Thymus Degeneration in Women and the Influence of Female Sexual Hormones on Thymic Epithelial Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Thymus Degeneration in Women
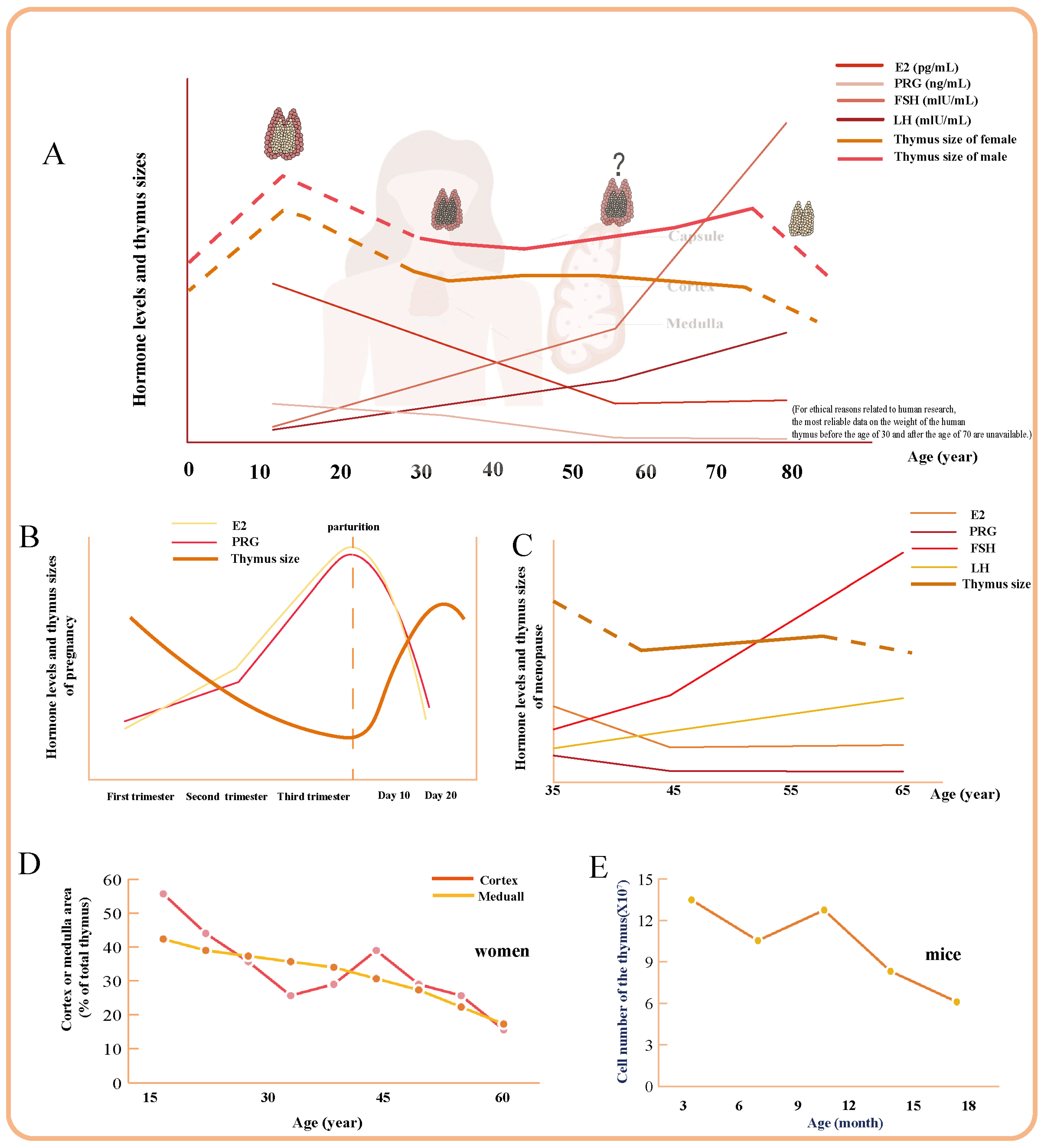
2.1. The Overall Process of Thymus Degeneration in Women
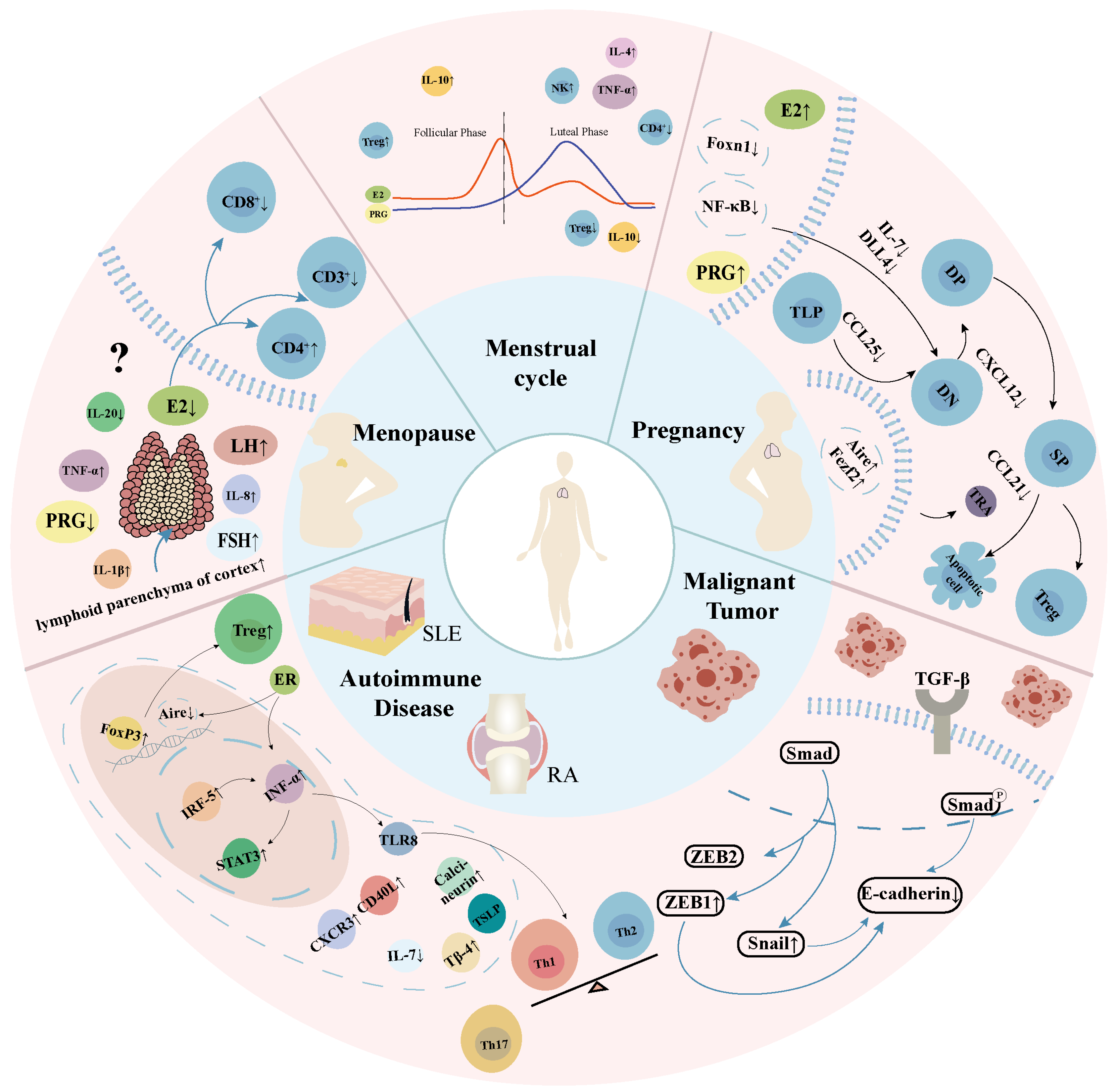
2.2. Transient Physiological Thymus Degeneration During Pregnancy
2.3. Special Modifications in the Thymus of Postmenopausal Women
2.4. Menstrual Cycle
2.5. Pathological Degeneration of the Thymus in Women
2.5.1. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
2.5.2. Rheumatoid Arthritis
2.5.3. Malignant Tumor
3. Female Sexual Hormones and Thymus
3.1. Estrogen and Its Receptors
3.2. Progesterone
3.3. Luteinizing Hormone Releasing Hormone
3.4. Follistatin
3.5. Prolactin
3.6. Growth Hormone
3.7. Glucocorticoid
3.8. Androgen
3.9. Others
4. Regulatory Mechanisms of Thymic Involution in Women
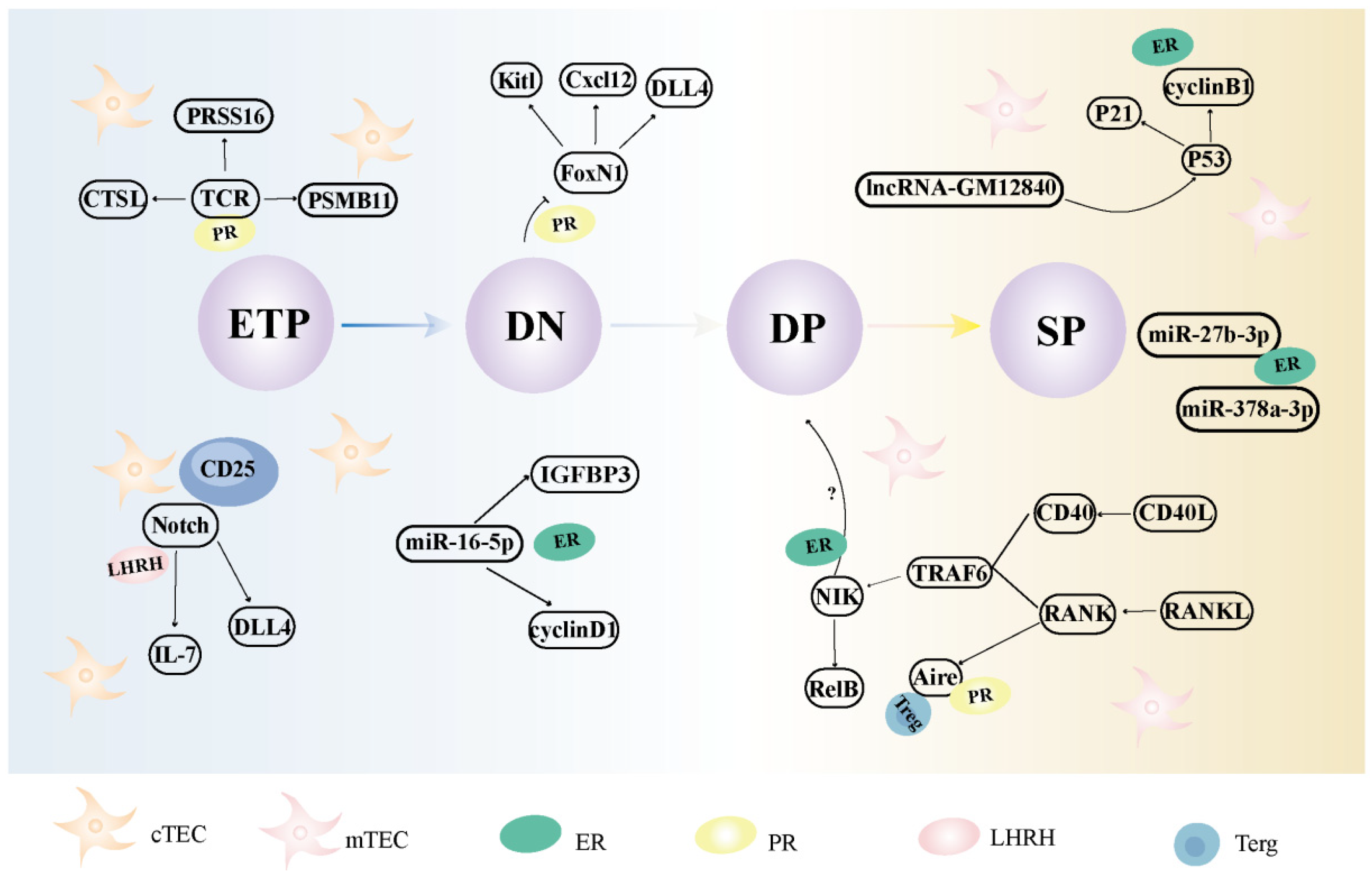
4.1. The Effects and Mechanisms of Female Sexual Hormones on Thymic Epithelial Cells
4.2. The Effects and Mechanisms of Female Sexual Hormones on Thymocytes
5. Future Perspectives
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nishino, M.; Ashiku, S.K.; Kocher, O.N.; Thurer, R.L.; Boiselle, P.M.; Hatabu, H. The Thymus: A Comprehensive Review. Radiographics 2006, 26, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aspinall, R.; Andrew, D. Immunosenescence: Potential Causes and Strategies for Reversal. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2000, 28, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinmann, G.G.; Klaus, B.; Müller-Hermelink, H.K. The Involution of the Ageing Human Thymic Epithelium Is Independent of Puberty. A Morphometric Study. Scand. J. Immunol. 1985, 22, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araki, T.; Nishino, M.; Gao, W.; Dupuis, J.; Hunninghake, G.M.; Murakami, T.; Washko, G.R.; O’Connor, G.T.; Hatabu, H. Normal Thymus in Adults: Appearance on CT and Associations with Age, Sex, BMI and Smoking. Eur. Radiol. 2016, 26, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, S.; Shri, A.; Sidhu, S.; Lahre, Y.; Bag, N.D.; Bhoi, S.K.; Mohakud, S. Multidetector Computed Tomography Evaluation of Normal Thymus and Variations with Age. J. Minim Access. Surg. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, G.; Takahama, Y. Thymic Epithelial Cells: Working Class Heroes for T Cell Development and Repertoire Selection. Trends Immunol. 2012, 33, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauce, D.; Appay, V. Altered thymic activity in early life: How does it affect the immune system in young adults? Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2011, 23, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Meis, J.; Aurélio Farias-de-Oliveira, D.; Nunes Panzenhagen, P.H.; Maran, N.; Villa-Verde, D.M.; Morrot, A.; Savino, W. Thymus Atrophy and Double-Positive Escape Are Common Features in Infectious Diseases. J. Parasitol. Res. 2012, 2012, 574020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandropoulos, K.; Danzl, N.M. Thymic Epithelial Cells: Antigen Presenting Cells that Regulate T Cell Repertoire and Tolerance Development. Immunol. Res. 2012, 54, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramson, J.; Anderson, G. Thymic Epithelial Cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 35, 85–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohigashi, I.; Kozai, M.; Takahama, Y. Development and Developmental Potential of Cortical Thymic Epithelial Cells. Immunol. Rev. 2016, 271, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumont-Lagacé, M.; St-Pierre, C.; Perreault, C. Sex Hormones Have Pervasive Effects on Thymic Epithelial Cells. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lepletier, A.; Hun, M.L.; Hammett, M.V.; Wong, K.; Naeem, H.; Hedger, M.; Loveland, K.; Chidgey, A.P. Interplay Between Follistatin, Activin A, and BMP4 Signaling Regulates Postnatal Thymic Epithelial Progenitor Cell Differentiation During Aging. Cell Rep. 2019, 27, 3887–3901.e3884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackman, J.B.; Kovacina, B.; Carter, B.W.; Wu, C.C.; Sharma, A.; Shepard, J.A.; Halpern, E.F. Sex Difference in Normal Thymic Appearance in Adults 20–30 Years of Age. Radiology 2013, 268, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, J.G.; Gray, E.S.; Beck, J.S. Age Involution in the Normal Human Adult Thymus. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1975, 19, 261–265. [Google Scholar]
- Katayama, M.; Fukuda, T.; Hatabu, T.; Narabara, K.; Abe, A.; Kondo, Y. Changes in Estrogen Receptor Expression in the Chick Thymus During Late Embryonic Development. Anim. Sci. J. 2014, 85, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavaert, M.; Valcke, B.; Vandekerckhove, B.; Leclercq, G.; Liang, K.L.; Taghon, T. Conventional and Computational Flow Cytometry Analyses Reveal Sustained Human Intrathymic T Cell Development from Birth Until Puberty. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leposavic, G.; Perisic, M.; Pilipovic, I. Role of Gonadal Hormones in Programming Developmental Changes in Thymopoietic Efficiency and Sexual Diergism in Thymopoiesis. Immunol. Res. 2012, 52, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, I.; Uhrinova, A.; Toth, F.; Mistinova, J. Assessment of the Thymic Morphometry Using Ultrasound in Full-Term Newborns. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2011, 33, 689–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, J.; Mustachio, L.M.; Su, D.M.; Craig, R.W. Thymus Size and Age-related Thymic Involution: Early Programming, Sexual Dimorphism, Progenitors and Stroma. Aging Dis. 2012, 3, 280–290. [Google Scholar]
- Stankiewicz, L.N.; Salim, K.; Flaschner, E.A.; Wang, Y.X.; Edgar, J.M.; Lin, B.Z.; Bingham, G.C.; Major, M.C.; Jones, R.D.; Blau, H.M.; et al. Sex Biased Human Thymic Architecture Guides T Cell Development Through Spatially Defined Niches. Dev. Cell. 2025, 60, 152–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, G.; Liu, A.; Teng, A.; Zheng, J. Study on Comparison of the Immune of Thymus and Spleen between Male and Female Mice. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2011, 39, 9743–9745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoller, A.L.; Kersh, G.J. Estrogen Induces Thymic Atrophy by Eliminating Early Thymic Progenitors and Inhibiting Proliferation of Beta-Selected Thymocytes. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 7371–7378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, Y.-Y.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Z.-W.; Gao, J.-L. Mechanism of Pregnancy-Induced Thymus Involution and Regeneration and Medication Rules of Postpartum Prescriptions. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2023, 48, 4275–4284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspinall, R.; Andrew, D. Gender-Related Differences in the Rates of age Associated Thymic Atrophy. J. Immunol. Res. 2001, 8, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hun, M.L.; Wong, K.; Gunawan, J.R.; Alsharif, A.; Quinn, K.; Chidgey, A.P. Gender Disparity Impacts on Thymus Aging and LHRH Receptor Antagonist-Induced Thymic Reconstitution Following Chemotherapeutic Damage. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arruvito, L.; Sanz, M.; Banham, A.H.; Fainboim, L. Expansion of CD4+CD25+and FOXP3+ Regulatory T Cells During the Follicular Phase of the Menstrual Cycle: Implications for Human Reproduction. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 2572–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pido-Lopez, J.; Imami, N.; Aspinall, R. Both Age and Gender Affect Thymic Output: More Recent Thymic Migrants in Females than Males as They Age. Clin. Exp. Immunology. 2001, 125, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leposavić, G.; Obradović, S.; Kosec, D.; Pejcić-Karapetrović, B.; Vidić-Danković, B. In Vivo Modulation of the Distribution of Thymocyte Subsets by Female Sex Steroid Hormones. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2001, 1, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nacka-Aleksić, M.; Pilipović, I.; Kotur-Stevuljević, J.; Petrović, R.; Sopta, J.; Leposavić, G. Sexual Dimorphism in Rat Thymic Involution: A Correlation with Thymic Oxidative Status and Inflammation. Biogerontology 2019, 20, 545–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, S.P.; Clarke, A.G. Measurement of Thymus Weight, Lumbar Node Weight and Progesterone Levels in Syngeneically Pregnant, Allogeneically Pregnant, and Pseudopregnant Mice. J. Reprod. Fertil. 1979, 55, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dooley, J.; Liston, A. Molecular Control Over Thymic Involution: From Cytokines and microRNA to Aging and Adipose Tissue. Eur. J. Immunol. 2012, 42, 1073–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsesis, S.; Gruenbaum, B.F.; Ohayon, S.; Boyko, M.; Gruenbaum, S.E.; Shapira, Y.; Weintraub, A.; Zlotnik, A. The Effects of Estrogen and Progesterone on Blood Glutamate Levels During Normal Pregnancy in Women. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2013, 29, 912–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laan, M.; Haljasorg, U.; Kisand, K.; Salumets, A.; Peterson, P. Pregnancy-Induced Thymic Involution is Associated with Suppression of Chemokines Essential for T-Lymphoid Progenitor Homing. Eur. J. Immunol. 2016, 46, 2008–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirshev, S.V.; Orlova, E.G.; Loginova, O.A.; Nekrasova, I.V.; Gorbunova, O.L.; Maslennikova, I.L. Hormonal Regulation of Dendritic Cell Differentiation in the Thymus. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2018, 165, 230–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumont-Lagacé, M.; Daouda, T.; Depoërs, L.; Zumer, J.; Benslimane, Y.; Brochu, S.; Harrington, L.; Lemieux, S.; Perreault, C. Qualitative Changes in Cortical Thymic Epithelial Cells Drive Postpartum Thymic Regeneration. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.H.; Nguyen, S.L.; Kim, T.H.; Jeong, J.W.; Arora, R.; Lydon, J.P.; Petroff, M.G. Nuclear Progesterone Receptor Expressed by the Cortical Thymic Epithelial Cells Dictates Thymus Involution in Murine Pregnancy. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 846226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, N.; Vachon, H.; Marie, J.; Irla, M. Administration of RANKL Boosts Thymic Regeneration upon Bone Marrow Transplantation. EMBO Mol. Med. 2017, 9, 835–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akyol, S.; Cınar, S.A.; Purisa, S.; Aydinli, K. Relationship Between Lymphocytes, IL2 and the Hormones E2, LH, PRG and FSH in Menopausal and Postmenopausal Women. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2011, 66, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malutan, A.M.; Dan, M.; Nicolae, C.; Carmen, M. Proinflammatory and Anti-Inflammatory Cytokine Changes Related to Menopause. Prz. Menopauzalny 2014, 13, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leposavić, G.; Nanut, M.P.; Pilipović, I.; Kosec, D.; Arsenović-Ranin, N.; Stojić-Vukanić, Z.; Djikić, J.; Nacka-Aleksić, M. Reshaping of T-Lymphocyte Compartment in Adult Prepubertaly Ovariectomised Rats: A Putative Role for Progesterone Deficiency. Immunobiology 2014, 219, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perisić, M.; Arsenović-Ranin, N.; Pilipović, I.; Kosec, D.; Pesić, V.; Radojević, K.; Leposavić, G. Role of Ovarian Hormones in Age-Associated Thymic Involution Revisited. Immunobiology 2010, 215, 275–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenz, T.K.; Heiman, J.R.; Demas, G.E. Sexual Activity Modulates Shifts in TH1/TH2 Cytokine Profile Across the Menstrual Cycle: An Observational Study. Fertil. Steril. 2015, 104, 1513–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Kim, J.; Jang, B.; Hur, S.; Jung, U.; Kil, K.; Na, B.; Lee, M.; Choi, Y.; Fukui, A.; et al. Fluctuation of Peripheral Blood T, B, and NK Cells During a Menstrual Cycle of Normal Healthy Women. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 756–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hospital Español de Pachuca Research Group; Licona-Meníndez, R.D.; Peón, A.N. Anti-COVID-19 Vaccination Alters the Menstrual Cycle and Dose Accumulation Enhances the Effect. Medicina 2024, 60, 956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faas, M.; Bouman, A.; Moesa, H.; Heineman, M.J.; de Leij, L.; Schuiling, G. The Immune Response During the Luteal Phase of the Ovarian Cycle: A Th2-Type Response? Fertil. Steril. 2000, 74, 1008–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brundin, P.M.A.; Landgren, B.M.; Fjällström, P.; Shamekh, M.M.; Gustafsson, J.; Johansson, A.F.; Nalvarte, I. Expression of Sex Hormone Receptor and Immune Response Genes in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells During the Menstrual Cycle. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 721813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falahatian, S.; Haddad, R.; Pakravan, N. Modulatory Effects of R10 Fraction of Garlic (Allium sativum L.) on Hormonal Levels, T Cell Polarization, and Fertility-Related Genes in Mice Model of Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome. J. Ovarian Res. 2022, 15, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodey, B. Thymic Hormones in Cancer Diagnostics and Treatment. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2001, 1, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragin, N.; Bismuth, J.; Cizeron-Clairac, G.; Biferi, M.G.; Berthault, C.; Serraf, A.; Nottin, R.; Klatzmann, D.; Cumano, A.; Barkats, M.; et al. Estrogen-Mediated Downregulation of AIRE Influences Sexual Dimorphism in Autoimmune Diseases. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 1525–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodd, K.C.; Menon, M. Sex bias in lymphocytes: Implications for Autoimmune Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 945762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, G.; Mackay, I.R. The Thymus in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Quantitative Histopathological Analysis and comparison with Stress Involution. BMJ 1967, 2, 475–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonelli, A.; Ferrari, S.M.; Giuggioli, D.; Ferrannini, E.; Ferri, C.; Fallahi, P. Chemokine (C-X-C Motif) Ligand (CXCL)10 in Autoimmune Diseases. Autoimmun. Rev. 2014, 13, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, Q.F.; Kayser, C.; Kallas, E.G.; Andrade, L.E. Decreased Recent Thymus Emigrant Number is Associated with Disease Activity in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. J. Rheumatol. 2008, 35, 1762–1767. [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz, O.M.; Turner, J.E.; Paust, H.J.; Lindner, M.; Peters, A.; Heiss, K.; Velden, J.; Hopfer, H.; Fehr, S.; Krieger, T.; et al. CXCR3 Mediates Renal Th1 and Th17 Immune Response in Murine Lupus Nephritis. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 4693–4704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, N.A.; Wu, L.C.; Burd, C.J.; Friedman, A.K.; Kaffenberger, B.H.; Rajaram, M.V.; Schlesinger, L.S.; James, H.; Shupnik, M.A.; Jarjour, W.N. Estrogen Modulation of Endosome-Associated Toll-Like Receptor 8: An IFNα-Independent Mechanism of Sex-Bias in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Clin. Immunol. 2014, 151, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yuan, J.; Pan, Y.; Fei, Y.; Qiu, X.; Hu, N.; Luo, Y.; Lei, W.; Li, Y.; Long, H.; et al. T cell CD40LG gene expression and the production of IgG by autologous B cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin. Immunol. 2009, 132, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.L.; Yen, J.H.; Chiou, S.S.; Tsai, W.C.; Ou, T.T.; Wu, C.C.; Liu, H.W. Estradiol Upregulates Calcineurin Expression via Overexpression of Estrogen Receptor Alpha Gene in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2011, 27, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Kyttaris, V.C. Interleukin-23 Deficiency Alters Thymic Selection in Lupus-Prone Mice. Lupus 2019, 28, 1007–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, F.; Li, T.; Zhang, K.; Wan, J.; Qi, X. CD4+ B220+ TCRγδ+ T Cells Produce IL-17 in Lupus-Prone MRL/lpr Mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2016, 38, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Cai, W.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Cheng, J.; Wei, F. Immunosenescence of T Cells: A Key Player in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Inflamm. Res. 2022, 71, 1449–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murata, O.; Suzuki, K.; Sugiura, H.; Kondo, Y.; Takeshita, M.; Koga, K.; Takiguchi, M.; Kurisu, R.; Kassai, Y.; Yasuoka, H.; et al. Thymus Variants on Imaging in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis-Clinical and Immunological Significance. Rheumatology 2021, 60, 5595–5600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathak, K. The Expanding Role of IL-7 and Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin as Therapeutic Target for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2014, 18, 581–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, R.; Choi, H.M.; Yang, H.I.; Yoo, M.C.; Park, Y.B.; Kim, K.S. Association Between Serum Thymosin β4 Levels of Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients and Disease Activity and Response to Therapy. Clin. Rheumatol. 2012, 31, 1253–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccia, F.; Guggino, G.; Rizzo, A.; Manzo, A.; Vitolo, B.; La Manna, M.P.; Giardina, G.; Sireci, G.; Dieli, F.; Montecucco, C.M.; et al. Potential Involvement of IL-9 and Th9 Cells in the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheumatology 2015, 54, 2264–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, U.; Schatz, A.; Baerwald, C.; Rossol, M. Brief report: Deficient Thymic Output in Rheumatoid Arthritis Despite Abundance of Prethymic Progenitors. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, 2567–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thewissen, M.; Somers, V.; Venken, K.; Linsen, L.; van Paassen, P.; Geusens, P.; Damoiseaux, J.; Stinissen, P. Analyses of Immunosenescent Markers in Patients with Autoimmune Disease. Clin. Immunol. 2007, 123, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koetz, K.; Bryl, E.; Spickschen, K.; O’Fallon, W.M.; Goronzy, J.J.; Weyand, C.M. T Cell Homeostasis in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 9203–9208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, L.E.; Schuch, J.B.; de Azeredo, L.A.; Baptista, T.S.A.; Motta, J.G.; do Prado, A.D.; Bauer, M.E. Characterization of Senescence Biomarkers in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Relevance to Disease Progression. Clin. Rheumatol. 2019, 38, 2909–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, U.G.; Koetz, K.; Weyand, C.M.; Goronzy, J.J. Perturbation of the T cell repertoire in rheumatoid arthritis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 14447–14452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minato, N.; Hattori, M.; Hamazaki, Y. Physiology and pathology of T-cell aging. Int. Immunol. 2020, 32, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weyand, C.M.; Yang, Z.; Goronzy, J.J. T-cell Aging in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2014, 26, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2023. CA Cancer. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 73, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, B.; Guo, W.; Shi, R.; Hoffman, R.D.; Luo, Q.; Hu, Y.J.; Gao, J. Ruyong Formula Improves Thymus Function of CUMS-Stimulated Breast Cancer Mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 319, 117164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Q.; Zhang, D.W.; Weyand, C.M.; Goronzy, J.J. Mechanisms shaping the naïve T cell repertoire in the Elderly—Thymic Involution or Peripheral Homeostatic Proliferation? Exp. Gerontol. 2014, 54, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prinz, I.; Sandrock, I. Dangerous γδ T Cells in Aged Mice. EMBO Rep. 2019, 20, e48678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.C.; Eling, N.; Martinez-Jimenez, C.P.; O’Brien, L.M.; Carbonaro, V.; Marioni, J.C.; Odom, D.T.; de la Roche, M. IL-7-Dependent Compositional Changes Within the γδ T Cell Pool in Lymph Nodes During Ageing Lead to an Unbalanced Anti-Tumour Response. EMBO Rep. 2019, 20, e47379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.J.; Yang, H.L.; Chang, K.K.; Meng, Y.; Wang, M.Y.; Yuan, M.M.; Li, M.Q.; Xie, F. Human Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin Promotes the Proliferation and Invasion of Cervical Cancer Cells by Downregulating microRNA-132 Expression. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 7910–7916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esslinger, C.W.; Wilson, A.; Sordat, B.; Beermann, F.; Jongeneel, C.V. Abnormal T Lymphocyte Development Induced by Targeted Overexpression of IkappaB Alpha. J. Immunol. 1997, 158, 5075–5078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hettmann, T.; Leiden, J.M. NF-kappa B is required for the positive selection of CD8+ thymocytes. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 5004–5010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Shui, Y.; Xu, X.; He, K.; Yang, F.; Gao, J. Thymic Function Affects Breast Cancer Development and Metastasis by Regulating Expression of Thymus Secretions PTMα and Tβ15b1. Transl. Oncol. 2021, 14, 100980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Dehghani, B.; Magrisso, I.J.; Rick, E.A.; Bonhomme, E.; Cody, D.B.; Elenich, L.A.; Subramanian, S.; Murphy, S.J.; Kelly, M.J.; et al. GPR30 contributes to Estrogen-Induced Thymic Atrophy. Mol. Endocrinol. 2008, 22, 636–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.L.; Toda, K.; Saibara, T.; Zhang, T.; Ono, M.; Iwasaki, S.; Maeda, T.; Okada, T.; Hayashi, Y.; Enzan, H.; et al. Estrogen Deficiency Results in Enhanced Expression of Smoothened of the Hedgehog Signaling in the Thymus and Affects Thymocyte Development. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2002, 2, 823–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berrih-Aknin, S.; Panse, R.L.; Dragin, N. AIRE: A Missing Link to Explain Female Susceptibility to Autoimmune Diseases. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2018, 1412, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.N. Effect of 17B-Estradiol on Expression of LncRNA in Mouse Thymic Epithelial Cells. Master’s Thesis, South China Agricultural University, Guangdong, China, August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, D.G. Sex Difference in Thymus miRNA Expression and miR-16-5p on Proliferation of Thymic Epithelial cells in Mice. Ph.D. Thesis, South China Agricultural University, Guangdong, China, May 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Guo, D.; Ma, Y.; Li, Y. iTRAQ-based proteomic analysis of 17β-Estradiol-induced anti-proliferation and apoptosis in mouse thymic epithelial cells by disturbing ribosomal biogenesis. IUBMB Life 2022, 74, 1094–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, G.; Hou, Y. Thymic Atrophy via Estrogen-Induced Apoptosis is Related to Fas/FasL Pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2004, 4, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.M.; Lai, P.F.; Imami, N.; Johnson, M.R. Progesterone-Related Immune Modulation of Pregnancy and Labor. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón, L.; Boehm, T. Three Chemokine Receptors Cooperatively Regulate Homing of Hematopoietic Progenitors to the Embryonic Mouse Thymus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 7517–7522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balciunaite, G.; Ceredig, R.; Fehling, H.J.; Zúñiga-Pflücker, J.C.; Rolink, A.G. The Role of Notch and IL-7 Signaling in Early Thymocyte Proliferation and Differentiation. Eur. J. Immunol. 2005, 35, 1292–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apavaloaei, A.; Brochu, S.; Dong, M.; Rouette, A.; Hardy, M.P.; Villafano, G.; Murata, S.; Melichar, H.J.; Perreault, C. PSMB11 Orchestrates the Development of CD4 and CD8 Thymocytes via Regulation of Gene Expression in Cortical Thymic Epithelial Cells. J. Immunol. 2019, 202, 966–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gommeaux, J.; Grégoire, C.; Nguessan, P.; Richelme, M.; Malissen, M.; Guerder, S.; Malissen, B.; Carrier, A. Thymus-Specific Serine Protease Regulates Positive Selection of a Subset of CD4+ Thymocytes. Eur. J. Immunol. 2009, 39, 956–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Rohrscheidt, J.; Petrozziello, E.; Nedjic, J.; Federle, C.; Krzyzak, L.; Ploegh, H.L.; Ishido, S.; Steinkasserer, A.; Klein, L. Thymic CD4 T Cell Selection Requires Attenuation of March8-Mediated MHCII Turnover in Cortical Epithelial Cells Through CD83. J. Exp. Med. 2016, 213, 1685–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kincaid, E.Z.; Murata, S.; Tanaka, K.; Rock, K.L. Specialized Proteasome Subunits Have an Essential Role in the Thymic Selection of CD8(+) T Cells. Nat. Immunol. 2016, 17, 938–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, T.; Zhang, N.; Guo, Z.; Chi, F.; Song, Y.; Zhu, X. Wnt4 Signaling is Associated with the Decrease of Proliferation and Increase of Apoptosis During Age-Related Thymic Involution. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 7568–7576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depoërs, L.; Dumont-Lagacé, M.; Trinh, V.Q.; Houques, C.; Côté, C.; Larouche, J.D.; Brochu, S.; Perreault, C. Klf4 Protects Thymus Integrity During Late Pregnancy. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1016378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaba, H.; Morishita, Y.; Tomofuji, Y.; Danks, L.; Nitta, T.; Komatsu, N.; Kodama, T.; Takayanagi, H. Fezf2 Orchestrates a Thymic Program of Self-Antigen Expression for Immune Tolerance. Cell 2015, 163, 975–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolino, M.; Koglgruber, R.; Cronin, S.J.F.; Uribesalgo, I.; Rauscher, E.; Harreiter, J.; Schuster, M.; Bancher-Todesca, D.; Pranjic, B.; Novatchkova, M.; et al. RANK Links Thymic Regulatory T Cells to Fetal Loss and Gestational Diabetes in Pregnancy. Nature 2021, 589, 442–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharova, L.; Sharova, V.; Izvolskaia, M. Mechanisms of Reciprocal Regulation of Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone (GnRH)-Producing and Immune Systems: The Role of GnRH, Cytokines and Their Receptors in Early Ontogenesis in Normal and Pathological Conditions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 22, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharova, L.A.; Malyukova, I.V.; Adamskaya, E.I.; Kuznetsova, T.A.; Shishkina, I.V. Luteinizing Hormone-Releasing Hormone in Thymus and Hypothalamus of Rat Fetuses: Suppressing Effect of Antagonist and of Antibodies on Concanavalin A-Induced Proliferation of Thymocytes. Biochemistry 2000, 65, 1135–1139. [Google Scholar]
- Marchetti, B.; Gallo, F.; Farinella, Z.; Tirolo, C.; Testa, N.; Romeo, C.; Morale, M.C. Luteinizing Hormone-Releasing Hormone is a Primary Signaling Molecule in the Neuroimmune Network. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1998, 840, 205–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, N.; LaPaglia, N.; Agrawal, L.; Steiner, J.; Uddin, S.; Williams, D.W.; Lawrence, A.M.; Emanuele, N.V. The Role of Gonadectomy and Testosterone Replacement on Thymic Luteinizing Hormone-Releasing Hormone Production. J. Endocrinol. 1998, 158, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakharova, L.A.; Potapova, A.A.; Maliukova, I.V.; Proshliakova, E.V.; Ugriumov, M.V. Effect of the Hypothalamo-Hypophyseal Part of Neuroendocrine System on Con A-Induced Proliferation of the Thymocytes from Rat Fetuses. Dokl. Akad. Nauk. 1997, 357, 269–271. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Velardi, E.; Tsai, J.J.; Holland, A.M.; Wertheimer, T.; Yu, V.W.; Zakrzewski, J.L.; Tuckett, A.Z.; Singer, N.V.; West, M.L.; Smith, O.M.; et al. Sex Steroid Blockade Enhances Thymopoiesis by Modulating Notch Signaling. J. Exp. Med. 2014, 211, 2341–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melnikova, V.I.; Lifantseva, N.V.; Voronova, S.N.; Zakharova, L.A. Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone in Regulation of Thymic Development in Rats: Profile of Thymic Cytokines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Yang, Y.; Wang, L.; Jia, X.; Lu, T.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, L.; Gao, Y. Follistatin-Like 1 Deficiency Impairs T Cell Development to Promote Lung Metastasis of Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Aging 2021, 13, 7211–7227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, D.W.; Shen, G.K.; Ulrich, E.D.; Steiner, L.L.; Parrish, P.R.; Zukoski, C.F. Human Thymocytes Express a Prolactin-Like Messenger Ribonucleic Acid and Synthesize Bioactive Prolactin-Like Proteins. Endocrinology 1992, 131, 3019–3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dardenne, M.; Kelly, P.A.; Bach, J.F.; Savino, W. Identification and Functional Activity of Prolactin Receptors in Thymic Epithelial Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 9700–9704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreño, P.C.; Sacedón, R.; Jiménez, E.; Vicente, A.; Zapata, A.G. Prolactin Affects Both Survival and Differentiation of T-Cell Progenitors. J. Neuroimmunol. 2005, 160, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, N.V.C.; Porto, F.L.; CA, D.E.M.; Santos Reis, M.D.D.; Smaniotto, S.; Lins, M.P. CXCL12-Driven Thymocyte Migration is Increased by Thymic Epithelial Cells Treated with Prolactin In Vitro. J. Biosci. 2021, 46, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepletier, A.; de Carvalho, V.F.; Rodrigues e Silva, P.M.; Villar, S.; Pérez, A.R.; Savino, W.; Morrot, A. Trypanosoma Cruzi Disrupts Thymic Homeostasis by Altering Intrathymic and Systemic Stress-Related Endocrine Circuitries. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, N.; Thellin, O.; Buckley, D.J.; Horseman, N.D.; Buckley, A.R. Prolactin Suppresses Glucocorticoid-Induced Thymocyte Apoptosis In Vivo. Endocrinology 2003, 144, 2102–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Recher, S.; Raccurt, M.; Lambert, A.; Lobie, P.E.; Mertani, H.C.; Morel, G. Prenatal and Adult Growth Hormone Gene Expression in Rat Lymphoid Organs. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2001, 49, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weigent, D.A.; Blalock, J.E. Production of Peptide Hormones and Neurotransmitters by the Immune System. In Neuroimmunoendocrinology; Blalock, J.E., Birmigham, A., Eds.; Chemical Immunology; Kargers: Basel, Switzerland, 1997; Volume 69, pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, M.; Veneziani, L.P.; Porto, F.L.; Lins, M.P.; Mendes-da-Cruz, D.A.; Savino, W. Intrathymic Somatotropic Circuitry: Consequences upon Thymus Involution. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1108630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, W.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, J.; Tang, Q.; Ozawa, A.; VanHoy, R.; Arkins, S.; Dantzer, R.; Kelley, K.W. The Immune-Endocrine Loop During Aging: Role of Growth Hormone and Insulin-Like Growth Factor-I. Neuroimmunomodulation 1999, 6, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorshkind, K.; Horseman, N.D. The Roles of Prolactin, Growth Hormone, Insulin-Like Growth Factor-I, and Thyroid Hormones in Lymphocyte Development and Function: Insights from Genetic Models of Hormone and Hormone Receptor Deficiency. Endocr. Rev. 2000, 21, 292–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woody, M.A.; Welniak, L.A.; Richards, S.; Taub, D.D.; Tian, Z.; Sun, R.; Longo, D.L.; Murphy, W.J. Use of Neuroendocrine Hormones to Promote Reconstitution After Bone Marrow Transplantation. Neuroimmunomodulation 1999, 6, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dardenne, M.; Mello-Coelho, V.; Gagnerault, M.C.; Postel-Vinay, M.C. Growth Hormone Receptors and Immunocompetent Cells. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1998, 840, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savino, W.; Smaniotto, S.; Binart, N.; Postel-Vinay, M.C.; Dardenne, M. In Vivo Effects of Growth Hormone on Thymic Cells. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2003, 992, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savino, W. Neuroendocrine Control of T Cell Development in Mammals: Role of Growth Hormone in Modulating Thymocyte Migration. Exp. Physiol. 2007, 92, 813–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, T.J.; Kim, J.W.; Yoon, J.S.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, K.M. The Anti-Apoptotic Effect of Ghrelin on Restraint Stress-Induced Thymus Atrophy in Mice. Immune Netw. 2016, 16, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lins, M.P.; de Araújo Vieira, L.F.; Rosa, A.A.; Smaniotto, S. Growth Hormone in the Presence of Laminin Modulates Interaction of Human Thymic Epithelial Cells and Thymocytes In Vitro. Biol. Res. 2016, 49, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, S.; Chen, L.; Okret, S.; Jondal, M. Age-Related Synthesis of Glucocorticoids in Thymocytes. Exp. Cell Res. 2008, 314, 3027–3035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taves, M.D.; Mittelstadt, P.R.; Presman, D.M.; Hager, G.L.; Ashwell, J.D. Single-Cell Resolution and Quantitation of Targeted Glucocorticoid Delivery in the Thymus. Cell Rep. 2019, 26, 3629–3642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J.J. Glucocorticoid-Induced Apoptosis in the Thymus. Semin. Immunol. 1992, 4, 363–369. [Google Scholar]
- Prenek, L.; Litvai, T.; Balázs, N.; Kugyelka, R.; Boldizsár, F.; Najbauer, J.; Németh, P.; Berki, T. Regulatory T Cells Are Less Sensitive to Glucocorticoid Hormone Induced Apoptosis than CD4+ T Cells. Apoptosis 2020, 25, 715–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, N.J.; Viselli, S.M.; Fan, J.; Kovacs, W.J. Androgens Accelerate Thymocyte Apoptosis. Endocrinology 1998, 139, 748–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, J.S.; Goldberg, G.L.; Hammett, M.V.; Uldrich, A.P.; Berzins, S.P.; Heng, T.S.; Blazar, B.R.; Millar, J.L.; Malin, M.A.; Chidgey, A.P.; et al. Activation of Thymic Regeneration in Mice and Humans Following Androgen Blockade. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 2741–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelmson, A.S.; Rodriguez, M.L.; Johansson, I.; Eriksson, E.S.; Stubelius, A.; Lindgren, S.; Fagman, J.B.; Fink, P.J.; Carlsten, H.; Ekwall, O.; et al. Androgen Receptors in Epithelial Cells Regulate Thymopoiesis and Recent Thymic Emigrants in Male Mice. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, K.M.; Lucas, P.J.; Bare, C.V.; Wang, J.; Chu, Y.W.; Tayler, E.; Kapoor, V.; Gress, R.E. CCL25 Increases Thymopoiesis After Androgen Withdrawal. Blood 2008, 112, 3255–3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matre, V.; Høvring, P.I.; Fjeldheim, A.K.; Helgeland, L.; Orvain, C.; Andersson, K.B.; Gautvik, K.M.; Gabrielsen, O.S. The Human Neuroendocrine Thyrotropin-Releasing Hormone Receptor Promoter is Activated by the Haematopoietic Transcription Factor c-Myb. Biochem. J. 2003, 372, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.K.; Yeh, C.L.; Chen, Y.L.; Wang, S.C.; Cheng, R.H.; Kao, P.F. The Frequency and Spectrum of Thymus 2-[Fluorine-18] Fluoro-2-Deoxy-D-Glucose Uptake Patterns in Hyperthyroidism Patients. Acad. Radiol. 2011, 18, 1292–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa-Verde, D.M.; Defresne, M.P.; Vannier-dos-Santos, M.A.; Dussault, J.H.; Boniver, J.; Savino, W. Identification of Nuclear Triiodothyronine Receptors in the Thymic Epithelium. Endocrinology 1992, 131, 1313–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro-Carvalho, M.M.; Farias-de-Oliveira, D.A.; Villa-Verde, D.M.; Savino, W. Triiodothyronine Modulates Extracellular Matrix-Mediated Interactions Between Thymocytes and Thymic Microenvironmental Cells. Neuroimmunomodulation 2002, 10, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro-Carvalho, M.M.; Lima-Quaresma, K.R.F.; Mouço, T.; Carvalho, V.F.; Mello-Coelho, V.; Savino, W. Triiodothyronine Modulates Thymocyte Migration. Scand. J. Immunol. 2007, 66, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Weerd, K.; van Hagen, P.M.; Schrijver, B.; Heuvelmans, S.J.; Hofland, L.J.; Swagemakers, S.M.; Bogers, A.J.; Dik, W.A.; Visser, T.J.; van Dongen, J.J.; et al. Thyrotropin Acts as a T-Cell Developmental Factor in Mice and Humans. Thyroid 2014, 24, 1051–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, S.V.; Salama, C.; Renovato-Martins, M.; Helal-Neto, E.; Citelli, M.; Savino, W.; Barja-Fidalgo, C. Increased Leptin Response and Inhibition of Apoptosis in Thymocytes of Young Rats Offspring from Protein Deprived Dams During Lactation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruver, A.L.; Ventevogel, M.S.; Sempowski, G.D. Leptin Receptor is Expressed in Thymus Medulla and Leptin Protects Against Thymic Remodeling During Endotoxemia-Induced Thymus Involution. J. Endocrinol. 2009, 203, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Ye, Y.; Qi, J.; Tan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Li, Y. Age and Sex Differences in microRNAs Expression During the Process of Thymus Aging. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2017, 49, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venables, T.; Griffith, A.V.; DeAraujo, A.; Petrie, H.T. Dynamic Changes in Epithelial Cell Morphology Control Thymic Organ Size During Atrophy and Regeneration. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Aili, A.; Sun, X.; Pang, X.; Ge, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, R. Th1 Biased Progressive Autoimmunity in Aged Aire-Deficient Mice Accelerated Thymic Epithelial Cell Senescence. Aging Dis. 2019, 10, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.T.; Feng, Y.K.; Cao, J.H.; Li, J.H.; Yuan, S.L.; Ding, Y.; Chai, Y.R. Dosage Effects of resveratrol on Thymus Involution in D-Galactose-Treated Mice. J. Food. Biochem. 2021, 45, e13709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.H.; Wei, T.T.; Guo, L.; Cao, J.H.; Feng, Y.K.; Guo, S.N.; Liu, G.H.; Ding, Y.; Chai, Y.R. Curcumin Protects Thymus Against D-Galactose-Induced Senescence in Mice. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2021, 394, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, A.V.; Swami, S.; Feldman, D. Vitamin D and breast cancer: Inhibition of Estrogen Synthesis and Signaling. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 121, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artusa, P.; Yamamoto, L.N.; Barbier, C.; Valbon, S.F.; Habashi, Y.A.; Djambazian, H.; Ismailova, A.; Lebel, M.; Salehi-Tabar, R.; Sarmadi, F.; et al. Skewed Epithelial Cell Differentiation and Premature Aging of the Thymus in the Absence of Vitamin D Signaling. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eadm9582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Hormone | Cell Type | Action | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Estrogen | mTEC | Reduces the expression of Aire in mTECs and TRAs and inhibits T cell negative selection; induces overexpressing of miR-16-5p and downregulates cyclinB1 and IGFBP3 in mTECs | [82,84,86] |
| Progesterone | cTEC mTEC | Influences Klf4 to maintain cTEC numbers; affects the expression of FoxN1, potentially synergizing with Wnt4; upregulates Aire expression in mTECs | [37,96,97] |
| Luteinizing hormone releasing hormone | cTEC | ModulatesDLL4 expression in the Notch pathway | [105] |
| Follistatin | mTEC | Inhibits activin A signaling, resulting in impaired TEPC and mTEC differentiation | [13] |
| Prolactin | mTEC | Enhances the chemotactic effect of CXCL12, while also influencing F-actin polymerization in mTECs | [111] |
| Growth hormone | cTEC, mTEC | TECs are regulated by increased cytokines (IL-1α, IL-1β, and IL-6) and secretion of the chemokine CXCL12, as well as the thymus hormone thymosin | [122] |
| Glucocorticoid | mTEC | Targets CD4+CD8+TCRhigh cells to promote positive selection | [126] |
| Thyroid hormone | cTEC mTEC | Affects the expression of DP and SP cell subsets | [138] |
| Androgen | cTEC | Suppresses cTEC expression of DLL4 and IL-7; influences thymocyte expression of Notch target genes | [105] |
| Leptin | mTEC | Promotes the proliferation of DN thymocytes; regulates IL-7 in mTECs | [140] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, M.; Shu, Y.; Gao, J. Thymus Degeneration in Women and the Influence of Female Sexual Hormones on Thymic Epithelial Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3014. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073014
Zhou M, Shu Y, Gao J. Thymus Degeneration in Women and the Influence of Female Sexual Hormones on Thymic Epithelial Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(7):3014. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073014
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Meiru, Yaoying Shu, and Jianli Gao. 2025. "Thymus Degeneration in Women and the Influence of Female Sexual Hormones on Thymic Epithelial Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 7: 3014. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073014
APA StyleZhou, M., Shu, Y., & Gao, J. (2025). Thymus Degeneration in Women and the Influence of Female Sexual Hormones on Thymic Epithelial Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(7), 3014. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073014






