Integrating Hypoxia Signatures from scRNA-seq and Bulk Transcriptomes for Prognosis Prediction and Precision Therapy in Cervical Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Endocervical Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
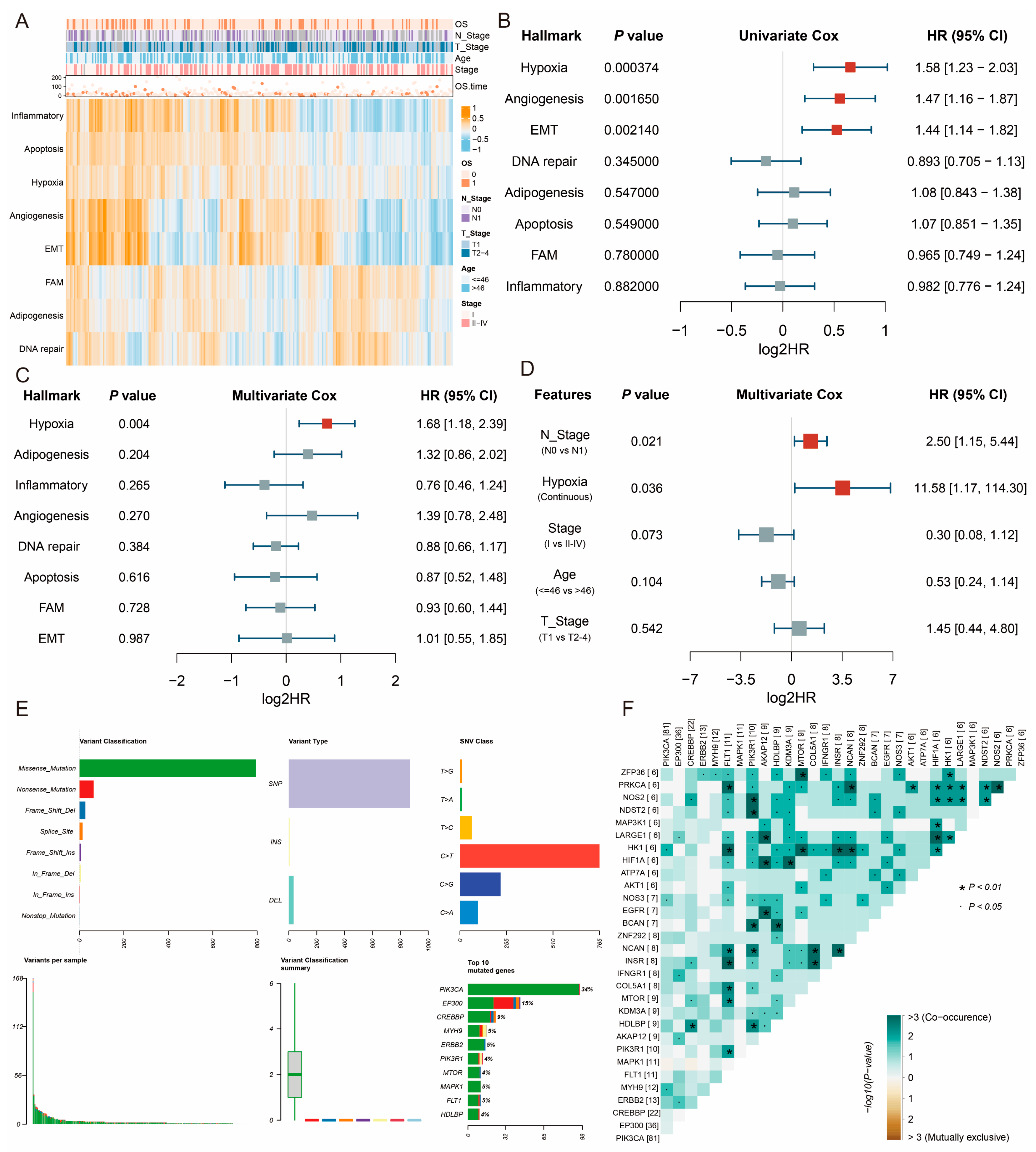
2.1. Hypoxia Is a Primary Prognosis Risk Factor in CESC
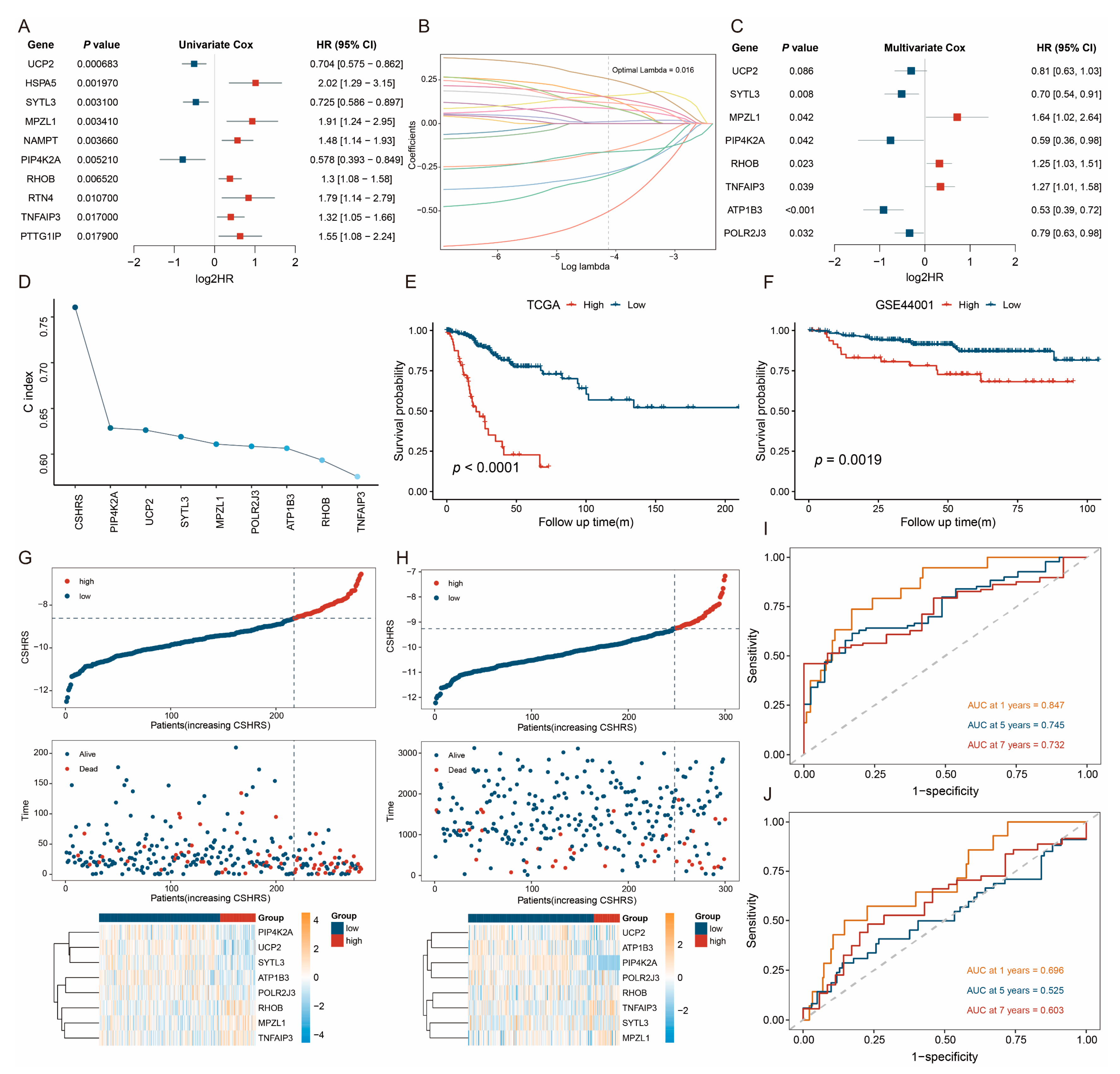
2.2. Identification of CESC-Specific Hypoxia-Related Genes
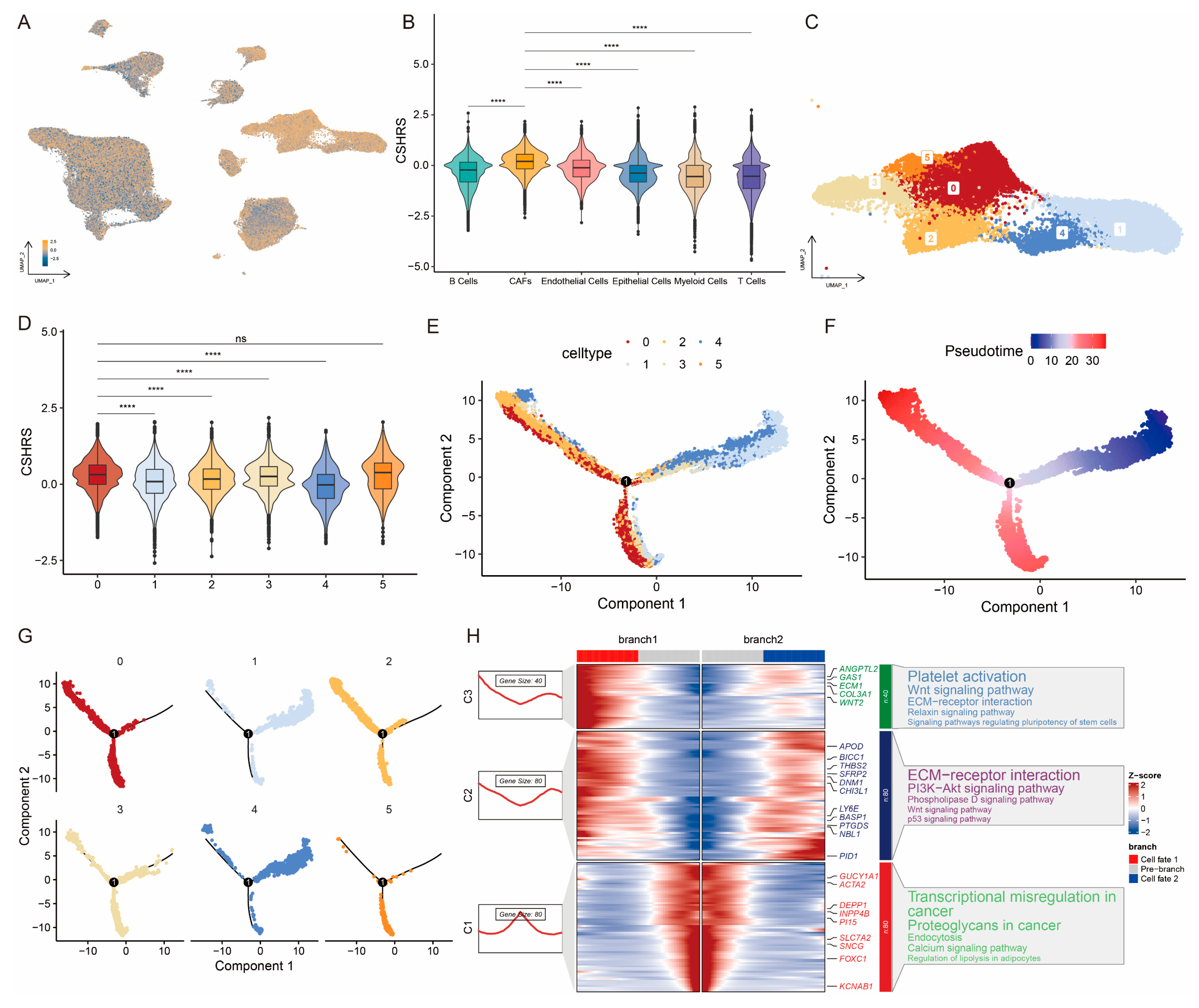
2.3. Construction and Validation of the CSHRS Risk Model
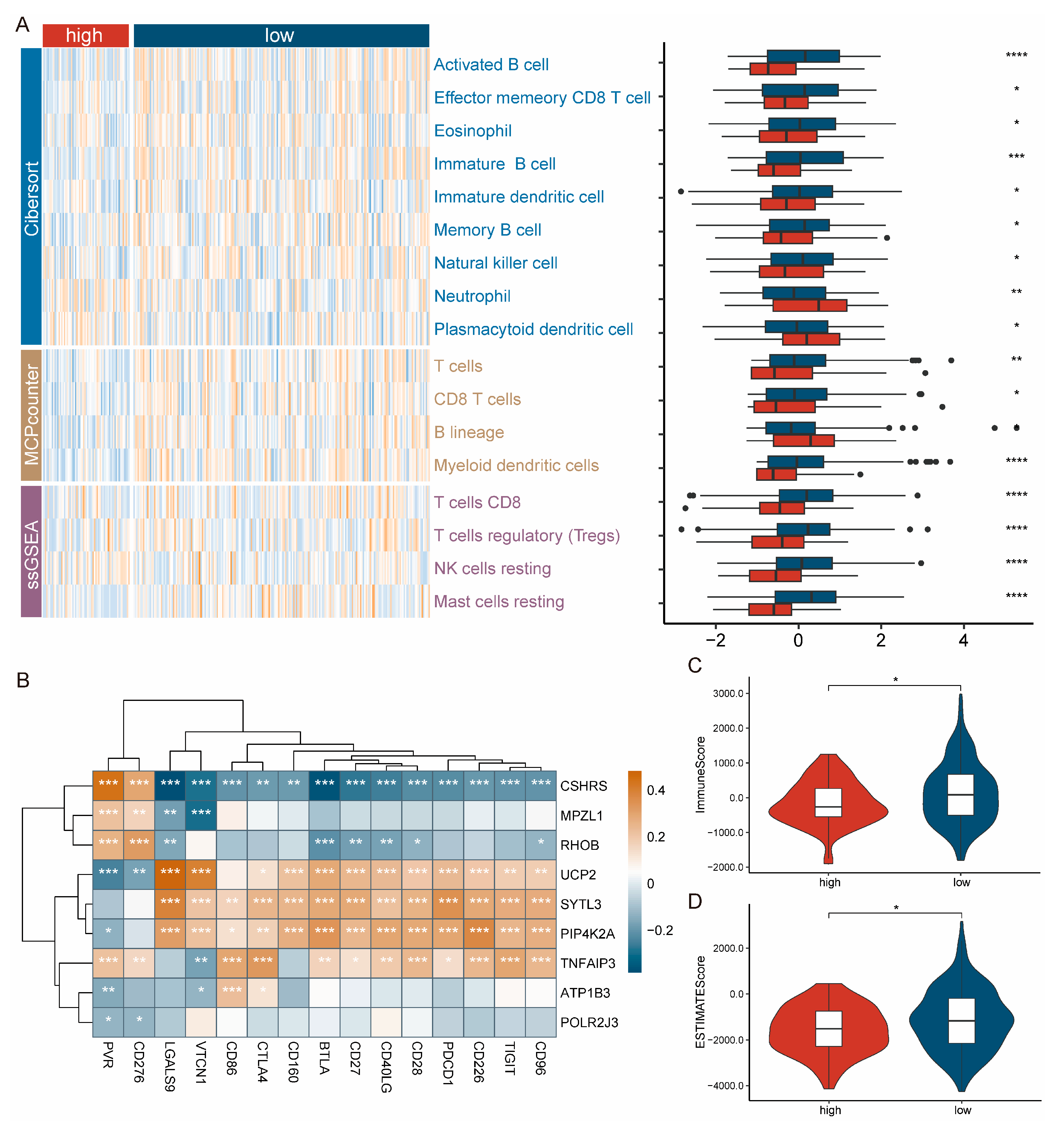
2.4. Patients with High-CSHRS Are Less Immune Infiltrated
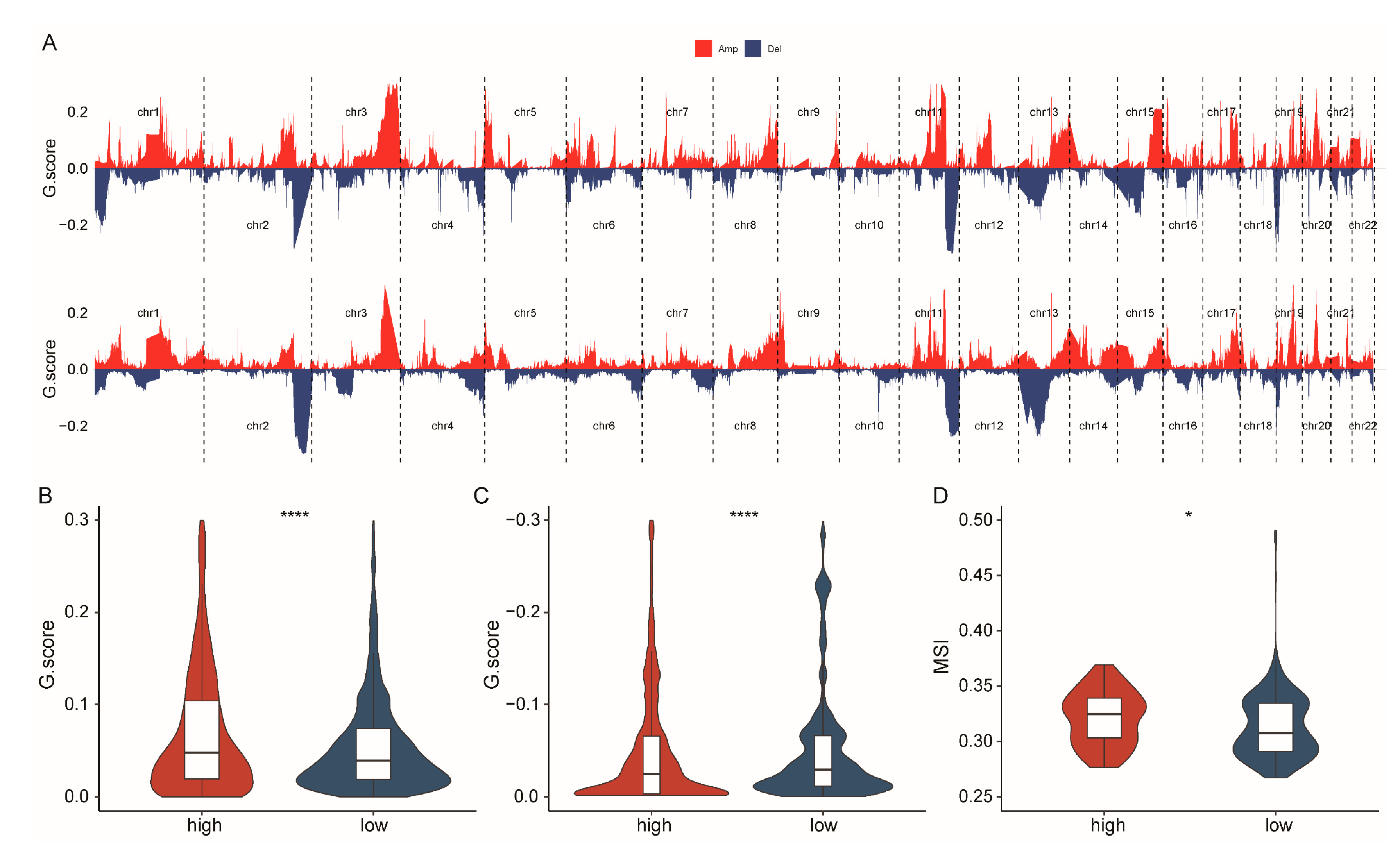
2.5. Patients with High-CSHRS Have Increased Genomic Instability
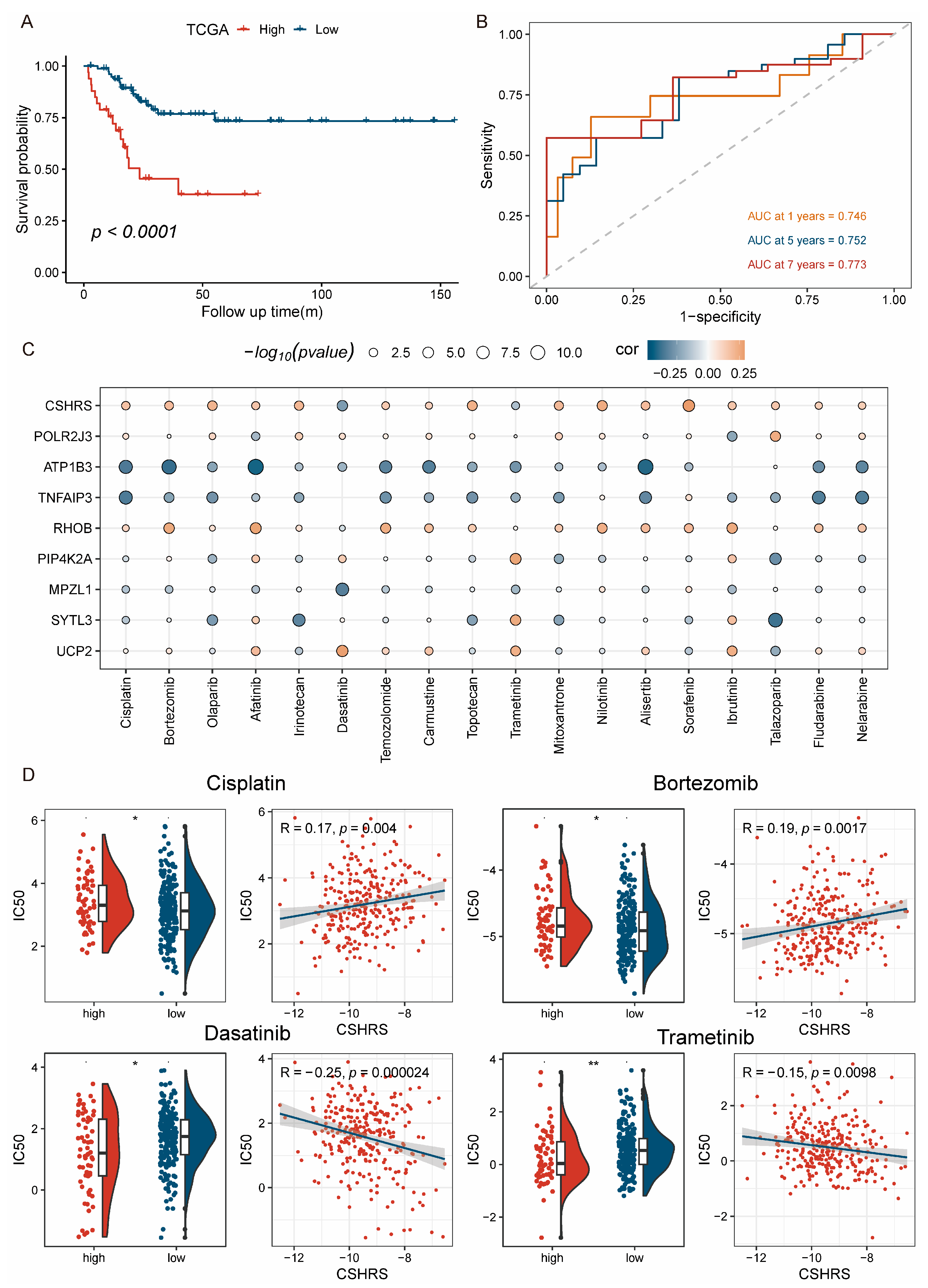
2.6. Patients with High-CSHRS Benefited Less from Chemoradiotherapy
2.7. Construction and Validation of the Nomogram Model
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Data Collection
4.2. scRNA-Seq Data Processing and Cell Annotation
4.3. Calculation of the Hallmarks Score
4.4. Detection and Selection of CESC-Specific Hypoxia-Responsive Genes
4.5. Construction of the CSHRS Risk Model
4.6. Immune Infiltration Analysis
4.7. Construction of the Nomogram Model
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pfaendler, K.S.; Tewari, K.S. Changing paradigms in the systemic treatment of advanced cervical cancer. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2016, 214, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogilvie, G.S.; van Niekerk, D.; Krajden, M.; Smith, L.W.; Cook, D.; Gondara, L.; Ceballos, K.; Quinlan, D.; Lee, M.; Martin, R.E.; et al. Effect of Screening With Primary Cervical HPV Testing vs Cytology Testing on High-grade Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia at 48 Months: The HPV FOCAL Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2018, 320, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Elfström, K.M.; Lagheden, C.; Eklund, C.; Sundström, K.; Sparén, P.; Dillner, J. Impact of cervical screening by human papillomavirus genotype: Population-based estimations. PLoS Med. 2023, 20, e1004304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenza, G.L. The hypoxic tumor microenvironment: A driving force for breast cancer progression. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1863, 382–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, C.; Yang, F.; Miao, S.; Liu, W.; Wang, C.; Shu, Y.; Shen, H. Role of hypoxia-induced exosomes in tumor biology. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bristow, R.G.; Hill, R.P. Hypoxia, DNA repair and genetic instability. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaupel, P. Hypoxia and Aggressive Tumor Phenotype: Implications for Therapy and Prognosis. The Oncologist 2008, 13, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, S.; McIntyre, A.; van Stiphout, R.G.; Winchester, L.M.; Wigfield, S.; Harris, A.L.; Buffa, F.M. Genomic alterations underlie a pan-cancer metabolic shift associated with tumour hypoxia. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukomoto, R.; Nashimoto, Y.; Terai, T.; Imaizumi, T.; Hiramoto, K.; Ino, K.; Yokokawa, R.; Miura, T.; Shiku, H. Oxygen consumption rate of tumour spheroids during necrotic-like core formation. Analyst 2020, 145, 6342–6348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wigerup, C.; Påhlman, S.; Bexell, D. Therapeutic targeting of hypoxia and hypoxia-inducible factors in cancer. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 164, 152–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, X.; Yang, F.; Shao, C.; Wei, K.; Xie, M.; Shen, H.; Shu, Y. Role of hypoxia in cancer therapy by regulating the tumor microenvironment. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Han, F.; Du, Y.; Shi, H.; Zhou, W. Hypoxic microenvironment in cancer: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic interventions. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wicks, E.E.; Semenza, G.L. Hypoxia-inducible factors: Cancer progression and clinical translation. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e159839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papalexi, E.; Satija, R. Single-cell RNA sequencing to explore immune cell heterogeneity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Z.; Li, J.; Cao, F.; Li, F. Integration of scRNA-Seq and Bulk RNA-Seq Reveals Molecular Characterization of the Immune Microenvironment in Acute Pancreatitis. Biomolecules 2022, 13, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, D.; Peng, M.; Tang, L.; Ouyang, J.; Xiong, F.; Guo, C.; Tang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liao, Q.; et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing in cancer research. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Silva, L.; Quevedo, L.; Varela, I. Tumor Functional Heterogeneity Unraveled by scRNA-seq Technologies. Trends Cancer 2020, 6, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meacham, C.E.; Morrison, S.J. Tumour heterogeneity and cancer cell plasticity. Nature 2013, 501, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedlund, E.; Deng, Q. Single-cell RNA sequencing: Technical advancements and biological applications. Mol. Asp. Med. 2018, 59, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Iliopoulos, D.; Zhang, Q.; Tang, Q.; Greenblatt, M.B.; Hatziapostolou, M.; Lim, E.; Tam, W.L.; Ni, M.; Chen, Y.; et al. XBP1 promotes triple-negative breast cancer by controlling the HIF1α pathway. Nature 2014, 508, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senft, D.; Ronai, Z.A. UPR, autophagy, and mitochondria crosstalk underlies the ER stress response. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2015, 40, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeNardo, D.G.; Ruffell, B. Macrophages as regulators of tumour immunity and immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, G.; Peng, X.; Wei, S.; Yang, S.; Li, X.; Huang, M.; Tang, S.; Jin, H.; Liu, J.; Zhang, S.; et al. Exosomes in the hypoxic TME: From release, uptake and biofunctions to clinical applications. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoppe-Seyler, K.; Bossler, F.; Braun, J.A.; Herrmann, A.L.; Hoppe-Seyler, F. The HPV E6/E7 Oncogenes: Key Factors for Viral Carcinogenesis and Therapeutic Targets. Trends Microbiol. 2018, 26, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koyasu, S.; Horita, S.; Saito, K.; Kobayashi, M.; Ishikita, H.; Chow, C.C.; Kambe, G.; Nishikawa, S.; Menju, T.; Morinibu, A.; et al. ZBTB2 links p53 deficiency to HIF-1-mediated hypoxia signaling to promote cancer aggressiveness. EMBO Rep. 2023, 24, e54042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.T.; Trzeciak, A.J.; Rojas, W.S.; Saavedra, P.; Chen, Y.T.; Chirayil, R.; Etchegaray, J.I.; Lucas, C.D.; Puleston, D.J.; Keshari, K.R.; et al. Metabolic adaptation supports enhanced macrophage efferocytosis in limited-oxygen environments. Cell Metab. 2023, 35, 316–331.e316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konieczny, P.; Xing, Y.; Sidhu, I.; Subudhi, I.; Mansfield, K.P.; Hsieh, B.; Biancur, D.E.; Larsen, S.B.; Cammer, M.; Li, D.; et al. Interleukin-17 governs hypoxic adaptation of injured epithelium. Science 2022, 377, eabg9302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Lee, A.R.; Choi, J.W.; Lee, C.R.; Cho, K.H.; Lee, J.H.; Cho, M.L. IL-17 Induces Autophagy Dysfunction to Promote Inflammatory Cell Death and Fibrosis in Keloid Fibroblasts via the STAT3 and HIF-1α Dependent Signaling Pathways. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 888719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangam, S.; Sun, X.; Schwantes-An, T.H.; Yegambaram, M.; Lu, Q.; Shi, Y.; Cook, T.; Fisher, A.; Frump, A.L.; Coleman, A.; et al. SOX17 Deficiency Mediates Pulmonary Hypertension: At the Crossroads of Sex, Metabolism, and Genetics. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2023, 207, 1055–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terekhanova, N.V.; Karpova, A.; Liang, W.W.; Strzalkowski, A.; Chen, S.; Li, Y.; Southard-Smith, A.N.; Iglesia, M.D.; Wendl, M.C.; Jayasinghe, R.G.; et al. Epigenetic regulation during cancer transitions across 11 tumour types. Nature 2023, 623, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, M.Z.; Jin, W.L. The updated landscape of tumor microenvironment and drug repurposing. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, F.F.; Liu, C.J.; Liu, L.L.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, A.Y. Expression profile of immune checkpoint genes and their roles in predicting immunotherapy response. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, bbaa176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R.; Zeisberg, M. Fibroblasts in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biffi, G.; Tuveson, D.A. Diversity and Biology of Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts. Physiol. Rev. 2021, 101, 147–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhowmick, N.A.; Neilson, E.G.; Moses, H.L. Stromal fibroblasts in cancer initiation and progression. Nature 2004, 432, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, L.; Peng, M.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Wan, X.; Hou, Y.; Qin, Y.; Yang, L.; Chen, S.; Zeng, H.; et al. Hypoxia-stimulated ATM activation regulates autophagy-associated exosome release from cancer-associated fibroblasts to promote cancer cell invasion. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2021, 10, e12146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwörer, S.; Cimino, F.V.; Ros, M.; Tsanov, K.M.; Ng, C.; Lowe, S.W.; Carmona-Fontaine, C.; Thompson, C.B. Hypoxia Potentiates the Inflammatory Fibroblast Phenotype Promoted by Pancreatic Cancer Cell-Derived Cytokines. Cancer Res. 2023, 83, 1596–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banushi, B.; Joseph, S.R.; Lum, B.; Lee, J.J.; Simpson, F. Endocytosis in cancer and cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2023, 23, 450–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.I.; Young, R.A. Transcriptional regulation and its misregulation in disease. Cell 2013, 152, 1237–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X. Targeting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, H.; Reale, M.; Ullah, H.; Sureda, A.; Tejada, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.J.; Xiao, J. Anti-cancer effects of polyphenols via targeting p53 signaling pathway: Updates and future directions. Biotechnol. Adv. 2020, 38, 107385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.K.; Choi, Y.L.; Kwon, M.; Park, P.J. Mechanisms and Consequences of Cancer Genome Instability: Lessons from Genome Sequencing Studies. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2016, 11, 283–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Feng, Y.L.; Wan, T.; Zhang, Y.N.; Cao, X.P.; Huang, Y.W.; Xiong, Y.; Huang, X.; Zheng, M.; Li, Y.F.; et al. Effectiveness of Sequential Chemoradiation vs Concurrent Chemoradiation or Radiation Alone in Adjuvant Treatment After Hysterectomy for Cervical Cancer: The STARS Phase 3 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2021, 7, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, R.; Dey, T.; Kumar, L.; Kar, S.; Sarkar, R.; Ghorai, M.; Malik, S.; Jha, N.K.; Vellingiri, B.; Kesari, K.K.; et al. Cellular landscaping of cisplatin resistance in cervical cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 153, 113345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Dong, W.; Ma, Y.; Dou, J.; Jiang, W.; Wang, L.; Wang, Q.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, M. Nanomedicines with high drug availability and drug sensitivity overcome hypoxia-associated drug resistance. Biomaterials 2023, 294, 122023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, C.; Qin, H.; Zhang, L. Identification and validation of a prognostic signature related to hypoxic tumor microenvironment in cervical cancer. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0269462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Wei, R.; Yao, S.; Meng, F.; Kong, L. HIF-1A as a prognostic biomarker related to invasion, migration and immunosuppression of cervical cancer. Heliyon 2024, 10, e24664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xiu, J.; Farrell, A.; Baca, Y.; Arai, H.; Battaglin, F.; Kawanishi, N.; Soni, S.; Zhang, W.; Millstein, J.; et al. Mutational analysis of microsatellite-stable gastrointestinal cancer with high tumour mutational burden: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2023, 24, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuma, H.S.; Watanabe, K.; Tsuchihashi, K.; Machida, R.; Sadachi, R.; Hirakawa, A.; Ariyama, H.; Kanai, M.; Kamikura, M.; Anjo, K.; et al. Phase II Trial of Nivolumab in Metastatic Rare Cancer with dMMR or MSI-H and Relation with Immune Phenotypic Analysis (the ROCK Trial). Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 29, 5079–5086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhao, C.; Xu, F.; Zhang, A.; Jin, M.; Zhang, K.; Liu, L.; Hua, Q.; Zhao, J.; Liu, J.; et al. Cisplatin-resistant NSCLC cells induced by hypoxia transmit resistance to sensitive cells through exosomal PKM2. Theranostics 2021, 11, 2860–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Costa, A.; Chowdhury, D.; Shapiro, G.I.; D’Andrea, A.D.; Konstantinopoulos, P.A. Targeting replication stress in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2023, 22, 38–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cybulla, E.; Vindigni, A. Leveraging the replication stress response to optimize cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2023, 23, 6–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takiguchi, E.; Nishimura, M.; Mineda, A.; Kawakita, T.; Abe, A.; Irahara, M. Growth inhibitory effect of the Src inhibitor dasatinib in combination with anticancer agents on uterine cervical adenocarcinoma cells. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 14, 4293–4299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kramer, B.; Kneissle, M.; Birk, R.; Rotter, N.; Aderhold, C. Tyrosine Kinase Inhibition in HPV-related Squamous Cell Carcinoma Reveals Beneficial Expression of cKIT and Src. Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 2723–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, Y.J.; Sa, J.K.; Lee, Y.; Kim, D.; Chang, N.; Cho, H.J.; Son, M.; Oh, M.Y.T.; Shin, K.; Lee, J.K.; et al. PIP4K2A as a negative regulator of PI3K in PTEN-deficient glioblastoma. J. Exp. Med. 2019, 216, 1120–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, D.; Tang, X.; Deng, H.; Yang, X.; Tao, J.; Xu, F.; Liu, Y.; Wu, K.; Wang, K.; Mei, Z.; et al. Metabolic Enzyme SLC27A5 Regulates PIP4K2A pre-mRNA Splicing as a Noncanonical Mechanism to Suppress Hepatocellular Carcinoma Metastasis. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, e2305374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prendergast, G.C. Actin’ up: RhoB in cancer and apoptosis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2001, 1, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Huang, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Tao, T.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, S.; Yang, J.; Chen, Z.S.; Cai, C.Y.; et al. Hsa-miR-3178/RhoB/PI3K/Akt, a novel signaling pathway regulates ABC transporters to reverse gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic cancer. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Jensen, M.A.; Zenklusen, J.C. A Practical Guide to The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA). Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 1418, 111–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, T.; Wilhite, S.E.; Ledoux, P.; Evangelista, C.; Kim, I.F.; Tomashevsky, M.; Marshall, K.A.; Phillippy, K.H.; Sherman, P.M.; Holko, M.; et al. NCBI GEO: Archive for functional genomics data sets--update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D991–D995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.S.; Chen, X.; Chen, T.T.; Zhu, J.W.; Tang, B.X.; Wang, A.K.; Dong, L.L.; Zhang, Z.W.; Sun, Y.L.; Yu, C.X.; et al. GSA-Human: Genome Sequence Archive for Human. Yi Chuan 2021, 43, 988–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.Y.; Kim, T.J.; Kim, J.Y.; Choi, C.H.; Do, I.G.; Song, S.Y.; Sohn, I.; Jung, S.H.; Bae, D.S.; Lee, J.W.; et al. Genetic profiling to predict recurrence of early cervical cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2013, 131, 650–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberzon, A.; Birger, C.; Thorvaldsdóttir, H.; Ghandi, M.; Mesirov, J.P.; Tamayo, P. The Molecular Signatures Database (MSigDB) hallmark gene set collection. Cell Syst. 2015, 1, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Furumichi, M.; Sato, Y.; Ishiguro-Watanabe, M.; Tanabe, M. KEGG: Integrating viruses and cellular organisms. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D545–D551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayakonda, A.; Lin, D.C.; Assenov, Y.; Plass, C.; Koeffler, H.P. Maftools: Efficient and comprehensive analysis of somatic variants in cancer. Genome Res. 2018, 28, 1747–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Ju, Z.; Zhao, W.; Wang, L.; Peng, Y.; Ge, Z.; Nagel, Z.D.; Zou, J.; Wang, C.; Kapoor, P.; et al. ARID1A deficiency promotes mutability and potentiates therapeutic antitumor immunity unleashed by immune checkpoint blockade. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Zeng, T.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wan, Y.; Shi, Z.; Cao, R.; Tang, H. Integrated bulk and single-cell transcriptomes reveal pyroptotic signature in prognosis and therapeutic options of hepatocellular carcinoma by combining deep learning. Brief. Bioinform. 2023, 25, bbad487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hänzelmann, S.; Castelo, R.; Guinney, J. GSVA: Gene set variation analysis for microarray and RNA-seq data. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langfelder, P.; Horvath, S. WGCNA: An R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charoentong, P.; Finotello, F.; Angelova, M.; Mayer, C.; Efremova, M.; Rieder, D.; Hackl, H.; Trajanoski, Z. Pan-cancer Immunogenomic Analyses Reveal Genotype-Immunophenotype Relationships and Predictors of Response to Checkpoint Blockade. Cell Rep. 2017, 18, 248–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Khodadoust, M.S.; Liu, C.L.; Newman, A.M.; Alizadeh, A.A. Profiling Tumor Infiltrating Immune Cells with CIBERSORT. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1711, 243–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becht, E.; Giraldo, N.A.; Lacroix, L.; Buttard, B.; Elarouci, N.; Petitprez, F.; Selves, J.; Laurent-Puig, P.; Sautès-Fridman, C.; Fridman, W.H.; et al. Estimating the population abundance of tissue-infiltrating immune and stromal cell populations using gene expression. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, K.; Zhang, S.; Shen, J.; Yu, M.; Su, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, K.; Liu, L.; Chen, X. Integrating Hypoxia Signatures from scRNA-seq and Bulk Transcriptomes for Prognosis Prediction and Precision Therapy in Cervical Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Endocervical Adenocarcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26031362
Yu K, Zhang S, Shen J, Yu M, Su Y, Wang Y, Zhou K, Liu L, Chen X. Integrating Hypoxia Signatures from scRNA-seq and Bulk Transcriptomes for Prognosis Prediction and Precision Therapy in Cervical Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Endocervical Adenocarcinoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(3):1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26031362
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Kexin, Shibo Zhang, Jiali Shen, Meini Yu, Yangguang Su, Ying Wang, Kun Zhou, Lei Liu, and Xiujie Chen. 2025. "Integrating Hypoxia Signatures from scRNA-seq and Bulk Transcriptomes for Prognosis Prediction and Precision Therapy in Cervical Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Endocervical Adenocarcinoma" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 3: 1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26031362
APA StyleYu, K., Zhang, S., Shen, J., Yu, M., Su, Y., Wang, Y., Zhou, K., Liu, L., & Chen, X. (2025). Integrating Hypoxia Signatures from scRNA-seq and Bulk Transcriptomes for Prognosis Prediction and Precision Therapy in Cervical Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Endocervical Adenocarcinoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(3), 1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26031362






