The First Report on the Structure of Polysaccharide Surface Antigens of the Clinical Klebsiella oxytoca 0.062 Strain and the Contribution in the Serological Cross-Reactions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
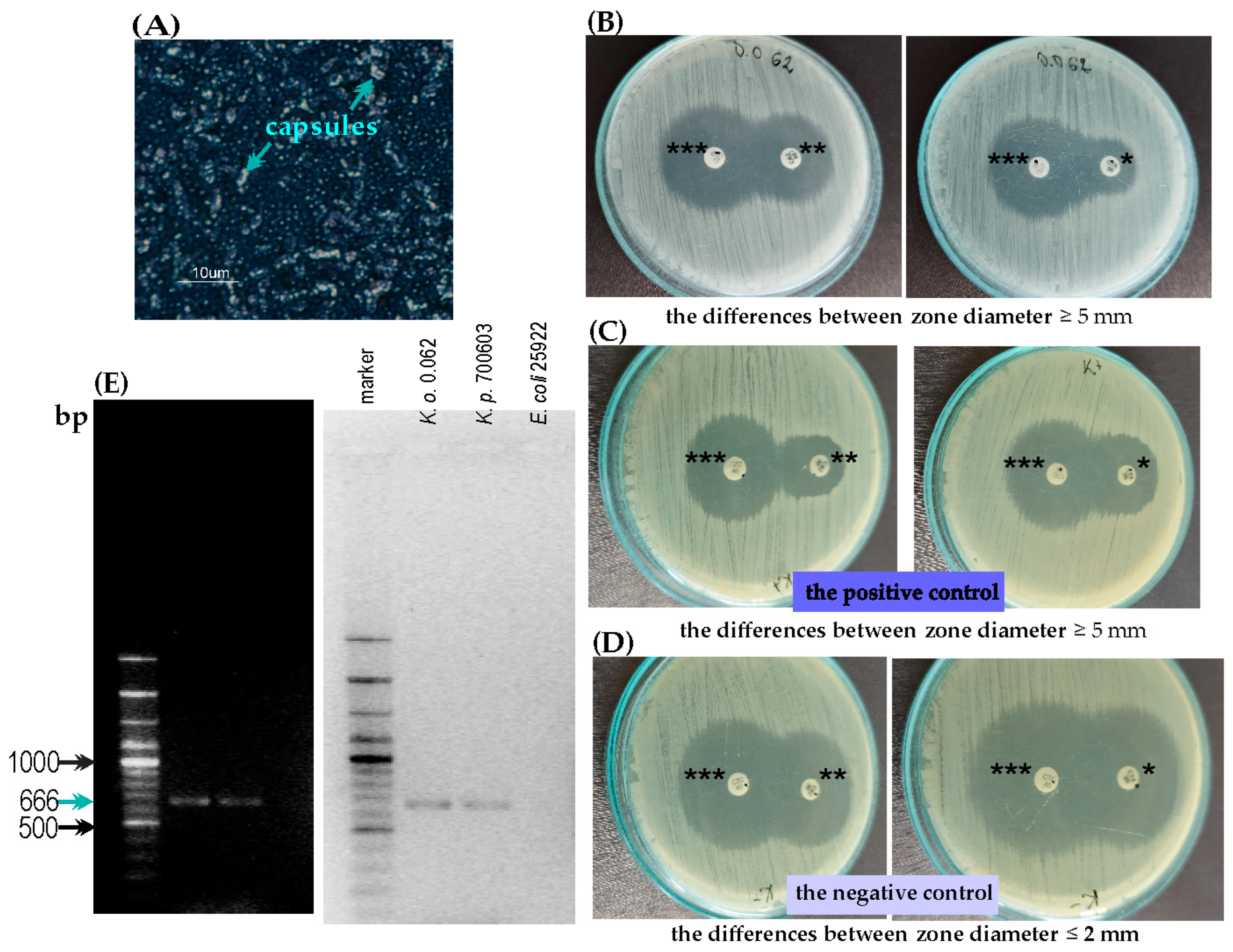
2.1. Characterization of K. oxytoca 0.062 Strain
2.1.1. The String Test and Maneval’s Staining
2.1.2. The Antibiotic Susceptibility Pattern and ESBL Detection
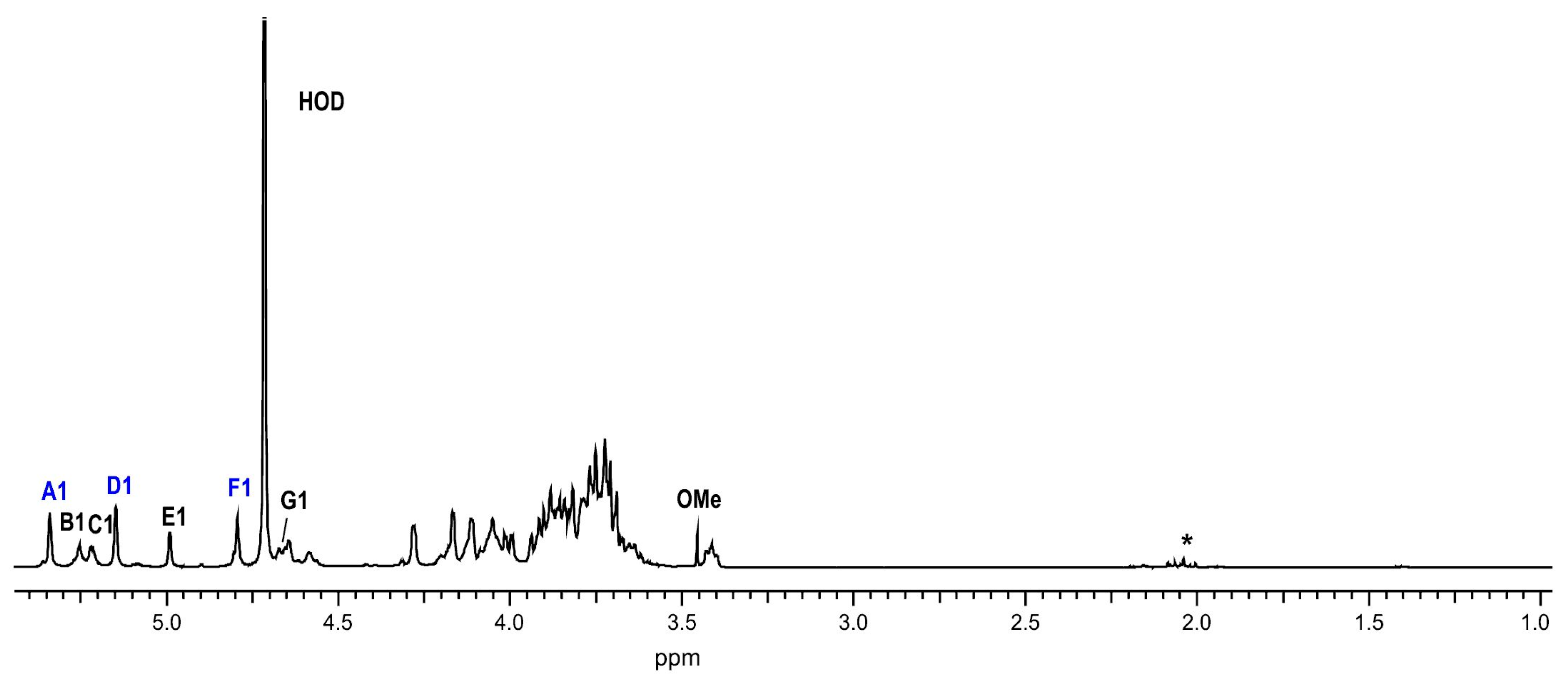
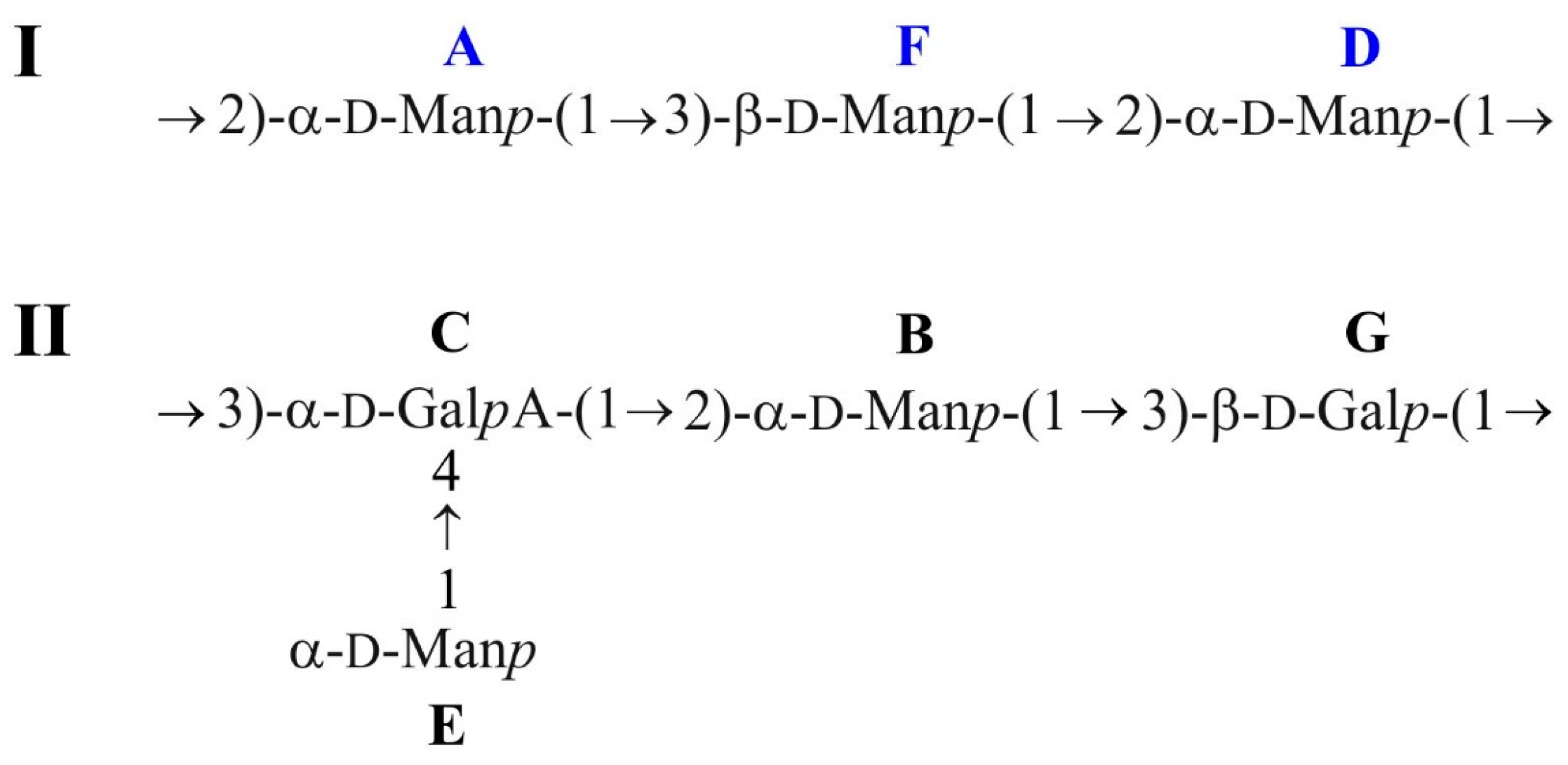
2.2. Structural Studies of O-Polysaccharide (OPS)
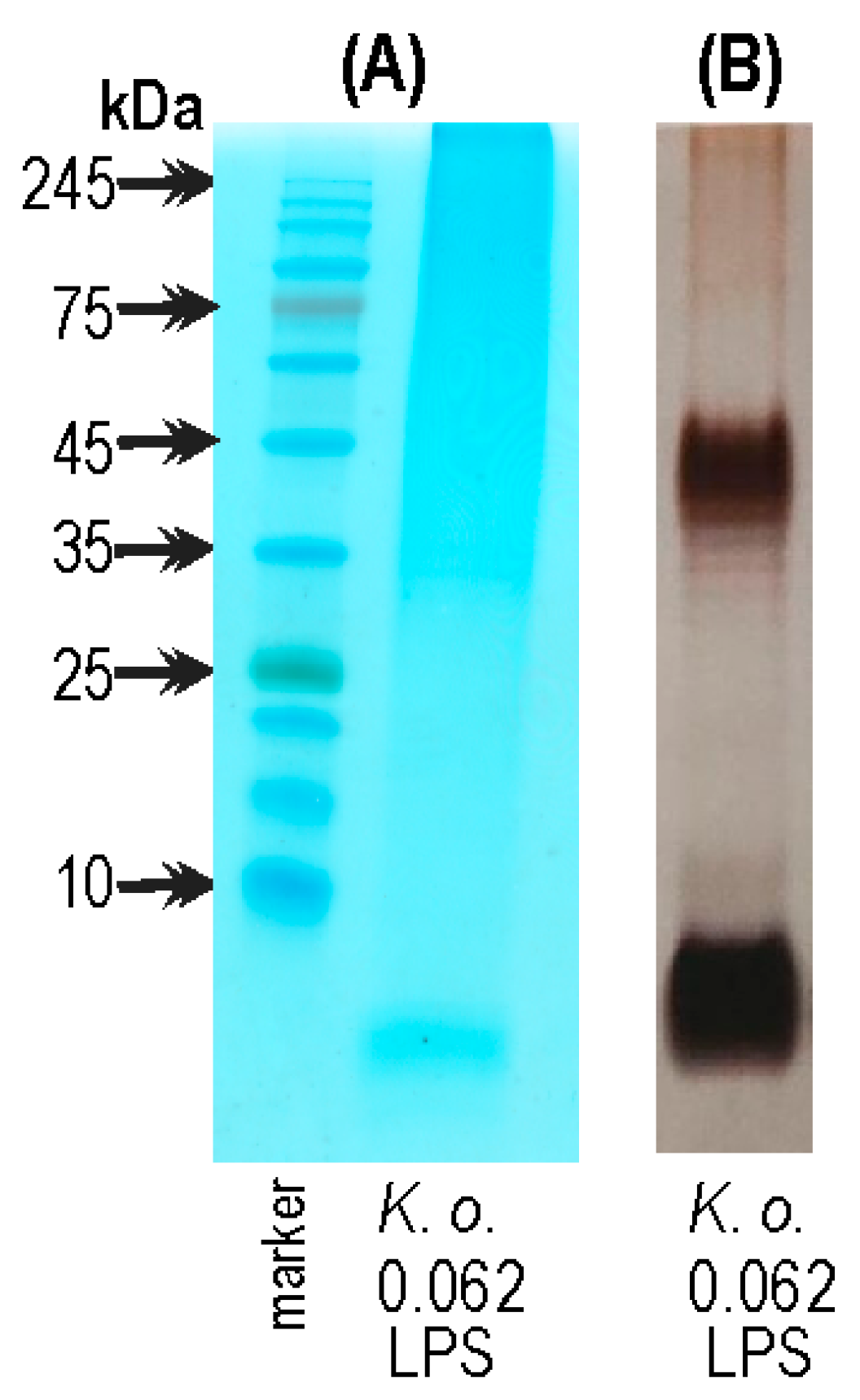
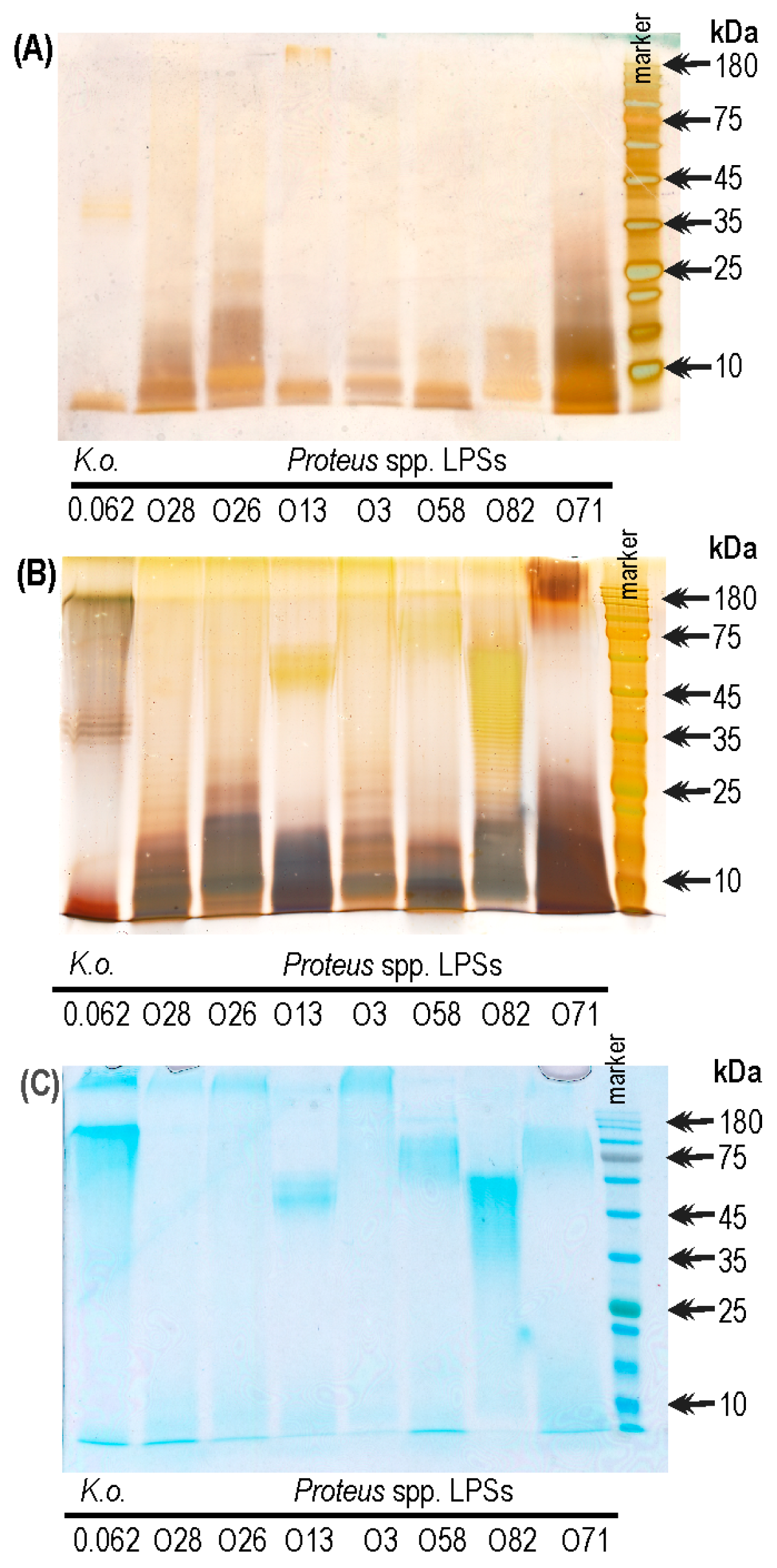
2.3. The Electrophoretic Pattern of K. oxytoca 0.062 LPS in Alcian Blue/Silver Staining Method
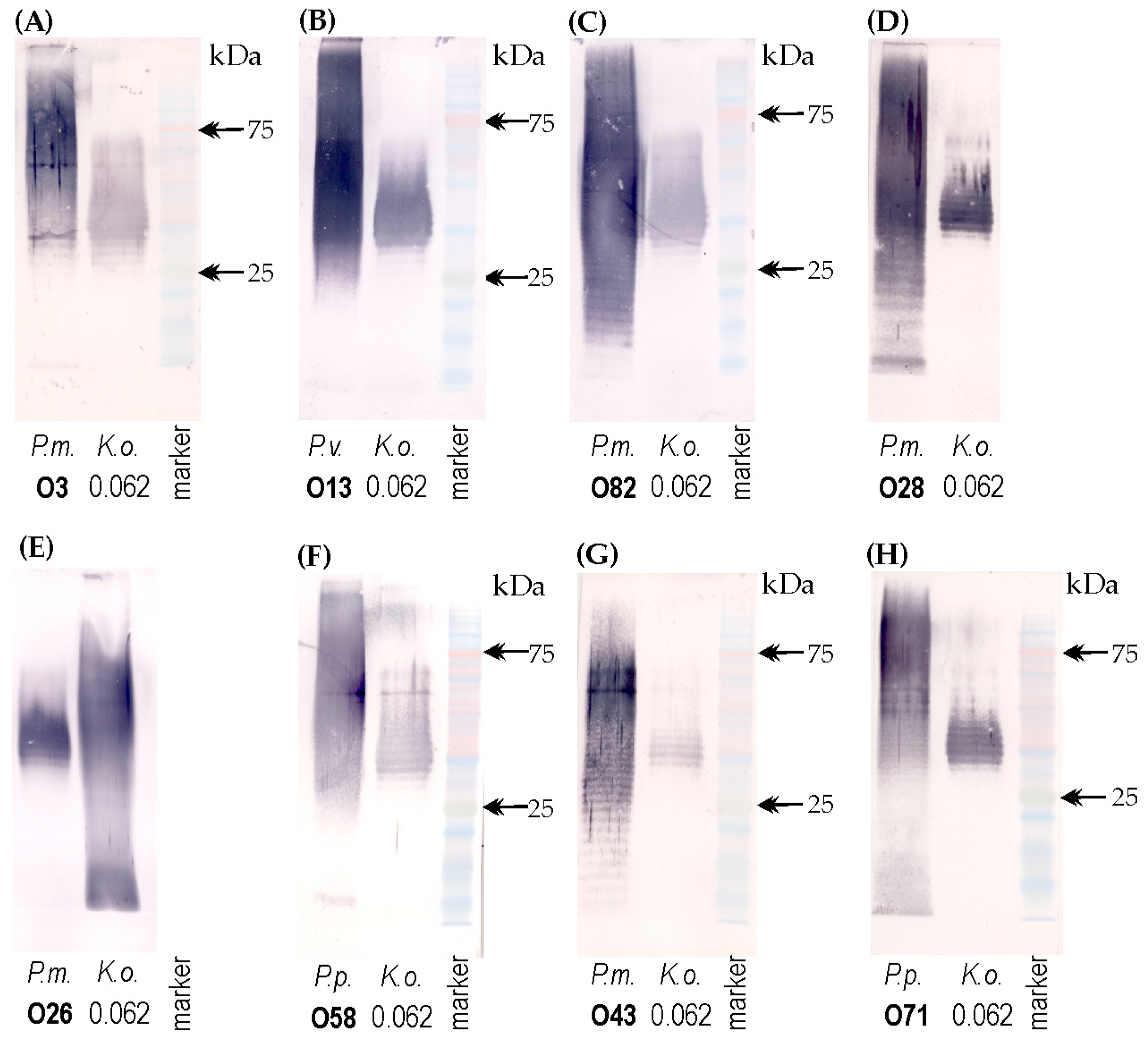
2.4. Serological Studies
2.5. The Electrophoretic Pattern of Cross-Reacting Proteus spp. LPSs in Combined Alcian Blue/Silver Staining Method
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains
4.2. The Capsule Staining and the String Test
4.3. Antibiotic Susceptibility
4.4. Determination of ESBL Phenotype
4.5. Determination of ESBL Genotype
4.6. The LPS Extraction
4.7. Degradation of LPS and Isolation of the Polysaccharide Fraction
4.8. Analytical Procedures
4.9. NMR Spectroscopy
4.10. SDS-PAGE Electrophoresis, Western Blotting, and Silver-Staining Procedures
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ATCC | American Type Culture Collection |
| CAZ | Ceftazidime |
| CDT | Combination Disk Test |
| CPS | Capsular Polysaccharide |
| CTX | Cefoxitin |
| D-GalNAc | N-acetyl-D-galactosamine |
| D-Gal | D-Galactose |
| D-GlcA | D-glucuronic acid |
| D-GlcNAc | N-acetyl-D-glucosamine |
| ESBL | Extended-Spectrum β-lactamases |
| EUCAST | European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing |
| D-GalA | D-Galacturonic Acid |
| Galp | Galactopyranose |
| GLC-MS | Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry |
| L-Lys | L-Lysine |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| L-Thr | L-Threonine |
| L-Rha | L-Rhamnose |
| L-Ser | L-Serine |
| Manp | Mannopyranose |
| MDR | Multidrug Resistant |
| MIC | Minimal Inhibitory Concentration |
| NMR | Nuclear Magnetic Resonance |
| OPS | O-polysaccharide |
| PAGE | Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis |
| PCR | Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| R-Cet-L-Lys | Nε-[(R)-1-Carboxyethyl]-L-lysine |
| Rha | Rhamnose |
| (S)-Lac | (S)-Lactic acid [(S)-2-hydroxypropanoic acid] |
References
- Yang, J.; Long, H.; Hu, Y.; Feng, Y.; McNally, A.; Zong, Z. Klebsiella oxytoca complex: Update on taxonomy, antimicrobial resistance, and virulence. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2022, 35, e00006-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibu, P.; McCuaig, F.; McCartney, A.L.; Kujawska, M.; Hall, L.J.; Hoyles, L. Improved molecular characterization of the Klebsiella oxytoca complex reveals the prevalence of the kleboxymycin biosynthetic gene cluster. Microb. Genom. 2021, 7, 000592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, J.; Judd, L.M.; Jenney, A.; Holt, K.E.; Wyres, K.L.; Hawkey, J. Epidemiology and genomic analysis of Klebsiella oxytoca from a single hospital network in Australia. BMC Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moradigaravand, D.; Martin, V.; Peacock, S.J.; Parkhill, J. Population structure of multidrug-resistant Klebsiella oxytoca within hospitals across the United Kingdom and Ireland identifies sharing of virulence and resistance genes with K. pneumoniae. Genome Biol. Evol. 2017, 9, 574–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palusiak, A. Proteus mirabilis and Klebsiella pneumoniae as pathogens capable of causing co-infections and exhibiting similarities in their virulence factors. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 991657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regué, M.; Izquierdo, L.; Fresno, S.; Piqué, N.; Corsaro, M.M.; Naldi, T.; De Castro, C.; Waidelich, D.; Merino, S.; Tomás, J.M. A second outer-core region in Klebsiella pneumoniae lipopolysaccharide. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 4198–4206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knirel, Y.A. Structure of O-antigens. In Bacterial Lipopolysaccharides; Knirel, Y.A., Valvano, M.A., Eds.; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 2011; pp. 41–115. [Google Scholar]
- Knirel, Y.A.; Perepelov, A.V.; Kondakova, A.N.; Senchenkova, S.N.; Sidorczyk, Z.; Rozalski, A.; Kaca, W. Structure and serology of O-antigens as the basis for classification of Proteus strains. Innate. Immun. 2011, 17, 70–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palusiak, A. The antigens contributing to the serological cross-reactions of Proteus antisera with Klebsiella representatives. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 64, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palusiak, A. The contribution of polysaccharide antigens from clinical Proteus spp. and Klebsiella spp. isolates to the serological cross-reactions. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 707578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artyszuk, D.; Jachymek, W.; Izdebski, R.; Gniadkowski, M.; Lukasiewicz, J. The OL101 O antigen locus specifies a novel Klebsiella pneumoniae serotype O13 structure. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 326, 121581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drzewiecka, D.; Levina, E.A.; Shashkov, A.S.; Kalinchuk, N.A.; Knirel, Y.A. Structural and serological characterization of yet another new O antigen, O86, in Proteus mirabilis clinical strains. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 13642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osbelt, L.; Wende, M.; Almási, É.; Derksen, E.; Muthukumarasamy, U.; Lesker, T.R.; Galvez, E.J.C.; Pils, M.C.; Schalk, E.; Chhatwal, P.; et al. Klebsiella oxytoca causes colonization resistance against multidrug-resistant K. pneumoniae in the gut via cooperative carbohydrate competition. Cell Host Microbe 2021, 29, 1663–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipkind, G.M.; Shashkov, A.S.; Knirel, Y.A.; Vinogradov, E.V.; Kochetkov, N.K. A computer-assisted structural analysis of regular polysaccharides on the basis of 13C-N.M.R. data. Carbohydr. Res. 1988, 175, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shashkov, A.S.; Lipkind, G.M.; Knirel, Y.A.; Kochetkov, N.K. Stereochemical factors determining the effects of glycosylation on the 13C chemical shifts in carbohydrates. Magn. Reson. Chem. 1988, 26, 735–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLean, L.L.; Webb, A.C.; Perry, M.B. Structural elucidation of the O-antigenic polysaccharide from enterohemorrhagic (EHEC) Escherichia coli O48:H21. Carbohydr. Res. 2006, 341, 2543–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, K.; Pedersen, C. Carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of monosaccharides. Adv. Carbohydr. Chem. Biochem. 1983, 41, 27–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansson, P.-E.; Kenne, L.; Widmalm, G. Computer-assisted structural analysis of polysaccharides with an extended version of casper using 1H- and 13C-n.m.r. data. Carbohydr. Res. 1989, 188, 169–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigida, E.N.; Shashkov, A.S.; Zdorovenko, E.L.; Konnova, S.A.; Fedonenko, Y.P. Structure of the O-specific polysaccharide from Azospirillum formosense CC-Nfb-7(T). Carbohydr. Res. 2020, 494, 108060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipkind, G.M.; Shashkov, A.S.; Mamyan, S.S.; Kochetkov, N.K. The Nuclear Overhauser effect and structural factors de-termining the conformations of disaccharide glycosides. Carbohydr. Res. 1988, 181, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinogradov, E.; Frirdich, E.; MacLean, L.L.; Perry, M.B.; Petersen, B.O.; Duus, J.Ø.; Whitfield, C. Structures of lipopolysaccharides from Klebsiella pneumoniae. Elucidation of the structure of the linkage region between core and polysaccharide O chain and identification of the residues at the non-reducing termini of the O chains. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 25070–25081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EUCAST. EUCAST Guidelines for Detection of Resistance Mechanisms and Specific Resistances of Clinical and/or Epidemiological Importance; EUCAST: Växjö, Sweden, 2013; pp. 1–40. Available online: https://www.eucast.org/resistance_mechanisms (accessed on 11 December 2013).
- Kim, M.H.; Lee, H.J.; Park, K.S.; Suh, J.T. Molecular Characteristics of Extended Spectrum β-Lactamases in Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae and the prevalence of qnr in Extended Spectrum β-Lactamase isolates in a Tertiary Care Hospital in Korea. Yonsei Med. J. 2010, 51, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazemian, H.; Heidari, H.; Ghanavati, R.; Ghafourian, S.; Yazdani, F.; Sadeghifard, N.; Valadbeigi, H.; Maleki, A.; Pakzad, I. Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of ESBL-, AmpC-, and carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae and Escherichia coli isolates. Med. Princ. Pract. 2019, 28, 547–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, S.M.; Abd El-Aziz, A.M.; Hassan, R.; Abdelmegeed, E.S. β-lactam resistance associated with β-lactamase production and porin alteration in clinical isolates of E. coli and K. pneumoniae. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0251594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akenten, C.W.; Khan, N.A.; Mbwana, J.; Krumkamp, R.; Fosu, D.; Paintsil, E.K.; Boahen, K.G.; Osei-Mensa, J.; Maiga-Ascofare, O.; May, J.; et al. Carriage of ESBL-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae and Escherichia coli among children in rural Ghana: A cross-sectional study. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2023, 12, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensor, V.M.; Livermore, D.M.; Hawkey, P.M. A novel reverse-line hybridization assay for identifying genotypes of CTX-M-type extended-spectrum β-lactamases. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2007, 59, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunstan, R.A.; Bamert, R.S.; Belousoff, M.J.; Short, F.L.; Barlow, C.K.; Pickard, D.J.; Wilksch, J.J.; Schittenhelm, R.B.; Strugnell, R.A.; Dougan, G.; et al. Mechanistic insights into the capsule-targeting depolymerase from a Klebsiella pneumoniae bacteriophage. Microbiol. Spectr. 2021, 9, e01023-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, T.; Chen, L.; Du, H. Virulence factors in hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 642484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaszowska, M.; Majkowska-Skrobek, G.; Markwitz, P.; Lood, C.; Jachymek, W.; Maciejewska, A.; Lukasiewicz, J.; Drulis-Kawa, Z. The mutation in wbaP cps gene cluster selected by phage-borne depolymerase abolishes capsule production and diminishes the virulence of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galván, E.M.; Mateyca, C.; Ielpi, L. Role of interspecies interactions in dual-species biofilms developed In vitro by uropathogens isolated from polymicrobial urinary catheter-associated bacteriuria. Biofouling 2016, 32, 1067–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macleod, S.M.; Stickler, D.J. Species interactions in mixedcommunity crystalline biofilms on urinary catheters. J. Med. Microbiol. 2007, 56, 1549–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Guard-Petter, J.; Asokan, K.; Hughes, C.; Carlson, R.W. The structure of the colony migration factor from pathogenic Proteus mirabilis. A capsular polysaccharide that facilitates swarming. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 22993–22998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, S.D.; Ovchinnikova, O.G.; Müller, F.; Steffen, M.; Braun, M.; Sweeney, R.P.; Kowarik, M.; Follador, R.; Lowary, T.L.; Serventi, F.; et al. Identification of a second glycoform of the clinically prevalent O1 antigen from Klebsiella pneumoniae. Microbiology 2023, 120, e2301302120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parolis, H.; Parolis, L.A.S.; Stanley, S.M.R. The use of bacteriophage-mediated depolymerisation in the structural investigation of the capsular polysaccharide from Escherichia coli serotype K36. Carbohydr. Res. 1988, 175, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palusiak, A.; Maciejewska, A.; Ługowski, C.; Różalski, A. The amide of galacturonic acid with lysine as an immunodominant component of the lipopolysaccharide core region from Proteus penneri 42 strain. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2014, 61, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siwińska, M.; Levina, E.A.; Shashkov, A.S.; Kalinchuk, N.A.; Drzewiecka, D.; Knirel, Y.A. Structural and serological characterization of the O82 antigen of a Proteus mirabilis strain isolated from a patient in Poland. Carbohydr. Res. 2019, 486, 107831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fresno, S.; Jiménez, N.; Izquierdo, L.; Merino, S.; Corsaro, M.M.; De Castro, C.; Parrilli, M.; TNaldi, T.; Regué, M.; Tomás, J.M. The ionic interaction of Klebsiella pneumoniae K2 capsule and core lipopolysaccharide. Microbiology 2006, 152, 1807–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenmenger, E.F.; Emmanuel Guajardo, E.; Finch, N.; Atmar, R.L.; Zaven Sargsyan, Z. ‘String Test’ for hypermucoviscous Klebsiella pneumoniae. Am. J. Med. 2021, 134, 520–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maneval, W.E. Staining bacteria and yeasts with acid dyes. Stain. Technol. 1941, 16, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Breakpoint Tables for Interpretation of MICs and Zone Diameters; Version 14.0; The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing: Växjö, Sweden, 2024; Available online: http://www.eucast.org (accessed on 1 January 2024).
- M100 Clinical and Laboratory Standard Institute. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 30th ed.; M100 Clinical and Laboratory Standard Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2020; Available online: https://www.nih.org.pk (accessed on 10 January 2020).
- Westphal, O.; Jann, K. Bacterial lipopolysaccharides. Extraction with phenol-water and further applications of the procedure. Methods Carbohydr. Chem. 1965, 5, 83–89. [Google Scholar]
- Kurzylewska, M.; Turska-Szewczuk, A.; Dworaczek, K.; Bomba, A.; Drzewiecka, D.; Pękala-Safińska, A. Immunochemical studies and gene cluster relationships of closely related O-antigens of Aeromonas hydrophila Pt679, Aeromonas popoffii A4, and Aeromonas sobria K928 strains classified into the PGO1 serogroup dominant in Polish aquaculture of carp and rainbow trout. Carbohydr. Res. 2023, 531, 108896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciucanu, I.; Kerek, F. A simple and rapid method for the permethylation of carbohydrates. Carbohydr. Res. 1984, 131, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leontein, K.; Lindberg, B.; Lönngren, J. Assignment of absolute configuration of sugars by g.l.c. of their acetylated glycosides formed from chiral alcohols. Carbohydr. Res 1978, 62, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.M.; Frasch, C.E. A Sensitive silver-stain for detecting lipopolysaccharide in polyacrylamide gels. Anal. Biochem. 1982, 119, 115–119. [Google Scholar]
- Møller, H.J.; Poulsen, J.H. Improved method for silver staining of glycoproteins in thin sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gels. Anal. Biochem. 1995, 226, 371–374. [Google Scholar]



| The Strain | Norfloxacin | Amoxicillin/ Clavulanic Acid | Ampicillin | Cephalothin | Cefuroxim | Trimethoprim/ Sulfametoxazole | Nitrofurantoin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E. coli ATCC 25922 | 0.5 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| K. oxytoca 0.062 | 1 | 16 | >512 | >512 | >512 | >512 | 16 |
| Sugar Residue | Unit | H-1 C-1 | H-2 C-2 | H-3 C-3 | H-4 C-4 | H-5 C-5 | H-6 C-6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| →2)-α-D-Manp-(1→ 1JC,H = 175 Hz; 3JH1,H2 = ~2 Hz | A | 5.34 101.9 | 4.12 79.7 | 4.01 71.3 | 3.71 68.2 | 3.75 74.5 | 3.76; 3.88 62.2 |
| →2)-α-D-Manp-(1→ 1JC,H = 175 Hz; 3JH1,H2 = ~2 Hz | B | 5.25 95.8 | 4.05 81.2 | 4.05 71.5 | 3.73 67.8 | 3.87 73.9 | 3.82; 3.92 62.0 |
| →3,4)-α-D-GalpA-(→ 1JC,H = 174 Hz; 3JH1,H2 = ~3.5 Hz | C | 5.22 102.1 | 4.08 69.2 | 4.18 78.2 | 4.64 79.1 | 4.58 72.1 | – 175.1 |
| →2)-α-D-Manp-(1→ 1JC,H =174 Hz; 3JH1,H2 = ~2 Hz | D | 5.15 101.2 | 4.28 78.2 | 3.87 70.9 | 3.72 68.1 | 3.77 74.5 | 3.82; 3.92 61.9 |
| T-α-D-Manp3OMe-(1→ 1JC,H = 174 Hz, 3JH1,H2 = ~2 Hz | E’ | 5.15 103.6 | 4.32 67.0 | 3.61 81.0 | 3.71 67.6 | 3.75 74.2 | 3.76; 61.9 |
| T-α-D-Manp-(1→ 1JC,H = 174 Hz; 3JH1,H2 = ~2 Hz | E | 4.99 101.4 | 3.88 71.4 | 3.84 71.3 | 3.70 67.9 | 4.06 73.8 | 3.79; 3.90 62.1 |
| →3)-β-D-Manp-(1→ 1JC,H = 163 Hz; 3JH1,H2 = ~2 Hz | F | 4.79 99.5 | 4.17 71.8 | 3.73 81.5 | 3.71 67.4 | 3.41 77.3 | 3.75; 3.93 62.2 |
| →3)-β-D-Galp-(1→ 1JC,H = 161 Hz; 3JH1,H2 = 8 Hz | G | 4.66 105.6 | 3.63 70.9 | 3.74 77.6 | 4.13 65.6 | 3.66 76.2 | 3.75;3.84 62.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Palusiak, A.; Turska-Szewczuk, A. The First Report on the Structure of Polysaccharide Surface Antigens of the Clinical Klebsiella oxytoca 0.062 Strain and the Contribution in the Serological Cross-Reactions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3177. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073177
Palusiak A, Turska-Szewczuk A. The First Report on the Structure of Polysaccharide Surface Antigens of the Clinical Klebsiella oxytoca 0.062 Strain and the Contribution in the Serological Cross-Reactions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(7):3177. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073177
Chicago/Turabian StylePalusiak, Agata, and Anna Turska-Szewczuk. 2025. "The First Report on the Structure of Polysaccharide Surface Antigens of the Clinical Klebsiella oxytoca 0.062 Strain and the Contribution in the Serological Cross-Reactions" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 7: 3177. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073177
APA StylePalusiak, A., & Turska-Szewczuk, A. (2025). The First Report on the Structure of Polysaccharide Surface Antigens of the Clinical Klebsiella oxytoca 0.062 Strain and the Contribution in the Serological Cross-Reactions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(7), 3177. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073177








