Kinsenoside Suppresses DGAT1-Mediated Lipid Droplet Formation to Trigger Ferroptosis in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
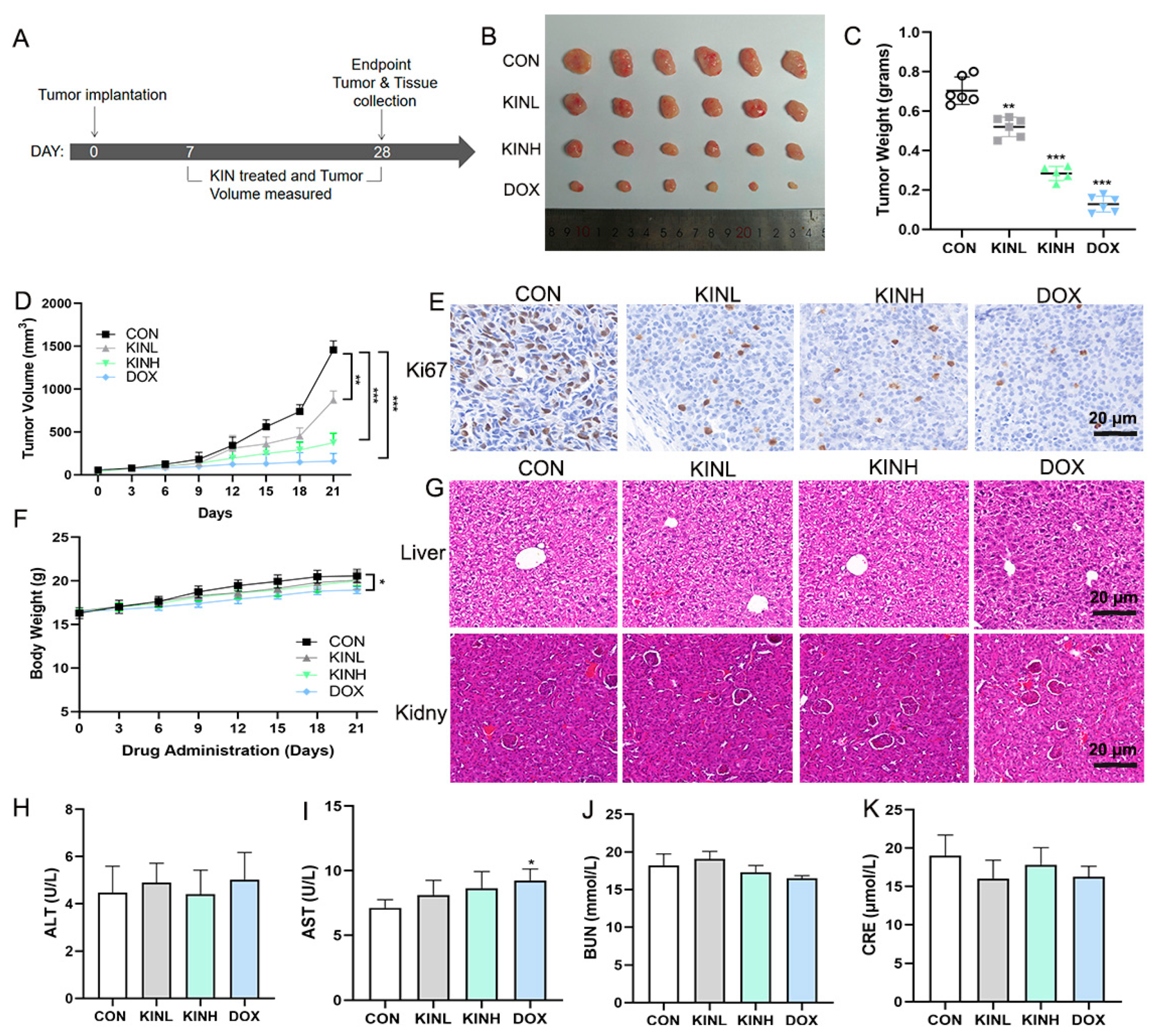
2.1. KIN Inhibited Tumor Growth in Mouse Xenograft Tumor Models
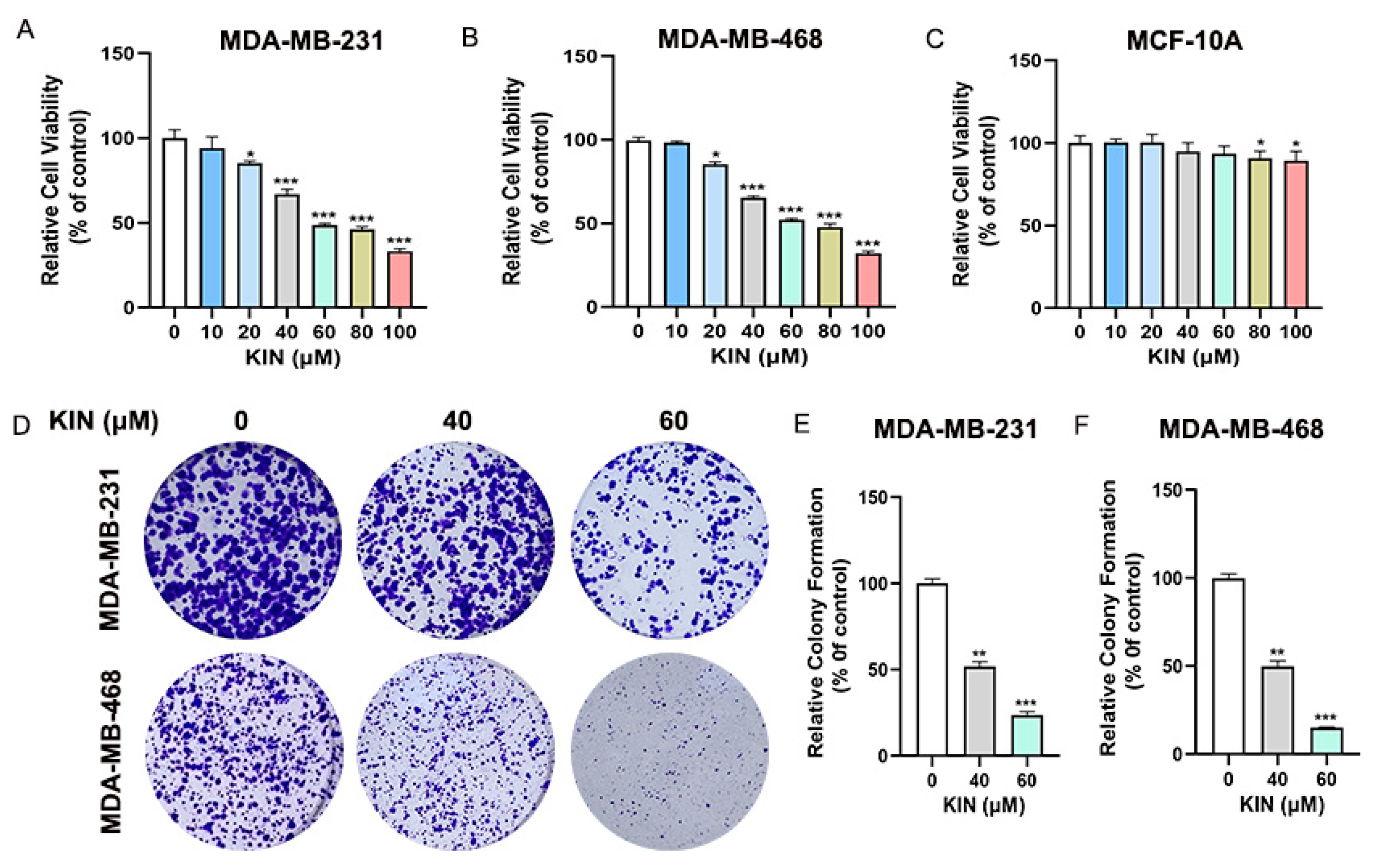
2.2. KIN Inhibits Growth of TNBC Cells In Vitro
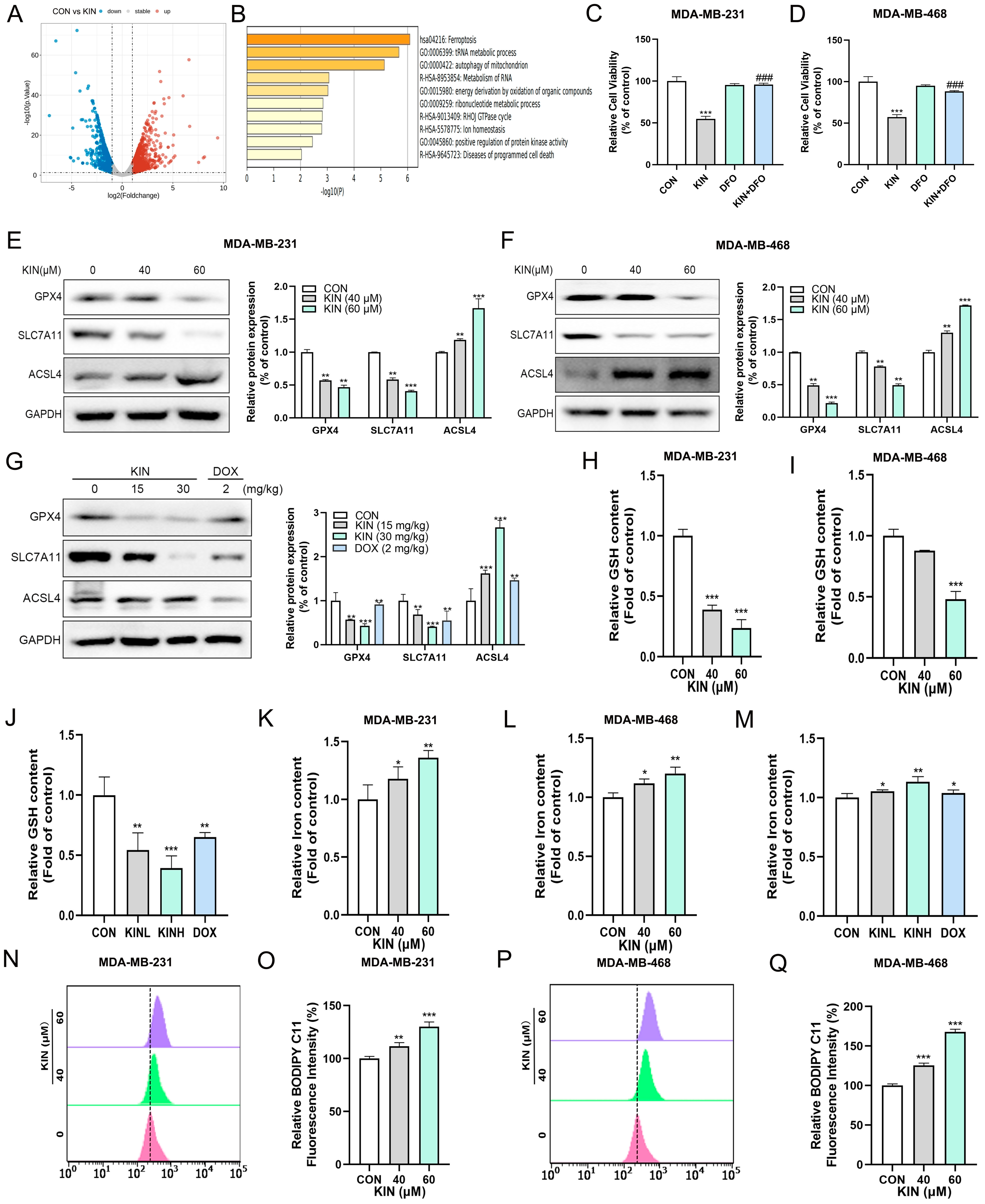
2.3. KIN-Induced Ferroptosis in TNBC Cells
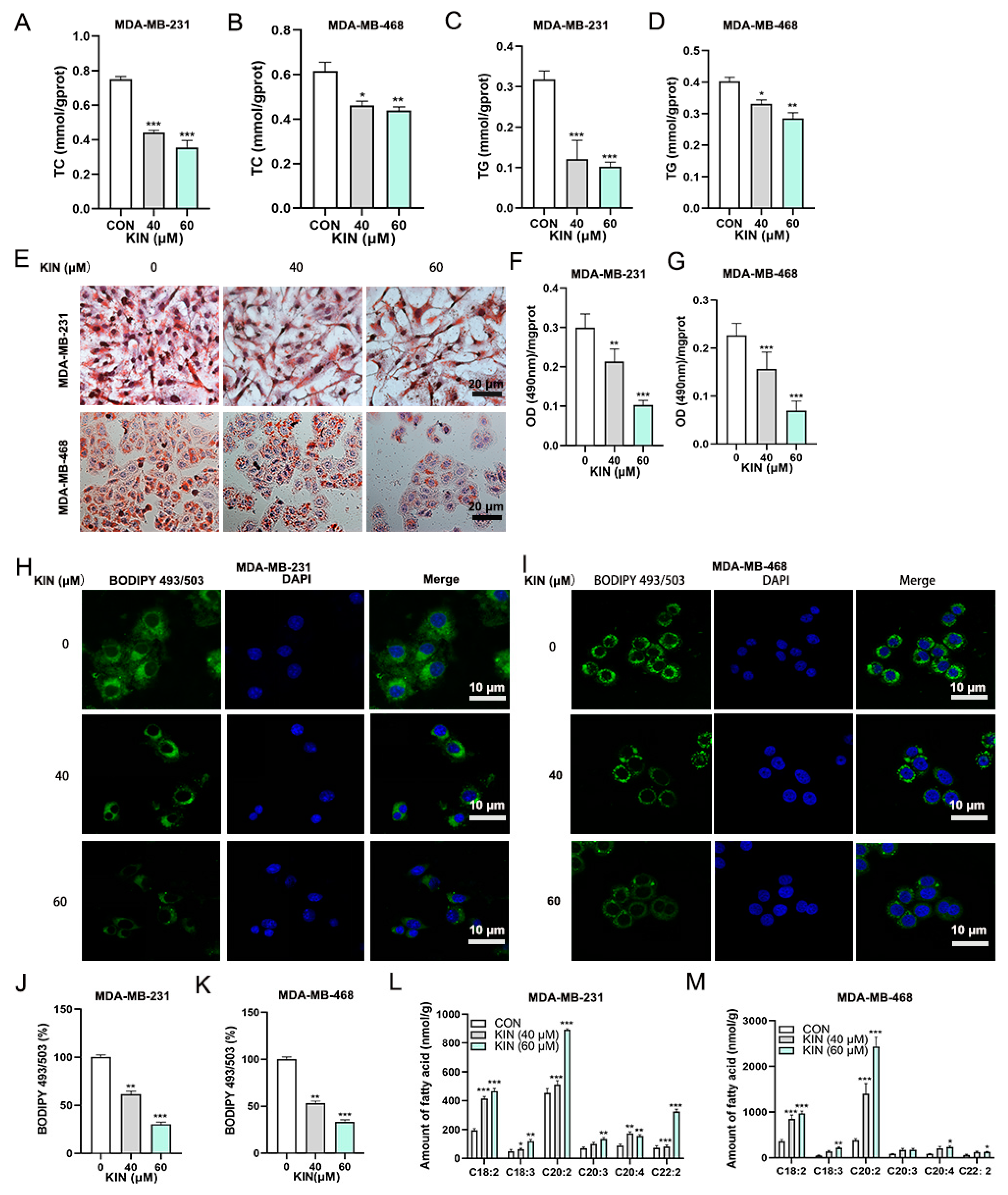
2.4. KIN Inhibits Lipid Droplet Formation in TNBC Cells
2.5. KIN Induces Ferroptosis in TNBC Cells by Inhibiting Lipid Droplet Formation
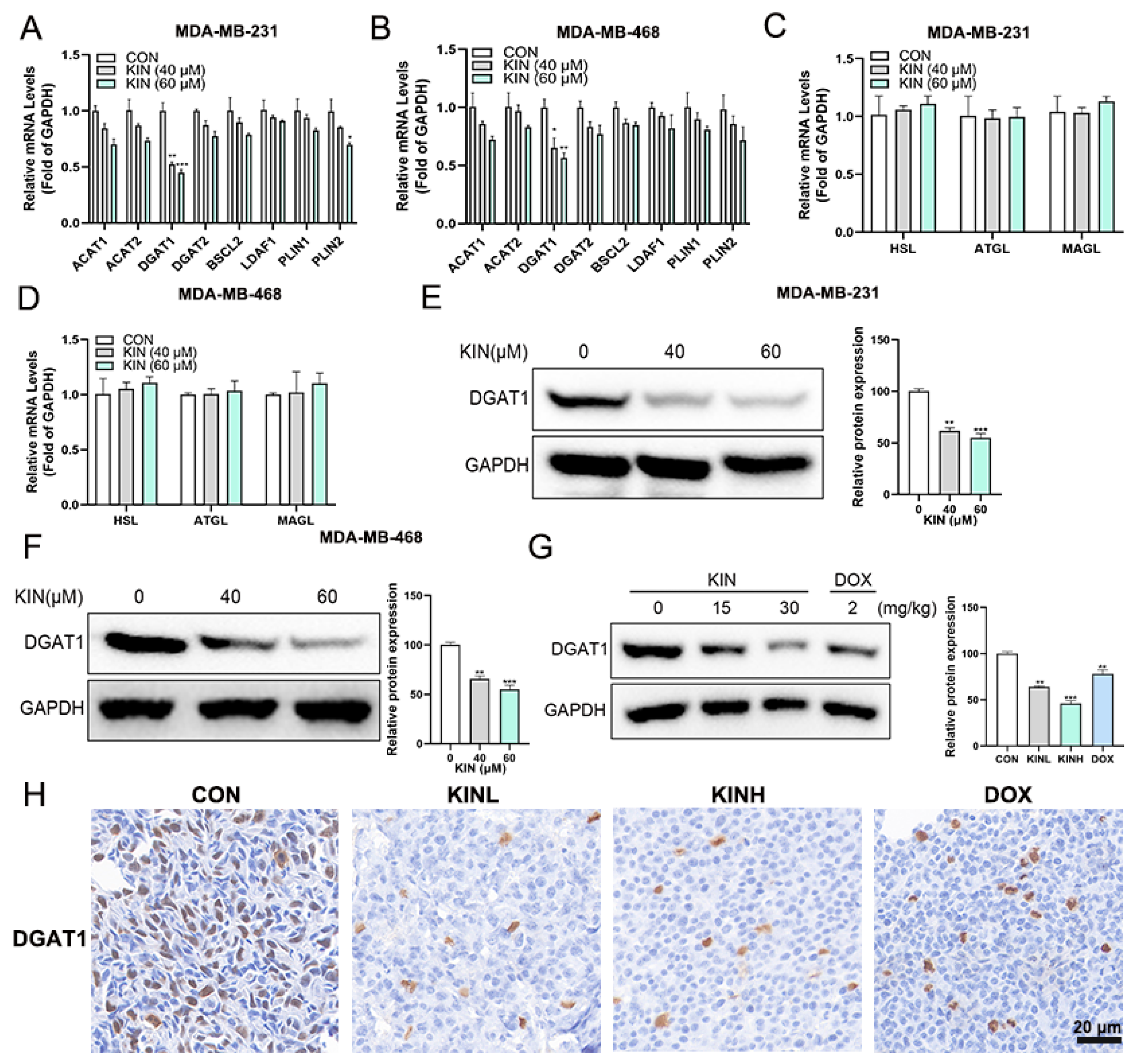
2.6. KIN Inhibits the Expression of the Key Lipid Droplet Formation Protein DGAT1
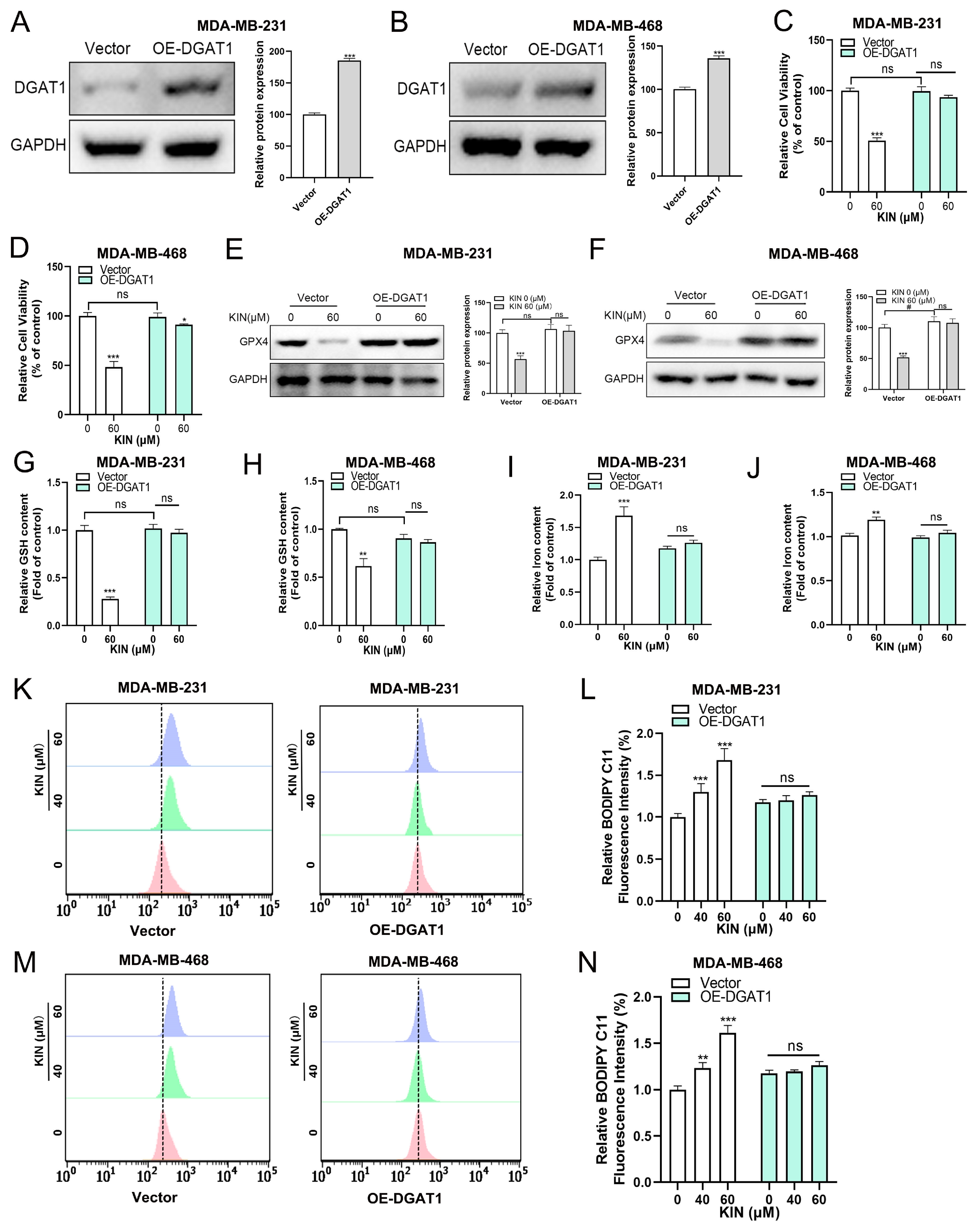
2.7. DGAT1 Mediates KIN-Induced Ferroptosis in TNBC Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. In Vivo Tumor Xenograft Study
4.3. HE Staining and IHC Analysis
4.4. Cell Lines and Cell Culture
4.5. Cell Viability Assay
4.6. Colony Formation Assay
4.7. Oil Red O Staining
4.8. BODIPY 493/503 Fluorescence Staining
4.9. Western Blotting
4.10. Biomedical Measurement
4.11. RNA-Sequencing (RNA-Seq)
4.12. RT-qPCR
4.13. Measurement of Lipid ROS
4.14. Lentiviral-Mediated DGAT1 Overexpression
4.15. PUFAs Quantification
4.16. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALT | alanine aminotransferase |
| AST | aspartate aminotransferase |
| BCA | bicinchoninic acid |
| BUN | blood urea nitrogen |
| CoA | coenzyme A |
| CON | control group |
| CRE | Creatinine |
| DAPI | 4′,6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole |
| DFO | deferoxamine |
| DGAT1 | diacylglycerol acyltransferase 1 |
| DOX | 2 mg/kg doxorubicin positive control group |
| ER | estrogen receptor |
| GSH | glutatione |
| HE | Hematoxylin and eosin |
| HER-2 | human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 |
| IHC | immunohistochemistry |
| KIN | Kinsenoside |
| KINL | 15 mg/kg KIN group |
| KINH | 30 mg/kg KIN group |
| LD | lipid droplet |
| OA | oleic acid |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| PR | progesterone receptor |
| PUFAs | polyunsaturated fatty acids |
| RNA-Seq | RNA-Sequencing |
| RT-qPCR | quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction |
| TC | triglycerides |
| TCM | traditional Chinese medicine |
| TG | total cholesterol |
| TNBC | triple-negative breast cancer |
References
- Bianchini, G.; De Angelis, C.; Licata, L.; Gianni, L. Treatment landscape of triple-negative breast cancer—Expanded options, evolving needs. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 19, 91–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, G.; Liang, J.; Bian, Y.; Shan, G.; Huang, Y.; Lu, T.; Zhang, H.; Jin, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, M.; et al. Polyamine-mediated ferroptosis amplification acts as a targetable vulnerability in cancer. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, N.; Vinik, Y.; Saroha, A.; Nair, N.U.; Ruppin, E.; Mills, G.; Karn, T.; Dubey, V.; Khera, L.; Raj, H.; et al. Synthetic lethal combination targeting BET uncovered intrinsic susceptibility of TNBC to ferroptosis. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaba8968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; He, D.; Li, S.; Xiao, J.; Zhu, Z. Ferroptosis: The emerging player in remodeling triple-negative breast cancer. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1284057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snaebjornsson, M.T.; Janaki-Raman, S.; Schulze, A. Greasing the Wheels of the Cancer Machine: The Role of Lipid Metabolism in Cancer. Cell Metab. 2020, 31, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Outschoorn, U.E.; Peiris-Pagés, M.; Pestell, R.G.; Sotgia, F.; Lisanti, M.P. Cancer metabolism: A therapeutic perspective. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 11–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olzmann, J.A.; Carvalho, P. Dynamics and functions of lipid droplets. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 137–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLelland, G.L.; Lopez-Osias, M.; Verzijl, C.R.C.; Ellenbroek, B.D.; Oliveira, R.A.; Boon, N.J.; Dekker, M.; van den Hengel, L.G.; Ali, R.; Janssen, H.; et al. Identification of an alternative triglyceride biosynthesis pathway. Nature 2023, 621, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarc, E.; Kump, A.; Malavašič, P.; Eichmann, T.O.; Zimmermann, R.; Petan, T. Lipid droplets induced by secreted phospholipase A2 and unsaturated fatty acids protect breast cancer cells from nutrient and lipotoxic stress. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2018, 1863, 247–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorito, N.; Subbiani, A.; Smiriglia, A.; Bacci, M.; Bonechi, F.; Tronci, L.; Romano, E.; Corrado, A.; Longo, D.L.; Iozzo, M.; et al. FADS1/2 control lipid metabolism and ferroptosis susceptibility in triple-negative breast cancer. EMBO Mol. Med. 2024, 16, 1533–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Z.; Sun, M.; Zhou, R.; Fu, Z.F.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, M. Z-Ligustilide restricts rabies virus replication by inducing ferroptosis through the ACSL4-LPCAT3-POR pathway. Vet. Microbiol. 2024, 298, 110260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Fang, C.; Luo, J.; Gong, C.; Wang, L.; Zhu, S. Traditional Chinese Medicine for Cancer Treatment. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2024, 52, 583–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Shao, Q.; Zhang, A. Anoectochilus roxburghii: A review of its phytochemistry, pharmacology, and clinical applications. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 209, 184–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shyur, L.F.; Chen, C.H.; Lo, C.P.; Wang, S.Y.; Kang, P.L.; Sun, S.J.; Chang, C.A.; Tzeng, C.M.; Yang, N.S. Induction of apoptosis in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells by phytochemicals from Anoectochilus formosanus. J. Biomed. Sci. 2004, 11, 928–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, C.C.; Shang, H.F.; Wang, L.F.; Su, B.; Hsu, C.C.; Kao, H.Y.; Cheng, K.T. Antitumor and immunostimulating effects of Anoectochilus formosanus Hayata. Phytomedicine 2006, 13, 366–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; He, X.; Chen, H.; Lin, Y.; Zheng, C.; Zheng, B. Extraction and characterization of hepatoprotective polysaccharides from Anoectochilus roxburghii against CCl4-induced liver injury via regulating lipid metabolism and the gut microbiota. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 277, 134305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Lin, S.; Zhang, J.; Huang, L.; Yao, H.; Li, S. Purification of polysaccharide from artificially cultivated Anoectochilus roxburghii (wall.) Lindl. by high-speed counter current chromatography and its antitumor activity. J. Sep. Sci. 2017, 40, 4338–4346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.G.; Sue, Y.M.; Lee, C.K.; Huang, H.M.; He, J.J.; Wang, Y.S.; Juan, S.H. Synergistic effects of cAMP-dependent protein kinase A and AMP-activated protein kinase on lipolysis in kinsenoside-treated C3H10T1/2 adipocytes. Phytomedicine 2019, 55, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.T.; Wang, Y.S.; Chou, H.C.; Chang, C.C.; Lee, C.K.; Juan, S.H. Kinsenoside-mediated lipolysis through an AMPK-dependent pathway in C3H10T1/2 adipocytes: Roles of AMPK and PPARα in the lipolytic effect of kinsenoside. Phytomedicine 2015, 22, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, N.; An, Z.; Fu, Z.; Chen, X.; Tong, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, H. Kinsenoside alleviates oxidative stress-induced blood-brain barrier dysfunction via promoting Nrf2/HO-1 pathway in ischemic stroke. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 949, 175717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Chen, X.; Fu, Z.; Yin, J.; Wang, Y.; Sun, W.; Ren, H.; Zhang, Y. Kinsenoside Alleviates Alcoholic Liver Injury by Reducing Oxidative Stress, Inhibiting Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, and Regulating AMPK-Dependent Autophagy. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 747325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danielli, M.; Perne, L.; Jarc Jovičić, E.; Petan, T. Lipid droplets and polyunsaturated fatty acid trafficking: Balancing life and death. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1104725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, F.; Mei, J.; Han, X.; Li, H.; Yang, S.; Wang, M.; Chu, L.; Qiao, H.; Tang, T. Kinsenoside attenuates osteoarthritis by repolarizing macrophages through inactivating NF-κB/MAPK signaling and protecting chondrocytes. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2019, 9, 973–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, C.X.; Zhou, Q.; Yuan, Z.; Luo, Z.W.; Dai, C.; Zhu, H.C.; Chen, C.M.; Xue, Y.B.; Wang, J.P.; Wang, Y.F.; et al. Kinsenoside: A Promising Bioactive Compound from Anoectochilus Species. Curr. Med. Sci. 2018, 38, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Yan, Y.; Niu, F.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Su, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Qian, L.; Liu, P.; et al. Ferroptosis: A cell death connecting oxidative stress, inflammation and cardiovascular diseases. Cell Death Discov. 2021, 7, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Minikes, A.M.; Jiang, X. Ferroptosis at the intersection of lipid metabolism and cellular signaling. Mol. Cell 2022, 82, 2215–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doll, S.; Proneth, B.; Tyurina, Y.Y.; Panzilius, E.; Kobayashi, S.; Ingold, I.; Irmler, M.; Beckers, J.; Aichler, M.; Walch, A.; et al. ACSL4 dictates ferroptosis sensitivity by shaping cellular lipid composition. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2017, 13, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Zhao, W.; Tang, S.Y.; Levin, M.G.; Ibrahim, A.; Yang, Y.; Roberts, E.; Lai, L.; Li, J.; Assoian, R.K.; et al. Endothelial lipid droplets suppress eNOS to link high fat consumption to blood pressure elevation. J. Clin. Investig. 2023, 133, e173160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Yao, W. LPCAT2-mediated lipid droplet production supports pancreatic cancer chemoresistance and cell motility. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 139, 112681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardaci, T.D.; VanderVeen, B.N.; Huss, A.R.; Bullard, B.M.; Velázquez, K.T.; Frizzell, N.; Carson, J.A.; Price, R.L.; Murphy, E.A. Decreased skeletal muscle intramyocellular lipid droplet-mitochondrial contact contributes to myosteatosis in cancer cachexia. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2024, 327, C684–C697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, A.P.; Koster, G.; Guillermier, C.; Hirst, E.M.; MacRae, J.I.; Lechene, C.P.; Postle, A.D.; Gould, A.P. Antioxidant Role for Lipid Droplets in a Stem Cell Niche of Drosophila. Cell 2015, 163, 340–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Xi, F.; Jin, C.; Zhu, H.L.; Tu, M.; Li, Z. A ferrous fluorescence lifetime response probe for monitoring changes in lipid droplets during ferroptosis and imaging in liver disease model. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2025, 267, 116742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VandeKopple, M.J.; Wu, J.; Auer, E.N.; Giaccia, A.J.; Denko, N.C.; Papandreou, I. HILPDA Regulates Lipid Metabolism, Lipid Droplet Abundance, and Response to Microenvironmental Stress in Solid Tumors. Mol. Cancer Res. 2019, 17, 2089–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.B.; Louie, S.M.; Daniele, J.R.; Tran, Q.; Dillin, A.; Zoncu, R.; Nomura, D.K.; Olzmann, J.A. DGAT1-Dependent Lipid Droplet Biogenesis Protects Mitochondrial Function during Starvation-Induced Autophagy. Dev. Cell 2017, 42, 9–21.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, H.; Lou, S.; Zheng, F.; Gao, H.; Wang, N.; Tian, S.; Huang, G.; Zhao, H. Hydnocarpin D attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via MAPK/NF-κB and Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Phytomedicine 2022, 101, 154143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.N.; Lou, S.Y.; Lu, J.; Zheng, F.L.; Tang, Y.M.; Zhang, E.J.; Cui, S.L.; Zhao, H.J. Selective PI3Kδ inhibitor TYM-3-98 suppresses AKT/mTOR/SREBP1-mediated lipogenesis and promotes ferroptosis in KRAS-mutant colorectal cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2024, 15, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, S.; Gao, H.; Hong, H.; Zhu, Z.; Zhao, H. Inhibition of retinoic acid receptor α phosphorylation represses the progression of triple-negative breast cancer via transactivating miR-3074-5p to target DHRS3. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierge, E.; Debock, E.; Guilbaud, C.; Corbet, C.; Mignolet, E.; Mignard, L.; Bastien, E.; Dessy, C.; Larondelle, Y.; Feron, O. Peroxidation of n-3 and n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids in the acidic tumor environment leads to ferroptosis-mediated anticancer effects. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 1701–1715.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.; Chen, D.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, H. Kinsenoside Suppresses DGAT1-Mediated Lipid Droplet Formation to Trigger Ferroptosis in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2322. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26052322
Yang Y, Chen D, Zhu Y, Zhang M, Zhao H. Kinsenoside Suppresses DGAT1-Mediated Lipid Droplet Formation to Trigger Ferroptosis in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(5):2322. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26052322
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Yaqin, Dandan Chen, Yuru Zhu, Min Zhang, and Huajun Zhao. 2025. "Kinsenoside Suppresses DGAT1-Mediated Lipid Droplet Formation to Trigger Ferroptosis in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 5: 2322. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26052322
APA StyleYang, Y., Chen, D., Zhu, Y., Zhang, M., & Zhao, H. (2025). Kinsenoside Suppresses DGAT1-Mediated Lipid Droplet Formation to Trigger Ferroptosis in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(5), 2322. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26052322



