Cul2 Is Essential for the Drosophila IMD Signaling-Mediated Antimicrobial Immune Defense
Abstract
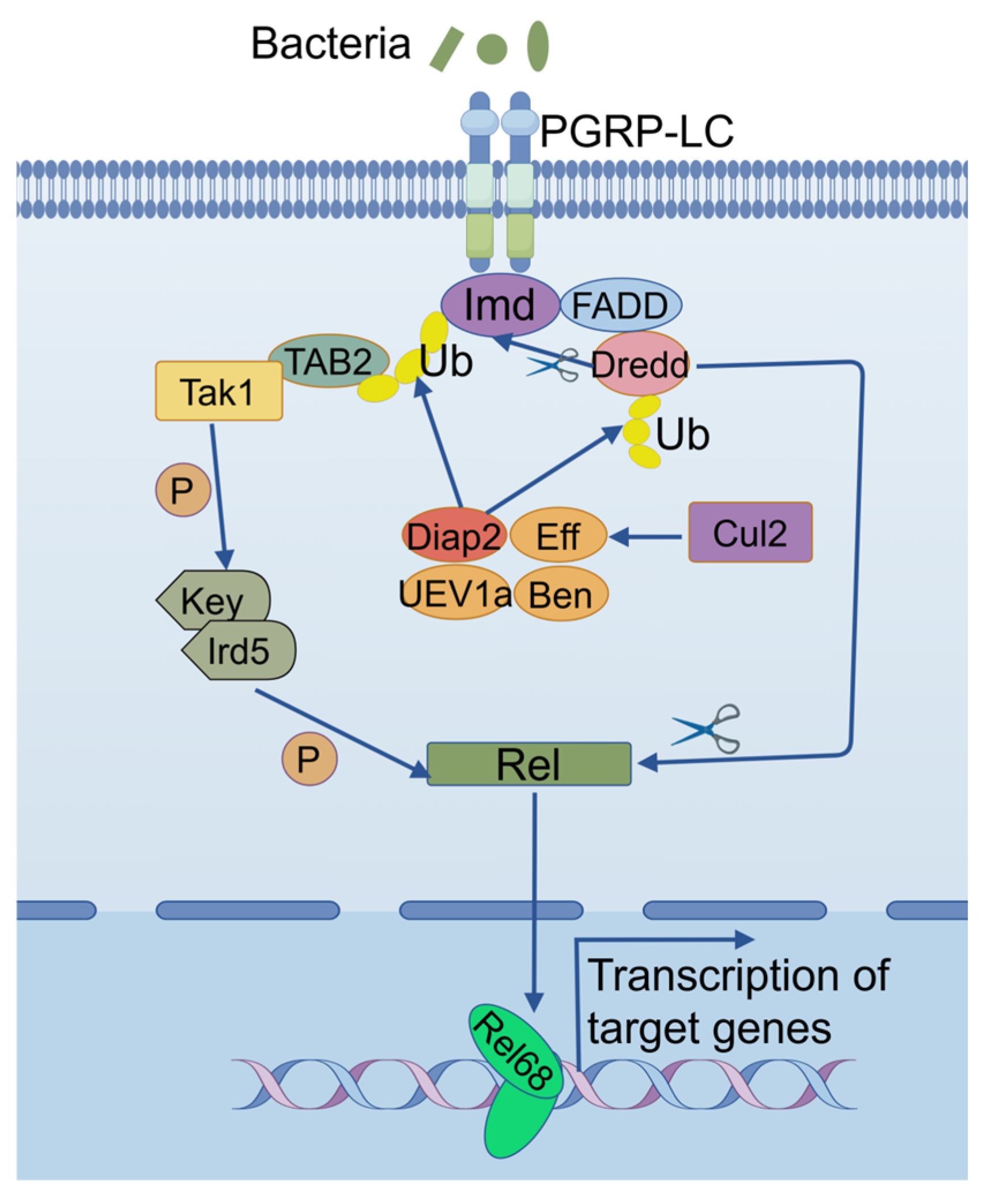
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Loss-of-Function of Cul2 Prevents AMP Induction in Adult Flies upon Bacterial Stimuli
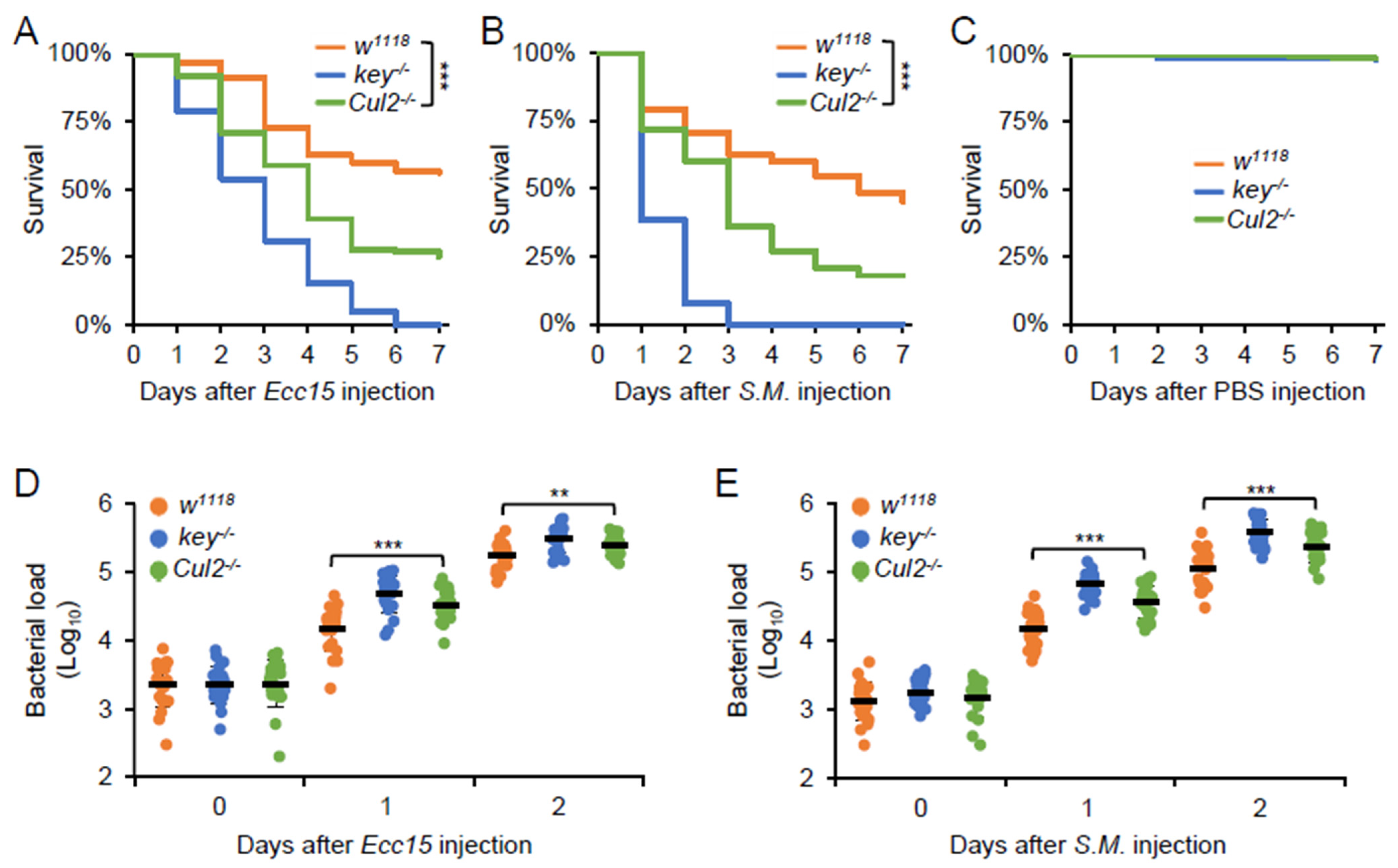
2.2. Cul2 Mediates the Fly Defense Against Bacterial Infection
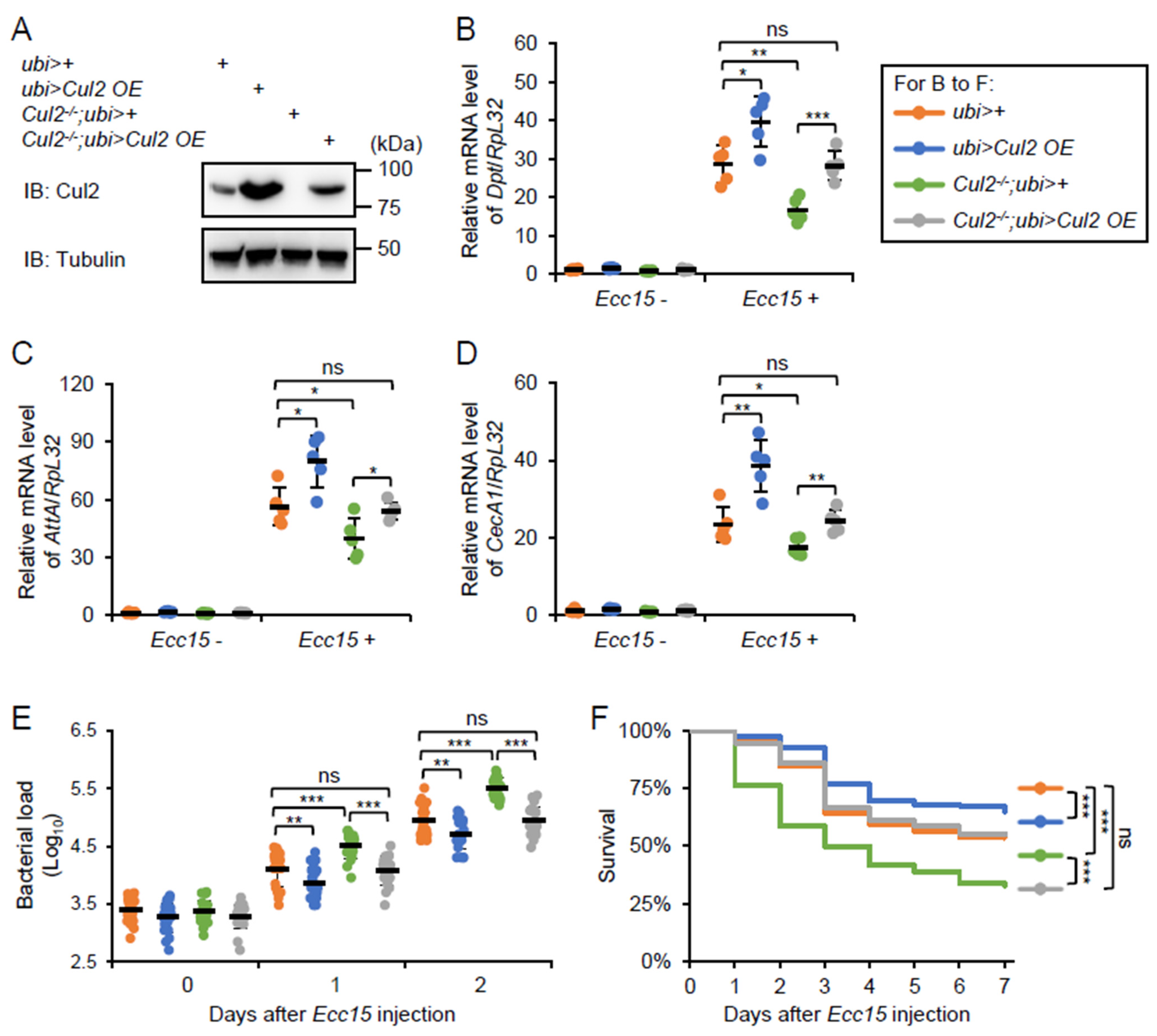
2.3. Overexpression of Cul2 Rescues the Immune Defects in Cul2 LOF Mutants
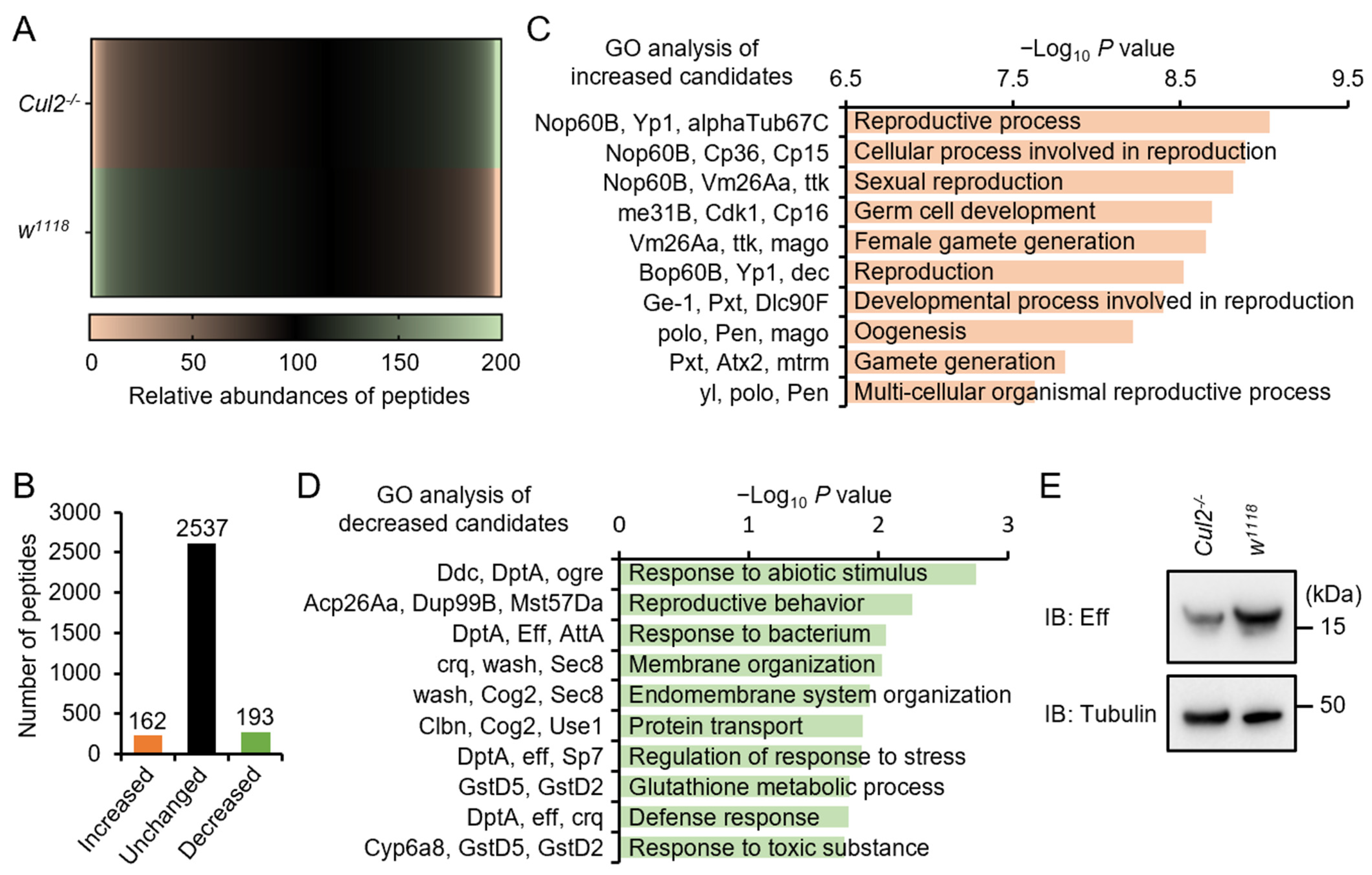
2.4. Loss-of-Function of Cul2 Prevents Eff Expression in Adult Flies
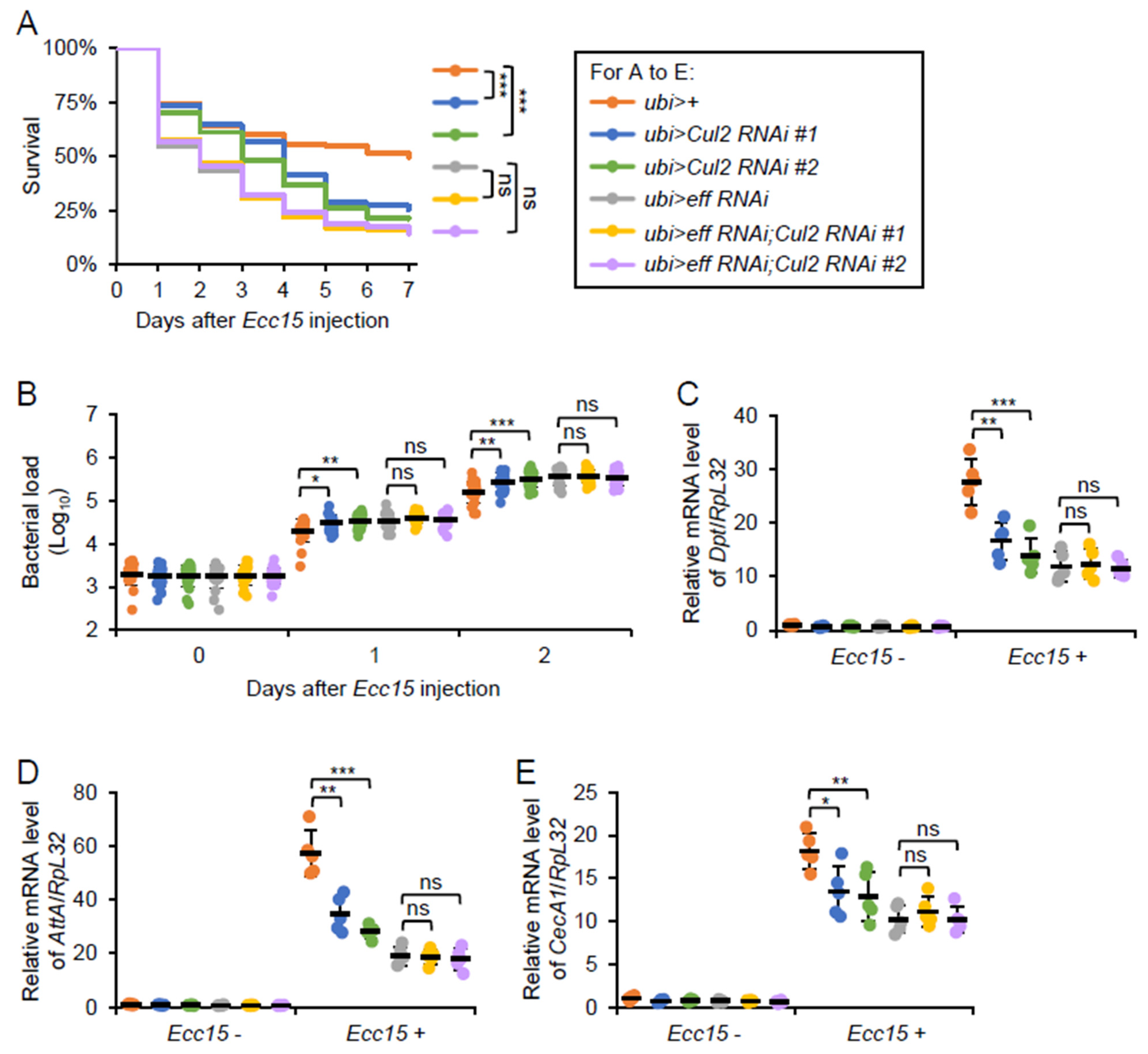
2.5. Cul2 Modulates Drosophila Antibacterial Immune Defense in an Eff-Dependent Manner
3. Discussion
3.1. Cul2 Mediates Drosophila Innate Immunity in an Eff-Dependent Manner
3.2. Possible Molecular Mechanism by Which Cul2 Regulates Eff Expression
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Fly Strain and Husbandry
4.2. Bacterial Infection, Survival, and Bacterial Burden Assay
4.3. RT-qPCR Assay
4.4. Western Blot Assay
4.5. Proteomic Analysis
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Beutler, B. Innate immunity: An overview. Mol. Immunol. 2004, 40, 845–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akira, S.; Uematsu, S.; Takeuchi, O. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell 2006, 124, 783–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janeway, C.A., Jr.; Medzhitov, R. Innate immune recognition. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 20, 197–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, J.A. The immune response of Drosophila. Nature 2003, 426, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Luo, F.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, L.H. Drosophila Innate Immunity Involves Multiple Signaling Pathways and Coordinated Communication Between Different Tissues. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 905370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrandon, D.; Imler, J.L.; Hoffmann, J.A. Sensing infection in Drosophila: Toll and beyond. Semin. Immunol. 2004, 16, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchon, N.; Silverman, N.; Cherry, S. Immunity in Drosophila melanogaster--from microbial recognition to whole-organism physiology. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 796–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleino, A.; Silverman, N. The Drosophila IMD pathway in the activation of the humoral immune response. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2014, 42, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemaitre, B.; Hoffmann, J. The host defense of Drosophila melanogaster. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 25, 697–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myllymaki, H.; Valanne, S.; Ramet, M. The Drosophila imd signaling pathway. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 3455–3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, A.; Ji, S.; Chtarbanova, S.; Kuraishi, T. Editorial: Inflammatory and inflammatory-like responses in insects. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1184429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, N.; Shabek, N. Ubiquitin Ligases: Structure, Function, and Regulation. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2017, 86, 129–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swatek, K.N.; Komander, D. Ubiquitin modifications. Cell Res. 2016, 26, 399–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paquette, N.; Broemer, M.; Aggarwal, K.; Chen, L.; Husson, M.; Erturk-Hasdemir, D.; Reichhart, J.M.; Meier, P.; Silverman, N. Caspase-mediated cleavage, IAP binding, and ubiquitination: Linking three mechanisms crucial for Drosophila NF-kappaB signaling. Mol. Cell 2010, 37, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinander, A.; Runchel, C.; Tenev, T.; Chen, L.; Kim, C.H.; Ribeiro, P.S.; Broemer, M.; Leulier, F.; Zvelebil, M.; Silverman, N.; et al. Ubiquitylation of the initiator caspase DREDD is required for innate immune signalling. EMBO J. 2012, 31, 2770–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aalto, A.L.; Mohan, A.K.; Schwintzer, L.; Kupka, S.; Kietz, C.; Walczak, H.; Broemer, M.; Meinander, A. M1-linked ubiquitination by LUBEL is required for inflammatory responses to oral infection in Drosophila. Cell Death. Differ. 2019, 26, 860–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Paquette, N.; Mamoor, S.; Rus, F.; Nandy, A.; Leszyk, J.; Shaffer, S.A.; Silverman, N. Innate immune signaling in Drosophila is regulated by transforming growth factor beta (TGFbeta)-activated kinase (Tak1)-triggered ubiquitin editing. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 8738–8749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petroski, M.D.; Deshaies, R.J. Function and regulation of cullin-RING ubiquitin ligases. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 6, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarikas, A.; Hartmann, T.; Pan, Z.Q. The cullin protein family. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, J.W.; Schulman, B.A. Cullin-RING Ubiquitin Ligase Regulatory Circuits: A Quarter Century Beyond the F-Box Hypothesis. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2021, 90, 403–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, E.S.; Schulman, B.A.; Zheng, N. Structural assembly of cullin-RING ubiquitin ligase complexes. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2010, 20, 714–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, F.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Xiao, Y.; Saeed, M.A.R.; Li, W.; Goto, A.; Cai, Q.; Ji, S. Drosophila Cul3 contributes to Diap2-mediated innate immune signaling for antimicrobial defense. hLife 2025, 3, 38–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neyen, C.; Bretscher, A.J.; Binggeli, O.; Lemaitre, B. Methods to study Drosophila immunity. Methods 2014, 68, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutschmann, S.; Jung, A.C.; Zhou, R.; Silverman, N.; Hoffmann, J.A.; Ferrandon, D. Role of Drosophila IKK gamma in a toll-independent antibacterial immune response. Nat. Immunol. 2000, 1, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.; Yan, J.; Duan, R.; Zhu, Y.; Hua, Y.; Liao, Y.; Li, Q.; Li, W.; Ji, S. E3 ligase Cul2 mediates Drosophila early germ cell differentiation through targeting Bam. Dev. Biol. 2023, 493, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyub, C.; Banerjee, K.K.; Joti, P. Reduction of Cullin-2 in somatic cells disrupts differentiation of germline stem cells in the Drosophila ovary. Dev. Biol. 2015, 405, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyub, C. Cullin-5 and cullin-2 play a role in the development of neuromuscular junction and the female germ line of Drosophila. J. Genet. 2011, 90, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Ng, C.L.; Schulz, C. CSN maintains the germline cellular microenvironment and controls the level of stem cell genes via distinct CRLs in testes of Drosophila melanogaster. Dev. Biol. 2015, 398, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monahan, A.J.; Starz-Gaiano, M. Socs36E limits STAT signaling via Cullin2 and a SOCS-box independent mechanism in the Drosophila egg chamber. Mech. Dev. 2015, 138 Pt 3, 313–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.S.; Elangovan, M.; Kim, Y.J.; Yoo, Y.J. UbcD4, an ortholog of E2-25K/Ube2K, is essential for activation of the immune deficiency pathway in Drosophila. Biochem. Biophy. Res. Commun. 2016, 469, 891–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, L.; Chao, A.; Deneke, V.E.; Vergassola, M.; Puliafito, A.; Di Talia, S. Cullin-5 mutants reveal collective sensing of the nucleocytoplasmic ratio in Drosophila embryogenesis. Curr. Biol. 2022, 32, 2084–2092.e2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudson, A.M.; Cooley, L. Drosophila Kelch functions with Cullin-3 to organize the ring canal actin cytoskeleton. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 188, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tare, M.; Chimata, A.V.; Gogia, N.; Narwal, S.; Deshpande, P.; Singh, A. An E3 ubiquitin ligase, cullin-4 regulates retinal differentiation in Drosophila eye. Genesis 2020, 58, e23395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mistry, H.; Wilson, B.A.; Roberts, I.J.; O’Kane, C.J.; Skeath, J.B. Cullin-3 regulates pattern formation, external sensory organ development and cell survival during Drosophila development. Mech. Dev. 2004, 121, 1495–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, A.M.; Mannix, K.M.; Cooley, L. Actin cytoskeletal organization in Drosophila germline Ring Canals Depends on Kelch Function in a Cullin-RING E3 Ligase. Genetics 2015, 201, 1117–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, S.; Yim, J. Drosophila Cand1 regulates Cullin3-dependent E3 ligases by affecting the neddylation of Cullin3 and by controlling the stability of Cullin3 and adaptor protein. Dev. Biol. 2010, 346, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, N.E.; Bhattacharya, A.; Firth, L.C. Regulation of Hh signal transduction as Drosophila eye differentiation progresses. Dev. Biol. 2009, 335, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kugler, J.M.; Lem, C.; Lasko, P. Reduced cul-5 activity causes aberrant follicular morphogenesis and germ cell loss in Drosophila oogenesis. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipressa, F.; Cenci, G. Effete, an E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme with multiple roles in Drosophila development and chromatin organization. Fly 2013, 7, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, L.C.; Curley, M.; Nyamkondiwa, K.; Stephan, A.; Jiao, J.; Kavdia, K.; Pagala, V.R.; Peng, J.; Demontis, F. The ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme UBE2D maintains a youthful proteome and ensures protein quality control during aging by sustaining proteasome activity. PLoS Biol. 2025, 23, e3002998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duda, D.M.; Scott, D.C.; Calabrese, M.F.; Zimmerman, E.S.; Zheng, N.; Schulman, B.A. Structural regulation of cullin-RING ubiquitin ligase complexes. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2011, 21, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristensen, L.S.; Andersen, M.S.; Stagsted, L.V.W.; Ebbesen, K.K.; Hansen, T.B.; Kjems, J. The biogenesis, biology and characterization of circular RNAs. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2019, 20, 675–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H. circRNA: A promising all-around star in the future. Epigenomics 2023, 15, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.Y.; Cai, Z.R.; Liu, J.; Wang, D.S.; Ju, H.Q.; Xu, R.H. Circular RNA: Metabolism, functions and interactions with proteins. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, X.; Shen, J.; An, W. Advances in Circular RNA and Its Applications. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2022, 19, 975–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Chen, S.; Han, J.X.; Qian, B.; Wang, X.R.; Zhong, W.L.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, H.; Gao, W.F.; Lei, Y.Y.; et al. Twist1 Regulates Vimentin through Cul2 Circular RNA to Promote EMT in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 4150–4162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Sang, H.; Wei, S.; Li, Y.; Jin, D.; Zhu, X.; Li, X.; Dang, Y.; Zhang, G. circCUL2 regulates gastric cancer malignant transformation and cisplatin resistance by modulating autophagy activation via miR-142-3p/ROCK2. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.L.; Liu, G.Q.; Li, P.; Li, X.H. Circular RNA CUL2 regulates the development of colorectal cancer by modulating apoptosis and autophagy via miR-208a-3p/PPP6C. Aging 2022, 14, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Kong, F.; Guo, H.; Hua, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Qadeer, A.; Xiao, Y.; Cai, Q.; Ji, S. Drosophila eIF3f1 mediates host immune defense by targeting dTak1. EMBO Rep. 2024, 25, 1415–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Sun, M.; Zheng, X.; Li, L.; Sun, L.; Chen, D.; Sun, Q. Cell-surface localization of Pellino antagonizes Toll-mediated innate immune signalling by controlling MyD88 turnover in Drosophila. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, C.; Han, T.; Duan, R.; Jin, Y.; Guo, H.; She, K.; Xiao, Y.; et al. Endoplasmic reticulum-associated protein degradation contributes to Toll innate immune defense in Drosophila melanogaster. Front. Immunol. 2023, 13, 1099637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, S.; Kong, F.; Xiao, Y.; She, K.; Jin, Y.; Li, J.; Qadeer, A.; Zheng, X.; Ji, S.; et al. Ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase L5 plays an essential role in the fly innate immune defense against bacterial infection. Front. Biosci. 2023, 28, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, S.; Hoffmann, J.A. Toll-9 prevents the proliferation of injected oncogenic cells in adult flies. J. Genet. Genom. 2024, 51, 1331–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Yang, Y.; Kong, F.; Feng, Y.; Guo, H.; Saeed, M.A.R.; Ali, U.; et al. MESR4 targets bam to mediate intestinal homeostasis and aging in adult flies. Insect Sci. 2025, 32, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Q.; Guo, H.; Fang, R.; Hua, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zheng, X.; Yan, J.; Wang, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, C.; et al. A Toll-dependent Bre1/Rad6-cact feedback loop in controlling host innate immune response. Cell Rep. 2022, 41, 111795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Kong, F.; Duan, R.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, S.; Jin, Y.; Ye, Y.; et al. A feedback regulatory loop involving dTrbd/dTak1 in controlling IMD signaling in Drosophila melanogaster. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 932268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.; Qadeer, A.; Xie, Y.; Jin, Y.; Li, Q.; Xiao, Y.; She, K.; Zheng, X.; Li, J.; Ji, S.; et al. Dietary supplementation of aspirin promotes Drosophila defense against viral infection. Molecules 2023, 28, 5300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Zhou, X.; Hoffmann, J.A. Toll-mediated airway homeostasis is essential for fly survival upon injection of RasV12-GFP oncogenic cells. Cell Rep. 2024, 43, 113677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Cai, Q.; Zheng, X.; Liu, L.; Hua, Y.; Du, B.; Zhao, G.; Yu, J.; Zhuo, Z.; Xie, Z.; et al. Aspirin positively contributes to Drosophila intestinal homeostasis and delays aging through targeting Imd. Aging Dis. 2021, 12, 1821–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, Y.; Guo, H.; Duan, R.; Xiao, Y.; Hu, B.; Yang, Y.; Ding, E.; et al. RNA-binding protein Roq modulates the Drosophila STING antiviral immune response. Cell Investig. 2025, 1, 100002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duan, R.; Hu, B.; Ding, E.; Zhang, S.; Wu, M.; Jin, Y.; Ali, U.; Saeed, M.A.R.; Raza, B.; Usama, M.; et al. Cul2 Is Essential for the Drosophila IMD Signaling-Mediated Antimicrobial Immune Defense. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2627. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062627
Duan R, Hu B, Ding E, Zhang S, Wu M, Jin Y, Ali U, Saeed MAR, Raza B, Usama M, et al. Cul2 Is Essential for the Drosophila IMD Signaling-Mediated Antimicrobial Immune Defense. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(6):2627. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062627
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuan, Renjie, Baoyi Hu, Erwen Ding, Shikun Zhang, Mingfei Wu, Yiheng Jin, Umar Ali, Muhammad Abdul Rehman Saeed, Badar Raza, Muhammad Usama, and et al. 2025. "Cul2 Is Essential for the Drosophila IMD Signaling-Mediated Antimicrobial Immune Defense" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 6: 2627. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062627
APA StyleDuan, R., Hu, B., Ding, E., Zhang, S., Wu, M., Jin, Y., Ali, U., Saeed, M. A. R., Raza, B., Usama, M., Batool, S. S., Cai, Q., & Ji, S. (2025). Cul2 Is Essential for the Drosophila IMD Signaling-Mediated Antimicrobial Immune Defense. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(6), 2627. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062627






