Small Molecule B-RAF Inhibitors as Anti-Cancer Therapeutics: Advances in Discovery, Development, and Mechanistic Insights
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. B-RAF Mutations in Cancer
2.1. Melanoma
2.2. Hepatocellular Carcinoma
2.3. Colorectal Cancer
2.4. Thyroid Cancer
3. Challenges in Targeting B-RAF
3.1. Mechanisms of B-RAF Inhibitor Resistance
3.2. Tumor Microenvironment and Adaptive Resistance
3.3. Overcoming Resistance: Combination Therapies
4. Discovery and Development of B-RAF Inhibitors
4.1. Classification of B-RAF Inhibitors
4.2. Generations of B-RAF Inhibitors
- -
- First-Generation B-RAF Inhibitors:
- -
- Second-Generation B-RAF Inhibitors:
- -
- Third-Generation B-RAF Inhibitors:
4.3. High-Throughput Screening and Preclinical Development
5. Current Clinical Trials and Combination Therapies
5.1. B-RAF Inhibitors in Clinical Trials
5.1.1. Vemurafenib Clinical Trials (Phase I–III)
5.1.2. Dabrafenib Clinical Trials
5.1.3. Encorafenib Clinical Trials (Second-Generation)
5.1.4. Resistance Mechanisms and Future Directions
5.2. Combination Therapy in Clinical Trials
5.3. Phase III Clinical Trials
6. Future Directions and Clinical Implications
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Roskoski, R. RAF Protein-Serine/Threonine Kinases: Structure and Regulation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 399, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dankner, M.; Rose, A.A.N.; Rajkumar, S.; Siegel, P.M.; Watson, I.R. Classifying B-RAF Alterations in Cancer: New Rational Therapeutic Strategies for Actionable Mutations. Oncogene 2018, 37, 3183–3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maji, L.; Teli, G.; Raghavendra, N.M.; Sengupta, S.; Pal, R.; Ghara, A.; Matada, G.S.P. An Updated Literature on B-RAF Inhibitors (2018–2023). Mol. Divers. 2023, 28, 2689–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, R.; Yin, Q.; Snell, A.H.; Wan, L. RAF-MEK-ERK Pathway in Cancer Evolution and Treatment. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 85, 123–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercer, K.E.; Pritchard, C.A. RAF Proteins and Cancer: B-RAF Is Identified as a Mutational Target. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Rev. Cancer 2003, 1653, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepote, A.; Avallone, G.; Ribero, S.; Cavallo, F.; Roccuzzo, G.; Mastorino, L.; Conforti, C.; Paruzzo, L.; Poletto, S.; Schianca, F.C.; et al. Current Controversies and Challenges on B-RAF V600K-Mutant Cutaneous Melanoma. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, C.; Carragher, L.; Aldridge, V.; Giblett, S.; Jin, H.; Foster, C.; Andreadi, C.; Kamata, T. Mouse Models for B-RAF-Induced Cancers. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2007, 35 Pt 5, 1329–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, A.; Wu, W.; Bivona, T.G. Targeting Oncogenic B-RAF: Past, Present, and Future. Cancers 2019, 11, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, R.D.; Kudchadkar, R.R. B-RAF Mutations: Signaling, Epidemiology, and Clinical Experience in Multiple Malignancies. Cancer Control 2014, 21, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyer, M.B.; Abdel-Wahab, O.; Tallman, M.S. B-RAF in the Cross-Hairs. Expert Rev. Hematol. 2019, 12, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapp, U.R.; Goldsborough, M.D.; Mark, G.E.; Bonner, T.I.; Groffen, J.; Reynolds, F.H.; Stephenson, J.R. Structure and Biological Activity of V-Raf, a Unique Oncogene Transduced by a Retrovirus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1983, 80, 4218–4222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikawa, S.; Fukui, M.; Ueyama, Y.; Tamaoki, N.; Yamamoto, T.; Toyoshima, K. B-Raf, a New Member of the Raf Family, Is Activated by DNA Rearrangement. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1988, 8, 2651–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanrahan, A.J.; Solit, D.B. B-RAF Mutations: The Discovery of Allele- and Lineage-Specific Differences. Cancer Res. 2022, 82, 12–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, M.R.M.; Baig, M.; Mohamoud, H.S.A.; Ulhaq, Z.; Hoessli, D.C.; Khogeer, G.S.; Al-Sayed, R.R.; Al-Aama, J.Y. B-RAF Gene: From Human Cancers to Developmental Syndromes. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2015, 22, 359–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emuss, V.; Garnett, M.; Mason, C.; Marais, R. Mutations of C-RAF Are Rare in Human Cancer Because C-RAF Has a Low Basal Kinase Activity Compared with B-RAF. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 9719–9726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonner, T.I.; Kerby, S.B.; Sutrave, P.; Gunnell, M.A.; Mark, G.; Rapp, U.R. Structure and Biological Activity of Human Homologs of the Raf/Mil Oncogene. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1985, 5, 1400–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huebner, K.; Abbas Ar-Rushdi; Griffin, C.A.; Isobe, M.; Kozak, C.A.; Emanuel, B.S.; Nagarajan, L.; Cleveland, J.L.; Bonner, T.I.; Goldsborough, M.D. Actively Transcribed Genes in the Raf Oncogene Group, Located on the X Chromosome in Mouse and Human. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 3934–3938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BRAF Mutation and Cancer. Hopkinsmedicine.org. Available online: https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/braf-mutation-and-cancer (accessed on 29 April 2024).
- Ascierto, P.A.; Kirkwood, J.M.; Grob, J.-J.; Simeone, E.; Grimaldi, A.M.; Maio, M.; Palmieri, G.; Testori, A.; Marincola, F.M.; Mozzillo, N. The Role of B-RAF V600 Mutation in Melanoma. J. Transl. Med. 2012, 10, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnoni, A.; Licchetta, A.; Memeo, R.; Argentiero, A.; Solimando, A.G.; Longo, V.; Delcuratolo, S.; Brunetti, O. Role of B-RAF in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Rationale for Future Targeted Cancer Therapies. Medicina 2019, 55, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, I.; Hirota, T.; Shinozaki, E. B-RAF Mutation in Colorectal Cancers: From Prognostic Marker to Targetable Mutation. Cancers 2020, 12, 3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, M. B-RAF Mutation in Thyroid Cancer. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2005, 12, 245–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Gao, C.; Gao, X.; Zhang, D.H.; Kuan, S.-F.; Burns, T.F.; Hu, J. Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway Activation Mediates Adaptive Resistance to B-RAF Inhibition in Colorectal Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2018, 17, 806–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakadia, S.; Yarlagadda, N.; Awad, R.; Kundranda, M.; Niu, J.; Naraev, B.; Mina, L.; Dragovich, T.; Gimbel, M.; Mahmoud, F. Mechanisms of Resistance to B-RAF and MEK Inhibitors and Clinical Update of US Food and Drug Administration-Approved Targeted Therapy in Advanced Melanoma. Onco Targets Ther. 2018, 11, 7095–7107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, A.; Siewe, N. Overcoming Drug Resistance to B-RAF Inhibitor. Bull. Math. Biol. 2020, 82, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Wang, L.; Huang, S.; Heynen, G.J.J.E.; Prahallad, A.; Robert, C.; Haanen, J.; Blank, C.; Wesseling, J.; Willems, S.M.; et al. Reversible and Adaptive Resistance to B-RAF(V600E) Inhibition in Melanoma. Nature 2014, 508, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascierto, P.A.; Dummer, R. Immunological Effects of B-RAF+MEK Inhibition. Oncoimmunology 2018, 7, e1468955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCain, J. The MAPK (ERK) Pathway. P&T 2013, 38, 96–108. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.A.; Salajegheh, A.; Smith, R.A.; Lam, A.K.-Y. B-RAF Inhibitors: From the Laboratory to Clinical Trials. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2014, 90, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; Streu, C.; Qin, J.; Bregman, H.; Pagano, N.; Meggers, E.; Marmorstein, R. The Crystal Structure of B-RAF in Complex with an Organoruthenium Inhibitor Reveals a Mechanism for Inhibition of an Active Form of B-RAF Kinase. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 5187–5198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Sonawane, P.; Kumar, A.; Singh, H.; Naumovich, V.; Pathak, P.; Grishina, M.; Khalilullah, H.; Jaremko, M.; Emwas, A.-H.; et al. Challenges and Opportunities in the Crusade of B-RAF Inhibitors: From 2002 to 2022. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 27819–27844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.; Cohen, M.S. The Discovery of Vemurafenib for the Treatment of B-RAF-Mutated Metastatic Melanoma. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2016, 11, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikanjam, M.; Tinajero, J.; Barkauskas, D.A.; Kurzrock, R. B-RAF V600E/V600K Mutations vs. Non-Standard Alterations: Prognostic Implications and Therapeutic Outcomes. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2021, 20, 1072–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumimoto, H.; Imabayashi, F.; Iwata, T.; Kawakami, Y. The B-RAF–MAPK Signaling Pathway Is Essential for Cancer-Immune Evasion in Human Melanoma Cells. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 1651–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mor, J.M.; Heindl, L.M. Systemic B-RAF/MEK Inhibitors as a Potential Treatment Option in Metastatic Conjunctival Melanoma. Ocul. Oncol. Pathol. 2017, 3, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, N.; Guo, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, S.; Li, X. B-RAF-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Current Treatment Status and Future Perspective. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 863043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Torres, J.M.; Viteri, S.; Molina, M.A.; Rosell, R. B-RAF Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and Treatment with B-RAF Inhibitors. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2013, 2, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, W.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, B.; Wu, F.; Wang, Q.; Wang, S.; Rong, D.; Reiter, F.P.; et al. The Mechanisms of Sorafenib Resistance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Theoretical Basis and Therapeutic Aspects. Sig. Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barras, D. B-RAF Mutation in Colorectal Cancer: An Update. Biomark. Cancer 2015, 7 (Suppl. S1), 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limberg, J.; Egan, C.E.; Gray, K.D.; Singh, M.; Loewenstein, Z.; Yang, Y.; Riascos, M.C.; Al Asadi, H.; Safe, P.; El Eshaky, S.; et al. Activation of the JAK/STAT Pathway Leads to B-RAF Inhibitor Resistance in B-RAFV600E Positive Thyroid Carcinoma. Mol. Cancer Res. 2023, 21, 397–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattei, P.L.; Alora-Palli, M.B.; KRAFt, S.; Lawrence, D.P.; Flaherty, K.T.; Kimball, A.B. Cutaneous Effects of B-RAF Inhibitor Therapy: A Case Series. Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, C.H.; Brage, S.E. B-RAF Inhibitors in Cancer Therapy. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 142, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ros, J.; Saoudi, N.; Baraibar, I.; Salva, F.; Tabernero, J.; Elez, E. Encorafenib plus Cetuximab for the Treatment of B-RAF-V600E-Mutated Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2022, 15, 17562848221110644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunderwala, A.Y.; Nimbvikar, A.A.; Cope, N.J.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z. Development of Allosteric B-RAF Peptide Inhibitors Targeting the Dimer Interface of B-RAF. ACS Chem. Biol. 2019, 14, 1471–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ros, J.; Baraibar, I.; Sardo, E.; Mulet, N.; Salvà, F.; Argilés, G.; Martini, G.; Ciardiello, D.; Cuadra, J.L.; Tabernero, J.; et al. B-RAF, MEK and EGFR Inhibition as Treatment Strategies in B-RAF V600E Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2021, 13, 1758835921992974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.H.; Cohen, D.N.; Rady, P.L.; Tyring, S.K. B-RAF Inhibitor-Associated Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma: New Mechanistic Insight, Emerging Evidence for Viral Involvement and Perspectives on Clinical Management. Br. J. Dermatol. 2017, 177, 914–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algazi, A.P.; Moon, J.; Lao, C.D.; Chmielowski, B.; Kendra, K.L.; Lewis, K.D.; Gonzalez, R.; Kim, K.; Godwin, J.E.; Curti, B.D.; et al. A Phase 1 Study of Triple-Targeted Therapy with BRAF, MEK, and AKT Inhibitors for Patients with BRAF-Mutated Cancers. Cancer 2024, 130, 1784–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planchard, D.; Wolf, J.; Solomon, B.; Sebastian, M.; Wermke, M.; Heist, R.S.; Sun, J.-M.; Min Kim, T.; Reguart, N.; Sanmamed, M.F.; et al. A Phase Ib Study of the Combination of Naporafenib with Rineterkib or Trametinib in Patients with Advanced and Metastatic KRAS- or BRAF-Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Lung Cancer Amst. Neth. 2024, 197, 107964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez Tejeda Zañudo, J.; Barroso-Sousa, R.; Jain, E.; Jin, Q.; Li, T.; Buendia-Buendia, J.E.; Pereslete, A.; Abravanel, D.L.; Ferreira, A.R.; Wrabel, E.; et al. Exemestane plus Everolimus and Palbociclib in Metastatic Breast Cancer: Clinical Response and Genomic/Transcriptomic Determinants of Resistance in a Phase I/II Trial. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eroglu, Z.; Chen, Y.A.; Smalley, I.; Li, J.; Markowitz, J.K.; Brohl, A.S.; Tetteh, L.; Taylor, H.; Sondak, V.K.; Khushalani, N.I.; et al. Combined BRAF, MEK, and Heat-Shock Protein 90 Inhibition in Advanced BRAF V600-Mutant Melanoma. Cancer 2024, 130, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaeger, R.; McKean, M.A.; Haq, R.; Beck, J.T.; Taylor, M.H.; Cohen, J.E.; Bowles, D.W.; Gadgeel, S.M.; Mihalcioiu, C.; Papadopoulos, K.P.; et al. A Next-Generation BRAF Inhibitor Overcomes Resistance to BRAF Inhibition in Patients with BRAF-Mutant Cancers Using Pharmacokinetics-Informed Dose Escalation. Cancer Discov. 2024, 14, 1599–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Tilburg, C.M.; Kilburn, L.B.; Perreault, S.; Schmidt, R.; Azizi, A.A.; Cruz-Martínez, O.; Zápotocký, M.; Scheinemann, K.; Meeteren, A.Y.S.V.; Sehested, A.; et al. LOGGIC/FIREFLY-2: A Phase 3, Randomized Trial of Tovorafenib vs. Chemotherapy in Pediatric and Young Adult Patients with Newly Diagnosed Low-Grade Glioma Harboring an Activating RAF Alteration. BMC Cancer 2024, 24, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schadendorf, D.; Dummer, R.; Flaherty, K.T.; Robert, C.; Arance, A.; Willem, J.; Garbe, C.; Gogas, H.J.; Gutzmer, R.; Krajsová, I.; et al. COLUMBUS 7-Year Update: A Randomized, Open-Label, Phase III Trial of Encorafenib plus Binimetinib versus Vemurafenib or Encorafenib in Patients with BRAF V600E/K-Mutant Melanoma. Eur. J. Cancer 2024, 204, 114073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudnichenko, O.; Penkov, K.; McKean, M.; Mandalà, M.; Kukushkina, M.; Panella, T.; Csőszi, T.; Gerletti, P.; Thakur, M.; Polli, A.; et al. First-Line Encorafenib plus Binimetinib and Pembrolizumab for Advanced BRAF V600-Mutant Melanoma: Safety Lead-in Results from the Randomized Phase III STARBOARD Study. Eur. J. Cancer (Oxf. Engl. 1990) 2024, 213, 115070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Moreno, D.; Baer, B.R.; Barbour, P.; Bettendorf, T.; Bouhana, K.; Brown, K.; Brown, S.A.; Fell, J.B.; Hartley, D.P.; et al. Identification of the Clinical Candidate PF-07284890 (ARRY-461), a Highly Potent and Brain Penetrant BRAF Inhibitor for the Treatment of Cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 67, 13019–13032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puzanov, I.; Burnett, P.; Flaherty, K.T. Biological Challenges of B-RAF Inhibitor Therapy. Mol. Oncol. 2011, 5, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciardiello, D.; Martinelli, E.; Troiani, T.; Mauri, G.; Rossini, D.; Martini, G.; Napolitano, S.; Famiglietti, V.; Tufo, S.D.; Masi, G.; et al. Anti-EGFR Rechallenge in Patients with Refractory CtDNA RAS/BRAF Wt Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. JAMA Netw. Open 2024, 7, e245635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of Cancer: The Next Generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degirmenci, U.; Wang, M.; Hu, J. Targeting Aberrant RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK Signaling for Cancer Therapy. Cells 2020, 9, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetu, S.A.; Bandyopadhyay, D. Small-Molecule RAS Inhibitors as Anticancer Agents: Discovery, Development, and Mechanistic Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubair, T.; Bandyopadhyay, D. Small Molecule EGFR Inhibitors as Anti-Cancer Agents: Discovery, Mechanisms of Action, and Opportunities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Progress and Challenges in Developing RAF Inhibitors. Cancer.gov. Available online: https://www.cancer.gov/research/key-initiatives/ras/news-events/dialogue-blog/2016/bollag-raf-inhibitors (accessed on 28 December 2024).
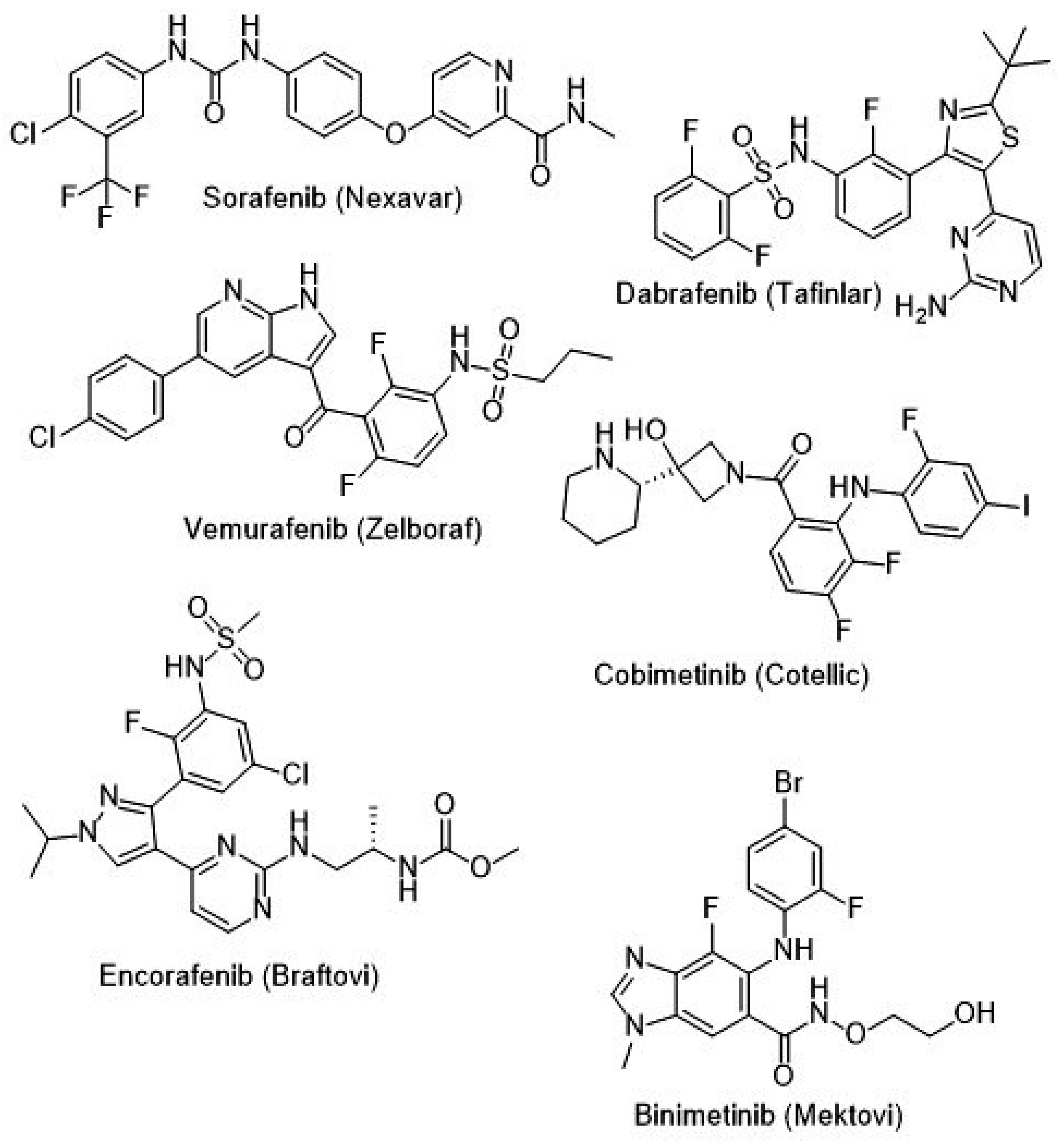
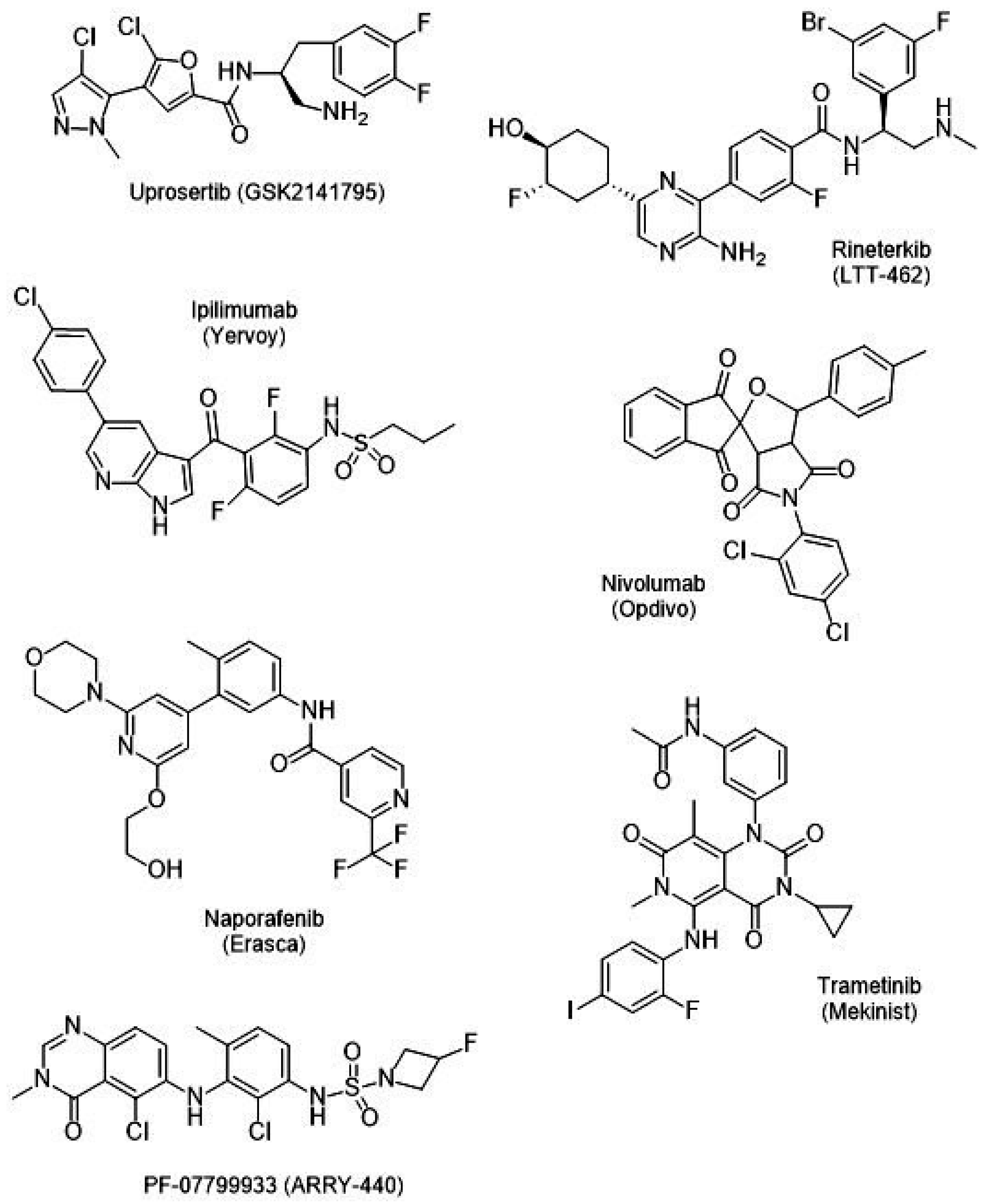

| RAF Isoform | Mutation | Cancer Type(s) | Prevalence | Clinical Relevance | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B-RAF (1983) | V600E | Melanoma | ~50% | Highly oncogenic | [1,11,12,15,18] |
| Colorectal | ~5–15% | Poor prognosis and resistance to B-RAF inhibitor monotherapy | [1,11,12,15,18] | ||
| Thyroid (Papillary) | ~40–45% | highly aggressive | [1,11,12,15,18] | ||
| Ovarian | ~30% | Sensitive to MEK inhibitors | [1,11,12,15,18] | ||
| Non-small Cell Lung Carcinoma (NSCLC) | ~1–3% | Targeted therapy includes B-RAF and MEK inhibitors | [1,11,12,15,18] | ||
| B-RAF | V600K | Hairy Cell Leukemia | ~99% | Highly sensitive to B-RAF inhibition | [1,11,12,15,18] |
| B-RAF | Non-V600 | Melanoma | ~5–30% | Targetable with B-RAF and MEK inhibitors | [1,11,12,15,18] |
| B-RAF | F595L, L597Q, and G469A | Lung, Colorectal, Thyroid, and Melanoma | ~5–20% | Associated with weak/intermediate kinase activity and sometimes respond better to MEK inhibitors instead of B-RAF inhibitors | [1,11,12,15,18] |
| C-RAF (1985) | F133L and S257L | Melanoma and Colorectal | Rare (~1–5%) | B-RAF inhibitors | [1,11,12,15,18] |
| A-RAF (1986) | Rare Mutations | Lung, Ovarian, and Pancreatic | Rare | Limited therapeutic targeting due to complexity of RAF dimerization | |
| Limited therapeutic options (less studied) | [1,11,15,16,18] | ||||
| Colorectal and Gliomas | Very Rare | [1,11,15,17,18] |
| Cancer Type | B-RAF Mutation Prevalence | Primary Treatment | Mechanism of Action | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Melanoma | ~50% (V600E/K) | B-RAF inhibitors + MEK inhibitors (e.g., Trametinib, Dabrafenib, Vemurafenib) | Trametinib inhibits MEK1/MEK2, blocking MAPK signaling | [28,33,34,35] |
| Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) | 1–2% of adenocarcinomas | B-RAF inhibitors ± EGFR/ALK inhibitors | B-RAF inhibitors block MAPK pathway; EGFR/ALK inhibitors target alternative pathways | [36,37] |
| Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) | Rare | Sorafenib (multi-kinase inhibitor) | Blocks RAF-1, B-RAF, VEGFR2, c-KIT, and PDGFR-β | [21,38] |
| Colorectal Cancer (CRC) | 8–12% of metastatic cases | Combination therapy targeting the entire RAS–RAF–MEK–MAPK axis | Inhibition of B-RAF alone leads to CRAF and RAS-mediated reactivation of EGFR | [39] |
| Thyroid Carcinoma | 40–45% in Papillary Thyroid Cancer | Sorafenib, Lenvatinib (RTK inhibitors) | Target RAF kinases and VEGF receptors | [38,40] |
| Trial Number | Combination | Target Pathway | Findings | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT01902173 | Uprosertib + Dabrafenib + Trametinib | AKT + B-RAF + MEK | AKT inhibition reduces cell proliferation and survival. Concurrent Uprosertib + Trametinib lowered Dabrafenib exposure | [47] |
| NCT02974725 | Naporafenib + Rineterkib or Trametinib | B-RAF + AKT + MEK | Partial response in NSCLC patients with B-RAF non-V600 and KRAS mutations | [48] |
| Trial Number | Combination | Target Pathway | Findings | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT02871791 | Exemestane + Everolimus + Palbociclib | CDK4/6 + mTOR | Studied CDK4/6 resistance in metastatic breast cancer; CBR was 18.8% | [49] |
| Trial Number | Combination | Target Pathway | Findings | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT02721459 | Vemurafenib + Cobimetinib + XL888 | B-RAF + MEK + HSP90 | Good tumor response but high toxicity | [50] |
| Trial Number | Combination | Target Pathway | Findings | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT05355701 | PF-07799933 ± Binimetinib | B-RAF + MEK | Inhibited MAPK reactivation in resistant B-RAF tumors | [51] |
| Trial Number | Combination | Target Pathway | Findings | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT05566795 | Tovorafenib vs. Chemotherapy | B-RAF | Phase III trial in pediatric gliomas with RAF alterations | [52] |
| NCT01909453 | Encorafenib + Binimetinib vs. Vemurafenib | B-RAF + MEK | Longest follow-up data of B-RAF/MEK inhibitors in melanoma | [53] |
| NCT04657991 | Encorafenib + Binimetinib + Pembrolizumab | B-RAF + MEK + PD-1 | Phase III trial in cutaneous melanoma with 65% ORR | [54] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anaya, Y.A.; Bracho, R.P.; Chauhan, S.C.; Tripathi, M.K.; Bandyopadhyay, D. Small Molecule B-RAF Inhibitors as Anti-Cancer Therapeutics: Advances in Discovery, Development, and Mechanistic Insights. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2676. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062676
Anaya YA, Bracho RP, Chauhan SC, Tripathi MK, Bandyopadhyay D. Small Molecule B-RAF Inhibitors as Anti-Cancer Therapeutics: Advances in Discovery, Development, and Mechanistic Insights. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(6):2676. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062676
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnaya, Yamile Abuchard, Ricardo Pequeno Bracho, Subhash C. Chauhan, Manish K. Tripathi, and Debasish Bandyopadhyay. 2025. "Small Molecule B-RAF Inhibitors as Anti-Cancer Therapeutics: Advances in Discovery, Development, and Mechanistic Insights" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 6: 2676. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062676
APA StyleAnaya, Y. A., Bracho, R. P., Chauhan, S. C., Tripathi, M. K., & Bandyopadhyay, D. (2025). Small Molecule B-RAF Inhibitors as Anti-Cancer Therapeutics: Advances in Discovery, Development, and Mechanistic Insights. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(6), 2676. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062676










