Lidocaine Modulates Cytokine Production and Reprograms the Tumor Immune Microenvironment to Enhance Anti-Tumor Immune Responses in Gastric Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
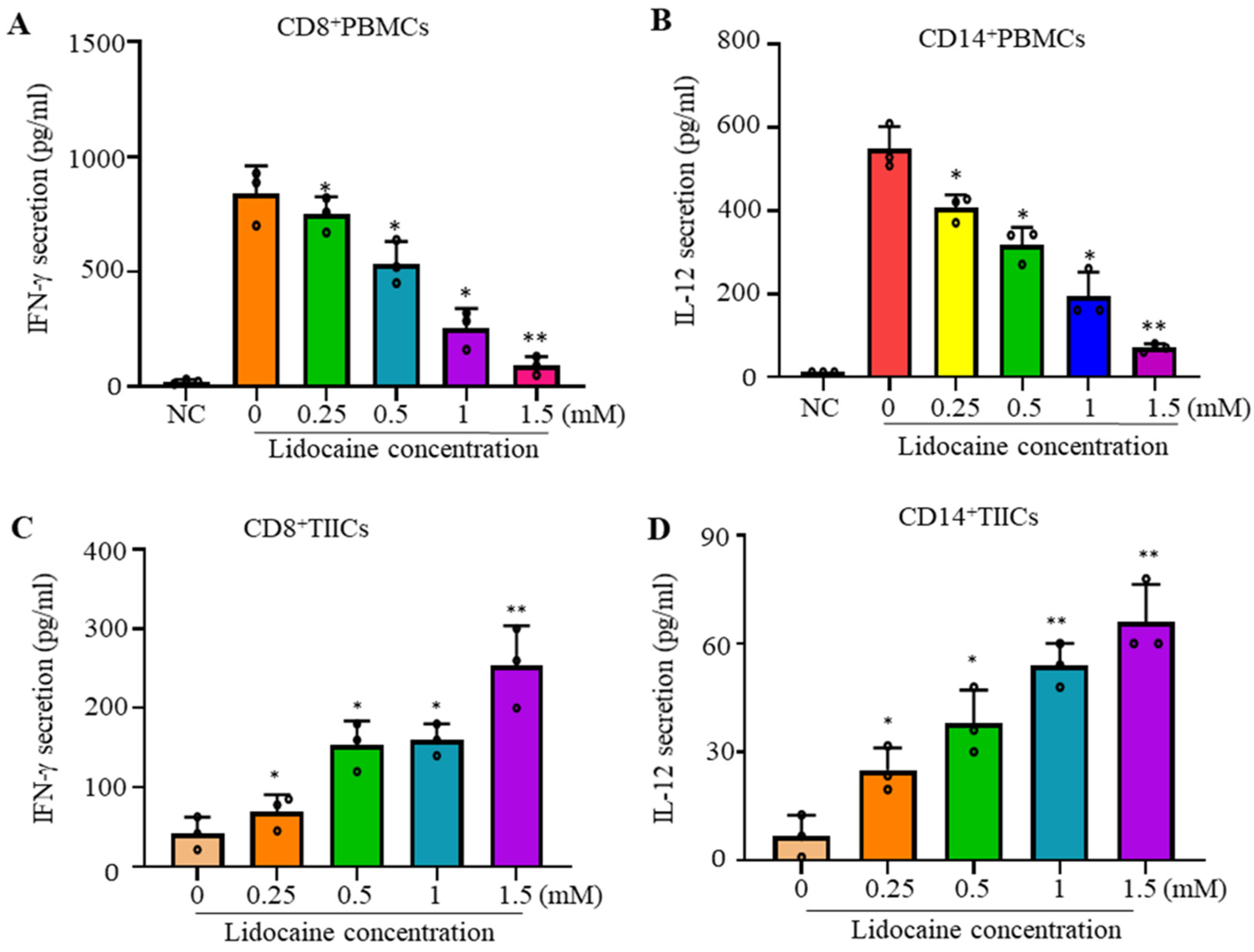
2.1. Lidocaine Inhibits IFN-γProduction by Sorted CD8+PBMCs and IL-12 Production by Sorted CD14+PBMCs
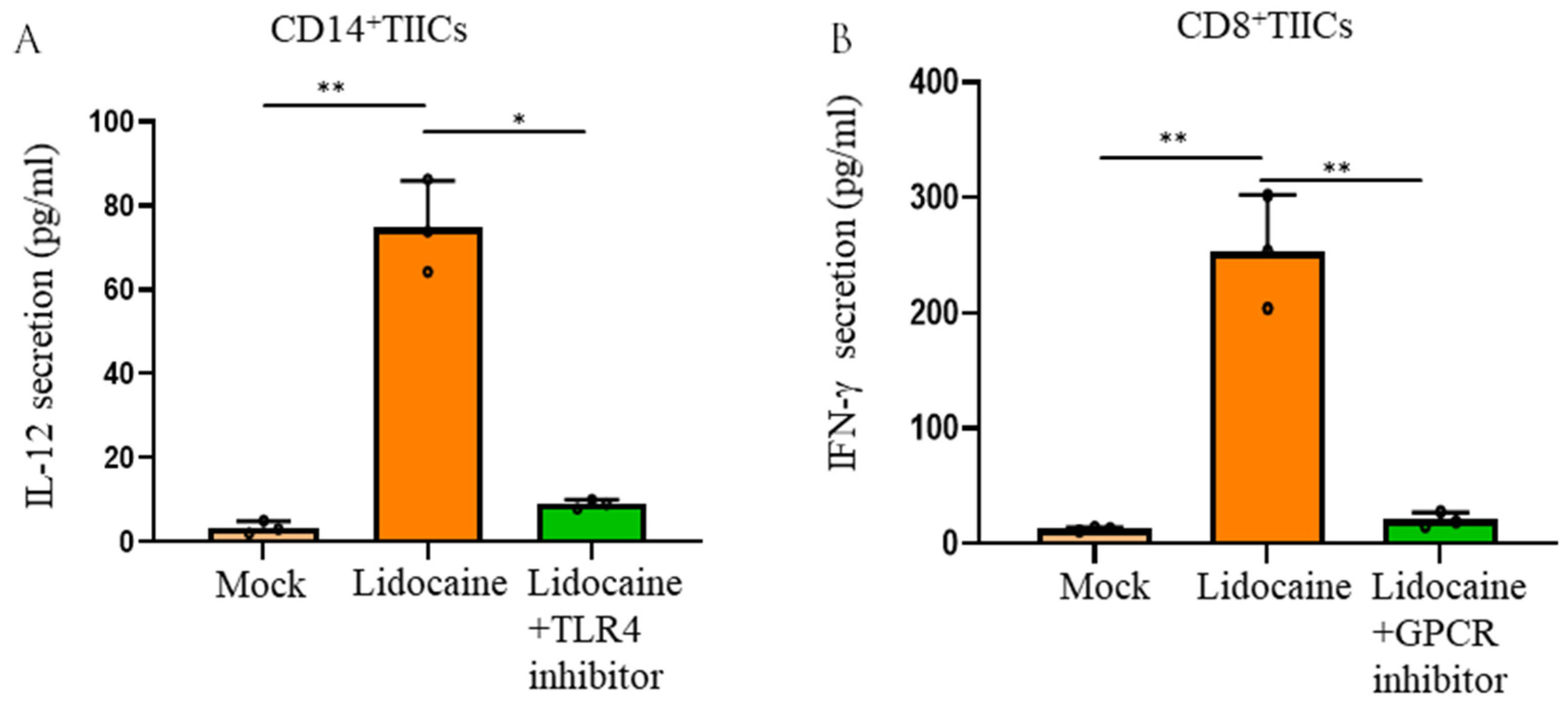
2.2. Lidocaine Increases the Anti-Cancer-Related Cytokines IFN-γ by Sorted CD8+ TIICs and IL-12 by Sorted CD14+ TIICs
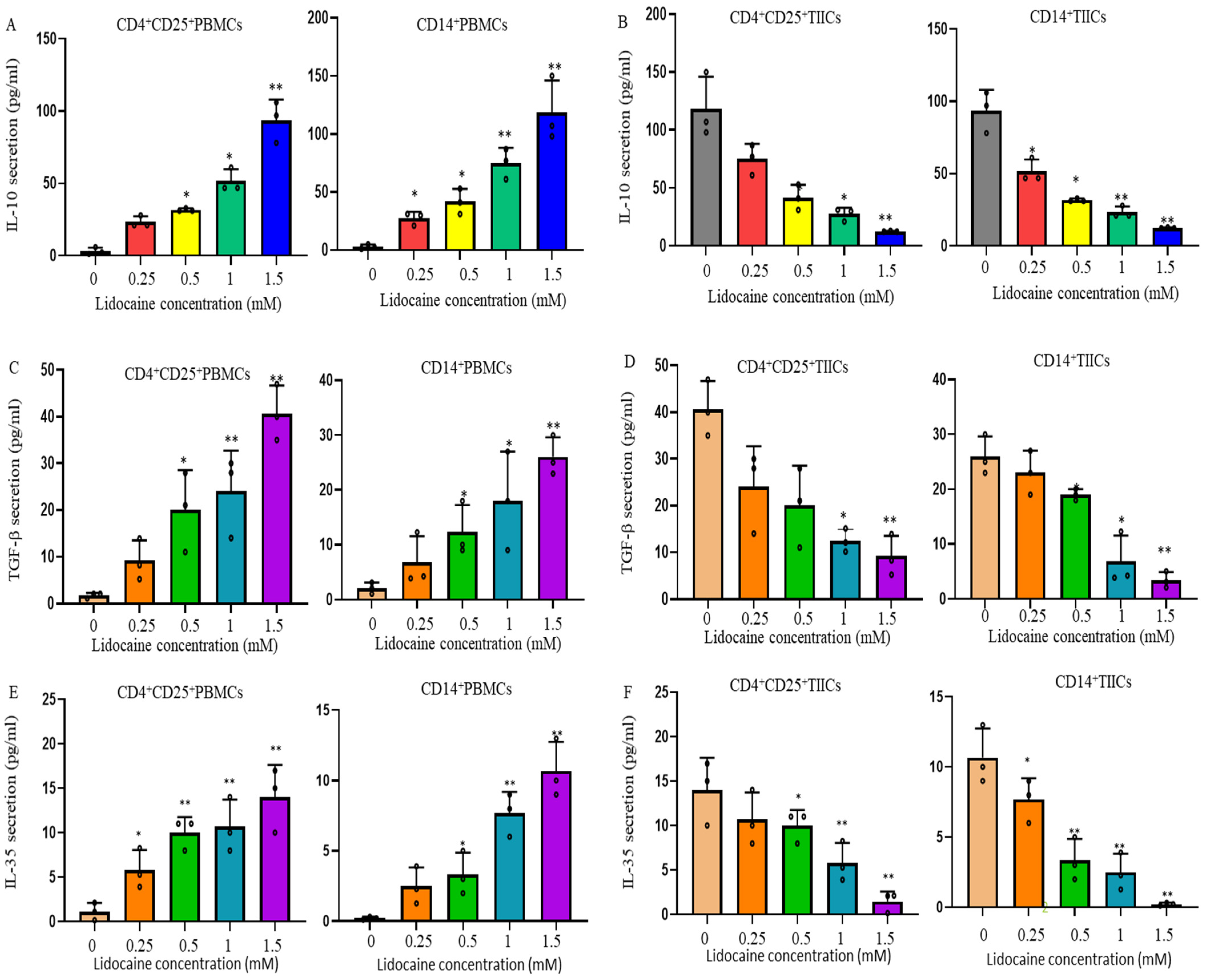
2.3. Lidocaine Increases the Production of Anti-Inflammatory Cytokine IL-10 by Sorted CD4+CD25+PBMCs and Sorted CD14+PBMCs
2.4. Lidocaine Increases the Secretion of the Treg-Related Cytokine TGF-β by CD4+CD25+ Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells (PBMCs) and the M2 Macrophage-Associated Cytokine TGF-β by CD14+ PBMCs
2.5. Lidocaine Increases a Novel Immunomodulator Cytokine IL-35 by Sorted CD4+CD25+PBMCs and Sorted CD14+PBMCs
2.6. Lidocaine Does Not Affect the Viability of Sorted CD4+CD25+, CD8+, and CD14+ PBMCs
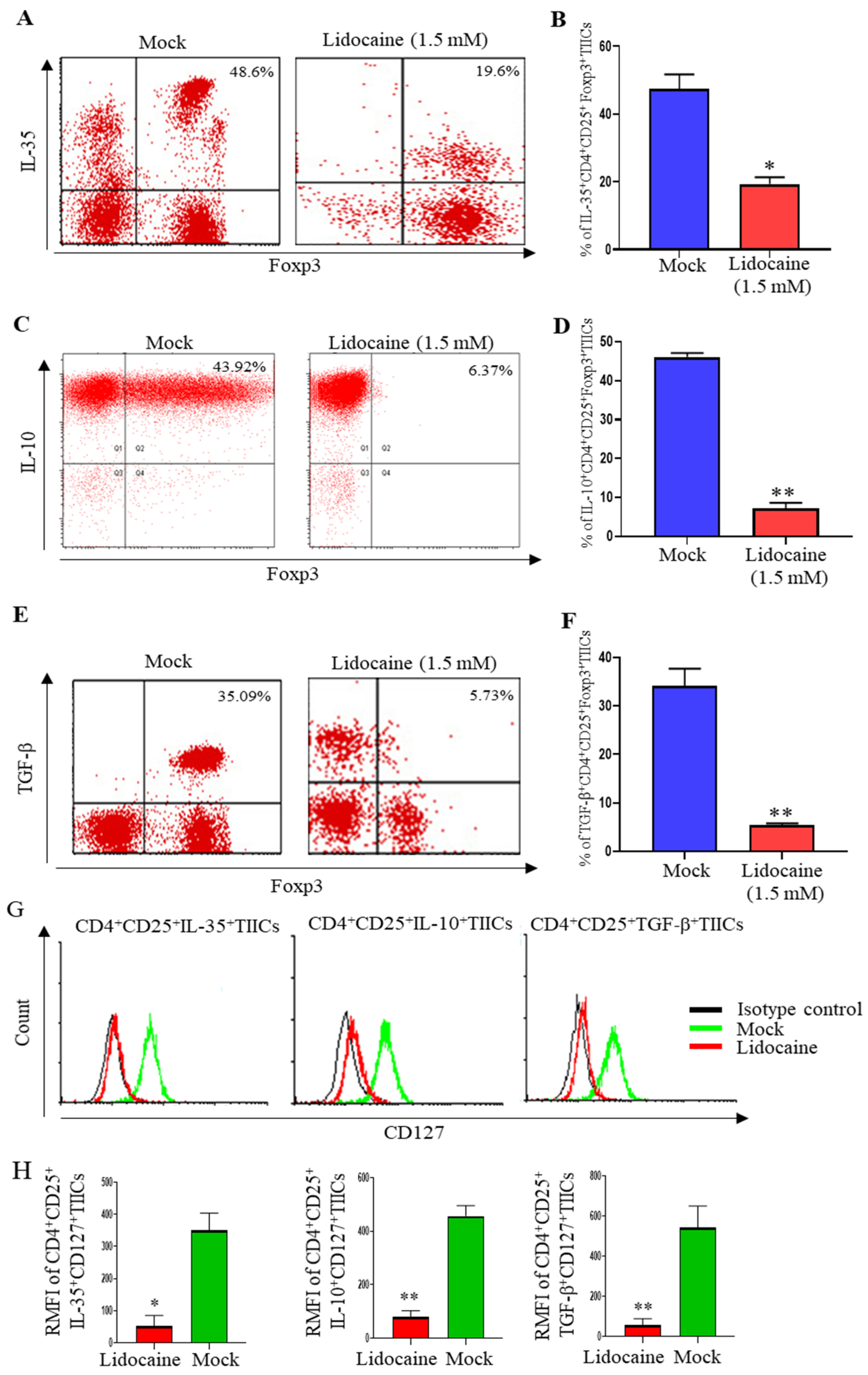
2.7. Lidocaine Inhibits IL-10, TGF-β, and IL-35 Production by Sorted CD4+CD25+ and Sorted CD14+TIICs
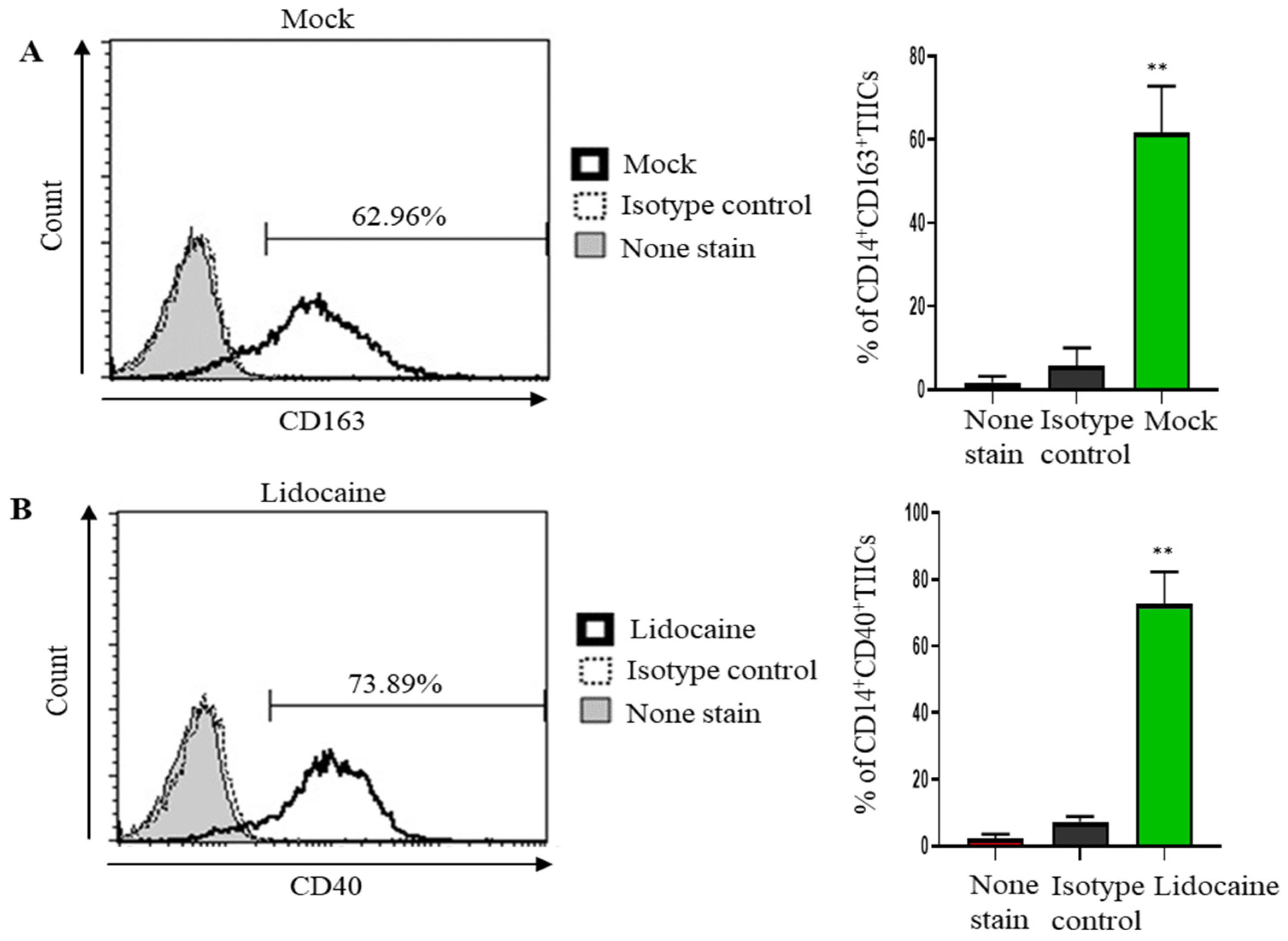
2.8. Lidocaine May Modulate Macrophage Polarization, Promoting a Pro-Inflammatory and Potentially Anti-Tumor Immune Environment
2.9. Lidocaine Enhances the Production of the Anti-Cancer-Related Cytokine IFN-γ by Sorted CD8+ TIICs Through G-Protein-Coupled Receptor (GPCR) Signaling and Increases IL-12 Production by Sorted CD14+ TIICs by the TLR4 Signaling Pathway
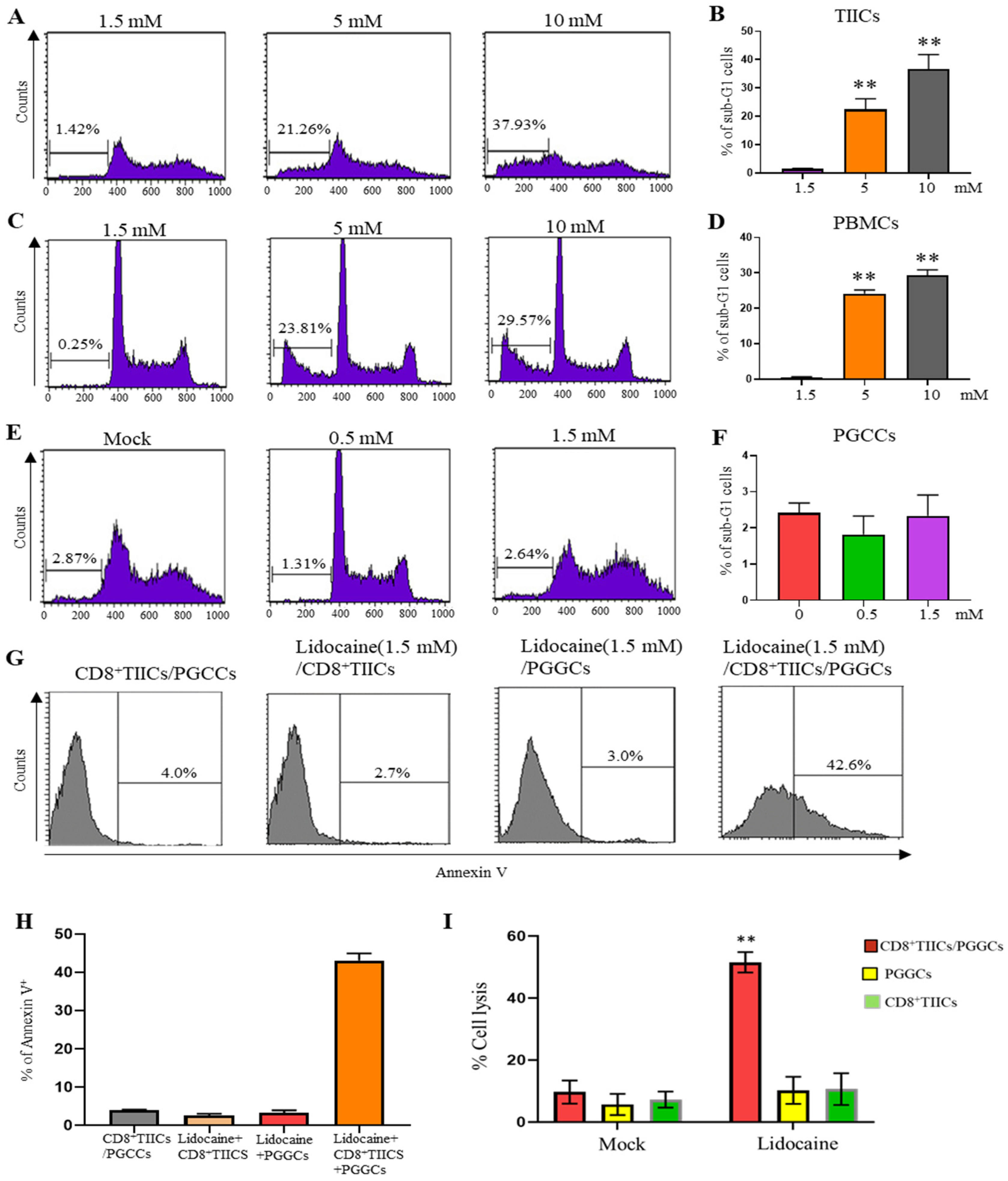
2.10. Lidocaine Does Not Affect the Viability of Sorted CD4+CD25+, CD8+, and CD14+ TIICs
2.11. Lidocaine Inhibits IL-10, TGF-β and IL-35 Production by the High Levels of FoxP3+ but Low Levels of CD127+CD4+CD25+ TIICs
2.12. A Significant Decrease in PD-1 and Significant Increase IFN-γ Expression Was Observed in Lidocaine-Treated CD8+ TIICs Through the NF-κB Signaling Pathway
2.13. Lidocaine Does Not Affect the Viability of Sorted GRN+ Primary Gastric Cancer Cells
2.14. Lidocaine Enhances the Cytotoxic Activity of CD8+ TIICs Against Primary Gastric Cancer Cells
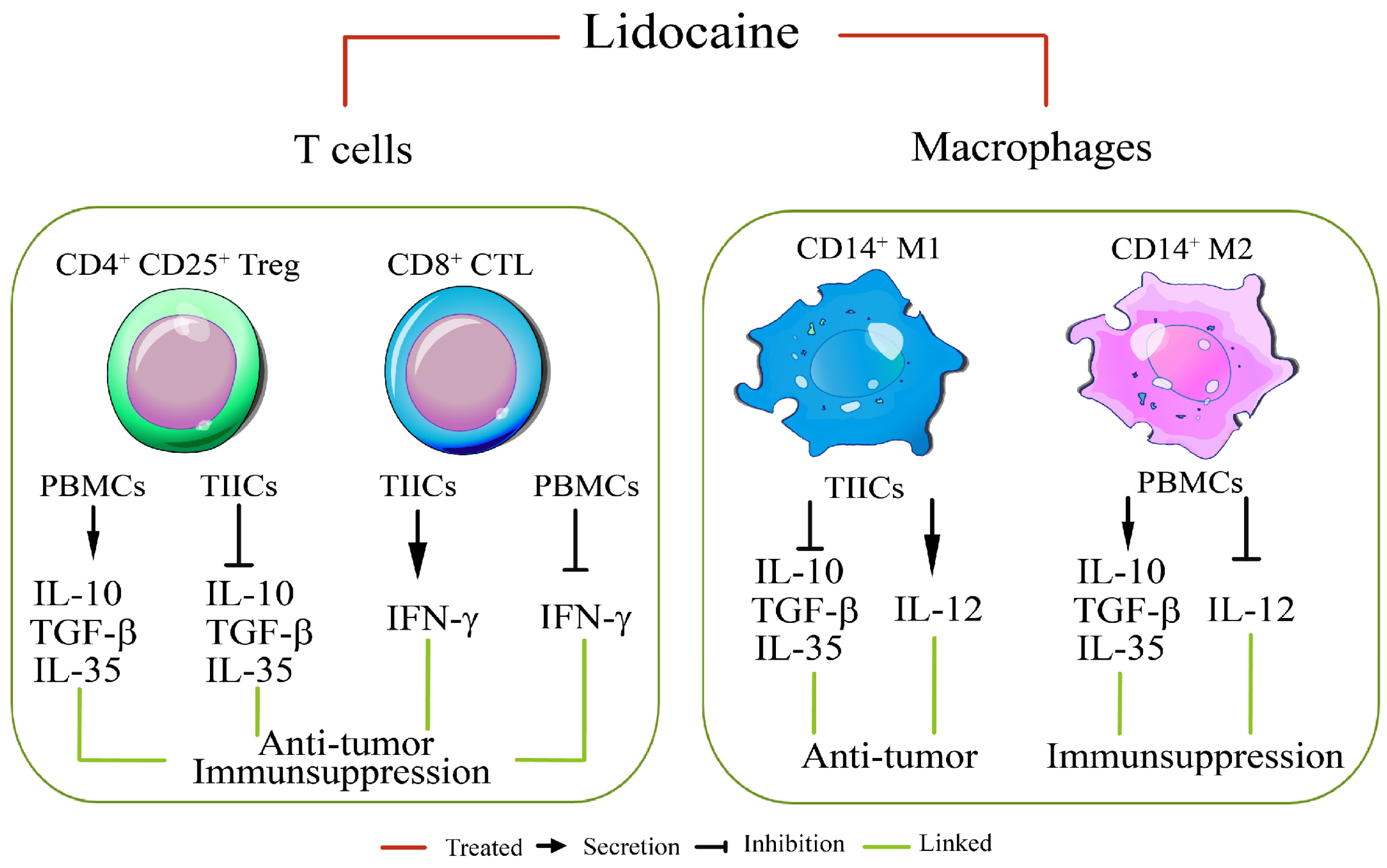
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Isolation and Culture of PBMCs from Healthy Adult Volunteers
4.2. Reagents and Antibodies
4.3. Isolation of a Mixed Population Single Cells (Including TIICs and PGCCs) from Gastric Cancer Patients
4.4. PGCCs and TIICs Culture from Fresh Surgical Malignant Gastric Tissues
4.5. Sorting of CD8+ Cells, CD4+CD25+ Cells, CD14+ Cells, and GRN+ PGCCs
4.6. Human CD8+, CD4+CD25+, CD14+PBMCs’ and CD8+, CD4+CD25+, CD14+ TIICs’ Viability
4.7. CD8+ Primary T Cells and CD14+ Primary Macrophage Activation
4.8. Analysis of Cytokines by ELISA
4.9. Foxp3 Staining and Intracellular Cytokine Staining
4.10. Detection of PD-1+ Analysis of TIICs by Flow Cytometry
4.11. Apoptosis Assays
4.12. Detection of Cytotoxicity of CD8+TIICs and PGCCs
4.13. Lidocaine-Treated CD8+TIICs’ Mediated Cytotoxicity Assay Using Time-Resolved Fluorometry
4.14. Statistical Analysis
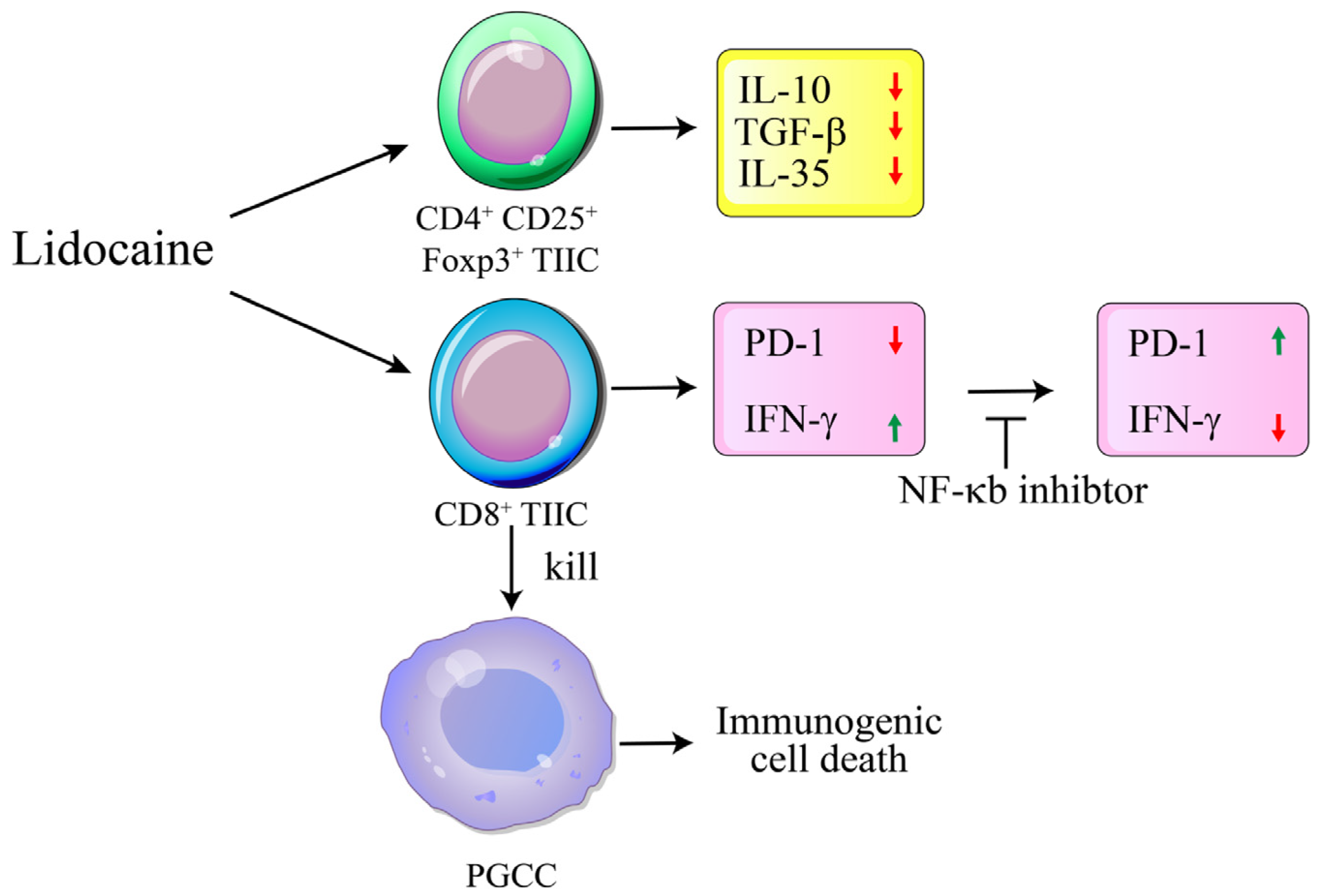
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Loftus, J.P.; Williams, J.M.; Belknap, J.K.; Black, S.J. In Vivo Priming and Ex Vivo Activation of Equine Neutrophils in Black Walnut Extract-induced Equine Laminitis is Not Attenuated by Systemic Lidocaine Administration. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2010, 138, 60–69. [Google Scholar]
- Renzi, P.M.; Ginns, L.C. Effect of Lidocaine on Natural Killer Activity: Rapid Inhibition of Lysis. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 1990, 12, 417–437. [Google Scholar]
- Elizagaray, M.L.; Mazitelli, I.; Pontoriero, A.; Baumeister, E.; Docena, G.; Raimondi, C.; Correger, E.; Rumbo, M. Lidocaine Reinforces the Anti-inflammatory Action of Dexamethasone on Myeloid and Epithelial Cells Activated by Inflammatory Cytokines or SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Biomed. J. 2023, 46, 81–92. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, G.; Liu, S.; Wang, G.L.; Liu, G.J. Lidocaine Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-induced Acute Lung Injury Through Inhibiting NF-kappaB Activation. Pharmacology 2008, 81, 32–40. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.; Sun, Y. Lidocaine Inhibits Proliferation and Metastasis of Lung Cancer Cell via Regulation of MiR-539/EGFR Axis. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 2866–2874. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.J.; Ding, Y.B.; Ma, P.L.; Jiang, S.H.; Li, K.Z.; Li, M.C.; Shi, C.X.; Du, J.; Zhou, H.D. The Protective Effect of Lidocaine on Lipopolysaccharide-induced Acute Lung Injury in Rats Through NF-κB and P38 MAPK Signaling Pathway and Excessive Inflammatory Responses. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 2099–2108. [Google Scholar]
- Lahat, A.; Ben-Horin, S.; Lang, A.; Fudim, E.; Picard, O.; Chowers, Y. Lidocaine Down-Regulates Nuclear Factor-kappaB Signalling and Inhibits Cytokine Production and T cell Proliferation. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2008, 152, 320–327. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, B.D.; Jing, W.; Orentas, R.J. CD25+ Regulatory T cell Inhibition Enhances Vaccine-induced Immunity to Neuroblastoma. J. Immunother. 2007, 30, 203–214. [Google Scholar]
- Hesse, M.; Piccirillo, C.A.; Belkaid, Y.; Prufer, J.; Mentink-Kane, M.; Leusink, M.; Cheever, A.W.; Shevach, E.M.; Wynn, T.A. The Pathogenesis of Schistosomiasis is Controlled by Cooperating IL-10-producing Innate Effector and Regulatory T Cells. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 3157–3166. [Google Scholar]
- Farhood, B.; Najafi, M.; Mortezaee, K. CD8+ Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes in Cancer Immunotherapy: A Review. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 8509–8521. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dinarello, C.A. Anti-cytokine Therapeutics and Infections. Vaccine 2003, 21 (Suppl. S2), S24–S34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macedo, N.; Miller, D.M.; Haq, R.; Kaufman, H.L. Clinical Landscape of Oncolytic Virus Research in 2020. J. Immunother. Cancer. 2020, 8, e001486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Cao, S.; Mitsuhashi, M.; Xiang, Z.; Ma, X. Genome-wide Analysis of Molecular Changes in IL-12-induced Control of Mammary Carcinoma via IFN-gamma-independent Mechanisms. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 4111–4122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, C.H.; Hsu, H.Y.; Chiou, H.C.; Tsai, M.L.; You, H.L.; Lin, Y.C.; Liao, W.T. Arsenic Induces M2 Macrophage Polarization and Shifts M1/M2 Cytokine Production via Mitophagy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.J.; Jang, A.R.; Park, J.Y.; Ahn, J.H.; Lee, T.S.; Kim, D.Y.; Lee, D.W.; Hwang, S.; Jeong, Y.J.; Park, J.H. IL-10 Protects Mice From the Lung Infection of Acinetobacter baumannii and Contributes to Bacterial Clearance by Regulating STAT3-Mediated MARCO Expression in Macrophages. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collison, L.W.; Workman, C.J.; Kuo, T.T.; Boyd, K.; Wang, Y.; Vignali, K.M.; Cross, R.; Sehy, D.; Blumberg, R.S.; Vignali, D.A. The Inhibitory Cytokine IL-35 Contributes to Regulatory T-cell Function. Nature 2007, 450, 566–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Wu, Y. Interleukin-35 Ameliorates Cardiovascular Disease by Suppressing Inflammatory Responses and Regulating Immune Homeostasis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 110, 108938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Hao, S.; Dong, X.; Zhang, D.; Jia, Z. Circulating Cytokine Profile and Modulation of Regulatory T cells in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Biomol. Biomed. 2023, 23, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Liu, D.; Li, L. PD-1/PD-L1 Pathway: Current Researches in Cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2020, 10, 727–742. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wei, S.C.; Levine, J.H.; Cogdill, A.P.; Zhao, Y.; Anang, N.A.S.; Andrews, M.C.; Sharma, P.; Wang, J.; Wargo, J.A.; Pe’er, D.; et al. Distinct Cellular Mechanisms Underlie Anti-CTLA-4 and Anti-PD-1 Checkpoint Blockade. Cell 2017, 170, 1120–1133.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Wu, X.; Wang, Z.; Xiangyu, C.; Lisha, W.; Yijun, L.; Dan, X.; Qiao, L.; Yuhan, T.; Huayu, L.; et al. The Primordial Differentiation of Tumor-specific Memory CD8+ T cells as Bona Fide Responders to PD-1/PD-L1 Blockade in Draining Lymph Nodes. Cell 2022, 185, 4049–4066.e4025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez-Duran, G.; Luque-Martin, R.; Patel, M.; Bernard, S.; Sharp, C.; Buchan, N.; Rea, C.; de Winther, M.P.J.; Turan, N.; Angell, D.; et al. Pharmacological Validation of Targets Regulating CD14 During Macrophage Differentiation. EBioMedicine 2020, 61, 103039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Yu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, T. Tumor-Associated Macrophages in Tumor Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 583084. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Q.; Xu, M.; Yu, F.; Jin, Y. CD4+CD25+ Regulatory T cells as a Therapeutic Target in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Cent. Eur. J. Immunol. 2014, 39, 100–103. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Yang, C.; Wang, S.; Shi, D.; Wei, C.; Song, J.; Lin, X.; Dou, R.; Bai, J.; Xiang, Z.; et al. Wnt5a-induced M2 Polarization of Tumor-associated Macrophages via IL-10 Promotes Colorectal Cancer Progression. Cell Commun. Signal. 2020, 18, 51. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Gao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J.; Yang, C.; Bao, C.; Wang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Song, X.; Qiao, S. M2-Type Macrophages Induce Tregs Generation by Activating the TGF-β/Smad Signalling Pathway to Promote Colorectal Cancer Development. Onco. Targets Ther. 2021, 14, 5391–5402. [Google Scholar]
- Vogel, D.Y.; Glim, J.E.; Stavenuiter, A.W.; Breur, M.; Heijnen, P.; Amor, S.; Dijkstra, C.D.; Beelen, R.H. Human Macrophage Polarization in Vitro: Maturation and Activation Methods Compared. Immunobiology 2014, 219, 695–703. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Karnina, R.; Arif, S.K.; Hatta, M.; Bukhari, A. Molecular Mechanisms of Lidocaine. Ann. Med. Surg. 2021, 17, 102733. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, Y.; Yang, W.Y.; Saaoud, F.; Drummer, C., 4th; Sun, Y.; Xu, K.; Lu, Y.; Shan, H.; Shevach, E.M.; Jiang, X.; et al. IL-35 Promotes CD4+Foxp3+ Tregs and Inhibits Atherosclerosis via Maintaining CCR5-amplified Treg-suppressive Mechanisms. JCI Insight 2021, 6, e152511. [Google Scholar]
- Lou, W.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Han, D.; Zhang, L. Responses of CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ and IL-10-secreting type I T Regulatory Cells to Cluster-specific Immunotherapy for Allergic Rhinitis in Children. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2012, 23, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Laouar, Y.; Li, M.O.; Green, E.A.; Flavell, R.A. TGF-beta Regulates in vivo Expansion of Foxp3-expressing CD4+CD25+ Regulatory T cells Responsible for Protection Against Diabetes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 4572–4577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dons, E.M.; Raimondi, G.; Cooper, D.K.; Thomson, A.W. Induced Regulatory T cells: Mechanisms of Conversion and Suppressive Potential. Hum. Immunol. 2012, 73, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinchuk, I.V.; Beswick, E.J.; Saada, J.I.; Boya, G.; Schmitt, D.; Raju, G.S.; Brenmoehl, J.; Rogler, G.; Reyes, V.E.; Powell, D.W. Human Colonic Myofibroblasts Promote Expansion of CD4+ CD25high Foxp3+ Regulatory T Cells. Gastroenterology 2011, 140, 2019–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gocher, A.M.; Workman, C.J.; Vignali, D.A.A. Interferon-γ: Teammate or Opponent in the Tumour Microenvironment? Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2022, 22, 158–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banta, K.L.; Xu, X.; Chitre, A.S.; Amelia, A.Y.; Takahashi, C.; O’Gorman, W.E.; Wu, T.D.; Mittman, S.; Cubas, R.; Comps-Agrar, L. Mechanistic Convergence of the TIGIT and PD-1 Inhibitory Pathways Necessitates Co-blockade to Optimize Anti-tumor CD8+ T Cell Responses. Immunity 2022, 55, 512–526.e519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Pei, T.; Huang, R.; Xiao, Y.; Yan, J.; Zhu, J.; Zheng, C.; Xiao, W.; Huang, C. Platycodon grandiflorum Triggers Antitumor Immunity by Restricting PD-1 Expression of CD8+ T Cells in Local Tumor Microenvironment. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 774440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, S.K.; Welsh, E.A.; Fang, B.; Hernandez, Y.I.; Rose, T.; Gray, J.; Koomen, J.M.; Berglund, A.; Mulé, J.J.; Markowitz, J. Multi-Omics and Informatics Analysis of FFPE Tissues Derived from Melanoma Patients with Long/Short Responses to Anti-PD1 Therapy Reveals Pathways of Response. Cancers 2020, 12, 3515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bally, A.P.; Lu, P.; Tang, Y.; Austin, J.W.; Scharer, C.D.; Ahmed, R.; Boss, J.M. NF-κB Regulates PD-1 Expression in Macrophages. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 4545–4554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Sun, Z.; Wang, Y.; Miao, C. Long-term Use of Indomethacin Leads to Poor Prognoses Through Promoting The Expression of PD-1 and PD-L2 via TRIF/NF-κB Pathway and JAK/STAT3 Pathway to Inhibit TNF-α and IFN-γ in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Exp. Cell Res. 2015, 337, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.J.; Liu, Q. Anti-tumor Effects of Lidocaine on Human Gastric Cancer Cells in Vitro. Bratisl. Lek. Listy. 2019, 120, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, Y.; Fox, J.G.; Gonda, T.; Worthley, D.L.; Muthupalani, S.; Wang, T.C. Mouse Models of Gastric Cancer. Cancers 2013, 5, 92–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, A.; Perica, K.; Klebanoff, C.A.; Wolchok, J.D. Clinical Implications of T cell Exhaustion for Cancer Immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 19, 775–790. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, Z.; Sun, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Zheng, S.; Bin, J.; Liao, Y.; Shi, M.; Zhou, R.; Liao, W. High Baseline Tumor Burden-Associated Macrophages Promote an Immunosuppressive Microenvironment and Reduce the Efficacy of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Through the IGFBP2-STAT3-PD-L1 Pathway. Cancer Commun. 2023, 43, 562–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steen, E.H.; Wang, X.; Balaji, S.; Butte, M.J.; Bollyky, P.L.; Keswani, S.G. The Role of the Anti-Inflammatory Cytokine Interleukin-10 in Tissue Fibrosis. Adv. Wound Care 2020, 9, 184–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degboé, Y.; Rauwel, B.; Baron, M.; Boyer, J.F.; Ruyssen-Witrand, A.; Constantin, A.; Davignon, J.L. Polarization of Rheumatoid Macrophages by TNF Targeting Through an IL-10/STAT3 Mechanism. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, M.; Li, T.; Niu, M.; Zhang, H.; Wu, Y.; Wu, K.; Dai, Z. Targeting Cytokine and Chemokine Signaling Pathways for Cancer Therapy. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 2024, 9, 176. [Google Scholar]
- Vignali, D.A.; Collison, L.W.; Workman, C.J. How Regulatory T cells work. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, R.; Cao, Y.; Gu, Y.; Lin, C.; Liu, X.; Lv, K.; He, X.; Fang, H.; Jin, K. Poor Clinical Outcomes and Immunoevasive Contexture in Intratumoral IL-10-Producing Macrophages Enriched Gastric Cancer Patients. Ann. Surg. 2022, 275, e626–e635. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, E.; Araki, K.; Hashimoto, M.; Li, W.; Riley, J.L.; Cheung, J.; Sharpe, A.H.; Freeman, G.J.; Irving, B.A.; Ahmed, R. Role of PD-1 During Effector CD8 T cell Differentiation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 4749–4754. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Z.; Zhang, S.; Wu, P.; Ren, Q.; Wei, P.; Hong, M.; Feng, Y.; Wong, C.K.; Tang, H.; Zeng, H. A Novel Potential Target of IL-35-regulated JAK/STAT Signaling Pathway in Lupus Nephritis. Clin. Transl. Med. 2021, 11, e309. [Google Scholar]
- Moeini, S.; Saeidi, M.; Fotouhi, F.; Mondanizadeh, M.; Shirian, S.; Mohebi, A.; Gorji, A.; Ghaemi, A. Synergistic Effect of Programmed Cell Death Protein 1 Blockade and Secondary Lymphoid Tissue Chemokine in the Induction of Anti-tumor Immunity by a Therapeutic Cancer Vaccine. Arch. Virol. 2017, 162, 333–346. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; Jiang, H.; Li, Y.; Yan, M.X. IL-35 Expression is Increased in Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma and in the Peripheral Blood of Patients. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 3303–3308. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.; Zhang, T.; Yan, M.X.; Wu, W. IL-35 Inhibits CD8+ T cells Activity by Suppressing Expression of Costimulatory Molecule CD28 and Th1 Cytokine Production. Transl. Cancer Res. 2019, 8, 1319–1325. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, J.C.; Zhang, Z.; Li, T.Y.; Liang, Y.F.; Wang, H.M.; Bao, J.J.; Zhang, J.A.; Wang, W.D.; Xiang, W.Y.; Kong, B.; et al. Assessing the Role of IL-35 in Colorectal Cancer Progression and Prognosis. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2013, 6, 1806–1816. [Google Scholar]
- Turnis, M.E.; Sawant, D.V.; Szymczak-Workman, A.L.; Andrews, L.P.; Delgoffe, G.M.; Yano, H.; Beres, A.J.; Vogel, P.; Workman, C.J.; Vignali, D.A. Interleukin-35 Limits Anti-Tumor Immunity. Immunity 2016, 44, 316–329. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Hu, H.; Liu, L.; Ye, J.; Wang, Z.; Que, B.; Liu, W.; Shi, Y.; Zeng, T.; Shi, L.; et al. Interleukin-12p35 Deficiency Reverses the Th1/Th2 Imbalance, Aggravates the Th17/Treg Imbalance, and Ameliorates Atherosclerosis in ApoE-/- Mice. Mediat. Inflamm. 2019, 2019, 3152040. [Google Scholar]
- Olson, B.M.; Jankowska-Gan, E.; Becker, J.T.; Vignali, D.A.; Burlingham, W.J.; McNeel, D.G. Human Prostate Tumor Antigen-Specific CD8+ Regulatory T cells are Inhibited by CTLA-4 or IL-35 Blockade. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 5590–5601. [Google Scholar]
- Vinay, D.S.; Ryan, E.P.; Pawelec, G.; Talib, W.H.; Stagg, J.; Elkord, E.; Lichtor, T.; Decker, W.K.; Whelan, R.L.; Kumara, H.M.C.S.; et al. Immune Evasion in Cancer: Mechanistic Basis and Therapeutic Strategies. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2015, 35, S185–S198. [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer, L.M. The Role of Nuclear Factor κB in the Interferon Response. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2011, 31, 553–559. [Google Scholar]
- Jorgovanovic, D.; Song, M.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y. Roles of IFN-γ in Tumor Progression and Regression: A Review. Biomark Res. 2020, 8, 49. [Google Scholar]
- Hayakawa, T.; Sugiyama, J.; Yaguchi, T.; Imaizumi, A.; Kawakami, Y. Enhanced Anti-tumor Effects of The PD-1/PD-L1 Blockade by Combining a Highly Absorptive Form of NF-kB/STAT3 Inhibitor Curcumin. J. Immunother. Cancer 2014, 2, 210. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, D.; Wang, L.; Cui, Q.; Iftikhar, R.; Xia, Y.; Xu, P. Repositioning Lidocaine as an Anticancer Drug: The Role Beyond Anesthesia. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 17, 565. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Yang, W.C.; Chang, Y.K.; Wang, C.Y.; Huang, W.R.; Li, J.Y.; Chuang, K.P.; Wu, H.Y.; Chang, C.D.; Nielsen, B.L.; et al. Construction of Polycistronic Baculovirus Surface Display Vectors to Express the PCV2 Cap(d41) Protein and Analysis of Its Immunogenicity in Mice and Swine. Vet. Res. 2020, 51, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudley, M.E.; Wunderlich, J.R.; Shelton, T.E.; Even, J.; Rosenberg, S.A. Generation of Tumor-infiltrating Lymphocyte Cultures for Use in Adoptive Transfer Therapy for Melanoma Patients. J. Immunother. 2003, 26, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.Y.; Wu, F.H.; Chen, I.C.; Liao, T.L.; Munir, M.; Liu, H.J. Oncolytic Avian Reovirus-sensitized Tumor infiltrating CD8+ T cells Triggering Immunogenic Apoptosis in Gastric Cancer. Cell Commun. Signal. 2024, 22, 514. [Google Scholar]
- Aziz, F.; Yang, X.; Wen, Q.; Yan, Q. A Method for Establishing Human Primary Gastric Epithelial Cell Culture from Fresh Surgical Gastric Tissues. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 2939–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smoot, D.T.; Sewchand, J.; Young, K.; Desbordes, B.C.; Allen, C.R.; Naab, T. A Method for Establishing Primary Cultures of Human Gastric Epithelial Cells. Methods Cell Sci. 2000, 22, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, M.; Alghetaa, H.; Mohammed, A.; Osama, A.A.; Paul, J.W.; Narendra, S.; Prakash, N.; Mitzi, N. The Endocannabinoid Anandamide Attenuates Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome by Downregulating miRNA that Target Inflammatory Pathways. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 644281. [Google Scholar]
- Vergis, J.; Malik, S.V.S.; Pathak, R.; Kumar, M.; Kurkure, N.V.; Barbuddhe, S.B.; Rawool, D.B. Exploring Galleria Mellonella Larval Model to Evaluate Antibacterial Efficacy of Cecropin A (1-7)-Melittin Against Multi-drug Resistant Enteroaggregative Escherichia coli. Pathog. Dis. 2021, 79, ftab010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilkow, C.S.; Marguerie, M.; Batenchuk, C.; Mayer, J.; Neriah, D.B.; Cousineau, S.; Falls, T.; Jennings, V.A.; Boileau, M.; Bellamy, D.; et al. Reciprocal Cellular Cross-talk Within the Tumor Microenvironment Promotes Oncolytic Virus Activity. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 530–536. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, C.L.; Jiang, S.W.; Feng, Y.; Yuan, L.; Chen, P.; Zhang, L.; Huang, S.; Li, J.; Xia, J.C.; et al. Retrospective Analysis of the Efficacy of Adjuvant CIK Cell Therapy in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Patients Who Received Postoperative Chemotherapy. Oncoimmunology 2019, 8, e1528411. [Google Scholar]
- Snyder, K.M.; Dixon, K.J.; Davis, Z.; Hosking, M.; Hart, G.; Khaw, M.; Matson, A.; Bjordahl, R.; Hancock, B.; Shirinbak, S.; et al. IPSC-derived Natural Killer Cells Expressing the FcγR Fusion CD64/16A Can be Armed with Antibodies for Multitumor Antigen Targeting. J. Immunother. Cancer 2023, 11, e007280. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, L.; Hou, J.; Wu, X.; Lu, Y.; Jin, Z.; Yu, Z.; Yu, B.; Li, J.; Yang, Z.; Li, C.; et al. Cancer-associated Fibroblasts Impair the Cytotoxic Function of NK cells in Gastric Cancer by Inducing Ferroptosis via Iron Regulation. Redox Biol. 2023, 67, 102923. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Jiang, G.; Ng, Y.Y.; Xiao, L.; Du, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhu, J. T cells with Split CARs Specific for NKG2D Ligands and PD-L1 Exhibit Improved Selectivity Towards Monocyte-derived Cells While Effective in Eliminating Acute Myeloid Leukaemia in Vivo. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 149, 10189–10201. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Y.-Y.; Chen, M.-S.; Chen, I.-C.; Wu, F.-H.; Liao, T.-L.; Wen, H.-W.; Nielsen, B.L.; Liu, H.-J. Lidocaine Modulates Cytokine Production and Reprograms the Tumor Immune Microenvironment to Enhance Anti-Tumor Immune Responses in Gastric Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3236. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073236
Wu Y-Y, Chen M-S, Chen I-C, Wu F-H, Liao T-L, Wen H-W, Nielsen BL, Liu H-J. Lidocaine Modulates Cytokine Production and Reprograms the Tumor Immune Microenvironment to Enhance Anti-Tumor Immune Responses in Gastric Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(7):3236. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073236
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Yi-Ying, Ming-Shan Chen, I-Chun Chen, Feng-Hsu Wu, Tsai-Ling Liao, Hsiao-Wei Wen, Brent L. Nielsen, and Hung-Jen Liu. 2025. "Lidocaine Modulates Cytokine Production and Reprograms the Tumor Immune Microenvironment to Enhance Anti-Tumor Immune Responses in Gastric Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 7: 3236. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073236
APA StyleWu, Y.-Y., Chen, M.-S., Chen, I.-C., Wu, F.-H., Liao, T.-L., Wen, H.-W., Nielsen, B. L., & Liu, H.-J. (2025). Lidocaine Modulates Cytokine Production and Reprograms the Tumor Immune Microenvironment to Enhance Anti-Tumor Immune Responses in Gastric Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(7), 3236. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073236






