PD-L1+ Regulatory B Cells from Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Have Impaired Function in Suppressing IFN-ү and IL-21 Production
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
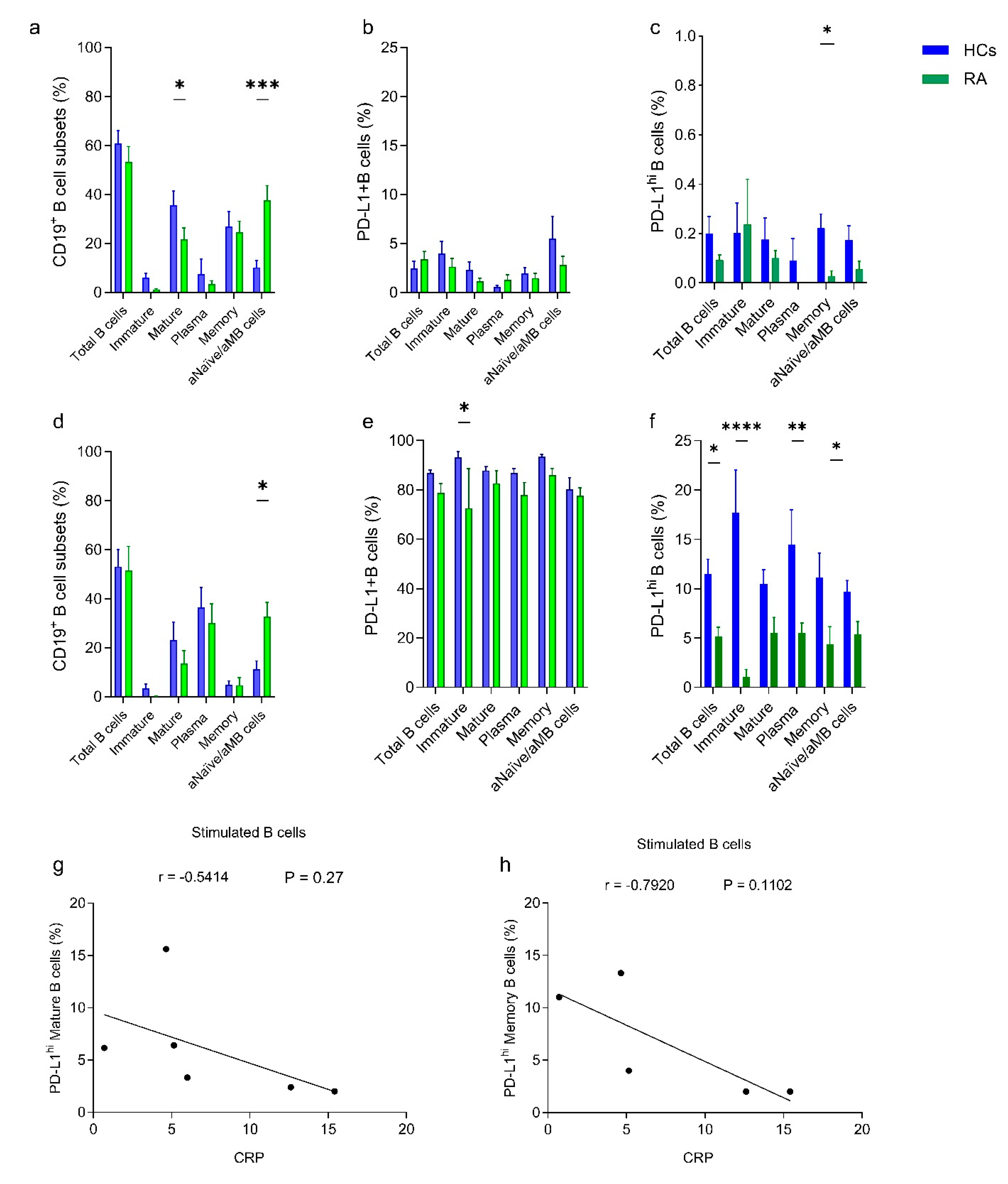
2.1. B-Cell Subsets and PD-L1 Expression Are Differentially Distributed Among HCs and RA Patients
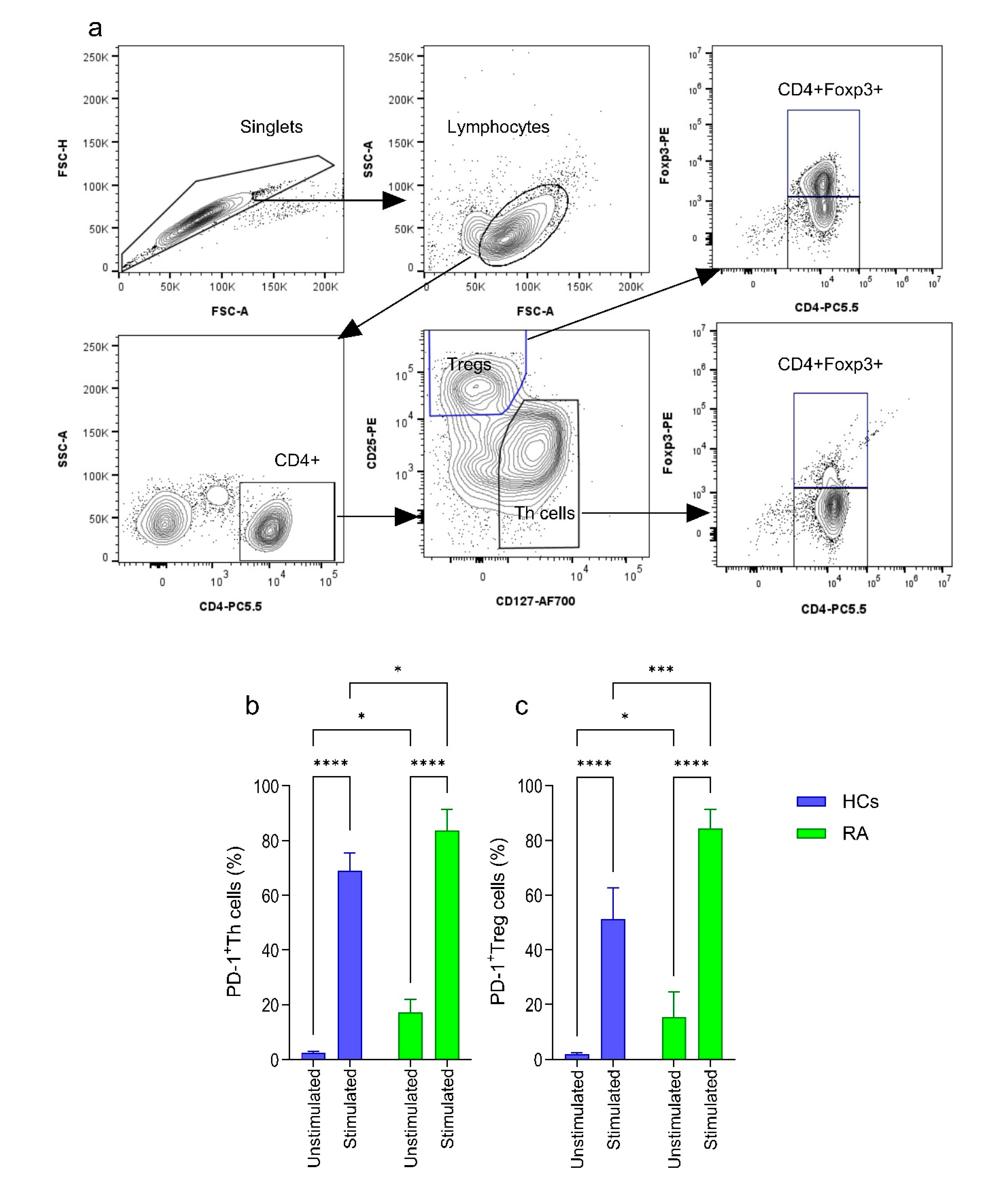
2.2. Expression of PD-1 on CD4+ Th and Treg Cells
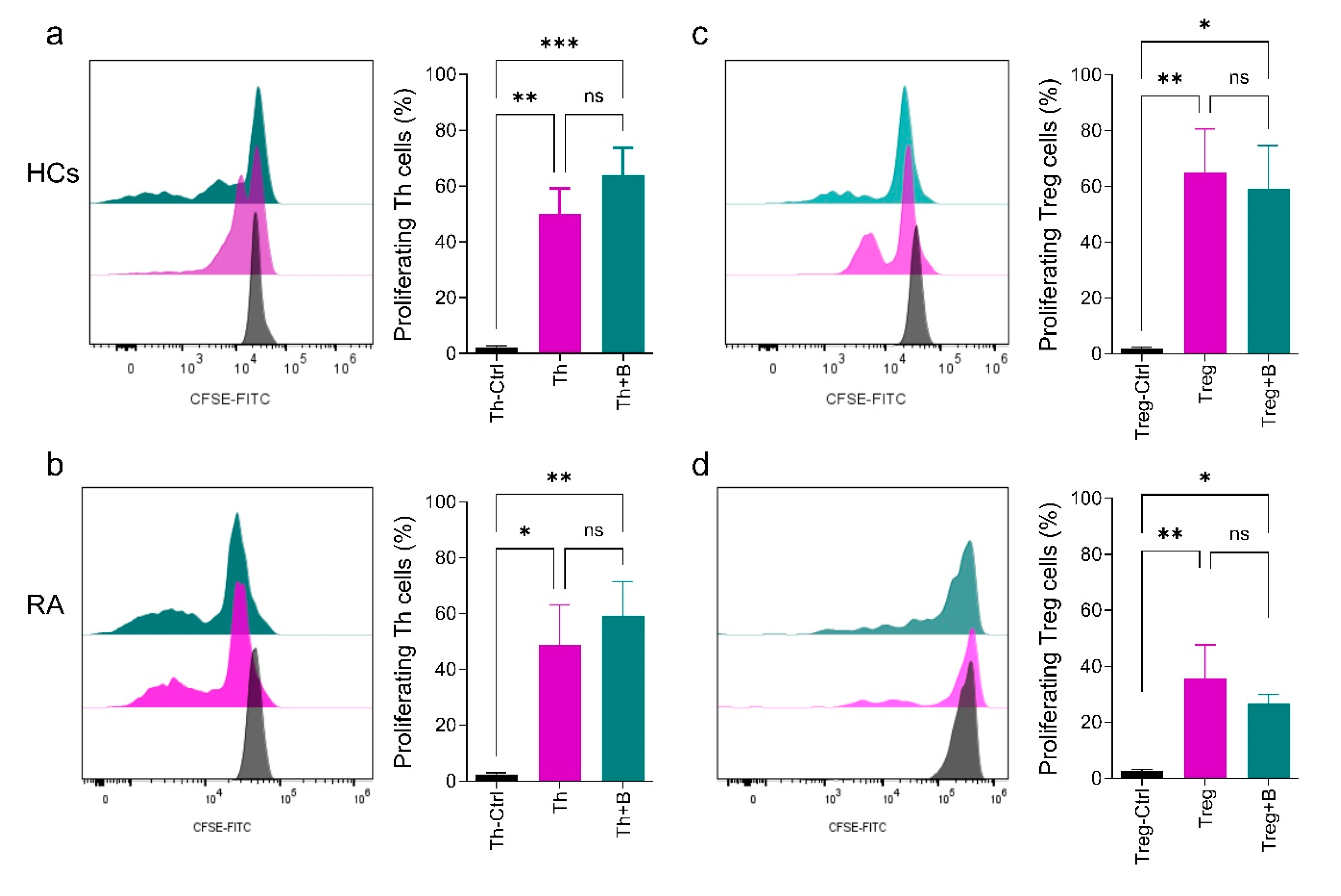
2.3. Th and Treg Cell Proliferation Is Not Significantly Affected by PD-L1+ Breg Cells
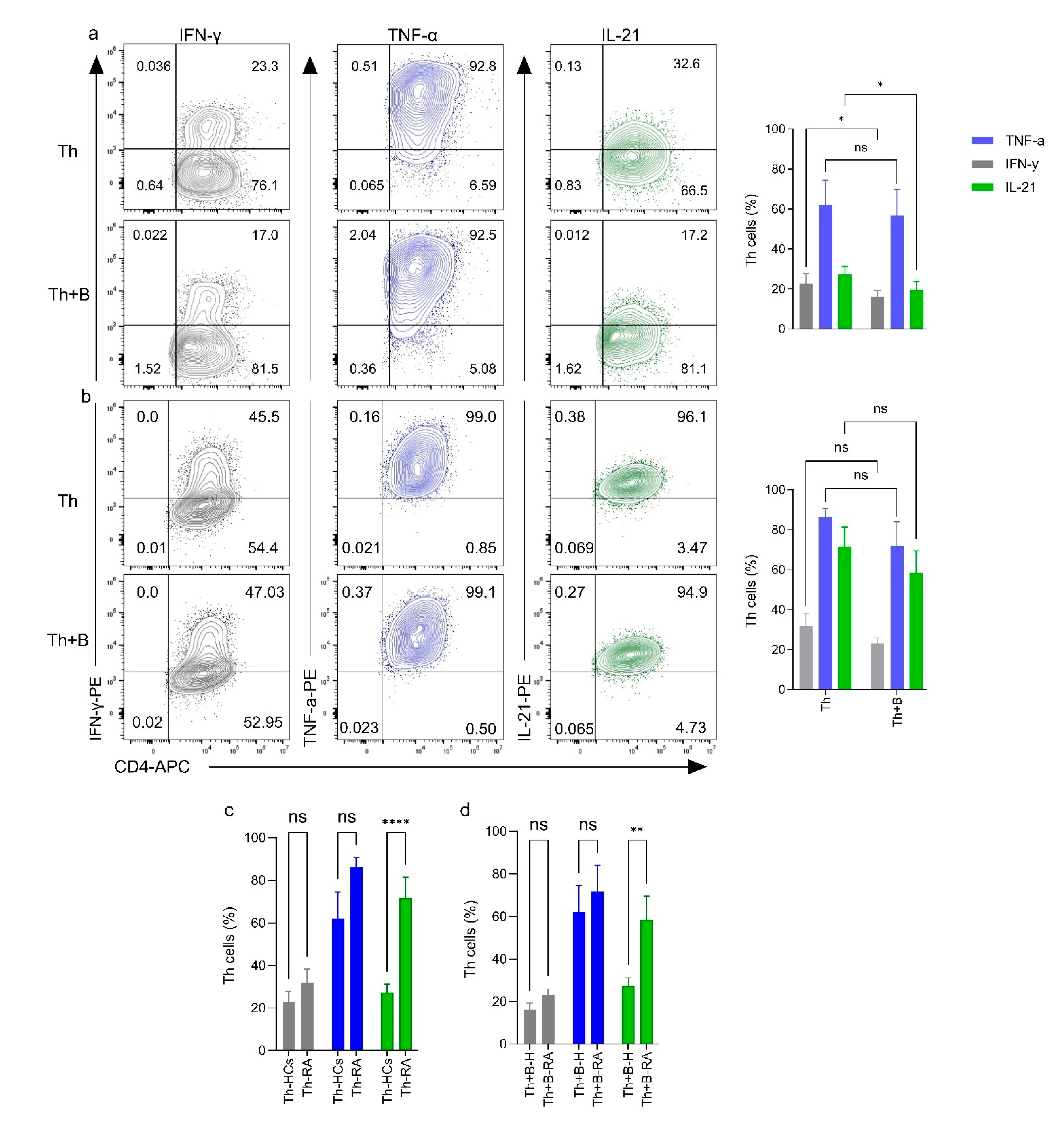
2.4. Functional Analysis of PD-L1+ Breg Cells by Comparing Cytokine Production
3. Discussion
4. Methods
4.1. Patients and Controls
4.2. B and T Cell Isolation
4.3. Flow Cytometry and Cell Sorting
4.4. B and Th Cell Activation
4.5. Proliferation Assay
4.6. Evaluation of Cytokine Production
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 7AAD | 7-AminoactinomycinD |
| ACPA | Anti-citrullinated protein antibody |
| CFSE | Carboxyfluorescein diacetate Succinimidyl ester “mixed isomer” |
| MACS | Magneticactivating cells sorting |
| MB | Memory B cells |
| PB | Plasma blast cells |
| PBMCs | Peripheral blood mononuclear cells |
| PC | Plasma B cells |
| PD-1 | Programmed cell death protein 1 |
| PMA | Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate |
| RF | Rheumatoid factor |
| Tfh | follicular T helper cells |
| Tph | peripheral T helper cells |
References
- Yang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, R.; Cheng, B.; Wu, Y.; Fu, X. IL-10+ CD19+ regulatory B cells induce CD4+ Foxp3+ regulatory T cells in serum of cervical cancer patients. Autoimmunity 2024, 57, 2290909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalán, D.; Mansilla, M.A.; Ferrier, A.; Soto, L.; Oleinika, K.; Aguillón, J.C.; Aravena, O. Immunosuppressive mechanisms of regulatory B cells. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 611795. [Google Scholar]
- Wortel, C.M.; Heidt, S. Regulatory B cells: Phenotype, function and role in transplantation. Transpl. Immunol. 2017, 41, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessel, A.; Haj, T.; Peri, R.; Snir, A.; Melamed, D.; Sabo, E.; Toubi, E. Human CD19+ CD25high B regulatory cells suppress proliferation of CD4+ T cells and enhance Foxp3 and CTLA-4 expression in T-regulatory cells. Autoimmun. Rev. 2012, 11, 670–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, L.; Li, M.; Zhang, F.; Zeng, X. The PD-1/PD-L pathway in rheumatic diseases. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2021, 120, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ray, A.; Wang, L.; Dittel, B.N. IL-10-independent regulatory B-cell subsets and mechanisms of action. Int. Immunol. 2015, 27, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Ellis, G.; Pallant, C.; Lopes, A.R.; Khanna, P.; Peppa, D.; Chen, A.; Blair, P.; Dusheiko, G.; Gill, U.; et al. IL-10-producing regulatory B cells in the pathogenesis of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 3925–3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, P.A.; Norena, L.Y.; Flores-Borja, F.; Rawlings, D.J.; Isenberg, D.A.; Ehrenstein, M.R.; Mauri, C. CD19+CD24hiCD38hi B cells exhibit regulatory capacity in healthy individuals but are functionally impaired in systemic Lupus Erythematosus patients. Immunity 2010, 32, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Borja, F.; Bosma, A.; Ng, D.; Reddy, V.; Ehrenstein, M.R.; Isenberg, D.A.; Mauri, C. CD19+ CD24hiCD38hi B cells maintain regulatory T cells while limiting TH1 and TH17 differentiation. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 173ra23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, M.; Baba, A.; Yokota, T.; Nishikawa, H.; Ohkawa, Y.; Kayama, H.; Kallies, A.; Nutt, S.L.; Sakaguchi, S.; Takeda, K. Interleukin-10-producing plasmablasts exert regulatory function in autoimmune inflammation. Immunity 2014, 41, 1040–1051. [Google Scholar]
- van de Veen, W.; Stanic, B.; Yaman, G.; Wawrzyniak, M.; Söllner, S.; Akdis, D.G.; Rückert, B.; Akdis, C.A.; Akdis, M. IgG4 production is confined to human IL-10–producing regulatory B cells that suppress antigen-specific immune responses. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 131, 1204–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zha, B.; Wang, L.; Liu, X.; Liu, J.; Chen, Z.; Xu, J.; Sheng, L.; Li, Y.; Chu, Y. Decrease in proportion of CD19+ CD24hiCD27+ B cells and impairment of their suppressive function in Graves’ disease. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49835. [Google Scholar]
- van der Vlugt, L.E.P.M.; Mlejnek, E.; Ozir-Fazalalikhan, A.; Janssen Bonas, M.; Dijksman, T.R.; Labuda, L.A.; Schot, R.; Guigas, B.; Möller, G.M.; Hiemstra, P.S. CD 24hi CD 27+ B cells from patients with allergic asthma have impaired regulatory activity in response to lipopolysaccharide. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2014, 44, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aravena, O.; Ferrier, A.; Menon, M.; Mauri, C.; Aguillón, J.C.; Soto, L.; Catalán, D. TIM-1 defines a human regulatory B cell population that is altered in frequency and function in systemic sclerosis patients. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2017, 19, 8. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Correale, J.; Farez, M.; Razzitte, G. Helminth infections associated with multiple sclerosis induce regulatory B cells. Ann. Neurol. 2008, 64, 187–199. [Google Scholar]
- Mauri, C.; Menon, M. Human regulatory B cells in health and disease: Therapeutic potential. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 772–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, M.; Blair, P.A.; Isenberg, D.A.; Mauri, C. A regulatory feedback between plasmacytoid dendritic cells and regulatory B cells is aberrant in systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunity 2016, 44, 683–697. [Google Scholar]
- Daien, C.I.; Gailhac, S.; Mura, T.; Audo, R.; Combe, B.; Hahne, M.; Morel, J. Regulatory B10 cells are decreased in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and are inversely correlated with disease activity. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014, 66, 2037–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Liu, B.; Jiang, Z.; Jiang, Y. Reduced numbers of regulatory B cells are negatively correlated with disease activity in patients with new-onset rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2014, 33, 187–195. [Google Scholar]
- Bankó, Z.; Pozsgay, J.; Szili, D.; Tóth, M.; Gáti, T.; Nagy, G.; Rojkovich, B.; Sármay, G. Induction and differentiation of IL-10–producing regulatory B cells from healthy blood donors and rheumatoid arthritis patients. J. Immunol. 2017, 198, 1512–1520. [Google Scholar]
- Buch, M.H.; Smolen, J.S.; Betteridge, N.; Breedveld, F.C.; Burmester, G.; Dörner, T.; Ferraccioli, G.; Gottenberg, J.E.; Isaacs, J.; Kvien, T.K.; et al. Updated consensus statement on the use of rituximab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2011, 70, 909–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.R.; Hams, E.; Floudas, A.; Sparwasser, T.; Weaver, C.T.; Fallon, P.G. PD-L1hi B cells are critical regulators of humoral immunity. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 5997. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Radu, A.-F. and S.G. Bungau, Management of rheumatoid arthritis: An overview. Cells 2021, 10, 2857. [Google Scholar]
- Abbasi, M.; Mousavi, M.J.; Jamalzehi, S.; Alimohammadi, R.; Bezvan, M.H.; Mohammadi, H.; Aslani, S. Strategies toward rheumatoid arthritis therapy; the old and the new. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 10018–10031. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nagy, G.; Roodenrijs, N.M.T.; Welsing, P.M.J.; Kedves, M.; Hamar, A.; Van Der Goes, M.C.; Kent, A.; Bakkers, M.; Blaas, E.; Senolt, L. EULAR definition of difficult-to-treat rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nagy, G.; Roodenrijs, N.M.T.; Welsing, P.M.J.; Kedves, M.; Hamar, A.; van der Goes, M.C.; Kent, A.; Bakkers, M.; Pchelnikova, P.; Blaas, E. EULAR points to consider for the management of difficult-to-treat rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 81, 20–33. [Google Scholar]
- Nagy, G.; Gunkl-Tóth, L.; Dorgó, A.M.; McInnes, I.B. The concept of difficult-to-treat disease in rheumatology: Where next? Lancet Rheumatol. 2025, 7, e274–e289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, T.; Su, R.; Wu, R.; Xue, H.; Wang, Y.; Su, R.; Gao, C.; Li, X.; Wang, C. Frontiers of Autoantibodies in Autoimmune Disorders: Crosstalk Between Tfh/Tfr and Regulatory B Cells. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 641013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heine, G.; Drozdenko, G.; Grün, J.R.; Chang, H.D.; Radbruch, A.; Worm, M. Autocrine IL-10 promotes human B-cell differentiation into IgM- or IgG-secreting plasmablasts. Eur. J. Immunol. 2014, 44, 1615–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Kang, K.; Chen, P.; Zeng, Z.; Li, G.; Xiong, W.; Yi, M.; Xiang, B. Regulatory mechanisms of PD-1/PD-L1 in cancers. Mol. Cancer 2024, 23, 108. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, D.; Zhang, L.; Chen, J.; Zhu, M.; Hou, L.; Chen, B.; Shen, B. Changes in regulatory B cells and their relationship with rheumatoid arthritis disease activity. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 15, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Wan, Y.; Lan, J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Shen, Y. PD-L1 is a critical mediator of regulatory B cells and T cells in invasive breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz, I.; Wei, C.; Jenks, S.A.; Cashman, K.S.; Tipton, C.; Woodruff, M.C.; Hom, J.; Lee, F.E.-H. Challenges and opportunities for consistent classification of human B cell and plasma cell populations. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straube, J.; Bukhari, S.; Lerrer, S.; Winchester, R.J.; Gartshteyn, Y.; Henick, B.S.; Dragovich, M.A.; Mor, A. PD-1 signaling uncovers a pathogenic subset of T cells in inflammatory arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2024, 26, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, B.; Ming, Y.; Yang, C. Regulatory B cells: The cutting edge of immune tolerance in kidney transplantation. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacca, E.R.; Onofrio, L.I.; Acosta, C.D.V.; Ferrero, P.V.; Alonso, S.M.; Ramello, M.C.; Mussano, E.; Onetti, L.; Cadile, I.I.; Stancich, M.I. PD-L1+ regulatory B cells are significantly decreased in rheumatoid arthritis patients and increase after successful treatment. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2241. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, A.; Odendahl, M.; Reiter, K.; Jacobi, A.M.; Feist, E.; Scholze, J.; Burmester, G.R.; Lipsky, P.E.; Dörner, T. Diminished peripheral blood memory B cells and accumulation of memory B cells in the salivary glands of patients with Sjögren’s syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 2002, 46, 2160–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekete, A.; Soos, L.; Szekanecz, Z.; Szabo, Z.; Szodoray, P.; Barath, S.; Lakos, G. Disturbances in B-and T-cell homeostasis in rheumatoid arthritis: Suggested relationships with antigen-driven immune responses. J. Autoimmun. 2007, 29, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto-Carneiro, M.M.; Mahadevan, V.; Takada, K.; Fritsch-Stork, R.; Nanki, T.; Brown, M.; Fleisher, T.A.; Wilson, M.; Goldbach-Mansky, R.; Lipsky, P.E. Alterations in peripheral blood memory B cells in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis are dependent on the action of tumour necrosis factor. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2009, 11, R84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobi, A.M.; Reiter, K.; Mackay, M.; Aranow, C.; Hiepe, F.; Radbruch, A.; Hansen, A.; Burmester, G.R.; Diamond, B.; Lipsky, P.E. Activated memory B cell subsets correlate with disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus: Delineation by expression of CD27, IgD, and CD95. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 58, 1762–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, C.; Chen, W.; Ding, G. The skewed frequency of B-cell subpopulation CD19+ CD24 hiCD38 hi cells in peripheral blood mononuclear cells is correlated with the elevated serum sCD40L in patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 11490–11497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buffa, S.; Pellicanò, M.; Bulati, M.; Martorana, A.; Goldeck, D.; Caruso, C.; Pawelec, G.; Colonna-Romano, G. A novel B cell population revealed by a CD38/CD24 gating strategy: CD38− CD24− B cells in centenarian offspring and elderly people. Age 2013, 35, 2009–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoder, A.; Sarvaria, A.; Alsuliman, A.; Chew, C.; Sekine, T.; Cooper, N.; Mielke, S.; De Lavallade, H.; Muftuoglu, M.; Fernandez Curbelo, I. Regulatory B cells are enriched within the IgM memory and transitional subsets in healthy donors but are deficient in chronic GVHD. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2014, 124, 2034–2045. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Xu, H.; Gao, R.; Leng, F.; Huo, F.; Li, Y.; Liu, S.; Xu, M.; Bai, J. CD19+ CD24hiCD38hi regulatory B cells deficiency revealed severity and poor prognosis in patients with sepsis. BMC Immunol. 2022, 23, 54. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, J.; Su, Q.Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, X.; Yang, S.Q.; Liu, Y.R.; Gao, H.Y.; Yu, Q.; He, P.F.; Li, X. POS0455 The Status of Breg Cells and Breg-Related Cytokines in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis; BMJ Publishing Group Ltd.: London, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Talib, M.; Gyebrovszki, B.; Bőgér, D.; Csomor, R.; Mészáros, A.; Fodor, A.; Rojkovich, B.; Sármay, G. Helper T Cells are Hyperactive and Contribute to the Dysregulation of Antibody Production in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarvaria, A.; Madrigal, J.A.; Saudemont, A. B cell regulation in cancer and anti-tumor immunity. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2017, 14, 662–674. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Su, Y.; Jiao, A.; Wang, X.; Zhang, B. T cells in health and disease. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 235. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baker, K.F.; McDonald, D.; Hulme, G.; Hussain, R.; Coxhead, J.; Swan, D.; Schulz, A.R.; Mei, H.E.; MacDonald, L.; Pratt, A.G. Single-cell insights into immune dysregulation in rheumatoid arthritis flare versus drug-free remission. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1063. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, M.; La Cava, A.; Hahn, B.H. Blockade of programmed death-1 in young (New Zealand Black× New Zealand White) F1 mice promotes the suppressive capacity of CD4+ regulatory T cells protecting from lupus-like disease. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 5402–5410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felson, D.T.; Smolen, J.S.; Wells, G.; Zhang, B.; Van Tuyl, L.H.D.; Funovits, J.; Aletaha, D.; Allaart, C.F.; Bathon, J.; Bombardieri, S. American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism provisional definition of remission in rheumatoid arthritis for clinical trials. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 573–586. [Google Scholar]
| RA (n = 25) | Reference Value (RV) | |
|---|---|---|
| Age (y; mean [range]) | 63.60 (43–84) | — |
| M/F (N) | 4/30 | — |
| Disease duration (y; mean [range]) | 15.00 (4.00–29.00) | — |
| Treatments: | ||
| Methotrexate | 6 | — |
| Methotrexate + folic acid | 1 | — |
| Methotrexate + Medrol | 1 | — |
| Methotrexate + Hydroxychloroquine | 2 | — |
| Methotrexate + adalimumab-adaz | 1 | — |
| Methotrexate + folic acid + Medrol | 1 | — |
| Methotrexate + rituximab | 2 | — |
| Methotrexate + Medrol + tofacitinib | 1 | — |
| Certolizumab pegol + leflunomide | 1 | — |
| Leflunomide + Medrol | 1 | — |
| Leflunomide | 1 | — |
| Etanercept + Leflunomide | 1 | — |
| Adalimumab-adaz | 2 | — |
| Sulfasalazine + Methotrexate + Adalimumab | 1 | — |
| Adalimumab-adaz + hydroxychloroquine + Methotrexate + folic acid | 1 | — |
| Methotrexate + folic acid + sulfasalazine + adalimumab-adaz | 1 | — |
| Adalimumab + Methotrexate + folic acid + medrol+ hydroxychloroquine | 1 | — |
| CRP (mg/L; mean [range]) | 12.30 (0.58–53.00) | <8 mg/L |
| DAS28 [ESR-based] (mean [range]) | 4.00 (2.3–6.70.00) | |
| aCCP (IU/mL) | <20 IU/mL | |
| aCCP − | n = 5 | |
| aCCP + (mean [range]) | 2161.00 (25.00–32,000.00) | |
| RF (IU/mL) | <20 IU/mL | |
| RF − | n = 8 | |
| RF + (mean[range]) | 151.85 (13.00–961.00) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Talib, M.; Gyebrovszki, B.; Fodor, A.; Mészáros, A.; Balog Virág, K.; Barta, L.G.; Rojkovich, B.; Nagy, G.; Sármay, G. PD-L1+ Regulatory B Cells from Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Have Impaired Function in Suppressing IFN-ү and IL-21 Production. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2998. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26072998
Talib M, Gyebrovszki B, Fodor A, Mészáros A, Balog Virág K, Barta LG, Rojkovich B, Nagy G, Sármay G. PD-L1+ Regulatory B Cells from Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Have Impaired Function in Suppressing IFN-ү and IL-21 Production. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(7):2998. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26072998
Chicago/Turabian StyleTalib, Mustafa, Balázs Gyebrovszki, Anna Fodor, Anna Mészáros, Kata Balog Virág, Leila Gloria Barta, Bernadette Rojkovich, György Nagy, and Gabriella Sármay. 2025. "PD-L1+ Regulatory B Cells from Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Have Impaired Function in Suppressing IFN-ү and IL-21 Production" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 7: 2998. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26072998
APA StyleTalib, M., Gyebrovszki, B., Fodor, A., Mészáros, A., Balog Virág, K., Barta, L. G., Rojkovich, B., Nagy, G., & Sármay, G. (2025). PD-L1+ Regulatory B Cells from Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Have Impaired Function in Suppressing IFN-ү and IL-21 Production. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(7), 2998. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26072998






