Neurons Co-Expressing GLP-1, CCK, and PYY Receptors Particularly in Right Nodose Ganglion and Innervating Entire GI Tract in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
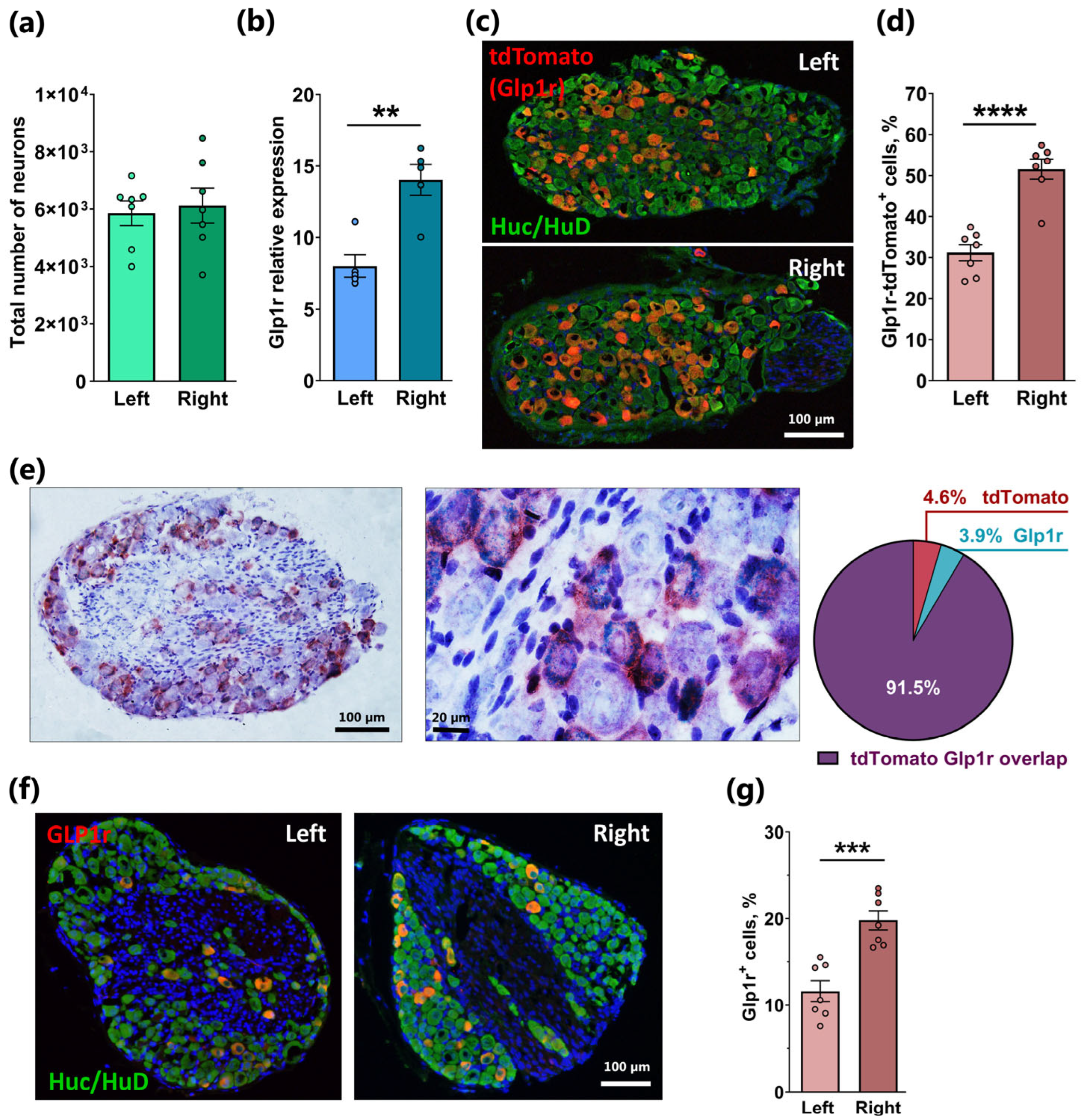
2.1. Asymmetrical Expression of Glp1r in the Left and Right Nodose Ganglia
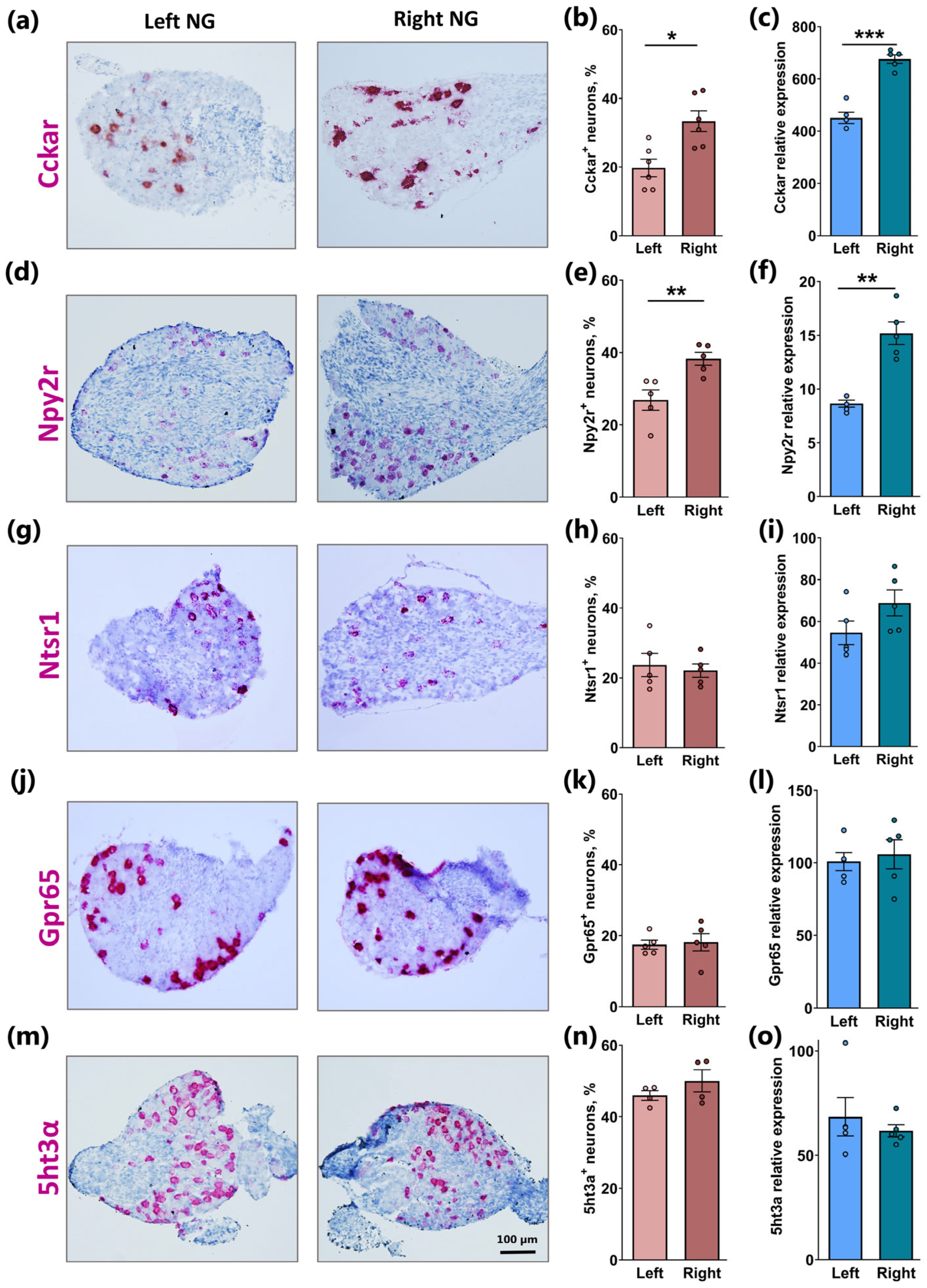
2.2. Similar Lateralization of Cckar and Npy2r but Not Ntsr1, Gpr65, and 5ht3a in Right Versus Left NG
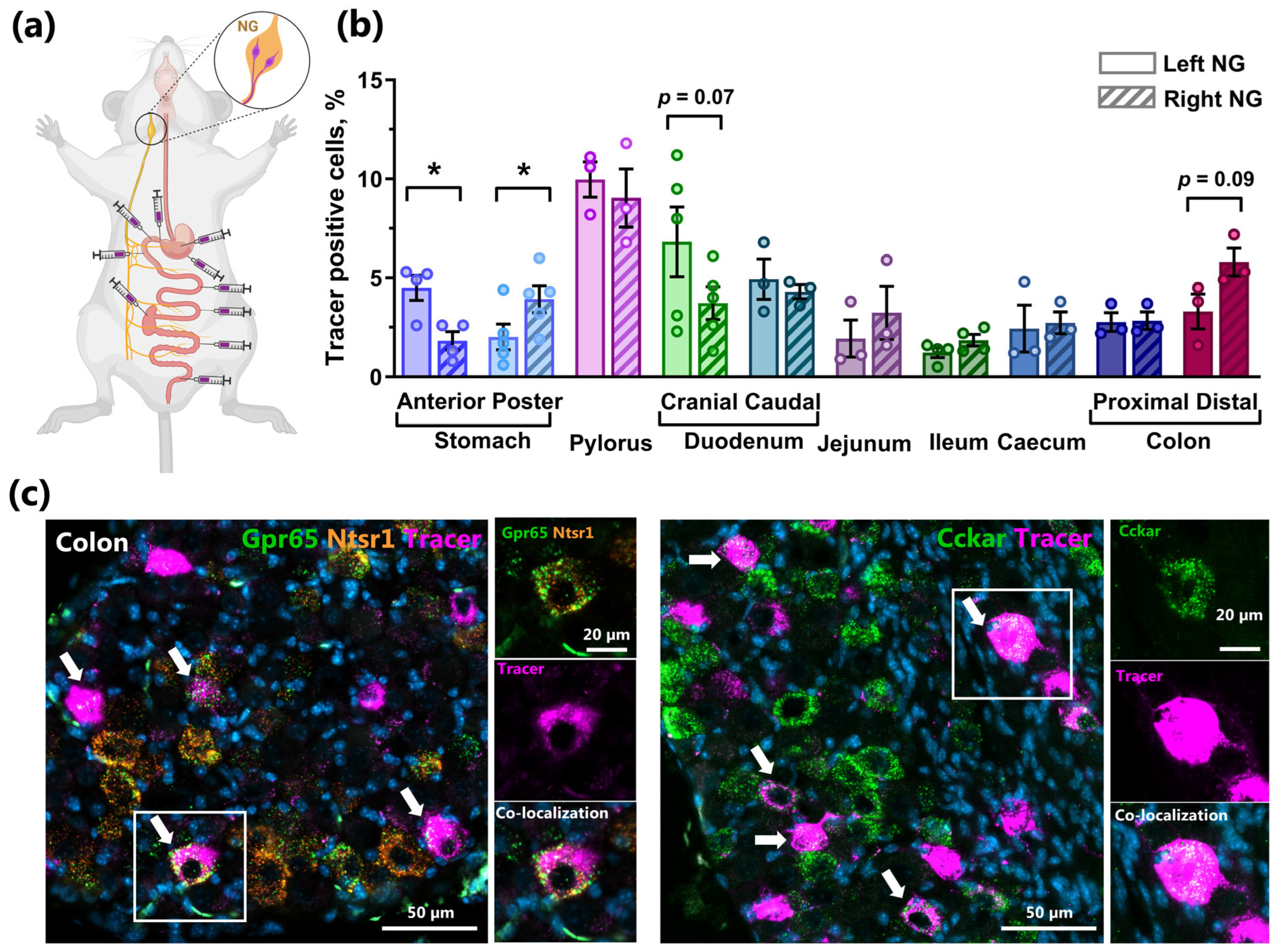
2.3. Mapping of Co-Expression of Key Receptors in NG Neurons by RNAscope
2.4. Revisiting Glp1r Expression in NG Cell Clusters Based on Single-Cell RNAseq
2.5. Retrograde Tracing Demonstrates NG Lateralization of Stomach Innervation and Strong Innervation of the Distal Intestine in Mice
2.6. Functional Studies of NG Lateralization
3. Discussion
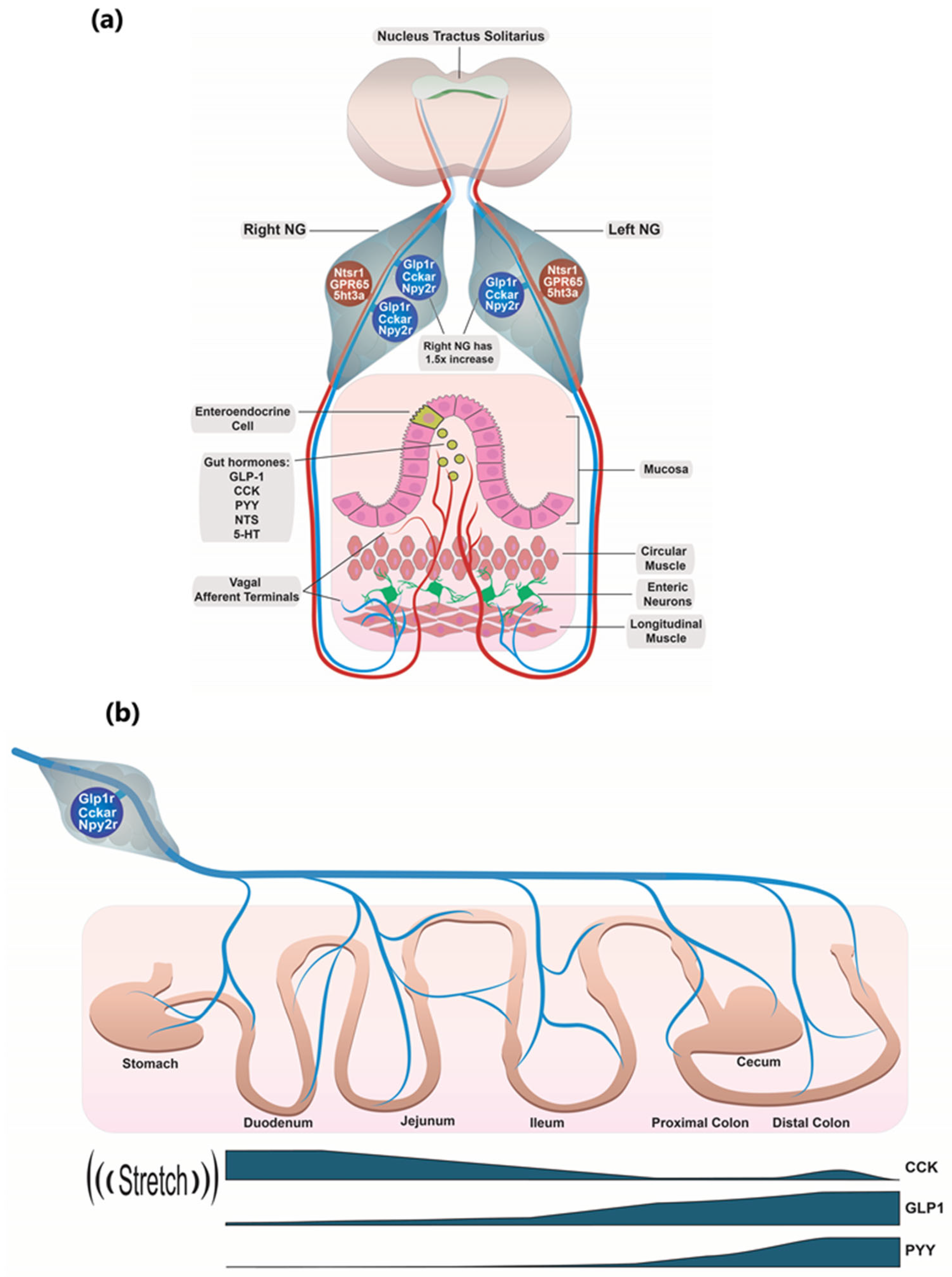
3.1. Glp1r/Cckar/Npy2r Co-Expressing NG Neurons
3.2. Individual Glp1r/Cckar/Npy2r Co-Expressing Neurons Can Apparently Sense the Entire GI Tract
3.3. Why Do GLP1R Neurons in the Literature Appear to Respond to Stretch Rather than Food?
3.4. The GPR65/NTSR1 Co-Expressing NG Neurons and Their Role in Sensing Gut Hormones
3.5. Gut Hormone Signaling Through Right Versus Left NG
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Tissue Preparation
4.3. Retrograde Tracer Injection
4.4. Immunohistochemistry
4.5. Stereology
4.6. RNAscope
4.7. Gene Expression Analysis
4.8. Glp1r Single-Cell Data Analysis
4.9. Nodose Ganglia Explants Preparation and Field Nerve Potential Recording
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 5ht3a | 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 3A |
| CCK | cholecystokinin |
| CCKAR | cholecystokinin A receptor |
| DVC | dorsal vagal complex |
| EECs | enteroendocrine cells |
| GI tract | gastrointestinal tract |
| GLP1 | glucagon-like peptide-1 |
| GLP1R | glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor |
| IGLEs | intraganglionic laminar endings |
| IHC | immunohistochemistry |
| NG | nodose ganglia |
| NPY2R | Neuropeptide Y Y2 Receptor |
| NPY | Neuropeptide Y |
| NTSR1 | neurotensin receptor 1 |
| PYY | peptide YY |
| Trpv1 | transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 1 |
| VNS | vagal nerve stimulation |
Appendix A
| Gene Name(s) | Catalog Number | Temperature of Incubation | Time of Incubation | Label: Red (R), Duplex (D), Multiplex (M) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5htr3a | 411141 411141-C2 | 42 °C | 2 h | R M |
| Cckar | 313751 313751-C2 | 42 °C | 2 h | R M |
| Glp1r | 418851 418851-C3 | 42 °C | 2 h | R, D M |
| Gpr65 | 431431 431431-C2 | 42 °C | 2 h | R M |
| Npy2r | 315951 | 42 °C | 2 h | R, M |
| Ntsr1 | 422411 | 42 °C | 2 h | R, M |
| Trpv1 | 313331-C2 | 42 °C | 2 h | M |
| Piezo2 | 400191 | 42 °C | 2 h | M |
| tdTomato | 317041-C2 | 42 °C | 2 h | D |
| 3-Plex positive control | 320881 | 42 °C | 2 h | M |
| 2-Plex positive control | 320761 | 42 °C | 2 h | D |
| Positive control probe—Ppib | 313911 | 42 °C | 2 h | R |
| 3-Plex negative control | 320751 | 42 °C | 2 h | M |
| 2-Plex negative control | 320871 | 42 °C | 2 h | D |
| Negative control probe—DapB | 310043 | 42 °C | 2 h | R |
| Target Gene | Forward (5′-3′) | Reverse (5′-3′) | Amplicon Length (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| β-actin | TTCTACAATGAGCTGCGTGTG | GGGGTGTTGAAGGTCTCAAA | 122 |
| Cckar | TCTGCAGACCCCTACAATCC | GTTCGCCGTCTGGTTATTGT | 155 |
| GAPDH | GGATGCAGGGATGATGTT | AAGGGCTCATGACCACAGTC | 116 |
| Glp1r | GGGTCTCTGGCTACATAAGGACAAC | AAGGATGGCTGAAGCGATGAC | 178 |
| Gpr65 | GCCAGCCTCCTCAGTCAAGA | GATTGGAGATTGGTCGGTGC | 125 |
| Htr3a | AAATCAGGGCGAGTGGGAGCTG | GACACGATGATGAGGAAGACTG | 264 |
| HuD | CGTCACCATGACCAACTACG | CAGGATTTGTGGGCTTTGTT | 117 |
| Npy2r | GCCAGGGCACACTACTCCTA | CTACCCCTAGCAAGATGATGGA | 131 |
| Ntr1 | GGCAATTCCTCAGAATCCATCC | ATACAGCGGTCACCAGCAC | 88 |
| Tubb3 | TGAGGCCTCCTCTCACAAGT | TGCAGGCAGTCACAATTCTC | 237 |
| Ywhaz | AGACGGAAGGTGCTGAGAAA | GAAGCATTGGGGATCAAGAA | 127 |
References
- Agostoni, E.; Chinnock, J.E.; de Daly, M.B.; Murray, J.G. Functional and Histological Studies of the Vagus Nerve and Its Branches to the Heart, Lungs and Abdominal Viscera in the Cat. J. Physiol. 1957, 135, 182–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waise, T.M.Z.; Dranse, H.J.; Lam, T.K.T. The Metabolic Role of Vagal Afferent Innervation. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 625–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berthoud, H.R.; Carlson, N.R.; Powley, T.L. Topography of Efferent Vagal Innervation of the Rat Gastrointestinal Tract. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 1991, 260, R200–R207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egerod, K.L.; Petersen, N.; Timshel, P.N.; Rekling, J.C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Schwartz, T.W.; Gautron, L. Profiling of G Protein-Coupled Receptors in Vagal Afferents Reveals Novel Gut-to-Brain Sensing Mechanisms. Mol. Metab. 2018, 12, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vana, V.; Laerke, M.K.; Rehfeld, J.F.; Arnold, M.; Dmytriyeva, O.; Langhans, W.; Schwartz, T.W.; Hansen, H.S. Vagal Afferent Cholecystokinin Receptor Activation Is Required for Glucagon-like Peptide-1-Induced Satiation. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2022, 24, 268–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Tellez, L.A.; Perkins, M.H.; Perez, I.O.; Qu, T.; Ferreira, J.; Ferreira, T.L.; Quinn, D.; Liu, Z.W.; Gao, X.B.; et al. A Neural Circuit for Gut-Induced Reward. Cell 2018, 175, 887–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iepsen, E.W.; Torekov, S.S.; Holst, J.J. Therapies for Inter-Relating Diabetes and Obesity—GLP-1 and Obesity. Expert. Opin. Pharmacother. 2014, 15, 2487–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimann, F.; Gribble, F.M. Mechanisms Underlying Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide and Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Secretion. J. Diabetes Investig. 2016, 7, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, G.J. Roles for Gut Vagal Sensory Signals in Determining Energy Availability and Energy Expenditure. Brain Res. 2018, 1693, 151–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, G.J.; Moran, T.H. CCK Elicits and Modulates Vagal Afferent Activity Arising from Gastric and Duodenal Sites. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1994, 713, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohórquez, D.V.; Shahid, R.A.; Erdmann, A.; Kreger, A.M.; Wang, Y.; Calakos, N.; Wang, F.; Liddle, R.A. Neuroepithelial Circuit Formed by Innervation of Sensory Enteroendocrine Cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 782–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaelberer, M.M.; Rupprecht, L.E.; Liu, W.W.; Weng, P.; Bohórquez, D.V. Neuropod Cells: The Emerging Biology of Gut-Brain Sensory Transduction. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2020, 43, 337–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, E.K.K.; Chang, R.B.B.; Strochlic, D.E.E.; Umans, B.D.D.; Lowell, B.B.B.; Liberles, S.D.D. Sensory Neurons That Detect Stretch and Nutrients in the Digestive System. Cell 2016, 166, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, L.; Mesgarzadeh, S.; Ramesh, K.S.; Huey, E.L.; Liu, Y.; Gray, L.A.; Aitken, T.J.; Chen, Y.; Beutler, L.R.; Ahn, J.S.; et al. Genetic Identification of Vagal Sensory Neurons That Control Feeding. Cell 2019, 179, 1129–1143.e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verzele, N.A.J.; Chua, B.Y.; Short, K.R.; Moe, A.A.K.; Edwards, I.N.; Bielefeldt-Ohmann, H.; Hulme, K.D.; Noye, E.C.; Tong, M.Z.W.; Reading, P.C.; et al. Evidence for Vagal Sensory Neural Involvement in Influenza Pathogenesis and Disease. PLoS Pathog. 2024, 20, e1011635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prechtl, J.C.; Powley, T.L. Organization and Distribution of the Rat Subdiaphragmatic Vagus and Associated Paraganglia. J. Comp. Neurol. 1985, 235, 182–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthoud, H.-R.; Neuhuber, W.L. Functional and Chemical Anatomy of the Afferent Vagal System; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2000; Volume 85. [Google Scholar]
- Prescott, S.L.; Umans, B.D.; Williams, E.K.; Brust, R.D.; Liberles, S.D. An Airway Protection Program Revealed by Sweeping Genetic Control of Vagal Afferents. Cell 2020, 181, 574–589.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCoy, M.E.; Kamitakahara, A.K. Ontogeny and Trophic Factor Sensitivity of Gastrointestinal Projecting Vagal Sensory Cell Types. eNeuro 2023, 10, ENEURO.0511-22.2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beutler, L.R.; Chen, Y.; Ahn, J.S.; Lin, Y.C.; Essner, R.A.; Knight, Z.A. Dynamics of Gut-Brain Communication Underlying Hunger. Neuron 2017, 96, 461–475.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egerod, K.L.; Engelstoft, M.S.; Grunddal, K.V.; Nøhr, M.K.; Secher, A.; Sakata, I.; Pedersen, J.; Windeløv, J.A.; Füchtbauer, E.M.; Olsen, J.; et al. A Major Lineage of Enteroendocrine Cells Coexpress CCK, Secretin, GIP, GLP-1, PYY, and Neurotensin but Not Somatostatin. Endocrinology 2012, 153, 5782–5795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, R.B.; Strochlic, D.E.; Williams, E.K.; Umans, B.D.; Liberles, S.D. Vagal Sensory Neuron Subtypes That Differentially Control Breathing. Cell 2015, 161, 622–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grunddal, K.V.; Ratner, C.F.; Svendsen, B.; Sommer, F.; Engelstoft, M.S.; Madsen, A.N.; Pedersen, J.; Nøhr, M.K.; Egerod, K.L.; Nawrocki, A.R.; et al. Neurotensin Is Coexpressed, Coreleased, and Acts Together with GLP-1 and PYY in Enteroendocrine Control of Metabolism. Endocrinology 2016, 157, 176–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kupari, J.; Häring, M.; Agirre, E.; Castelo-Branco, G.; Ernfors, P. An Atlas of Vagal Sensory Neurons and Their Molecular Specialization. Cell Rep. 2019, 27, 2508–2523.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, N.J.; Kyloh, M.A.; Travis, L.; Hibberd, T.J. Identification of Vagal Afferent Nerve Endings in the Mouse Colon and Their Spatial Relationship with Enterochromaffin Cells. Cell Tissue Res. 2024, 396, 313–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Taché, Y. The Parasympathetic and Sensory Innervation of the Proximal and Distal Colon in Male Mice. Front. Neuroanat. 2024, 18, 1422403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malin, S.A.; Christianson, J.A.; Bielefeldt, K.; Davis, B.M. TRPV1 Expression Defines Functionally Distinct Pelvic Colon Afferents. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercado-Perez, A.; Beyder, A. Gut Feelings: Mechanosensing in the Gastrointestinal Tract. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 19, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamedova, E.; Dmytriyeva, O.; Rekling, J.C. Thyrotropin-Releasing Hormone Induces Ca2+ Increase in a Subset of Vagal Nodose Ganglion Neurons. Neuropeptides 2022, 94, 102261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Yu, C.D.; Wang, R.; Xu, Q.J.; Dai Pra, R.; Zhang, L.; Chang, R.B. A Multidimensional Coding Architecture of the Vagal Interoceptive System. Nature 2022, 603, 878–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, M.L.; Egerod, K.L.; Engelstoft, M.S.; Dmytriyeva, O.; Theodorsson, E.; Patel, B.A.; Schwartz, T.W. Enterochromaffin 5-HT Cells—A Major Target for GLP-1 and Gut Microbial Metabolites. Mol. Metab. 2018, 11, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Lin, J.; Gao, X.; Su, H.; Lin, R.; Gao, H.; Feng, Z.; Wu, H.; Feng, B.; Zuo, K.; et al. Intestinal Epithelial PH-Sensing Receptor GPR65 Maintains Mucosal Homeostasis via Regulating Antimicrobial Defense and Restrains Gut Inflammation in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2257269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, S.F.; Novak, I.; Alves, F.; Schwab, A.; Pardo, L.A. Alternating PH Landscapes Shape Epithelial Cancer Initiation and Progression: Focus on Pancreatic Cancer. Bioessays 2017, 39, 1600253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashley, S.W.; Schwarz, M.; Alvarez, C.; Nguyen, T.N.; Vdovenko, A.; Reber, H.A. Pancreatic Interstitial PH Regulation: Effects of Secretory Stimulation. Surgery 1994, 115, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Castagliuolo, I.; Wang, C.-C.; Valenick, L.; Pasha, A.; Nikulasson, S.; Carraway, R.E.; Pothoulakis, C. Neurotensin Is a Proinflammatory Neuropeptide in Colonic Inflammation. J. Clin. Investig. 1999, 103, 843–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, T.H.; Field, D.G.; Knipp, S.; Carrigan, T.S.; Schwartz, G.J. Endogenous CCK in the Control of Gastric Emptying of Glucose and Maltose. Peptides 1997, 18, 547–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, D.B.; Grunddal, K.V.; Pedersen, J.; Kuhre, R.E.; Lund, M.L.; Holst, J.J.; Ørskov, C. Using a Reporter Mouse to Map Known and Novel Sites of GLP-1 Receptor Expression in Peripheral Tissues of Male Mice. Endocrinology 2021, 162, bqaa246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundersen, H.J.G.; Bagger, P.; Bendtsen, T.F.; Evans, S.M.; Korbo, L.; Marcussen, N.; MØLler, A.; Nielsen, K.; Nyengaard, J.R.; Pakkenberg, B.; et al. The New Stereological Tools: Disector, Fractionator, Nucleator and Point Sampled Intercepts and Their Use in Pathological Research and Diagnosis. APMIS 1988, 96, 857–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Flanagan, J.; Su, N.; Wang, L.-C.; Bui, S.; Nielson, A.; Wu, X.; Vo, H.-T.; Ma, X.-J.; Luo, Y. RNAscope: A Novel in Situ RNA Analysis Platform for Formalin-Fixed, Paraffin-Embedded Tissues. J. Mol. Diagn. 2012, 14, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An Open-Source Platform for Biological-Image Analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinrichs, A.S.; Karolchik, D.; Baertsch, R.; Barber, G.P.; Bejerano, G.; Clawson, H.; Diekhans, M.; Furey, T.S.; Harte, R.A.; Hsu, F.; et al. The UCSC Genome Browser Database: Update 2006. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, D590–D598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Nambiar, R.; Zheng, D.; Tian, B. PolyA_DB 3 Catalogs Cleavage and Polyadenylation Sites Identified by Deep Sequencing in Multiple Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D315–D319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dana, H.; Sun, Y.; Mohar, B.; Hulse, B.K.; Kerlin, A.M.; Hasseman, J.P.; Tsegaye, G.; Tsang, A.; Wong, A.; Patel, R.; et al. High-Performance Calcium Sensors for Imaging Activity in Neuronal Populations and Microcompartments. Nat. Methods 2019, 16, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lansbury, E.L.; Vana, V.; Lund, M.L.; Ludwig, M.Q.; Mamedova, E.; Gautron, L.; Arnold, M.; Egerod, K.L.; Kuhre, R.E.; Holst, J.J.; et al. Neurons Co-Expressing GLP-1, CCK, and PYY Receptors Particularly in Right Nodose Ganglion and Innervating Entire GI Tract in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2053. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26052053
Lansbury EL, Vana V, Lund ML, Ludwig MQ, Mamedova E, Gautron L, Arnold M, Egerod KL, Kuhre RE, Holst JJ, et al. Neurons Co-Expressing GLP-1, CCK, and PYY Receptors Particularly in Right Nodose Ganglion and Innervating Entire GI Tract in Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(5):2053. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26052053
Chicago/Turabian StyleLansbury, Elizabeth Laura, Vasiliki Vana, Mari Lilith Lund, Mette Q. Ludwig, Esmira Mamedova, Laurent Gautron, Myrtha Arnold, Kristoffer Lihme Egerod, Rune Ehrenreich Kuhre, Jens Juul Holst, and et al. 2025. "Neurons Co-Expressing GLP-1, CCK, and PYY Receptors Particularly in Right Nodose Ganglion and Innervating Entire GI Tract in Mice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 5: 2053. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26052053
APA StyleLansbury, E. L., Vana, V., Lund, M. L., Ludwig, M. Q., Mamedova, E., Gautron, L., Arnold, M., Egerod, K. L., Kuhre, R. E., Holst, J. J., Rekling, J., Schwartz, T. W., Pankratova, S., & Dmytriyeva, O. (2025). Neurons Co-Expressing GLP-1, CCK, and PYY Receptors Particularly in Right Nodose Ganglion and Innervating Entire GI Tract in Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(5), 2053. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26052053







