Evidence of Oxytosis/Ferroptosis in Niemann–Pick Disease Type C
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
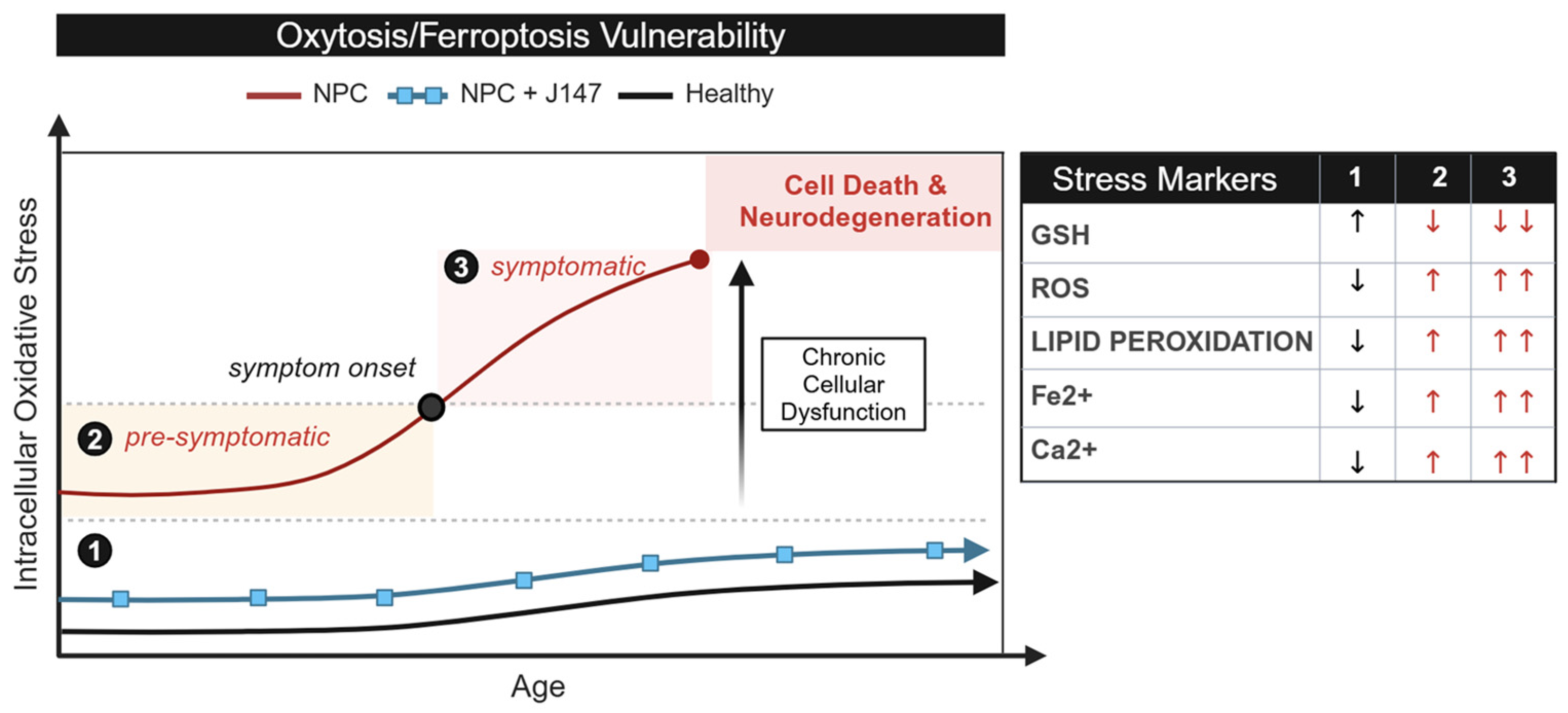
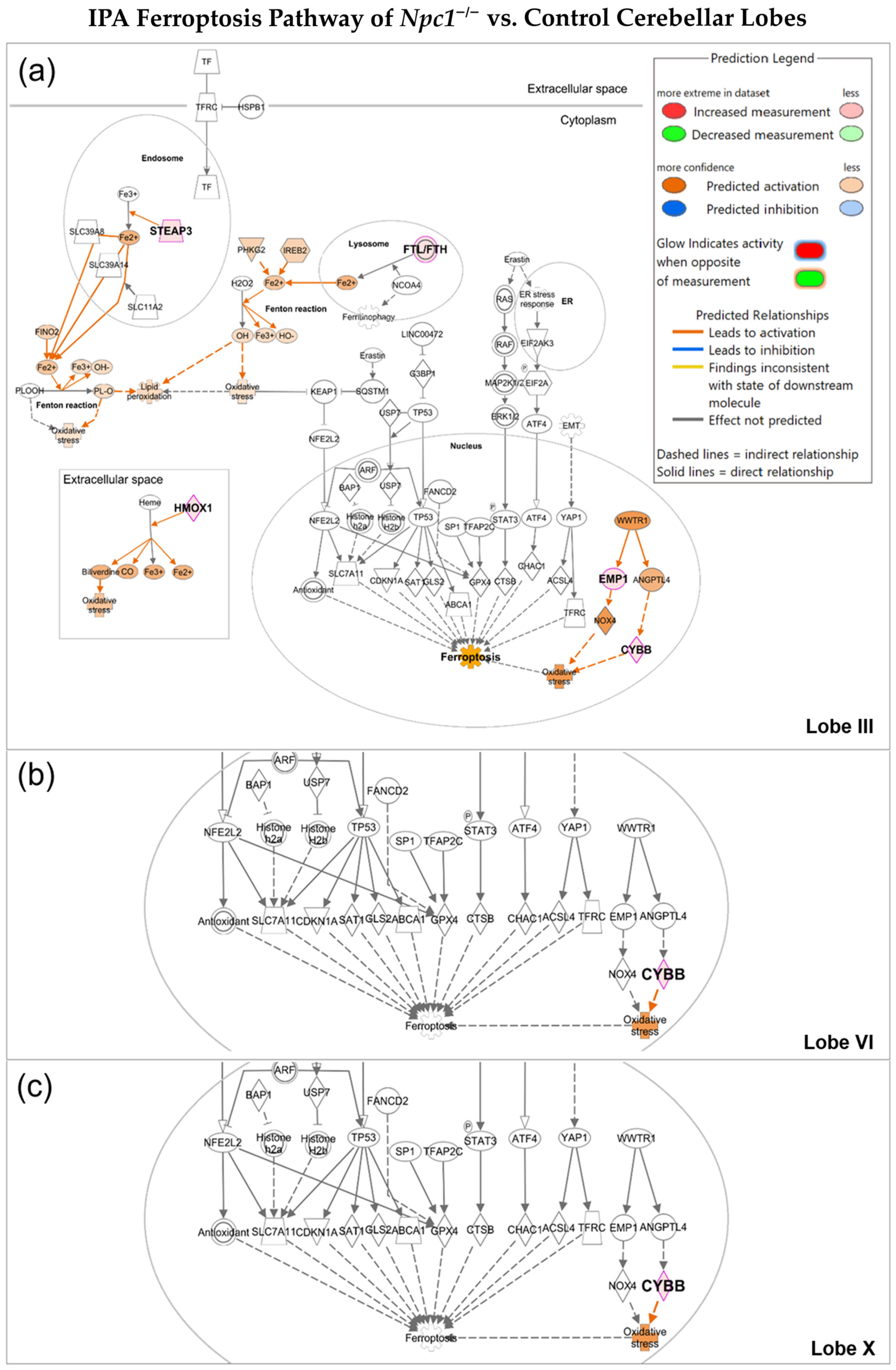
2.1. Oxytosis/Ferroptosis Is Upregulated in NPC Purkinje Cells of Cerebellar Lobule III
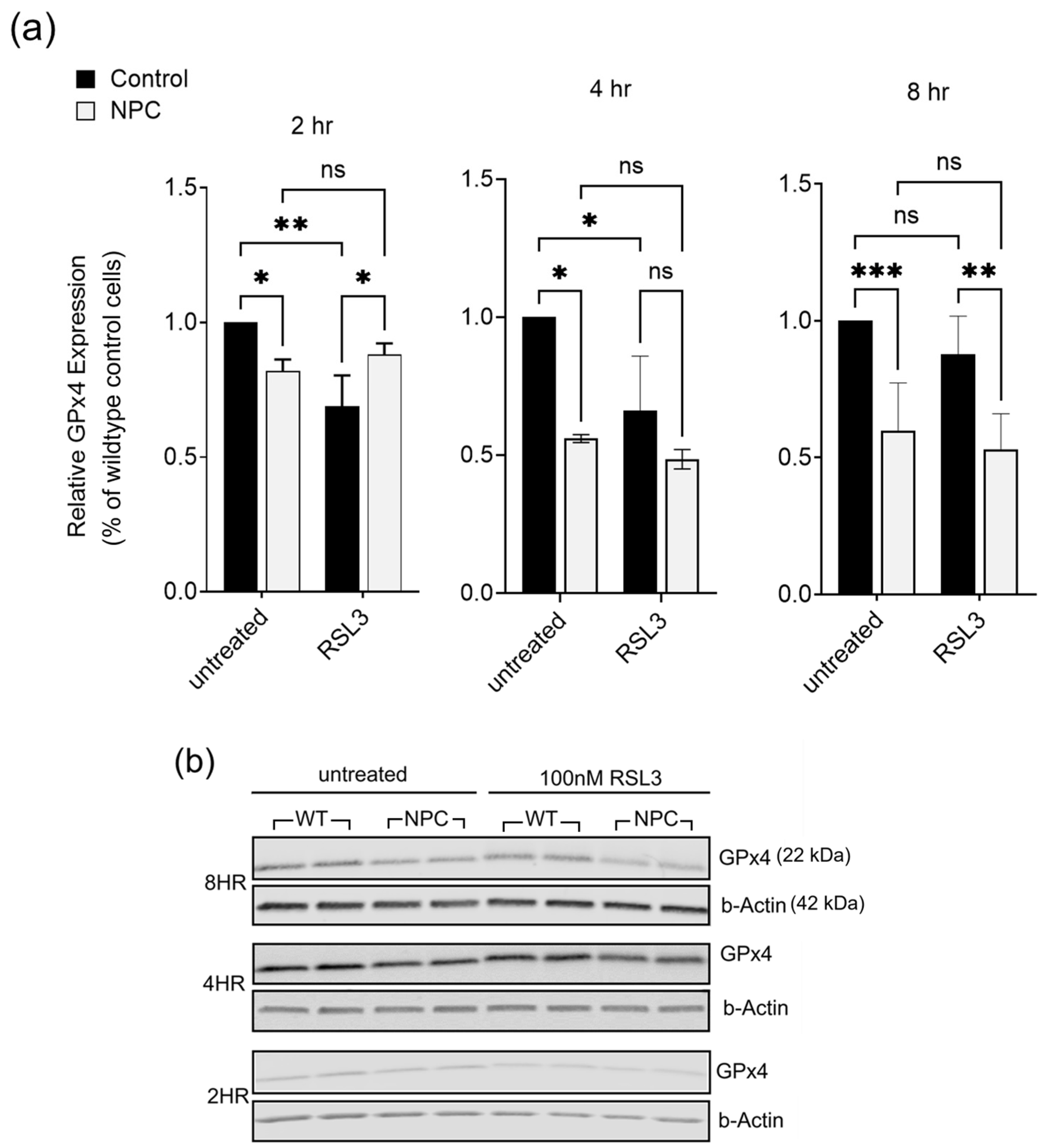
2.2. NPC Cells Are More Vulnerable to Ferroptosis than Age-Matched Controls
2.3. Glutathione Peroxidase 4 (GPx4) Is Lower in NPC Compared to Age-Matched Controls
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Lines
4.2. Ingenuity Pathway Analysis
4.3. MTT Cytotoxicity Assay
4.4. Western Blot Analysis
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NPC | Niemann–Pick Disease Type C1 |
| AD | Alzheimer’s Disease |
References
- Qian, H.; Wu, X.; Du, X.; Yao, X.; Zhao, X.; Lee, J.; Yang, H.; Yan, N. Structural Basis of Low-pH-Dependent Lysosomal Cholesterol Egress by NPC1 and NPC2. Cell 2020, 182, 98–111.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wraith, J.; Guffon, N.; Rohrbach, M.; Hwu, W.; Korenke, G.; Bembi, B.; Luzy, C.; Giorgino, R.; Sedel, F. Natural history of Niemann-Pick disease type C in a multicentre observational retrospective cohort study. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2009, 98, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanier, M.T. Niemann-Pick disease type C. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2010, 5, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, M. Niemann-Pick Disease Type C. In GeneReviews®; Adam, M.P., Feldman, J., Mirzaa, G.M., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Bean, L.J., Gripp, K.W., Amemiya, A., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 1993. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1296/ (accessed on 25 September 2024).
- Bianconi, S.E.; Hammond, D.I.; Farhat, N.Y.; Do, A.D.; Jenkins, K.; Cougnoux, A.; Martin, K.; Porter, F.D. Evaluation of Age of Death in Niemann-Pick Disease, type C: Utility of Disease Support Group Websites to Understand Natural History. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2019, 126, 466–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Pérez, C.; Weruaga, E.; Díaz, D. Lobe X of the Cerebellum: A Natural Neuro-Resistant Region. Anatomia 2023, 2, 43–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, D.C.; Milenkovic, L.; Beier, S.M.; Manuel, H.; Buchanan, J.; Scott, M.P. Cell-Autonomous Death of Cerebellar Purkinje Neurons with Autophagy in Niemann-Pick Type C Disease. PLoS Genet. 2005, 1, e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, Y.H.; Faux, N.G.; Killilea, D.W.; Yanjanin, N.; Firnkes, S.; Volitakis, I.; Ganio, G.; Walterfang, M.; Hastings, C.; Porter, F.D.; et al. Altered transition metal homeostasis in Niemann-Pick disease, type C1. Metallomics 2014, 6, 542–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.D.; Shin, A.; Mayagoitia, K.; Wilson, C.G.; Bellinger, D.L.; Soriano, S. Interferon downstream signaling is activated early in pre-symptomatic Niemann-Pick disease type C. Neurosci. Lett. 2019, 706, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiscione, S.A.; Vivas, O.; Ginsburg, K.S.; Bers, D.M.; Ory, D.S.; Santana, L.F.; Dixon, R.E.; Dickson, E.J. Disease-associated mutations in Niemann-Pick type C1 alter ER calcium signaling and neuronal plasticity. J. Cell Biol. 2019, 218, 4141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woś, M.; Szczepanowska, J.; Pikuła, S.; Tylki-Szymańska, A.; Zabłocki, K.; Bandorowicz-Pikuła, J. Mitochondrial dysfunction in fibroblasts derived from patients with Niemann-Pick type C disease. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2016, 593, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.; Sagara, Y.; Liu, Y.; Maher, P.; Schubert, D. The regulation of reactive oxygen species production during programmed cell death. J. Cell Biol. 1998, 141, 1423–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, B.R.; Hare, D.J.; Bush, A.I.; Roberts, B.R. Glutathione peroxidase 4: A new player in neurodegeneration? Mol. Psychiatry 2017, 22, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winterbourn, C.C. Toxicity of iron and hydrogen peroxide: The Fenton reaction. Toxicol. Lett. 1995, 82–83, 969–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarna, J.R.; Larouche, M.; Marzban, H.; Sillitoe, R.V.; Rancourt, D.E.; Hawkes, R. Patterned Purkinje cell degeneration in mouse models of Niemann-Pick type C disease. J. Comp. Neurol. 2003, 456, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marschalek, N.; Albert, F.; Meske, V.; Ohm, T.G. The natural history of cerebellar degeneration of Niemann-Pick C mice monitored in vitro. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2014, 40, 933–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, K.B.; Williams, I.M.; Cluzeau, C.V.; Cougnoux, A.; Dale, R.K.; Iben, J.R.; Cawley, N.X.; Wassif, C.A.; Porter, F.D. Identification of Novel Pathways Associated with Patterned Cerebellar Purkinje Neuron Degeneration in Niemann-Pick Disease, Type C1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyoy, A.; Olguín-Albuerne, M.; Martínez-Briseño, P.; Morán, J. Role of reactive oxygen species and NADPH-oxidase in the development of rat cerebellum. Neurochem. Int. 2013, 62, 998–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarazona-Santos, E.; Bernig, T.; Burdett, L.; Magalhaes, W.C.; Fabbri, C.; Liao, J.; Redondo, R.A.; Welch, R.; Yeager, M.; Chanock, S.J. CYBB, an NADPH-oxidase gene: Restricted diversity in humans and evidence for differential long-term purifying selection on transmembrane and cytosolic domains. Hum. Mutat. 2008, 29, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, S.J.; Patel, D.N.; Welsch, M.; Skouta, R.; Lee, E.D.; Hayano, M.; Thomas, A.G.; Gleason, C.E.; Tatonetti, N.P.; Slusher, B.S.; et al. Pharmacological inhibition of cystine–glutamate exchange induces endoplasmic reticulum stress and ferroptosis. eLife 2014, 3, e02523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagoda, N.; Von Rechenberg, M.; Zaganjor, E.; Bauer, A.J.; Yang, W.S.; Fridman, D.J.; Wolpaw, A.J.; Smukste, I.; Peltier, J.M.; Boniface, J.J.; et al. RAS–RAF–MEK-dependent oxidative cell death involving voltage-dependent anion channels. Nature 2007, 447, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, W.; Currais, A.; Liang, Z.; Pinto, A.; Maher, P. Old age-associated phenotypic screening for Alzheimer’s disease drug candidates identifies sterubin as a potent neuroprotective compound from Yerba santa. Redox Biol. 2019, 21, 101089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maher, P. Modulation of the Neuroprotective and Anti-inflammatory Activities of the Flavonol Fisetin by the Transition Metals Iron and Copper. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, M.; Angeli, J.P.F. Glutathione peroxidase 4 (Gpx4) and ferroptosis: What’s so special about it? Mol. Cell Oncol. 2015, 2, e995047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecsernyés, M.; Fenyvesi, F.; Bácskay, I.; Deli, M.A.; Szente, L.; Fenyvesi, É. Cyclodextrins, blood-brain barrier, and treatment of neurological diseases. Arch. Med. Res. 2014, 45, 711–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastings, C.; Liu, B.; Hurst, B.; Cox, G.F.; Hrynkow, S. Intravenous 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (Trappsol® CycloTM) demonstrates biological activity and impacts cholesterol metabolism in the central nervous system and peripheral tissues in adult subjects with Niemann-Pick Disease Type C1: Results of a phase 1 trial. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2022, 137, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, A.D.; Eden, E.R.; Zanlungo, S. Treating Niemann-Pick C lysosomal storage: Approved and emerging approaches. Trends Mol. Med. 2025, 31, 195–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freihuber, C.; Dahmani-Rabehi, B.; Brassier, A.; Broué, P.; Cances, C.; Chabrol, B.; Eyer, D.; Labarthe, F.; Latour, P.; Levade, T.; et al. Effects of miglustat therapy on neurological disorder and survival in early-infantile Niemann-Pick disease type C: A national French retrospective study. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2023, 18, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengel, E.; Patterson, M.C.; Da Riol, R.M.; Del Toro, M.; Deodato, F.; Gautschi, M.; Grunewald, S.; Grønborg, S.; Harmatz, P.; Héron, B.; et al. Efficacy and safety of arimoclomol in Niemann-Pick disease type C: Results from a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, multinational phase 2/3 trial of a novel treatment. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2021, 44, 1463–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremova-Ertl, T.; Ramaswami, U.; Brands, M.; Foltan, T.; Gautschi, M.; Gissen, P.; Gowing, F.; Hahn, A.; Jones, S.; Kay, R.; et al. Trial of N-Acetyl-l-Leucine in Niemann–Pick Disease Type C. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, E.; A Smith, D.; Smith, C.; Morris, L.; Bremova-Ertl, T.; Cortina-Borja, M.; Fineran, P.; Morten, K.J.; Poulton, J.; Boland, B.; et al. Acetyl-leucine slows disease progression in lysosomal storage disorders. Brain Commun. 2020, 3, fcaa148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prior, M.; Dargusch, R.; Ehren, J.L.; Chiruta, C.; Schubert, D. The neurotrophic compound J147 reverses cognitive impairment in aged Alzheimer’s disease mice. Alz Res. Ther. 2013, 5, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Currais, A.; Huang, L.; Goldberg, J.; Petrascheck, M.; Ates, G.; Pinto-Duarte, A.; Shokhirev, M.N.; Schubert, D.; Maher, P.; States, U. Elevating acetyl-CoA levels reduces aspects of brain aging. eLife 2019, 8, e47866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyoshi, K.; Hishinuma, E.; Matsukawa, N.; Shirasago, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Sato, T.; Sato, Y.; Kumondai, M.; Kikuchi, M.; Koshiba, S.; et al. Global Proteomics for Identifying the Alteration Pathway of Niemann–Pick Disease Type C Using Hepatic Cell Models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Wang, H.; Yao, J.; Wei, Q.; Lu, Y.; Wang, T.; Cao, X. NPC1 Deficiency Contributes to Autophagy-Dependent Ferritinophagy in HEI-OC1 Auditory Cells. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 952608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, P.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Song, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, T.; Liu, W.; Peng, B.; Yin, J.; et al. Neurotoxic A1 astrocytes promote neuronal ferroptosis via CXCL10/CXCR3 axis in epilepsy. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2023, 195, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sanchez, K.L.; Kim, J.; White, J.B.; Tolan, A.; Rajagopal, N.P.; Anderson, D.W.; Shin, A.N.; Shin, S.D.; Currais, A.; Soriano-Castell, D.; et al. Evidence of Oxytosis/Ferroptosis in Niemann–Pick Disease Type C. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2915. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26072915
Sanchez KL, Kim J, White JB, Tolan A, Rajagopal NP, Anderson DW, Shin AN, Shin SD, Currais A, Soriano-Castell D, et al. Evidence of Oxytosis/Ferroptosis in Niemann–Pick Disease Type C. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(7):2915. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26072915
Chicago/Turabian StyleSanchez, Kayla L., Jeanyoung Kim, Jacob B. White, Andrew Tolan, Naren P. Rajagopal, Douglas W. Anderson, Alexandra N. Shin, Samuel D. Shin, Antonio Currais, David Soriano-Castell, and et al. 2025. "Evidence of Oxytosis/Ferroptosis in Niemann–Pick Disease Type C" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 7: 2915. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26072915
APA StyleSanchez, K. L., Kim, J., White, J. B., Tolan, A., Rajagopal, N. P., Anderson, D. W., Shin, A. N., Shin, S. D., Currais, A., Soriano-Castell, D., Maher, P., & Soriano, S. (2025). Evidence of Oxytosis/Ferroptosis in Niemann–Pick Disease Type C. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(7), 2915. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26072915






