Novel Insights into the Therapeutic Effect of Amentoflavone Against Aeromonas hydrophila Infection by Blocking the Activity of Aerolysin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
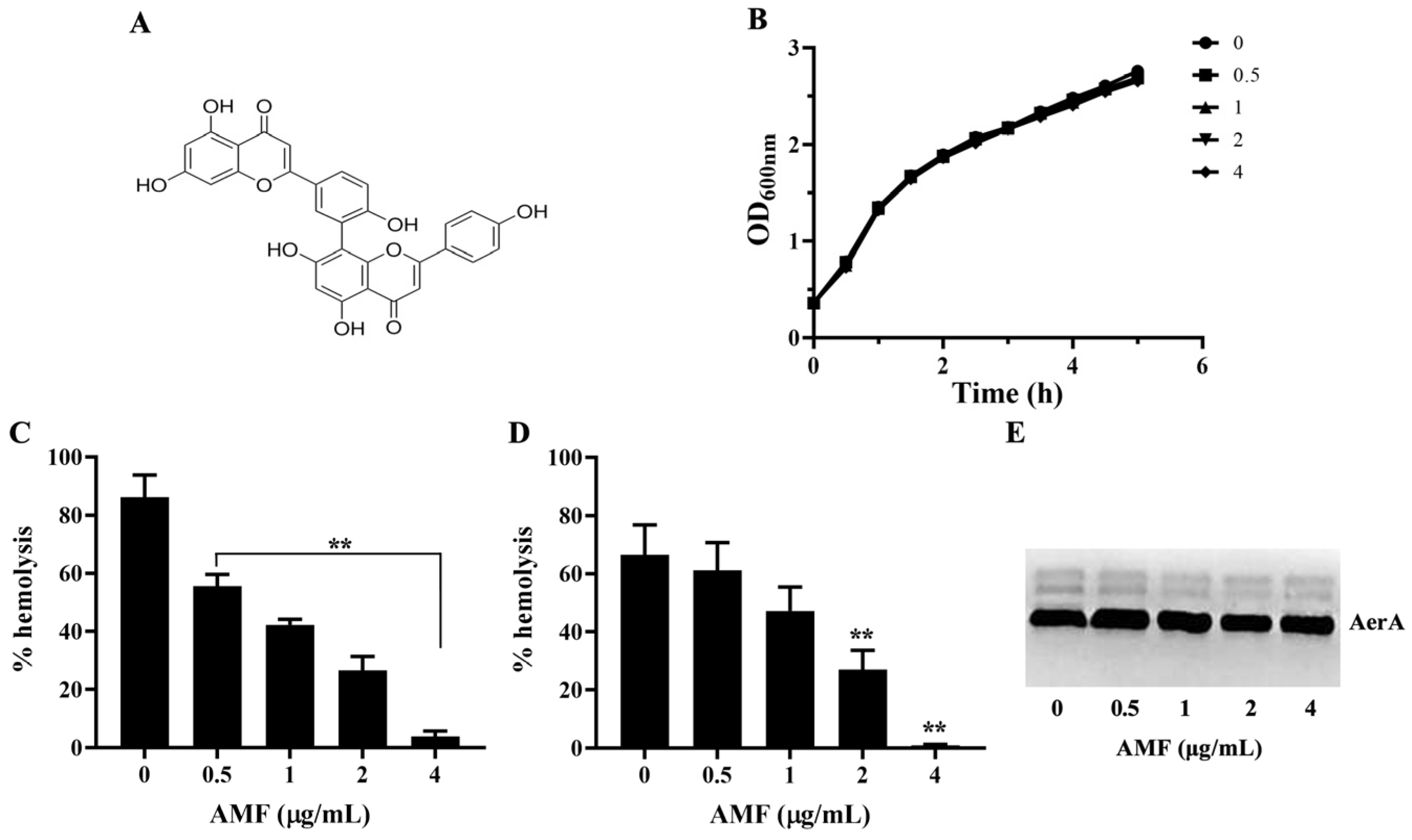
2.1. AMF Had No Role on Bacterial Growth
2.2. AMF Decreased the Hemolytic Activity of AerA
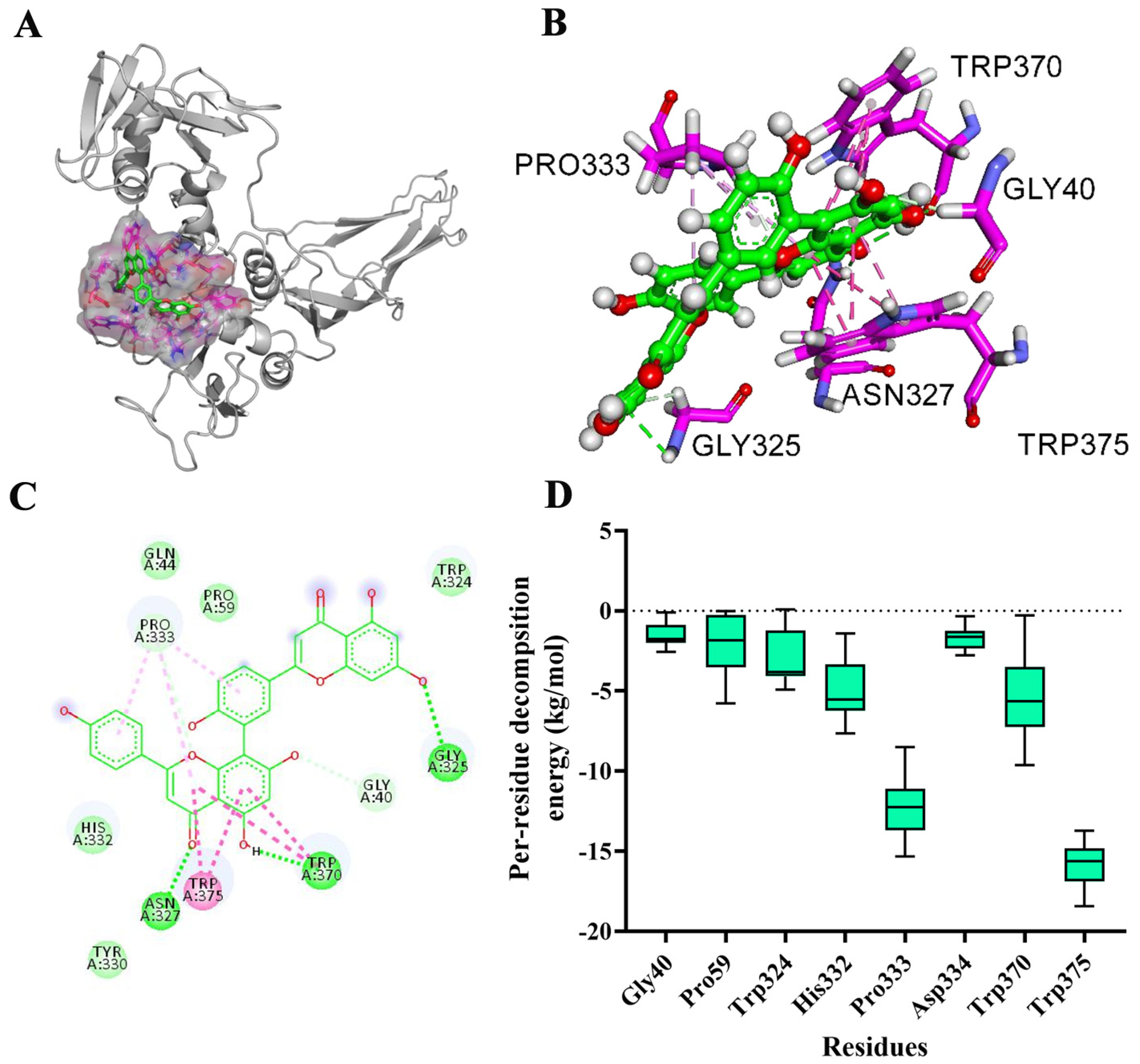
2.3. Determination of Binding Sites
2.4. Confirmation of the Main Binding Sites of AMF-AerA Complex
2.5. AMF Reduced Pore-Forming Activity of AerA
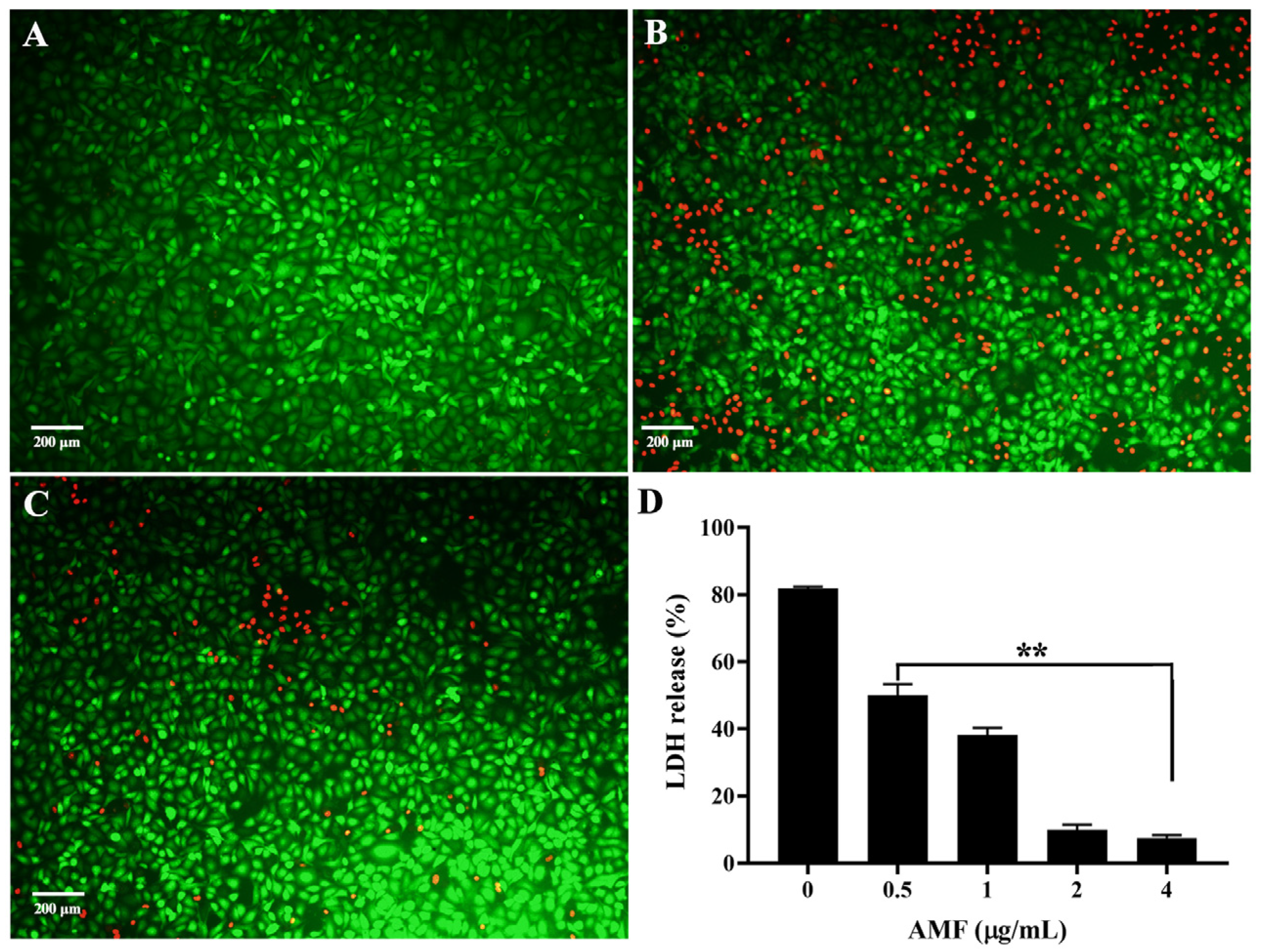
2.6. AMF Protected A549 Cells from AerA-Mediated Cell Injury
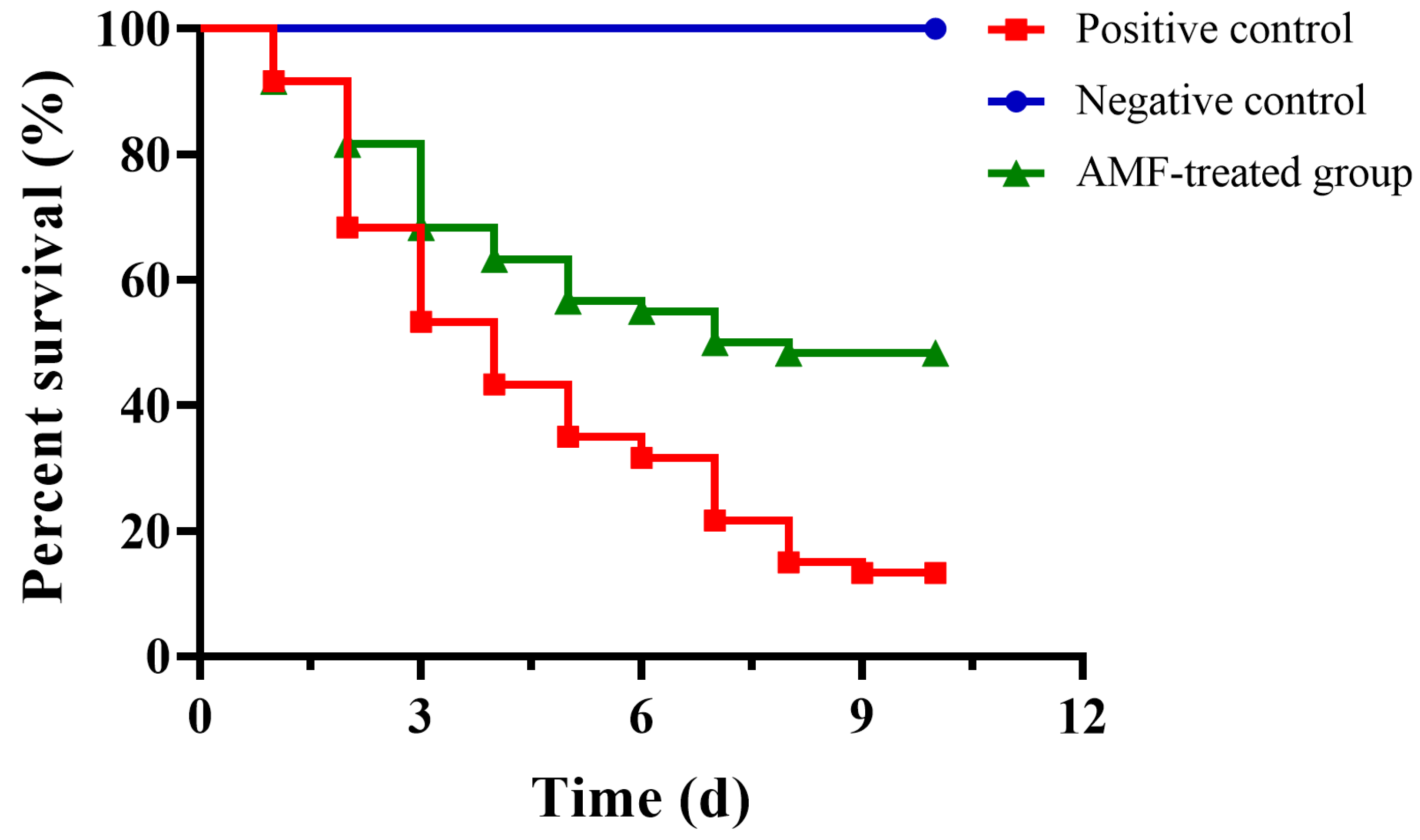
2.7. AMF Decreased the Mortality of Channel Catfish Infected with A. hydrophila
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Microorganisms and Reagents
4.2. Minimum Inhibitory Concentrations (MICs) Determination
4.3. Growth Curves
4.4. Hemolytic Assays
4.5. Immuno-Blot
4.6. Molecular Docking
4.7. Molecular Dynamics (MD) Simulation
4.8. Expression and Purification of AerA Mutants
4.9. Fluorescence Quenching Assay
4.10. Oligomerization Assay
4.11. Cytotoxicity Assay
4.12. Animal Study
4.13. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hou, Y.; Wu, Z.; Ren, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.A.; Zhou, Y. Characterization and application of a lytic jumbo phage ZPAH34 against multidrug-resistant Aeromonas hydrophila. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1178876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathak, N.K.; Rana, K.; Rana, N.; Panda, A.K.; Chahota, R.; Thakur, S.D. Molecular detection of enterotoxins in multidrug resistant Aeromonas from ready to eat foods in North Western Himalayas: Public health significance. Acta Trop. 2024, 256, 107258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, C.; Jiao, H.; Ran, J.; Li, D.; Li, Z.; Wang, B.; Luo, H.; Li, Y.; Lin, Y.; Yao, J.; et al. A comprehensive understanding of the influence and molecular mechanism of exeA on the pathogenicity in Aeromonas hydrophila. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 284, 138080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.M.; Kim, H.W.; Choi, C.; Rhee, M.S. Pathogenicity and seasonal variation of Aeromonas hydrophila isolated from seafood and ready-to-eat sushi in South Korea. Food Res. Int. 2021, 147, 110484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, K.; Chen, M.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Z.; Deng, L.; Li, T.; Feng, Y.; Ouyang, P.; Huang, X.; Chen, D.; et al. Genotype diversity and antibiotic resistance risk in Aeromonas hydrophila in Sichuan, China. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2024, 55, 901–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-González, I.; Gallego-Rodrigo, M.; Barrios-Andrés, J.L. Multiresistant Aeromonas hydrophila bacteremia. Enferm. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. 2023, 41, 247–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Bravo, A.; Figueras, M.J. An update on the genus Aeromonas: Taxonomy, epidemiology, and pathogenicity. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Guia, A.C.M.; Guia, M.; Monserate, J.J.; Salazar, J.R.; Velasco, R.R.; Mingala, C.N.; Quiazon, K.M.A. Detection of Aeromonas hydrophila possessing aerolysin gene using gold nanoparticle probe. J. Adv. Vet. Anim. Res. 2023, 10, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, S.P.; Buckley, J.T. Activation of the hole-forming toxin aerolysin by extracellular processing. J. Bacteriol. 1985, 163, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuethrich, I.; Peeters, J.G.; Blom, A.E.; Theile, C.S.; Li, Z.; Spooner, E.; Ploegh, H.L.; Guimaraes, C.P. Site-specific chemoenzymatic labeling of aerolysin enables the identification of new aerolysin receptors. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, T.; Huhle, B.; Hof, H.; Bergbauer, H.; Goebel, W. Marker exchange mutagenesis of the aerolysin determinant in Aeromonas hydrophila demonstrates the role of aerolysin in A. hydrophila-associated systemic infections. Infect. Immun. 1987, 55, 2274–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okigawa, M.; Hwa, C.W.; Kawano, N.; Rahman, W. Biflavones in Selaginella species. Phytochemistry 1971, 10, 3286–3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Yan, H.; Zhang, L.; Shan, M.; Chen, P.; Ding, A.; Li, S.F. A review on the phytochemistry, pharmacology, and pharmacokinetics of amentoflavone, a naturally-occurring biflavonoid. Molecules 2017, 22, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saroni Arwa, P.; Zeraik, M.L.; Ximenes, V.F.; da Fonseca, L.M.; Bolzani Vda, S.; Siqueira Silva, D.H. Redox-active biflavonoids from Garcinia brasiliensis as inhibitors of neutrophil oxidative burst and human erythrocyte membrane damage. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 174, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, I.S.; Lee, J.; Jin, H.G.; Woo, E.R.; Lee, D.G. Amentoflavone stimulates mitochondrial dysfunction and induces apoptotic cell death in Candida albicans. Mycopathologia 2012, 173, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangmool, S.; Duangrat, R.; Rujirayunyong, T.; Anantachoke, N. Anti-inflammatory effects of the Thai herbal remedy Yataprasen and biflavonoids isolated from Putranjiva roxburghii in RAW264.7 macrophages. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 327, 117997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, W.K.; Choi, H.J.; Ahmad, S.S.; Choi, I.; Ma, J.Y. Antiviral effect of amentoflavone against influenza viruses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alherz, F.A.; El-Masry, T.A.; Negm, W.A.; El-Kadem, A.H. Potential cardioprotective effects of Amentoflavone in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 154, 113643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albarral, V.; Sanglas, A.; Palau, M.; Miñana-Galbis, D.; Fusté, M.C. Potential pathogenicity of Aeromonas hydrophila complex strains isolated from clinical, food, and environmental sources. Can. J. Microbiol. 2016, 62, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsheten, T.; Tshering, D.; Gyem, K.; Dorji, S.; Wangchuk, S.; Tenzin, T.; Norbu, L.; Jamtsho, T. An outbreak of Aeromonas hydrophila food poisoning in deptsang village, Samdrup Jongkhar, Bhutan, 2016. J. Res. Health Sci. 2016, 16, 224–227. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, W.; Zhou, Z.; Xie, L.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Gui, L.; Xu, X.; Shen, Y.; Li, J.; Qiu, J. Pathological and molecular characterization of grass carp co-infected with two Aeromonas Species. Animals 2025, 15, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nhinh, D.T.; Le, D.V.; Van, K.V.; Huong Giang, N.T.; Dang, L.T.; Hoai, T.D. Prevalence, virulence gene distribution and alarming the multidrug resistance of Aeromonas hydrophila associated with disease outbreaks in freshwater aquaculture. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.H.; Choi, H.; Woo, E.R.; Lee, D.G. Antibacterial effect of amentoflavone and its synergistic effect with antibiotics. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 23, 953–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, Q.Z.; Li, C.T. Antibacterial Effect of 47 Chinese herbal medicines on bacterium Aeromonas hydrophila in vitro. Fish. Sci. 2012, 31, 387–391. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, C.K.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Lei, L.; Deng, X.X.; Pu, D.C.; Zheng, Z.L.; Zhou, C.W.; Zheng, Y.H. Antimicrobial activities for 150 kinds of Chinese herbal medicines agsinst Aeromonas veronii in vitro. Freshw. Fish. 2018, 48, 80–85+96. [Google Scholar]
- Spiegel, M.; Krzyżek, P.; Dworniczek, E.; Adamski, R.; Sroka, Z. In Silico Screening and In Vitro Assessment of Natural Products with Anti-virulence activity against Helicobacter pylori. Molecules 2021, 27, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Zhu, X.; Yin, Z.; Gao, R.; Li, Y.; Li, C.; Meng, Q.; Zhu, X.; Song, W.; Su, X. Dual role of Baimao-Longdan-Congrong-Fang in inhibiting Staphylococcus aureus virulence factors and regulating TNF-alpha/TNFR1/NF-kappaB/MMP9 axis. Phytomedicine 2025, 139, 156477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yang, Q.; Cheng, B.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, S.; Ai, X.; Dong, J. Neem oil against Aeromonas hydrophila infection by disrupting quorum sensing and biofilm formation. Biofouling 2023, 39, 867–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshni, P.S.; Alexpandi, R.; Abirami, G.; Durgadevi, R.; Cai, Y.; Kumar, P.; Ravi, A.V. Hesperidin methyl chalcone, a citrus flavonoid, inhibits Aeromonas hydrophila infection mediated by quorum sensing. Microb. Pathog. 2023, 177, 106029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, M.J.; Swift, S.; Kirke, D.F.; Keevil, C.W.; Dodd, C.E.; Williams, P. The regulation of biofilm development by quorum sensing in Aeromonas hydrophila. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 4, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Z.X.; Liu, Y.J.; Lu, C.P. Contribution of AhyR to virulence of Aeromonas hydrophila J-1. Res. Vet. Sci. 2007, 83, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulhuq, F.R.; Mariano, G. Bacterial pore-forming toxins. Microbiology 2022, 168, 001154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podobnik, M.; Kisovec, M.; Anderluh, G. Molecular mechanism of pore formation by aerolysin-like proteins. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2017, 372, 20160209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumugam, M.; Manikandan, D.B.; Marimuthu, S.K.; Muthusamy, G.; Kari, Z.A.; Tellez-Isaias, G.; Ramasamy, T. Evaluating biofilm inhibitory potential in fish pathogen, Aeromonas hydrophila by agricultural waste extracts and assessment of aerolysin inhibitors using in silico approach. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossjohn, J.; Feil, S.C.; McKinstry, W.J.; Tsernoglou, D.; van der Goot, G.; Buckley, J.T.; Parker, M.W. Aerolysin--a paradigm for membrane insertion of beta-sheet protein toxins? J. Struct. Biol. 1998, 121, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Liu, Y.; Xu, N.; Yang, Q.; Ai, X. Morin protects channel catfish from Aeromonas hydrophila infection by blocking aerolysin activity. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Xu, N.; Zhou, S.; Yang, Y.; Yang, Q.; Ai, X. Luteolin decreases the pathogenicity of Aeromonas hydrophila via inhibiting the activity of aerolysin. Virulence 2021, 12, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yang, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, T.; Hu, N.; Deng, X.; Bai, X.; Wang, J. Amentoflavone attenuates Clostridium perfringens gas gangrene by targeting alpha-toxin and perfringolysin O. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tingting, W.; Tianqi, F.; Xinyu, W.; Can, Z.; Xue, S.; Xuming, D.; Jianfeng, W. Amentoflavone attenuates Listeria monocytogenes pathogenicity through an LLO-dependent mechanism. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 179, 3839–3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, X.; Niu, X.; Li, G.; Deng, X.; Wang, J. Amentoflavone ameliorates Streptococcus suis-induced infection in vitro and in vivo. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e01804-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Liu, B.; Liu, S.; Wang, L.; Wang, J. Anticytotoxin effects of amentoflavone to pneumolysin. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2017, 40, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muema, F.W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, G.; Guo, M. Flavonoids from Selaginella doederleinii Hieron and their antioxidant and antiproliferative activities. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurasekova, Z.; Marconi, G.; Sanchez-Cortes, S.; Torreggiani, A. Spectroscopic and molecular modeling studies on the binding of the flavonoid luteolin and human serum albumin. Biopolymers 2009, 91, 917–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, N.; Ibrahim, H.; Kim, S.; Nallet, J.P.; Nepveu, F. Interactions between antimalarial indolone-N-oxide derivatives and human serum albumin. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 3341–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacovache, I.; Degiacomi, M.T.; Pernot, L.; Ho, S.; Schiltz, M.; Dal Peraro, M.; van der Goot, F.G. Dual chaperone role of the C-terminal propeptide in folding and oligomerization of the pore-forming toxin aerolysin. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| WT-AerA | AerA-W375A | AerA-P333 A | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ΔGbind (kcal/mol) | −22.16 | −15.99 | −12.34 |
| KA (1 × 105) L/mol | 3.52 | 1.41 | 1.38 |
| n | 1.3178 | 1.1988 | 1.1959 |
| Primer | Sequence |
|---|---|
| P333A-F | CTGGTATACCCATGCGGACAACCGC |
| P333A-R | GCGGTTGTCCGCATGGGTATACCAG |
| W375A-F | GTGGTGGGACTGGAACGCGACCATACAGCAGAAC |
| W375A-R | GTTCTGCTGTATGGTCGCGTTCCAGTCCCACCAC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, J.; Li, S.; Zhou, S.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Q.; Xu, N.; Yang, Y.; Cheng, B.; Ai, X. Novel Insights into the Therapeutic Effect of Amentoflavone Against Aeromonas hydrophila Infection by Blocking the Activity of Aerolysin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2370. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26052370
Dong J, Li S, Zhou S, Liu Y, Yang Q, Xu N, Yang Y, Cheng B, Ai X. Novel Insights into the Therapeutic Effect of Amentoflavone Against Aeromonas hydrophila Infection by Blocking the Activity of Aerolysin. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(5):2370. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26052370
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Jing, Shengping Li, Shun Zhou, Yongtao Liu, Qiuhong Yang, Ning Xu, Yibin Yang, Bo Cheng, and Xiaohui Ai. 2025. "Novel Insights into the Therapeutic Effect of Amentoflavone Against Aeromonas hydrophila Infection by Blocking the Activity of Aerolysin" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 5: 2370. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26052370
APA StyleDong, J., Li, S., Zhou, S., Liu, Y., Yang, Q., Xu, N., Yang, Y., Cheng, B., & Ai, X. (2025). Novel Insights into the Therapeutic Effect of Amentoflavone Against Aeromonas hydrophila Infection by Blocking the Activity of Aerolysin. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(5), 2370. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26052370






