Administration of Noggin Suppresses Fibrinogen Leakage into the Brain in the Acute Phase After Traumatic Brain Injury in Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
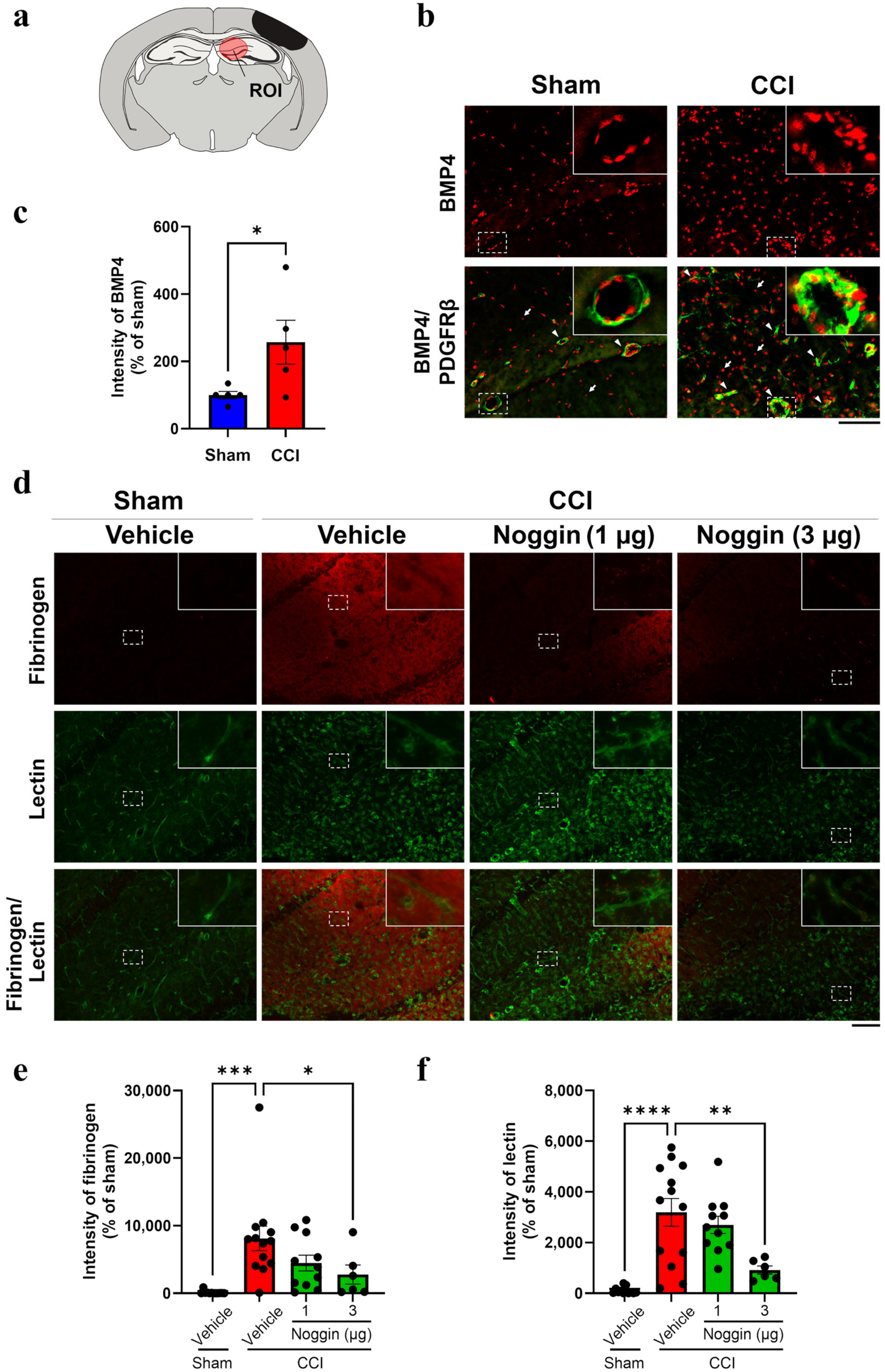
2.1. Effect of Noggin Administration on Fibrinogen Leakage into the Ipsilateral Hippocampus of CCI Mice Showing Increased BMP4 Levels
2.2. Effects of Noggin on the Activation of NVU-Constituting Cell Types in CCI Mice
2.3. Effects of Noggin on Neuronal Damage in CCI Mice
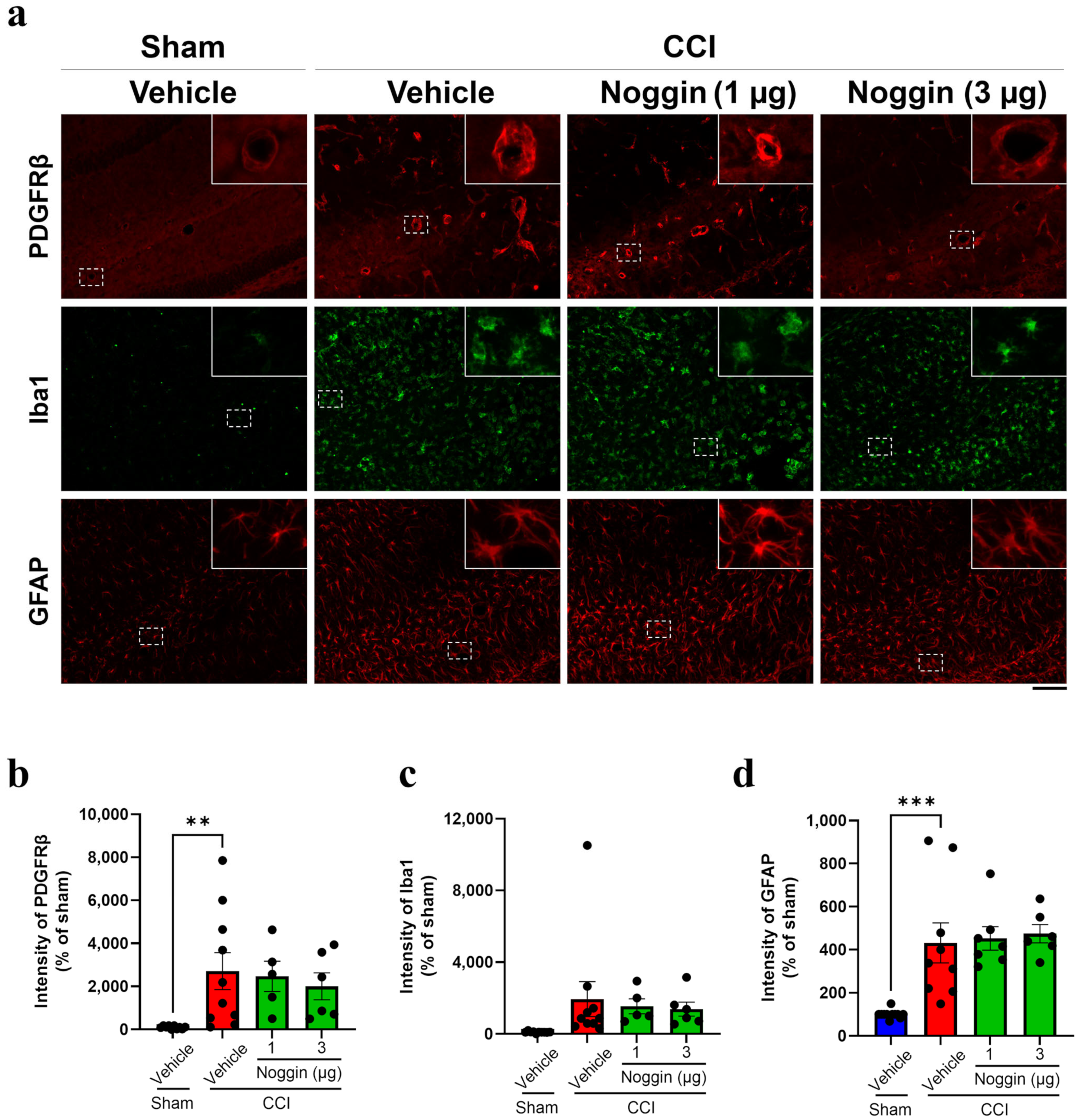
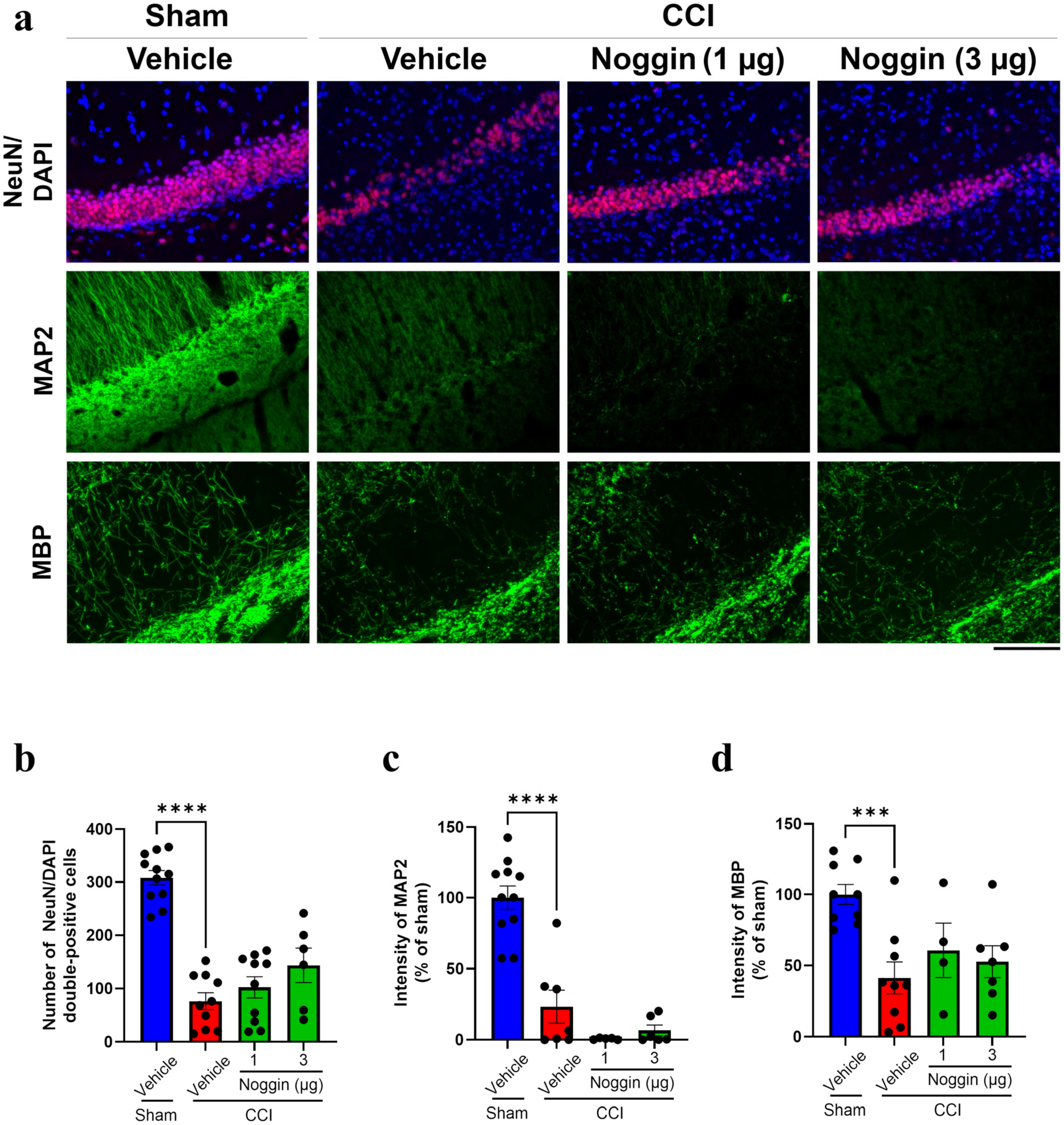
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Preparation of a TBI Mouse Model Through CCI
4.3. Administration of Noggin
4.4. Histological Analyses
4.4.1. Sample Preparation
4.4.2. Immunohistochemical Assay
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BBB | blood–brain barrier |
| BMP | bone morphogenetic protein |
| CCI | controlled cortical impact |
| GFAP | glial fibrillary acidic protein |
| Iba1 | ionized calcium-binding adaptor protein 1 |
| MAP2 | microtubule-associated protein 2 |
| MBP | myelin basic protein |
| NeuN | neuronal nuclei |
| NVU | neurovascular unit |
| PBS | phosphate-buffered saline |
| PDGFRβ | platelet-derived growth factor receptor β |
| TBI | traumatic brain injury |
| TGF | transforming growth factor |
References
- VanItallie, T.B. Traumatic brain injury (TBI) in collision sports: Possible mechanisms of transformation into chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE). Metab. Clin. Exp. 2019, 100s, 153943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, H.; Hardy, J.; Zetterberg, H. Neurological consequences of traumatic brain injuries in sports. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2015, 66, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearn, M.L.; Niesman, I.R.; Egawa, J.; Sawada, A.; Almenar-Queralt, A.; Shah, S.B.; Duckworth, J.L.; Head, B.P. Pathophysiology Associated with Traumatic Brain Injury: Current Treatments and Potential Novel Therapeutics. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 37, 571–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jochems, D.; van Rein, E.; Niemeijer, M.; van Heijl, M.; van Es, M.A.; Nijboer, T.; Leenen, L.P.H.; Houwert, R.M.; van Wessem, K.J.P. Incidence, causes and consequences of moderate and severe traumatic brain injury as determined by Abbreviated Injury Score in the Netherlands. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brett, B.L.; Gardner, R.C.; Godbout, J.; Dams-O’Connor, K.; Keene, C.D. Traumatic Brain Injury and Risk of Neurodegenerative Disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 2022, 91, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, V.E.; Stewart, W.; Smith, D.H. Axonal pathology in traumatic brain injury. Exp. Neurol. 2013, 246, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, D.C.; Sturm, V.E.; Peterson, M.J.; Pieper, C.F.; Bullock, T.; Boeve, B.F.; Miller, B.L.; Guskiewicz, K.M.; Berger, M.S.; Kramer, J.H.; et al. Association of traumatic brain injury with subsequent neurological and psychiatric disease: A meta-analysis. J. Neurosurg. 2016, 124, 511–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulimai, N.; Brown, J.; Lominadze, D. The Effect of Reduced Fibrinogen on Cerebrovascular Permeability during Traumatic Brain Injury in Fibrinogen Gene Heterozygous Knockout Mice. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, K.; Takata, F.; Yamanaka, G.; Yasunaga, M.; Hashiguchi, K.; Tominaga, K.; Itoh, K.; Kataoka, Y.; Yamauchi, A.; Dohgu, S. Reactive pericytes in early phase are involved in glial activation and late-onset hypersusceptibility to pilocarpine-induced seizures in traumatic brain injury model mice. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 145, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, T.; Mendiola, A.S.; Yan, Z.; Meza-Acevedo, R.; Cabriga, B.; Akassoglou, K.; Ryu, J.K. Fibrin promotes oxidative stress and neuronal loss in traumatic brain injury via innate immune activation. J. Neuroinflammation 2024, 21, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loane, D.J.; Kumar, A. Microglia in the TBI brain: The good, the bad, and the dysregulated. Exp. Neurol. 2016, 275 Pt 3, 316–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Li, H.; Li, H.; Xie, F.; Zhang, J. Research progress of neuroinflammation-related cells in traumatic brain injury: A review. Medicine 2023, 102, e34009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, M.A.; Ryu, J.K.; Akassoglou, K. Fibrinogen in neurological diseases: Mechanisms, imaging and therapeutics. Nat. Rev. 2018, 19, 283–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divolis, G.; Stavropoulos, A.; Manioudaki, M.; Apostolidou, A.; Doulou, A.; Gavriil, A.; Dafnis, I.; Chroni, A.; Mummery, C.; Xilouri, M.; et al. Activation of both transforming growth factor-β and bone morphogenetic protein signalling pathways upon traumatic brain injury restrains pro-inflammatory and boosts tissue reparatory responses of reactive astrocytes and microglia. Brain Commun. 2019, 1, fcz028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, T.T.; Villapol, S.; Symes, A.J. TGF-β superfamily gene expression and induction of the Runx1 transcription factor in adult neurogenic regions after brain injury. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helbing, T.; Arnold, L.; Wiltgen, G.; Hirschbihl, E.; Gabelmann, V.; Hornstein, A.; Esser, J.S.; Diehl, P.; Grundmann, S.; Busch, H.J.; et al. Endothelial BMP4 Regulates Leukocyte Diapedesis and Promotes Inflammation. Inflammation 2017, 40, 1862–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Huang, W.; Wang, Y.; Sun, W.; Tang, J.; Li, D.; Xu, P.; Guo, L.; Yin, Z.Q.; Fan, X. The function of BMP4 during neurogenesis in the adult hippocampus in Alzheimer’s disease. Ageing Res. Rev. 2013, 12, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, W.A.; Mehler, M.F.; Kessler, J.A. Transgenic overexpression of BMP4 increases astroglial and decreases oligodendroglial lineage commitment. Dev. Biol. 2003, 255, 164–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, J.; Alden, T.; Gobeske, K.; Kan, L.; Kessler, J.A. Noggin protects against ischemic brain injury in rodents. Stroke 2010, 41, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Moreno, M.; Armenteros, T.; Gradari, S.; Hortigüela, R.; García-Corzo, L.; Fontán-Lozano, Á.; Trejo, J.L.; Mira, H. Noggin rescues age-related stem cell loss in the brain of senescent mice with neurodegenerative pathology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 11625–11630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sammarraie, N.; Mahmood, M.; Ray, S.K. Neuroprotective role of Noggin in spinal cord injury. Neural Regen. Res. 2023, 18, 492–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, L.; Kohli, S.; Sprague, S.M.; Scranton, R.A.; Lipton, S.A.; Parra, A.; Jimenez, D.F.; Digicaylioglu, M. Intranasal delivery of erythropoietin plus insulin-like growth factor-I for acute neuroprotection in stroke. Laboratory investigation. J. Neurosurg. 2009, 111, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, P.K.; Lo, A.W.; Wang, K.K.; Lau, H.C.; Leung, K.K.; Li, K.T.; Lai, P.B.; Poon, W.S. Transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells to the brain by topical application in an experimental traumatic brain injury model. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2013, 20, 306–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nebie, O.; Carvalho, K.; Barro, L.; Delila, L.; Faivre, E.; Renn, T.Y.; Chou, M.L.; Wu, Y.W.; Nyam-Erdene, A.; Chou, S.Y.; et al. Human platelet lysate biotherapy for traumatic brain injury: Preclinical assessment. Brain J. Neurol. 2021, 144, 3142–3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.A.; Lim, S.M.; Jeong, S.I.; Kang, J.L.; Park, E.M. Noggin improves ischemic brain tissue repair and promotes alternative activation of microglia in mice. Brain Behav. Immun. 2014, 40, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, D.A.; Tramontin, A.D.; Trevejo, J.M.; Herrera, D.G.; García-Verdugo, J.M.; Alvarez-Buylla, A. Noggin antagonizes BMP signaling to create a niche for adult neurogenesis. Neuron 2000, 28, 713–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, G.S.; Leon-Palmer, N.E.; Townsend, K.L. Bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) in the central regulation of energy balance and adult neural plasticity. Metab. Clin. Exp. 2021, 123, 154837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, R.; Kreipke, C.W.; Roberts, G.; Bagchi, M.; Rafols, J.A. Neovascularization following traumatic brain injury: Possible evidence for both angiogenesis and vasculogenesis. Neurol. Res. 2007, 29, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigau, V.; Morin, M.; Rousset, M.C.; de Bock, F.; Lebrun, A.; Coubes, P.; Picot, M.C.; Baldy-Moulinier, M.; Bockaert, J.; Crespel, A.; et al. Angiogenesis is associated with blood-brain barrier permeability in temporal lobe epilepsy. Brain J. Neurol. 2007, 130, 1942–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Vliet, E.A.; Otte, W.M.; Wadman, W.J.; Aronica, E.; Kooij, G.; de Vries, H.E.; Dijkhuizen, R.M.; Gorter, J.A. Blood-brain barrier leakage after status epilepticus in rapamycin-treated rats II: Potential mechanisms. Epilepsia 2016, 57, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, C.; Guzman, A.; Knaus, P. Noggin. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2011, 43, 478–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merlini, M.; Rafalski, V.A.; Rios Coronado, P.E.; Gill, T.M.; Ellisman, M.; Muthukumar, G.; Subramanian, K.S.; Ryu, J.K.; Syme, C.A.; Davalos, D.; et al. Fibrinogen Induces Microglia-Mediated Spine Elimination and Cognitive Impairment in an Alzheimer’s Disease Model. Neuron 2019, 101, 1099–1108.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, J.K.; Davalos, D.; Akassoglou, K. Fibrinogen signal transduction in the nervous system. J. Thromb. Haemost. JTH 2009, 7 (Suppl. S1), 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conforti, P.; Mezey, S.; Nath, S.; Chu, Y.H.; Malik, S.C.; Martínez Santamaría, J.C.; Deshpande, S.S.; Pous, L.; Zieger, B.; Schachtrup, C. Fibrinogen regulates lesion border-forming reactive astrocyte properties after vascular damage. Glia 2022, 70, 1251–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulimai, N.; Brown, J.; Lominadze, D. Fibrinogen Interaction with Astrocyte ICAM-1 and PrP(C) Results in the Generation of ROS and Neuronal Death. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendiola, A.S.; Yan, Z.; Dixit, K.; Johnson, J.R.; Bouhaddou, M.; Meyer-Franke, A.; Shin, M.G.; Yong, Y.; Agrawal, A.; MacDonald, E.; et al. Defining blood-induced microglia functions in neurodegeneration through multiomic profiling. Nat. Immunol. 2023, 24, 1173–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burda, J.E.; Bernstein, A.M.; Sofroniew, M.V. Astrocyte roles in traumatic brain injury. Exp. Neurol. 2016, 275 Pt 3, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullen, D.K.; Vernekar, V.N.; LaPlaca, M.C. Trauma-induced plasmalemma disruptions in three-dimensional neural cultures are dependent on strain modality and rate. J. Neurotrauma 2011, 28, 2219–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, J.R.; Johnson, V.E.; Young, A.M.; Smith, D.H.; Stewart, W. Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption Is an Early Event That May Persist for Many Years After Traumatic Brain Injury in Humans. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2015, 74, 1147–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yasunaga, M.; Takata, F.; Iwao, T.; Mizoguchi, J.; Tajima, N.; Dohgu, S. Administration of Noggin Suppresses Fibrinogen Leakage into the Brain in the Acute Phase After Traumatic Brain Injury in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3002. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073002
Yasunaga M, Takata F, Iwao T, Mizoguchi J, Tajima N, Dohgu S. Administration of Noggin Suppresses Fibrinogen Leakage into the Brain in the Acute Phase After Traumatic Brain Injury in Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(7):3002. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073002
Chicago/Turabian StyleYasunaga, Miho, Fuyuko Takata, Takuro Iwao, Junko Mizoguchi, Nanako Tajima, and Shinya Dohgu. 2025. "Administration of Noggin Suppresses Fibrinogen Leakage into the Brain in the Acute Phase After Traumatic Brain Injury in Mice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 7: 3002. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073002
APA StyleYasunaga, M., Takata, F., Iwao, T., Mizoguchi, J., Tajima, N., & Dohgu, S. (2025). Administration of Noggin Suppresses Fibrinogen Leakage into the Brain in the Acute Phase After Traumatic Brain Injury in Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(7), 3002. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073002





