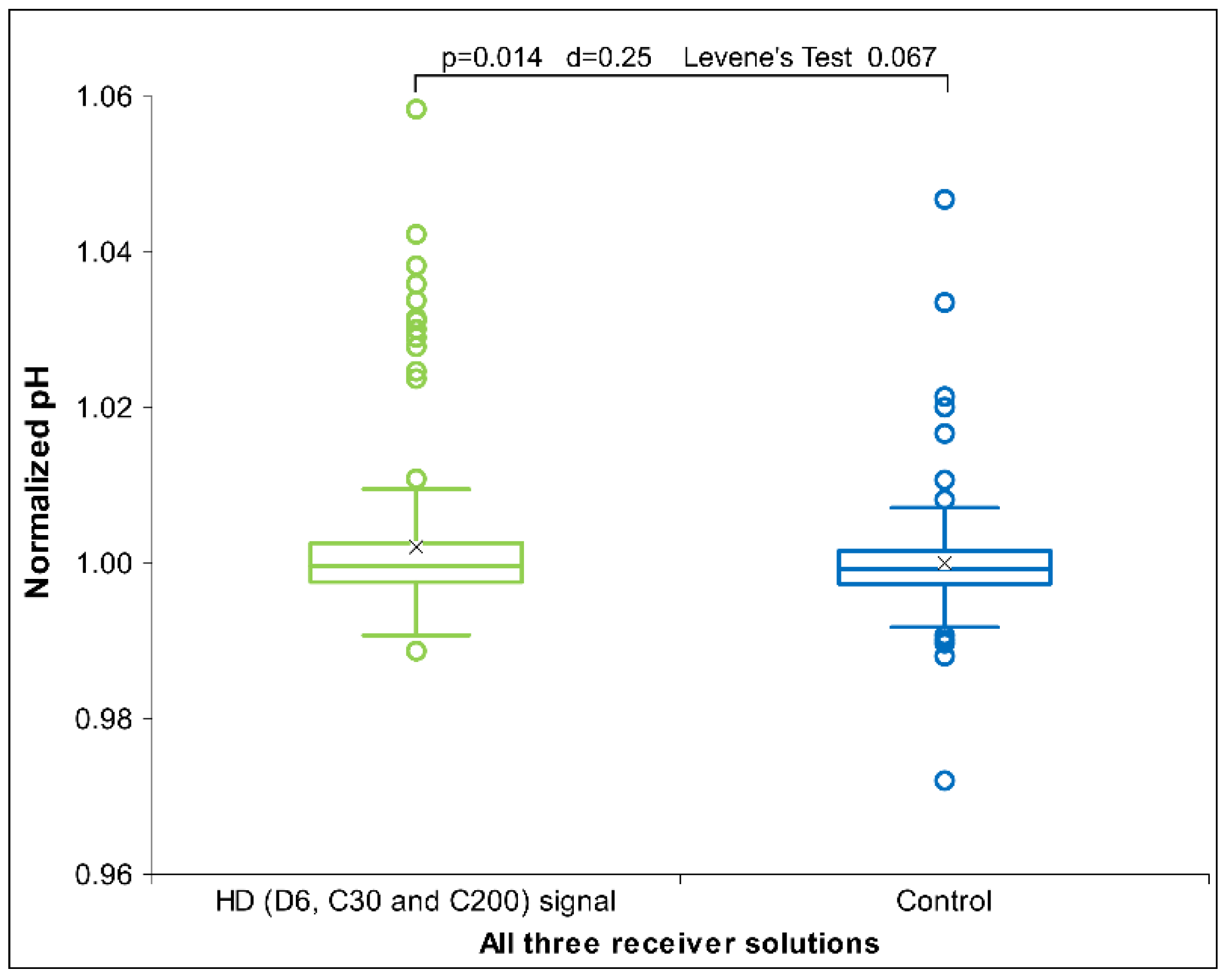
2.3. HD Signal Transfer Detection in Alkaline Receiver Solutions
3. Discussion
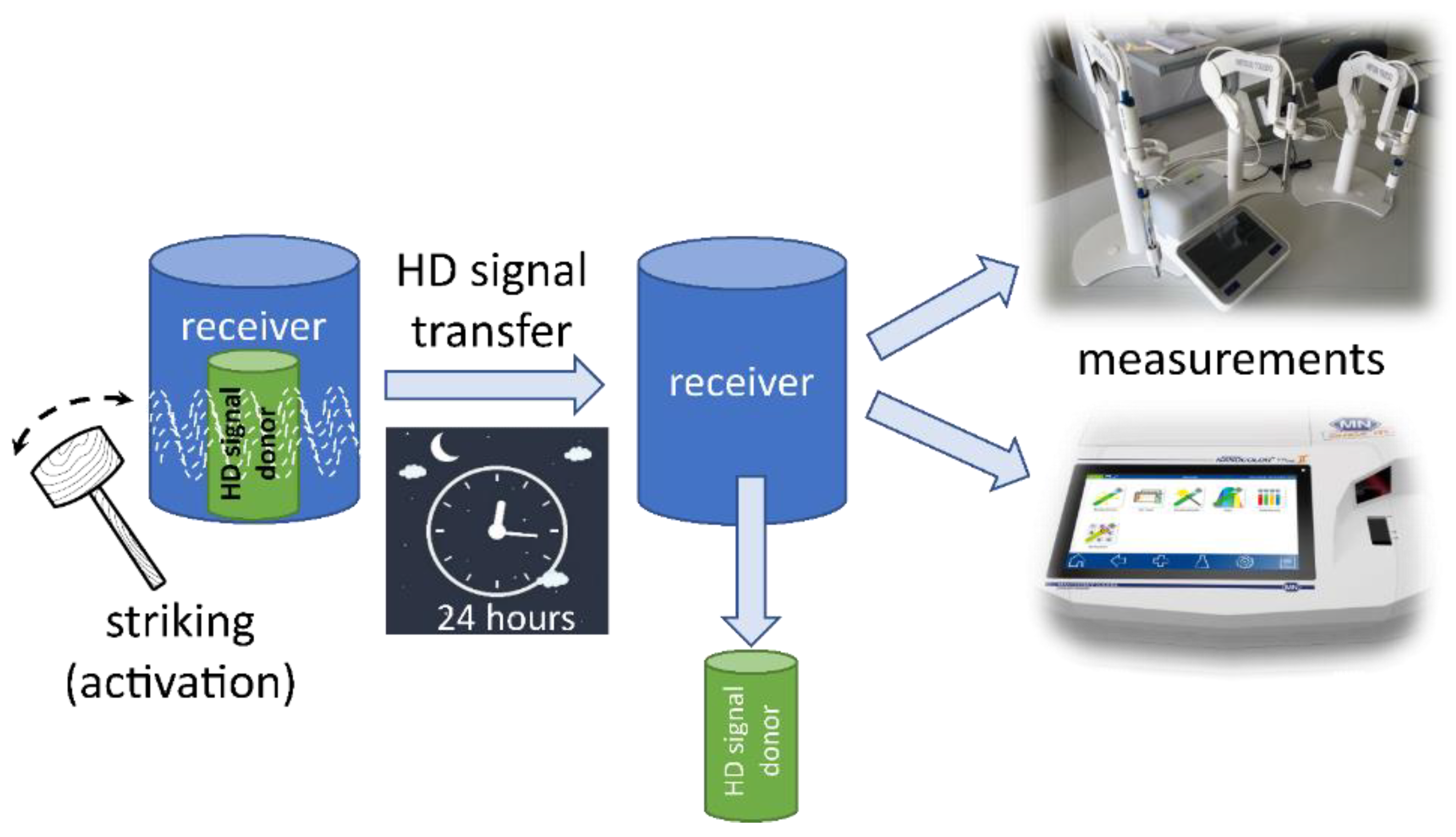
4. Materials and Methods
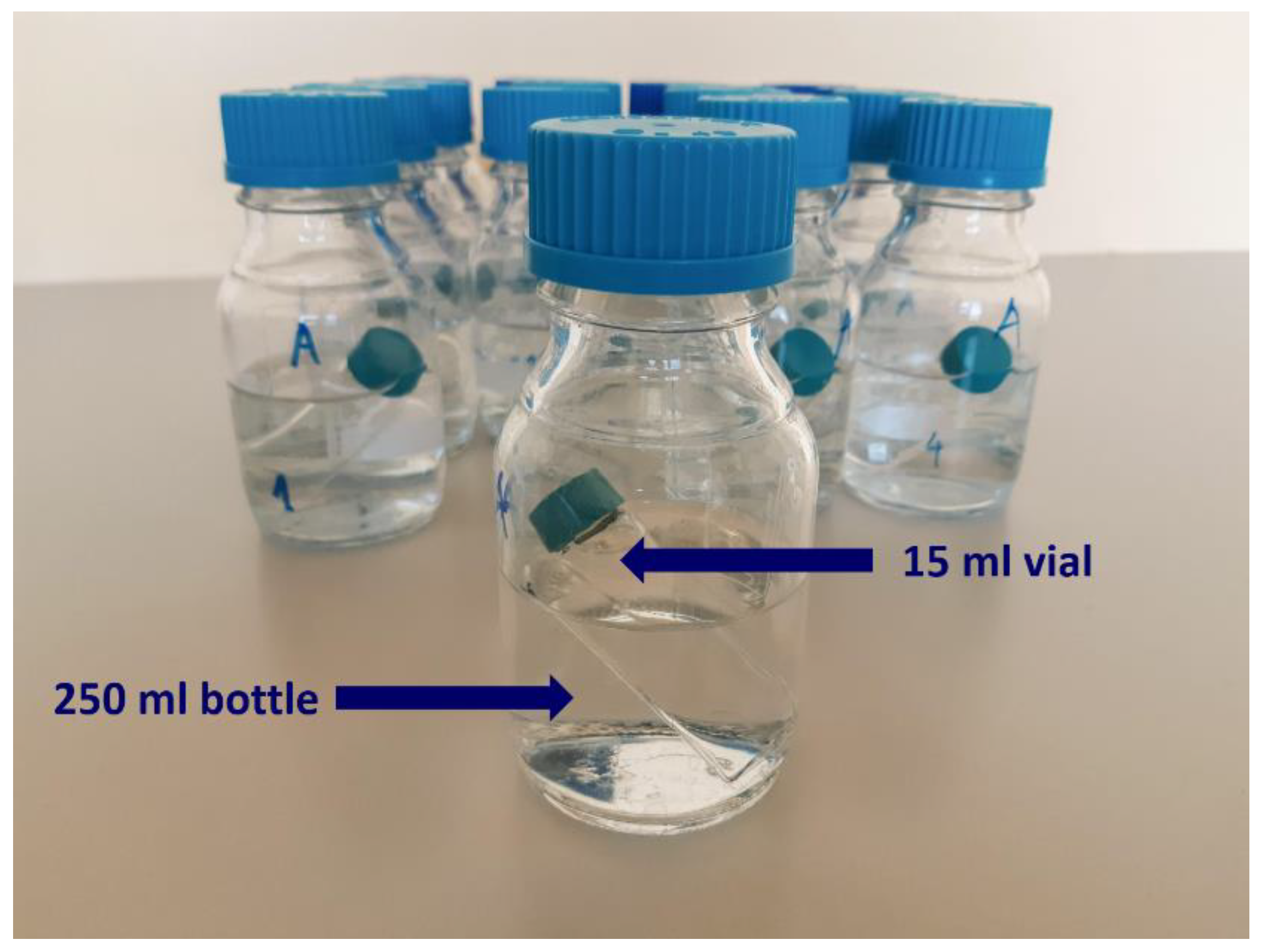
4.1. Material and Devices
- UHD signal situations:
- ○
- D6: the 15 mL vials were placed into the 250 mL bottles containing the receiver solution with specified pH (see Section 4.1.1 for more information),
- ○
- C30: same treatment,
- ○
- C200: same treatment,
- Control situation (C): same treatment stemming from the control granules.
4.1.1. Water Used for the Receiver Solutions
Original Fiji Water
Further Processing of FIJI Water to Attain Three Targeted Receiver Solutions
4.1.2. Measurement Devices and Methods
4.2. Experimental Protocol
4.2.1. Blinding
4.2.2. Sequential Process Management
4.2.3. Measurement Protocol
4.3. Statistical Analysis of the Results
Normalization in Multi-Experiment Evaluation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Foletti, A.; Ledda, M.; Lolli, M.G.; Grimaldi, S.; Lisi, A. Electromagnetic information transfer through aqueous system. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2017, 36, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foletti, A.; Ledda, M.; D’Emilia, E.; Grimaldi, S.; Lisi, A. Experimental finding on the electromagnetic information transfer of specific molecular signals mediated through the aqueous system on two human cellular models. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2012, 18, 258–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagai, M.Y.D.d.O.; Mohammad, S.N.; Pinto, A.A.G.; Coimbra, E.N.; Peres, G.B.; Suffredini, I.B.; Bernardi, M.M.; Tournier, A.L.; Jerman, I.; Cartwright, S.J.; et al. Highly diluted glyphosate mitigates its effects on Artemia Salina: Physicochemical implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galeazzi, B.V.; Manzalini, A.; Cartwright, S.; Bonamin, L.; Medeiros, N.; Suffredini, I. Silicea Terra 200cH evaluated by two different spectroscopy methods: A pilot study. Int. J. High Dilution Res. 2022, 21, 21–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghini, F.; Dinelli, G.; Marotti, I.; Trebbi, G.; Borghini, G.; Betti, L. Electromagnetic information transfer (EMIT) by ultra high diluted (UHD) solutions: The suggestive hypothesis of an epigenetic action. Int. J. High Dilution Res. 2021, 11, 113–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerman, I.; Ogrizek, L.; Jan, L.; Periček Krapež, V. Physicochemical study of the molecular signal transfer of ultra-high diluted antibodies to interferon gamma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerman, I.; Ogrizek, L.; Krapež, V.P.; Jan, L. Molecular signal transfer of highly diluted antibodies to interferon-gamma regarding kind, time, and distance of exposition. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penkov, N. Antibodies processed using high dilution technology distantly change structural properties of IFNγ aqueous solution. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novikov, V.V.; Yablokova, E.V. Interaction between highly diluted samples, protein solutions and water in a controlled magnetic field. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fesenko, E.E.; Yablokova, E.V.; Novikov, V.V. Weak magnetic fields regulate the ability of high dilutions of water to enhance ROS production by neutrophils. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parafiniuk, A.; Kromer, K.; Fleszar, M.G.; Kreitschitz, A.; Wiśniewski, J.; Gamian, A. Localization of sesquiterpene lactones biosynthesis in flowers of Arnica taxa. Molecules 2023, 28, 4379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Röhrl, J.; Piqué-Borràs, M.-R.; Jaklin, M.; Werner, M.; Werz, O.; Josef, H.; Hölz, H.; Ammendola, A.; Künstle, G. Anti-inflammatory activities of Arnica montana planta tota versus flower extracts: Analytical, in vitro and in vivo mouse paw oedema model studies. Plants 2023, 12, 1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kriplani, P.; Guarve, K.; Baghael, U.S. Arnica montana L.—A plant of healing: Review. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2017, 69, 925–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, E.; Pittler, M. Efficacy of homeopathic arnica: A systematic review of placebo-controlled clinical trials. Arch. Surg. 1998, 133, 1187–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnyk, N.; Vlasova, I.; Skowrońska, W.; Bazylko, A.; Piwowarski, J.P.; Granica, S. Current knowledge on interactions of plant materials traditionally used in skin diseases in Poland and Ukraine with human skin microbiota. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirzajani, F.; Mirzajani, F.; Aelaei, M. Study of germination efficiency and temperature/drowning resistance in some ornamental plants treated with ultra high dilute compounds. Int. J. High Dilution Res. 2021, 20, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinian, S.; Maute, C.; Rahimi, F.; Maute, C.; Hamedi, M.; Mirzajani, F. The influence of ultra-high diluted compounds on the growth and the metabolites of Oriza sativa L. Int. J. High Dilution Res. 2020, 19, 39–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endler, P.; Thieves, K.; Reich, C.; Matthiessen, P.; Bonamin, L.; Scherr, C.; Baumgartner, S. Repetitions of fundamental research models for homeopathically prepared dilutions beyond 10−23: A bibliometric study. Homeopathy 2010, 99, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonamin, L.V. Homeopathy and experimental infections: In vivo and in vitro experiments with bacteria, fungi and protozoan. La Rev. D’homéopathie 2019, 10, e29–e32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, A.A.G.; Nagai, M.Y.d.O.; Coimbra, E.N.; Mohammad, S.N.; Silva, J.S.; Ancken, A.V.; Pinto, S.A.G.; Aguiar, M.S.; Dutra-Correa, M.; Hortellani, M.A.; et al. Bioresilience to mercury chloride of the brine shrimp artemia salina after treatment with homeopathic mercurius corrosivus. Homeopathy 2021, 110, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, M.Y.O.; Von Ancken, A.C.B.; Bonamin, L.V. Effects of highly diluted substances on aquatic animals: A Review. Water—A Multidiscip. Res. J. 2022, 13, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, S.D.; Würtenberger, S.; Wolf, U.; Baumgartner, S.; Tournier, A. Physicochemical investigations of homeopathic preparations: A systematic review and bibliometric analysis—Part 1. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2018, 24, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tournier, A.; Klein, S.D.; Würtenberger, S.; Wolf, U.; Baumgartner, S. Physicochemical investigations of homeopathic preparations: A systematic review and bibliometric Analysis—Part 2. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2019, 25, 890–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonamin, L.V.; Pedro, R.R.P.; Mota, H.M.G.; Aguiar, M.S.C.; Pinto, S.A.G.; de Souza, J.; de Oliveira, L.H.S.; Aparicio, A.C.; Peres, G.B.; Suffredini, I.; et al. Characterization of antimonium crudum activity using solvatochromic dyes. Homeopathy 2020, 109, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tournier, A.; Würtenberger, S.; Klein, S.D.; Baumgartner, S. Physicochemical investigations of homeopathic preparations: A systematic review and bibliometric Analysis—Part 3. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2021, 27, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Post, S.T.; Hsieh, C.-S.; Okuno, M.; Nagata, Y.; Bakker, H.J.; Bonn, M.; Hunger, J. Strong frequency dependence of vibrational relaxation in bulk and surface water reveals sub-picosecond structural heterogeneity. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Giudice, E.; Preparata, G.; Vitiello, G. Water as a free electric dipole laser. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1988, 61, 1085–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arani, R.; Bono, I.; Del Giudice, E.D.; Preparata, G. Qed coherence and the thermodynamics of water. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 1995, 9, 1813–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bono, I.; Del Giudice, E.; Gamberale, L.; Henry, M. Emergence of the coherent structure of liquid water. Water 2012, 4, 510–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yinnon, C.A.; Yinnon, T.A. Domains in aqueous solutions: Theory and experimental evidence. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 2009, 23, 1959–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, S.; Gupta, K.S.; Coey, J.M.D. Mesoscopic structure formation in condensed matter due to vacuum fluctuations. Phys. Rev. B 2015, 92, 155115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzalini, A.; Galeazzi, B. Explaining homeopathy with quantum electrodynamics. Homeopathy 2019, 108, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messori, C. Deep into the water: Exploring the hydro-electromagnetic and quantum-electrodynamic properties of interfacial water in living systems. Open Access Libr. J. 2019, 6, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scirè, A. A Mesoscopic model for the collective dynamics of water coherence domains. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.07545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konovalov, A.I.; Ryzhkina, I.S. Formation of nanoassociates as a key to understanding of physicochemical and biological properties of highly dilute aqueous solutions. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2014, 63, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedlák, M.; Rak, D. Large-scale inhomogeneities in solutions of low molar mass compounds and mixtures of liquids: Supramolecular structures or nanobubbles? J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 2495–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meessen, A. Water memory due to chains of nano-pearls. J. Mod. Phys. 2018, 9, 2657–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellavite, P.; Marzotto, M.; Olioso, D.; Moratti, E.; Conforti, A. High-dilution effects revisited. 1. physicochemical aspects. Homeopathy 2014, 103, 4–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yinnon, T.; Kalia, K.; Kikar, D. Very dilute aqueous solutions-structural and electromagnetic phenomena. Water 2017, 9, 28–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerman, I.; Ružič, R.; Krašovec, R.; Škarja, M.; Mogilnicki, L. Electrical transfer of molecule information into water, its storage, and bioeffects on plants and bacteria. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2005, 24, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruzic, R.; Jerman, I.; Skarja, M.; Leskovar, R.; Mogilnicki, L. Electromagnetic transference of molecular information in garden cress germination. Int. J. High Dilution Res. 2008, 7, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montagnier, L.; Aissa, J.; Del Giudice, E.D.; Lavallee, C.; Tedeschi, A.; Vitiello, G. DNA waves and water. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2011, 306, 12007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yinnon, T. Liquids Prepared by Serially Diluting and Vigorously Shaking of Aqueous Solutions: Unveiling Effects of the Solute on Their Properties. Water 2020, 10, 115–134. Available online: https://waterjournal.org/uploads/vol10/yinnon-2/WATER.2019.2.Yinnon.pdf (accessed on 23 December 2024).
- Gudkov, S.V.; Penkov, N.V.; Baimler, I.V.; Lyakhov, G.A.; Pustovoy, V.I.; Simakin, A.V.; Sarimov, R.M.; Scherbakov, I.A. Effect of mechanical shaking on the physicochemical properties of aqueous solutions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandyopadhyay, P.; Bera, D.; Das, K.; Kumar, B.; Das, S.; Bhar, D.S.; Manchanda, R.; Khurana, A.; Nayak, D.; Basu, R.; et al. Vigorous Shaking Enhances Voltage and Power Generation in Polar Liquids due to Domain Formation as Predicted by QED. Water J. 2017, 13, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, F.; Wolf, U.; Baumgartner, S. NMR relaxation time investigation of highly diluted aqueous solutions of silica-lactose. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 337, 115975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.Q.; Li, T.; Bai, X.; Zhao, M.; Wang, B.; Rein, G.; Yang, Y.; Gao, P.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Rate limiting factors for DNA transduction induced by weak electromagnetic field. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2019, 38, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rad, I.; Jalali, K. Electronic transmission of antibacterial property into water at extremely low frequency range: A preliminary study. J. ACM 2018, 24, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kernbach, S. Electrochemical characterization of ionic dynamics resulting from spin conversion of water isomers. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2022, 169, 67504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kernbach, S.; Kernbach, O. Environment-dependent fluctuations of potentiometric pH dynamics in geomagnetic field. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2022, 41, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Giudice, E.D.; Spinetti, P.R.; Tedeschi, A. Water dynamics at the root of metamorphosis in living organisms. Water 2010, 2, 566–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liboff, A.R. Geomagnetic cyclotron resonance in living things. J. Biol. Phys. 1985, 13, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liboff, A.R. Ion Cyclotron Resonance Interactions in Living Systems. SIBE, ATTI IV, PAVIA. 2013, 19, 1–14. Available online: https://emmind.net/openpapers_repos/Applied_Fields-Experimental/ELF_LF_Effects/ELF-EMF/2013_Ion_Cyclotron_Resonance_interactions_in_living_systems.pdf (accessed on 26 December 2023).
- Del Giudice, E.D.; Fleischmann, M.; Preparata, G.; Talpo, G. On the “unreasonable” effects of ELF magnetic fields upon a system of ions. Bioelectromagnetics 2002, 23, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhadin, M.; Giuliani, L. Some problems in modern bioelectromagnetics. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2006, 25, 227–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedlák, M. Large-scale supramolecular structure in solutions of low molar mass compounds and mixtures of liquids: I. light scattering characterization. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 4329–4338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedlák, M. Large-scale supramolecular structure in solutions of low molar mass compounds and mixtures of liquids: II. kinetics of the formation and long-time stability. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 4339–4345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedlák, M. Large-scale supramolecular structure in solutions of low molar mass compounds and mixtures of liquids. III. correlation with molecular properties and interactions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 13976–13984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunkin, N.F.; Shkirin, A.V.; Penkov, N.V.; Chirikov, S.N.; Ignatiev, P.S.; Kozlov, V.A. The physical nature of mesoscopic inhomogeneities in highly diluted aqueous suspensions of protein particles. Phys. Wave Phenom. 2019, 27, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikramane, P.S.; Suresh, A.K.; Bellare, J.R.; Kane, S.G. Extreme homeopathic dilutions retain starting materials: A nanoparticulate perspective. Homeopathy 2010, 99, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Giudice, E.; Tedeschi, A.; Vitiello, G.; Voeikov, V. Coherent Structures in Liquid Water Close to Hydrophilic Surfaces. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2013, 442, 12028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollack, G.H. The Fourth Phase of Water: Beyond Solid, Liquid, and Vapor; Ebner & Sons: Seattle, WA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germano, R.; Del Giudice, E.; de Ninno, A.; Elia, V.; Hison, C.; Napoli, E.; Tontodonato, V.; Tuccinardi, F.P.; Vitiello, G. Oxhydroelectric effect in bi-distilled water. Key Eng. Mater. 2013, 543, 455–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yinnon, T. Aqueous solutions and other polar liquids perturbed by serial dilutions and vigorous shaking: Analyses of their UV spectra. Water 2018, 10, 11–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, B.; Zheng, J.; Zhao, Q.; Pollack, G.H. Spectroscopic studies of solutes in aqueous solution. J. Phys. Chem. A 2008, 112, 2242–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, Y. Kinetic insight on the long-range exclusion of dissolved substances by interfacial interactions of water and hydrophilic surface. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 349, 118118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elia, V.; Oliva, R.; Napoli, E.; Germano, R.; Pinto, G.; Lista, L.; Niccoli, M.; Toso, D.; Vitiello, G.; Trifuoggi, M.; et al. Experimental study of physicochemical changes in water by iterative contact with hydrophilic polymers: A comparison between cellulose and nafion. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 268, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryzhkina, I.S.; Murtazina, L.I.; Kiseleva, Y.V.; Konovalov, A.I. Self-Organization and Physicochemical Properties of Aqueous Solutions of the Antibodies to Interferon Gamma at Ultrahigh Dilution. Dokl. Phys. Chem. 2015, 462, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayrapetyan, S.N.; Amyan, A.M.; Ayrapetyan, G.S. The effects of static magnetic fields, low frequency electromagnetic fields and mechanical vibration on some physicochemical properties of water. In Water and the Cell; Pollack, G.H., Cameron, I.L., Wheatley, D.N., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radin, D.; Lund, N.; Emoto, M.; Kizu, T. Effects of distant intention on water crystal formation: A triple-blind replication. J. Sci. Explor. 2008, 22, 481–493. [Google Scholar]








| Neutral Receiver Solutions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spectral Band | D6 | C30 | C200 | |
| UV-C | 200–280 | 0.48 | −0.06 | 0.22 |
| UV-B | 280–315 | −0.39 | 0.01 | 0.23 |
| UV-A | 315–400 | −0.34 | 0.04 | 0.24 |
| Violet | 400–450 | −0.28 | 0.05 | 0.30 |
| Blue | 450–485 | −0.25 | 0.08 | 0.27 |
| Cyan | 485–500 | −0.26 | 0.10 | 0.25 |
| Green | 500–565 | −0.25 | 0.14 | 0.18 |
| Yellow | 565–590 | −0.26 | 0.19 | 0.06 |
| Orange | 590–625 | −0.26 | 0.20 | 0.05 |
| Red | 625–750 | −0.15 | 0.20 | 0.20 |
| Infrared | 750–898 | −0.11 | 0.18 | 0.30 |
| Neutral Receiver Solutions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| D6 | C30 | C200 | |
| Conductivity | −0.39 | −0.02 | 0.27 |
| ORP | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| pH | 0.13 | 0.23 | 0.72 |
| Acidic Receiver Solutions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spectral Band | D6 | C30 | C200 | |
| UV-C | 200–280 | −0.34 | −0.20 | 0.12 |
| UV-B | 280–315 | −0.33 | −0.20 | 0.16 |
| UV-A | 315–400 | −0.32 | −0.13 | 0.14 |
| Violet | 400–450 | −0.24 | −0.09 | 0.09 |
| Blue | 450–485 | −0.21 | −0.08 | 0.05 |
| Cyan | 485–500 | −0.20 | −0.08 | 0.08 |
| Green | 500–565 | −0.23 | −0.09 | 0.08 |
| Yellow | 565–590 | −0.27 | −0.09 | 0.15 |
| Orange | 590–625 | −0.24 | −0.09 | 0.16 |
| Red | 625–750 | −0.20 | −0.06 | −0.02 |
| Infrared | 750–898 | −0.18 | −0.07 | −0.08 |
| Acidic Receiver Solutions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| D6 | C30 | C200 | |
| Conductivity | −0.26 | 0.00 | 0.02 |
| ORP | 0.00 | −0.01 | 0.00 |
| pH | 0.34 | 0.12 | −0.01 |
| Alkaline Receiver Solutions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spectral Band | D6 | C30 | C200 | |
| UV-C | 200–280 | 0.47 | −0.35 | 0.94 |
| UV-B | 280–315 | 0.04 | 0.07 | 0.59 |
| UV-A | 315–400 | 0.08 | 0.02 | 0.45 |
| Violet | 400–450 | 0.12 | 0.06 | 0.39 |
| Blue | 450–485 | 0.12 | 0.08 | 0.35 |
| Cyan | 485–500 | 0.12 | 0.09 | 0.34 |
| Green | 500–565 | 0.14 | 0.06 | 0.35 |
| Yellow | 565–590 | 0.19 | −0.03 | 0.36 |
| Orange | 590–625 | 0.21 | −0.07 | 0.38 |
| Red | 625–750 | 0.20 | −0.19 | 0.38 |
| Infrared | 750–898 | 0.25 | −0.30 | 0.40 |
| Alkaline Receiver Solutions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| D6 | C30 | C200 | |
| Conductivity | −0.35 | −0.03 | −0.47 |
| ORP | −0.21 | −0.03 | −0.15 |
| pH | 0.54 | 0.02 | −0.18 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jerman, I.; Ogrizek, L.; Pihir, J.; Senica, M. Interactions of Highly Diluted Arnica montana Extract with Water Across Glass Interfaces. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1115. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26031115
Jerman I, Ogrizek L, Pihir J, Senica M. Interactions of Highly Diluted Arnica montana Extract with Water Across Glass Interfaces. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(3):1115. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26031115
Chicago/Turabian StyleJerman, Igor, Linda Ogrizek, Jonatan Pihir, and Mateja Senica. 2025. "Interactions of Highly Diluted Arnica montana Extract with Water Across Glass Interfaces" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 3: 1115. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26031115
APA StyleJerman, I., Ogrizek, L., Pihir, J., & Senica, M. (2025). Interactions of Highly Diluted Arnica montana Extract with Water Across Glass Interfaces. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(3), 1115. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26031115


_Kim.png)




