Endoplasmic Reticulum-Mitochondria Crosstalk in Fuchs Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy: Current Status and Future Prospects
Abstract
1. Fuchs Burden
2. Fuchs Pathogenesis
- (a)
- It remains unknown whether MAM disruptions are primary or secondary factors contributing to Fuchs’s pathophysiology.
- (b)
- How disrupted MAMs impair MAM proteins and their functions is also unknown.
- (c)
- Do MAM proteins mediate differential effects on ER or mitochondrial stress pathways that lead to CEnC apoptosis in FECD?
3. ER Stress and Corneal Endothelial Cells
4. ER Stress and FECD
5. Mitochondrial Stress and FECD
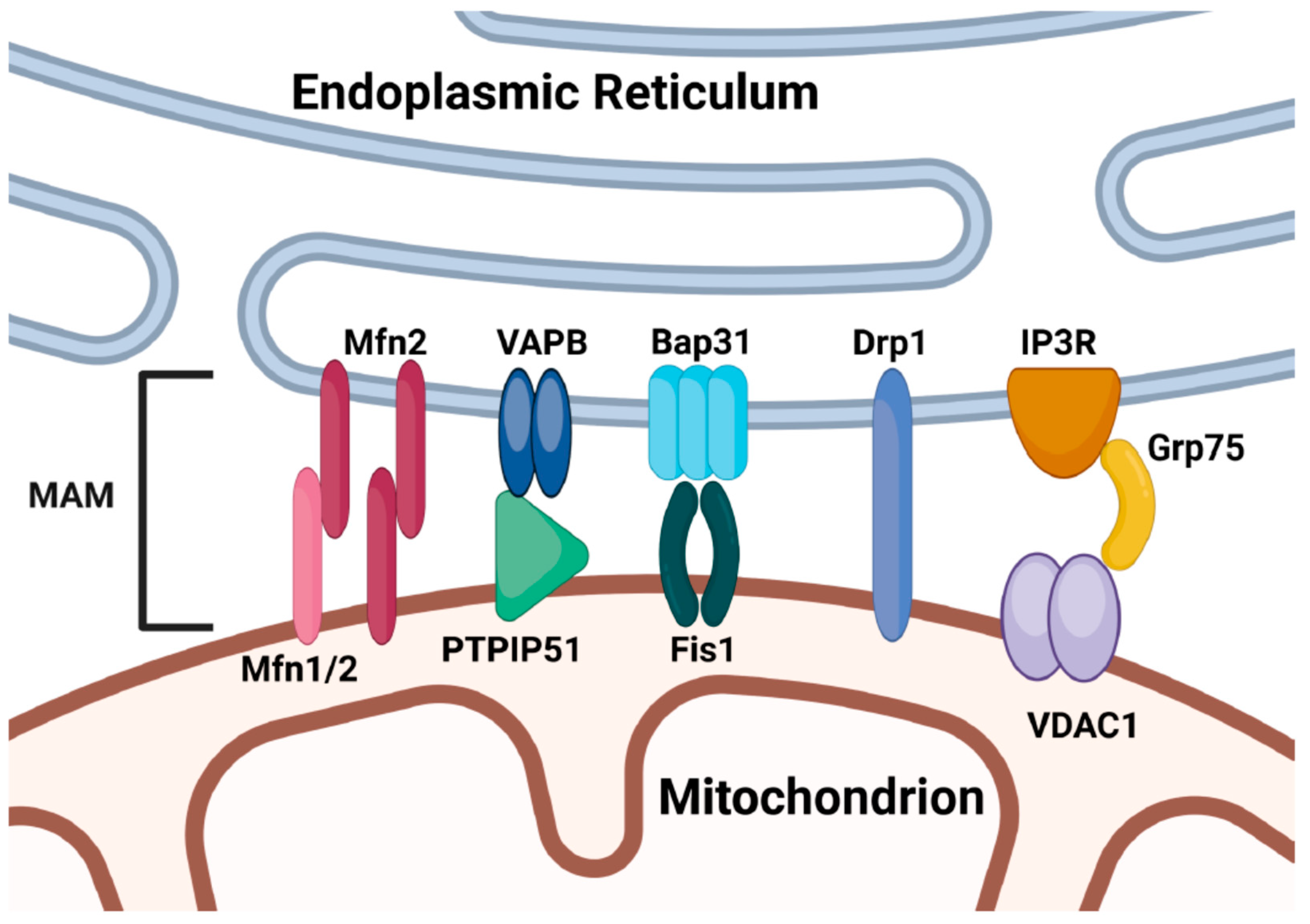
6. ER-Mitochondrial Crosstalk
6.1. MAM-Dependent ER-Mitochondrial Crosstalk
6.2. MAM-Independent ER-Mitochondrial Crosstalk
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Iliff, B.W.; Riazuddin, S.A.; Gottsch, J.D. The genetics of Fuchs’ corneal dystrophy. Expert Rev. Ophthalmol. 2012, 7, 363–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, A.Y.; Eberhart, C.G.; Jun, A.S. Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy: A neurodegenerative disorder? JAMA Ophthalmol. 2014, 132, 377–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krachmer, J.H.; Purcell, J.J., Jr.; Young, C.W.; Bucher, K.D. Corneal endothelial dystrophy: A study of 64 families. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1978, 96, 2036–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenblum, P.; Stark, W.J.; Maumenee, I.H.; Hirst, L.W.; Maumenee, A.E. Hereditary Fuchs’ Dystrophy. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1980, 90, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.B.; Parmar, U.P.S.; Kahale, F.; Jeng, B.H.; Jhanji, V. Prevalence and Economic Burden of Fuchs Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy in the Medicare Population in the United States. Cornea 2024, 43, 1022–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhalis, H.; Azizi, B.; Jurkunas, U.V. Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy. Ocul. Surf. 2010, 8, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kornmann, H.L.; Gedde, S.J. Glaucoma management after corneal transplantation surgeries. Curr. Opin. Ophthalmol. 2016, 27, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, M.O.; Price, D.A.; Price, F.W., Jr. Long-Term Risk of Steroid-Induced Ocular Hypertension/Glaucoma with Topical Prednisolone Acetate 1% After Descemet Stripping Endothelial Keratoplasty. Cornea 2024, 43, 323–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhaliwal, D.K.; Chirikov, V.; Schmier, J.; Rege, S.; Newton, S. Cost Burden of Endothelial Keratoplasty in Fuchs Endothelial Dystrophy: Real-World Analysis of a Commercially Insured US Population (2014–2019). Clin. Ophthalmol. 2022, 16, 1055–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong Tone, S.; Kocaba, V.; Bohm, M.; Wylegala, A.; White, T.L.; Jurkunas, U.V. Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy: The vicious cycle of Fuchs pathogenesis. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2021, 80, 100863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Wang, C.; Zhao, H.; He, Y.; Lan, B.; Sun, L.; Gao, Y. The MAMs Structure and Its Role in Cell Death. Cells 2021, 10, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Vliet, A.R.; Verfaillie, T.; Agostinis, P. New functions of mitochondria associated membranes in cellular signaling. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1843, 2253–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qureshi, S.; Lee, S.; Steidl, W.; Ritzer, L.; Parise, M.; Chaubal, A.; Kumar, V. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Disrupts Mitochondrial Bioenergetics, Dynamics and Causes Corneal Endothelial Cell Apoptosis. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2023, 64, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okumura, N.; Kitahara, M.; Okuda, H.; Hashimoto, K.; Ueda, E.; Nakahara, M.; Kinoshita, S.; Young, R.D.; Quantock, A.J.; Tourtas, T.; et al. Sustained Activation of the Unfolded Protein Response Induces Cell Death in Fuchs’ Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2017, 58, 3697–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qureshi, S.; Lee, S.; Ritzer, L.; Kim, S.Y.; Steidl, W.; Krest, G.J.; Kasi, A.; Kumar, V. ATF4 regulates mitochondrial dysfunction, mitophagy, and autophagy, contributing to corneal endothelial apoptosis under chronic ER stress in Fuchs dystrophy. bioRxiv 2024, 2024.2011.2014.623646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Shi, C.; He, M.; Xiong, S.; Xia, X. Endoplasmic reticulum stress: Molecular mechanism and therapeutic targets. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engler, C.; Kelliher, C.; Spitze, A.R.; Speck, C.L.; Eberhart, C.G.; Jun, A.S. Unfolded protein response in fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy: A unifying pathogenic pathway? Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2010, 149, 194–202.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, A.S.; Meng, H.; Ramanan, N.; Matthaei, M.; Chakravarti, S.; Bonshek, R.; Black, G.C.; Grebe, R.; Kimos, M. An alpha 2 collagen VIII transgenic knock-in mouse model of Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy shows early endothelial cell unfolded protein response and apoptosis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2012, 21, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Rong, Z.; Gong, X.; Zhou, Z.; Sharma, V.K.; Xing, C.; Watts, J.K.; Corey, D.R.; Mootha, V.V. Oligonucleotides targeting TCF4 triplet repeat expansion inhibit RNA foci and mis-splicing in Fuchs’ dystrophy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2018, 27, 1015–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, T.; Okumura, N.; Ikegawa, M.; Toyama, Y.; Nirasawa, T.; Mascarelli, F.; Vaitinadapoule, H.; Aouimeur, I.; He, Z.; Gain, P.; et al. Shotgun proteomics identification of proteins expressed in the Descemet’s membrane of patients with Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 10401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okumura, N.; Hashimoto, K.; Kitahara, M.; Okuda, H.; Ueda, E.; Watanabe, K.; Nakahara, M.; Sato, T.; Kinoshita, S.; Tourtas, T.; et al. Activation of TGF-β signaling induces cell death via the unfolded protein response in Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, H.; Matthaei, M.; Ramanan, N.; Grebe, R.; Chakravarti, S.; Speck, C.L.; Kimos, M.; Vij, N.; Eberhart, C.G.; Jun, A.S. L450W and Q455K Col8a2 knock-in mouse models of Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy show distinct phenotypes and evidence for altered autophagy. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013, 54, 1887–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Jurkunas, U.V. Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Mitophagy in Fuchs Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy. Cells 2021, 10, 1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halilovic, A.; Schmedt, T.; Benischke, A.S.; Hamill, C.; Chen, Y.; Santos, J.H.; Jurkunas, U.V. Menadione-Induced DNA Damage Leads to Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Fragmentation During Rosette Formation in Fuchs Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2016, 24, 1072–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Miyajima, T.; Melangath, G.; Miyai, T.; Vasanth, S.; Deshpande, N.; Kumar, V.; Ong Tone, S.; Gupta, R.; Zhu, S.; et al. Ultraviolet A light induces DNA damage and estrogen-DNA adducts in Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy causing females to be more affected. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyai, T.; Vasanth, S.; Melangath, G.; Deshpande, N.; Kumar, V.; Benischke, A.S.; Chen, Y.; Price, M.O.; Price, F.W., Jr.; Jurkunas, U.V. Activation of PINK1-Parkin–Mediated Mitophagy Degrades Mitochondrial Quality Control Proteins in Fuchs Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy. Am. J. Pathol. 2019, 189, 2061–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benischke, A.S.; Vasanth, S.; Miyai, T.; Katikireddy, K.R.; White, T.; Chen, Y.; Halilovic, A.; Price, M.; Price, F., Jr.; Liton, P.B.; et al. Activation of mitophagy leads to decline in Mfn2 and loss of mitochondrial mass in Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gendron, S.P.; Theriault, M.; Proulx, S.; Brunette, I.; Rochette, P.J. Restoration of Mitochondrial Integrity, Telomere Length, and Sensitivity to Oxidation by In Vitro Culture of Fuchs’ Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy Cells. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2016, 57, 5926–5934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czarny, P.; Seda, A.; Wielgorski, M.; Binczyk, E.; Markiewicz, B.; Kasprzak, E.; Jimenez-Garcia, M.P.; Grabska-Liberek, I.; Pawlowska, E.; Blasiak, J.; et al. Mutagenesis of mitochondrial DNA in Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy. Mutat. Res. 2014, 760, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashraf, S.; Deshpande, N.; Vasanth, S.; Melangath, G.; Wong, R.J.; Zhao, Y.; Price, M.O.; Price, F.W., Jr.; Jurkunas, U.V. Dysregulation of DNA repair genes in Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy. Exp. Eye Res. 2023, 231, 109499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Methot, S.; Proulx, S.; Brunette, I.; Rochette, P.J. The Presence of Guttae in Fuchs Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy Explants Correlates with Cellular Markers of Disease Progression. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2023, 64, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Methot, S.; Proulx, S.; Brunette, I.; Rochette, P.J. Rescuing cellular function in Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy by healthy exogenous mitochondrial internalization. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedskog, L.; Pinho, C.M.; Filadi, R.; Ronnback, A.; Hertwig, L.; Wiehager, B.; Larssen, P.; Gellhaar, S.; Sandebring, A.; Westerlund, M.; et al. Modulation of the endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria interface in Alzheimer’s disease and related models. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 7916–7921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maity, S.; Komal, P.; Kumar, V.; Saxena, A.; Tungekar, A.; Chandrasekar, V. Impact of ER Stress and ER-Mitochondrial Crosstalk in Huntington’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vig, S.; Lambooij, J.M.; Zaldumbide, A.; Guigas, B. Endoplasmic Reticulum-Mitochondria Crosstalk and Beta-Cell Destruction in Type 1 Diabetes. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 669492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, H.; Ou, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Sun, K.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Deng, W.; Zeng, W.; Xia, R.; et al. XBP1 modulates endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria crosstalk via regulating NLRP3 in renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. Cell Death Discov. 2023, 9, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janikiewicz, J.; Szymanski, J.; Malinska, D.; Patalas-Krawczyk, P.; Michalska, B.; Duszynski, J.; Giorgi, C.; Bonora, M.; Dobrzyn, A.; Wieckowski, M.R. Mitochondria-associated membranes in aging and senescence: Structure, function, and dynamics. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shyam, R.; Ogando, D.G.; Bonanno, J.A. Mitochondrial ROS in Slc4a11 KO Corneal Endothelial Cells Lead to ER Stress. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 878395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanges, D.; Comitato, A.; Tammaro, R.; Marigo, V. Apoptosis in retinal degeneration involves cross-talk between apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF) and caspase-12 and is blocked by calpain inhibitors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 17366–17371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunaga, D.; Sreekumar, P.G.; Ishikawa, K.; Terasaki, H.; Barron, E.; Cohen, P.; Kannan, R.; Hinton, D.R. Humanin Protects RPE Cells from Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Induced Apoptosis by Upregulation of Mitochondrial Glutathione. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreekumar, P.G.; Hinton, D.R.; Kannan, R. Endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondrial crosstalk: A novel role for the mitochondrial peptide humanin. Neural. Regen. Res. 2017, 12, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patergnani, S.; Suski, J.M.; Agnoletto, C.; Bononi, A.; Bonora, M.; De Marchi, E.; Giorgi, C.; Marchi, S.; Missiroli, S.; Poletti, F.; et al. Calcium signaling around Mitochondria Associated Membranes (MAMs). Cell Commun. Signal. 2011, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, T.; Domingues, M.R.; Moreira, P.I.; Pereira, C.F. A Perspective on the Link between Mitochondria-Associated Membranes (MAMs) and Lipid Droplets Metabolism in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Biology 2023, 12, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yao, J.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.; Shi, X. Mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum membranes (MAMs): Possible therapeutic targets in heart failure. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 10, 1083935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paillusson, S.; Stoica, R.; Gomez-Suaga, P.; Lau, D.H.W.; Mueller, S.; Miller, T.; Miller, C.C.J. There’s Something Wrong with my MAM; the ER–Mitochondria Axis and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Trends Neurosci. 2016, 39, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoudam, T.; Jeon, J.H.; Ha, C.M.; Lee, I.K. Role of Mitochondria-Associated Endoplasmic Reticulum Membrane in Inflammation-Mediated Metabolic Diseases. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 1851420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Sun, C.; Gong, Q.; Feng, D. Mitochondria-Associated Endoplasmic Reticulum Membranes in Breast Cancer. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 629669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, X. Endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria tethering in neurodegenerative diseases. Transl. Neurodegener. 2017, 6, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vos, K.J.; Morotz, G.M.; Stoica, R.; Tudor, E.L.; Lau, K.F.; Ackerley, S.; Warley, A.; Shaw, C.E.; Miller, C.C. VAPB interacts with the mitochondrial protein PTPIP51 to regulate calcium homeostasis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2012, 21, 1299–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasawa, R.; Mahul-Mellier, A.L.; Datler, C.; Pazarentzos, E.; Grimm, S. Fis1 and Bap31 bridge the mitochondria-ER interface to establish a platform for apoptosis induction. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 556–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Stefani, D.; Bononi, A.; Romagnoli, A.; Messina, A.; De Pinto, V.; Pinton, P.; Rizzuto, R. VDAC1 selectively transfers apoptotic Ca2+ signals to mitochondria. Cell Death Differ. 2012, 19, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Brito, O.M.; Scorrano, L. Mitofusin 2 tethers endoplasmic reticulum to mitochondria. Nature 2008, 456, 605–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filadi, R.; Greotti, E.; Turacchio, G.; Luini, A.; Pozzan, T.; Pizzo, P. Mitofusin 2 ablation increases endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria coupling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E2174–E2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naon, D.; Zaninello, M.; Giacomello, M.; Varanita, T.; Grespi, F.; Lakshminaranayan, S.; Serafini, A.; Semenzato, M.; Herkenne, S.; Hernandez-Alvarez, M.I.; et al. Critical reappraisal confirms that Mitofusin 2 is an endoplasmic reticulum–mitochondria tether. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 11249–11254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verfaillie, T.; Rubio, N.; Garg, A.D.; Bultynck, G.; Rizzuto, R.; Decuypere, J.P.; Piette, J.; Linehan, C.; Gupta, S.; Samali, A.; et al. PERK is required at the ER-mitochondrial contact sites to convey apoptosis after ROS-based ER stress. Cell Death Differ. 2012, 19, 1880–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, A.; Nagashima, S.; Tokuyama, T.; Amo, T.; Matsuki, Y.; Ishido, S.; Kudo, Y.; McBride, H.M.; Fukuda, T.; Matsushita, N.; et al. MITOL regulates endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria contacts via Mitofusin2. Mol. Cell 2013, 51, 20–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, K.; Nagashima, S.; Shiiba, I.; Uda, A.; Tokuyama, T.; Ito, N.; Fukuda, T.; Matsushita, N.; Ishido, S.; Iwawaki, T.; et al. MITOL prevents ER stress-induced apoptosis by IRE1α ubiquitylation at ER–mitochondria contact sites. EMBO J. 2019, 38, e100999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cali, T.; Ottolini, D.; Negro, A.; Brini, M. Enhanced parkin levels favor ER-mitochondria crosstalk and guarantee Ca2+ transfer to sustain cell bioenergetics. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1832, 495–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basso, V.; Marchesan, E.; Peggion, C.; Chakraborty, J.; von Stockum, S.; Giacomello, M.; Ottolini, D.; Debattisti, V.; Caicci, F.; Tasca, E.; et al. Regulation of ER-mitochondria contacts by Parkin via Mfn2. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 138, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Ma, X.; Fujioka, H.; Liu, J.; Chen, S.; Zhu, X. DJ-1 regulates the integrity and function of ER-mitochondria association through interaction with IP3R3-Grp75-VDAC1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 25322–25328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitar, M.S.; Liu, C.; Ziaei, A.; Chen, Y.; Schmedt, T.; Jurkunas, U.V. Decline in DJ-1 and decreased nuclear translocation of Nrf2 in Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 5806–5813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Cui, H.; Xie, N.; Banerjee, S.; Liu, R.M.; Dai, H.; Thannickal, V.J.; Liu, G. ATF4 Mediates Mitochondrial Unfolded Protein Response in Alveolar Epithelial Cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2020, 63, 478–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perea, V.; Cole, C.; Lebeau, J.; Dolina, V.; Baron, K.R.; Madhavan, A.; Kelly, J.W.; Grotjahn, D.A.; Wiseman, R.L. PERK signaling promotes mitochondrial elongation by remodeling membrane phosphatidic acid. EMBO J. 2023, 42, e113908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, L.; Zhong, W.; Dong, H.; Guo, W.; Sun, X.; Zhang, W.; Yue, R.; Li, T.; Griffiths, A.; Ahmadi, A.R.; et al. ATF4 activation promotes hepatic mitochondrial dysfunction by repressing NRF1–TFAM signalling in alcoholic steatohepatitis. Gut 2021, 70, 1933–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dlamini, M.B.; Gao, Z.; Hasenbilige; Jiang, L.; Geng, C.; Li, Q.; Shi, X.; Liu, Y.; Cao, J. The crosstalk between mitochondrial dysfunction and endoplasmic reticulum stress promoted ATF4-mediated mitophagy induced by hexavalent chromium. Environ. Toxicol. 2021, 36, 1162–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebeau, J.; Saunders, J.M.; Moraes, V.W.R.; Madhavan, A.; Madrazo, N.; Anthony, M.C.; Wiseman, R.L. The PERK Arm of the Unfolded Protein Response Regulates Mitochondrial Morphology during Acute Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. Cell Rep. 2018, 22, 2827–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, J.; Kim, D.K.; Choi, W.; Koo, S.H.; Lee, C.H.; Back, S.H.; Kaufman, R.J.; Choi, H.S. Transcriptional cross talk between orphan nuclear receptor ERRγ and transmembrane transcription factor ATF6α coordinates endoplasmic reticulum stress response. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 6960–6974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Halling, J.F.; Pilegaard, H. PGC-1α-mediated regulation of mitochondrial function and physiological implications. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2020, 45, 927–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, W.C.; Chan, P.; Wissinger, B.; Vincent, A.; Skorczyk-Werner, A.; Krawczynski, M.R.; Kaufman, R.J.; Tsang, S.H.; Heon, E.; Kohl, S.; et al. Achromatopsia mutations target sequential steps of ATF6 activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.J.; Diaz-Aguilar, M.S.; Min, H.; Choi, J.; Valdez Duran, D.A.; Grandjean, J.M.; Wiseman, R.L.; Kroeger, H.; Lin, J.H. Mitochondria and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Retinal Organoids from Patients with Vision Loss. Am. J. Pathol. 2023, 193, 1721–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, T.; Liang, X.; Liu, H.; Zhang, F.; Meng, W.; Hu, F. Mitochondrial stress protein HSP60 regulates ER stress-induced hepatic lipogenesis. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2020, 64, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidramagowda Patil, S.; Soundararajan, R.; Fukumoto, J.; Breitzig, M.; Hernandez-Cuervo, H.; Alleyn, M.; Lin, M.; Narala, V.R.; Lockey, R.; Kolliputi, N.; et al. Mitochondrial Protein Akap1 Deletion Exacerbates Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Mice Exposed to Hyperoxia. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 762840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Protein | Model | Role in Apoptosis | Role in FECD | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PERK | Immortalized human CEnCs from FECD | Apoptosis inducer | Upregulated | [14] |
| IRE1α | Immortalized human CEnCs from FECD | Apoptosis inducer | Upregulated | [14] |
| CHOP | Human FECD specimens | Apoptosis inducer | Upregulated | [17] |
| Immortalized human CEnCs from FECD | [14] | |||
| Normal HCEnC-21T cells treated with ER stressor tunicamycin | [13] | |||
| L450W, Q455K Col8a2 Knock-In Mouse Models of Fuchs Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy | [22] | |||
| eIF2α | Human FECD specimens | Apoptosis inducer | Upregulated | [17] |
| HCEnC-21T cells treated with tunicamycin | [13] | |||
| GRP78 | Human FECD specimens | Apoptosis inducer | Upregulated | [17] |
| Immortalized human CEnCs from FECD | [13,14] | |||
| L450W, Q455K Col8a2 Knock-In Mouse Models of Fuchs Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy | [22] | |||
| XBP1 | HCEnC-21T cells treated with tunicamycin and Immortalized human CEnCs from FECD | Apoptosis inducer | Upregulated | [13] |
| Protein | Model | Role in Fuchs | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mfn2 | Human FECD specimens, Human FECD cell lines, normal and FECD cell lines treated with mitochondrial depolarization agent, Carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenyl hydrazone (CCCP) | Downregulated and involved in altered mitochondria quality control/mitophagy in FECD | [27] |
| Parkin | Human FECD specimens, Normal HCEnC-21T cell line treated with oxidative stress inducer, menadione and Human FECD cell line treated with CCCP | Upregulated and implicated in altered mitophagy in FECD | [26] |
| Fis-1 | Normal HCEnC-21T cell line treated with tunicamycin | Upregulated and contributes to mitochondrial fragmentation in FECD | [13] |
| Drp1 | HCEnC-21T cell line treated with tunicamycin | Upregulated and contributes to mitochondrial fragmentation in FECD | [13] |
| Human FECD specimens | Upregulated and contributes to altered mitochondria quality control/dynamics in FECD | [26] | |
| PINK1 | Human FECD specimens | Upregulated and involved in altered mitochondria quality control/mitophagy in FECD | [26] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kasi, A.; Steidl, W.; Kumar, V. Endoplasmic Reticulum-Mitochondria Crosstalk in Fuchs Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy: Current Status and Future Prospects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 894. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26030894
Kasi A, Steidl W, Kumar V. Endoplasmic Reticulum-Mitochondria Crosstalk in Fuchs Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy: Current Status and Future Prospects. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(3):894. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26030894
Chicago/Turabian StyleKasi, Anisha, William Steidl, and Varun Kumar. 2025. "Endoplasmic Reticulum-Mitochondria Crosstalk in Fuchs Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy: Current Status and Future Prospects" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 3: 894. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26030894
APA StyleKasi, A., Steidl, W., & Kumar, V. (2025). Endoplasmic Reticulum-Mitochondria Crosstalk in Fuchs Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy: Current Status and Future Prospects. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(3), 894. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26030894






