Profiling Blood-Based Neural Biomarkers and Cytokines in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis Model of Multiple Sclerosis Using Single-Molecule Array Technology
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
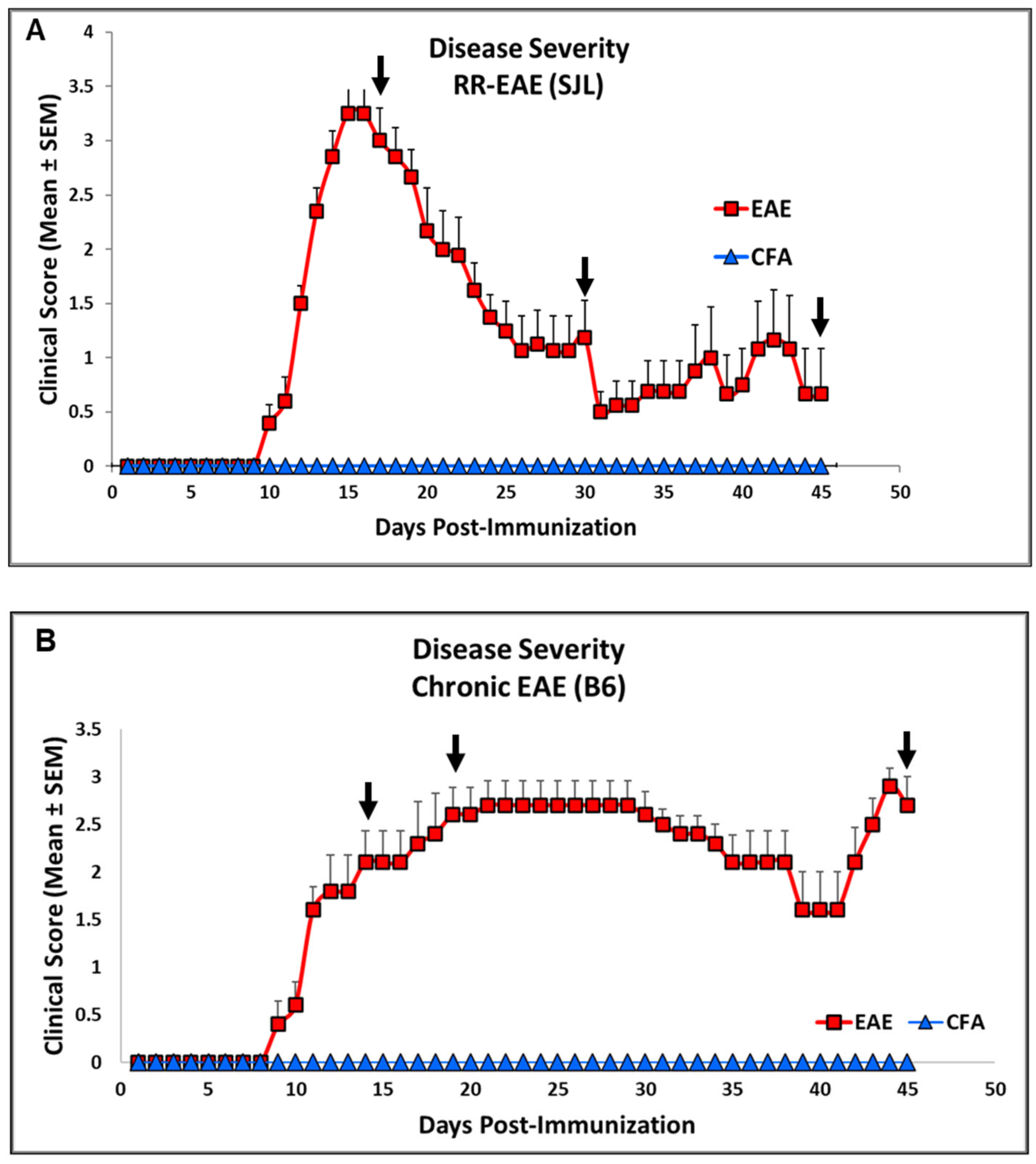
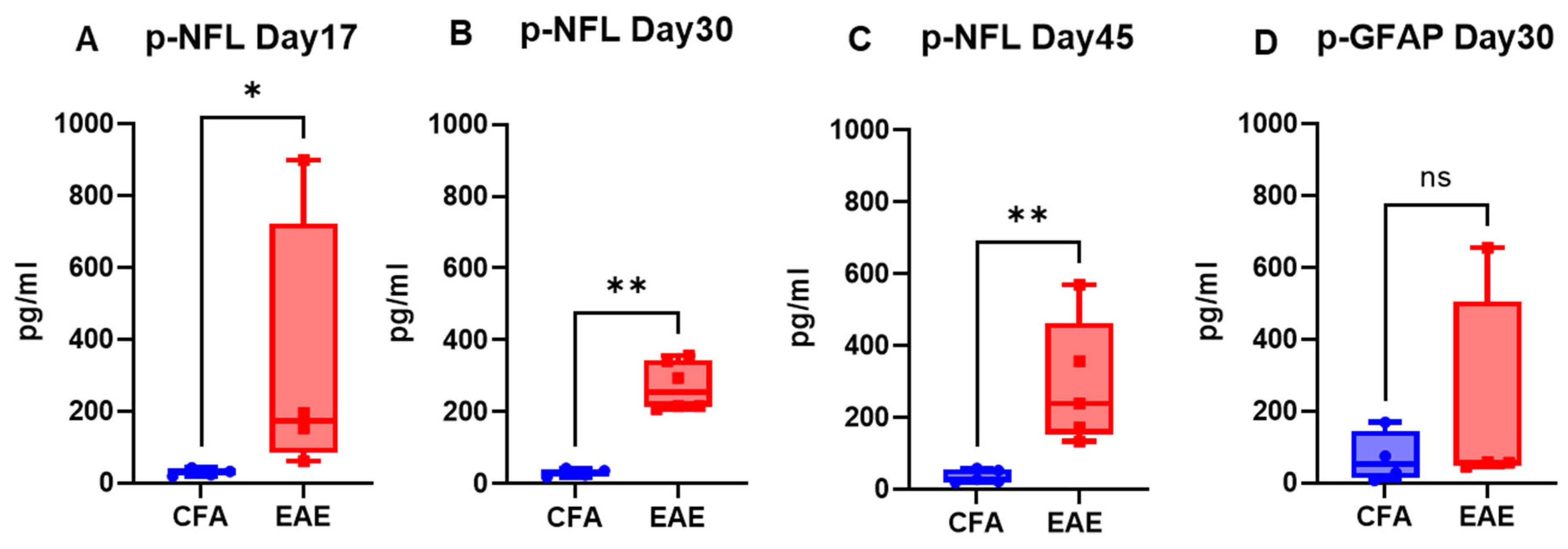
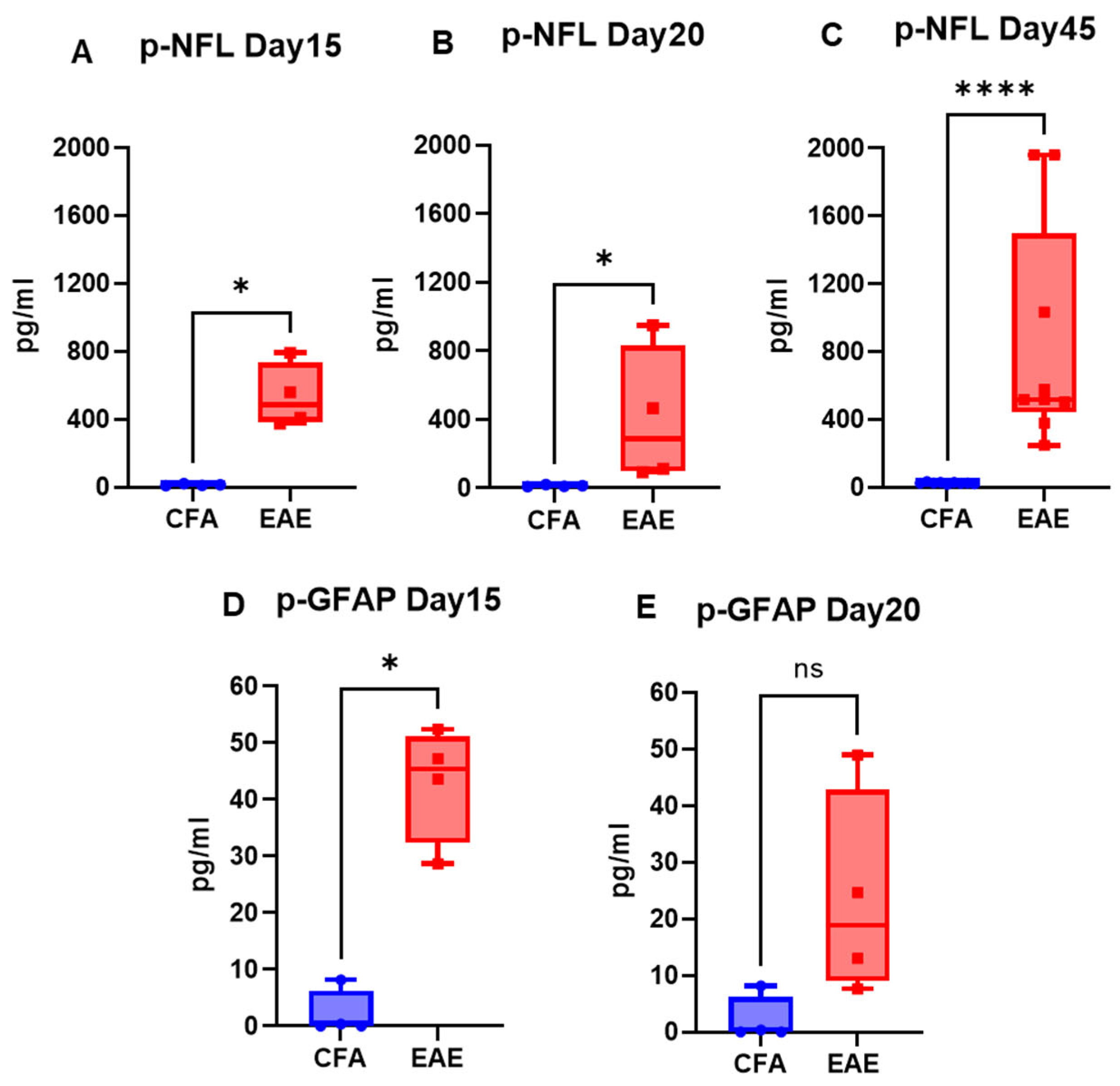
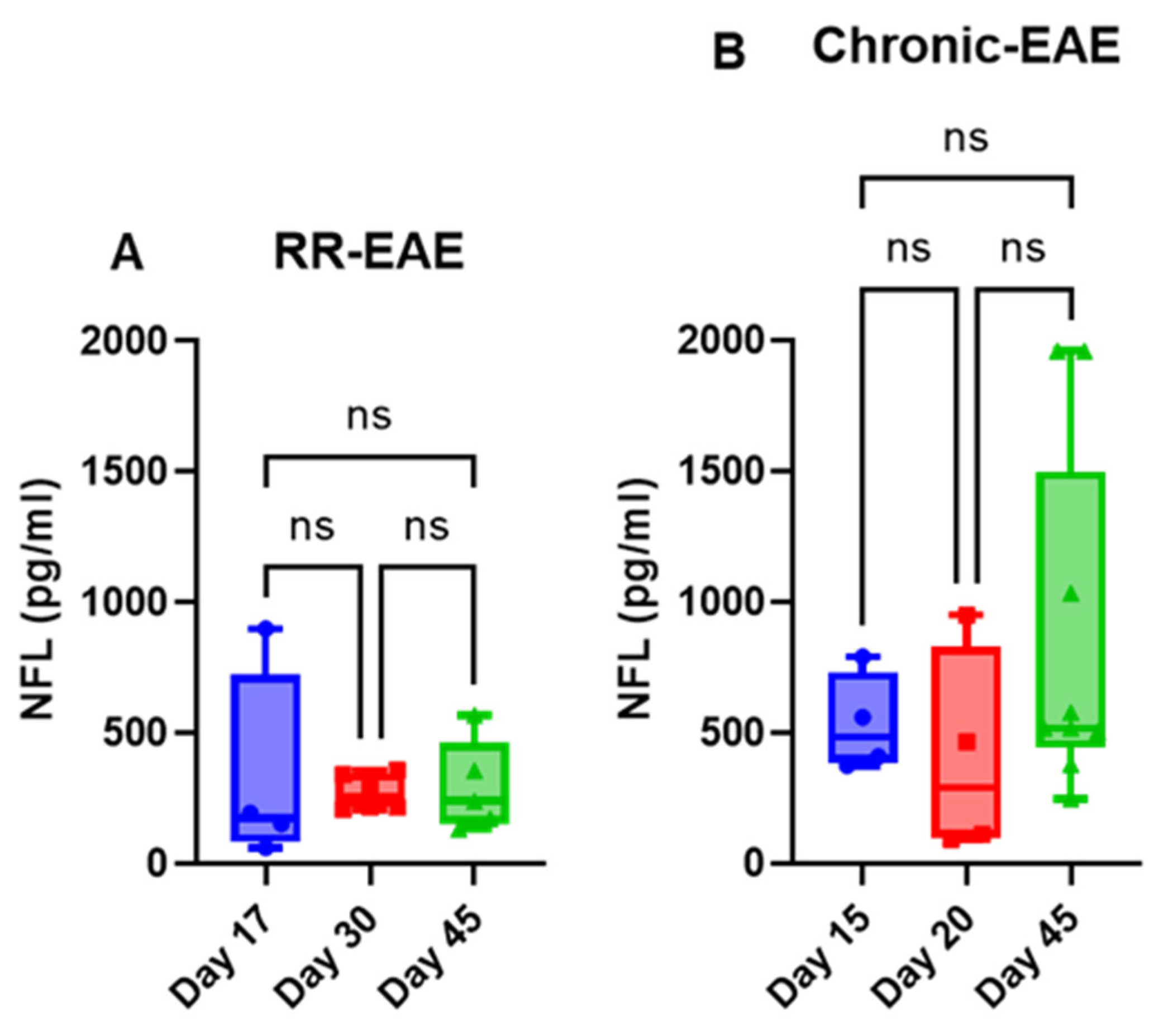
2.1. EAE Increases NFL and GFAP Leakage in the Peripheral Circulation
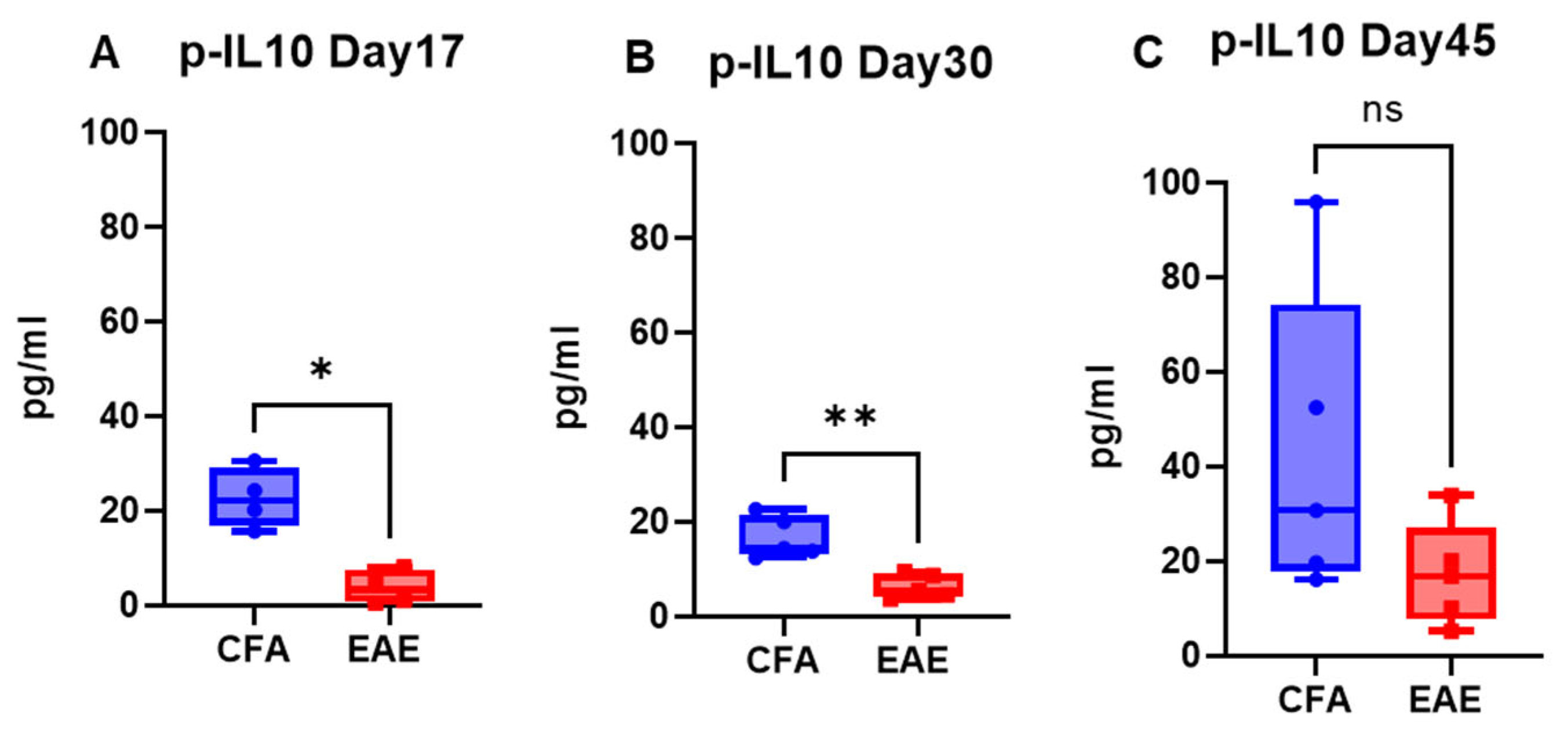
2.2. EAE Decreases the Level of the Anti-Inflammatory Cytokine IL-10 in the Blood
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. EAE Model Induction
4.2. Clinical Assessment of EAE Models
4.3. Experimental Groups and Blood Sampling
4.4. Single Molecule Array (SIMOA) Assay
4.5. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gold, R.; Linington, C.; Lassmann, H. Understanding pathogenesis and therapy of multiple sclerosis via animal models: 70 years of merits and culprits in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis research. Brain 2006, 129 Pt 8, 1953–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinman, L.; Zamvil, S.S. Virtues and pitfalls of EAE for the development of therapies for multiple sclerosis. Trends Immunol. 2005, 26, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinman, L.; Zamvil, S.S. How to successfully apply animal studies in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis to research on multiple sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 2006, 60, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farooqi, N.; Gran, B.; Constantinescu, C.S. Are current disease-modifying therapeutics in multiple sclerosis justified on the basis of studies in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis? J. Neurochem. 2010, 115, 829–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjelobaba, I.; Begovic-Kupresanin, V.; Pekovic, S.; Lavrnja, I. Animal models of multiple sclerosis: Focus on experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Neurosci. Res. 2018, 96, 1021–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinman, L. A molecular trio in relapse and remission in multiple sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 6, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinman, L.; Patarca, R.; Haseltine, W. Experimental encephalomyelitis at age 90, still relevant and elucidating how viruses trigger disease. J. Exp. Med. 2023, 220, e20221322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Baker, D.; Amor, S. Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis is a good model of multiple sclerosis if used wisely. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2014, 3, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, D.; Amor, S. Mouse models of multiple sclerosis: Lost in translation? Curr. Pharm. Des. 2015, 21, 2440–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amor, S.; Baker, D. Checklist for reporting and reviewing studies of experimental animal models of multiple sclerosis and related disorders. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2012, 1, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, S.D.; McMahon, E.J.; Schreiner, B.; Bailey, S.L. Antigen presentation in the CNS by myeloid dendritic cells drives progression of relapsing experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2007, 1103, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Constantinescu, C.S.; Farooqi, N.; O’Brien, K.; Gran, B. Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) as a model for multiple sclerosis (MS). Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 164, 1079–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- McCarthy, D.P.; Richards, M.H.; Miller, S.D. Mouse models of multiple sclerosis: Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and Theiler’s virus-induced demyelinating disease. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 900, 381–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kipp, M.; Nyamoya, S.; Hochstrasser, T.; Amor, S. Multiple sclerosis animal models: A clinical and histopathological perspective. Brain Pathol. 2017, 27, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Birmpili, D.; Charmarke Askar, I.; Bigaut, K.; Bagnard, D. The Translatability of Multiple Sclerosis Animal Models for Biomarkers Discovery and Their Clinical Use. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Momtazmanesh, S.; Shobeiri, P.; Saghazadeh, A.; Teunissen, C.E.; Burman, J.; Szalardy, L.; Klivenyi, P.; Bartos, A.; Fernandes, A.; Rezaei, N. Neuronal and glial CSF biomarkers in multiple sclerosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Rev. Neurosci. 2021, 32, 573–595. [Google Scholar]
- Jahan-Abad, A.J.; Karima, S.; Shateri, S.; Baram, S.M.; Rajaei, S.; Morteza-Zadeh, P.; Borhani-Haghighi, M.; Salari, A.A.; Nikzamir, A.; Gorji, A. Serum pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines and the pathogenesis of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Neuropathology 2020, 40, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuenz, B.; Deisenhammer, F.; Berger, T.; Reindl, M. Diagnostic biomarkers in multiple sclerosis. Expert. Opin. Med. Diagn. 2007, 1, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Göbel, K.; Ruck, T.; Meuth, S.G. Cytokine signaling in multiple sclerosis: Lost in translation. Mult. Scler. J. 2018, 24, 432–439. [Google Scholar]
- Imitola, J.; Chitnis, T.; Khoury, S.J. Cytokines in multiple sclerosis: From bench to bedside. Pharmacol. Ther. 2005, 106, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palle, P.; Monaghan, K.L.; Milne, S.M.; Wan, E.C.K. Cytokine Signaling in Multiple Sclerosis and Its Therapeutic Applications. Med. Sci. 2017, 5, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aharoni, R.; Eilam, R.; Lerner, S.; Shavit-Stein, E.; Dori, A.; Chapman, J.; Arnon, R. Neuroprotective Effect of Glatiramer Acetate on Neurofilament Light Chain Leakage and Glutamate Excess in an Animal Model of Multiple Sclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnanapavan, S.; Grant, D.; Pryce, G.; Jackson, S.; Baker, D.; Giovannoni, G. Neurofilament a biomarker of neurodegeneration in autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Autoimmunity 2012, 45, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brummer, T.; Schillner, M.; Steffen, F.; Kneilmann, F.; Wasser, B.; Uphaus, T.; Zipp, F.; Bittner, S. Spatial transcriptomics and neurofilament light chain reveal changes in lesion patterns in murine autoimmune neuroinflammation. J. Neuroinflamm. 2023, 20, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kuhle, J.; Barro, C.; Andreasson, U.; Derfuss, T.; Lindberg, R.; Sandelius, Å.; Liman, V.; Norgren, N.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H. Comparison of three analytical platforms for quantification of the neurofilament light chain in blood samples: ELISA, electrochemiluminescence immunoassay and Simoa. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2016, 54, 1655–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, L.; Keegan, A.; Walt, D.R. Single-Molecule Arrays for Ultrasensitive Detection of Blood-Based Biomarkers for Immunotherapy. Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2055, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasseter, H.C.; Provost, A.C.; Chaby, L.E.; Daskalakis, N.P.; Haas, M.; Jeromin, A. Cross-platform comparison of highly sensitive immunoassay technologies for cytokine markers: Platform performance in post-traumatic stress disorder and Parkinson’s disease. Cytokine X 2020, 2, 100027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Revendova, K.Z.; Zeman, D.; Bunganic, R.; Karasova, K.; Volny, O.; Bar, M.; Kusnierova, P. Serum neurofilament levels in patients with multiple sclerosis: A comparison of SIMOA and high sensitivity ELISA assays and contributing factors to ELISA levels. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2022, 67, 104177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pafiti, A.; Krashias, G.; Tzartos, J.; Tzartos, S.; Stergiou, C.; Gaglia, E.; Smoleski, I.; Christodoulou, C.; Pantzaris, M.; Lambrianides, A. A Comparison of Two Analytical Approaches for the Quantification of Neurofilament Light Chain, a Biomarker of Axonal Damage in Multiple Sclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.; Yi, N.; Jiang, D. Advances in single molecule arrays (SIMOA) for ultra-sensitive detection of biomolecules. Talanta 2024, 270, 125529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poisson, L.M.; Suhail, H.; Singh, J.; Datta, I.; Denic, A.; Labuzek, K.; Hoda, M.N.; Shankar, A.; Kumar, A.; Cerghet, M.; et al. Untargeted Plasma Metabolomics Identifies Endogenous Metabolite with Drug-like Properties in Chronic Animal Model of Multiple Sclerosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 30697–30712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Porro, C.; Cianciulli, A.; Panaro, M.A. The Regulatory Role of IL-10 in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rissin, D.M.; Kan, C.W.; Campbell, T.G.; Howes, S.C.; Fournier, D.R.; Song, L.; Piech, T.; Patel, P.P.; Chang, L.; Rivnak, A.J.; et al. Single-molecule enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay detects serum proteins at subfemtomolar concentrations. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 595–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Arroyo Pereiro, P.; Muñoz-Vendrell, A.; León Moreno, I.; Bau, L.; Matas, E.; Romero-Pinel, L.; Yélamos, A.M.; Yélamos, S.M.; Andrés-Benito, P. Baseline serum neurofilament light chain levels differentiate aggressive from benign forms of relapsing–remitting multiple sclerosis: A 20-year follows-up cohort. J. Neurol. 2023, 271, 1599–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, K.K. Glial fibrillary acidic protein: From intermediate filament assembly and gliosis to neurobiomarker. Trends Neurosci. 2015, 38, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Barro, C.; Benkert, P.; Disanto, G.; Tsagkas, C.; Amann, M.; Naegelin, Y.; Leppert, D.; Gobbi, C.; Granziera, C.; Yaldizli, O.; et al. Serum neurofilament as a predictor of disease worsening and brain and spinal cord atrophy in multiple sclerosis. Brain 2018, 141, 2382–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bridel, C.; van Wieringen, W.N.; Zetterberg, H.; Tijms, B.M.; Teunissen, C.E.; The NFL Group. Diagnostic Value of Cerebrospinal Fluid Neurofilament Light Protein in Neurology: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Neurol. 2019, 76, 1035–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Uher, T.; McComb, M.; Galkin, S.; Srpova, B.; Oechtering, J.; Barro, C.; Tyblova, M.; Bergsland, N.; Krasensky, J.; Dwyer, M.; et al. Neurofilament levels are associated with blood–brain barrier integrity, lymphocyte extravasation, and risk factors following the first demyelinating event in multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. J. 2021, 27, 220–231. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, C.A.; Roqué, P.J.; Goverman, J.M. Pathogenic T cell cytokines in multiple sclerosis. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20190460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bhise, V.; Dhib-Jalbut, S. Further understanding of the immunopathology of multiple sclerosis: Impact on future treatments. Expert. Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2016, 12, 1069–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.C.; Yang, X.; Miao, L.; Liu, Z.G.; Li, W.; Zhao, Z.X.; Sun, X.J.; Jiang, G.X.; Chen, S.D.; Cheng, Q. Serum level of interleukin-6 in Chinese patients with multiple sclerosis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2012, 249, 109–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.C.; Chen, S.D.; Miao, L.; Liu, Z.G.; Li, W.; Zhao, Z.X.; Sun, X.J.; Jiang, G.X.; Cheng, Q. Serum levels of interleukin (IL)-18, IL-23 and IL-17 in Chinese patients with multiple sclerosis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2012, 243, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, T.B.; Rose, J.W.; Jaskowski, T.D.; Wilson, A.R.; Husebye, D.; Seraj, H.S.; Hill, H.R. Analysis of proinflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokine serum concentrations in patients with multiple sclerosis by using a multiplexed immunoassay. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2011, 136, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandenbark, A.A.; Morgan, E.; Bartholomew, R.; Bourdette, D.; Whitham, R.; Carlo, D.; Gold, D.; Hashim, G.; Offner, H. TCR peptide therapy in human autoimmune diseases. Neurochem. Res. 2001, 26, 713–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettelli, E.; Das, M.P.; Howard, E.D.; Weiner, H.L.; Sobel, R.A.; Kuchroo, V.K. IL-10 is critical in the regulation of autoimmune encephalomyelitis as demonstrated by studies of IL-10- and IL-4-deficient and transgenic mice. J. Immunol. 1998, 161, 3299–3306. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cua, D.J.; Groux, H.; Hinton, D.R.; Stohlman, S.A.; Coffman, R.L. Transgenic interleukin 10 prevents induction of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Exp. Med. 1999, 189, 1005–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zahoor, I.; Nematullah, M.; Ahmed, M.E.; Fatma, M.; Sajad, M.; Ayasolla, K.; Cerghet, M.; Palaniyandi, S.; Ceci, V.; Carrera, G.; et al. Maresin-1 promotes neuroprotection and modulates metabolic and inflammatory responses in disease-associated cell types in preclinical models of Multiple Sclerosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2025, 301, 108226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahoor, I.; Suhail, H.; Datta, I.; Ahmed, M.E.; Poisson, L.M.; Waters, J.; Rashid, F.; Bin, R.; Singh, J.; Cerghet, M.; et al. Blood-based untargeted metabolomics in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis revealed the testable therapeutic target. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2123265119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zahoor, I.; Waters, J.; Datta, I.; Cerghet, M.; Poisson, L.; Rattan, R.; Giri, S. Predicting Disease Progression in Multiple Sclerosis by using a Combination of Highly Sensitive Single Molecule Array Technology (SIMOA) and Untargeted Metabolomics. Mult. Scler. 2022, 28 (Suppl. S1), 43. [Google Scholar]
- Mangalam, A.; Poisson, L.; Nemutlu, E.; Datta, I.; Denic, A.; Dzeja, P.; Rodriguez, M.; Rattan, R.; Giri, S. Profile of Circulatory Metabolites in a Relapsing-remitting Animal Model of Multiple Sclerosis using Global Metabolomics. J. Clin. Cell Immunol. 2013, 4, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mangalam, A.K.; Rattan, R.; Suhail, H.; Singh, J.; Hoda, M.N.; Deshpande, M.; Fulzele, S.; Denic, A.; Shridhar, V.; Kumar, A.; et al. AMP-Activated Protein Kinase Suppresses Autoimmune Central Nervous System Disease by Regulating M1-Type Macrophage-Th17 Axis. J. Immunol. 2016, 197, 747–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Analyte | Conc Range (SJL) (pg/mL) | Status in EAE | Conc Range (B6) (pg/mL) | Status in EAE | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CFA | RR-EAE | CFA | Chronic-EAE | |||
| NFL | 18.35 to 57.75 | 60.43 to 899.25 | Increase | 9.53 to 34.77 | 92.47 to 1960.59 | Increase |
| GFAP | 7.22 to 168.70 | 45.65 to 654.52 | Increase | 0.00 to 8.17 | 7.62 to 52.40 | Increase |
| IL-10 | 12.38 to 95.88 | 0.46 to 33.87 | Decrease | 5.07 to 114.40 | 1.92 to 14.80 | Decrease |
| IL-6 | Level below low calibrator | Level below low calibrator | Not conclusive | Level below low calibrator | Level below low calibrator | Not conclusive |
| IL-12p70 | Level below low calibrator | Level below low calibrator | Not conclusive | Level below low calibrator | Level below low calibrator | Not conclusive |
| TNF-α | Level below low calibrator | Level below low calibrator | Not conclusive | Level below low calibrator | Level below low calibrator | Not conclusive |
| IL-17 | Level below low calibrator | Level below low calibrator | Not conclusive | Level below low calibrator | Level below low calibrator | Not conclusive |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zahoor, I.; Mir, S.; Giri, S. Profiling Blood-Based Neural Biomarkers and Cytokines in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis Model of Multiple Sclerosis Using Single-Molecule Array Technology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3258. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073258
Zahoor I, Mir S, Giri S. Profiling Blood-Based Neural Biomarkers and Cytokines in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis Model of Multiple Sclerosis Using Single-Molecule Array Technology. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(7):3258. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073258
Chicago/Turabian StyleZahoor, Insha, Sajad Mir, and Shailendra Giri. 2025. "Profiling Blood-Based Neural Biomarkers and Cytokines in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis Model of Multiple Sclerosis Using Single-Molecule Array Technology" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 7: 3258. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073258
APA StyleZahoor, I., Mir, S., & Giri, S. (2025). Profiling Blood-Based Neural Biomarkers and Cytokines in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis Model of Multiple Sclerosis Using Single-Molecule Array Technology. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(7), 3258. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073258






