Effects of Vinorelbine on M2 Macrophages in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
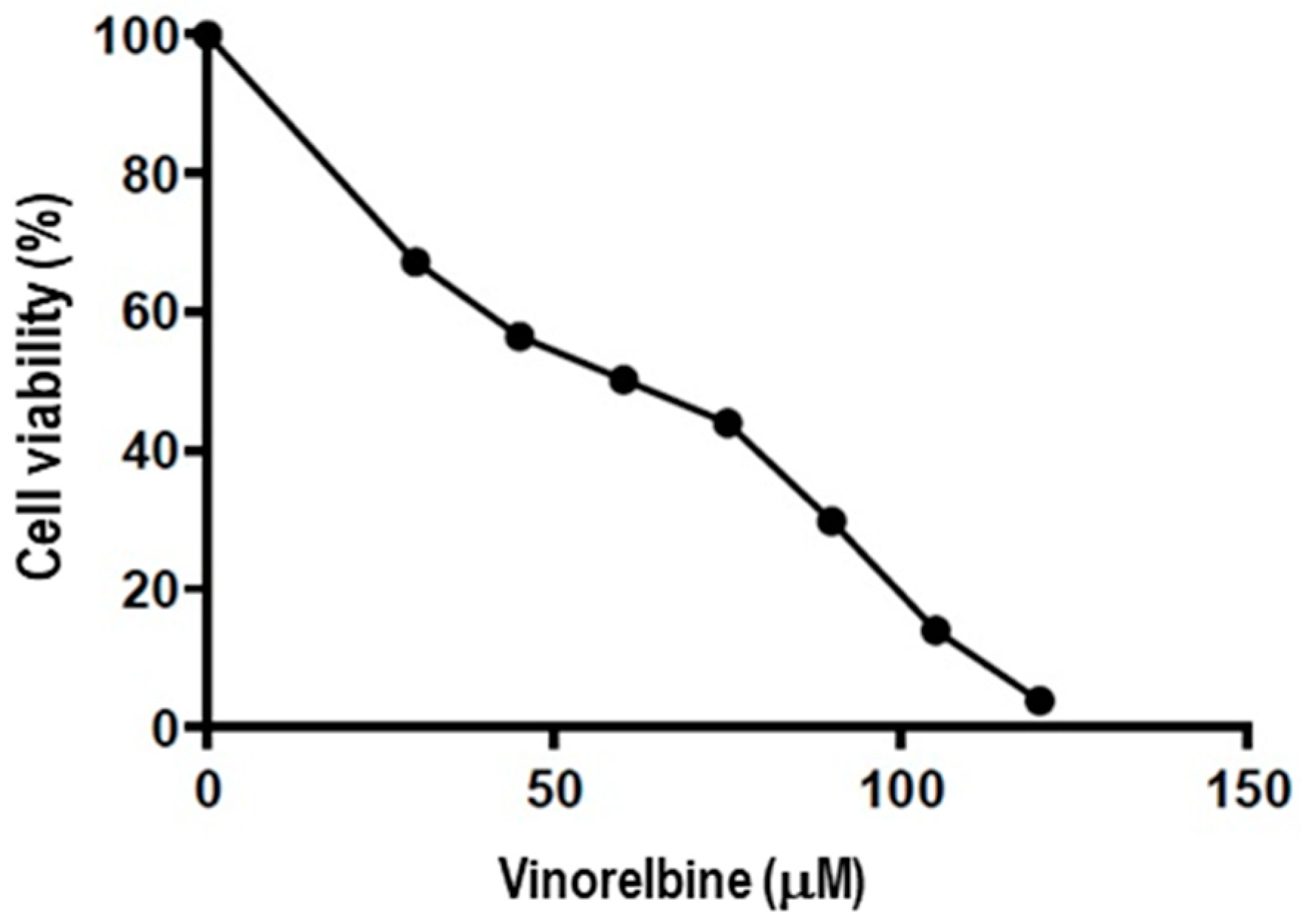
2.1. Vinorelbine Inhibits the Proliferation of NSCLC
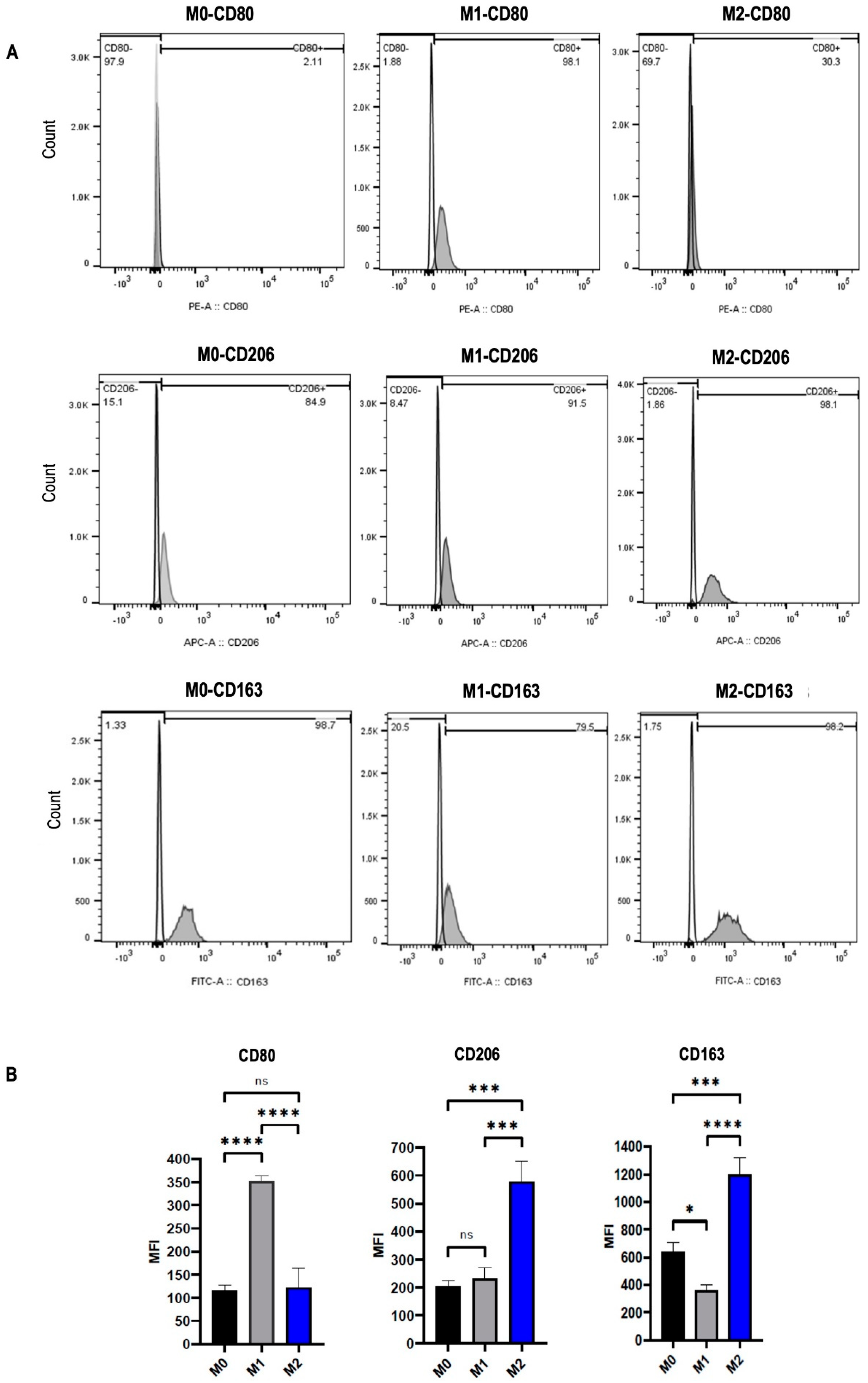
2.2. Macrophage Polarization into M1 and M2 Phenotypes
2.3. Vinorelbine Modulates M2 Macrophages into the M1 Phenotype
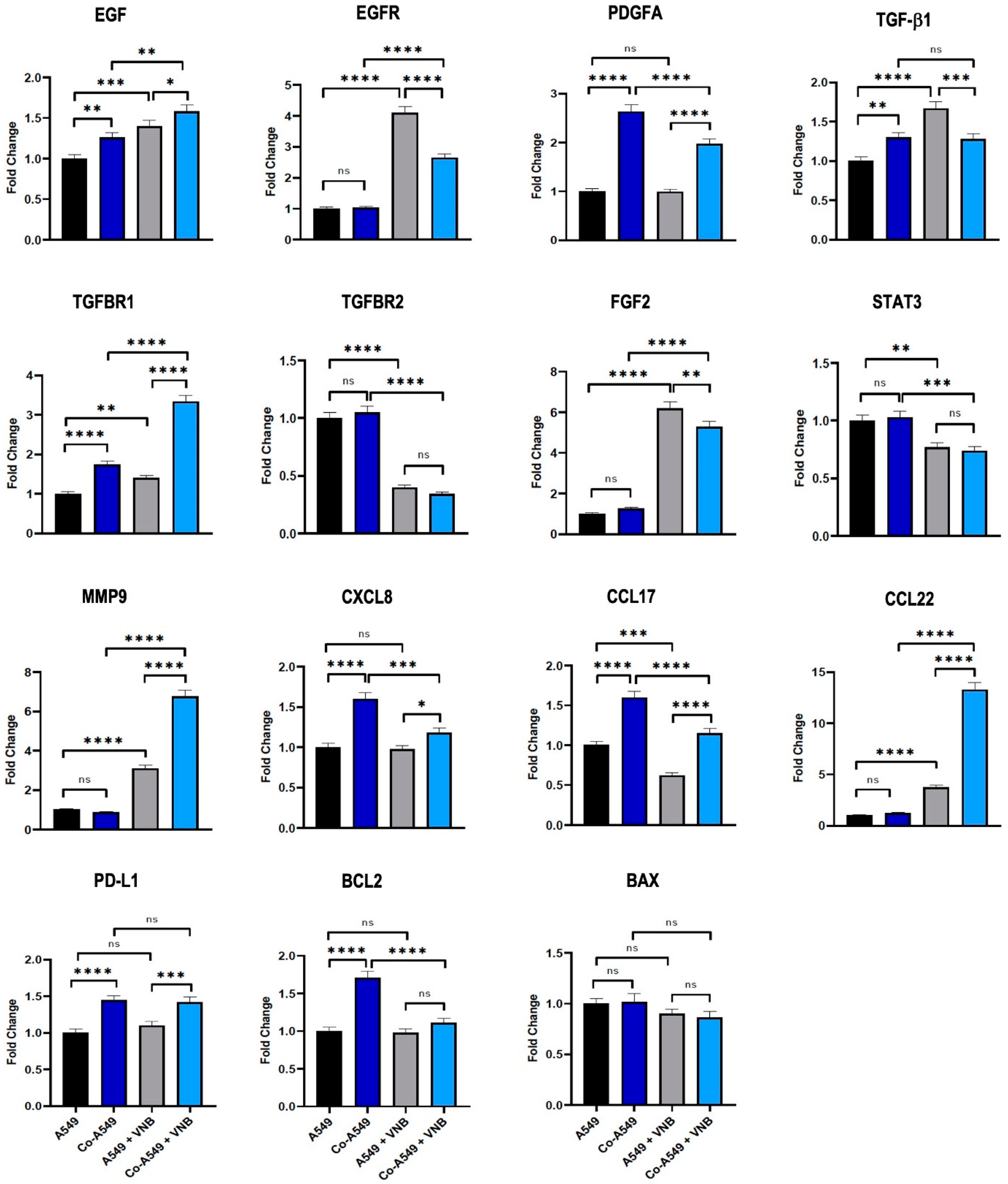
2.4. The Effect of M2 Macrophages and Vinorelbine on Gene Expression Levels of A549 Cells
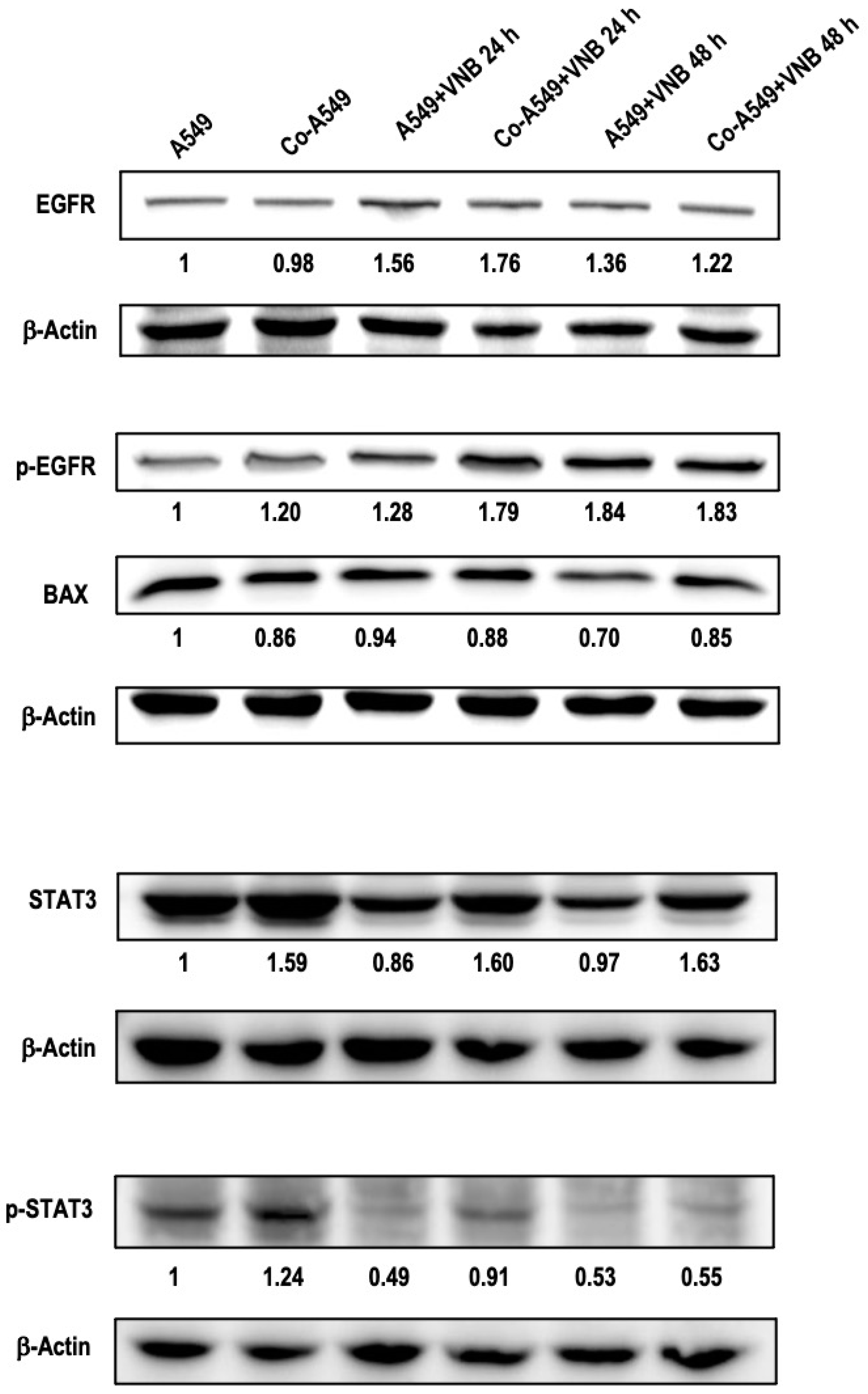
2.5. The Effects of M2 Macrophages and Vinorelbine on A549 Cells at the Protein Level
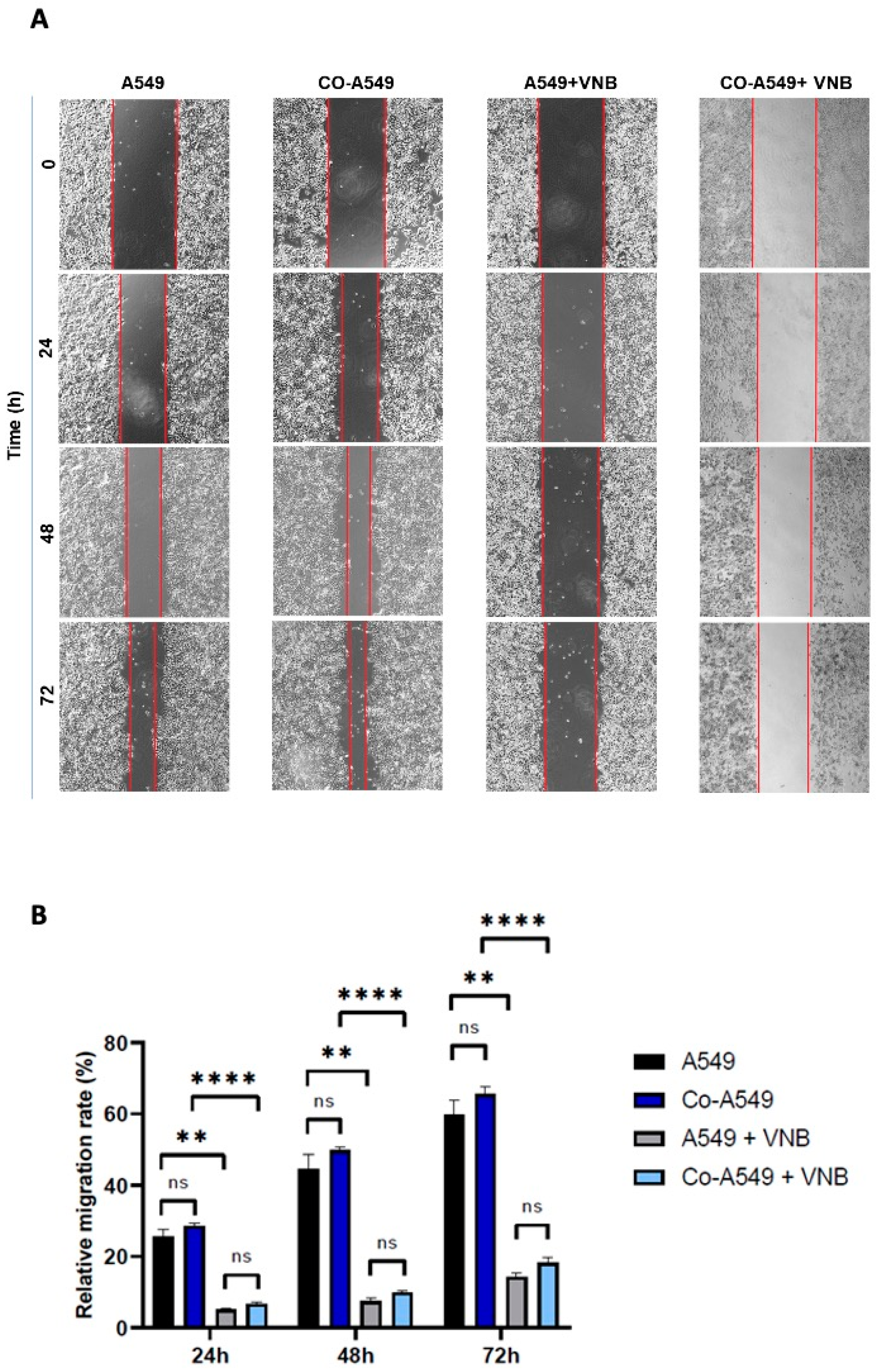
2.6. Vinorelbine Inhibits the Migration of NSCLC
3. Discussion
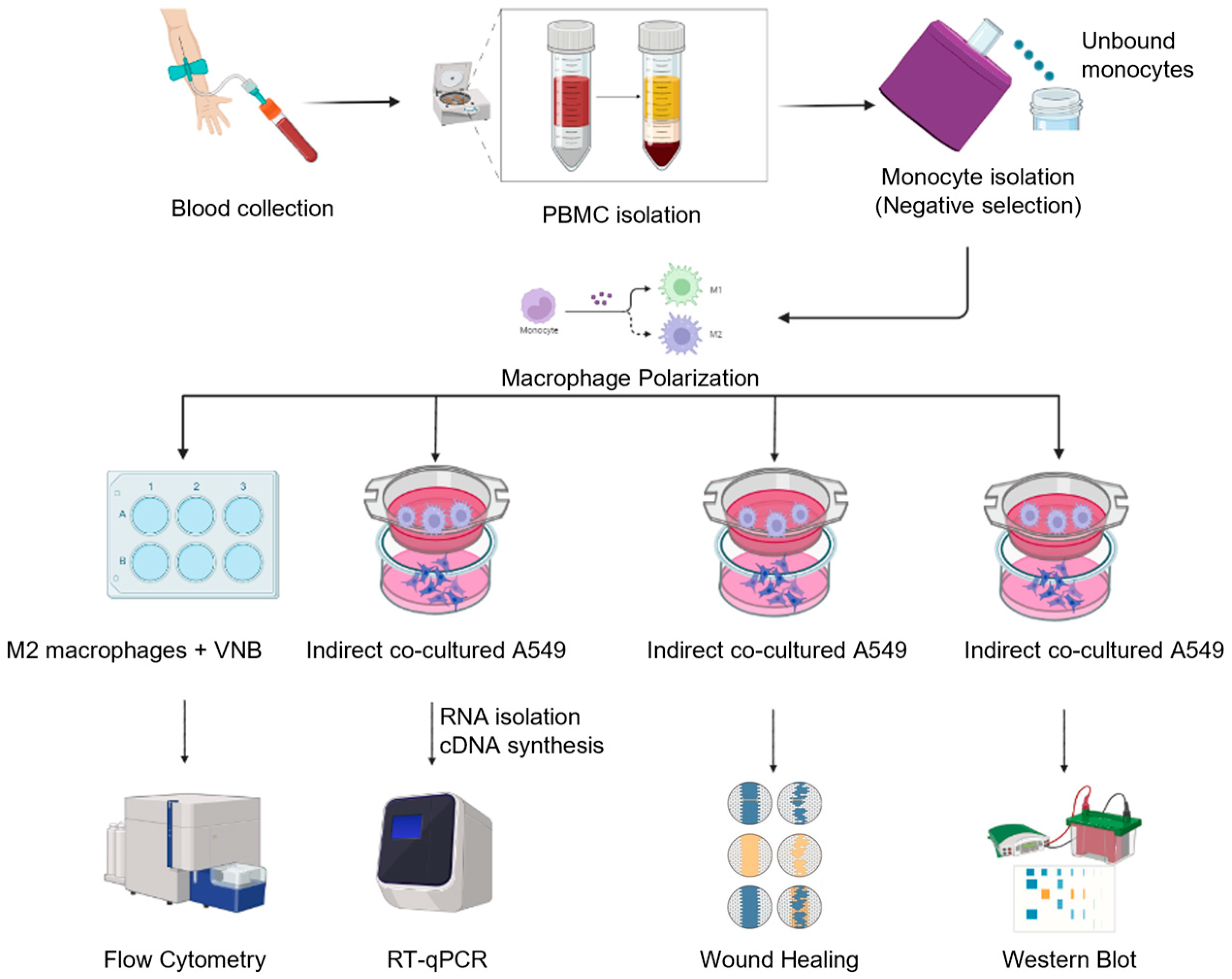
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Lines and Reagents
4.2. Cell Viability Assay
4.3. Cell Culture and Polarization of Macrophages
4.4. Flow Cytometry
4.5. Indirect Co-Culture
4.6. Quantitative Real-Time Reverse-Transcription PCR
4.7. Wound Healing Assay
4.8. Western Blot Analysis
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| A549 | Adenocarcinomic human alveolar basal epithelial cells |
| NSCLC | Non-small-cell lung cancer |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| FBS | Fetal Bovine Serum |
| RT-qPCR | Reverse-Transcriptase Quantitative PCR |
| VNB | Vinorelbine |
References
- Shuman Moss, L.A.; Jensen-Taubman, S.; Stetler-Stevenson, W.G. Matrix Metalloproteinases: Changing Roles in Tumor Progression and Metastasis. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 181, 1895–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provencio, M.; Nadal, E.; Insa, A.; García-Campelo, M.R.; Casal-Rubio, J.; Dómine, M.; Majem, M.; Rodríguez-Abreu, D.; Martínez-Martí, A.; De Castro Carpeño, J.; et al. Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy and Nivolumab in Resectable Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (NADIM): An Open-Label, Multicentre, Single-Arm, Phase 2 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 1413–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zappa, C.; Mousa, S.A. Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Current Treatment and Future Advances. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2016, 5, 288–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, H.; McCleod, M.; Hussein, M.; Morabito, A.; Rittmeyer, A.; Conter, H.J.; Kopp, H.G.; Daniel, D.; McCune, S.; Mekhail, T.; et al. Atezolizumab in Combination with Carboplatin plus Nab-Paclitaxel Chemotherapy Compared with Chemotherapy Alone as First-Line Treatment for Metastatic Non-Squamous Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (IMpower130): A Multicentre, Randomised, Open-Label, Phase 3 Tria. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 924–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanderley, C.W.; Colón, D.F.; Luiz, J.P.M.; Oliveira, F.F.; Viacava, P.R.; Leite, C.A.; Pereira, J.A.; Silva, C.M.; Silva, C.R.; Silva, R.L.; et al. Paclitaxel Reduces Tumor Growth by Reprogramming Tumor-Associated Macrophages to an M1 Profile in a TLR4-Dependent Manner. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 5891–5900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Song, J.; Hao, J.; Zhao, H.; Du, X.; Li, E.; Kuang, Y.; Yang, F.; Wang, W.; Deng, J.; et al. M2 Macrophages Promote NSCLC Metastasis by Upregulating CRYAB. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, F.O.; Sica, A.; Mantovani, A.; Locati, M. Macrophage Activation and Polarization. Front. Biosci. 2008, 13, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komohara, Y.; Fujiwara, Y.; Ohnishi, K.; Takeya, M. Tumor-Associated Macrophages: Potential Therapeutic Targets for Anti-Cancer Therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 99, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchabhai, S.; Kelemen, K.; Ahmann, G.; Sebastian, S.; Mantei, J.; Fonseca, R. Tumor-Associated Macrophages and Extracellular Matrix Metalloproteinase Inducer in Prognosis of Multiple Myeloma. Leukemia 2016, 30, 951–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Xu, J.; Lan, H. Tumor-Associated Macrophages in Tumor Metastasis: Biological Roles and Clinical Therapeutic Applications. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Shi, J. Post-Slippage Multinucleation Renders Cytotoxic Variation in Anti-Mitotic Drugs That Target the Microtubules or Mitotic Spindle. Cell Cycle 2014, 13, 1756–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douillard, J.Y.; Tribodet, H.; Aubert, D.; Shepherd, F.A.; Rosell, R.; Ding, K.; Veillard, A.S.; Seymour, L.; Le Chevalier, T.; Spiro, S.; et al. Adjuvant Cisplatin and Vinorelbine for Completely Resected Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Subgroup Analysis of the Lung Adjuvant Cisplatin Evaluation. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2010, 5, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, M.A.; Thrower, D.; Wilson, L. Mechanism of Inhibition of Cell Proliferation by Vinca Alkaloids. Cancer Res. 1991, 51, 2212–2222. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, B.; Sun, T.; Wang, S.; Lin, Y. Metronomic Therapy in Advanced Breast Cancer and NSCLC: Vinorelbine as a Paradigm of Recent Progress. Expert. Rev. Anticancer. Ther. 2021, 21, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmaninejad, A.; Valilou, S.F.; Soltani, A.; Ahmadi, S.; Abarghan, Y.J.; Rosengren, R.J.; Sahebkar, A. Tumor-Associated Macrophages: Role in Cancer Development and Therapeutic Implications. Cell. Oncol. 2019, 42, 591–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zitvogel, L.; Galluzzi, L.; Smyth, M.J.; Kroemer, G. Mechanism of Action of Conventional and Targeted Anticancer Therapies: Reinstating Immunosurveillance. Immunity 2013, 39, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiringhelli, F.; Larmonier, N.; Schmitt, E.; Parcellier, A.; Cathelin, D.; Garrido, C.; Chauffert, B.; Solary, E.; Bonnotte, B.; Martin, F. CD4+CD25+ Regulatory T Cells Suppress Tumor Immunity but Are Sensitive to Cyclophosphamide Which Allows Immunotherapy of Established Tumors to Be Curative. Eur. J. Immunol. 2004, 34, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goel, S.; Decristo, M.J.; Watt, A.C.; Brinjones, H.; Sceneay, J.; Li, B.B.; Khan, N.; Ubellacker, J.M.; Xie, S.; Metzger-Filho, O.; et al. CDK4/6 Inhibition Triggers Anti-Tumour Immunity. Nature 2017, 548, 471–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladoire, S.; Mignot, G.; Dabakuyo, S.; Arnould, L.; Apetoh, L.; Rébé, C.; Coudert, B.; Martin, F.; Bizollon, M.H.; Vanoli, A.; et al. In Situ Immune Response after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer Predicts Survival. J. Pathol. 2011, 224, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resman, N.; Oblak, A.; Gioannini, T.L.; Weiss, J.P.; Jerala, R. Tetraacylated Lipid A and Paclitaxel-Selective Activation of TLR4/MD-2 Conferred through Hydrophobic Interactions. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 1887–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Adamek, P.; Zhang, H.; Tatsui, C.E.; Rhines, L.D.; Mrozkova, P.; Li, Q.; Kosturakis, A.K.; Cassidy, R.M.; Harrison, D.S.; et al. The Cancer Chemotherapeutic Paclitaxel Increases Human and Rodent Sensory Neuron Responses to TRPV1 by Activation of TLR4. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 13487–13500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreuter, M.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Fischer, J.R.; Eberhardt, W.; Zabeck, H.; Kollmeier, J.; Serke, M.; Frickhofen, N.; Reck, M.; Engel-Riedel, W.; et al. Randomized Phase 2 Trial on Refinement of Early-Stage NSCLC Adjuvant Chemotherapy with Cisplatin and Pemetrexed versus Cisplatin and Vinorelbine: The TREAT Study. Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, 986–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altinoz, M.A.; Ozpinar, A.; Alturfan, E.E.; Elmaci, I. Vinorelbine’s Anti-Tumor Actions May Depend on the Mitotic Apoptosis, Autophagy and Inflammation: Hypotheses with Implications for Chemo-Immunotherapy of Advanced Cancers and Pediatric Gliomas. J. Chemother. 2018, 30, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, P.J.; Allen, J.E.; Biswas, S.K.; Fisher, E.A.; Gilroy, D.W.; Goerdt, S.; Gordon, S.; Hamilton, J.A.; Ivashkiv, L.B.; Lawrence, T.; et al. Macrophage Activation and Polarization: Nomenclature and Experimental Guidelines. Immunity 2014, 41, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sica, A.; Mantovani, A. Macrophage Plasticity and Polarization: In Vivo Veritas. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 787–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Caro, G.; Cortese, N.; Castino, G.F.; Grizzi, F.; Gavazzi, F.; Ridolfi, C.; Capretti, G.; Mineri, R.; Todoric, J.; Zerbi, A.; et al. Dual Prognostic Significance of Tumour-Associated Macrophages in Human Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma Treated or Untreated with Chemotherapy. Gut 2015, 65, 1710–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.N.; Wang, Y.Y.; Wang, J.; Bai, W.J.; Miao, N.J.; Wang, J. Vinblastine Resets Tumor-Associated Macrophages toward M1 Phenotype and Promotes Antitumor Immune Response. J. Immunother. Cancer 2023, 11, e007253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camerini, A.; Morabito, A.; Montanino, A.; Bernabé, R.; Grossi, F.; Ramlau, R.; Ciuleanu, T.E.; Ceresoli, G.L.; Pasello, G.; de Marinis, F.; et al. Metronomic Oral Vinorelbine in Previously Untreated Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients Unfit for Platinum-Based Chemotherapy: Results of the Randomized Phase II Tempo Lung Trial. ESMO Open 2021, 6, 100051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deswal, B.; Bagchi, U.; Santra, M.K.; Garg, M.; Kapoor, S. Inhibition of STAT3 by 2-Methoxyestradiol Suppresses M2 Polarization and Protumoral Functions of Macrophages in Breast Cancer. BMC Cancer 2024, 24, 1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Fu, Q.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yu, P.; Liu, Z.; Sun, X. Anti-Tubulin Agent Vinorelbine Inhibits Metastasis of Cancer Cells by Regulating Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 200, 112332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollard, J.W. Tumour-Educated Macrophages Promote Tumour Progression and Metastasis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komohara, Y.; Jinushi, M.; Takeya, M. Clinical Significance of Macrophage Heterogeneity in Human Malignant Tumors. Cancer Sci. 2014, 105, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mills, C.D. M1 and M2 Macrophages: Oracles of Health and Disease. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 32, 463–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lança, T.; Silva-Santos, B. The Split Nature of Tumor-Infiltrating Leukocytes: Implications for Cancer Surveillance and Immunotherapy. Oncoimmunology 2012, 1, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessenbrock, K.; Plaks, V.; Werb, Z. Matrix Metalloproteinases: Regulators of the Tumor Microenvironment. Cell 2010, 141, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantovani, A.; Sozzani, S.; Locati, M.; Allavena, P.; Sica, A. Macrophage Polarization: Tumor-Associated Macrophages as a Paradigm for Polarized M2 Mononuclear Phagocytes. Trends Immunol. 2002, 23, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimbourg, J.; Joalland, M.P.; Cabart, M.; De Plater, L.; Bouquet, F.; Savina, A.; Decaudin, D.; Bennouna, J.; Vallette, F.M.; Lalier, L. Sensitization of EGFR Wild-Type Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells to EGFR-Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Erlotinib. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2017, 16, 1634–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlandi, P.; Di Desidero, T.; Salvia, G.; Muscatello, B.; Francia, G.; Bocci, G. Metronomic Vinorelbine Is Directly Active on Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells and Sensitizes the EGFRL858R/T790M Cells to Reversible EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 152, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Bello, M.G.; Alama, A.; Barletta, G.; Coco, S.; Truini, A.; Vanni, I.; Boccardo, S.; Genova, C.; Rijavec, E.; Biello, F.; et al. Sequential Use of Vinorelbine Followed by Gefitinib Enhances the Antitumor Effect in NSCLC Cell Lines Poorly Responsive to Reversible EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 137, 2947–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsukawa, A.; Takeda, K.; Kudo, S.; Maeda, T.; Kagayama, M.; Akira, S. Aberrant Inflammation and Lethality to Septic Peritonitis in Mice Lacking STAT3 in Macrophages and Neutrophils. J. Immunol. 2003, 171, 6198–6205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sica, A.; Bronte, V. Altered Macrophage Differentiation and Immune Dysfunction in Tumor Development. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 1155–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Kortylewski, M.; Pardoll, D. Crosstalk between Cancer and Immune Cells: Role of STAT3 in the Tumour Microenvironment. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 7, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iriki, T.; Ohnishi, K.; Fujiwara, Y.; Horlad, H.; Saito, Y.; Pan, C.; Ikeda, K.; Mori, T.; Suzuki, M.; Ichiyasu, H.; et al. The Cell-Cell Interaction between Tumor-Associated Macrophages and Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells Is Involved in Tumor Progression via STAT3 Activation. Lung Cancer 2017, 106, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Gene Name | Sequence |
|---|---|
| β-Actin | 5′-ATGATGATATCGCCGCGCTC-3′ 5′-TCGTCGCCCACATAGGAATC-3′ |
| MMP9 | 5′-CTGGAGGTTCGACGTGAAGG-3′ 5′-TCGGTACTGGAAGACGTCGTG-3′ |
| CXCL8 | 5′-CCAGGAAGAAACCACCGGAA-3′ 5′-CGCAGTGTGGTCCACTCTCAA-3′ |
| EGF | 5′-CAGTGAAGTCAGCCAGAGCA-3′ 5′-TGGGGCATCTTTTACTCTCCT-3′ |
| EGFR | 5′-CTACAACCCCACCACGTACC-3′ 5′-GCCCTTCGCACTTCTTACACT-3′ |
| PDGFA | 5′-TTAAAAATCGGGGAGGGGAGT-3′ 5′-TCAGGCTGGTGTCCAAAGAA-3′ |
| TGF-β1 | 5′-TGGACATCAACGGGTTCACT-3′ 5′-CTTGGGCTCGTGGATCCACTT-3′ |
| TGFBR1 | 5′-TAACTGAGGTTAGAGCTAGTG-3′ 5′-AATGTAAGAAGACCATGACAA-3′ |
| TGFBR2 | 5′-GACAATCACACATGCAGTGG-3′ 5′-AAGAGAAGTGCTAGGCAGGGA-3′ |
| STAT3 | 5′-GGTGCCTGTGGGAAGAATCA-3′ 5′-GACATCCTGAAGGTGCTGCT-3′ |
| FGF2 | 5′-GAAGAGCGACCCTCACATCA-3′ 5′-AGCCAGGTAACGGTTAGCAC-3′ |
| PD-L1 | 5′-GGTGCCGACTACAAGCGAA-3′ 5′-TCTTGGAATTGGTGGTGGTGG-3′ |
| CCL17 | 5′-ATTCAAAACCAGGGTGTCTC-3′ 5′-GGTACCACGTCTTCAGCTTTC-3′ |
| CCL22 | 5′-CCTGGGCTGAGACATACAGGA-3′ 5′-CGGTAACGGACGTAATCACGG-3′ |
| BCL2 | 5′-GAACTGGGGGAGGATTGTGG-3′ 5′-CCGTACAGTTCCACAAAGGC-3′ |
| BAX | 5′-GTCTTTTTCCGAGTGGCAGC-3′ 5′-GGGACATCAGTCGCTTCAGT-3′ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Omar, A.; Asadi, M.; Mert, U.; Muftuoglu, C.; Karakus, H.S.; Goksel, T.; Caner, A. Effects of Vinorelbine on M2 Macrophages in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2252. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26052252
Al-Omar A, Asadi M, Mert U, Muftuoglu C, Karakus HS, Goksel T, Caner A. Effects of Vinorelbine on M2 Macrophages in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(5):2252. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26052252
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Omar, Ahmed, Milad Asadi, Ufuk Mert, Can Muftuoglu, Haydar Soydaner Karakus, Tuncay Goksel, and Ayse Caner. 2025. "Effects of Vinorelbine on M2 Macrophages in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 5: 2252. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26052252
APA StyleAl-Omar, A., Asadi, M., Mert, U., Muftuoglu, C., Karakus, H. S., Goksel, T., & Caner, A. (2025). Effects of Vinorelbine on M2 Macrophages in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(5), 2252. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26052252





