Abstract
Emerging resistance to colistin in Acinetobacter baumannii is concerning because of the limited therapeutic options for this important clinical pathogen. Given the shortage of new antibiotics, one strategy that has been proven to be therapeutically effective is to overcome antibiotic-resistant pathogens by combining existing antibiotics with another antibiotic or non-antibiotic. This study was designed to investigate the potential synergistic antibacterial activity of amorolfine, a morpholine antifungal drug, in combination with colistin against A. baumannii. In this work, antibiotic susceptibility testing, checkerboard assays, and time-kill curves were used to investigate the synergistic efficacy of colistin combined with amorolfine. The molecular mechanisms of combination therapy were analyzed using fluorometric assays, UV-vis spectroscopy, and molecular docking. Finally, we evaluated the in vivo efficacy of combination therapy against A. baumannii. In brief, the combination therapy showed significant synergistic activity against A. baumannii (FICI = 0.094). In addition, the combination of amorolfine improved the membrane disruption of colistin, and amorolfine exhibited the capacity of binding to DNA. Moreover, in a mouse sepsis model, this combination therapy increased survival compared to colistin monotherapy. Our findings demonstrated that amorolfine serves as a potential colistin adjuvant against Acinetobacter baumannii.
1. Introduction
Acinetobacter baumannii is a ubiquitous Gram-negative bacterium that is commonly isolated from the environment [1]. Its ability to form biofilm and its resistance to desiccation and disinfectants allows A. baumannii to thrive in the hospital environment and, as an opportunistic pathogen, has caused hospital-acquired infections [2,3]. In addition, due to its resistance to last-resort antibiotics, such as colistin, tigecycline, and carbapenems, A. baumannii has been classified as an ESKAPE pathogen by the WHO, and the research and development of new antibiotics is critically needed [4].
Colistin is a polypeptide antibiotic discovered by Y. Koyama, who derived it from Paenibacillus polymyxa in 1947 [5]. Colistin is effective against most Gram-negative bacteria but is ineffective against Gram-positive bacteria, anaerobic bacteria, and mycoplasmas [6]. It targets the lipopolysaccharide (LPS) of GNB out-membranes. The divalent cations, including Ca2+ and Mg2+, could be displaced by colistin from the anionic phosphate groups of LPS and destabilize the out-membrane, ultimately leading to the leakage of intracellular contents and bacterial death [7,8]. Early on, colistin was replaced in clinics by new and more effective antibiotics, due to reports of nephrotoxic and neurotoxic adverse events [9,10,11]. However, in the 1990s, with the emergence of MDR and XDR Gram-negative bacteria, colistin re-emerged as the last-resort treatment against superbugs [12]. Alarmingly, the plasmid-borne colistin-resistant mcr gene has spread in GNB worldwide, limiting the use of colistin and leaving clinicians with few choices among the existing antibiotics [13].
A large body of literature supports the hypothesis that a combination therapy of colistin may be a novel therapeutic option for multidrug-resistant bacteria [14,15]. For example, Ku et al. reported the synergistic effect of colistin in combination with fosfomycin in a mouse model of MDR A. baumannii pneumonia [16]. Amorolfine (AMO, Figure 1A) is a morpholine antifungal drug that inhibits Δ14-sterol reductase and cholestenol Δ-isomerase, which depletes ergosterol and causes ignosterol to accumulate in the fungal cytoplasmic cell membranes [17]. AMO is commonly applied as a lacquer for onychomycosis but is also used for superficial dermatomycosis [18,19]. However, there has been no report on the synergistic activity between AMO and colistin against A. baumannii. Here, we found that AMO could potentiate the sensitivity of colistin against A. baumannii, both in vitro and in vivo, providing a new and attractive combination therapy for A. baumannii infection in the future.
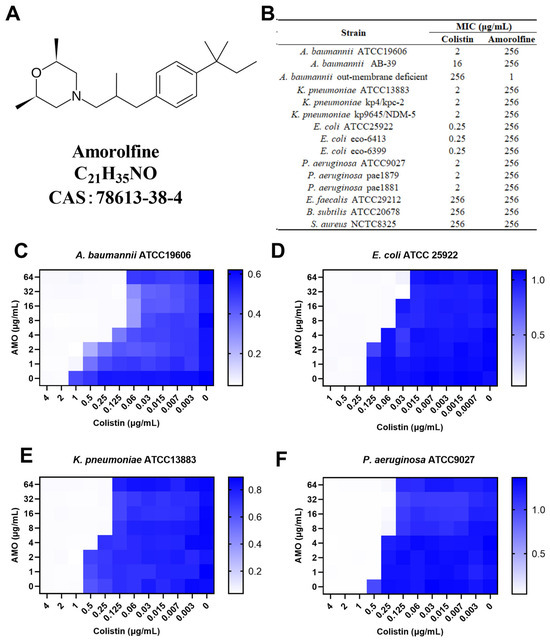
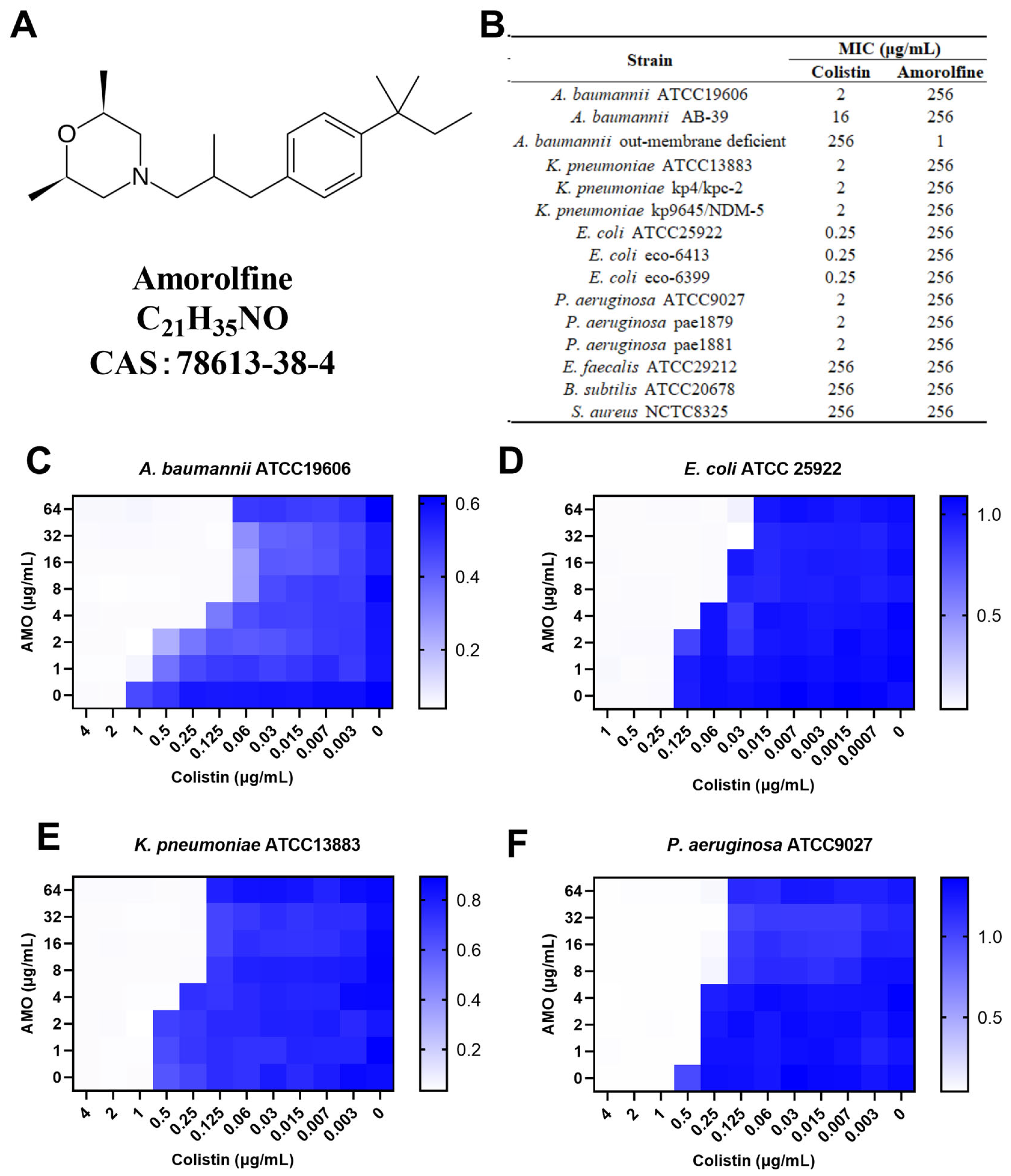
Figure 1.
(A) The chemical structure of amorolfine. (B) The MIC values of AMO and colistin. (C–F) The synergistic effect of AMO combined with colistin against GNB, as shown by the checkerboard assay. The data represent the values at OD600 nm of bacterial culture. Dark blue regions represent higher cell density.
2. Results
2.1. In Vitro Synergistic Effect of the Amorolfine and Colistin Combination on Gram-Negative Bacteria
To determine the synergistic activity of AMO with colistin, the MIC of AMO was first determined (Figure 1B). Here, AMO is considered to have no antimicrobial activity against the strains tested in the table with an MIC value greater than 256 mg/L, regardless of whether it is being used against Gram-negative or Gram-positive bacteria, except for the outer membrane-deficient strain of A. baumannii. We then tested the synergistic activity of AMO in combination with colistin (Figure 1C–F). For four Gram-negative bacteria, using colistin in combination with AMO showed a 4- to 16-fold decrease in MIC values, including A. baumannii ATCC19606 (FICI = 0.094), E. coli ATCC 25922 (FICI = 0.28), K. pneumoniae ATCC13883 (FICI = 0.28) and P. aeruginosa ATCC9027 (FICI = 0.28). These results collectively suggest the general synergistic activity of AMO in combination with colistin against a broad spectrum of Gram-negative bacteria, with the best synergistic activity seen against A. baumannii.
2.2. Synergistic Effect of the Amorolfine and Colistin Combination on A. baumannii and Inhibition of Biofilm Formation
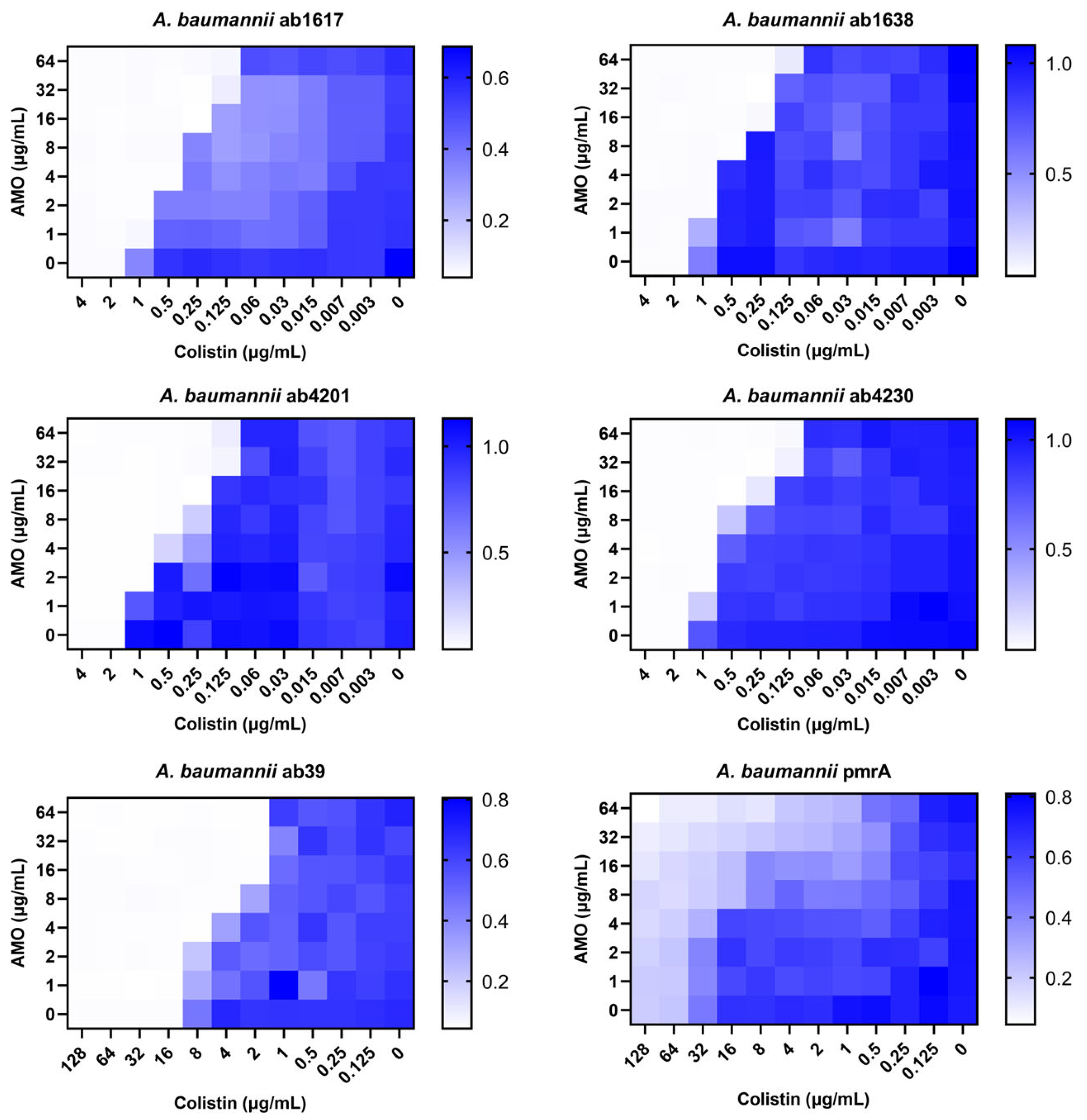
Against A. baumannii, a common clinical opportunistic pathogen and multidrug-resistant bacterium, the combination of amorolfine and colistin showed the best synergistic effect. To further assess the clinical value of the combination therapy, six clinically resistant A. baumannii strains were selected for testing, including two colistin-resistant strains. The combination showed good synergistic effects for all strains except the pmrA strain [20], which it was ineffective against due to the strain’s high resistance to colistin (Figure 2). In addition, for the pmrA strain, a decrease in bacterial concentration was observed in some of the wells of the 96-well plate test species that were co-administered, indicating that the synergistic effect was still present. Meanwhile, for colistin medium-resistance strain ab39, the combination still exhibited synergistic activity. These findings indicated that the synergistic activity of the combination of AMO and colistin remained unaffected by colistin resistance.
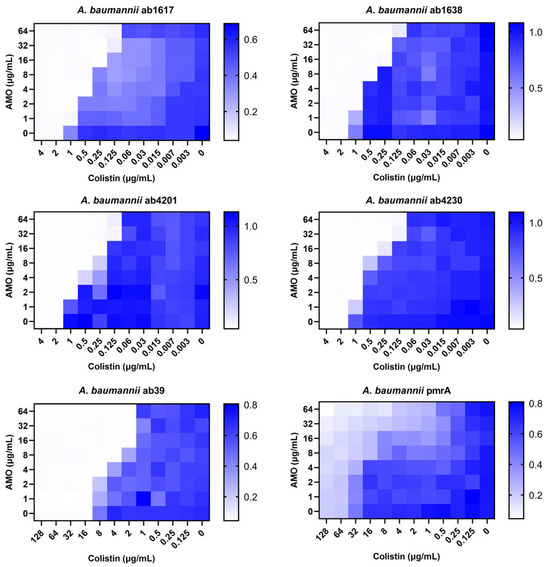
Figure 2.
The synergistic effect of AMO combined with colistin against clinical A. baumannii isolates (ab1617, ab1638, ab4230-MEM, CN, AMP; ab4201-MEM, CN; ab39, pmrA-COL), as shown by the checkerboard assay. MEM—MeropeneM; CN—Cefalexin; AMP—Ampicillin; COL—Colistin.
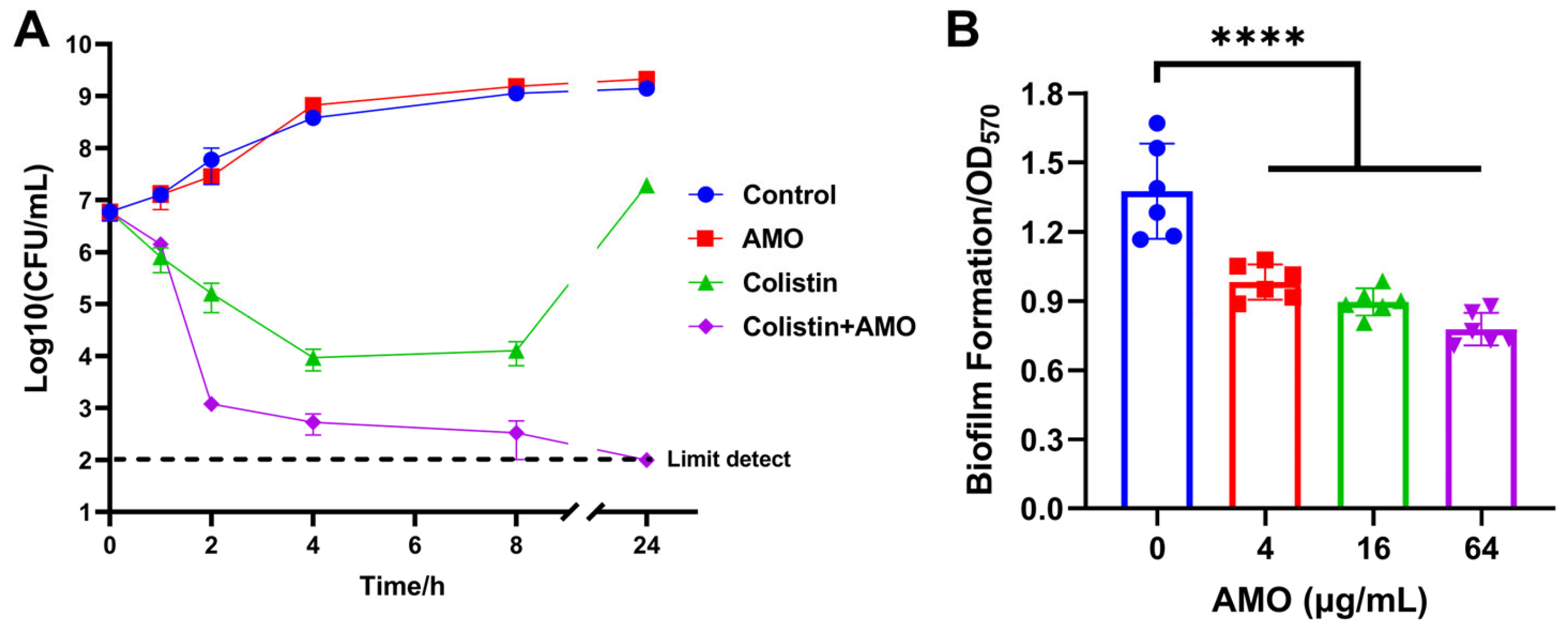
Time-kill experiments revealed that AMO monotherapy exhibited no bactericidal effect on A. baumannii, while colistin monotherapy led to a reduction in bacterial concentration during the initial phase. However, the bacteria continued to proliferate after 8 h. In contrast, the combination of AMO and colistin resulted in bacterial concentrations reaching the limit of detection (Figure 3A). The capacity of AMO to impede biofilm formation was evaluated using the CV staining method. The results of the checkerboard analysis demonstrated that AMO significantly inhibited A. baumannii biofilm formation by approximately 29% at 4 μg/mL, exhibiting a dose-dependent decrease (Figure 3B).
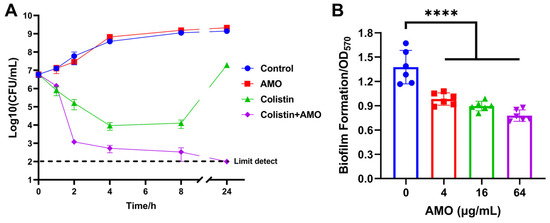
Figure 3.
(A) Time–kill curves of A. baumannii ATCC19606 incubated with colistin (1 μg/mL), AMO (16 μg/mL) alone, or their combination. (B) The biofilm formation of A. baumannii ATCC19606 after exposure to different concentrations of AMO. (****, p < 0.0001).
2.3. Effect of Amorolfine on the Membrane-Damaging Capacity of Colistin
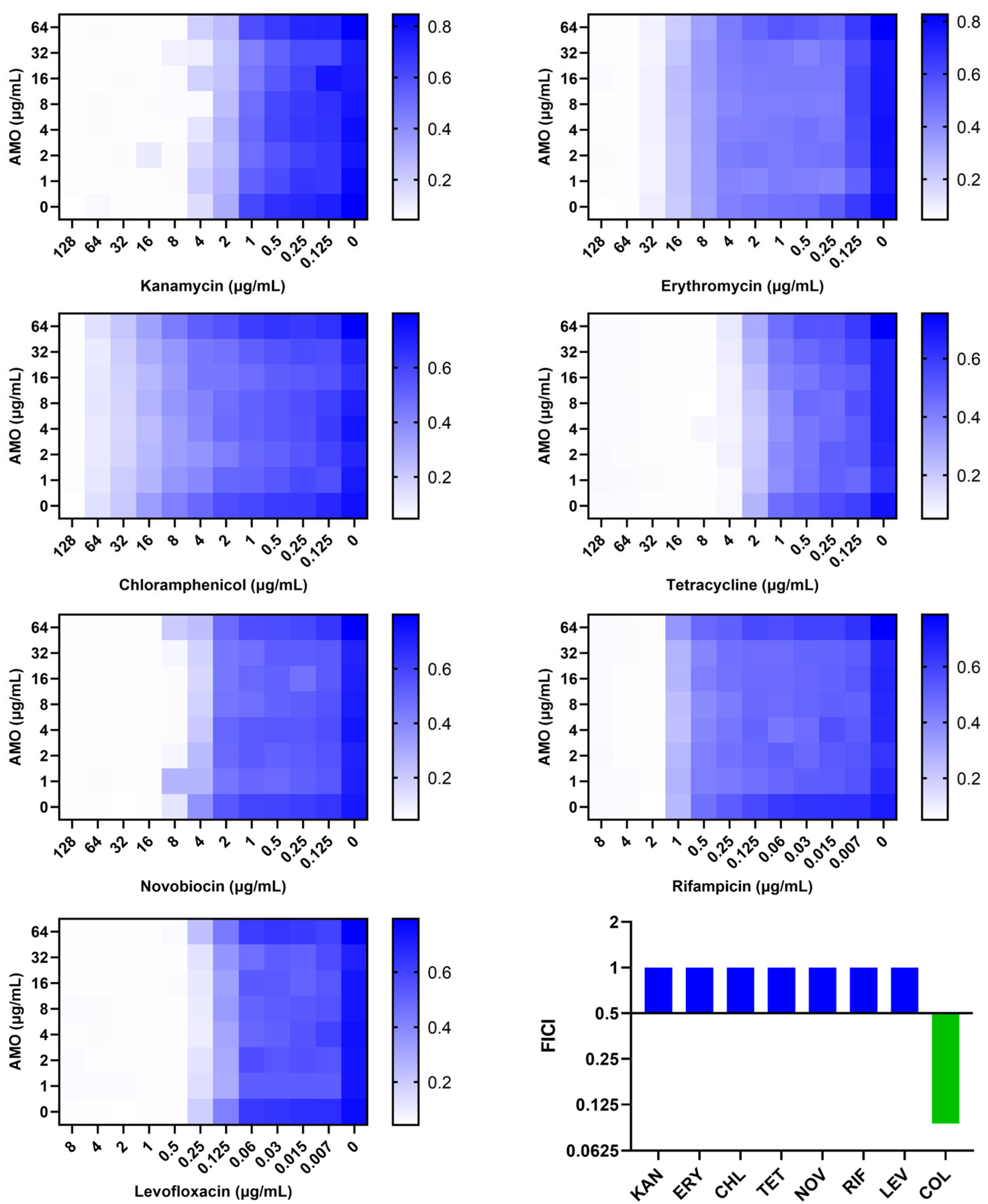
A comparison was made of the synergistic effect of AMO in combination with antibiotics on different mechanisms (Figure 4). AMO was found to demonstrate synergistic antibacterial activity exclusively with colistin, which targets the outer membrane (OM). Consequently, the hypothesis was formulated that AMO might enhance OM disruption synergistically with colistin.
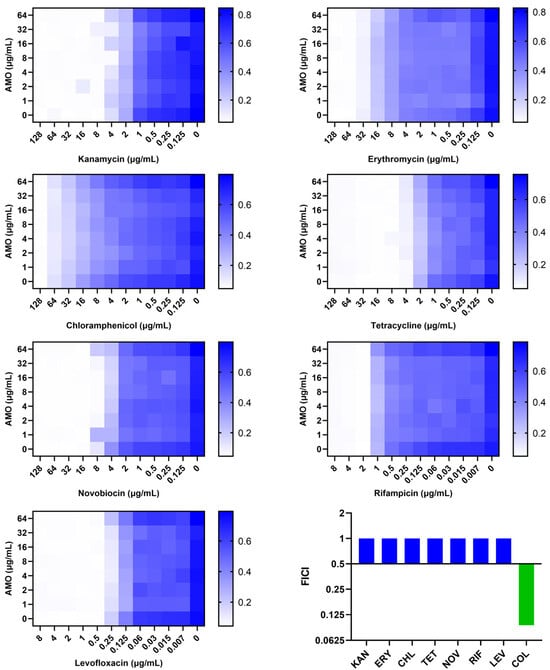
Figure 4.
The synergistic effect of AMO combined with different antibiotics against A. baumannii ATCC19606, as shown by the checkerboard assay, and their FICI.
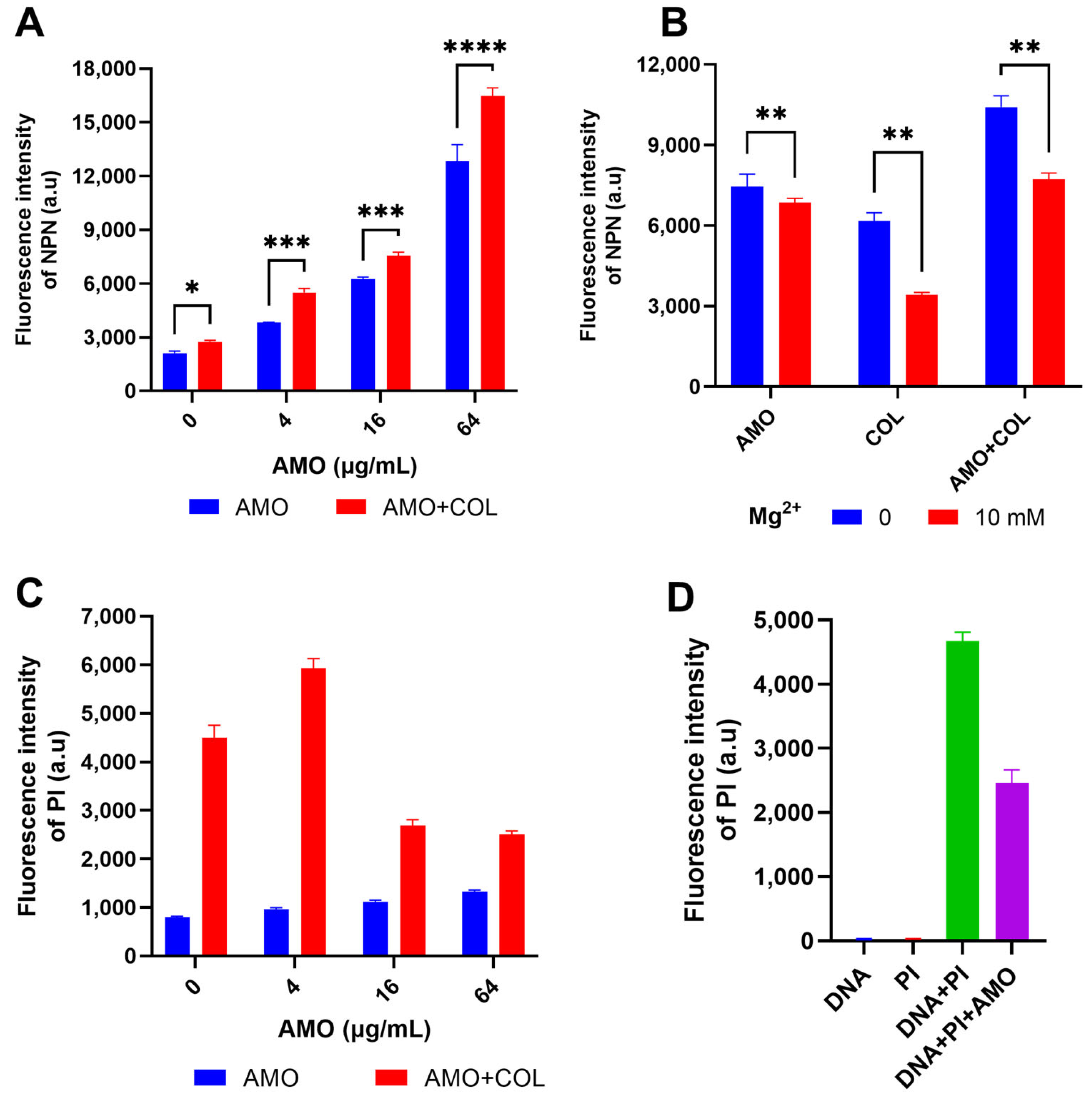
NPN was used to detect OM permeability by the enhancement of fluorescence upon binding to the hydrophobic part of the phospholipid bilayer [21]. The fluorescence intensity of NPN increased dramatically when AMO was combined with colistin (Figure 5A), indicating that the combination observably improved the permeability of the OM. Concurrently, both AMO and colistin have been observed to induce outer membrane disruption, a process that can be counteracted by excess Mg2+ (Figure 5B) [22]. This observation suggests the possibility of a shared mechanism for the binding of outer membrane cations by these two compounds. In order to gain further insight into the effect of colistin and AMO combination treatment on bacterial inner membrane (IM) permeability, PI was used as it binds to nucleic acids in membrane-damaged bacteria [23]. The combination treatment of AMO and colistin in this study resulted in a significant increase in IM permeability at low AMO concentrations (Figure 5C). Unexpectedly, the fluorescence values were instead reduced with high concentrations of AMO. Following the implementation of a fluorescence-based analysis, it was determined that AMO exhibits interference with PI binding to DNA, a phenomenon that is likely attributable to the capacity of AMO to bind DNA itself (Figure 5D).
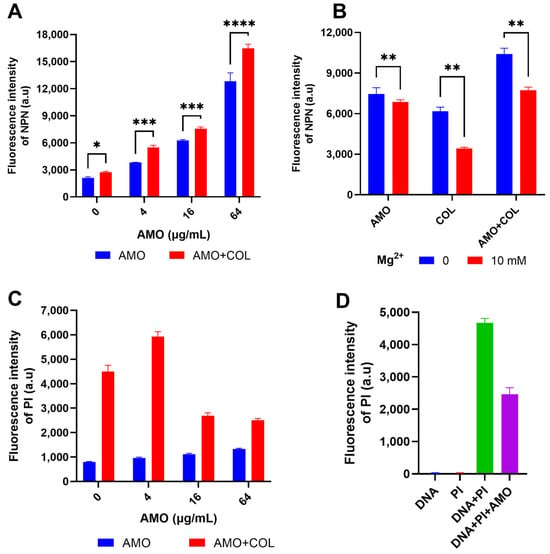
Figure 5.
(A) Detection of the OM permeability of A. baumannii ATCC19606 under different concentrations of AMO (0, 4, 16 and 64 μg/mL), with or without colistin (1 μg/mL). (B) Detection of the OM permeability of A. baumannii ATCC19606 treated with AMO (16 μg/mL), colistin (1 μg/mL) alone, or their combination, with or without Mg2+. (C) Detection of the IM permeability of A. baumannii ATCC19606 under different concentrations of AMO (0, 4, 16, and 64 μg/mL) with or without colistin (1 μg/mL). (D) The fluorescence values for the different systems. (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001; ****, p < 0.0001).
2.4. Binding of Amorolfine to DNA Leads to Potential Bactericidal Activity
Despite the fact that AMO is not effective against Gram-negative or -positive bacteria, it has been demonstrated to possess bactericidal activity against outer membrane-deficient A. baumannii and shows synergistic activity with colistin, which suggests the potential for biological activity. In addition to the disruptive effect of AMO on the outer membrane, it is conceivable that the synergistic ability of AMO with colistin stems from its potential biological activity, in particular, its capacity to bind to DNA. In the absence of reports indicating AMO binding to DNA, further experimentation was conducted to investigate their binding mechanism.
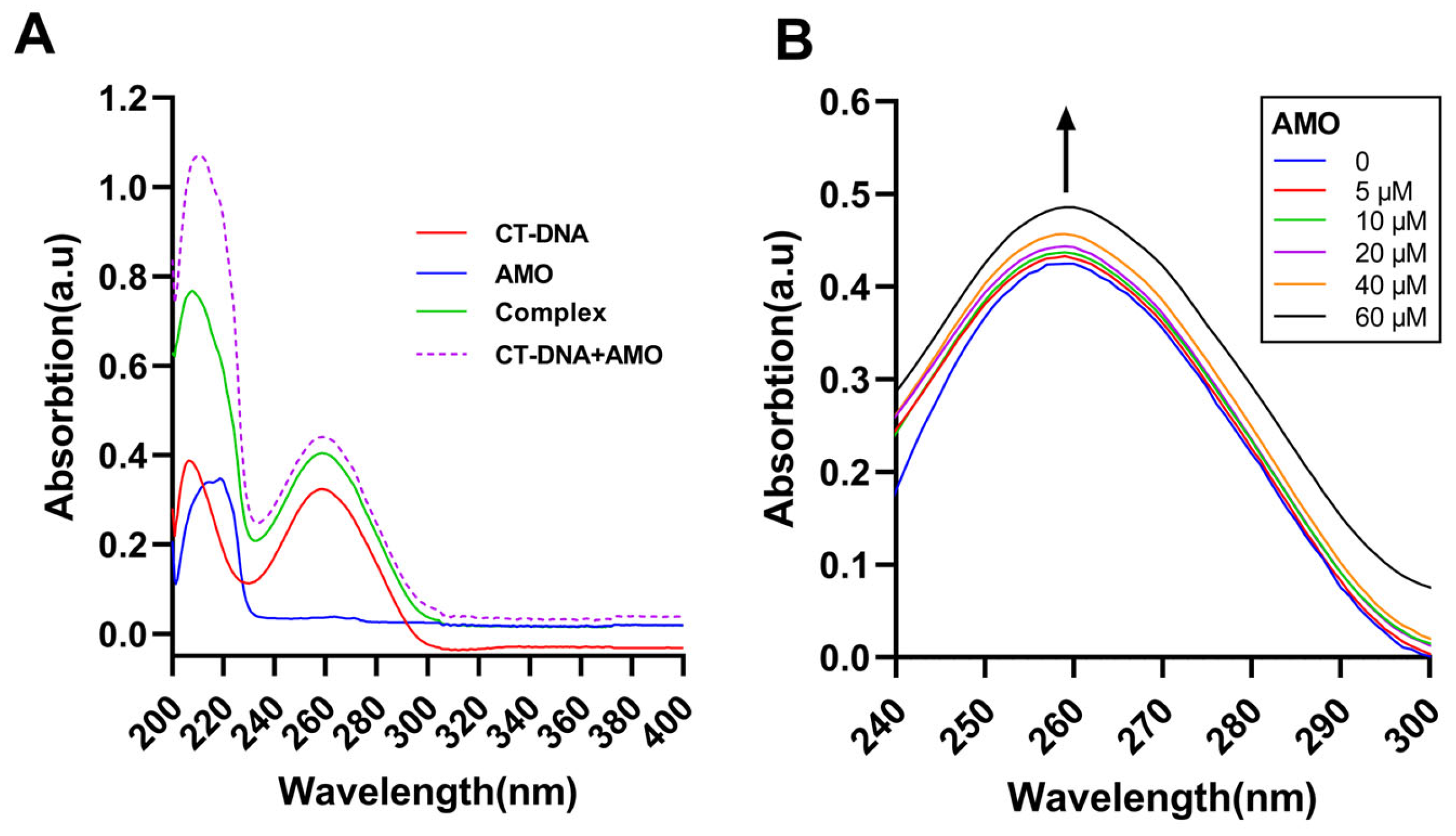
Ultraviolet-visible absorption spectroscopy can be a common method to study DNA stability and its interaction with small ligand molecules. UV-vis analysis of CT-DNA in the absence and presence of AMO and the uptake of free AMO, CT-DNA, and its complex was conducted (Figure 6A). The results suggested a complex formation between AMO and DNA as the sum of the absorbance values of AMO and free CT-DNA was different from the complex. Moreover, with increasing concentrations of AMO, the absorption increased and hyperchromism was observed (Figure 6B). These results suggested a possible non-covalent interaction between AMO and CT-DNA.
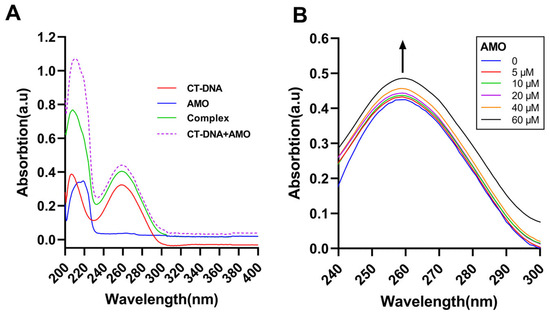
Figure 6.
(A) UV-vis absorption spectra of CT-DNA (30 μM), AMO (2 μM) alone, and their complex. (B) UV-vis absorption spectra of CT-DNA (40 μM) in the presence of increasing concentrations of AMO (0–60 μM). The arrow shows the emission intensity changes upon increasing AMO concentrations.
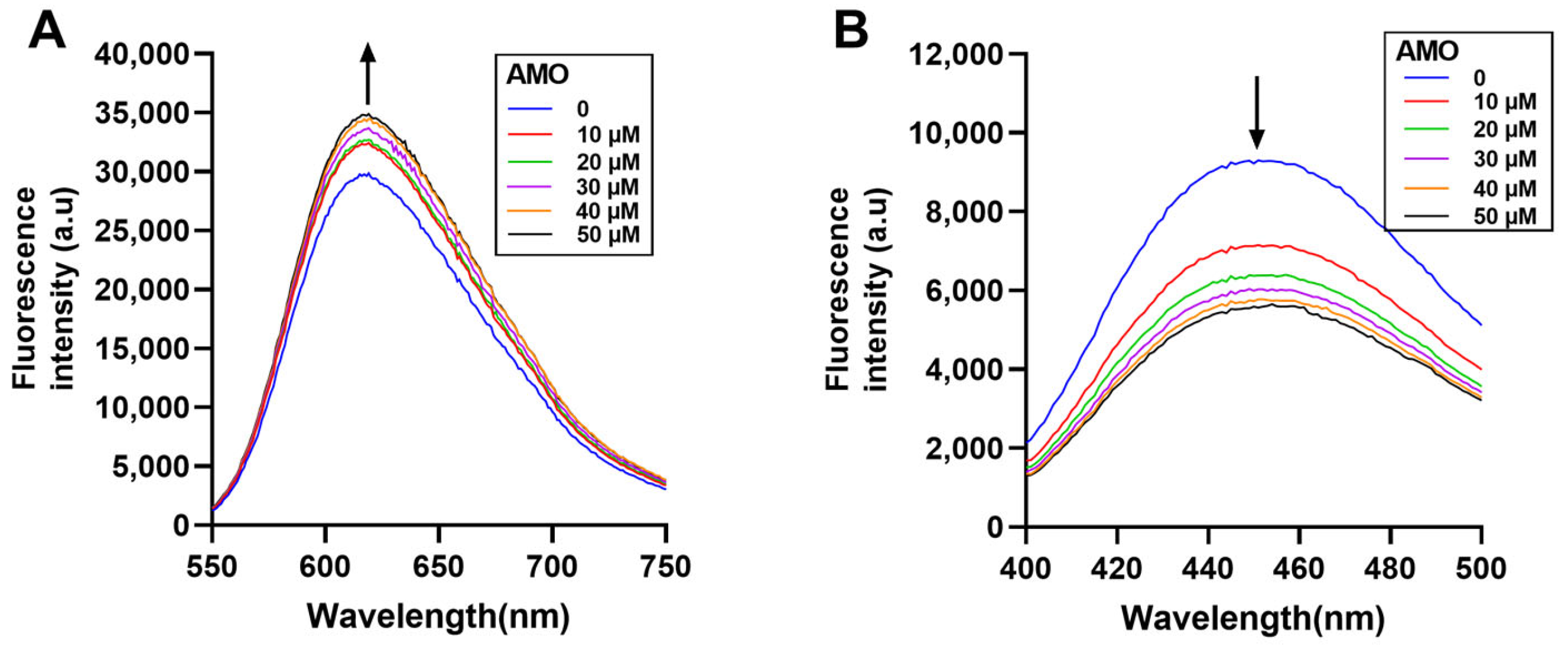
Fluorescence spectroscopy is an effective method to study the DNA binding mode [24]. In general, EB and Hoechst 33258 bind to DNA through the insertion and groove binding modes, respectively, after which there is an increase in the emission spectra. If the drug binds to DNA in a similar mode, the dye will be displaced from the DNA helix, resulting in reduced fluorescence emissions [25]. Here, the emission spectra of the EB-DNA complex increased with increasing AMO concentration (Figure 7A), while the emission spectra of the Hoechst-DNA complex decreased (Figure 7B). These results showed that AMO binds to DNA primarily through a minor groove binding mode, but this binding leads to structural damage and base exposure of the DNA, which, in turn, binds better to the EB, leading to an increase in the emission spectrum of the EB-DNA complex.
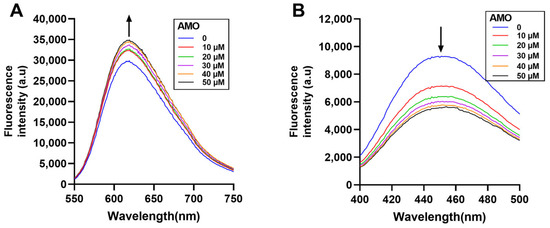
Figure 7.
Displacement assays using nucleic acid fluorescent dyes. The CT-DNA and EB (A) complex and CT-DNA and Hoechst 33258 (B) complex were excited in the presence of increasing concentrations of AMO (0–50 μM). The arrow shows the emission intensity changes upon increasing AMO concentrations.
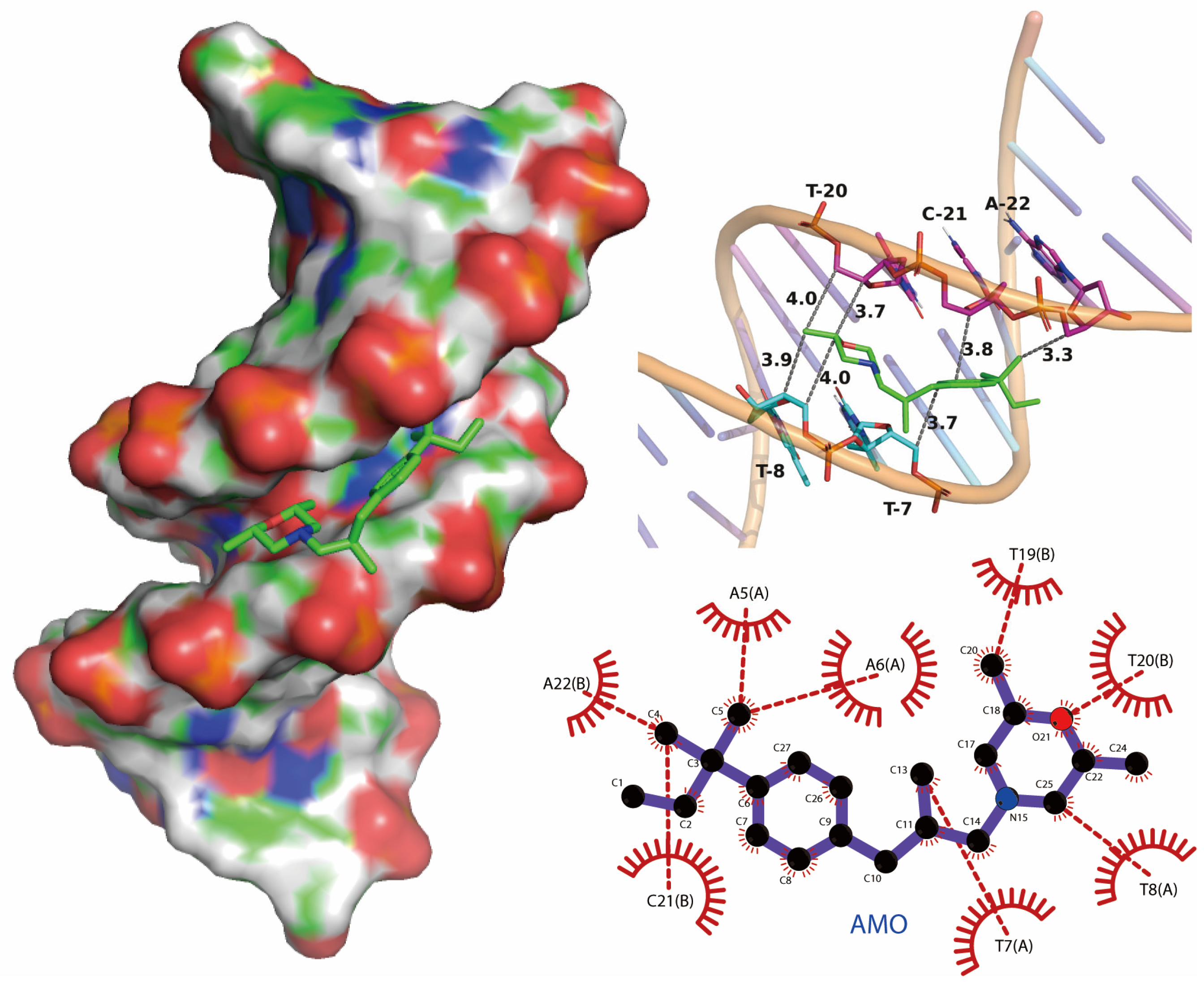
We performed molecular docking studies using the AutoDock Vina docking modules. The molecular docking result showed that the binding mode of AMO is groove-binding in nature, which is consistent with previous experimental results (Figure 8). The maximum affinity conformation of AMO with DNA showed that AMO interacts with DNA near the AT region and had a minimum binding energy of −6.0 kcal/mole, which is similar to groove-binding drugs that prefer to interact with AT-rich regions rather than GC-rich regions [26,27].
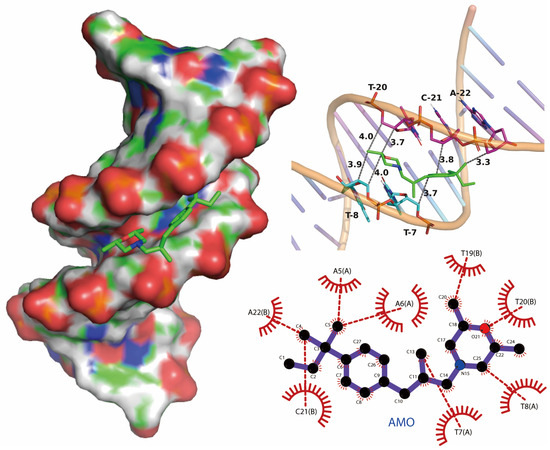
Figure 8.
Potential binding mode between AMO and DNA using molecular docking.
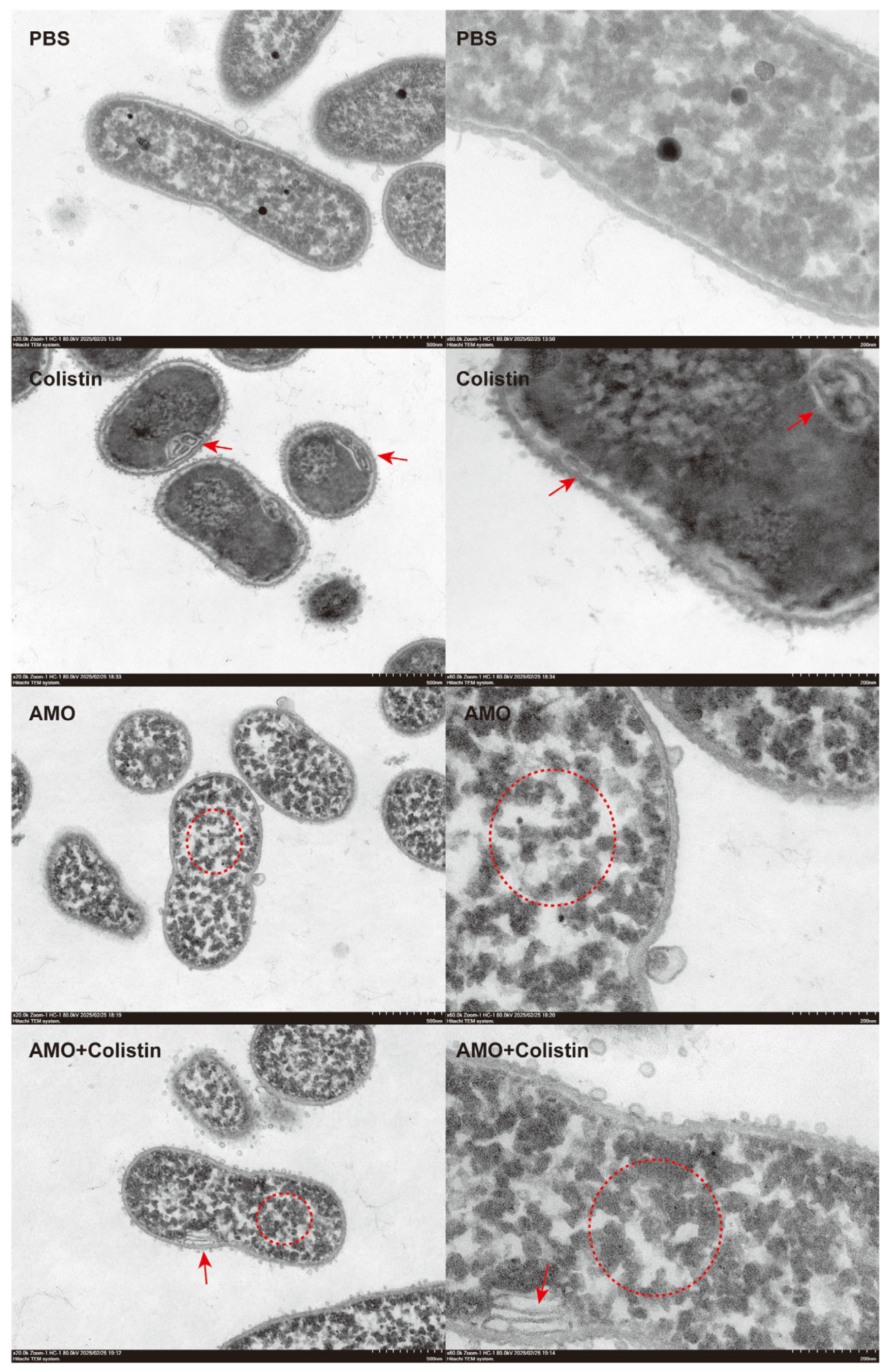
To further evaluate the synergistic antibacterial mechanism of AMO and colistin [28], the structure and morphology of bacteria treated with different drugs were observed using TEM. Compared with the control group, bacterial structure was dramatically affected in both the colistin and AMO monotherapy groups (Figure 9). However, the effect of colistin on the bacteria was mainly focused on the structure of the envelope, giving it the appearance of discontinuous or wrinkled membranes, as shown by the red arrows, which finding is consistent with its mechanism targeting the outer membrane. Meanwhile, in the AMO-treated group, the cytoplasm within the bacteria manifested aggregation, as shown by the red circle. Previous reports have indicated that DNA-binding drugs induce a comparable phenomenon, resulting in the concentration of cytoplasm in the nucleoid region of the bacterial cells [29,30]. In contrast, the combined group exhibited both phenomena simultaneously, thereby suggesting that the DNA binding of AMO and the envelope disruption of colistin occurred concurrently. This finding may provide a rationale for the observed synergy between AMO and colistin.
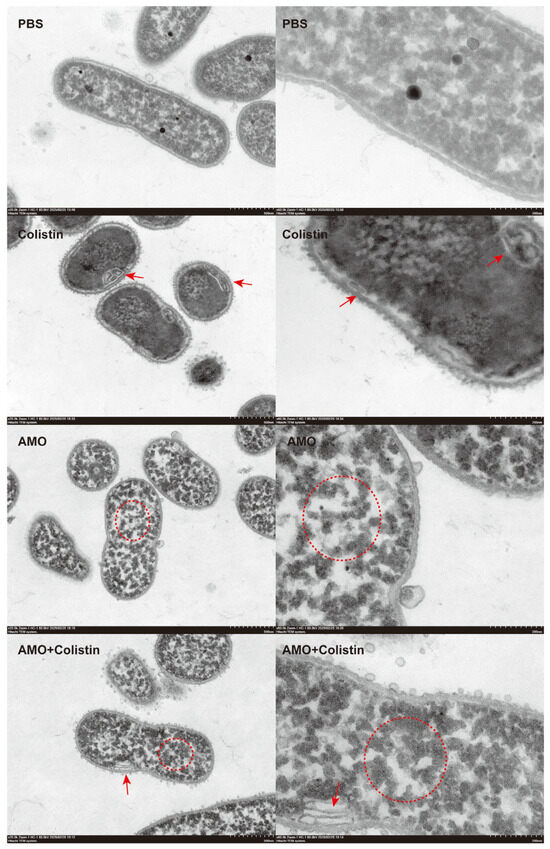
Figure 9.
Morphological analysis of A. baumannii ATCC19606 treated with colistin (1 μg/mL), AMO (32 μg/mL) alone, or their combination, elucidated by transmission electron microscopy (scale bar: 500 nm and 200 nm).
2.5. Amorolfine Enhances the Efficacy of Colistin In Vivo Infection Models
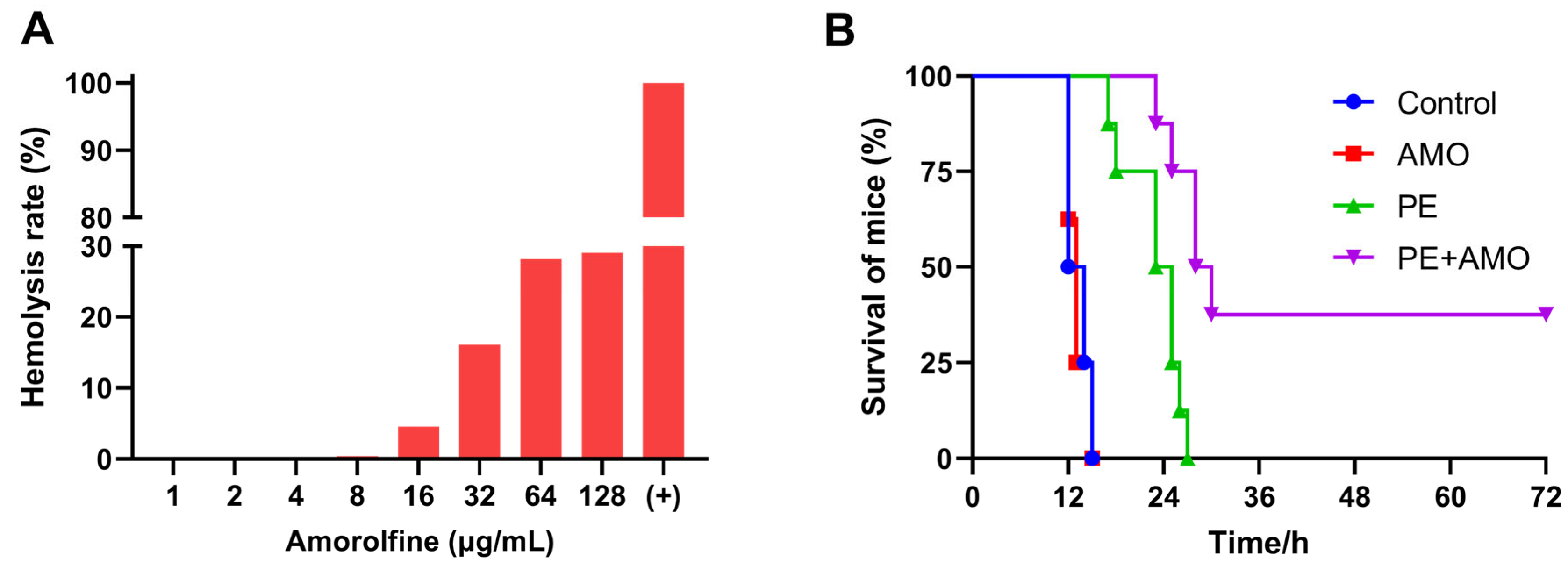
Given that the combination of AMO and colistin showed outstanding synergistic bactericidal activity against A. baumannii in vitro, we next evaluated its therapeutic efficacy in vivo with a mouse sepsis model. First, the hemolytic activity of AMO was assessed using mouse blood erythrocytes to ensure appropriate and safe drug dosing. The in vivo drug concentration in AMO was set at 16 mg/kg, as hemolysis is generally considered to be in the safe range of less than 5% (Figure 10A) [31]. In the mouse sepsis model, the survival rate was used to evaluate the effect of synergistic therapy. All mice treated with saline or AMO died within 24 h, while colistin monotherapy slightly prolonged the survival time of the mice, but all still died within 36 h. In comparison, the combination of 0.5 mg/kg colistin and 16 mg/kg AMO increased the survival rate to 37.5% (3/8) (Figure 10B). This result demonstrated the significant synergistic antibacterial effects of the combination of colistin and AMO in the treatment of A. baumannii infectious in vivo, highlighting its potential for clinical application.
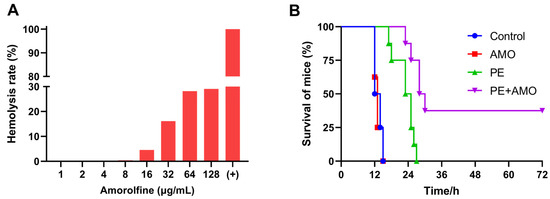
Figure 10.
(A) Hemolysis rate of AMO. (B) The survival rates of mice (n = 8 per group) in the mouse A. baumannii ATCC19606 sepsis model.
3. Discussion
In 2019 alone, antimicrobial resistance was estimated to have directly resulted in more than 1.2 million deaths, and, without preventative measures, this will increase to approximately 10 million by 2050 [32,33]. This fact has emerged as a pressing concern within the domain of public health. However, the development of new antibiotics faces numerous challenges, as evidenced by the fact that only 43 phase 1–3 clinical trials were registered for antibiotics by the end of 2020, compared to 1300 trials for anticancer agents [34]. Antibiotic synergy is a promising strategy to combat antibiotic-resistant bacteria, particularly those antibiotics that have become neglected and disused because of toxicity or moderate activity [35,36,37].
In this study, we identified a new potential colistin adjuvant—amorolfine, which enhanced the bactericidal activity of colistin against A. baumannii, both in vitro and in vivo. Amorolfine is a morpholine antifungal drug for topical use, like toenail onychomycosis [38], but it has never been reported that AMO has potential antibacterial activity. The results of the checkerboard studies and time-killing curve assay showed that a combination of AMO and colistin dramatically increased the bactericidal activity of colistin against A. baumannii, compared to monotherapy. In addition, the combination had a synergistic bacteriostatic effect on all clinical strains tested, regardless of whether they were colistin-resistant or not. The results of the biofilm formation inhibition assay demonstrate that AMO exhibits anti-biofilm activity. Biofilm is a three-dimensional bacterial community structure composed of polysaccharides, proteins, extracellular DNA, and others [39,40]. It represents an important barrier for bacteria to resist the harsh external environment, especially disinfectants and antibiotics in hospital environments [41]. In previous experiments, we demonstrated the DNA-binding capability of AMO, which may lead to the absence of eDNA during biofilm formation and to its inhibition.
Herein, in order to explore how AMO and colistin work synergistically, a comparison was made of other types of antibiotics with different mechanisms in combination with AMO. The results demonstrated that AMO is only synergistic with colistin, suggesting that the synergy between the two is dependent on colistin’s bactericidal mechanism. In consideration of the mechanism by which colistin targets LPS, resulting in bacterial OM disruption [42], bacterial OM permeability was measured using NPN following the combination treatment of AMO and colistin. This demonstrated that AMO enhanced the OM breaking efficiency of colistin; it was influenced by Mg2, which is similar to colistin. In accordance with the theory proposed by Buchholz et al. [43], it is hypothesized here that the similar outer membrane disruption mechanism of AMO and colistin contributes to the initial disruption of the outer membrane structure, thereby facilitating the release of additional LPS binding sites for binding to colistin. Membrane permeability is one of the most important factors for antibiotic activity, and membrane-targeted antibiotics, like colistin, usually show rapid bactericidal activity. The combination of AMO and colistin showed a rapid bactericidal effect in the time-killing curve; the bacterial count dropped rapidly within 4 h. Furthermore, the PI measurement of IM permeability reflected the synergistic enhancement of IM damage by AMO and colistin. Concurrently, we found that AMO seems to affect the fluorescence intensity of the nucleic acid fluorescent dye PI, suggesting that AMO may be a DNA-binding drug.
The ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy and competitive displacement assays showed that AMO binds to DNA and displayed a minor groove binding mode [44]. DNA is an important drug target [45]; for example, the anticancer drug cisplatin exerts its inhibitory effect on DNA replication and cell growth by binding to the DNA [46]. Similarly, quinolone antibiotics are known to bind to DNA and DNA topoisomerases, thereby facilitating their bactericidal activity [47,48]. We used molecular docking to investigate the binding modes of AMO and DNA; consistent with previous experimental findings, we found that AMO binds to DNA via a minor groove binding mode. The DNA-binding capacity of AMO and the membrane-disrupting activity of colistin in bacterial structures were further confirmed by TEM images.
Finally, we tested the synergistic effect of AMO and colistin in a mouse A. baumannii sepsis model, and the combination therapy was effective in improving survival in mice. In consideration of the nephrotoxicity and neurotoxicity of colistin and the prevalence of colistin-resistant A. baumannii, its combination with AMO has the potential to reduce the actual drug dosage while ensuring the efficacy of colistin [49]. This combination represents a viable method to overcome the limitations of the clinical use of colistin.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents and Bacterial Strains
AMO (CAS No. 78613-38-4) and colistin sulfate (CAS No. 8068-28-8) were purchased from Macklin Biochemical Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). CT-DNA (CAS No. 91080-16-9) was purchased from Meryer Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China), and porcine mucin (CAS No. 84082-64-4) was purchased from Shanghai Yuanye Bio-Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). All other antibiotics were obtained from Sangon Biotech Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). All strains used in this study were isolated and preserved in our laboratory.
4.2. The Antimicrobial Susceptibility Test and Checkerboard Assays
The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) values of antibiotics were determined by the broth microdilution method according to the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) [50]. Bacteria were cultured to the logarithmic growth stage and the cell density was adjusted to 106 CFU. Antibiotics were 2-fold serial dilutions in the Mueller–Hinton (MH) culture. The MIC was recorded with no visible growth after incubation at 37 °C for 16 h. Synergistic antibacterial activity was determined by calculating the fractional inhibitory concentration index (FICI) through the checkerboard experiment. FICI ≤ 0.5 was defined as synergistic, 0.5 ≤ FICI ≤ 1 was defined as addition, 1 < FICI ≤ 4 was defined as indifference, and FICI > 4 was defined as antagonism.
4.3. The Time-Kill Assay
The time-kill assay was conducted to evaluate the synergistic effect of the tested combination, following the results obtained from the checkerboard assay. Briefly, A. baumannii ATCC19606 was inoculated into 5 mL of MH containing colistin (1 μg/mL) and AMO (16 μg/mL), either alone or in combination, at a concentration of 107 CFU/mL. The various drug-treated groups were subjected to cultivation at 37 °C with shaking at 220 rpm. At different time points (0, 1, 2, 4, 8, and 24 h), appropriate dilutions were made, and colony-forming units (CFU) were enumerated on MH agar plates.
4.4. The Biofilm Formation Assay
The biofilm inhibition assay was conducted on 96-well flat-bottom microtiter plates [51]. A. baumannii ATCC19606 was inoculated into 100 μL MH containing AMO (0, 4, 16, and 64 μg/mL) at a cell density of 106 CFU/mL. Six wells were used for each agent concentration. After incubating the 96-well plate at 37 °C for 24 h, planktonic cells were discarded, and the wells were washed twice with PBS. Subsequently, the plates were air-dried to facilitate the straightforward fixation of the biofilm. Staining and destaining were carried out using 1% crystal violet solution and ethanol, respectively. Between these steps, the wells were washed with 1 × PBS and left to air-dry. Finally, the absorbance of each well was measured at 595 nm using a microplate reader.
4.5. Membrane Permeability Evaluation
A. baumannii ATCC19606 was grown overnight at 37 °C with shaking at 220 rpm. Then, the cultures were washed and suspended with 5 mM HEPES (pH 7.0, plus 5 mM glucose). In the same buffer, the OD600 of the bacterial suspension was standardized to 0.5 and the fluorescent dye was added. After incubation at 37 °C for 30 min, the bacterial suspension was mixed with AMO and colistin, either alone or in combination. After incubation for 1 h, 200 µL of bacterial suspension was added to the 96-well plate. Subsequently, fluorescence intensity was measured by an Infinite 200 PRO plate reader (Tecan, Männedorf, Switzerland). A fluorescent probe of 1-N-phenylnaphthylamine (NPN) (10 μM) was used to evaluate the outer membrane (OM) integrity, using an excitation wavelength of 350 nm and an emission wavelength of 420 nm, and propidium iodide (PI) (5 μM) was used to evaluate the inner membrane (IM) integrity using an excitation wavelength at 535 nm and an emission wavelength of 615 nm.
4.6. Ultraviolet-Visible Spectroscopy
The interaction of AMO with CT-DNA was studied using UV-vis spectroscopy (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan). A fixed concentration of CT-DNA (40 μM) was titrated with varying AMO concentrations from 0 to 120 μM in 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.2) buffer. To obtain the absorption spectra, the required amount of AMO was added to both the compound solution and the reference solution to eliminate the absorbance of the AMO itself. The samples were incubated at 25 °C for 24 h and the spectra were scanned from 240 to 300 nm.
4.7. The Competitive Displacement Assays
Ethidium bromide (EB) and acridine Hoechst 33258 are intercalating dyes and the minor groove binding dye is separate; they are commonly used to study the binding mode of drugs with CT-DNA. A fixed concentration (5 μM) of EB or Hoechst 33258 was taken in the presence of 50 μM CT-DNA in 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.2) buffer. The EB-DNA complex was excited at 471 nm and emissions spectra were recorded from 550 to 750 nm in the presence of an increasing concentration of AMO. Similarly, the Hoechst-DNA complex was excited at 343 nm, and emission spectra were recorded from 400 to 500 nm.
4.8. The Molecular Docking Assay
The CT-DNA sequence d(CGTGAATTCACG)2 dodecamer (PDB ID: 5T4W) was obtained from the Protein Data Bank. Receptor (DNA) and ligand (complex) files were prepared using MGLtools1.4.2 and OpenObabel3.0.0. A molecular docking program, AutoDock Vina v1.2.5, was used to study the interaction of AMO with DNA. Docking pockets were predicted using CavityPlus v1.0 and the first ranked result was used as the docking center. The grid box was set as a square with 18 Å sides, for which 20 conformations were output, and the optimal conformations were selected according to docking scores. PyMol 3.1.3.1 (Educational Version) was used to visualize the docked complex.
4.9. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
The morphological appearance and morphometric analysis of the cell membrane of A. baumannii were determined using TEM. Briefly, the bacterial suspensions were washed twice with PBS and exposed to 32 μg/mL AMO, 1 μg/mL colistin alone, or their combination (32 μg/mL AMO + 1 μg/mL colistin) at 37 °C. After 4 h, the cells were centrifuged, collected, and fixed using 2.5% glutaraldehyde at 4 °C overnight. Then, the samples were fixed with 1% osmium acid, embedded in Epon 812 epoxy resin, sectioned, stained with 2% uranyl acetate, and observed using TEM (HT7800 HITACHI, Tokyo, Japan).
4.10. The Hemolysis Test
To further evaluate the security of AMO, a mouse red blood cell (RBS) hemolysis assay was used. Various concentrations of AMO from 0 to 128 μg/mL were incubated with the RBC suspension at 37 °C for 2 h. Meanwhile, 0.1% Triton X-100 served as the corresponding positive control group. Following incubation, the supernatant was obtained by centrifugation at 12,000 rpm for 5 min, and its absorbance at 545 nm was measured. Hemolysis rate (%) = (OD545 experimental group − OD545 negative control group)/(OD545 positive control group − OD545 negative control group).
4.11. The Mouse Infection Model In Vivo
Specified pathogen-free (SPF) female BALB/c mice (5 to 6 weeks old, ~20 g) were randomly grouped, with eight mice in each group. Before the formal experiment, the mice were fed for one week to adapt to the environment and then divided equally into four groups based on weight (n = 8 per group). Referring to the sepsis model established by Harris [52], minor modifications were made based on our research. Briefly, A. baumannii ATCC19606, cultured under exponential growth conditions, was collected and the bacterial concentration was adjusted to OD600 = 1.0 with saline. The inoculum was prepared by mixing the bacterial solution with 10% porcine mucin solution at a ratio of 1:1. Mice were injected intraperitoneally with 0.5 mL of the inocula. Then, after 1 h, the mice were injected with saline, AMO (16 mg/kg), colistin (0.5 mg/kg), and their combination (0.5 mg/kg + 16 mg/kg). The mice were observed, and death was recorded within 72 h.
4.12. Statistical Analysis
The sample size for each statistical analysis was greater than or equal to three. All data were analyzed using GraphPad Prism 9.0 software. Comparisons between two groups were calculated using two-way ANOVA (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001; ****, p < 0.0001).
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, our study suggests the synergistic activity of AMO and colistin against GNB, notably A. baumannii; combination therapy enhanced the therapeutic efficacy of colistin in a mouse sepsis model. Moreover, mechanistic studies suggested that AMO enhanced the ability of colistin to damage the membrane and that AMO may cross the OM via this process to bind to intracellular DNA and exert additional bactericidal activity. The dual-target bactericidal mechanism of AMO–colistin will effectively reduce the possibility of bacterial drug resistance, which finding is of high clinical value [53]. In addition, we are currently engaged in the modification of AMO, with the objective of producing molecules that exhibit enhanced antimicrobial activity and identifying additional application scenarios.
Author Contributions
T.L. designed and drafted this article. D.C. designed and reviewed the entire contents of the manuscript. S.L., X.C. and L.L. carried out the experiments. F.G. analyzed the data. Y.Y. revised and supervised the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 82473820).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal studies were conducted in accordance with SJTU Institutional Animal Welfare and Ethics guidelines and were approved by the Animal Research Committees of SJTU (A2024410).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
| E. coli | Escherichia coli |
| A. baumannii | Acinetobacter baumannii |
| FICI | Fractional inhibitory concentration index |
| CV | Crystal violet |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| OM | Outer membranes |
| IM | Inner membrane |
| MDR | Multidrug-resistant |
| XDR | Extensively drug-resistant |
| AMO | Amorolfine |
| K. pneumoniae | Klebsiella pneumoniae |
| P. aeruginosa | Pseudomonas aeruginosa |
| NPN | 1-N-phenylnaphthylamine |
| PI | Propidium iodide |
| EB | Ethidium bromide |
| CT-DNA | Calf thymus DNA |
| MIC | Minimum inhibitory concentration |
| CLSI | Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute |
| MH | Mueller–Hinton |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| TEM | Transmission electron microscopy |
| RBC | Red blood cell |
| SPF | Specified pathogen-free |
| CFU | Colony-forming unit |
| HEPES | 4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethanesulfonic acid |
References
- Whiteway, C.; Breine, A.; Philippe, C.; Van der Henst, C. Acinetobacter baumannii. Trends Microbiol. 2022, 30, 199–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarshar, M.; Behzadi, P.; Scribano, D.; Palamara, A.T.; Ambrosi, C. Acinetobacter baumannii: An Ancient Commensal with Weapons of a Pathogen. Pathogens 2021, 10, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gedefie, A.; Demsis, W.; Ashagrie, M.; Kassa, Y.; Tesfaye, M.; Tilahun, M.; Bisetegn, H.; Sahle, Z. Acinetobacter baumannii Biofilm Formation and Its Role in Disease Pathogenesis: A Review. Infect. Drug Resist. 2021, 14, 3711–3719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira, D.M.P.; Forde, B.M.; Kidd, T.J.; Harris, P.N.A.; Schembri, M.A.; Beatson, S.A.; Paterson, D.L.; Walker, M.J. Antimicrobial Resistance in ESKAPE Pathogens. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 33, e00181-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stansly, P.G.; Schlosser, M.E. Studies on Polymyxin: Isolation and Identification of Bacillus polymyxa and Differentiation of Polymyxin from Certain Known Antibiotics. J. Bacteriol. 1947, 54, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bialvaei, A.Z.; Samadi Kafil, H. Colistin, mechanisms and prevalence of resistance. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2015, 31, 707–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabnis, A.; Hagart, K.L.; Klockner, A.; Becce, M.; Evans, L.E.; Furniss, R.C.D.; Mavridou, D.A.; Murphy, R.; Stevens, M.M.; Davies, J.C.; et al. Colistin kills bacteria by targeting lipopolysaccharide in the cytoplasmic membrane. Elife 2021, 10, e65836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Liu, Y.; Huang, X.; Ding, S.; Wang, Y.; Shen, J.; Zhu, K. A broad-spectrum antibiotic adjuvant reverses multidrug-resistant Gram-negative pathogens. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 1040–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, Z.; Samodelov, S.L.; Kullak-Ublick, G.A.; Visentin, M. Molecular Mechanisms of Colistin-Induced Nephrotoxicity. Molecules 2019, 24, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordooei Javan, A.; Shokouhi, S.; Sahraei, Z. A review on colistin nephrotoxicity. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2015, 71, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolinsky, E.; Hines, J.D. Neurotoxic and nephrotoxic effects of colistin in patients with renal disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1962, 266, 759–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamel, M.; Rolain, J.M.; Baron, S.A. The History of Colistin Resistance Mechanisms in Bacteria: Progress and Challenges. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.H.; Liu, Y.Y.; Shen, Y.B.; Yang, J.; Walsh, T.R.; Wang, Y.; Shen, J. Plasmid-mediated colistin-resistance genes: Mcr. Trends Microbiol. 2024, 32, 365–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Tong, Z.; Shi, J.; Li, R.; Upton, M.; Wang, Z. Drug repurposing for next-generation combination therapies against multidrug-resistant bacteria. Theranostics 2021, 11, 4910–4928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Duran, N.; Leon-Buitimea, A.; Morones-Ramirez, J.R. Unraveling resistance mechanisms in combination therapy: A comprehensive review of recent advances and future directions. Heliyon 2024, 10, e27984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, N.S.; Lee, S.H.; Lim, Y.S.; Choi, H.; Ahn, J.Y.; Jeong, S.J.; Shin, S.J.; Choi, J.Y.; Choi, Y.H.; Yeom, J.S.; et al. In vivo efficacy of combination of colistin with fosfomycin or minocycline in a mouse model of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii pneumonia. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polak-Wyss, A. Mechanism of action of antifungals and combination therapy. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 1995, 4, S11–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haria, M.; Bryson, H.M. Amorolfine. A review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic potential in the treatment of onychomycosis and other superficial fungal infections. Drugs 1995, 49, 103–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Jiang, S.; Zheng, K.; Song, J.; Liang, P. Interaction Between Amorolfine and Voriconazole Against Fusarium species. Mycopathologia 2021, 186, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Aurosree, B.; Gopalakrishnan, B.; Balada-Llasat, J.-M.; Pancholi, V.; Pancholi, P. The role of LpxA/C/D and pmrA/B gene systems in colistin-resistant clinical strains of Acinetobacter baumannii. Front. Lab. Med. 2017, 1, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, B.; Grant, C.; Hancock, R.E. Use of the fluorescent probe 1-N-phenylnaphthylamine to study the interactions of aminoglycoside antibiotics with the outer membrane of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1984, 26, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newton, B.A. Site of action of Polymyxin on Pseudomonas aeruǵinosa: Antagonism by Cations. Microbiology 1954, 10, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Günther, S.; Hübschmann, T.; Wick, L.Y.; Harms, H.; Müller, S. Limits of propidium iodide as a cell viability indicator for environmental bacteria. Cytom. Part A 2007, 71A, 592–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwer, R.; Ahmad, N.; Al Qumaizi, K.I.; Al Khamees, O.A.; Al Shaqha, W.M.; Fatma, T. Interaction of procarbazine with calf thymus DNA—A biophysical and molecular docking study. J. Mol. Recognit. 2017, 30, e2599. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, D.; Gauri; Kaur, N. Multispectroscopic and computational techniques to study the interaction of anthraquinone appended sensor with calf thymus DNA. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2024, 42, 4370–4378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimal, R.; Nur Unal, D.; Erkmen, C.; Bozal-Palabiyik, B.; Siddiq, M.; Eren, G.; Shah, A.; Uslu, B. Development of the electrochemical, spectroscopic and molecular docking approaches toward the investigation of interaction between DNA and anti-leukemic drug azacytidine. Bioelectrochemistry 2022, 146, 108135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.T.; O’Donovan, L.A.; Venter, H.; Russell, C.C.; McCluskey, A.; Page, S.W.; Trott, D.J.; Ogunniyi, A.D. Comparison of two transmission electron microscopy methods to visualize drug-induced alterations of gram-negative bacterial morphology. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, A.; Nanjunda, R.; Wilson, W.D. Binding to the DNA minor groove by heterocyclic dications: From AT specific to GC recognition compounds. Curr. Protoc. 2023, 3, e729. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Xu, Y.; Hu, J. Intracellular mechanism of antimicrobial peptide HJH-3 against Salmonella pullorum. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 14485–14491. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; Xie, X.; Liu, H.; Huang, Y.; Wu, H.; Jiang, M.; Xu, P.; Ye, X.; Zhou, C. Potent antibacterial activity of MSI-1 derived from the magainin 2 peptide against drug-resistant bacteria. Theranostics 2020, 10, 1373. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Hu, P.; Liu, H.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Chen, L.; Feng, L.; Chen, L.; Zhou, T. Combining with domiphen bromide restores colistin efficacy against colistin-resistant Gram-negative bacteria in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2024, 63, 107066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almutairy, B. Extensively and multidrug-resistant bacterial strains: Case studies of antibiotics resistance. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1381511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, K.W.K.; Millar, B.C.; Moore, J.E. Antimicrobial resistance (AMR). Br. J. Biomed. Sci. 2023, 80, 11387. [Google Scholar]
- Brüssow, H. The antibiotic resistance crisis and the development of new antibiotics. Microb. Biotechnol. 2024, 17, e14510. [Google Scholar]
- Otto, R.G.; van Gorp, E.; Kloezen, W.; Meletiadis, J.; van den Berg, S.; Mouton, J.W. An alternative strategy for combination therapy: Interactions between polymyxin B and non-antibiotics. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2019, 53, 34–39. [Google Scholar]
- Tängdén, T. Combination antibiotic therapy for multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria. Upsala J. Med. Sci. 2014, 119, 149–153. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, G.D. Antibiotic adjuvants: Rescuing antibiotics from resistance. Trends Microbiol. 2016, 24, 862–871. [Google Scholar]
- Auvinen, T.; Tiihonen, R.; Soini, M.; Wangel, M.; Sipponen, A.; Jokinen, J. Efficacy of topical resin lacquer, amorolfine and oral terbinafine for treating toenail onychomycosis: A prospective, randomized, controlled, investigator-blinded, parallel-group clinical trial. Br. J. Dermatol. 2015, 173, 940–948. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, E.A.; Raafat, M.M.; Samir Mohamed, R.; Ali, A.E.E. Acinetobacter baumannii biofilm and its potential therapeutic targets. Future J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 9, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, N.; Perumal, G.; Doble, M. Bacterial resistance in biofilm-associated bacteria. Future Microbiol. 2015, 10, 1743–1750. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, S.; Mohler, J.; Mahajan, S.D.; Schwartz, S.A.; Bruggemann, L.; Aalinkeel, R. Microbial biofilm: A review on formation, infection, antibiotic resistance, control measures, and innovative treatment. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, S.; Liu, X.; Lin, W.; Zhu, K. Equisetin restores colistin sensitivity against multi-drug resistant gram-negative bacteria. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchholz, K.R.; Reichelt, M.; Johnson, M.C.; Robinson, S.J.; Smith, P.A.; Rutherford, S.T.; Quinn, J.G. Potent activity of polymyxin B is associated with long-lived super-stoichiometric accumulation mediated by weak-affinity binding to lipid A. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 4733. [Google Scholar]
- Sirajuddin, M.; Ali, S.; Badshah, A. Drug–DNA interactions and their study by UV–Visible, fluorescence spectroscopies and cyclic voltametry. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2013, 124, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Bolhuis, A.; Aldrich-Wright, J.R. DNA as a target for antimicrobials. Bioorg. Chem. 2014, 55, 51–59. [Google Scholar]
- Aldossary, S.A. Review on pharmacology of cisplatin: Clinical use, toxicity and mechanism of resistance of cisplatin. Biomed. Pharmacol. J. 2019, 12, 7–15. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharya, P.; Mukherjee, S.; Mandal, S.M. Fluoroquinolone antibiotics show genotoxic effect through DNA-binding and oxidative damage. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2020, 227, 117634. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Wang, L.; Liu, H.; Wang, R.; Chen, J. Studies on the interaction between antibiotics and DNA. Talanta 2007, 73, 444–450. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, L.M.; Ly, N.; Anderson, D.; Yang, J.C.; Macander, L.; Jarkowski III, A.; Forrest, A.; Bulitta, J.B.; Tsuji, B.T. Resurgence of colistin: A review of resistance, toxicity, pharmacodynamics, and dosing. Pharmacother. J. Hum. Pharmacol. Drug Ther. 2010, 30, 1279–1291. [Google Scholar]
- Wikler, M.A. Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria That Grow Aerobically: Approved Standard; Clsi (Nccls): Wayne, PA, USA, 2006; Volume 26. [Google Scholar]
- Biswas, I.; Mettlach, J. A simple static biofilm assay for Acinetobacter baumannii. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1946, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, G.; Holbein, B.E.; Zhou, H.; Xu, H.H.; Chen, W. Potential mechanisms of mucin-enhanced Acinetobacter baumannii virulence in the mouse model of intraperitoneal infection. Infect. Immun. 2019, 87, e00591-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.K.; Sheehan, J.P.; Bratton, B.P.; Moore, G.M.; Mateus, A.; Li, S.H.J.; Kim, H.; Rabinowitz, J.D.; Typas, A.; Savitski, M.M.; et al. A Dual-Mechanism Antibiotic Kills Gram-Negative Bacteria and Avoids Drug Resistance. Cell 2020, 181, 1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).