Pseudomonas aeruginosa Vaccine Development: Lessons, Challenges, and Future Innovations
Abstract
1. Pseudomonas aeruginosa: A Clinically Relevant Pathogen
2. Pathogenesis and Virulence Factors of P. aeruginosa
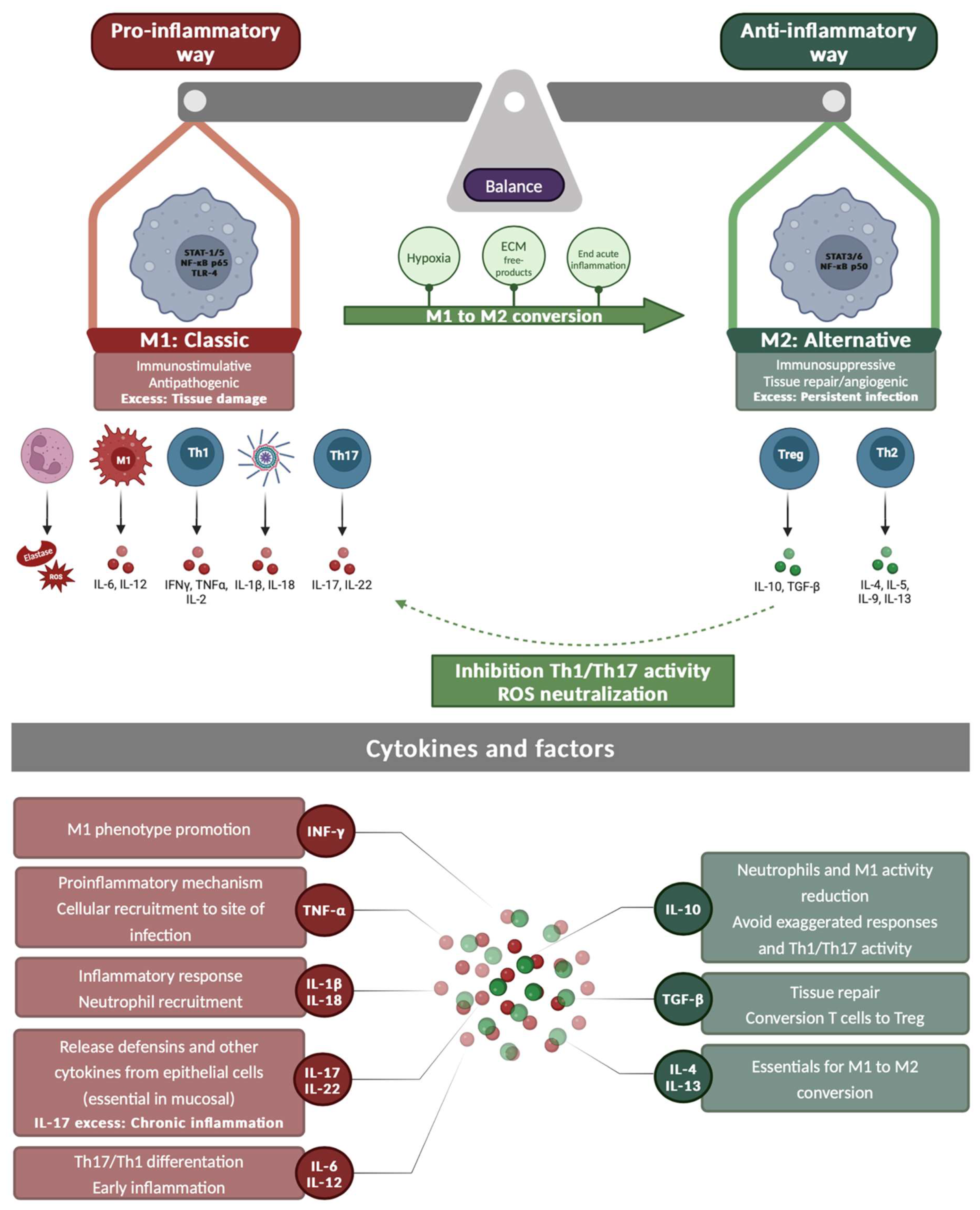
3. Immunology of P. aeruginosa Infections
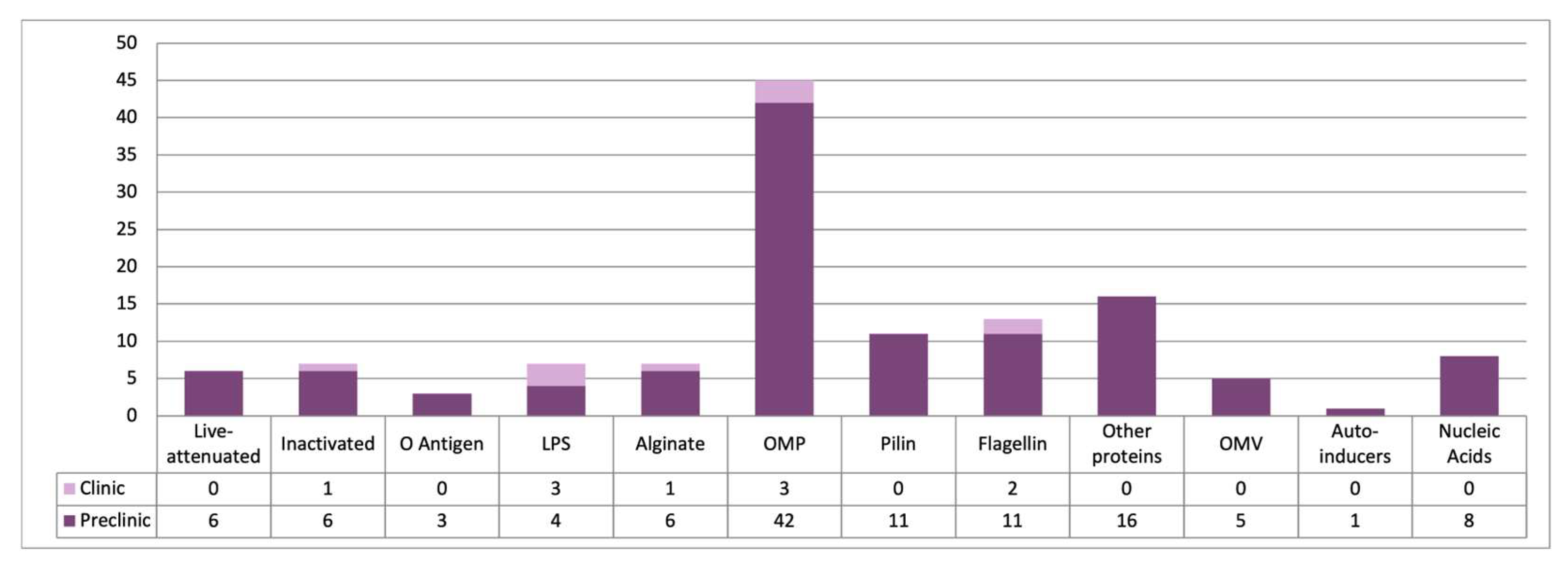
4. Vaccination Against P. aeruginosa
4.1. Live-Attenuated Vaccines
4.1.1. Live Auxotrophic Vaccines
4.1.2. Recombinant Vaccines with Attenuated Carriers
4.1.3. Killed but Metabolically Active (KBMA) Vaccines
4.2. Inactivated Vaccines
4.3. LPS-Based Vaccines
4.4. Alginate-Based Vaccines
4.5. OMP-Based Vaccines
4.6. Pili-Based Vaccines
4.7. Flagellin-Based Vaccines
4.8. Other Protein-Based Vaccines
4.9. Outer Membrane Vesicle-Based Vaccines
4.10. Autoinducer Vaccines
4.11. Nucleic Acid Vaccines
5. Conclusions and Future Prospects
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Ten Threats to Global Health in 2019; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, C.J.L.; Ikuta, K.S.; Sharara, F.; Swetschinski, L.; Aguilar, G.R.; Gray, A.; Han, C.; Bisignano, C.; Rao, P.; Wool, E.; et al. Global Burden of Bacterial Antimicrobial Resistance in 2019: A Systematic Analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Global Antimicrobial Resistance and Use Surveillance System (GLASS) Report 2022; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022; p. 82. [Google Scholar]
- Pirnay, J.-P.; Bilocq, F.; Pot, B.; Cornelis, P.; Zizi, M.; Van Eldere, J.; Deschaght, P.; Vaneechoutte, M.; Jennes, S.; Pitt, T.; et al. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Population Structure Revisited. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiner-Lastinger, L.M.; Abner, S.; Edwards, J.R.; Kallen, A.J.; Karlsson, M.; Magill, S.S.; Pollock, D.; See, I.; Soe, M.M.; Walters, M.S.; et al. Antimicrobial-Resistant Pathogens Associated with Adult Healthcare-Associated Infections: Summary of Data Reported to the National Healthcare Safety Network, 2015–2017. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2020, 41, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raoofi, S.; Pashazadeh Kan, F.; Rafiei, S.; Hosseinipalangi, Z.; Noorani Mejareh, Z.; Khani, S.; Abdollahi, B.; Seyghalani Talab, F.; Sanaei, M.; Zarabi, F.; et al. Global Prevalence of Nosocomial Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0274248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irek, E.O.; Amupitan, A.A.; Obadare, T.O.; Aboderin, A.O. A Systematic Review of Healthcare-Associated Infections in Africa: An Antimicrobial Resistance Perspective. Afr. J. Lab. Med. 2018, 7, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MSD Manual. Pseudomonas and Related Infections. 2022. Available online: https://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/infectious-diseases/gram-negative-bacilli/pseudomonas-and-related-infections (accessed on 17 September 2024).
- Killough, M.; Rodgers, A.M.; Ingram, R.J. Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Recent Advances in Vaccine Development. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hortal, J.; Muñoz, P.; Cuerpo, G.; Litvan, H.; Rosseel, P.M.; Bouza, E. Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia in Patients Undergoing Major Heart Surgery: An Incidence Study in Europe. Crit. Care 2009, 13, R80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berra, L.; Sampson, J.; Wiener-Kronish, J. Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Acute Lung Injury or Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia? Minerva Anestesiol. 2010, 76, 824–832. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chou, C.-C.; Shen, C.-F.; Chen, S.-J.; Chen, H.-M.; Wang, Y.-C.; Chang, W.-S.; Chang, Y.-T.; Chen, W.-Y.; Huang, C.-Y.; Kuo, C.-C.; et al. Recommendations and Guidelines for the Treatment of Pneumonia in Taiwan. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2019, 52, 172–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jean, S.-S.; Chang, Y.-C.; Lin, W.-C.; Lee, W.-S.; Hsueh, P.-R.; Hsu, C.-W. Epidemiology, Treatment, and Prevention of Nosocomial Bacterial Pneumonia. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luyt, C.-E.; Hekimian, G.; Koulenti, D.; Chastre, J. Microbial Cause of ICU-Acquired Pneumonia: Hospital-Acquired Pneumonia versus Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2018, 24, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anwar, S.; Peng, J.-L.; Zahid, K.R.; Zhou, Y.-M.; Ali, Q.; Qiu, C.-R. Cystic Fibrosis: Understanding Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Regulator Mutation Classification and Modulator Therapies. Adv. Respir. Med. 2024, 92, 263–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elborn, J.S. Cystic Fibrosis. Lancet 2016, 388, 2519–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, M.I.; Prince, A. Opportunistic Infections in Lung Disease: Pseudomonas Infections in Cystic Fibrosis. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2007, 7, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarych, D.; Augustynowicz-Kopec, E.; Iwanska, A.; Parniewski, P.; Majchrzak, M. Molecular Analysis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Strains Isolated from Cystic Fibrosis Patients. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strateva, T.; Mitov, I. Contribution of an Arsenal of Virulence Factors to Pathogenesis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infections. Ann. Microbiol. 2011, 61, 717–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadal Jimenez, P.; Koch, G.; Thompson, J.A.; Xavier, K.B.; Cool, R.H.; Quax, W.J. The Multiple Signaling Systems Regulating Virulence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2012, 76, 46–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, D.; Schneper, L.; Kumari, H.; Mathee, K. A Dynamic and Intricate Regulatory Network Determines Pseudomonas aeruginosa Virulence. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurado-Martín, I.; Sainz-Mejías, M.; McClean, S. Pseudomonas aeruginosa: An Audacious Pathogen with an Adaptable Arsenal of Virulence Factors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huszczynski, S.M.; Lam, J.S.; Khursigara, C.M. The Role of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Lipopolysaccharide in Bacterial Pathogenesis and Physiology. Pathogens 2019, 9, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Yoon, S.S. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilm, a Programmed Bacterial Life for Fitness. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 27, 1053–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, E.E.; Wozniak, D.J. Pseudomonas Biofilm Matrix Composition and Niche Biology. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 36, 893–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, L.R.; D’Argenio, D.A.; MacCoss, M.J.; Zhang, Z.; Jones, R.A.; Miller, S.I. Aminoglycoside Antibiotics Induce Bacterial Biofilm Formation. Nature 2005, 436, 1171–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goltermann, L.; Tolker-Nielsen, T. Importance of the Exopolysaccharide Matrix in Antimicrobial Tolerance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Aggregates. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e02696-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams McMackin, E.A.; Djapgne, L.; Corley, J.M.; Yahr, T.L. Fitting Pieces into the Puzzle of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Type III Secretion System Gene Expression. J. Bacteriol. 2019, 201, e00209-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauser, A.R. The Type III Secretion System of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Infection by Injection. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 654–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sana, T.G.; Berni, B.; Bleves, S. The T6SSs of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Strain PAO1 and Their Effectors: Beyond Bacterial-Cell Targeting. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2016, 6, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarzer, C.; Fischer, H.; Machen, T.E. Chemotaxis and Binding of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to Scratch-Wounded Human Cystic Fibrosis Airway Epithelial Cells. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haiko, J.; Westerlund-Wikström, B. The Role of the Bacterial Flagellum in Adhesion and Virulence. Biology 2013, 2, 1242–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, T.; Bardiaux, B.; Francetic, O.; Izadi-Pruneyre, N.; Nilges, M. Structure and Function of Minor Pilins of Type IV Pili. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2020, 209, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perraud, Q.; Cantero, P.; Roche, B.; Gasser, V.; Normant, V.P.; Kuhn, L.; Hammann, P.; Mislin, G.L.A.; Ehret-Sabatier, L.; Schalk, I.J. Phenotypic Adaption of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by Hacking Siderophores Produced by Other Microorganisms. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2020, 19, 589–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paola, T.P. Visión panorámica del sistema inmune. Rev. Medica Clin. Las Condes 2012, 23, 446–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sainz-Mejías, M.; Jurado-Martín, I.; McClean, S. Understanding Pseudomonas aeruginosa–Host Interactions: The Ongoing Quest for an Efficacious Vaccine. Cells 2020, 9, 2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavoie, E.G.; Wangdi, T.; Kazmierczak, B.I. Innate Immune Responses to Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection. Microbes Infect. 2011, 13, 1133–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, A.E.; Liggitt, H.D.; Hawn, T.R.; Skerrett, S.J. Role of Toll-like Receptor 5 in the Innate Immune Response to Acute P. aeruginosa Pneumonia. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2009, 297, L1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.L.; Harrison, R.E.; Grinstein, S. Phagocytosis by Neutrophils. Microbes Infect. 2003, 5, 1299–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jouault, A.; Saliba, A.M.; Touqui, L. Modulation of the Immune Response by the Pseudomonas aeruginosa Type-III Secretion System. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 1064010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moser, C.; Jensen, P.Ø.; Thomsen, K.; Kolpen, M.; Rybtke, M.; Lauland, A.S.; Trøstrup, H.; Tolker-Nielsen, T. Immune Responses to Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilm Infections. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 625597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastings, C.J.; Himmler, G.E.; Patel, A.; Marques, C.N.H. Immune Response Modulation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa Persister Cells. mBio 2023, 14, e00056-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, T.W.; Saunders, M.E.; Jett, B.D. (Eds.) Chapter 12—Mucosal and Cutaneous Immunity. In Primer to the Immune Response, 2nd ed.; Academic Cell: Burlington, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 269–292. ISBN 978-0-12-385245-8. [Google Scholar]
- Bayes, H.K.; Ritchie, N.D.; Evans, T.J. Interleukin-17 Is Required for Control of Chronic Lung Infection Caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect. Immun. 2016, 84, 3507–3516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, T.W.; Saunders, M.E.; Jett, B.D. (Eds.) Chapter 9—T Cell Development, Activation and Effector Functions. In Primer to the Immune Response, 2nd ed.; Academic Cell: Burlington, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 197–226. ISBN 978-0-12-385245-8. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, F.; Han, L.; Fu, Q.; Fan, X.; Tang, R.; Lv, C.; Xue, Y.; Tian, X.; Zhang, M. IL-17 Aggravates Pseudomonas aeruginosa Airway Infection in Acute Exacerbations of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Front. Immunol. 2022, 12, 811803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wonnenberg, B.; Bischoff, M.; Beisswenger, C.; Dinh, T.; Bals, R.; Singh, B.; Tschernig, T. The Role of IL-1β in Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Lung Infection. Cell Tissue Res. 2016, 364, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovewell, R.R.; Patankar, Y.R.; Berwin, B. Mechanisms of Phagocytosis and Host Clearance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2014, 306, L591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malhotra, S.; Don Hayes, J.; Wozniak, D.J. Cystic Fibrosis and Pseudomonas aeruginosa: The Host-Microbe Interface. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, e00138-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajj Hussein, I.; Chams, N.; Chams, S.; El Sayegh, S.; Badran, R.; Raad, M.; Gerges-Geagea, A.; Leone, A.; Jurjus, A. Vaccines Through Centuries: Major Cornerstones of Global Health. Front. Public Health 2015, 3, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polack, F.P.; Thomas, S.J.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Marc, G.P.; Moreira, E.D.; Zerbini, C.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2603–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbett, K.S.; Edwards, D.K.; Leist, S.R.; Abiona, O.M.; Boyoglu-Barnum, S.; Gillespie, R.A.; Himansu, S.; Schäfer, A.; Ziwawo, C.T.; DiPiazza, A.T.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 mRNA Vaccine Design Enabled by Prototype Pathogen Preparedness. Nature 2020, 586, 567–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mak, T.W.; Saunders, M.E.; Jett, B.D. (Eds.) Chapter 14—Vaccination. In Primer to the Immune Response, 2nd ed.; Academic Cell: Burlington, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 333–375. ISBN 978-0-12-385245-8. [Google Scholar]
- Kamei, A.; Coutinho-Sledge, Y.S.; Goldberg, J.B.; Priebe, G.P.; Pier, G.B. Mucosal Vaccination with a Multivalent, Live-Attenuated Vaccine Induces Multifactorial Immunity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Acute Lung Infection. Infect. Immun. 2011, 79, 1289–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuentes-Valverde, V.; García, P.; Moscoso, M.; Bou, G. Double Auxotrophy to Improve the Safety of a Live Anti-Pseudomonas aeruginosa Vaccine. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, M.P.; Correia, A.; Vilanova, M.; Gärtner, F.; Moscoso, M.; García, P.; Vallejo, J.A.; Pérez, A.; Francisco-Tomé, M.; Fuentes-Valverde, V.; et al. A Live Auxotrophic Vaccine Confers Mucosal Immunity and Protection against Lethal Pneumonia Caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priebe, G.P.; Meluleni, G.J.; Coleman, F.T.; Goldberg, J.B.; Pier, G.B. Protection against Fatal Pseudomonas aeruginosa Pneumonia in Mice after Nasal Immunization with a Live, Attenuated aroA Deletion Mutant. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 1453–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priebe, G.P.; Brinig, M.M.; Hatano, K.; Grout, M.; Coleman, F.T.; Pier, G.B.; Goldberg, J.B. Construction and Characterization of a Live, Attenuated aroA Deletion Mutant of Pseudomonas aeruginosa as a Candidate Intranasal Vaccine. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priebe, G.P.; Walsh, R.L.; Cederroth, T.A.; Kamei, A.; Coutinho-Sledge, Y.S.; Goldberg, J.B.; Pier, G.B. IL-17 Is a Critical Component of Vaccine-Induced Protection against Lung Infection by LPS-Heterologous Strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 4965–4975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabral, M.P.; García, P.; Beceiro, A.; Rumbo, C.; Pérez, A.; Moscoso, M.; Bou, G. Design of Live Attenuated Bacterial Vaccines Based on D-Glutamate Auxotrophy. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pigula, M.; Lai, Y.-C.; Koh, M.; Diercks, C.S.; Rogers, T.F.; Dik, D.A.; Schultz, P.G. An Unnatural Amino Acid Dependent, Conditional Pseudomonas Vaccine Prevents Bacterial Infection. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 6766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiGiandomenico, A.; Rao, J.; Goldberg, J.B. Oral Vaccination of BALB/c Mice with Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Expressing Pseudomonas aeruginosa O Antigen Promotes Increased Survival in an Acute Fatal Pneumonia Model. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 7012–7021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiGiandomenico, A.; Rao, J.; Harcher, K.; Zaidi, T.S.; Gardner, J.; Neely, A.N.; Pier, G.B.; Goldberg, J.B. Intranasal Immunization with Heterologously Expressed Polysaccharide Protects against Multiple Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infections. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 4624–4629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarff, J.M.; Goldberg, J.B. Vaccination against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Pneumonia in Immunocompromised Mice. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2008, 15, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Moustafa, D.A.; DiGiandomenico, A.; Raghuram, V.; Schulman, M.; Scarff, J.M.; Michael R Davis, J.; Varga, J.J.; Dean, C.R.; Goldberg, J.B. Efficacy of a Pseudomonas aeruginosa Serogroup O9 Vaccine. Infect. Immun. 2023, 91, e00247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bridge, D.R.; Whitmire, J.M.; Makobongo, M.O.; Merrell, D.S. Heterologous Pseudomonas aeruginosa O-Antigen Delivery Using a Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium wecA Mutant Strain. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2016, 306, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubensky, T.W.; Skoble, J.; Lauer, P.; Brockstedt, D.G. Killed but Metabolically Active Vaccines. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2012, 23, 917–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meynet, E.; Laurin, D.; Lenormand, J.L.; Camara, B.; Toussaint, B.; Le Gouëllec, A. Killed but Metabolically Active Pseudomonas aeruginosa-Based Vaccine Induces Protective Humoral- and Cell-Mediated Immunity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Pulmonary Infections. Vaccine 2018, 36, 1893–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Office of Infectious Disease and HIV/AIDS, Vaccine Types. Available online: https://www.hhs.gov/immunization/basics/types/index.html (accessed on 20 September 2024).
- Cripps, A.W.; Dunkley, M.L.; Clancy, R.L. Mucosal and Systemic Immunizations with Killed Pseudomonas aeruginosa Protect against Acute Respiratory Infection in Rats. Infect. Immun. 1994, 62, 1427–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cripps, A.W.; Dunkley, M.L.; Clancy, R.L.; Kyd, J. Vaccine Strategies against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection in the Lung. Behring Inst. Mitt. 1997, 262–268. [Google Scholar]
- Cripps, A.W.; Peek, K.; Dunkley, M.; Vento, K.; Marjason, J.K.; McIntyre, M.E.; Sizer, P.; Croft, D.; Sedlak-Weinstein, L. Safety and Immunogenicity of an Oral Inactivated Whole-Cell Pseudomonas aeruginosa Vaccine Administered to Healthy Human Subjects. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 968–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, A.M.; McCrudden, M.T.C.; Vincente-Perez, E.M.; Dubois, A.V.; Ingram, R.J.; Larrañeta, E.; Kissenpfennig, A.; Donnelly, R.F. Design and Characterisation of a Dissolving Microneedle Patch for Intradermal Vaccination with Heat-Inactivated Bacteria: A Proof of Concept Study. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 549, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackwood, C.B.; Sen-Kilic, E.; Boehm, D.T.; Hall, J.M.; Varney, M.E.; Wong, T.Y.; Bradford, S.D.; Bevere, J.R.; Witt, W.T.; Damron, F.H.; et al. Innate and Adaptive Immune Responses against Bordetella pertussis and Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a Murine Model of Mucosal Vaccination against Respiratory Infection. Vaccines 2020, 8, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen-Kilic, E.; Blackwood, C.B.; Huckaby, A.B.; Horspool, A.M.; Weaver, K.L.; Malkowski, A.C.; Witt, W.T.; Bevere, J.R.; Damron, F.H.; Barbier, M. Defining the Mechanistic Correlates of Protection Conferred by Whole-Cell Vaccination against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Acute Murine Pneumonia. Infect. Immun. 2021, 89, e00451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Mu, Y.; Lu, L.; Tian, Y.; Yuan, F.; Zhou, B.; Yu, C.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Lei, S.; et al. Hydrogen Peroxide-Inactivated Bacteria Induces Potent Humoral and Cellular Immune Responses and Releases Nucleic Acids. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 69, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amara, A.A.; Salem-Bekhit, M.M.; Alanazi, F.K. Sponge-Like: A New Protocol for Preparing Bacterial Ghosts. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 545741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheweita, S.A.; Amara, A.A.; Gamal, H.; Ghazy, A.A.; Hussein, A.; Bahey-El-Din, M. Bacterial Ghosts of Pseudomonas aeruginosa as a Promising Candidate Vaccine and Its Application in Diabetic Rats. Vaccines 2022, 10, 910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, B.; Luo, Y.; Yan, N.; Shen, Z.; Li, W.; Hou, C.; Xiao, L.; Ma, C.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.; et al. An X-Ray Inactivated Vaccine against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Keratitis in Mice. Vaccine 2023, 41, 4700–4709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, M.W.; Devlin, H.B.; Gnabasik, F.J. New Immunotype Schema for Pseudomonas aeruginosa Based on Protective Antigens. J. Bacteriol. 1969, 98, 835–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanessian, S.; Regan, W.; Watson, D.; Haskell, T.H. Isolation and Characterization of Antigenic Components of a New Heptavalent Pseudomonas Vaccine. Nat. New Biol. 1971, 229, 209–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, J.W.; Fisher, M.W.; MacMillan, B.G.; Altemeier, W.A. Prevention of Invasive Pseudomonas Infection in Burns with a New Vaccine. Arch. Surg. 1969, 99, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, J.W.; Fisher, M.W. Immunological Determinants of Pseudomonas Infections of Man Accompanying Severe Burn Injury. J. Trauma. 1970, 10, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, J.W.; Fisher, M.W. Vaccination for Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Am. J. Surg. 1970, 120, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, J.W.; Fisher, M.W.; MacMillan, B.G. Immunological Control of Pseudomonas Infection in Burn Patients: A Clinical Evaluation. Arch. Surg. 1971, 102, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, L.S.; Meyer, R.D.; Armstrong, D. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Vaccine in Cancer Patients. Ann. Intern. Med. 1973, 79, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennington, J.E.; Reynolds, H.Y.; Wood, R.E.; Robinson, R.A.; Levine, A.S. Use of a Pseudomonas aeruginosa Vaccine in Pateints with Acute Leukemia and Cystic Fibrosis. Am. J. Med. 1975, 58, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haghbin, M.; Armstrong, D.; Murphy, M.L. Controlled Prospective Trial of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Vaccine in Children with Acute Leukemia. Cancer 1973, 32, 761–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennington, J.E. Preliminary Investigations of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Vaccine in Patients with Leukemia and Cystic Fibrosis. J. Infect. Dis. 1974, 130, S159–S162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miler, J.M.; Spilbury, J.F.; Jones, R.J.; Ror, E.A.; Lowbury, E.J.L. A New Polyvalent Pseudomonas Vaccine. J. Med. Microbiol. 1977, 10, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roe, E.A.; Jones, R.J. Immunization of Burned Patients against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection at Safdarjang Hospital, New Delhi. Rev. Infect. Dis. 1983, 5 (Suppl. 5), S922–S930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, R.J.; Roe, E.A.; Lowbury, E.J.L.; Miler, J.J.; Spilsbury, J.F. A New Pseudomonas Vaccine: Preliminary Trial on Human Volunteers. Epidemiol. Infect. 1976, 76, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langford, D.T.; Hiller, J. Prospective, Controlled Study of a Polyvalent Pseudomonas Vaccine in Cystic Fibrosis—Three Year Results. Arch. Dis. Child. 1984, 59, 1131–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cryz, S.J.; Furer, E.; Sadoff, J.C.; Germanier, R. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Immunotype 5 Polysaccharide-Toxin A Conjugate Vaccine. Infect. Immun. 1986, 52, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cryz, S.J.; Fürer, E.; Cross, A.S.; Wegmann, A.; Germanier, R.; Sadoff, J.C. Safety and Immunogenicity of a Pseudomonas aeruginosa O-Polysaccharide Toxin A Conjugate Vaccine in Humans. J. Clin. Investig. 1987, 80, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cryz, S.J.; Lang, A.; Rüdeberg, A.; Wedgwood, J.; Que, J.U.; Fürer, E.; Schaad, U. Immunization of Cystic Fibrosis Patients with a Pseudomonas aeruginosa O-Polysaccharide-Toxin A Conjugate Vaccine. Behring Inst. Mitt. 1997, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schaad, U.B.; Lang, A.B.; Wedgwood, J.; Ruedeberg, A.; Que, J.U.; Fürer, E.; Cryz, S.J. Safety and Immunogenicity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Conjugate A Vaccine in Cystic Fibrosis. Lancet 1991, 338, 1236–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cryz, S.J.; Sadoff, J.C.; Fürer, E. Immunization with a Pseudomonas aeruginosa Immunotype 5 O Polysaccharide-Toxin A Conjugate Vaccine: Effect of a Booster Dose on Antibody Levels in Humans. Infect. Immun. 1988, 56, 1829–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Döring, G. Prevention of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection in Cystic Fibrosis Patients. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2010, 300, 573–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahy, R.; Fatyan, E.; Saafan, A.E.; El-Gebaly, E.A.E.A. Preparation and Evaluation of a New Combined Conjugated Vaccine against Klebsiella pneumoniae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 133, 1543–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pier, G.B. Promises and Pitfalls of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Lipopolysaccharide as a Vaccine Antigen. Carbohydr. Res. 2003, 338, 2549–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatano, K.; Boisot, S.; DesJardins, D.; Wright, D.C.; Brisker, J.; Pier, G.B. Immunogenic and Antigenic Properties of a Heptavalent High-Molecular-Weight O-Polysaccharide Vaccine Derived from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect. Immun. 1994, 62, 3608–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saylor, K.; Gillam, F.; Lohneis, T.; Zhang, C. Designs of Antigen Structure and Composition for Improved Protein-Based Vaccine Efficacy. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuon, F.F.; Dantas, L.R.; Suss, P.H.; Tasca Ribeiro, V.S. Pathogenesis of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilm: A Review. Pathogens 2022, 11, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pier, G.B.; Small, G.J.; Warren, H.B. Protection against Mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Rodent Models of Endobronchial Infections. Science 1990, 249, 537–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pier, G.B.; DesJardin, D.; Grout, M.; Garner, C.; Bennett, S.E.; Pekoe, G.; Fuller, S.A.; Thornton, M.O.; Harkonen, W.S.; Miller, H.C. Human Immune Response to Pseudomonas aeruginosa Mucoid Exopolysaccharide (Alginate) Vaccine. Infect. Immun. 1994, 62, 3972–3979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cryz, S.J.; Fürer, E.; Que, J.U. Synthesis and Characterization of a Pseudomonas aeruginosa Alginate-Toxin A Conjugate Vaccine. Infect. Immun. 1991, 59, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theilacker, C.; Coleman, F.T.; Mueschenborn, S.; Llosa, N.; Grout, M.; Pier, G.B. Construction and Characterization of a Pseudomonas aeruginosa Mucoid Exopolysaccharide-Alginate Conjugate Vaccine. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 3875–3884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azimi, S.; Safari Zanjani, L. Immunization against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Using Alg-PLGA Nano-Vaccine. Iran. J. Basic. Med. Sci. 2021, 24, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afshari, H.; Maleki, M.; Hakimian, M.; Tanha, R.A.; Salouti, M. Immunogenicity Evaluating of the SLNs-Alginate Conjugate against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Immunol. Methods 2021, 488, 112938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, J.; Yang, Y. A Semisynthetic Oligomannuronic Acid-Based Glycoconjugate Vaccine against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. ACS Cent. Sci. 2024, 10, 1515–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moyle, P.M.; Toth, I. Modern Subunit Vaccines: Development, Components, and Research Opportunities. ChemMedChem 2013, 8, 360–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finke, M.; Duchêne, M.; Eckhardt, A.; Domdey, H.; von Specht, B.U. Protection against Experimental Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection by Recombinant P. aeruginosa Lipoprotein I Expressed in Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 1990, 58, 2241–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parvaei, M.; Habibi, M.; Shahbazi, S.; Babaluei, M.; Farokhi, M.; Asadi Karam, M.R. Immunostimulatory Chimeric Protein Encapsulated in Gelatin Nanoparticles Elicits Protective Immunity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Respiratory Tract Infection. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 277, 133964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews-Greer, J.M.; Robertson, D.E.; Gilleland, L.B.; Gilleland, H.E. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Outer Membrane Protein F Produced in Escherichia coli Retains Vaccine Efficacy. Curr. Microbiol. 1990, 20, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilleland, H.E.; Gilleland, L.B.; Fowler, M.R. Vaccine Efficacies of Elastase, Exotoxin A, and Outer-Membrane Protein F in Preventing Chronic Pulmonary Infection by Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a Rat Model. J. Med. Microbiol. 1993, 38, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peluso, L.; de Luca, C.; Bozza, S.; Leonardi, A.; Giovannini, G.; Lavorgna, A.; Rosa, G.D.; Mascolo, M.; Luna, L.O.D.; Catania, M.R.; et al. Protection against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Lung Infection in Mice by Recombinant OprF-Pulsed Dendritic Cell Immunization. BMC Microbiol. 2010, 10, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worgall, S.; Krause, A.; Rivara, M.; Hee, K.-K.; Vintayen, E.V.; Hackett, N.R.; Roelvink, P.W.; Bruder, J.T.; Wickham, T.J.; Kovesdi, I.; et al. Protection against P. aeruginosa with an Adenovirus Vector Containing an OprF Epitope in the Capsid. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause, A.; Whu, W.Z.; Qiu, J.; Wafadari, D.; Hackett, N.R.; Sharma, A.; Crystal, R.G.; Worgall, S. RGD Capsid Modification Enhances Mucosal Protective Immunity of a Non-Human Primate Adenovirus Vector Expressing Pseudomonas aeruginosa OprF. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2013, 173, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worgall, S.; Krause, A.; Qiu, J.; Joh, J.; Hackett, N.R.; Crystal, R.G. Protective Immunity to Pseudomonas aeruginosa Induced with a Capsid-Modified Adenovirus Expressing P. aeruginosa OprF. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 13801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause, A.; Whu, W.Z.; Xu, Y.; Joh, J.; Crystal, R.G.; Worgall, S. Protective Anti-Pseudomonas aeruginosa Humoral and Cellular Mucosal Immunity by AdC7-Mediated Expression of the P. aeruginosa Protein OprF. Vaccine 2011, 29, 2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahey-El-Din, M.; Mohamed, S.A.; Sheweita, S.A.; Haroun, M.; Zaghloul, T.I. Recombinant N-Terminal Outer Membrane Porin (OprF) of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Is a Promising Vaccine Candidate against Both P. aeruginosa and Some Strains of Acinetobacter baumannii. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2020, 310, 151415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayeux, G.; Gayet, L.; Liguori, L.; Odier, M.; Martin, D.K.; Cortès, S.; Schaack, B.; Lenormand, J.-L. Cell-Free Expression of the Outer Membrane Protein OprF of Pseudomonas aeruginosa for Vaccine Purposes. Life Sci. Alliance 2021, 4, e202000958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thanvi, R.; Nada, S.; Dissanayake, R.; Vartak, A.; Sebilleau, C.O.; Alom, N.-E.; Prestwich, E.G.; Wall, K.A.; Sucheck, S.J. Synthesis and Evaluation of a Self-Adjuvanting Pseudomonal Vaccine Based on Major Outer Membrane Porin OprF Epitopes Formulated with Low-Toxicity QS-21-Containing Liposomes. Bioconjugate Chem. 2023, 34, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomi, R.; Sharma, A.; Wu, W.; Sung, B.; Worgall, S. Post-Exposure Immunization by Capsid-Modified AdC7 Vector Expressing Pseudomonas aeruginosa OprF Clears P. Aeruginosa Respiratory Infection. Vaccine 2017, 35, 7174–7180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.-Y.; Shang, H.-F.; Chen, T.-L.; Lin, C.-P.; Hui, C.-F.; Hwang, J. Recombinant Protein Composed of Pseudomonas Exotoxin A, Outer Membrane Proteins I and F as Vaccine against P. aeruginosa Infection. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1999, 52, 524–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Parlane, N.A.; Wedlock, D.N.; Rehm, B.H.A. Bioengineering a Bacterial Pathogen to Assemble Its Own Particulate Vaccine Capable of Inducing Cellular Immunity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Sun, C.; Gu, J.; Yan, X.; Wang, B.; Cui, Z.; Sun, X.; Tong, C.; Feng, X.; Lei, L.; et al. Salmonella Typhimurium Strain Expressing OprF-OprI Protects Mice against Fatal Infection by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbiol. Immunol. 2015, 59, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Z.; Han, D.; Sun, X.; Zhang, M.; Feng, X.; Sun, C.; Gu, J.; Tong, C.; Lei, L.; Han, W. Mannose-Modified Chitosan Microspheres Enhance OprF-OprI-Mediated Protection of Mice against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection via Induction of Mucosal Immunity. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 667–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, R.; El-Naggar, W.; Abd El-Aziz, A.M.; Shaaban, M.; Kenawy, H.I.; Ali, Y.M. Immunization with Outer Membrane Proteins (OprF and OprI) and Flagellin B Protects Mice from Pulmonary Infection with Mucoid and Nonmucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2018, 51, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, H.; Zhang, X.; Zou, J.; Yuan, Y.; Chen, Z.; Liu, D.; Wu, W.; Yang, F.; Lu, D.; Zou, Q.; et al. Oligomerization of IC43 Resulted in Improved Immunogenicity and Protective Efficacy against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Lung Infection. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 159, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westritschnig, K.; Hochreiter, R.; Wallner, G.; Firbas, C.; Schwameis, M.; Jilma, B. A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Phase I Study Assessing the Safety and Immunogenicity of a Pseudomonas aeruginosa Hybrid Outer Membrane Protein OprF/I Vaccine (IC43) in Healthy Volunteers. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2014, 10, 170–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansouri, E.; Gabelsberger, J.; Knapp, B.; Hundt, E.; Lenz, U.; Hungerer, K.-D.; Gilleland, H.E.; Staczek, J.; Domdey, H.; von Specht, B.-U. Safety and Immunogenicity of a Pseudomonas aeruginosa Hybrid Outer Membrane Protein F-I Vaccine in Human Volunteers. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 1461–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansouri, E.; Blome-Eberwein, S.; Gabelsberger, J.; Germann, G.; von Specht, B.U. Clinical Study to Assess the Immunogenicity and Safety of a Recombinant Pseudomonas aeruginosa OprF-OprI Vaccine in Burn Patients. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2003, 37, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Rello, J.; Krenn, C.-G.; Locker, G.; Pilger, E.; Madl, C.; Balica, L.; Dugernier, T.; Laterre, P.-F.; Spapen, H.; Depuydt, P.; et al. A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Phase II Study of a Pseudomonas Vaccine in Ventilated ICU Patients. Crit. Care 2017, 21, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adlbrecht, C.; Wurm, R.; Depuydt, P.; Spapen, H.; Lorente, J.A.; Staudinger, T.; Creteur, J.; Zauner, C.; Meier-Hellmann, A.; Eller, P.; et al. Efficacy, Immunogenicity, and Safety of IC43 Recombinant Pseudomonas aeruginosa Vaccine in Mechanically Ventilated Intensive Care Patients-a Randomized Clinical Trial. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larbig, M.; Mansouri, E.; Freihorst, J.; Tümmler, B.; Köhler, G.; Domdey, H.; Knapp, B.; Hungerer, K.D.; Hundt, E.; Gabelsberger, J.; et al. Safety and Immunogenicity of an Intranasal Pseudomonas aeruginosa Hybrid Outer Membrane Protein F-I Vaccine in Human Volunteers. Vaccine 2001, 19, 2291–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumann, U.; Göcke, K.; Gewecke, B.; Freihorst, J.; von Specht, B.U. Assessment of Pulmonary Antibodies with Induced Sputum and Bronchoalveolar Lavage Induced by Nasal Vaccination against Pseudomonas aeruginosa: A Clinical Phase I/II Study. Respir. Res. 2007, 8, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Göcke, K.; Baumann, U.; Hagemann, H.; Gabelsberger, J.; Hahn, H.; Freihorst, J.; von Specht, B.U. Mucosal Vaccination with a Recombinant OprF-I Vaccine of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Healthy Volunteers: Comparison of a Systemic vs. a Mucosal Booster Schedule. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2003, 37, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzaga, Z.J.C.; Merakou, C.; DiGiandomenico, A.; Priebe, G.P.; Rehm, B.H.A. A Pseudomonas aeruginosa-Derived Particulate Vaccine Protects against P. aeruginosa Infection. Vaccines 2021, 9, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzaga, Z.J.C.; Zhang, J.; Rehm, B.H.A. Intranasal Delivery of Antigen-Coated Polymer Particles Protects against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection. ACS Infect. Dis. 2022, 8, 744–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaikh, M.O.F.; Schaefers, M.M.; Merakou, C.; DiBlasi, M.; Bonney, S.; Liao, T.; Zurakowski, D.; Kehl, M.; Tabor, D.E.; DiGiandomenico, A.; et al. Multicomponent Pseudomonas aeruginosa Vaccines Eliciting Th17 Cells and Functional Antibody Responses Confer Enhanced Protection against Experimental Acute Pneumonia in Mice. Infect. Immun. 2022, 90, e00203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabzehali, F.; Goudarzi, H.; Goudarzi, M.; Chirani, A.S.; Izad, M.H.Y. Immunopotentiating properties of chimeric OprF-OprI-PopB protein against Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 in the infected burned rat model. Iran. J. Basic. Med. Sci. 2022, 25, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Huang, J.; Duan, B.; Traficante, D.C.; Hong, H.; Risech, M.; Lory, S.; Priebe, G.P. Th17-Stimulating Protein Vaccines Confer Protection against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Pneumonia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 186, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, C.; Yang, F.; Wang, Y.; Liao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zeng, H.; Zou, Q.; Gu, J. Vaccination with a Recombinant OprL Fragment Induces a Th17 Response and Confers Serotype-Independent Protection against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection in Mice. Clin. Immunol. 2017, 183, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Pan, X.; Xia, B.; Chen, F.; Jin, Y.; Bai, F.; Priebe, G.; Cheng, Z.; Jin, S.; Wu, W. Construction of a Protective Vaccine Against Lipopolysaccharide-Heterologous Pseudomonas aeruginosa Strains Based on Expression Profiling of Outer Membrane Proteins During Infection. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, S.M.; Pociask, D.; Clements, J.D.; McLachlan, J.B.; Morici, L.A. Intradermal Vaccination with a Pseudomonas aeruginosa Vaccine Adjuvanted with a Mutant Bacterial ADP-Ribosylating Enterotoxin Protects against Acute Pneumonia. Vaccine 2019, 37, 808–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Gong, Q.; Zhu, S.; Li, Y. Extracellular Polysaccharide of Lactobacillus Plantarum Enhance Immune Efficacy of oprH Gene Recombinant Subunit Vaccine from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2023, 85, 1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golpasha, I.D.; Mousavi, S.F.; Owlia, P.; Siadat, S.D.; Irani, S. Immunization with 3-Oxododecanoyl-L-Homoserine Lactone-r-PcrV Conjugate Enhances Survival of Mice against Lethal Burn Infections Caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Bosn. J. Basic. Med. Sci. 2015, 15, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asadi Karam, M.R.; Badmasti, F.; Ahmadi, K.; Habibi, M. Vaccination of Mice with Hybrid Protein Containing Exotoxin S and PcrV with Adjuvants Alum and MPL Protects Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infections. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fakoor, M.H.; Mousavi Gargari, S.L.; Owlia, P.; Sabokbar, A. Protective Efficacy of the OprF/OprI/PcrV Recombinant Chimeric Protein Against Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the Burned BALB/c Mouse Model. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 1651–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalantari, H.; Habibi, M.; Ferdousi, A.; Asadi Karam, M.R.; Mohammadian, T. Development of a Multi-Epitope Vaccine Candidate against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Causing Urinary Tract Infection and Evaluation of Its Immunoreactivity in a Rabbit Model. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2024, 42, 6212–6227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawa, T.; Yahr, T.L.; Ohara, M.; Kurahashi, K.; Gropper, M.A.; Wiener-Kronish, J.P.; Frank, D.W. Active and Passive Immunization with the Pseudomonas V Antigen Protects against Type III Intoxication and Lung Injury. Nat. Med. 1999, 5, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Gu, J.; Yang, L.; Gao, C.; Jing, H.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, H.; Zou, Q.; Lv, F.; Zhang, J. Protective Efficacy of the Trivalent Pseudomonas aeruginosa Vaccine Candidate PcrV-OprI-Hcp1 in Murine Pneumonia and Burn Models. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naito, Y.; Hamaoka, S.; Kinoshita, M.; Kainuma, A.; Shimizu, M.; Katoh, H.; Moriyama, K.; Ishii, K.J.; Sawa, T. The Protective Effects of Nasal PcrV-CpG Oligonucleotide Vaccination against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Pneumonia. Microbiol. Immunol. 2018, 62, 774–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, L.; Cheng, X.; Gao, C.; Wang, Y.; Xu, W.; Zou, Q.; Gu, J. Rational Design of a Chimeric Derivative of PcrV as a Subunit Vaccine Against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howlader, D.R.; Mandal, R.S.; Lu, T.; Maiti, S.; Dietz, Z.K.; Das, S.; Whittier, S.K.; Nagel, A.C.; Biswas, S.; Varisco, D.J.; et al. Development of a nano-emulsion based multivalent protein subunit vaccine against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1372349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Howlader, D.R.; Zheng, Q.; Ratnakaram, S.S.K.; Whittier, S.K.; Lu, T.; Keith, J.D.; Picking, W.D.; Birket, S.E.; Picking, W.L. Development of a Broadly Protective, Self-Adjuvanting Subunit Vaccine to Prevent Infections by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 583008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howlader, D.R.; Das, S.; Lu, T.; Hu, G.; Varisco, D.J.; Dietz, Z.K.; Walton, S.P.; Ratnakaram, S.S.K.; Gardner, F.M.; Ernst, R.K.; et al. Effect of Two Unique Nanoparticle Formulations on the Efficacy of a Broadly Protective Vaccine Against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 706157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howlader, D.R.; Das, S.; Lu, T.; Mandal, R.S.; Hu, G.; Varisco, D.J.; Dietz, Z.K.; Ratnakaram, S.S.K.; Ernst, R.K.; Picking, W.D.; et al. A Protein Subunit Vaccine Elicits a Balanced Immune Response That Protects against Pseudomonas Pulmonary Infection. NPJ Vaccines 2023, 8, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Cheng, X.; Wan, C.; Wei, J.; Gao, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, H.; Peng, L.; Luo, P.; Lu, D.; et al. Development of a Chimeric Vaccine Against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Based on the Th17-Stimulating Epitopes of PcrV and AmpC. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 601601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yu, T.; Cui, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhang, W.; Zou, Q.; Gu, J.; Zuo, Q. Intranasal Vaccination with rePcrV Protects against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Generates Lung Tissue-Resident Memory T Cells. J. Immunol. Res. 2022, 2022, 1403788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Pu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, Y.; Zeng, S.; Gao, C.; Wang, Y.; Yin, D.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Self-assembled ferritin nanoparticles displaying PcrV and OprI as an adjuvant-free Pseudomonas aeruginosa vaccine. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1184863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, K.; Kinoshita, M.; Muranishi, K.; Ohara, J.; Sudo, K.; Kawaguchi, K.; Shimizu, M.; Naito, Y.; Moriyama, K.; Sawa, T. Effect of a Novel Trivalent Vaccine Formulation against Acute Lung Injury Caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Vaccines 2023, 11, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bröms, J.E.; Forslund, A.-L.; Forsberg, A.; Francis, M.S. PcrH of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Is Essential for Secretion and Assembly of the Type III Translocon. J. Infect. Dis. 2003, 188, 1909–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Schaefers, M.M.; Duan, B.; Mizrahi, B.; Lu, R.; Reznor, G.; Kohane, D.S.; Priebe, G.P. PLGA-Encapsulation of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa PopB Vaccine Antigen Improves Th17 Responses and Confers Protection against Experimental Acute Pneumonia. Vaccine 2018, 36, 6926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Chen, Z.; Gao, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, L.; Wan, J.; Wei, Y.; Zeng, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Structural and Biological Insights into Outer Membrane Protein Lipotoxin F of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Implications for Vaccine Application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askarian, F.; Tsai, C.-M.; Cordara, G.; Zurich, R.H.; Bjånes, E.; Golten, O.; Sørensen, H.V.; Kousha, A.; Meier, A.; Chikwati, E.; et al. Immunization with Lytic Polysaccharide Monooxygenase CbpD Induces Protective Immunity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Pneumonia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2301538120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banadkoki, A.Z.; Keshavarzmehr, M.; Afshar, Z.; Aleyasin, N.; Fatemi, M.J.; Behrouz, B.; Hashemi, F.B. Protective Effect of Pilin Protein with Alum+naloxone Adjuvant against Acute Pulmonary Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection. Biologicals 2016, 44, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, C.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cui, Z.; Liao, Y.; Luo, P.; Wu, W.; et al. A Novel Structurally Identified Epitope Delivered by Macrophage Membrane-Coated PLGA Nanoparticles Elicits Protection against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kao, D.J.; Churchill, M.E.A.; Irvin, R.T.; Hodges, R.S. Animal Protection and Structural Studies of a Consensus Sequence VaccineTargeting the Receptor Binding Domain of the Type IV Pilus of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 374, 426–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kao, D.J.; Hodges, R.S. Advantages of a Synthetic Peptide Immunogen Over a Protein Immunogen in the Development of an Anti-Pilus Vaccine for Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2009, 74, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korpi, F.; Hashemi, F.B.; Irajian, G.; Fatemi, M.J.; Laghaei, P.; Behrouz, B. Flagellin and Pilin Immunization against Multi-Drug Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa Protects Mice in the Burn Wound Sepsis Model. Immunol. Lett. 2016, 176, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, M.; Behrouz, B.; Irajianm, G.; Mahdavi, M.; Korpi, F.; Motamedifar, M. Passive immunization against Pseudomonas aeruginosa recombinant PilA in a murine burn wound model. Microb Pathog. 2016, 101, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laghaei, P.; Hashemi, F.B.; Irajian, G.; Korpi, F.; Amirmozafari, N.; Behrouz, B. Immunogenicity and Protective Efficacy of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Type a and b Flagellin Vaccines in a Burned Mouse Model. Mol. Immunol. 2016, 74, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saffari, M.; Behbood, S.; Irajian, G.; Khorshidi, A.; Moniri, R.; Behrouz, B. Antibodies Raised against Divalent Type b Flagellin and Pilin Provide Effective Immunotherapy against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection of Mice with Burn Wounds. Biologicals 2017, 45, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakht azad, S.; Nikokar, I.; Faezi, S.; Rasooly, S.; Mahdavi, M. Evaluation of the Immune Responses Following Co-Administration of PilQ and Type b-Flagellin from Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the Burn Mouse Model. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 123, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, F.B.; Behrouz, B.; Irajian, G.; Laghaei, P.; Korpi, F.; Fatemi, M.J. A Trivalent Vaccine Consisting of “Flagellin A+B and Pilin” Protects against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection in a Murine Burn Model. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 138, 103697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heurtault, B.; Gentine, P.; Thomann, J.-S.; Baehr, C.; Frisch, B.; Pons, F. Design of a Liposomal Candidate Vaccine Against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Its Evaluation in Triggering Systemic and Lung Mucosal Immunity. Pharm. Res. 2009, 26, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gholami, M.; Chirani, A.S.; Razavi, S.; Falak, R.; Irajian, G. Immunogenicity of a Fusion Protein Containing PilQ and Disulphide Turn Region of PilA from Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Mice. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 65, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadbeigi, Y.; Chirani, A.S.; Soleimani, N.; Mahdavi, M.; Goudarzi, M. Immunopotentiation of the Engineered Low-Molecular-Weight Pilin Targeting Pseudomonas aeruginosa: A Combination of Immunoinformatics Investigation and Active Immunization. Mol. Immunol. 2020, 124, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jazi, M.A.; Chirani, A.S.; Hajikhani, B.; Ebrahimipour, G.; Goudarzi, M. Unraveling the Immunopotentiation of P. aeruginosa PAPI-1 Encoded Pilin: From Immunoinformatics Survey to Active Immunization. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 125, 111197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jazi, M.A.; Hajikhani, B.; Goudarzi, M.; Ebrahimipour, G. Exploiting Immunopotential PAPI-1 Encoded Type IVb Major Pilin Targeting Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Heliyon 2024, 10, e36859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, H.; Behrouz, B.; Irajian, G.; Amirmozafari, N.; Naghavi, S. Bivalent Flagellin Immunotherapy Protects Mice against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infections in Both Acute Pneumonia and Burn Wound Models. Biologicals 2017, 46, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holder, I.A.; Naglich, J.G. Experimental Studies of the Pathogenesis of Infections Due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Immunization Using Divalent Flagella Preparations. J. Trauma. 1986, 26, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holder, I.A.; Wheeler, R.; Montie, T.C. Flagellar Preparations from Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Animal Protection Studies. Infect. Immun. 1982, 35, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montie, T.C.; Craven, R.C.; Holder, I.A. Flagellar Preparations from Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Isolation and Characterization. Infect. Immun. 1982, 35, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faezi, S.; Bahrmand, A.R.; Mahdavi, M.; Siadat, S.D.; Sardari, S.; Nikokar, I.; Khanaki, K.; Mirzajani, E.; Goudarzi, G. Preparation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Alginate-Flagellin Immunoconjugate. Biologicals 2017, 47, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weimer, E.T.; Lu, H.; Kock, N.D.; Wozniak, D.J.; Mizel, S.B. A Fusion Protein Vaccine Containing OprF Epitope 8, OprI, and Type A and B Flagellins Promotes Enhanced Clearance of Nonmucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 2356–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campodónico, V.L.; Llosa, N.J.; Grout, M.; Döring, G.; Maira-Litrán, T.; Pier, G.B. Evaluation of Flagella and Flagellin of Pseudomonas aeruginosa as Vaccines. Infect. Immun. 2010, 78, 746–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campodónico, V.L.; Llosa, N.J.; Bentancor, L.V.; Maira-Litran, T.; Pier, G.B. Efficacy of a Conjugate Vaccine Containing Polymannuronic Acid and Flagellin against Experimental Pseudomonas aeruginosa Lung Infection in Mice. Infect. Immun. 2011, 79, 3455–3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behrouz, B.; Hashemi, F.B.; Fatemi, M.J.; Naghavi, S.; Irajian, G.; Halabian, R.; Imani Fooladi, A.A. Immunization with Bivalent Flagellin Protects Mice against Fatal Pseudomonas aeruginosa Pneumonia. J. Immunol. Res. 2017, 2017, 5689709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korpi, F.; Irajian, G.; Forouhi, F.; Mohammadian, T. A Chimeric Vaccine Targeting Pseudomonas aeruginosa Virulence Factors Protects Mice against Lethal Infection. Microb. Pathog. 2023, 178, 106033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, C.; Gao, C.; Xie, Q.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, X.; Fang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zou, Q.; Lu, G.; et al. Flagella Hook Protein FlgE Is a Novel Vaccine Candidate of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Identified by a Genomic Approach. Vaccine 2021, 39, 2386–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Cheng, X.; Liao, Y.; Zeng, S.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wan, J.; Gu, J.; et al. Recombinant Pseudomonas aeruginosa Flagellin Delivered Using Ferritin Nanoparticles Provides Enhanced Cross-Protection against Lung Infection in Mice. Mol. Immunol. 2023, 163, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.; Shridhar, S.; Fox, H.; Luo, K.; Amin, M.N.; Tennant, S.M.; Simon, R.; Cross, A.S. The O-Glycan Is Essential for the Induction of Protective Antibodies against Lethal Infection by Flagella A-Bearing Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect. Immun. 2024, 92, e00427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döring, G.; Pfeiffer, C.; Weber, U.; Mohr-Pennert, A.; Dorner, F. Parenteral Application of a Pseudomonas aeruginosa Flagella Vaccine Elicits Specific Anti-Flagella Antibodies in the Airways of Healthy Individuals. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1995, 151, 983–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowe, B.A.; Enzersberger, O.; Schober-Bendixen, S.; Mitterer, A.; Mundt, W.; Livey, I.; Pabst, H.; Kaeser, R.; Eibl, M.; Eibl, J. The First Clinical Trial of Immuno’s Experimental Pseudomonas aeruginosa Flagellar Vaccines. Antibiot Chemother 1991, 44, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Döring, G.; Meisner, C.; Stern, M. A Double-Blind Randomized Placebo-Controlled Phase III Study of a Pseudomonas aeruginosa Flagella Vaccine in Cystic Fibrosis Patients. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 11020–11025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokol, P.A.; Kooi, C.; Hodges, R.S.; Cachia, P.; Woods, D.E. Immunization with a Pseudomonas aeruginosa Elastase Peptide Reduces Severity of Experimental Lung Infections Due to P. aeruginosa or Burkholderia cepacia. J. Infect. Dis. 2000, 181, 1682–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamoto, S.; Shibano, Y.; Fukushima, J.; Ishii, N.; Morihara, K.; Okuda, K. Site-Directed Mutagenesis of Glu-141 and His-223 in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Elastase: Catalytic Activity, Processing, and Protective Activity of the Elastase against Pseudomonas Infection. Infect. Immun. 1993, 61, 1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, L.D.; Dunkley, M.L.; Moore, R.; Reynolds, S.; Bastin, D.A.; Kyd, J.M.; Cripps, A.W. Catalase Immunization from Pseudomonas aeruginosa Enhances Bacterial Clearance in the Rat Lung. Vaccine 2000, 19, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, L.D.; Cripps, A.W.; Kyd, J.M. Immune Response Mechanisms against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Associated with Mucosal Immunization with Protein Antigens in a Rat Model of Acute Lung Infection. Vaccine 2009, 27, 3324–3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sen-Kilic, E.; Blackwood, C.B.; Boehm, D.T.; Witt, W.T.; Malkowski, A.C.; Bevere, J.R.; Wong, T.Y.; Hall, J.M.; Bradford, S.D.; Varney, M.E.; et al. Intranasal Peptide-Based FpvA-KLH Conjugate Vaccine Protects Mice from Pseudomonas aeruginosa Acute Murine Pneumonia. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalska, M.; Wolf, P. Pseudomonas Exotoxin A: Optimized by Evolution for Effective Killing. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukac, M.; Pier, G.B.; Collier, R.J. Toxoid of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Exotoxin A Generated by Deletion of an Active-Site Residue. Infect. Immun. 1988, 56, 3095–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.-Y.; Lin, C.P.; Loa, C.-C.; Chen, T.-L.; Shang, H.-F.; Hwang, J.; Hui, C.-F. A Nontoxic Pseudomonas Exotoxin A Induces Active Immunity and Passive Protective Antibody against Pseudomonas Exotoxin a Intoxication. J. Biomed. Sci. 1999, 6, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, J.C.; Tham, D.M.; Feng, W.; Huang, F.; Embaie, S.; Liu, K.; Dean, D.; Hertle, R.; FitzGerald, D.J.; Mrsny, R.J. Intranasal Immunization Strategy To Impede Pilin-Mediated Binding of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to Airway Epithelial Cells. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 7705–7717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farajnia, S.; Peerayeh, S.N.; Tanomand, A.; Majidi, J.; Goudarzi, G.; Naghili, B.; Rahbarnia, L. Protective Efficacy of Recombinant Exotoxin A—Flagellin Fusion Protein against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection. Can. J. Microbiol. 2015, 61, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elhosary, M.A.; Bahey-El-Din, M.; AbdelBary, A.; El Guink, N.; Aboushleib, H.M. Immunization with the Ferric Iron-Binding Periplasmic Protein HitA Provides Protection against Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the Murine Infection Model. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 131, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamad, A.S.; Edward, E.A.; Sheta, E.; Aboushleib, H.M.; Bahey-El-Din, M. Iron Acquisition Proteins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa as Potential Vaccine Targets: In Silico Analysis and In Vivo Evaluation of Protective Efficacy of the Hemophore HasAp. Vaccines 2022, 11, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safari Zanjani, L.; Shapouri, R.; Dezfulian, M.; Mahdavi, M.; Shafiee Ardestani, M. Exotoxin A-PLGA Nanoconjugate Vaccine against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection: Protectivity in Murine Model. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 35, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasi, M.; Tanomand, A.; Kafilzadeh, F.; Zolghadri, S.; Hosainzadegan, H. Preparation and Evaluation of the Exotoxin A Nano-Gold Conjugate as a Vaccine Candidate for Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infections. Iran. J. Basic. Med. Sci. 2021, 24, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafzadeh, F.; Tanomand, A.; Haddadi, A.; Majidi, J. Immunological Properties of Exotoxin A Toxoid—Detoxified Lipopolysaccharide—Gold Nanoparticles Conjugate Against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection. Iran. J. Immunol. 2021, 18, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamshidi, M.P.; Cairns, C.; Chong, S.; St Michael, F.; Vinogradov, E.V.; Cox, A.D.; Sauvageau, J. Synthesis and Immunogenicity of a Methyl Rhamnan Pentasaccharide Conjugate from Pseudomonas aeruginosa A-Band Polysaccharide. ACS Infect. Dis. 2022, 8, 1347–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairns, C.M.; Michael, F.S.; Jamshidi, M.; van Faassen, H.; Yang, Q.; Henry, K.A.; Hussack, G.; Sauvageau, J.; Vinogradov, E.V.; Cox, A.D. Structural Characterization and Evaluation of an Epitope at the Tip of the A-Band Rhamnan Polysaccharide of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. ACS Infect. Dis. 2022, 8, 1336–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidi, M.P.; Cairns, C.; Khieu, N.H.; Chan, K.; Michael, F.S.; Cox, A.; Sauvageau, J. Optimization of the Synthesis and Conjugation of the Methyl Rhamnan Tip of Pseudomonas aeruginosa A-Band Polysaccharide and Immunogenicity Evaluation for the Continued Development of a Potential Glycoconjugate Vaccine. ACS Infect. Dis. 2024, 10, 1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavan, L.; Fang, H.; Johnston, E.L.; Whitchurch, C.; Greening, D.W.; Hill, A.F.; Kaparakis-Liaskos, M. The Mechanism of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Outer Membrane Vesicle Biogenesis Determines Their Protein Composition. Proteomics 2023, 23, 2200464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bomberger, J.M.; MacEachran, D.P.; Coutermarsh, B.A.; Ye, S.; O’Toole, G.A.; Stanton, B.A. Long-Distance Delivery of Bacterial Virulence Factors by Pseudomonas aeruginosa Outer Membrane Vesicles. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Wang, X.; Sun, X.; Guan, Z.; Sun, W. Outer Membrane Vesicles Displaying a Heterologous PcrV-HitA Fusion Antigen Promote Protection against Pulmonary Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection. mSphere 2021, 6, e00699-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Wang, X.; Sun, X.; Cimino, J.; Guan, Z.; Sun, W. Recombinant Pseudomonas Bionanoparticles Induce Protection against Pneumonic Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection. Infect. Immun. 2021, 89, e0039621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zare Banadkoki, E.; Rasooli, I.; Ghazanfari, T.; Siadat, S.D.; Shafiee Ardestani, M.; Owlia, P. Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 Outer Membrane Vesicles-Diphtheria Toxoid Conjugate as a Vaccine Candidate in a Murine Burn Model. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 22324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, I.; Guo, Z.; Zhou, J.; Gao, W.; Fang, R.H.; Zhang, L. Cellular Nanodiscs Made from Bacterial Outer Membrane as a Platform for Antibacterial Vaccination. ACS Nano 2022, 17, 1120–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, H.; Qin, J.; Huang, J.; Zhong, C.; Liu, Y. Outer Membrane Vesicles from X-ray-Irradiated Pseudomonas aeruginosa Alleviate Lung Injury Caused by P. aeruginosa Infection-Mediated Sepsis. APMIS 2024, 132, 646–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Luo, Y.; Yang, L.; Yang, Y.Y.; Yuan, P.; Chen, X.; Tian, G.-B.; Ding, X. A Multiantigenic Antibacterial Nanovaccine Utilizing Hybrid Membrane Vesicles for Combating Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infections. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2024, 13, e12524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahara, M.; Hirayama, S.; Futamata, H.; Nakao, R.; Tashiro, Y. Biofilm-Derived Membrane Vesicles Exhibit Potent Immunomodulatory Activity in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Microbiol. Immunol. 2024, 68, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papenfort, K.; Bassler, B. Quorum-Sensing Signal-Response Systems in Gram-Negative Bacteria. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 576–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyairi, S.; Tateda, K.; Fuse, E.T.; Ueda, C.; Saito, H.; Takabatake, T.; Ishii, Y.; Horikawa, M.; Ishiguro, M.; Standiford, T.J.; et al. Immunization with 3-Oxododecanoyl-l-Homoserine Lactone–Protein Conjugate Protects Mice from Lethal Pseudomonas aeruginosa Lung Infection. J. Med. Microbiol. 2006, 55, 1381–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Yuan, F. A Comprehensive Comparison of DNA and RNA Vaccines. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2024, 210, 115340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, B.M.; Galloway, D.R.; Baker, N.R.; Gilleland, L.B.; Staczek, J.; Gilleland, H.E. Protection against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Chronic Lung Infection in Mice by Genetic Immunization against Outer Membrane Protein F (OprF) of P. aeruginosa. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 3510–3515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, S.; Takeshita, F.; Sasaki, S.; Matsuda, T.; Tanaka, T.; Tozuka, M.; Takase, K.; Matsumoto, T.; Okuda, K.; Ishii, N.; et al. Multivalent DNA Vaccine Protects Mice against Pulmonary Infection Caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Vaccine 2006, 24, 6240–6249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Tian, L.; Zhao, X.; Jiang, X.; Qin, J.; Wang, Y.; Yu, X. Enhanced Protective Efficacy of an OprF/PcrV Bivalent DNA Vaccine against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Using a Hydrogel Delivery System. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 172, 116264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PubChem TLR5—Toll Like Receptor 5 (Human). Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/TLR5/human (accessed on 30 September 2024).
- Saha, S.; Takeshita, F.; Matsuda, T.; Jounai, N.; Kobiyama, K.; Matsumoto, T.; Sasaki, S.; Yoshida, A.; Xin, K.-Q.; Klinman, D.M.; et al. Blocking of the TLR5 Activation Domain Hampers Protective Potential of Flagellin DNA Vaccine. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 1147–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Wang, Y.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Q.; Lei, J. A DNA Vaccine Encoding VP22 of Herpes Simplex Virus Type I (HSV-1) and OprF Confers Enhanced Protection from Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Mice. Vaccine 2016, 34, 4399–4405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Q.; Ruan, M.D.; Niu, M.F.; Qin, C.L.; Hou, Y.; Guo, J.Z. Immune Efficacy of DNA Vaccines Based on oprL and oprF Genes of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Chickens. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 4219–4227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Q.; Ruan, M.; Niu, M.; Qin, C. Immune Efficacy of Different Immunization Doses of Divalent Combination DNA Vaccine pOPRL+pOPRF of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2021, 83, 1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhai, W.; Niu, M. Immune Responses and Protective Efficacy of a Trivalent Combination DNA Vaccine Based on oprL, oprF and flgE Genes of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Veterinární Medicína 2022, 67, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, C.; Rcheulishvili, N.; Papukashvili, D.; Xie, F.; Zhao, J.; Hu, X.; Yu, K.; Yang, N.; Pan, X.; et al. Strong Immune Responses and Protection of PcrV and OprF-I mRNA Vaccine Candidates against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. npj Vaccines 2023, 8, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santamarina-Fernández, R.; Fuentes-Valverde, V.; Silva-Rodríguez, A.; García, P.; Moscoso, M.; Bou, G. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Vaccine Development: Lessons, Challenges, and Future Innovations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2012. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26052012
Santamarina-Fernández R, Fuentes-Valverde V, Silva-Rodríguez A, García P, Moscoso M, Bou G. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Vaccine Development: Lessons, Challenges, and Future Innovations. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(5):2012. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26052012
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantamarina-Fernández, Rebeca, Víctor Fuentes-Valverde, Alis Silva-Rodríguez, Patricia García, Miriam Moscoso, and Germán Bou. 2025. "Pseudomonas aeruginosa Vaccine Development: Lessons, Challenges, and Future Innovations" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 5: 2012. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26052012
APA StyleSantamarina-Fernández, R., Fuentes-Valverde, V., Silva-Rodríguez, A., García, P., Moscoso, M., & Bou, G. (2025). Pseudomonas aeruginosa Vaccine Development: Lessons, Challenges, and Future Innovations. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(5), 2012. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26052012




