Effects of Lactococcus cremoris PS133 in 5-Hydroxytryptophan-Induced Irritable Bowel Syndrome Model Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
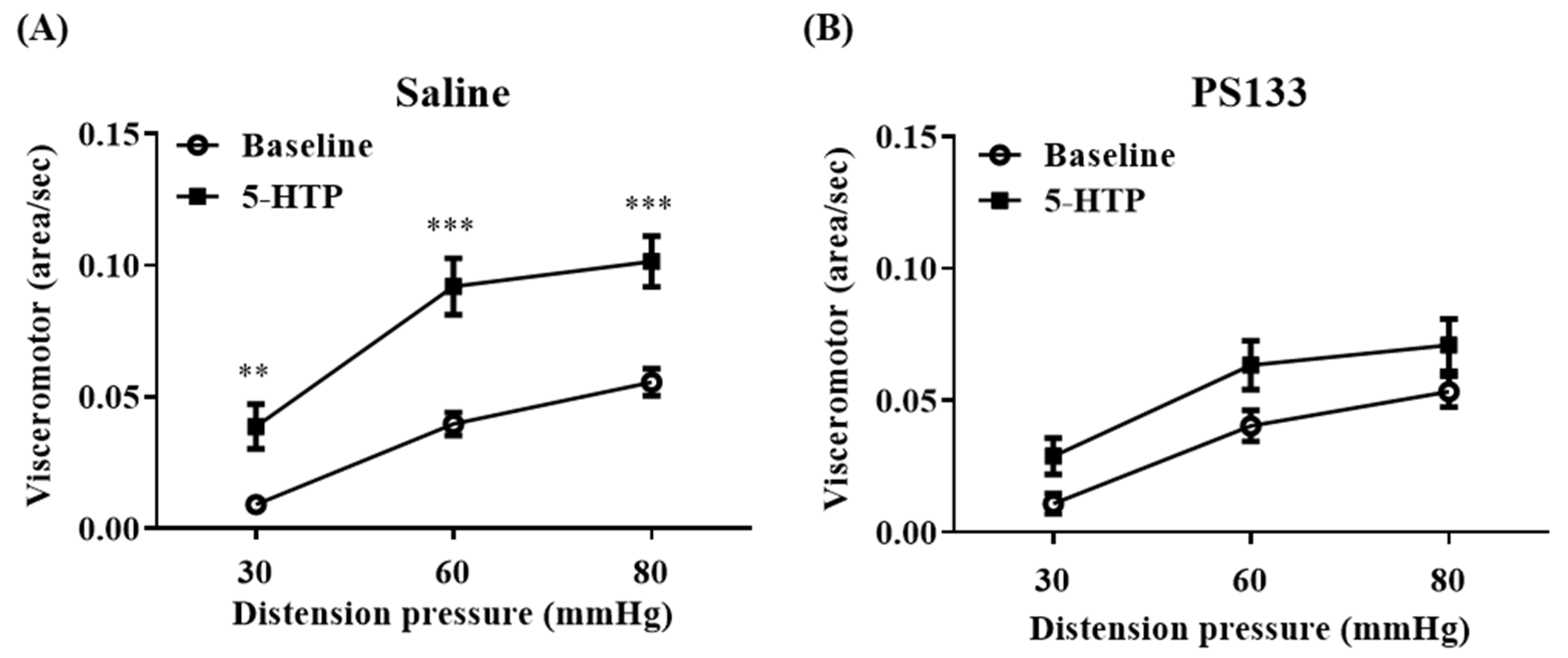
2.1. Effect of L. cremoris PS133 on 5-HTP-Induced VH
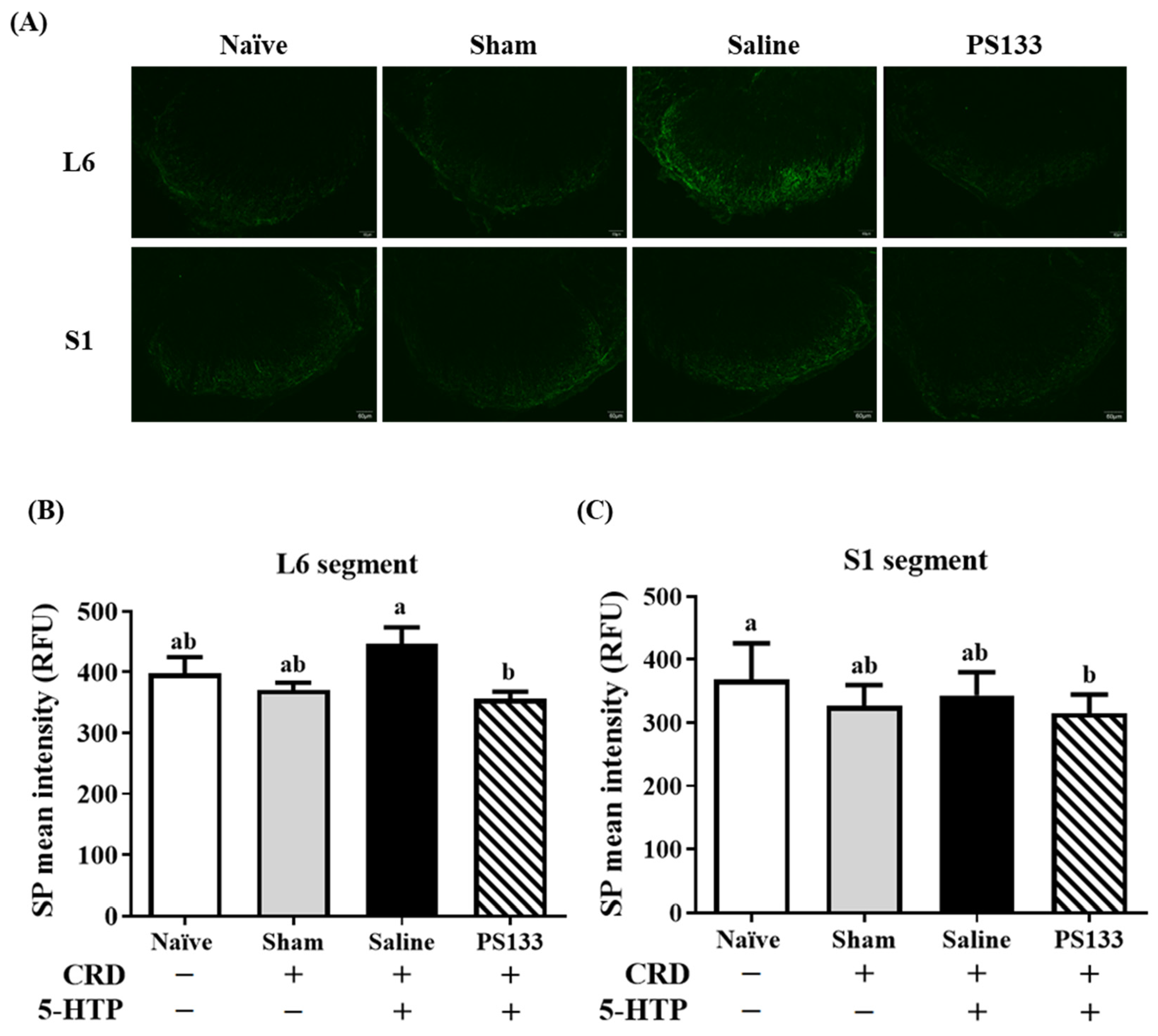
2.2. Effect of L. cremoris PS133 on Substance P (SP) Levels
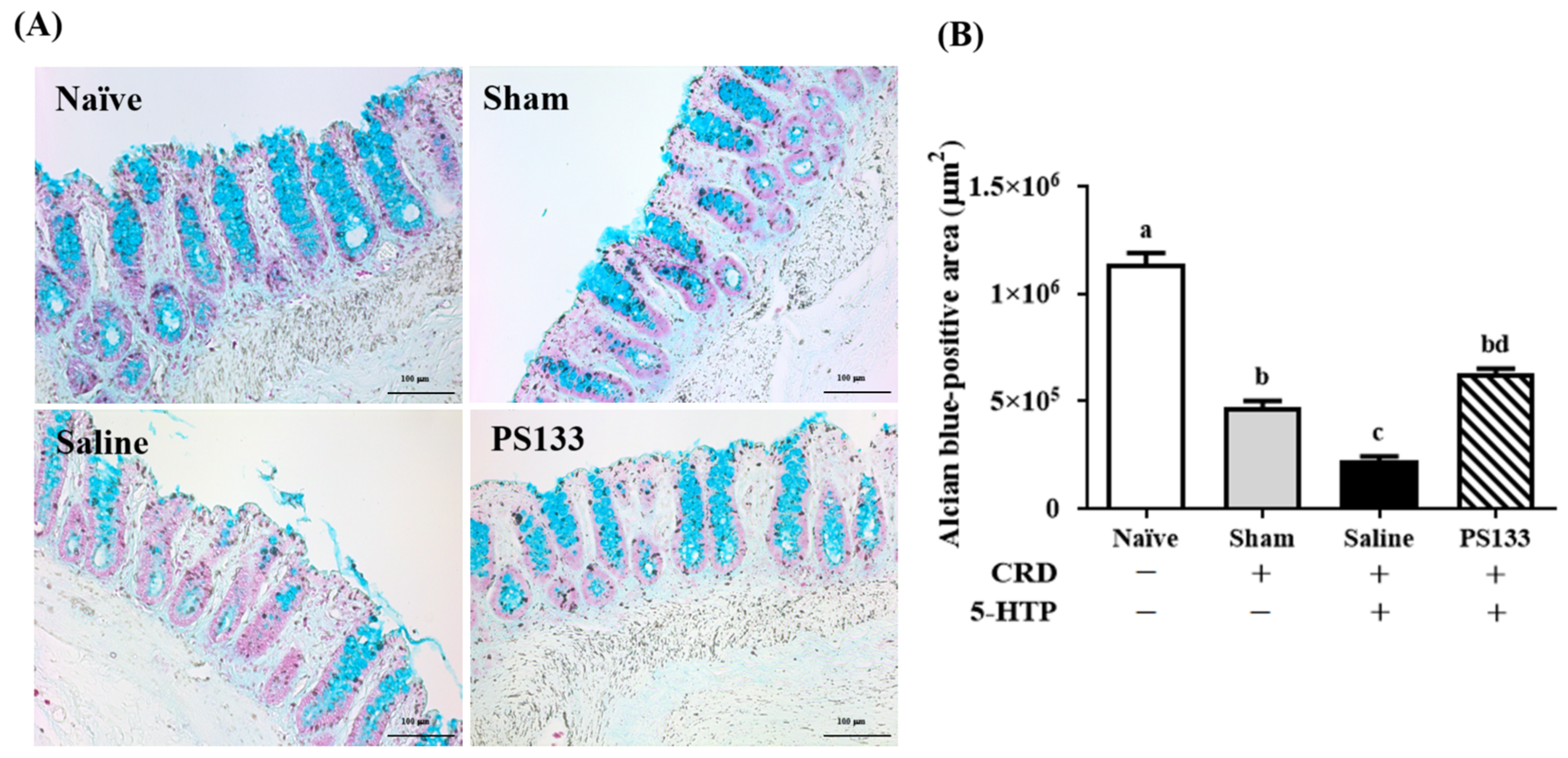
2.3. Effect of L. cremoris PS133 on Mucin Expression
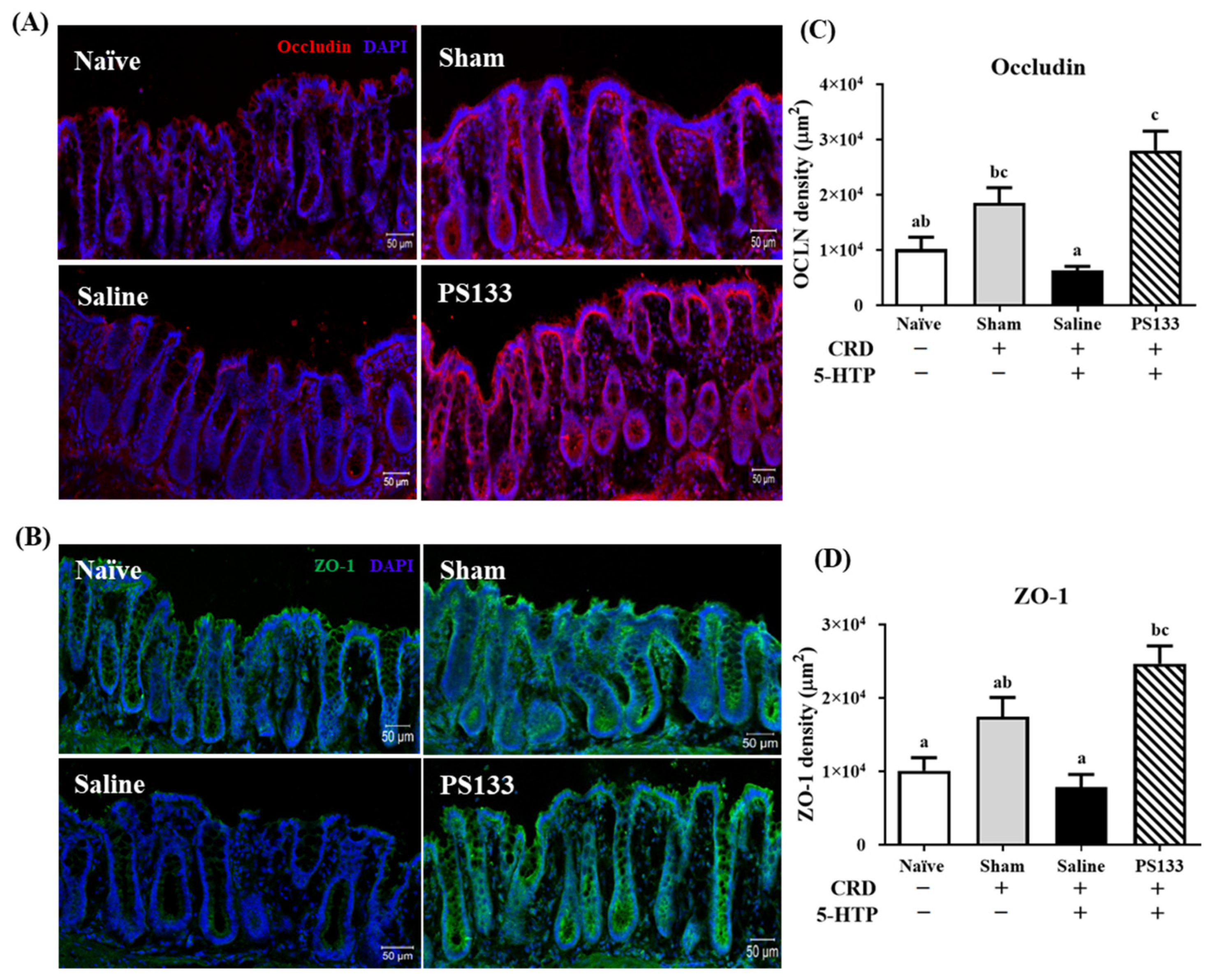
2.4. 5-HTP-Induced Changes in Tight Junction Protein Levels and Effect of L. cremoris PS133 Supplementation
2.5. Effects of L. cremoris PS133 on Neurotransmitter Expression in the Brains of 5-HTP-Induced IBS Model Rats
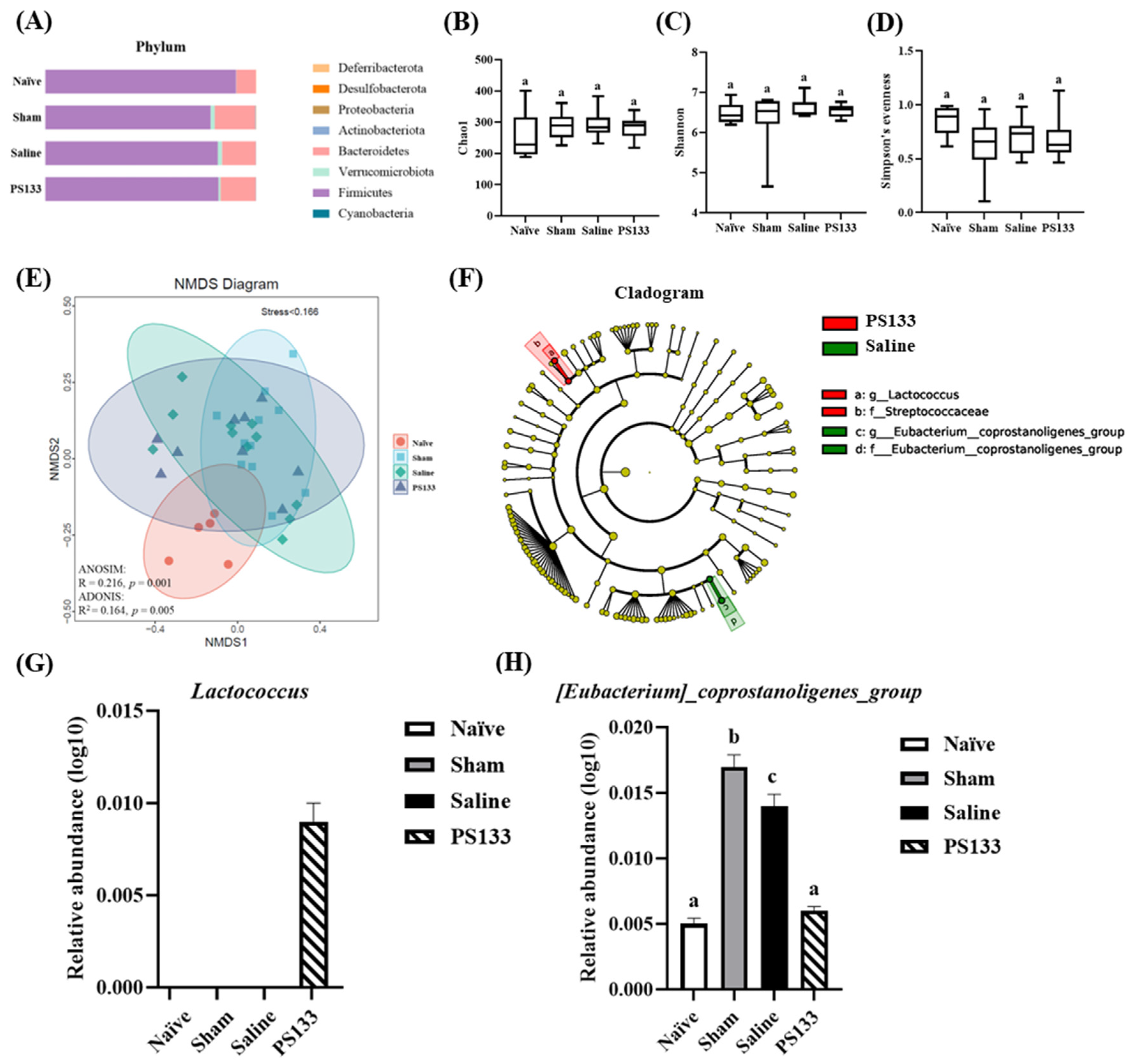
2.6. Effect of 5-HTP Induction and L. cremoris PS133 on the Gut Microbiota Profile
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation of L. cremoris PS133
4.2. Animal Preparation
4.3. Colorectal Distension (CRD) Procedure with Electromyography (EMG) Recording
4.4. Histological Analysis
4.5. Brain Neurotransmitter Analysis
4.6. Corticosterone Analysis
4.7. Gut Microbiota Analysis
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Canavan, C.; West, J.; Card, T. The epidemiology of irritable bowel syndrome. Clin. Epidemiol. 2014, 6, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellini, M.; Gambaccini, D.; Stasi, C.; Urbano, M.T.; Marchi, S.; Usai-Satta, P. Irritable bowel syndrome: A disease still searching for pathogenesis, diagnosis and therapy. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 8807–8820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, C.J.; Ford, A.C. Global burden of irritable bowel syndrome: Trends, predictions and risk factors. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 473–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chey, W.D.; Kurlander, J.; Eswaran, S. Irritable bowel syndrome: A clinical review. JAMA 2015, 313, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacy, B.E.; Chey, W.D.; Lembo, A.J. New and Emerging Treatment Options for Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 11, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, S.L.; Grundmann, O.; Koepp, L.; Farrell, L. Management of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) in adults: Conventional and complementary/alternative approaches. Altern. Med. Rev. 2011, 16, 134–151. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.; Verne, G.N. New insights into visceral hypersensitivity--clinical implications in IBS. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 8, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouin, M.; Meunier, P.; Riberdy-Poitras, M.; Poitras, P. Pain hypersensitivity in patients with functional gastrointestinal disorders: A gastrointestinal-specific defect or a general systemic condition? Dig. Dis. Sci. 2001, 46, 2542–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Ruan, G.; Chen, L.; Ying, S.; Li, G.; Xu, F.; Xiao, Z.; Tian, Y.; Lv, L.; Ping, Y.; et al. Neurotransmitter and Intestinal Interactions: Focus on the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis in Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 817100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowell, M.D. Role of serotonin in the pathophysiology of the irritable bowel syndrome. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 141, 1285–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Martinez, V.; Kimura, H.; Tache, Y. 5-Hydroxytryptophan activates colonic myenteric neurons and propulsive motor function through 5-HT4 receptors in conscious mice. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2007, 292, G419–G428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, A.C.; Brandt, L.J.; Young, C.; Chey, W.D.; Foxx-Orenstein, A.E.; Moayyedi, P. Efficacy of 5-HT3 antagonists and 5-HT4 agonists in irritable bowel syndrome: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 104, 1831–1843, quiz 1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, L.; Lembo, A.; Sultan, S. American Gastroenterological Association Institute Technical Review on the pharmacological management of irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 2014, 147, 1149–1172.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.; Guarner, F.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Merenstein, D.J.; Pot, B.; Morelli, L.; Canani, R.B.; Flint, H.J.; Salminen, S.; et al. Expert consensus document. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agirman, G.; Hsiao, E.Y. SnapShot: The microbiota-gut-brain axis. Cell 2021, 184, 2524–2524.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margolis, K.G.; Cryan, J.F.; Mayer, E.A. The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis: From Motility to Mood. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 1486–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Zou, D.W. Gut microbiota and irritable bowel syndrome. J. Dig. Dis. 2023, 24, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.W.; Wang, Y.P.; Yen, H.F.; Liu, P.Y.; Tzeng, W.J.; Tsai, C.F.; Lin, H.C.; Lee, F.Y.; Jeng, O.J.; Lu, C.L.; et al. Lactobacillus plantarum PS128 Ameliorated Visceral Hypersensitivity in Rats Through the Gut-Brain Axis. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2020, 12, 980–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Li, Y.Q.; Zuo, X.L.; Zhen, Y.B.; Yang, J.; Liu, C.H. Clinical trial: Effect of active lactic acid bacteria on mucosal barrier function in patients with diarrhoea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 28, 994–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.C.; Greenwood-Van Meerveld, B.; McRorie, J. Effects of Bifidobacterium infantis 35624 on post-inflammatory visceral hypersensitivity in the rat. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2011, 56, 3179–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Mahony, L.; McCarthy, J.; Kelly, P.; Hurley, G.; Luo, F.; Chen, K.; O’Sullivan, G.C.; Kiely, B.; Collins, J.K.; Shanahan, F.; et al. Lactobacillus and bifidobacterium in irritable bowel syndrome: Symptom responses and relationship to cytokine profiles. Gastroenterology 2005, 128, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ait-Belgnaoui, A.; Han, W.; Lamine, F.; Eutamene, H.; Fioramonti, J.; Bueno, L.; Theodorou, V. Lactobacillus farciminis treatment suppresses stress induced visceral hypersensitivity: A possible action through interaction with epithelial cell cytoskeleton contraction. Gut 2006, 55, 1090–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dapoigny, M.; Piche, T.; Ducrotte, P.; Lunaud, B.; Cardot, J.M.; Bernalier-Donadille, A. Efficacy and safety profile of LCR35 complete freeze-dried culture in irritable bowel syndrome: A randomized, double-blind study. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 2067–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdu, E.F.; Bercik, P.; Bergonzelli, G.E.; Huang, X.X.; Blennerhasset, P.; Rochat, F.; Fiaux, M.; Mansourian, R.; Corthesy-Theulaz, I.; Collins, S.M. Lactobacillus paracasei normalizes muscle hypercontractility in a murine model of postinfective gut dysfunction. Gastroenterology 2004, 127, 826–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, H.C.; Liu, Y.W.; Chiang, Y.C.; Chao, S.H.; Mei, N.W.; Liu, Y.W.; Tsai, Y.C. Immunomodulatory Activity of Lactococcus lactis A17 from Taiwan Fermented Cabbage in OVA-Sensitized BALB/c Mice. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat Med. 2013, 2013, 287803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Felipe, C.; Herrero, J.F.; O’Brien, J.A.; Palmer, J.A.; Doyle, C.A.; Smith, A.J.; Laird, J.M.; Belmonte, C.; Cervero, F.; Hunt, S.P. Altered nociception, analgesia and aggression in mice lacking the receptor for substance P. Nature 1998, 392, 394–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyloh, M.; Nicholas, S.; Zagorodnyuk, V.P.; Brookes, S.J.; Spencer, N.J. Identification of the visceral pain pathway activated by noxious colorectal distension in mice. Front. Neurosci. 2011, 5, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corfield, A.P. Mucins: A biologically relevant glycan barrier in mucosal protection. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1850, 236–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Zhang, B.; Verne, G.N. Intestinal membrane permeability and hypersensitivity in the irritable bowel syndrome. Pain 2009, 146, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H. Intestinal permeability regulation by tight junction: Implication on inflammatory bowel diseases. Intest. Res. 2015, 13, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Wu, D.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yu, D.; Wei, J.; Cai, Y.; Lin, Y.; Wu, B.; Huang, H. Characteristics of gut microbiota in male periadolescent rats with irritable bowel syndrome. Heliyon 2023, 9, e18995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drossman, D.A.; Camilleri, M.; Mayer, E.A.; Whitehead, W.E. AGA technical review on irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 2002, 123, 2108–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longstreth, G.F.; Thompson, W.G.; Chey, W.D.; Houghton, L.A.; Mearin, F.; Spiller, R.C. Functional bowel disorders. Gastroenterology 2006, 130, 1480–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gros, M.; Gros, B.; Mesonero, J.E.; Latorre, E. Neurotransmitter Dysfunction in Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Emerging Approaches for Management. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, S.J.; Shaker, R.; Silverman, A.; Kern, M.; Ward, D.B.; Li, W.; Xu, Z.; Chelimsky, G.; Sood, M.R. Reduced Functional Connectivity Between the Hypothalamus and High-order Cortical Regions in Adolescent Patients With Irritable Bowel Syndrome. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2017, 65, 516–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, J.L. Prefrontal cortical networks related to visceral function and mood. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1999, 877, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gschossmann, J.M.; Coutinho, S.V.; Miller, J.C.; Huebel, K.; Naliboff, B.; Wong, H.C.; Walsh, J.H.; Mayer, E.A. Involvement of spinal calcitonin gene-related peptide in the development of acute visceral hyperalgesia in the rat. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2001, 13, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.F.; Yang, Y.S.; Peng, L.H.; Sun, G. Alternation of substance P-containing neural pathways in a rat model of irritable bowel syndrome with rectal distension. Chin. J. Dig. Dis. 2006, 7, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekhbat, M.; Glasper, E.R.; Rowson, S.A.; Kelly, S.D.; Neigh, G.N. Measuring corticosterone concentrations over a physiological dynamic range in female rats. Physiol. Behav. 2018, 194, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Sundaresh, S.; Elliott, J.; Anton, P.A.; Baldi, P.; Licudine, A.; Mayer, M.; Vuong, T.; Hirano, M.; Naliboff, B.D.; et al. Dysregulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis in irritable bowel syndrome. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2009, 21, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinan, T.G.; Quigley, E.M.; Ahmed, S.M.; Scully, P.; O’Brien, S.; O’Mahony, L.; O’Mahony, S.; Shanahan, F.; Keeling, P.W. Hypothalamic-pituitary-gut axis dysregulation in irritable bowel syndrome: Plasma cytokines as a potential biomarker? Gastroenterology 2006, 130, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsenbruch, S.; Holtmann, G.; Oezcan, D.; Lysson, A.; Janssen, O.; Goebel, M.U.; Schedlowski, M. Are there alterations of neuroendocrine and cellular immune responses to nutrients in women with irritable bowel syndrome? Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2004, 99, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellissier, S.; Dantzer, C.; Mondillon, L.; Trocme, C.; Gauchez, A.S.; Ducros, V.; Mathieu, N.; Toussaint, B.; Fournier, A.; Canini, F.; et al. Relationship between vagal tone, cortisol, TNF-alpha, epinephrine and negative affects in Crohn’s disease and irritable bowel syndrome. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napolitano, M.; Fasulo, E.; Ungaro, F.; Massimino, L.; Sinagra, E.; Danese, S.; Mandarino, F.V. Gut Dysbiosis in Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Narrative Review on Correlation with Disease Subtypes and Novel Therapeutic Implications. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Wang, G.; Song, X.; Qian, Y.; Liao, Z.; Sui, L.; Ai, L.; Xia, Y. Understanding the Connection between Gut Homeostasis and Psychological Stress. J. Nutr. 2023, 153, 924–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Batt, S.M.; Wannemuehler, M.; Dispirito, A.; Beitz, D.C. Effect of feeding of a cholesterol-reducing bacterium, Eubacterium coprostanoligenes, to germ-free mice. Lab. Anim. Sci. 1998, 48, 253–255. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, D.; Zhao, Y.; Nan, X.; Xue, F.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Xiong, B. Effect of different glucogenic to lipogenic nutrient ratios on rumen fermentation and bacterial community in vitro. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 130, 1868–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paripati, N.; Nesi, L.; Sterrett, J.D.; Dawud, L.M.; Kessler, L.R.; Lowry, C.A.; Perez, L.J.; DeSipio, J.; Phadtare, S. Gut Microbiome and Lipidome Signatures in Irritable Bowel Syndrome Patients from a Low-Income, Food-Desert Area: A Pilot Study. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiecolt-Glaser, J.K.; Belury, M.A.; Andridge, R.; Malarkey, W.B.; Glaser, R. Omega-3 supplementation lowers inflammation and anxiety in medical students: A randomized controlled trial. Brain Behav. Immun. 2011, 25, 1725–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Agnihotri, A.; Pathak, M.K.; Shirazi, A.; Tiwari, R.P.; Sreenivas, V.; Sagar, R.; Makharia, G.K. Psychiatric, somatic and other functional gastrointestinal disorders in patients with irritable bowel syndrome at a tertiary care center. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2012, 18, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.L.; Hsieh, J.C.; Dun, N.J.; Oprea, T.I.; Wang, P.S.; Luo, J.C.; Lin, H.C.; Chang, F.Y.; Lee, S.D. Estrogen rapidly modulates 5-hydroxytrytophan-induced visceral hypersensitivity via GPR30 in rats. Gastroenterology 2009, 137, 1040–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, J.F.; Cheng, Y.F.; You, S.T.; Kuo, W.C.; Huang, C.W.; Chiou, J.J.; Hsu, C.C.; Hsieh-Li, H.M.; Wang, S.; Tsai, Y.C. Lactobacillus plantarum PS128 alleviates neurodegenerative progression in 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-induced mouse models of Parkinson’s disease. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 90, 26–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, F.-S.; Lin, M.-H.; Huang, C.-L.; Wu, C.-C.; Lu, C.-L.; Tsai, Y.-C. Effects of Lactococcus cremoris PS133 in 5-Hydroxytryptophan-Induced Irritable Bowel Syndrome Model Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2464. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062464
Deng F-S, Lin M-H, Huang C-L, Wu C-C, Lu C-L, Tsai Y-C. Effects of Lactococcus cremoris PS133 in 5-Hydroxytryptophan-Induced Irritable Bowel Syndrome Model Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(6):2464. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062464
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Fu-Sheng, Miao-Hui Lin, Chin-Lin Huang, Chien-Chen Wu, Ching-Liang Lu, and Ying-Chieh Tsai. 2025. "Effects of Lactococcus cremoris PS133 in 5-Hydroxytryptophan-Induced Irritable Bowel Syndrome Model Rats" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 6: 2464. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062464
APA StyleDeng, F.-S., Lin, M.-H., Huang, C.-L., Wu, C.-C., Lu, C.-L., & Tsai, Y.-C. (2025). Effects of Lactococcus cremoris PS133 in 5-Hydroxytryptophan-Induced Irritable Bowel Syndrome Model Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(6), 2464. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062464






