Unveiling Gestational Diabetes: An Overview of Pathophysiology and Management
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Search Strategy
3. Mechanistic Insights into the Progression from GDM to T1D and T2D
4. Genetic Risk Factors for GDM
5. Pathophysiology of GDM and Association with T1D and T2D
5.1. Molecular Mechanisms Underlying GDM
5.2. Immunological Aspects Connecting GDM and T1D Progression
5.3. Long-Term Effects of Hyperglycemia During Pregnancy on Pancreatic Function
5.4. Immunological Mechanisms in GDM
5.5. Role of Placental Hormones and Signaling in GDM
5.6. Hypothalamic Involvement in GDM
5.6.1. Hormonal Regulation and Hypothalamic Dysfunction in GDM
5.6.2. Hypothalamic Inflammation and Its Role in GDM
5.6.3. Neuroendocrine Regulation and Glucose Toxicity
6. Clinical Manifestations and Complications
6.1. Clinical Presentation of GDM
6.2. Potential Complications Associated with GDM
6.3. Gestational Influences on the Progression to DM
7. Screening and Diagnosis
7.1. Current Screening Methods for GDM During Pregnancy
7.2. Challenges in Identifying Individual Risk for T1D Post-GDM
7.3. Advances in Diagnostic Tools and Predictive Modeling
8. Management Strategies
8.1. Antenatal Management of GDM
8.2. Therapeutic Options and Long-Term Outlook Post-GDM
8.3. Role of Insulin Therapy in Preventing Diabetes Progression
8.4. Emerging Pharmacological Therapies for GDM
9. Long-Term Follow-Up and Outcomes
9.1. Tracking Outcomes of Individuals with a History of GDM
9.2. Identifying Biomarkers for T1D Progression
9.3. Challenges in Long-Term Follow-Up Studies
10. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Quintanilla Rodriguez, B.S.; Vadakekut, E.S.; Mahdy, H. Gestational Diabetes. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Sweeting, A.; Wong, J.; Murphy, H.R.; Ross, G.P. A Clinical Update on Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Endocr. Rev. 2022, 43, 763–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szmuilowicz, E.D.; Josefson, J.L.; Metzger, B.E. Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 48, 479–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, W.; Luo, C.; Huang, J.; Li, C.; Liu, Z.; Liu, F. Gestational diabetes mellitus and adverse pregnancy outcomes: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2022, 377, e067946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Champion, M.L.; Battarbee, A.N.; Biggio, J.R.; Casey, B.M.; Harper, L.M. Postpartum glucose intolerance following early gestational diabetes mellitus. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. MFM 2022, 4, 100609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzger, B.E.; Lowe, L.P.; Dyer, A.R.; Trimble, E.R.; Chaovarindr, U.; Coustan, D.R.; Hadden, D.R.; McCance, D.R.; Hod, M.; McIntyre, H.D.; et al. Hyperglycemia and adverse pregnancy outcomes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 1991–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billionnet, C.; Mitanchez, D.; Weill, A.; Nizard, J.; Alla, F.; Hartemann, A.; Jacqueminet, S. Gestational diabetes and adverse perinatal outcomes from 716,152 births in France in 2012. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 636–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regnault, N.; Lebreton, E.; Tang, L.; Fosse-Edorh, S.; Barry, Y.; Olié, V.; Billionnet, C.; Weill, A.; Vambergue, A.; Cosson, E. Maternal and neonatal outcomes according to the timing of diagnosis of hyperglycaemia in pregnancy: A nationwide cross-sectional study of 695,912 deliveries in France in 2018. Diabetologia 2024, 67, 516–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrn, M.; Penckofer, S. The relationship between gestational diabetes and antenatal depression. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Neonatal Nurs. 2015, 44, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, P.C.; Ling, L.P.; Omar, S.Z. The 50-g glucose challenge test and pregnancy outcome in a multiethnic Asian population at high risk for gestational diabetes. Int. J. Gynaecol. Obstet. 2009, 105, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeting, A.; Hannah, W.; Backman, H.; Catalano, P.; Feghali, M.; Herman, W.H.; Hivert, M.F.; Immanuel, J.; Meek, C.; Oppermann, M.L.; et al. Epidemiology and management of gestational diabetes. Lancet 2024, 404, 175–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaight, C.; Gross, J.; Horsch, A.; Puder, J.J. Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Endocr. Dev. 2016, 31, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiefari, E.; Arcidiacono, B.; Foti, D.; Brunetti, A. Gestational diabetes mellitus: An updated overview. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2017, 40, 899–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirabelli, M.; Tocci, V.; Donnici, A.; Giuliano, S.; Sarnelli, P.; Salatino, A.; Greco, M.; Puccio, L.; Chiefari, E.; Foti, D.P.; et al. Maternal Preconception Body Mass Index Overtakes Age as a Risk Factor for Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Ren, X.; He, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, S.; Chen, W. Maternal age and the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis of over 120 million participants. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2020, 162, 108044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Zhang, H.; Wu, J.; Zhang, B.; Lan, L. Analysis of Risk Factors Associated with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Retrospective Case-Control Study. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2024, 17, 4229–4238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; England, L.; Wilson, H.G.; Bish, C.; Satten, G.A.; Dietz, P. Percentage of gestational diabetes mellitus attributable to overweight and obesity. Am. J. Public Health 2010, 100, 1047–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. QuickStats: Percentage of Mothers with Gestational Diabetes, * by Maternal Age—National Vital Statistics System, United States, 2016 and 2021. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2023, 72, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Du, S.; Sun, D.; Li, X.; Heianza, Y.; Hu, G.; Sun, L.; Pei, X.; Shang, X.; Qi, L. Prevalence and Trends in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Among Women in the United States, 2006–2017: A Population-Based Study. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 868094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavicchia, P.P.; Liu, J.; Adams, S.A.; Steck, S.E.; Hussey, J.R.; Daguisé, V.G.; Hebert, J.R. Proportion of gestational diabetes mellitus attributable to overweight and obesity among non-Hispanic black, non-Hispanic white, and Hispanic women in South Carolina. Matern. Child. Health J. 2014, 18, 1919–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chu, S.Y.; Callaghan, W.M.; Kim, S.Y.; Schmid, C.H.; Lau, J.; England, L.J.; Dietz, P.M. Maternal obesity and risk of gestational diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 2070–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwash, S.M.; McIntyre, H.D.; Mamun, A. The association of general obesity, central obesity and visceral body fat with the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: Evidence from a systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2021, 15, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Q.; Yang, Y.; Cao, H.; Xu, Z.; Tian, Z.; Zhan, Y.; Li, Z.; Lu, M.; Gu, F.; Lu, Q.; et al. Contribution of Insulin Resistance and β Cell Dysfunction to Gestational Diabetes Stratified for Pre-pregnant Body Mass Index. Reprod. Sci. 2024, 31, 1151–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Nawsherwan; Fan, C.; Mubarik, S.; Nabi, G.; Ping, Y.X. The trend in delayed childbearing and its potential consequences on pregnancy outcomes: A single center 9-years retrospective cohort study in Hubei, China. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2022, 22, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathews, T.J.; Hamilton, B.E. Mean Age of Mothers is on the Rise: United States, 2000–2014. NCHS Data Brief 2016, 232, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Szoke, E.; Shrayyef, M.Z.; Messing, S.; Woerle, H.J.; van Haeften, T.W.; Meyer, C.; Mitrakou, A.; Pimenta, W.; Gerich, J.E. Effect of aging on glucose homeostasis: Accelerated deterioration of beta-cell function in individuals with impaired glucose tolerance. Diabetes Care 2008, 31, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lean, S.C.; Derricott, H.; Jones, R.L.; Heazell, A.E.P. Advanced maternal age and adverse pregnancy outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hincapie, M.A.; Badeghiesh, A.; Baghlaf, H.; Dahan, M.H. Association between pre-gestational diabetes in women with polycystic ovary syndrome and adverse obstetric outcomes. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2025, 304, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedula, K.L.; Hillier, T.A.; Schmidt, M.M.; Mullen, J.A.; Charles, M.A.; Pettitt, D.J. Ethnic differences in gestational oral glucose screening in a large US population. Ethn. Dis. 2009, 19, 414–419. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, G.L.; Huang, H.F. Paternal transgenerational glucose intolerance with epigenetic alterations in second generation offspring of GDM. Asian J. Androl. 2013, 15, 451–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, W.L., Jr. Genetics and Epigenetics: Implications for the Life Course of Gestational Diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, C.S.; Abell, S.; Aroni, R.; Nankervis, A.; Boyle, J.; Teede, H. Ethnic differences in prevalence, risk factors, and perinatal outcomes of gestational diabetes mellitus: A comparison between immigrant ethnic Chinese women and Australian-born Caucasian women in Australia. J. Diabetes 2019, 11, 809–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, H.R.; Moon, J.H.; Lim, J.S.; Lee, Y.A.; Shin, C.H.; Hong, J.S.; Kwak, S.H.; Choi, S.H.; Jang, H.C. Maternal Hyperglycemia during Pregnancy Increases Adiposity of Offspring. Diabetes Metab. J. 2021, 45, 730–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sole, K.B.; Staff, A.C.; Laine, K. Maternal diseases and risk of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy across gestational age groups. Pregnancy Hypertens. 2021, 25, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wicklow, B.; Retnakaran, R. Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Its Implications across the Life Span. Diabetes Metab. J. 2023, 47, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lee, N.K.; Moon, J.H. Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Mechanisms Underlying Maternal and Fetal Complications. Endocrinol. Metab. 2025, 40, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D. Pregnancy: A stress test for life. Curr. Opin. Obstet. Gynecol. 2003, 15, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gestational Hypertension and Preeclampsia: ACOG Practice Bulletin, Number 222. Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, 135, e237–e260. [CrossRef]
- Shoelson, S.E.; Lee, J.; Goldfine, A.B. Inflammation and insulin resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 1793–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosla, K.; Heimberger, S.; Nieman, K.M.; Tung, A.; Shahul, S.; Staff, A.C.; Rana, S. Long-Term Cardiovascular Disease Risk in Women After Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy: Recent Advances in Hypertension. Hypertension 2021, 78, 927–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lykke, J.A.; Langhoff-Roos, J.; Sibai, B.M.; Funai, E.F.; Triche, E.W.; Paidas, M.J. Hypertensive pregnancy disorders and subsequent cardiovascular morbidity and type 2 diabetes mellitus in the mother. Hypertension 2009, 53, 944–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löbner, K.; Knopff, A.; Baumgarten, A.; Mollenhauer, U.; Marienfeld, S.; Garrido-Franco, M.; Bonifacio, E.; Ziegler, A.G. Predictors of postpartum diabetes in women with gestational diabetes mellitus. Diabetes 2006, 55, 792–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lydon, K.; Dunne, F.P.; Owens, L.; Avalos, G.; Sarma, K.M.; O’Connor, C.; Nestor, L.; McGuire, B.E. Psychological stress associated with diabetes during pregnancy: A pilot study. Ir. Med. J. 2012, 105, 26–28. [Google Scholar]
- Bowers, K.; Laughon, S.K.; Kim, S.; Mumford, S.L.; Brite, J.; Kiely, M.; Zhang, C. The association between a medical history of depression and gestational diabetes in a large multi-ethnic cohort in the United States. Paediatr. Perinat. Epidemiol. 2013, 27, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kivimäki, M.; Bartolomucci, A.; Kawachi, I. The multiple roles of life stress in metabolic disorders. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2023, 19, 10–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, G.; Lightman, S. The human stress response. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, A.; Dougherty, S.; Cucchiara, A.; Marcus, C.L.; Brooks, L.J. Catecholamines, adiponectin, and insulin resistance as measured by HOMA in children with obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep 2010, 33, 1185–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surwit, R.S.; van Tilburg, M.A.; Zucker, N.; McCaskill, C.C.; Parekh, P.; Feinglos, M.N.; Edwards, C.L.; Williams, P.; Lane, J.D. Stress management improves long-term glycemic control in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2002, 25, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benton, M.; Silverio, S.A.; Ismail, K. “It feels like medically promoted disordered eating”: The psychosocial impact of gestational diabetes mellitus in the perinatal period. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0288395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, L.; Sims, R.; Glasziou, P.; Thomas, R. Women’s experiences of a diagnosis of gestational diabetes mellitus: A systematic review. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2020, 20, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhwava, L.S.; Murphy, K.; Zarowsky, C.; Levitt, N. Perspectives on the psychological and emotional burden of having gestational diabetes amongst low-income women in Cape Town, South Africa. BMC Womens Health 2020, 20, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidsen, E.; Maindal, H.T.; Rod, M.H.; Olesen, K.; Byrne, M.; Damm, P.; Nielsen, K.K. The stigma associated with gestational diabetes mellitus: A scoping review. eClinicalMedicine 2022, 52, 101614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Hinkle, S.N.; Grantz, K.L.; Kim, S.; Grewal, J.; Grobman, W.A.; Skupski, D.W.; Newman, R.B.; Chien, E.K.; Sciscione, A.; et al. Glycaemic status during pregnancy and longitudinal measures of fetal growth in a multi-racial US population: A prospective cohort study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 8, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansson, T.; Myatt, L.; Powell, T.L. The role of trophoblast nutrient and ion transporters in the development of pregnancy complications and adult disease. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2009, 7, 521–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neill, K.; Alexander, J.; Azuma, R.; Xiao, R.; Snyder, N.W.; Mesaros, C.A.; Blair, I.A.; Pinney, S.E. Gestational Diabetes Alters the Metabolomic Profile in 2nd Trimester Amniotic Fluid in a Sex-Specific Manner. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graca, G.; Duarte, I.F.; Barros, A.S.; Goodfellow, B.J.; Diaz, S.O.; Pinto, J.; Carreira, I.M.; Galhano, E.; Pita, C.; Gil, A.M. Impact of prenatal disorders on the metabolic profile of second trimester amniotic fluid: A nuclear magnetic resonance metabonomic study. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 6016–6024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combs, C.A.; Gunderson, E.; Kitzmiller, J.L.; Gavin, L.A.; Main, E.K. Relationship of fetal macrosomia to maternal postprandial glucose control during pregnancy. Diabetes Care 1992, 15, 1251–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ornoy, A.; Becker, M.; Weinstein-Fudim, L.; Ergaz, Z. Diabetes during Pregnancy: A Maternal Disease Complicating the Course of Pregnancy with Long-Term Deleterious Effects on the Offspring. A Clinical Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, S.H.; Choi, S.H.; Jung, H.S.; Cho, Y.M.; Lim, S.; Cho, N.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Park, K.S.; Jang, H.C. Clinical and genetic risk factors for type 2 diabetes at early or late post partum after gestational diabetes mellitus. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, E744–E752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, M.W.; Canick, J.A.; Hogan, J.W.; Shellum, C.; Somers, M.; Star, J.A. Amniotic fluid insulin at 14–20 weeks’ gestation: Association with later maternal glucose intolerance and birth macrosomia. Diabetes Care 2001, 24, 1259–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampl, M.; Jeanty, P. Exposure to maternal diabetes is associated with altered fetal growth patterns: A hypothesis regarding metabolic allocation to growth under hyperglycemic-hypoxemic conditions. Am. J. Hum. Biol. 2004, 16, 237–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, J.M. Case of Pregnancy and Labour Complicated with Diabetes Mellitus. Edinb. Med. J. 1873, 18, 696–698. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Plows, J.F.; Stanley, J.L.; Baker, P.N.; Reynolds, C.M.; Vickers, M.H. The Pathophysiology of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujishima, A.; Onodera, Y.; Miura, H.; Terada, Y. Anti-glutamic Acid Decarboxylase Antibody-Positive Gestational Diabetes Mellitus with Autoimmune Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus in the Early Postpartum Period: A Case Report and Literature Review. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2023, 259, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choy, K.H.A.; Wong, T.; Cao, R.H.M.; Flack, J.R. Fulminant type 1 diabetes mellitus in a GDM pregnancy: Early recognition is vital for maternal and fetal outcomes. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. Case Rep. 2022, 2022, 22-0262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Incani, M.; Baroni, M.G.; Cossu, E. Testing for type 1 diabetes autoantibodies in gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM): Is it clinically useful? BMC Endocr. Disord. 2019, 19, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfadhli, E.M. Gestational diabetes mellitus. Saudi Med. J. 2015, 36, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Füchtenbusch, M.; Ferber, K.; Standl, E.; Ziegler, A.G. Prediction of type 1 diabetes postpartum in patients with gestational diabetes mellitus by combined islet cell autoantibody screening: A prospective multicenter study. Diabetes 1997, 46, 1459–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chodick, G.; Elchalal, U.; Sella, T.; Heymann, A.D.; Porath, A.; Kokia, E.; Shalev, V. The risk of overt diabetes mellitus among women with gestational diabetes: A population-based study. Diabet. Med. 2010, 27, 779–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikoh Rph, C.L.; Tang Tinong, R. The Incidence and Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus After Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Cureus 2023, 15, e44468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retnakaran, R.; Qi, Y.; Sermer, M.; Connelly, P.W.; Hanley, A.J.; Zinman, B. Beta-cell function declines within the first year postpartum in women with recent glucose intolerance in pregnancy. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 1798–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huopio, H.; Hakkarainen, H.; Pääkkönen, M.; Kuulasmaa, T.; Voutilainen, R.; Heinonen, S.; Cederberg, H. Long-term changes in glucose metabolism after gestational diabetes: A double cohort study. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2014, 14, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benham, J.L.; Gingras, V.; McLennan, N.M.; Most, J.; Yamamoto, J.M.; Aiken, C.E.; Ozanne, S.E.; Reynolds, R.M. Precision gestational diabetes treatment: A systematic review and meta-analyses. Commun. Med. 2023, 3, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhang, C. Prevalence of Gestational Diabetes and Risk of Progression to Type 2 Diabetes: A Global Perspective. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2016, 16, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.K.; Sussel, L.; Davidson, H.W. Inherent Beta Cell Dysfunction Contributes to Autoimmune Susceptibility. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirci, C.; Ernst, S.; Alvarez-Perez, J.C.; Rosa, T.; Valle, S.; Shridhar, V.; Casinelli, G.P.; Alonso, L.C.; Vasavada, R.C.; García-Ocana, A. Loss of HGF/c-Met signaling in pancreatic β-cells leads to incomplete maternal β-cell adaptation and gestational diabetes mellitus. Diabetes 2012, 61, 1143–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akirav, E.M.; Lebastchi, J.; Galvan, E.M.; Henegariu, O.; Akirav, M.; Ablamunits, V.; Lizardi, P.M.; Herold, K.C. Detection of β cell death in diabetes using differentially methylated circulating DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 19018–19023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambelet, M.; Terra, L.F.; Fukaya, M.; Meyerovich, K.; Labriola, L.; Cardozo, A.K.; Allagnat, F. Dysfunctional autophagy following exposure to pro-inflammatory cytokines contributes to pancreatic β-cell apoptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eizirik, D.L.; Cardozo, A.K.; Cnop, M. The role for endoplasmic reticulum stress in diabetes mellitus. Endocr. Rev. 2008, 29, 42–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarim, A.L.; Heitmeier, M.R.; Corbett, J.A. Irreversible inhibition of metabolic function and islet destruction after a 36-hour exposure to interleukin-1beta. Endocrinology 1997, 138, 5301–5307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drucker, D.J. The biology of incretin hormones. Cell Metab. 2006, 3, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brelje, T.C.; Scharp, D.W.; Lacy, P.E.; Ogren, L.; Talamantes, F.; Robertson, M.; Friesen, H.G.; Sorenson, R.L. Effect of homologous placental lactogens, prolactins, and growth hormones on islet B-cell division and insulin secretion in rat, mouse, and human islets: Implication for placental lactogen regulation of islet function during pregnancy. Endocrinology 1993, 132, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes Association. 13. Management of Diabetes in Pregnancy. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, S114–S119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, L.; Poulsen, C.W.; Kampmann, U.; Smedegaard, S.B.; Ovesen, P.G.; Fuglsang, J. Diet and Healthy Lifestyle in the Management of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Retnakaran, M.; Viana, L.V.; Kramer, C.K. Lifestyle intervention for the prevention of type 2 diabetes in women with prior gestational diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2023, 25, 1196–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minschart, C.; Myngheer, N.; Maes, T.; De Block, C.; Van Pottelbergh, I.; Abrams, P.; Vinck, W.; Leuridan, L.; Driessens, S.; Mathieu, C.; et al. Effectiveness of a blended mobile-based lifestyle intervention in women with glucose intolerance after a recent history of gestational diabetes (MELINDA): A 1-year, prospective, multicentre, randomised controlled trial. eClinicalMedicine 2024, 70, 102523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampmann, U.; Knorr, S.; Fuglsang, J.; Ovesen, P. Determinants of Maternal Insulin Resistance during Pregnancy: An Updated Overview. J. Diabetes Res. 2019, 2019, 5320156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, M.J.; Parra, H.; Santeliz, R.; Bautista, J.; Luzardo, E.; Villasmil, N.; Martínez, M.S.; Chacín, M.; Cano, C.; Checa-Ros, A.; et al. The Placental Role in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Molecular Perspective. touchREV Endocrinol. 2024, 20, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, C.; Schwarz, S.; Moser, G.; Cvitic, S.; Jantscher-Krenn, E.; Gauster, M.; Hiden, U. Placental Endocrine Activity: Adaptation and Disruption of Maternal Glucose Metabolism in Pregnancy and the Influence of Fetal Sex. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco-Wong, I.; Moller, A.; Giachini, F.R.; Lima, V.V.; Toledo, F.; Stojanova, J.; Sobrevia, L.; San Martín, S. Placental structure in gestational diabetes mellitus. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2020, 1866, 165535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Anna, R.; Di Benedetto, A.; Scilipoti, A.; Santamaria, A.; Interdonato, M.L.; Petrella, E.; Neri, I.; Pintaudi, B.; Corrado, F.; Facchinetti, F. Myo-inositol Supplementation for Prevention of Gestational Diabetes in Obese Pregnant Women: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Obstet. Gynecol. 2015, 126, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asimakopoulos, G.; Pergialiotis, V.; Antsaklis, P.; Theodora, M.; Loutradis, D.; Daskalakis, G. Effect of dietary myo-inositol supplementation on the insulin resistance and the prevention of gestational diabetes mellitus: An open-label, randomized controlled trial. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2024, 310, 1895–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esmaeilzadeh, S.; Ghadimi, R.; Mashayekh-Amiri, S.; Delavar, M.A.; Basirat, Z. The effect of myo-inositol supplementation on the prevention of gestational diabetes in overweight pregnant women: A randomized, double-blind, controlled trial. Minerva Obstet. Gynecol. 2023, 75, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takele, W.W.; Vesco, K.K.; Josefson, J.; Redman, L.M.; Hannah, W.; Bonham, M.P.; Chen, M.; Chivers, S.C.; Fawcett, A.J.; Grieger, J.A.; et al. Effective interventions in preventing gestational diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Commun. Med. 2024, 4, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Xian, T.; Jia, X.; Zhang, L.; Liu, L.; Man, F.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Pan, Q.; Guo, L. A cross-sectional study on the associations of insulin resistance with sex hormone, abnormal lipid metabolism in T2DM and IGT patients. Medicine 2017, 96, e7378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, E.H.; Zhang, C.; Mumford, S.L.; Ye, A.; Trevisan, M.; Chen, L.; Browne, R.W.; Wactawski-Wende, J.; Schisterman, E.F. Longitudinal study of insulin resistance and sex hormones over the menstrual cycle: The BioCycle Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 5435–5442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuyama, H.; Hiramatsu, Y. Potential role of estradiol and progesterone in insulin resistance through constitutive androstane receptor. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2011, 47, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Yang, W.; Zhou, F.; Li, X.; Pan, Q.; Shen, Z.; Han, G.; Newell-Fugate, A.; Tian, Y.; Majeti, R.; et al. Estrogen Improves Insulin Sensitivity and Suppresses Gluconeogenesis via the Transcription Factor Foxo1. Diabetes 2019, 68, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemany, M. Estrogens and the regulation of glucose metabolism. World J. Diabetes 2021, 12, 1622–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, T.; Hori, S.; Sugiyama, M.; Fujisawa, E.; Nakano, T.; Tsuneki, H.; Nagira, K.; Saito, S.; Sasaoka, T. Progesterone inhibits glucose uptake by affecting diverse steps of insulin signaling in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 298, E881–E888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luiro, K.; Auvinen, A.M.; Auvinen, J.; Jokelainen, J.; Järvelä, I.; Knip, M.; Tapanainen, J.S. Autoantibodies predict type 1 diabetes after gestational diabetes—A 23-year cohort study. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1286375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Järvelä, I.Y.; Juutinen, J.; Koskela, P.; Hartikainen, A.L.; Kulmala, P.; Knip, M.; Tapanainen, J.S. Gestational diabetes identifies women at risk for permanent type 1 and type 2 diabetes in fertile age: Predictive role of autoantibodies. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, M.; Chen, S.; Lei, H.; Mu, H.; Yu, H.; Hou, Y.; Tang, K.; Chen, X.; et al. Aberrant NK cell profile in gestational diabetes mellitus with fetal growth restriction. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1346231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hara Cde, C.; França, E.L.; Fagundes, D.L.; de Queiroz, A.A.; Rudge, M.V.; Honorio-França, A.C.; Calderon Ide, M. Characterization of Natural Killer Cells and Cytokines in Maternal Placenta and Fetus of Diabetic Mothers. J. Immunol. Res. 2016, 2016, 7154524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McElwain, C.J.; McCarthy, F.P.; McCarthy, C.M. Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Maternal Immune Dysregulation: What We Know So Far. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheu, A.; Chan, Y.; Ferguson, A.; Bakhtyari, M.B.; Hawke, W.; White, C.; Chan, Y.F.; Bertolino, P.J.; Woon, H.G.; Palendira, U.; et al. A proinflammatory CD4+ T cell phenotype in gestational diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 1633–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiba, H.; Fukui, A.; Fuchinoue, K.; Funamizu, A.; Tanaka, K.; Mizunuma, H. Expression of Natural Cytotoxicity Receptors on and Intracellular Cytokine Production by NK Cells in Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2016, 75, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, T.F.; Borges, C.M.; Mattar, R.; Gomes, C.P.; de Angelo, A.G.S.; Pendeloski, K.P.T.; Daher, S. Impaired Treg and NK cells profile in overweight women with gestational diabetes mellitus. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2018, 79, e12810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sifnaios, E.; Mastorakos, G.; Psarra, K.; Panagopoulos, N.D.; Panoulis, K.; Vitoratos, N.; Rizos, D.; Creatsas, G. Gestational Diabetes and T-cell (Th1/Th2/Th17/Treg) Immune Profile. In Vivo 2019, 33, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giwa, A.M.; Ahmed, R.; Omidian, Z.; Majety, N.; Karakus, K.E.; Omer, S.M.; Donner, T.; Hamad, A.R.A. Current understandings of the pathogenesis of type 1 diabetes: Genetics to environment. World J. Diabetes 2020, 11, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, A.; Walters, R.K.; Pirinen, M.; Kurki, M.; Junna, N.; Goldstein, J.I.; Reeve, M.P.; Siirtola, H.; Lemmelä, S.M.; Turley, P.; et al. Distinct and shared genetic architectures of gestational diabetes mellitus and type 2 diabetes. Nat. Genet. 2024, 56, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizárraga, D.; Gómez-Gil, B.; García-Gasca, T.; Ávalos-Soriano, A.; Casarini, L.; Salazar-Oroz, A.; García-Gasca, A. Gestational diabetes mellitus: Genetic factors, epigenetic alterations, and microbial composition. Acta Diabetol. 2024, 61, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perišić, M.M.; Vladimir, K.; Karpov, S.; Štorga, M.; Mostashari, A.; Khanin, R. Polygenic Risk Score and Risk Factors for Preeclampsia and Gestational Hypertension. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, C.M.; Vassos, E. Polygenic risk scores: From research tools to clinical instruments. Genome Med. 2020, 12, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.W.; Mak, T.S.; O’Reilly, P.F. Tutorial: A guide to performing polygenic risk score analyses. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 2759–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, R.B.; Kristensen, K.; Katsarou, A.; Shaat, N. Association of single nucleotide polymorphisms with insulin secretion, insulin sensitivity, and diabetes in women with a history of gestational diabetes mellitus. BMC Med. Genom. 2021, 14, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruciat, G.; Florian, A.R.; Chaikh-Sulaiman, M.S.; Staicu, A.; Caracostea, G.V.; Procopciuc, L.M.; Stamatian, F.; Muresan, D. TCF7L2 Polymorphism rs7903146 (C/T) and Gestational Diabetes Influence on Obstetric Outcome: A Romanian Case-Control Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potasso, L.; Perakakis, N.; Lamprinou, A.; Polyzou, E.; Kassanos, D.; Peter, A.; Päth, G.; Seufert, J.; Laubner, K. Clinical Impact of the TCF7L2 Gene rs7903146 Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Risk Polymorphism in Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Impaired Glycemic Control and Increased Need of Insulin Therapy. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2020, 128, 663–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Li, P. Novel single nucleotide polymorphisms in gestational diabetes mellitus. Clin. Chim. Acta 2023, 538, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, U.S.M.; Parvez, N.; Rahman, T.A.; Hasan, M.R.; Das, K.C.; Jahan, S.; Hasanat, M.A.; Seraj, Z.I.; Salimullah, M. CDKAL1 gene rs7756992 A/G and rs7754840 G/C polymorphisms are associated with gestational diabetes mellitus in a sample of Bangladeshi population: Implication for future T2DM prophylaxis. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2022, 14, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.M.; Kim, T.H.; Lim, S.; Choi, S.H.; Shin, H.D.; Lee, H.K.; Park, K.S.; Jang, H.C. Type 2 diabetes-associated genetic variants discovered in the recent genome-wide association studies are related to gestational diabetes mellitus in the Korean population. Diabetologia 2009, 52, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, S.H.; Kim, S.H.; Cho, Y.M.; Go, M.J.; Cho, Y.S.; Choi, S.H.; Moon, M.K.; Jung, H.S.; Shin, H.D.; Kang, H.M.; et al. A genome-wide association study of gestational diabetes mellitus in Korean women. Diabetes 2012, 61, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.L.; Cai, J.J.; Huang, S.Y.; Cheng, P.J.; Chueh, H.Y.; Hsu, S.Y. Adaptive human CDKAL1 variants underlie hormonal response variations at the enteroinsular axis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Elssaig, E.H.; Ahmed-Abakur, E.H.; Alnour, T.M.S.; Alsubai, M.A.; Ali, A.E.; Ullah, M.F.; Saeedi, N.H.; Alenzi, F.D. Significant Association Between Genetic Polymorphism of Insulin-like Growth Factor-2 mRNA Binding Protein-2 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Population-Based Case-Control Study. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2025, 39, e25147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Yin, J.Y.; Dai, X.P.; Pei, Q.; Dong, M.; Zhou, Z.G.; Huang, X.; Yu, M.; Zhou, H.H.; Liu, Z.Q. IGF2BP2 variations influence repaglinide response and risk of type 2 diabetes in Chinese population. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2010, 31, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabadell-Basallote, J.; Astiarraga, B.; Castaño, C.; Ejarque, M.; Repollés-de-Dalmau, M.; Quesada, I.; Blanco, J.; Nuñez-Roa, C.; Rodríguez-Peña, M.M.; Martínez, L.; et al. SUCNR1 regulates insulin secretion and glucose elevates the succinate response in people with prediabetes. J. Clin. Investig. 2024, 134, e173214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Jia, X.; Tian, W.; Yan, X.; Wang, N.; Cai, D.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Jin, M.; Wu, N.; et al. Associations of SUCNR1, GRK4, CAMK1D gene polymorphisms and the susceptibility of type 2 diabetes mellitus and essential hypertension in a northern Chinese Han population. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2021, 35, 107752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atallah, R.; Gindlhuber, J.; Platzer, W.; Bärnthaler, T.; Tatzl, E.; Toller, W.; Strutz, J.; Rittchen, S.; Luschnig, P.; Birner-Gruenberger, R.; et al. SUCNR1 Is Expressed in Human Placenta and Mediates Angiogenesis: Significance in Gestational Diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshammary, A.F.; Ansar, S.; Farzan, R.; Alsobaie, S.F.; Alageel, A.A.; Al-Hakeem, M.M.; Ali Khan, I. Dissecting the Molecular Role of ADIPOQ SNPs in Saudi Women Diagnosed with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jääskeläinen, T.; Klemetti, M.M. Genetic Risk Factors and Gene-Lifestyle Interactions in Gestational Diabetes. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Zhang, C.; Mi, Y. IL-6 gene rs1800795 polymorphism and diabetes mellitus: A comprehensive analysis involving 42,150 participants from a meta-analysis. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2022, 14, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yehia, R.; Schaalan, M.; Abdallah, D.M.; Saad, A.S.; Sarhan, N.; Saleh, S. Impact of TNF-α Gene Polymorphisms on Pancreatic and Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer-Induced Cachexia in Adult Egyptian Patients: A Focus on Pathogenic Trajectories. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 783231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, P.; Fan, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Feng, H.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Mei, B. Genetic variants of the GLP-1R gene affect the susceptibility and glucose metabolism of gestational diabetes mellitus: A two-center nested case–control study. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2022, 14, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sitoris, G.; Veltri, F.; Ichiche, M.; Kleynen, P.; Praet, J.P.; Rozenberg, S.; Poppe, K.G. Association between thyroid autoimmunity and gestational diabetes mellitus in euthyroid women. Eur. Thyroid. J. 2022, 11, e210142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ustianowski, Ł.; Udzik, J.; Szostak, J.; Gorący, A.; Ustianowska, K.; Pawlik, A. Genetic and Epigenetic Factors in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Pathology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maestro, M.A.; Cardalda, C.; Boj, S.F.; Luco, R.F.; Servitja, J.M.; Ferrer, J. Distinct roles of HNF1beta, HNF1alpha, and HNF4alpha in regulating pancreas development, beta-cell function and growth. Endocr. Dev. 2007, 12, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odom, D.T.; Zizlsperger, N.; Gordon, D.B.; Bell, G.W.; Rinaldi, N.J.; Murray, H.L.; Volkert, T.L.; Schreiber, J.; Rolfe, P.A.; Gifford, D.K.; et al. Control of pancreas and liver gene expression by HNF transcription factors. Science 2004, 303, 1378–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haliyur, R.; Tong, X.; Sanyoura, M.; Shrestha, S.; Lindner, J.; Saunders, D.C.; Aramandla, R.; Poffenberger, G.; Redick, S.D.; Bottino, R.; et al. Human islets expressing HNF1A variant have defective β cell transcriptional regulatory networks. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, M.M.; Sturis, J.; Menzel, S.; Yamagata, K.; Fajans, S.S.; Dronsfield, M.J.; Bain, S.C.; Hattersley, A.T.; Velho, G.; Froguel, P.; et al. Altered insulin secretory responses to glucose in diabetic and nondiabetic subjects with mutations in the diabetes susceptibility gene MODY3 on chromosome 12. Diabetes 1996, 45, 1503–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagenfeldt-Johansson, K.A.; Herrera, P.L.; Wang, H.; Gjinovci, A.; Ishihara, H.; Wollheim, C.B. Beta-cell-targeted expression of a dominant-negative hepatocyte nuclear factor-1 alpha induces a maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY)3-like phenotype in transgenic mice. Endocrinology 2001, 142, 5311–5320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hunter, C.S.; Maestro, M.A.; Raum, J.C.; Guo, M.; Thompson, F.H., 3rd; Ferrer, J.; Stein, R. Hnf1α (MODY3) regulates β-cell-enriched MafA transcription factor expression. Mol. Endocrinol. 2011, 25, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beysel, S.; Pinarli, F.A.; Eyerci, N.; Kizilgul, M.; Hepsen, S.; Alhan, A.; Kan, S.; Caliskan, M.; Bozkurt, E.; Cakal, E. HNF1A gene p.I27L is associated with co-existing preeclampsia in gestational diabetes mellitus. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2020, 36, 530–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Li, W.; Ma, L.; Ping, F.; Liu, J.; Wu, X.; Mao, J.; Wang, X.; Nie, M. Variants in MODY genes associated with maternal lipids profiles in second trimester of pregnancy. J. Gene Med. 2017, 19, e2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaat, N.; Karlsson, E.; Lernmark, A.; Ivarsson, S.; Lynch, K.; Parikh, H.; Almgren, P.; Berntorp, K.; Groop, L. Common variants in MODY genes increase the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 2006, 49, 1545–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Dallali, H.; Hechmi, M.; Morjane, I.; Elouej, S.; Jmel, H.; Ben Halima, Y.; Abid, A.; Bahlous, A.; Barakat, A.; Jamoussi, H.; et al. Association of HNF1A gene variants and haplotypes with metabolic syndrome: A case-control study in the Tunisian population and a meta-analysis. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2022, 14, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.M.; Jiang, B.G.; Sun, L.L. HNF1A: From Monogenic Diabetes to Type 2 Diabetes and Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 829565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angueira, A.R.; Ludvik, A.E.; Reddy, T.E.; Wicksteed, B.; Lowe, W.L., Jr.; Layden, B.T. New insights into gestational glucose metabolism: Lessons learned from 21st century approaches. Diabetes 2015, 64, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alejandro, E.U.; Mamerto, T.P.; Chung, G.; Villavieja, A.; Gaus, N.L.; Morgan, E.; Pineda-Cortel, M.R.B. Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Harbinger of the Vicious Cycle of Diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murgia, C.; Orrù, M.; Portoghese, E.; Garau, N.; Zedda, P.; Berria, R.; Motzo, C.; Sulis, S.; Murenu, M.; Paoletti, A.M.; et al. Autoimmunity in gestational diabetes mellitus in Sardinia: A preliminary case-control report. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2008, 6, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, R.M.; Allayee, H.; Xiang, A.H.; Trigo, E.; Hartiala, J.; Lawrence, J.M.; Buchanan, T.A. Transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2) is associated with gestational diabetes mellitus and interacts with adiposity to alter insulin secretion in Mexican Americans. Diabetes 2007, 56, 1481–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulou, A.; Lynch, K.F.; Shaat, N.; Håkansson, R.; Ivarsson, S.A.; Berntorp, K.; Agardh, C.D.; Lernmark, Å. Gestational diabetes mellitus is associated with TCF7L2 gene polymorphisms independent of HLA-DQB1*0602 genotypes and islet cell autoantibodies. Diabet. Med. 2011, 28, 1018–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vejrazkova, D.; Lukasova, P.; Vankova, M.; Vcelak, J.; Bradnova, O.; Cirmanova, V.; Andelova, K.; Krejci, H.; Bendlova, B. MTNR1B Genetic Variability Is Associated with Gestational Diabetes in Czech Women. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 2014, 508923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlassi, M.; Gazouli, M.; Paltoglou, G.; Christopoulos, P.; Florentin, L.; Kassi, G.; Mastorakos, G. The rs10830963 variant of melatonin receptor MTNR1B is associated with increased risk for gestational diabetes mellitus in a Greek population. Hormones 2012, 11, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Chen, Q.; Feng, Y.; Yang, H.; Wu, W.; Zhang, P.; Wang, Y.; Ko, J.; Zhao, F.; Du, W.; et al. Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in CDKAL1 Gene Are Associated with Risk of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in Chinese Population. J. Diabetes Res. 2019, 2019, 3618103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatima, S.S.; Chaudhry, B.; Khan, T.A.; Farooq, S. KCNQ1 rs2237895 polymorphism is associated with Gestational Diabetes in Pakistani Women. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2016, 32, 1380–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.D.; Park, B.L.; Shin, H.J.; Kim, J.Y.; Park, S.; Kim, B.; Kim, S.H. Association of KCNQ1 polymorphisms with the gestational diabetes mellitus in Korean women. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 445–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, K.K.; Khan, I.A.; Abotalib, Z.; Al-Hakeem, M.M. Insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1) Gly927Arg: Correlation with gestational diabetes mellitus in Saudi women. bioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 146495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tok, E.C.; Ertunc, D.; Bilgin, O.; Erdal, E.M.; Kaplanoglu, M.; Dilek, S. Association of insulin receptor substrate-1 G972R variant with baseline characteristics of the patients with gestational diabetes mellitus. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2006, 194, 868–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groenewoud, M.J.; Dekker, J.M.; Fritsche, A.; Reiling, E.; Nijpels, G.; Heine, R.J.; Maassen, J.A.; Machicao, F.; Schäfer, S.A.; Häring, H.U.; et al. Variants of CDKAL1 and IGF2BP2 affect first-phase insulin secretion during hyperglycaemic clamps. Diabetologia 2008, 51, 1659–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, W.L., Jr.; Scholtens, D.M.; Sandler, V.; Hayes, M.G. Genetics of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Maternal Metabolism. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2016, 16, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moen, G.H.; LeBlanc, M.; Sommer, C.; Prasad, R.B.; Lekva, T.; Normann, K.R.; Qvigstad, E.; Groop, L.; Birkeland, K.I.; Evans, D.M.; et al. Genetic determinants of glucose levels in pregnancy: Genetic risk scores analysis and GWAS in the Norwegian STORK cohort. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 179, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, S.H.; Choi, S.H.; Kim, K.; Jung, H.S.; Cho, Y.M.; Lim, S.; Cho, N.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Park, K.S.; Jang, H.C. Prediction of type 2 diabetes in women with a history of gestational diabetes using a genetic risk score. Diabetologia 2013, 56, 2556–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, V.K.; Levinson, R.T.; Adefurin, A.; Kurnik, D.; Collier, S.P.; Conway, D.; Stein, C.M. A genetic risk score that includes common type 2 diabetes risk variants is associated with gestational diabetes. Clin. Endocrinol. 2017, 87, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamri, A.; Mao, S.; Desai, D.; Gupta, M.; Paré, G.; Anand, S.S. Fine-tuning of Genome-Wide Polygenic Risk Scores and Prediction of Gestational Diabetes in South Asian Women. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Li, P. Genetic risk score to improve prediction and treatment in gestational diabetes mellitus. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 955821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Meng, C.; Li, J.; Kong, Z.; Zhou, A. Integrating polygenic risk scores in the prediction of gestational diabetes risk in China. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1391296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guevara-Ramírez, P.; Paz-Cruz, E.; Cadena-Ullauri, S.; Ruiz-Pozo, V.A.; Tamayo-Trujillo, R.; Felix, M.L.; Simancas-Racines, D.; Zambrano, A.K. Molecular pathways and nutrigenomic review of insulin resistance development in gestational diabetes mellitus. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1228703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thilak, S.; Rajendra, A.; Ganesh, V. Association of obesity and insulin resistance to gestational diabetes mellitus. Bioinformation 2023, 19, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvist, A.A.S.; Sharma, A.; Sommer, C.; Qvigstad, E.; Gulseth, H.L.; Sollid, S.T.; Nermoen, I.; Sattar, N.; Gill, J.; Tannæs, T.M.; et al. Adipose Tissue Insulin Resistance in South Asian and Nordic Women after Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Metabolites 2024, 14, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumurbaatar, B.; Poole, A.T.; Olson, G.; Makhlouf, M.; Sallam, H.S.; Thukuntla, S.; Kankanala, S.; Ekhaese, O.; Gomez, G.; Chandalia, M.; et al. Adipose Tissue Insulin Resistance in Gestational Diabetes. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2017, 15, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellerbrock, J.; Spaanderman, B.; Drongelen, J.V.; Mulder, E.; Lopes van Balen, V.; Schiffer, V.; Jorissen, L.; Alers, R.J.; Leenen, J.; Ghossein-Doha, C.; et al. Role of Beta Cell Function and Insulin Resistance in the Development of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Park, S.Y.; Choi, C.S. Insulin Resistance: From Mechanisms to Therapeutic Strategies. Diabetes Metab. J. 2022, 46, 15–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaribeygi, H.; Farrokhi, F.R.; Butler, A.E.; Sahebkar, A. Insulin resistance: Review of the underlying molecular mechanisms. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 8152–8161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuel, V.T.; Shulman, G.I. Mechanisms for insulin resistance: Common threads and missing links. Cell 2012, 148, 852–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Højlund, K. Metabolism and insulin signaling in common metabolic disorders and inherited insulin resistance. Dan. Med. J. 2014, 61, B4890. [Google Scholar]
- Vargas, E.; Podder, V.; Carrillo Sepulveda, M.A. Physiology, Glucose Transporter Type 4. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Akbari-Alavijeh, S.; Parhar, R.S.; Gaugler, R.; Hashmi, S. Partners in diabetes epidemic: A global perspective. World J. Diabetes 2023, 14, 1463–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Meyts, P. The Insulin Receptor and Its Signal Transduction Network. In Endotext; Feingold, K.R., Anawalt, B., Blackman, M.R., Boyce, A., Chrousos, G., Corpas, E., de Herder, W.W., Dhatariya, K., Dungan, K., Hofland, J., et al., Eds.; MDText.com, Inc.: South Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd, P.R.; Kahn, B.B. Glucose transporters and insulin action--implications for insulin resistance and diabetes mellitus. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 341, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lende, M.; Rijhsinghani, A. Gestational Diabetes: Overview with Emphasis on Medical Management. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 9573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual, Z.N.; Langaker, M.D. Physiology, Pregnancy. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- McIntyre, H.D.; Chang, A.M.; Callaway, L.K.; Cowley, D.M.; Dyer, A.R.; Radaelli, T.; Farrell, K.A.; Huston-Presley, L.; Amini, S.B.; Kirwan, J.P.; et al. Hormonal and metabolic factors associated with variations in insulin sensitivity in human pregnancy. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sibiak, R.; Jankowski, M.; Gutaj, P.; Mozdziak, P.; Kempisty, B.; Wender-Ożegowska, E. Placental Lactogen as a Marker of Maternal Obesity, Diabetes, and Fetal Growth Abnormalities: Current Knowledge and Clinical Perspectives. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonagra, A.D.; Biradar, S.M.; Dattatreya, K.; Murthy, D.S.J. Normal pregnancy—A state of insulin resistance. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2014, 8, CC01–CC03. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyce, B.L.; Dolinsky, V.W. Maternal β-Cell Adaptations in Pregnancy and Placental Signalling: Implications for Gestational Diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchanan, T.A.; Xiang, A.H.; Page, K.A. Gestational diabetes mellitus: Risks and management during and after pregnancy. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2012, 8, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, R.R.; Cyphert, H.A.; Walker, E.M.; Chakravarthy, H.; Peiris, H.; Gu, X.; Liu, Y.; Conrad, E.; Goodrich, L.; Stein, R.W.; et al. Gestational Diabetes Mellitus from Inactivation of Prolactin Receptor and MafB in Islet β-Cells. Diabetes 2016, 65, 2331–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Pope, C.F.; Crawford, L.A.; Vasavada, R.C.; Jagasia, S.M.; Gannon, M. Gestational diabetes mellitus resulting from impaired beta-cell compensation in the absence of FoxM1, a novel downstream effector of placental lactogen. Diabetes 2010, 59, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntyre, H.D.; Serek, R.; Crane, D.I.; Veveris-Lowe, T.; Parry, A.; Johnson, S.; Leung, K.C.; Ho, K.K.; Bougoussa, M.; Hennen, G.; et al. Placental growth hormone (GH), GH-binding protein, and insulin-like growth factor axis in normal, growth-retarded, and diabetic pregnancies: Correlations with fetal growth. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 85, 1143–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rieck, S.; Kaestner, K.H. Expansion of beta-cell mass in response to pregnancy. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 21, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisi, F.; Milazzo, R.; Savasi, V.M.; Cetin, I. Maternal Low-Grade Chronic Inflammation and Intrauterine Programming of Health and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan Nguyen, K.; Bui Minh, T.; Dinh, H.T.; Viet Tran, T.; Dinh Le, T.; Phi Thi Nguyen, N.; Tran, T.T.H.; Hien Vu, T.; Ho Thi Nguyen, L.; Trung Nguyen, K.; et al. Low-Grade Inflammation in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Its Correlation with Maternal Insulin Resistance and Fetal Growth Indices. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2023, 16, 1429–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, N.R.; Chawes, B.; Bønnelykke, K.; Thorsen, J.; Stokholm, J.; Rasmussen, M.A.; Brix, S.; Bisgaard, H. Levels of Systemic Low-grade Inflammation in Pregnant Mothers and Their Offspring are Correlated. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, S.; Signorile, A.; Menato, G.; Gambino, R.; Bardelli, C.; Gallo, M.L.; Cassader, M.; Massobrio, M.; Pagano, G.F. C-reactive protein and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in gestational hyperglycemia. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2005, 28, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, R.P. Chronic oxidative stress as a central mechanism for glucose toxicity in pancreatic islet beta cells in diabetes. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 42351–42354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poitout, V.; Robertson, R.P. Glucolipotoxicity: Fuel excess and beta-cell dysfunction. Endocr. Rev. 2008, 29, 351–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šrámek, J.; Němcová-Fürstová, V.; Kovář, J. Kinase Signaling in Apoptosis Induced by Saturated Fatty Acids in Pancreatic β-Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachar, E.; Ariav, Y.; Ketzinel-Gilad, M.; Cerasi, E.; Kaiser, N.; Leibowitz, G. Glucose amplifies fatty acid-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress in pancreatic beta-cells via activation of mTORC1. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, D.A.; Hekerman, P.; Ladrière, L.; Bazarra-Castro, A.; Ortis, F.; Wakeham, M.C.; Moore, F.; Rasschaert, J.; Cardozo, A.K.; Bellomo, E.; et al. Initiation and execution of lipotoxic ER stress in pancreatic beta-cells. J. Cell Sci. 2008, 121, 2308–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrede, C.E.; Dickson, L.M.; Lingohr, M.K.; Briaud, I.; Rhodes, C.J. Fatty acid and phorbol ester-mediated interference of mitogenic signaling via novel protein kinase C isoforms in pancreatic beta-cells (INS-1). J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2003, 30, 271–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, T.O.; Chhetri, G.; Yeh, H.; Dong, H.H. Beta-cell compensation and gestational diabetes. J. Biol. Chem. 2023, 299, 105405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeyens, L.; Hindi, S.; Sorenson, R.L.; German, M.S. β-Cell adaptation in pregnancy. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2016, 18 (Suppl. S1), 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassie, K.; Giri, R.; Joham, A.E.; Teede, H.; Mousa, A. Human Placental Lactogen in Relation to Maternal Metabolic Health and Fetal Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, U.; Kahn, B.B. Adipose tissue regulates insulin sensitivity: Role of adipogenesis, de novo lipogenesis and novel lipids. J. Intern. Med. 2016, 280, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar-Petres, E.R.; Sferruzzi-Perri, A.N. Pregnancy-induced changes in β-cell function: What are the key players? J. Physiol. 2022, 600, 1089–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ernst, S.; Demirci, C.; Valle, S.; Velazquez-Garcia, S.; Garcia-Ocaña, A. Mechanisms in the adaptation of maternal β-cells during pregnancy. Diabetes Manag. 2011, 1, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomba, S.; Falbo, A.; Russo, T.; Rivoli, L.; Orio, M.; Cosco, A.G.; Vero, R.; Capula, C.; Tolino, A.; Zullo, F.; et al. The risk of a persistent glucose metabolism impairment after gestational diabetes mellitus is increased in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, J.C.; Yang, J.; Gunderson, E.P.; Hararah, M.K.; Gonzalez, J.R.; Ferrara, A. Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus following Gestational Diabetes Pregnancy in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. J. Diabetes Res. 2017, 2017, 5250162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Rees, D.A. Polycystic ovary syndrome: Pathophysiology and therapeutic opportunities. BMJ Med. 2023, 2, e000548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stener-Victorin, E.; Teede, H.; Norman, R.J.; Legro, R.; Goodarzi, M.O.; Dokras, A.; Laven, J.; Hoeger, K.; Piltonen, T.T. Polycystic ovary syndrome. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2024, 10, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauck, M.A.; Meier, J.J. Incretin hormones: Their role in health and disease. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20 (Suppl. S1), 5–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauck, M.A.; Meier, J.J. The incretin effect in healthy individuals and those with type 2 diabetes: Physiology, pathophysiology, and response to therapeutic interventions. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2016, 4, 525–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Rayner, C.K.; Horowitz, M. Incretins. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2016, 233, 137–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauck, M.A.; Müller, T.D. Incretin hormones and type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2023, 66, 1780–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferjan, S.; Jensterle, M.; Oblak, T.; Zitnik, I.P.; Marc, J.; Goricar, K.; Dolzan, V.; Janez, A. An impaired glucagon-like peptide-1 response is associated with prediabetes in polycystic ovary syndrome with obesity. J. Int. Med. Res. 2019, 47, 4691–4700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydin, K.; Arusoglu, G.; Koksal, G.; Cinar, N.; Aksoy, D.Y.; Yildiz, B.O. Fasting and post-prandial glucagon like peptide 1 and oral contraception in polycystic ovary syndrome. Clin. Endocrinol. 2014, 81, 588–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pontikis, C.; Yavropoulou, M.P.; Toulis, K.A.; Kotsa, K.; Kazakos, K.; Papazisi, A.; Gotzamani-Psarakou, A.; Yovos, J.G. The incretin effect and secretion in obese and lean women with polycystic ovary syndrome: A pilot study. J. Womens Health 2011, 20, 971–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pugliese, G.; de Alteriis, G.; Muscogiuri, G.; Barrea, L.; Verde, L.; Zumbolo, F.; Colao, A.; Savastano, S. Liraglutide and polycystic ovary syndrome: Is it only a matter of body weight? J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2023, 46, 1761–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Lin, T.C.; Liu, W. Gastrointestinal hormones and polycystic ovary syndrome. Endocrine 2014, 47, 668–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.M.; Wang, Y.X.; Zhan, Y.; Liu, A.H.; Wang, Y.X.; Shen, H.F.; Wang, Y.F.; Wang, L.Y.; Tao, Z.B.; Wang, Y.Q. Dulaglutide, a long-acting GLP-1 receptor agonist, can improve hyperandrogenemia and ovarian function in DHEA-induced PCOS rats. Peptides 2021, 145, 170624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.; Xie, T.; Song, Y.; Zhou, L. The role of androgen and its related signals in PCOS. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 1825–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, R.K. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Nurs. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 53, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunaif, A. Insulin resistance and the polycystic ovary syndrome: Mechanism and implications for pathogenesis. Endocr. Rev. 1997, 18, 774–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirmans, S.M.; Pate, K.A. Epidemiology, diagnosis, and management of polycystic ovary syndrome. Clin. Epidemiol. 2013, 6, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkind-Hirsch, K.E.; Chappell, N.; Shaler, D.; Storment, J.; Bellanger, D. Liraglutide 3 mg on weight, body composition, and hormonal and metabolic parameters in women with obesity and polycystic ovary syndrome: A randomized placebo-controlled-phase 3 study. Fertil. Steril. 2022, 118, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Qu, Z.; Lu, T.; Shao, X.; Cai, M.; Dilimulati, D.; Gao, X.; Mao, W.; Hu, F.; Su, L.; et al. Effects of a Dulaglutide plus Calorie-Restricted Diet versus a Calorie-Restricted Diet on Visceral Fat and Metabolic Profiles in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2023, 15, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednarz, K.; Kowalczyk, K.; Cwynar, M.; Czapla, D.; Czarkowski, W.; Kmita, D.; Nowak, A.; Madej, P. The Role of Glp-1 Receptor Agonists in Insulin Resistance with Concomitant Obesity Treatment in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nylander, M.; Frøssing, S.; Clausen, H.V.; Kistorp, C.; Faber, J.; Skouby, S.O. Effects of liraglutide on ovarian dysfunction in polycystic ovary syndrome: A randomized clinical trial. Reprod. Biomed. Online 2017, 35, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cena, H.; Chiovato, L.; Nappi, R.E. Obesity, Polycystic Ovary Syndrome, and Infertility: A New Avenue for GLP-1 Receptor Agonists. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105, e2695–e2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mladenović, D.; Vesković, M.; Šutulović, N.; Hrnčić, D.; Stanojlović, O.; Radić, L.; Macut, J.B.; Macut, D. Adipose-derived extracellular vesicles—A novel cross-talk mechanism in insulin resistance, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and polycystic ovary syndrome. Endocrine 2024, 85, 18–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, Y.B.; Seo, S.K.; Yun, B.H.; Cho, S.; Choi, Y.S.; Lee, B.S. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in polycystic ovary syndrome women. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzano-Nunez, R.; Santana-Dominguez, M.; Rivera-Esteban, J.; Sabiote, C.; Sena, E.; Bañares, J.; Tacke, F.; Pericàs, J.M. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Patients with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Meta-Regression. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Pang, Y. Metabolic Syndrome and PCOS: Pathogenesis and the Role of Metabolites. Metabolites 2021, 11, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfield, R.L.; Ehrmann, D.A. The Pathogenesis of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): The Hypothesis of PCOS as Functional Ovarian Hyperandrogenism Revisited. Endocr. Rev. 2016, 37, 467–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastnak, L.; Herman, R.; Ferjan, S.; Janež, A.; Jensterle, M. Prolactin in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: Metabolic Effects and Therapeutic Prospects. Life 2023, 13, 2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, X.; Nie, X.; He, B. Insulin resistance in polycystic ovary syndrome across various tissues: An updated review of pathogenesis, evaluation, and treatment. J. Ovarian Res. 2023, 16, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirsch, P.; Kunadia, J.; Shah, S.; Agrawal, N. Metabolic effects of prolactin and the role of dopamine agonists: A review. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1002320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pala, N.A.; Laway, B.A.; Misgar, R.A.; Dar, R.A. Metabolic abnormalities in patients with prolactinoma: Response to treatment with cabergoline. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2015, 7, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, G.; Khan, F.A.; Jamal, Q.M.; Saleem, A.; Masroor, H.; Abbas, K. Change in Insulin Sensitivity and Lipid Profile After Dopamine Agonist Therapy in Patients With Prolactinoma. Cureus 2021, 13, e17824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zatterale, F.; Longo, M.; Naderi, J.; Raciti, G.A.; Desiderio, A.; Miele, C.; Beguinot, F. Chronic Adipose Tissue Inflammation Linking Obesity to Insulin Resistance and Type 2 Diabetes. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beunen, K.; Vercauter, L.; Van Crombrugge, P.; Moyson, C.; Verhaeghe, J.; Vandeginste, S.; Verlaenen, H.; Vercammen, C.; Maes, T.; Dufraimont, E.; et al. Type 1 diabetes-related autoimmune antibodies in women with gestational diabetes mellitus and the long-term risk for glucose intolerance. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 973820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, S.; Menato, G.; Pinach, S.; Signorile, A.; Bardelli, C.; Lezo, A.; Marchisio, B.; Gentile, L.; Cassader, M.; Massobrio, M.; et al. Clinical characteristics and outcome of pregnancy in women with gestational hyperglycaemia with and without antibodies to beta-cell antigens. Diabet. Med. 2003, 20, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.K.; Singh, S.; Singh, H.; Mahajan, D.; Kolli, P.; Mandadapu, G.; Kumar, B.; Kumar, D.; Kumar, S.; Jena, M.K. Deep Insight of the Pathophysiology of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Cells 2022, 11, 2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossu, E.; Incani, M.; Pani, M.G.; Gattu, G.; Serafini, C.; Strazzera, A.; Bertoccini, L.; Cimini, F.A.; Barchetta, I.; Cavallo, M.G.; et al. Presence of diabetes-specific autoimmunity in women with gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) predicts impaired glucose regulation at follow-up. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2018, 41, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wucher, H.; Lepercq, J.; Timsit, J. Onset of autoimmune type 1 diabetes during pregnancy: Prevalence and outcomes. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 24, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapolla, A.; Dalfrà, M.G.; Fedele, D. Diabetes related autoimmunity in gestational diabetes mellitus: Is it important? Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2009, 19, 674–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccinni, M.P.; Lombardelli, L.; Logiodice, F.; Kullolli, O.; Parronchi, P.; Romagnani, S. How pregnancy can affect autoimmune diseases progression? Clin. Mol. Allergy 2016, 14, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, S.L. Pancreatic Disorders of Pregnancy. Clin. Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, 63, 226–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khant Aung, Z.; Kokay, I.C.; Grattan, D.R.; Ladyman, S.R. Prolactin-Induced Adaptation in Glucose Homeostasis in Mouse Pregnancy Is Mediated by the Pancreas and Not in the Forebrain. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 765976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hufnagel, A.; Dearden, L.; Fernandez-Twinn, D.S.; Ozanne, S.E. Programming of cardiometabolic health: The role of maternal and fetal hyperinsulinaemia. J. Endocrinol. 2022, 253, R47–R63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaresima, P.; Saccone, G.; Pellegrino, R.; Vaccarisi, S.; Taranto, L.; Mazzulla, R.; Bernardo, S.; Venturella, R.; Di Carlo, C.; Morelli, M. Incidental diagnosis of a pancreatic adenocarcinoma in a woman affected by gestational diabetes mellitus: Case report and literature review. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. MFM 2021, 3, 100471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Sun, H. Fetal-maternal interactions during pregnancy: A ’three-in-one’ perspective. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1198430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shima, T.; Inada, K.; Nakashima, A.; Ushijima, A.; Ito, M.; Yoshino, O.; Saito, S. Paternal antigen-specific proliferating regulatory T cells are increased in uterine-draining lymph nodes just before implantation and in pregnant uterus just after implantation by seminal plasma-priming in allogeneic mouse pregnancy. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2015, 108, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerin, L.R.; Moldenhauer, L.M.; Prins, J.R.; Bromfield, J.J.; Hayball, J.D.; Robertson, S.A. Seminal fluid regulates accumulation of FOXP3+ regulatory T cells in the preimplantation mouse uterus through expanding the FOXP3+ cell pool and CCL19-mediated recruitment. Biol. Reprod. 2011, 85, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, E.; Mokhtari, Z.; Salehi Abargouei, A.; Mishra, G.D.; Amani, R. Maternal circulating leptin, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and interleukine-6 in association with gestational diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2023, 39, 2183049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zgutka, K.; Tkacz, M.; Tomasiak, P.; Piotrowska, K.; Ustianowski, P.; Pawlik, A.; Tarnowski, M. Gestational Diabetes Mellitus-Induced Inflammation in the Placenta via IL-1β and Toll-like Receptor Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirwan, J.P.; Hauguel-De Mouzon, S.; Lepercq, J.; Challier, J.C.; Huston-Presley, L.; Friedman, J.E.; Kalhan, S.C.; Catalano, P.M. TNF-alpha is a predictor of insulin resistance in human pregnancy. Diabetes 2002, 51, 2207–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotamisligil, G.S.; Peraldi, P.; Budavari, A.; Ellis, R.; White, M.F.; Spiegelman, B.M. IRS-1-mediated inhibition of insulin receptor tyrosine kinase activity in TNF-alpha- and obesity-induced insulin resistance. Science 1996, 271, 665–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanety, H.; Feinstein, R.; Papa, M.Z.; Hemi, R.; Karasik, A. Tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1). Possible mechanism for suppression of insulin-stimulated tyrosine phosphorylation of IRS-1. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 23780–23784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plomgaard, P.; Bouzakri, K.; Krogh-Madsen, R.; Mittendorfer, B.; Zierath, J.R.; Pedersen, B.K. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces skeletal muscle insulin resistance in healthy human subjects via inhibition of Akt substrate 160 phosphorylation. Diabetes 2005, 54, 2939–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, T. IL-6 in inflammation, autoimmunity and cancer. Int. Immunol. 2021, 33, 127–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arruvito, L.; Sanz, M.; Banham, A.H.; Fainboim, L. Expansion of CD4+CD25+ and FOXP3+ regulatory T cells during the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle: Implications for human reproduction. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 2572–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polanczyk, M.J.; Carson, B.D.; Subramanian, S.; Afentoulis, M.; Vandenbark, A.A.; Ziegler, S.F.; Offner, H. Cutting edge: Estrogen drives expansion of the CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cell compartment. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 2227–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, P.; Wang, J.; Jin, H.; Song, X.; Yan, J.; Kang, Y.; Zhao, L.; An, X.; Du, X.; Chen, X.; et al. Induction of regulatory T cells by physiological level estrogen. J. Cell Physiol. 2008, 214, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, G.; Wang, J.; Kang, Y.; Tai, P.; Wen, J.; Zou, Q.; Li, G.; Ouyang, H.; Xia, G.; Wang, B. Progesterone increases systemic and local uterine proportions of CD4+CD25+ Treg cells during midterm pregnancy in mice. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 5477–5488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Li, M.; Zhao, M.; Lu, F.; Yu, X.; Li, L.; Gu, Z.; Deng, Y.; Guan, R. Progesterone modulates CD4+CD25+ FoxP3+ regulatory T Cells and TGF-β1 in the maternal-fetal interface of the late pregnant mouse. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2022, 88, e13541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rassie, K.L.; Giri, R.; Melder, A.; Joham, A.; Mousa, A.; Teede, H.J. Lactogenic hormones in relation to maternal metabolic health in pregnancy and postpartum: Protocol for a systematic review. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e055257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Román, M.A. Prolactin and lactation as modifiers of diabetes risk in gestational diabetes. Horm. Metab. Res. 2011, 43, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saucedo, R.; Ortega-Camarillo, C.; Ferreira-Hermosillo, A.; Díaz-Velázquez, M.F.; Meixueiro-Calderón, C.; Valencia-Ortega, J. Role of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.C.; Hsueh, Y.W.; Chang, C.W.; Hsu, H.C.; Yang, T.C.; Lin, W.C.; Chang, H.M. Establishment of the fetal-maternal interface: Developmental events in human implantation and placentation. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1200330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuckey, R.C. Progesterone synthesis by the human placenta. Placenta 2005, 26, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, N.K.; Evans, J.; Salamonsen, L.A.; Gardner, D.K.; Kaitu’u-Lino, T.J.; Hannan, N.J. Placental Growth Factor Is Secreted by the Human Endometrium and Has Potential Important Functions during Embryo Development and Implantation. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, B.; Liao, H.; Lin, W.; Li, Z.; Ma, X.; Xu, Q.; Yu, F. The Role of TGF-β during Pregnancy and Pregnancy Complications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedekind, L.; Belkacemi, L. Altered cytokine network in gestational diabetes mellitus affects maternal insulin and placental-fetal development. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2016, 30, 1393–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valencia-Ortega, J.; González-Reynoso, R.; Ramos-Martínez, E.G.; Ferreira-Hermosillo, A.; Peña-Cano, M.I.; Morales-Ávila, E.; Saucedo, R. New Insights into Adipokines in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czernek, L.; Düchler, M. Exosomes as Messengers Between Mother and Fetus in Pregnancy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fallen, S.; Baxter, D.; Wu, X.; Kim, T.K.; Shynlova, O.; Lee, M.Y.; Scherler, K.; Lye, S.; Hood, L.; Wang, K. Extracellular vesicle RNAs reflect placenta dysfunction and are a biomarker source for preterm labour. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 2760–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aharon, A.; Rebibo-Sabbah, A.; Ahmad, R.S.; Dangot, A.; Bar-Lev, T.H.; Brenner, B.; Cohen, A.H.; David, C.B.; Weiner, Z.; Solt, I. Associations of maternal and placental extracellular vesicle miRNA with preeclampsia. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1080419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlov, O.V.; Selutin, A.V.; Pavlova, O.M.; Selkov, S.A. Two patterns of cytokine production by placental macrophages. Placenta 2020, 91, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezouar, S.; Katsogiannou, M.; Ben Amara, A.; Bretelle, F.; Mege, J.L. Placental macrophages: Origin, heterogeneity, function and role in pregnancy-associated infections. Placenta 2021, 103, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, L.; Golos, T.G. Hofbauer Cells: Their Role in Healthy and Complicated Pregnancy. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geldenhuys, J.; Rossouw, T.M.; Lombaard, H.A.; Ehlers, M.M.; Kock, M.M. Disruption in the Regulation of Immune Responses in the Placental Subtype of Preeclampsia. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizárraga, D.; García-Gasca, A. The Placenta as a Target of Epigenetic Alterations in Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Potential Implications for the Offspring. Epigenomes 2021, 5, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.J.; Huang, R.; Zheng, T.; Du, Q.; Yang, M.N.; Xu, Y.J.; Liu, X.; Tao, M.Y.; He, H.; Fang, F.; et al. Genome-Wide Placental Gene Methylations in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus, Fetal Growth and Metabolic Health Biomarkers in Cord Blood. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 875180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hajj, N.; Pliushch, G.; Schneider, E.; Dittrich, M.; Müller, T.; Korenkov, M.; Aretz, M.; Zechner, U.; Lehnen, H.; Haaf, T. Metabolic programming of MEST DNA methylation by intrauterine exposure to gestational diabetes mellitus. Diabetes 2013, 62, 1320–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.L.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Tian, S.; Lv, X.D.; Wang, X.Q.; Su, X.; Li, Y.; Hu, Y.; Ma, X.; et al. Up-regulation of miR-98 and unraveling regulatory mechanisms in gestational diabetes mellitus. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanakis, K.; Upadhyay, J.; Ramirez-Cisneros, A.; Patel, N.; Sahai, A.; Mantzoros, C.S. Leptin physiology and pathophysiology in energy homeostasis, immune function, neuroendocrine regulation and bone health. Metabolism 2024, 161, 156056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martelli, D.; Brooks, V.L. Leptin Increases: Physiological Roles in the Control of Sympathetic Nerve Activity, Energy Balance, and the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Thyroid Axis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.M. Leptin and the endocrine control of energy balance. Nat. Metab. 2019, 1, 754–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrettini, S.; Caroli, A.; Torlone, E. Nutrition and Metabolic Adaptations in Physiological and Complicated Pregnancy: Focus on Obesity and Gestational Diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 611929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessier, D.R.; Ferraro, Z.M.; Gruslin, A. Role of leptin in pregnancy: Consequences of maternal obesity. Placenta 2013, 34, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, M.C.; Shulman, G.I. Mechanisms of Insulin Action and Insulin Resistance. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 2133–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoramipour, K.; Chamari, K.; Hekmatikar, A.A.; Ziyaiyan, A.; Taherkhani, S.; Elguindy, N.M.; Bragazzi, N.L. Adiponectin: Structure, Physiological Functions, Role in Diseases, and Effects of Nutrition. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziemke, F.; Mantzoros, C.S. Adiponectin in insulin resistance: Lessons from translational research. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 91, 258S–261S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhusal, A.; Rahman, M.H.; Suk, K. Hypothalamic inflammation in metabolic disorders and aging. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 79, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.H.; Bhusal, A.; Kim, J.H.; Jha, M.K.; Song, G.J.; Go, Y.; Jang, I.S.; Lee, I.K.; Suk, K. Astrocytic pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase-2 is involved in hypothalamic inflammation in mouse models of diabetes. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodolaki, K.; Pergialiotis, V.; Iakovidou, N.; Boutsikou, T.; Iliodromiti, Z.; Kanaka-Gantenbein, C. The impact of maternal diabetes on the future health and neurodevelopment of the offspring: A review of the evidence. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1125628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngema, M.; Xulu, N.D.; Ngubane, P.S.; Khathi, A. Pregestational Prediabetes Induces Maternal Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal (HPA) Axis Dysregulation and Results in Adverse Foetal Outcomes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Hou, X.; Yang, G.; Li, M.; Zhang, J.; Han, M.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y. Effects of the POMC System on Glucose Homeostasis and Potential Therapeutic Targets for Obesity and Diabetes. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2022, 15, 2939–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleger, B. Invasive and Non-invasive Stimulation of the Obese Human Brain. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrin, M.C.; Terry, M.B.; Kleinhaus, K.; Deutsch, L.; Yanetz, R.; Tiram, E.; Calderon, R.; Friedlander, Y.; Paltiel, O.; Harlap, S. Gestational diabetes as a risk factor for pancreatic cancer: A prospective cohort study. BMC Med. 2007, 5, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsarou, A.; Gudbjörnsdottir, S.; Rawshani, A.; Dabelea, D.; Bonifacio, E.; Anderson, B.J.; Jacobsen, L.M.; Schatz, D.A.; Lernmark, Å. Type 1 diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, A. Know the signs and symptoms of diabetes. Indian J. Med. Res. 2014, 140, 579–581. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Rui, L. Leptin signaling and leptin resistance. Front. Med. 2013, 7, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Pérez, A.; Vilariño-García, T.; Guadix, P.; Dueñas, J.L.; Sánchez-Margalet, V. Leptin and Nutrition in Gestational Diabetes. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trujillo-Güiza, M.L.; Señarís, R. Leptin resistance during pregnancy is also exerted at the periphery. Biol. Reprod. 2018, 98, 654–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kochhar, P.; Manikandan, C.; Ravikumar, G.; Dwarkanath, P.; Sheela, C.N.; George, S.; Thomas, A.; Crasta, J.; Thomas, T.; Kurpad, A.V.; et al. Placental expression of leptin: Fetal sex-independent relation with human placental growth. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 74, 1603–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Pérez, A.; Toro, A.; Vilariño-García, T.; Maymó, J.; Guadix, P.; Dueñas, J.L.; Fernández-Sánchez, M.; Varone, C.; Sánchez-Margalet, V. Leptin action in normal and pathological pregnancies. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 716–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.H.; Jang, H.C. Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Diagnostic Approaches and Maternal-Offspring Complications. Diabetes Metab. J. 2022, 46, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olerich, K.L.W.; Sewaybricker, L.E.; Kee, S.; Melhorn, S.J.; Chandrasekaran, S.; Schur, E.A. In utero exposure to maternal diabetes or hypertension and childhood hypothalamic gliosis. Int. J. Obes. 2024, 48, 594–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Committee on Practice Bulletins—Obstetrics. ACOG Practice Bulletin No. 190: Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Obstet. Gynecol. 2018, 131, e49–e64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummel, M. Gestational diabetes and pregnancy. MMW Fortschr. Med. 2014, 156, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampmann, U.; Madsen, L.R.; Skajaa, G.O.; Iversen, D.S.; Moeller, N.; Ovesen, P. Gestational diabetes: A clinical update. World J. Diabetes 2015, 6, 1065–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, N.I.; Gonzalez, J.M.; Anderson, C.A.M.; Judd, S.E.; Rexrode, K.M.; Hlatky, M.A.; Gunderson, E.P.; Stuart, J.J.; Vaidya, D. Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes and Cardiovascular Disease Risk: Unique Opportunities for Cardiovascular Disease Prevention in Women: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2021, 143, e902–e916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karkia, R.; Giacchino, T.; Shah, S.; Gough, A.; Ramadan, G.; Akolekar, R. Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Association with Maternal and Neonatal Complications. Medicina 2023, 59, 2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartáková, V.; Barátová, B.; Pácal, L.; Ťápalová, V.; Šebestová, S.; Janků, P.; Kaňková, K. Development of a New Risk Score for Stratification of Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus at High Risk of Persisting Postpartum Glucose Intolerance Using Routinely Assessed Parameters. Life 2021, 11, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, Z.; Wu, H.; Ren, L.; Bu, N.; Jiang, L.; Yang, H.; Zhang, J.; Guo, X. Long-Term Postpartum Outcomes of Insulin Resistance and β-cell Function in Women with Previous Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2020, 2020, 7417356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katayama, H.; Tachibana, D.; Hamuro, A.; Misugi, T.; Motoyama, K.; Morioka, T.; Fukumoto, S.; Emoto, M.; Inaba, M.; Koyama, M. Sustained Decrease of Early-Phase Insulin Secretion in Japanese Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Who Developed Impaired Glucose Tolerance and Impaired Fasting Glucose Postpartum. Jpn. Clin. Med. 2015, 6, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homko, C.; Sivan, E.; Chen, X.; Reece, E.A.; Boden, G. Insulin secretion during and after pregnancy in patients with gestational diabetes mellitus. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 568–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vounzoulaki, E.; Khunti, K.; Abner, S.C.; Tan, B.K.; Davies, M.J.; Gillies, C.L. Progression to type 2 diabetes in women with a known history of gestational diabetes: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2020, 369, m1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retnakaran, R.; Ye, C.; Hanley, A.J.; Connelly, P.W.; Sermer, M.; Zinman, B. Treatment of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Maternal Risk of Diabetes After Pregnancy. Diabetes Care 2023, 46, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turrentine, M.A.; Caughey, A.B.; Zahn, C.M. In Reply. Obstet. Gynecol. 2018, 131, 1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzger, B.E.; Gabbe, S.G.; Persson, B.; Buchanan, T.A.; Catalano, P.A.; Damm, P.; Dyer, A.R.; Leiva, A.; Hod, M.; Kitzmiler, J.L.; et al. International association of diabetes and pregnancy study groups recommendations on the diagnosis and classification of hyperglycemia in pregnancy. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeedi, M.; Cao, Y.; Fadl, H.; Gustafson, H.; Simmons, D. Increasing prevalence of gestational diabetes mellitus when implementing the IADPSG criteria: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2021, 172, 108642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanovic, L.; Savas, H.; Mehta, M.; Trujillo, A.; Pettitt, D.J. Frequent monitoring of A1C during pregnancy as a treatment tool to guide therapy. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 53–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butalia, S.; Donovan, L.; Savu, A.; Johnson, J.; Edwards, A.; Kaul, P. Postpartum Diabetes Testing Rates after Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in Canadian Women: A Population-Based Study. Can. J. Diabetes 2017, 41, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchanan, T.A.; Page, K.A. Approach to the patient with gestational diabetes after delivery. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 3592–3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auvinen, A.M.; Luiro, K.; Jokelainen, J.; Järvelä, I.; Knip, M.; Auvinen, J.; Tapanainen, J.S. Type 1 and type 2 diabetes after gestational diabetes: A 23 year cohort study. Diabetologia 2020, 63, 2123–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padayachee, C.; Coombes, J.S. Exercise guidelines for gestational diabetes mellitus. World J. Diabetes 2015, 6, 1033–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, M.D.; Baker, B.C.; Scott, E.M.; Forbes, K. Interaction between Metformin, Folate and Vitamin B12 and the Potential Impact on Fetal Growth and Long-Term Metabolic Health in Diabetic Pregnancies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzger, B.E.; Buchanan, T.A.; Coustan, D.R.; de Leiva, A.; Dunger, D.B.; Hadden, D.R.; Hod, M.; Kitzmiller, J.L.; Kjos, S.L.; Oats, J.N.; et al. Summary and recommendations of the Fifth International Workshop-Conference on Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Care 2007, 30 (Suppl. S2), S251–S260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, B.; Lentz, S.; Koyfman, A.; Gottlieb, M. Euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis: Etiologies, evaluation, and management. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2021, 44, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janež, A.; Guja, C.; Mitrakou, A.; Lalic, N.; Tankova, T.; Czupryniak, L.; Tabák, A.G.; Prazny, M.; Martinka, E.; Smircic-Duvnjak, L. Insulin Therapy in Adults with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: A Narrative Review. Diabetes Ther. 2020, 11, 387–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, G.A.; Sliem, H.A.; Ellethy, A.T.; Salama Mel, S. Role of immune system modulation in prevention of type 1 diabetes mellitus. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 16, 904–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skyler, J.S.; Krischer, J.P.; Wolfsdorf, J.; Cowie, C.; Palmer, J.P.; Greenbaum, C.; Cuthbertson, D.; Rafkin-Mervis, L.E.; Chase, H.P.; Leschek, E. Effects of oral insulin in relatives of patients with type 1 diabetes: The Diabetes Prevention Trial—Type 1. Diabetes Care 2005, 28, 1068–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skyler, J.S. Update on worldwide efforts to prevent type 1 diabetes. Ann. N. Y Acad. Sci. 2008, 1150, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thivolet, C.H.; Goillot, E.; Bedossa, P.; Durand, A.; Bonnard, M.; Orgiazzi, J. Insulin prevents adoptive cell transfer of diabetes in the autoimmune non-obese diabetic mouse. Diabetologia 1991, 34, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silver, H.J.; Olson, D.; Mayfield, D.; Wright, P.; Nian, H.; Mashayekhi, M.; Koethe, J.R.; Niswender, K.D.; Luther, J.M.; Brown, N.J. Effect of the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist liraglutide, compared to caloric restriction, on appetite, dietary intake, body fat distribution and cardiometabolic biomarkers: A randomized trial in adults with obesity and prediabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2023, 25, 2340–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, A.R.; Frias, J.P.; Brown, L.S.; Gorman, D.N.; Vasas, S.; Tsamandouras, N.; Birnbaum, M.J. Efficacy and Safety of Oral Small Molecule Glucagon-like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonist Danuglipron for Glycemic Control Among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2314493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Abbasi, F.; Nachmanoff, C.; Stefanakis, K.; Kumar, A.; Kalra, B.; Savjani, G.; Mantzoros, C.S. Effect of the glucagon-like peptide-1 analogue liraglutide versus placebo treatment on circulating proglucagon-derived peptides that mediate improvements in body weight, insulin secretion and action: A randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2021, 23, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Zong, Y.; Ma, Y.; Tian, Y.; Pang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Gao, J. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor: Mechanisms and advances in therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drucker, D.J. Mechanisms of Action and Therapeutic Application of Glucagon-like Peptide-1. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 740–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhu, C.; Lu, M.; Chen, C.; Nie, X.; Abudukerimu, B.; Zhang, K.; Ning, Z.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, J.; et al. The key role of a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist in body fat redistribution. J. Endocrinol. 2019, 240, 271–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariam, Z.; Niazi, S.K. Glucagon-like peptide agonists: A prospective review. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. 2024, 7, e462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdi, S.F.; Pusapati, S.; Anwar, M.S.; Lohana, D.; Kumar, P.; Nandula, S.A.; Nawaz, F.K.; Tracey, K.; Yang, H.; LeRoith, D.; et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1: A multi-faceted anti-inflammatory agent. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1148209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bułdak, Ł.; Machnik, G.; Bułdak, R.J.; Łabuzek, K.; Bołdys, A.; Belowski, D.; Basiak, M.; Okopień, B. Exenatide (a GLP-1 agonist) expresses anti-inflammatory properties in cultured human monocytes/macrophages in a protein kinase A and B/Akt manner. Pharmacol. Rep. 2016, 68, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Xie, T.; Guo, X.; Wu, D.; Li, S.; Li, X.; Lu, Y.; Wang, X. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist exendin-4 mitigates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses in RAW264.7 macrophages. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 77, 105969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurgel Penaforte-Saboia, J.; Couri, C.E.B.; Vasconcelos Albuquerque, N.; Lauanna Lima Silva, V.; Bitar da Cunha Olegario, N.; Oliveira Fernandes, V.; Montenegro Junior, R.M. Emerging Roles of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors in Delaying the Progression of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2021, 14, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, B.M.; Rice, M.M.; Landon, M.B.; Varner, M.W.; Reddy, U.M.; Wapner, R.J.; Rouse, D.J.; Biggio, J.R., Jr.; Thorp, J.M., Jr.; Chien, E.K.; et al. Effect of Treatment of Mild Gestational Diabetes on Long-Term Maternal Outcomes. Am. J. Perinatol. 2020, 37, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, J.H.; Olesen, C.R.; Kristiansen, T.M.; Bak, C.K.; Overgaard, C. Reasons for women’s non-participation in follow-up screening after gestational diabetes. Women Birth 2015, 28, e157–e163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, P. Gestational diabetes: Opportunities for improving maternal and child health. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 8, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retnakaran, R.; Shah, B.R. Glucose screening in pregnancy and future risk of cardiovascular disease in women: A retrospective, population-based cohort study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Li, H.; Yang, Q.; Nawsherwan. The Trend in Delayed Childbearing Age and Its Potential Impact on Adverse Maternal-Perinatal Outcomes in Developed and Developing Countries: A Narrative Review. Iran. J. Public Health 2025, 54, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, C.; Ursing, D.; Törn, C.; Aberg, A.; Landin-Olsson, M. Presence of GAD antibodies during gestational diabetes mellitus predicts type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 1968–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu, C.; Lahesmaa, R.; Bonifacio, E.; Achenbach, P.; Tree, T. Immunological biomarkers for the development and progression of type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 2252–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Tourino, I.; Arif, S.; Eichmann, M.; Peakman, M. T cells in type 1 diabetes: Instructors, regulators and effectors: A comprehensive review. J. Autoimmun. 2016, 66, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franzago, M.; Borrelli, P.; Di Nicola, M.; Cavallo, P.; D’Adamo, E.; Di Tizio, L.; Gazzolo, D.; Stuppia, L.; Vitacolonna, E. From Mother to Child: Epigenetic Signatures of Hyperglycemia and Obesity during Pregnancy. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
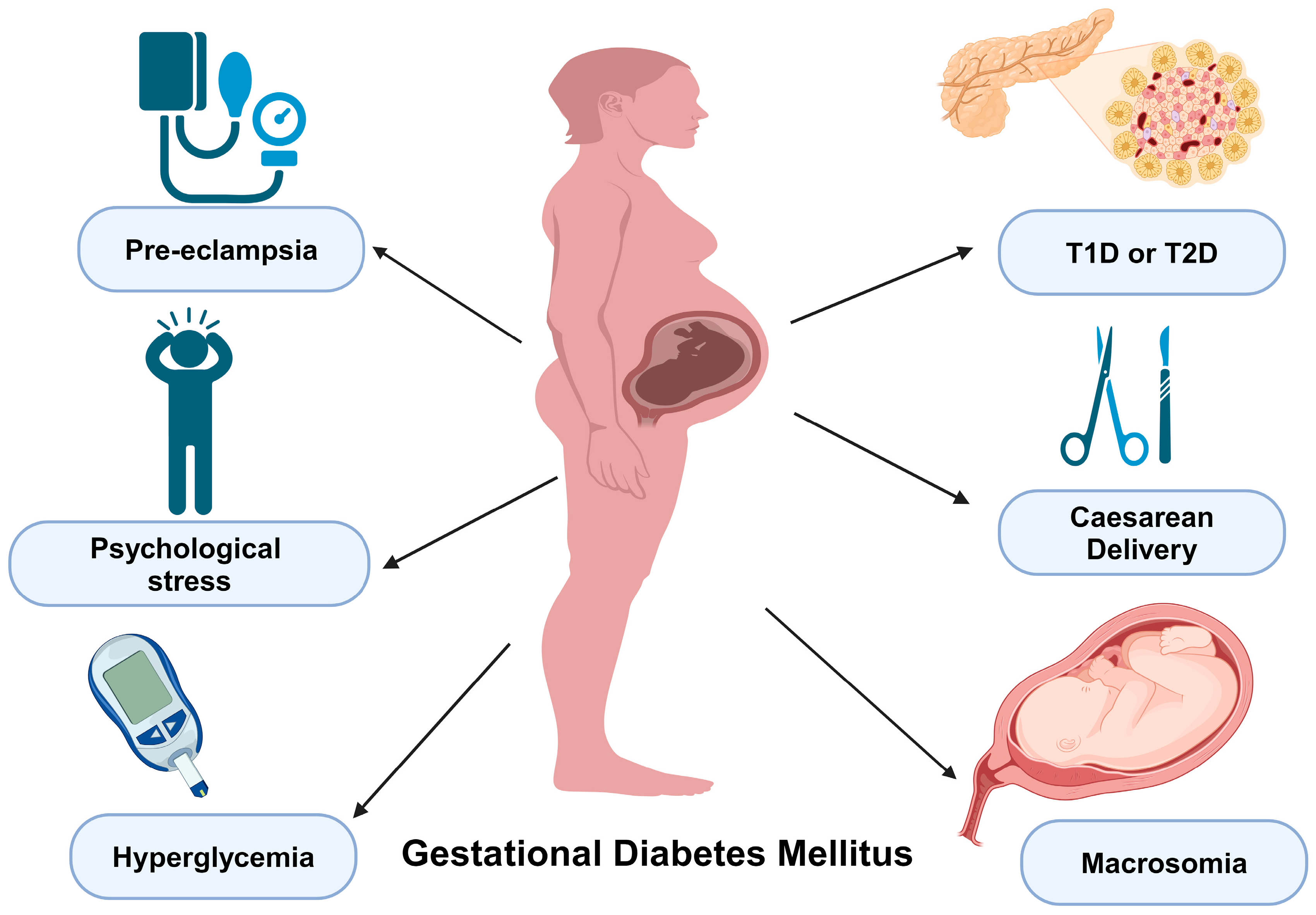

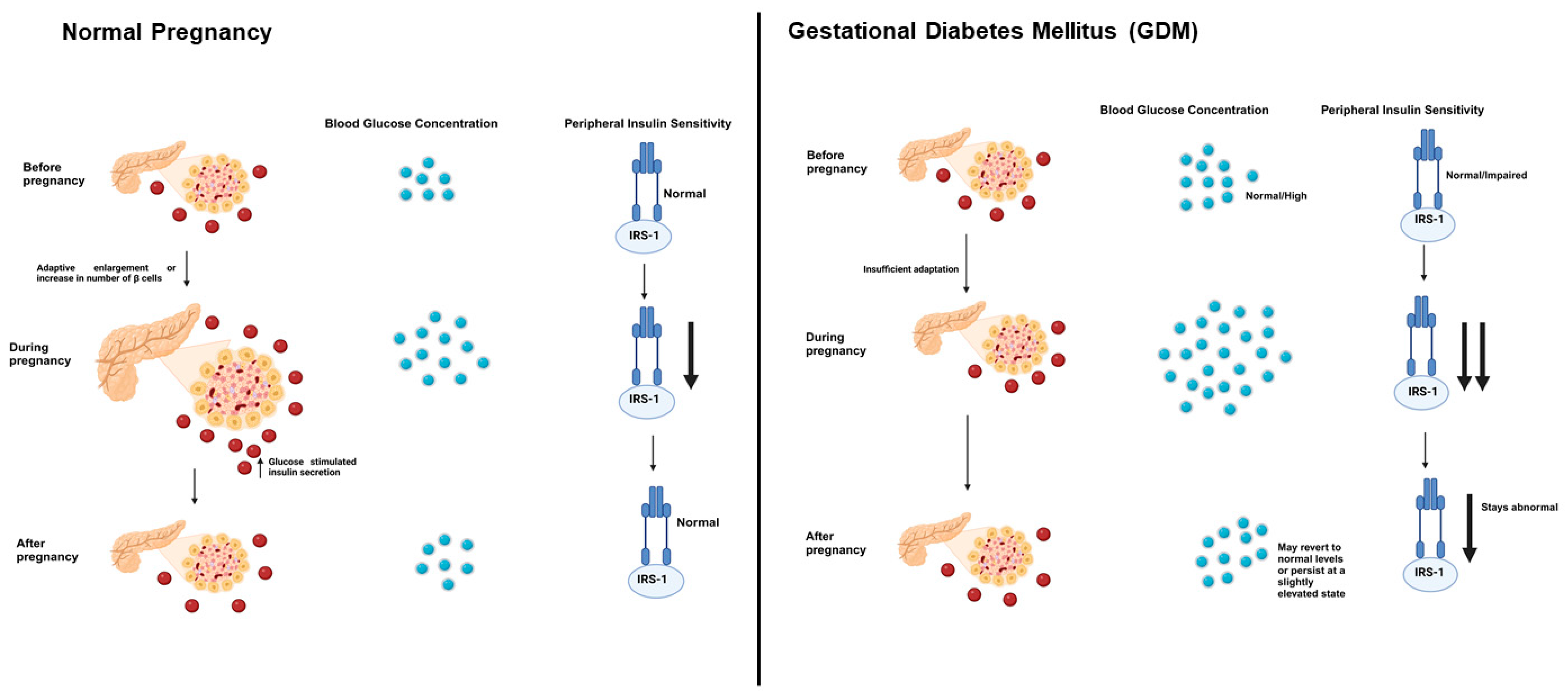
| SNP | Gene | Function | Affected Population |
|---|---|---|---|
| rs780094 | Glucokinase regulator (GCKR) gene | Glycogen and triglyceride synthesis | Western Pacific and South America |
| rs2237895 | Potassium voltage-gated (KCNQ1) gene | Calcium efflux from the β cells | South Korea and Middle East |
| rs1387153 | Melatonin 1B receptor gene (MTNR1B) | Regulatory process of insulin secretion, glucose metabolism, and heart rate | European, North American, and Western Pacific populations |
| rs10830963 | Melatonin 1B receptor gene (MTNR1B) | Regulatory process of insulin secretion, glucose metabolism, and heart rate | European, North American, and Western Pacific populations |
| rs1501299 rs2241766 | Adiponectin gene (ADIPOQ) | Adipose tissue and adipokine release | Saudi Arabia |
| rs7903146 | Transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2) gene | Impacts insulin secretion and β-cell function via the Wnt signaling pathway | European and Asian populations |
| rs7756992 | Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 regulatory subunit-associated protein 1-like 1 (CDKAL1) gene | Influences β-cell function and insulin secretion | Multiple ethnic groups |
| rs4402960 | Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 2 (IGF2BP2) gene | Involved in insulin secretion and β-cell function | Asian populations |
| Gene | Chromosome Location | Associated Risk | Function | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TCF7L2 | 10q25.3 | Increased risk of type 2 diabetes | Most strongly associated with type 2 diabetes risk | [150,151] |
| GCK | 7p13 | Altered glucose metabolism | Plays a crucial role in pancreatic beta-cell function | [135] |
| MTNR1B | 11q21 | Disrupted melatonin signaling | Melatonin receptor affecting insulin secretion | [152,153] |
| CDKAL1 | 6p22.3 | Impaired beta-cell function | Associated with reduced insulin release | [122,154] |
| IGF2BP2 | 3q27.2 | Regulation of insulin production | Influences insulin-mediated glucose homeostasis | [159,160] |
| KCNQ1 | 11p15.5 | Impaired insulin secretion | Encodes the pore-forming potassium (K+) channel alpha-subunit | [155,156] |
| IRS1 | 2q36.3 | Insulin resistance and impaired insulin secretion | Plays a critical role in the insulin-signaling pathway | [157,158] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mittal, R.; Prasad, K.; Lemos, J.R.N.; Arevalo, G.; Hirani, K. Unveiling Gestational Diabetes: An Overview of Pathophysiology and Management. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2320. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26052320
Mittal R, Prasad K, Lemos JRN, Arevalo G, Hirani K. Unveiling Gestational Diabetes: An Overview of Pathophysiology and Management. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(5):2320. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26052320
Chicago/Turabian StyleMittal, Rahul, Karan Prasad, Joana R. N. Lemos, Giuliana Arevalo, and Khemraj Hirani. 2025. "Unveiling Gestational Diabetes: An Overview of Pathophysiology and Management" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 5: 2320. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26052320
APA StyleMittal, R., Prasad, K., Lemos, J. R. N., Arevalo, G., & Hirani, K. (2025). Unveiling Gestational Diabetes: An Overview of Pathophysiology and Management. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(5), 2320. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26052320






