CD36 Induces Inflammation by Promoting Ferroptosis in Pancreas, Epididymal Adipose Tissue, and Adipose Tissue Macrophages in Obesity-Related Severe Acute Pancreatitis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
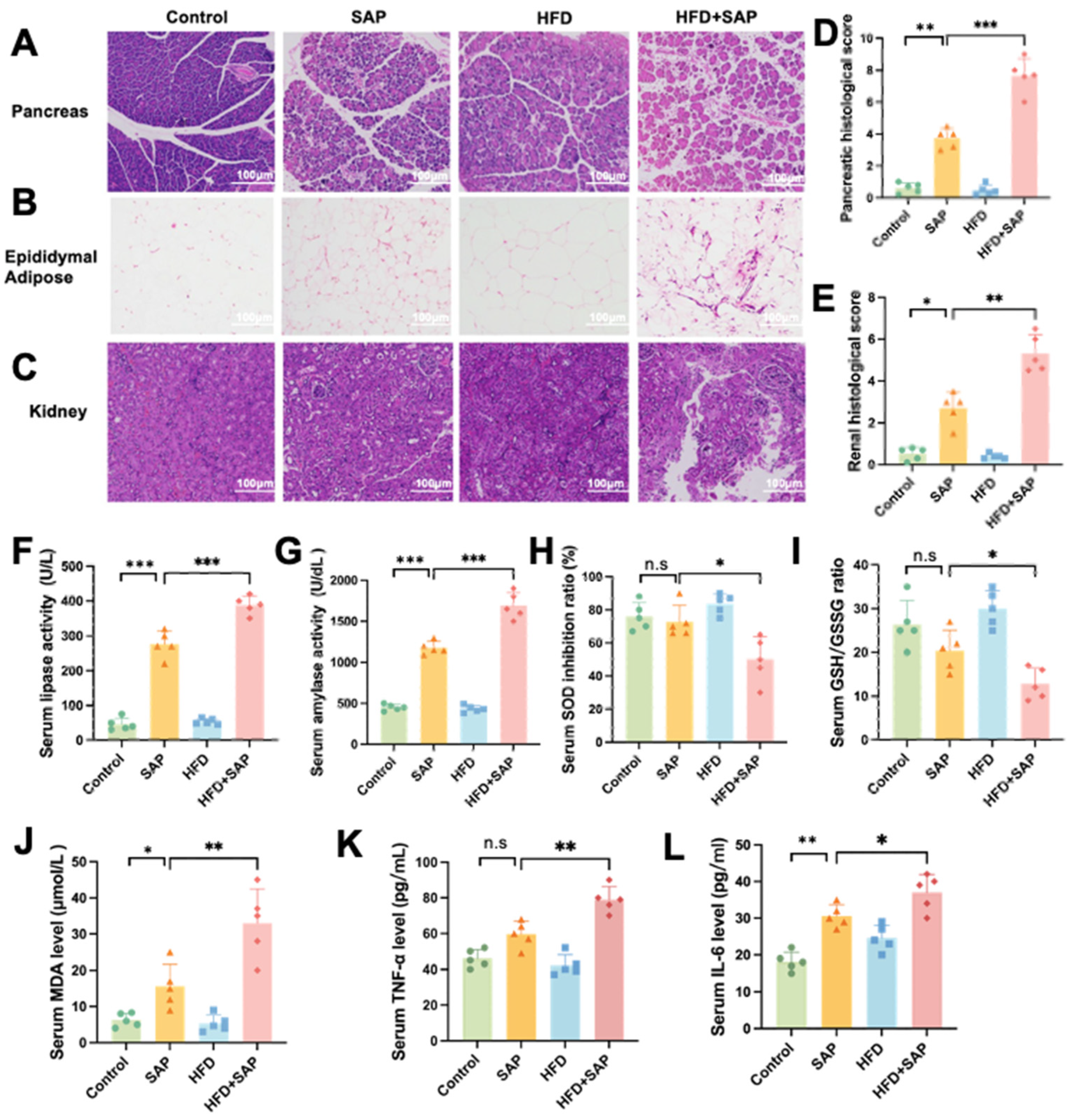
2.1. Obesity Aggravated Systemic Inflammation and Organ Injury During SAP
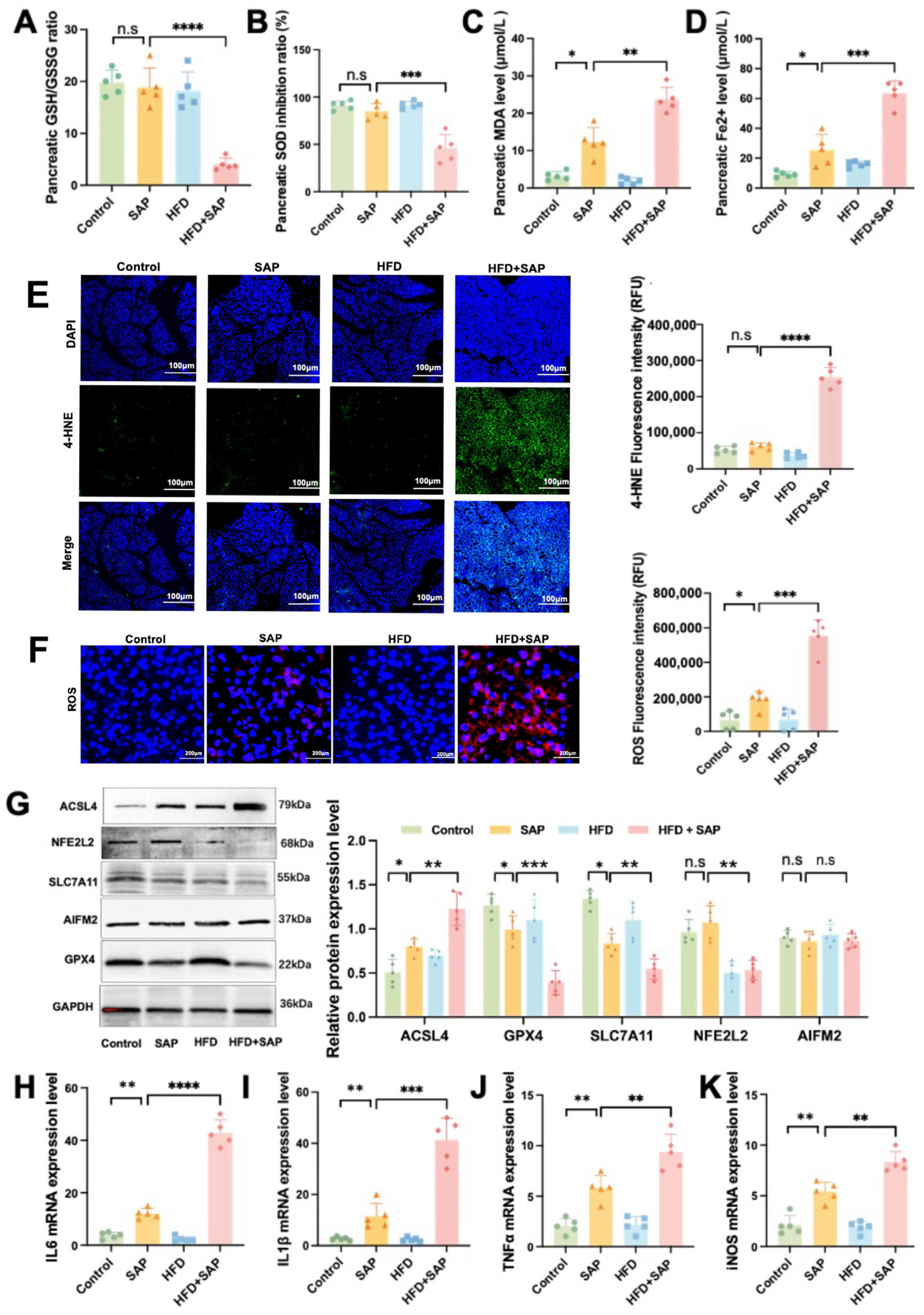
2.2. Obesity Aggravated Ferroptosis in Pancreatic Tissue During SAP
2.3. Obesity Aggravated Ferroptosis in Epididymal Adipose Tissue and ATMs During SAP
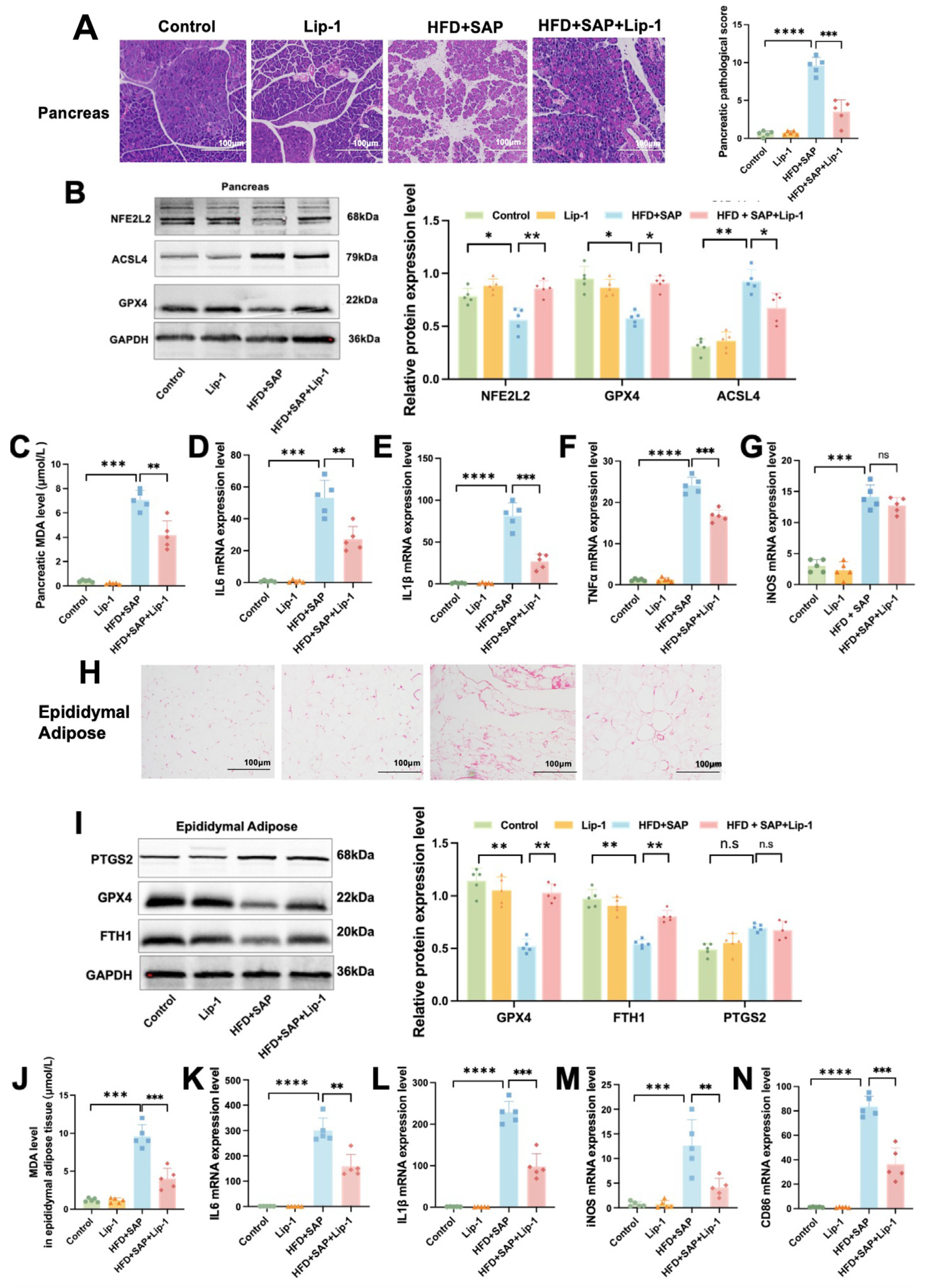
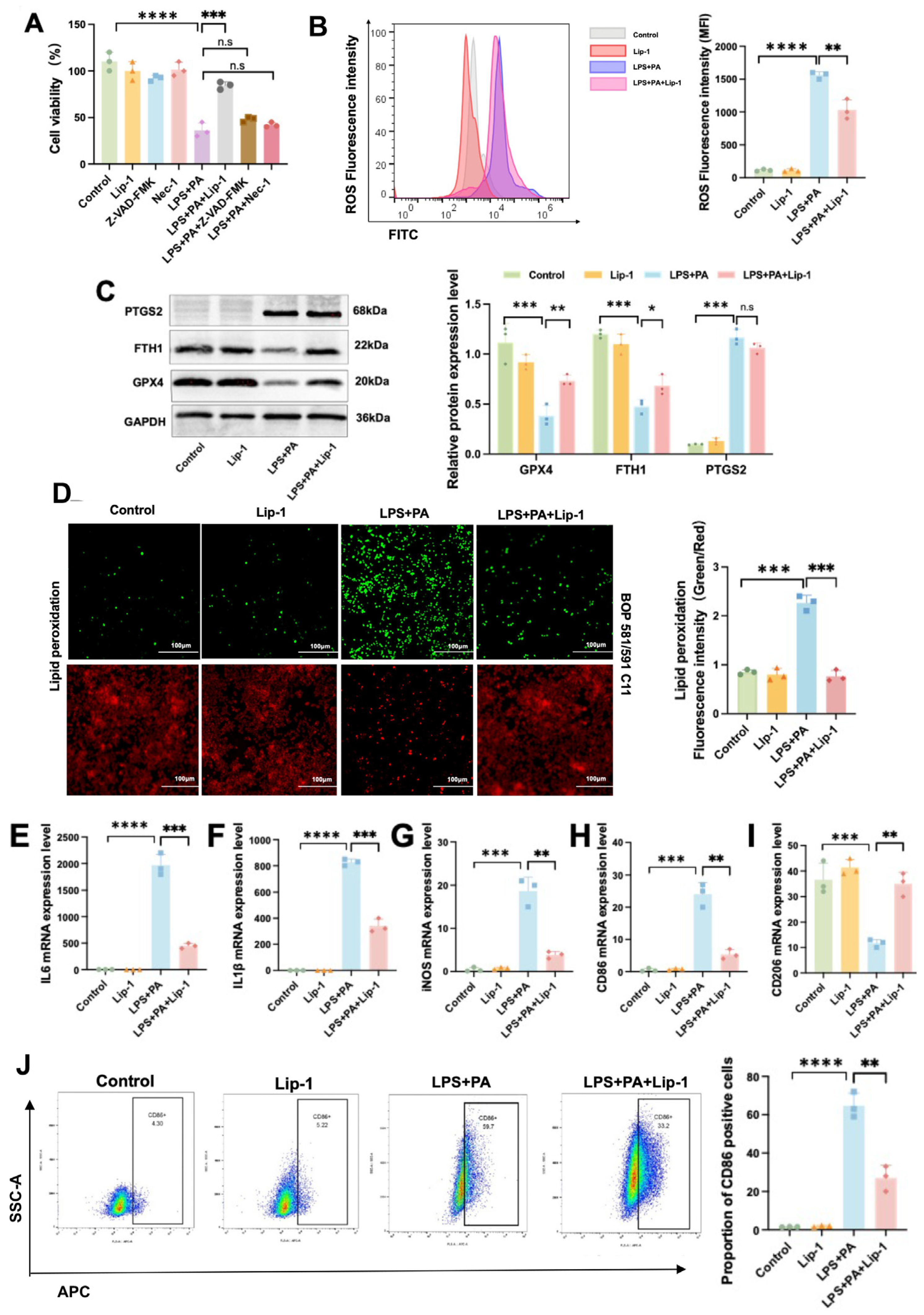
2.4. Lip-1 Alleviates Ferroptosis and Inflammation in the Pancreas and Epididymal Adipose Tissues in Obesity-Related SAP
2.5. CD36 Induces Inflammation by Promoting Ferroptosis in Pancreatic Tissue During Obesity-Related SAP
2.6. CD36 Induces Inflammation by Promoting Ferroptosis in Epididymal Adipose Tissue and ATMs During Obesity-Related SAP
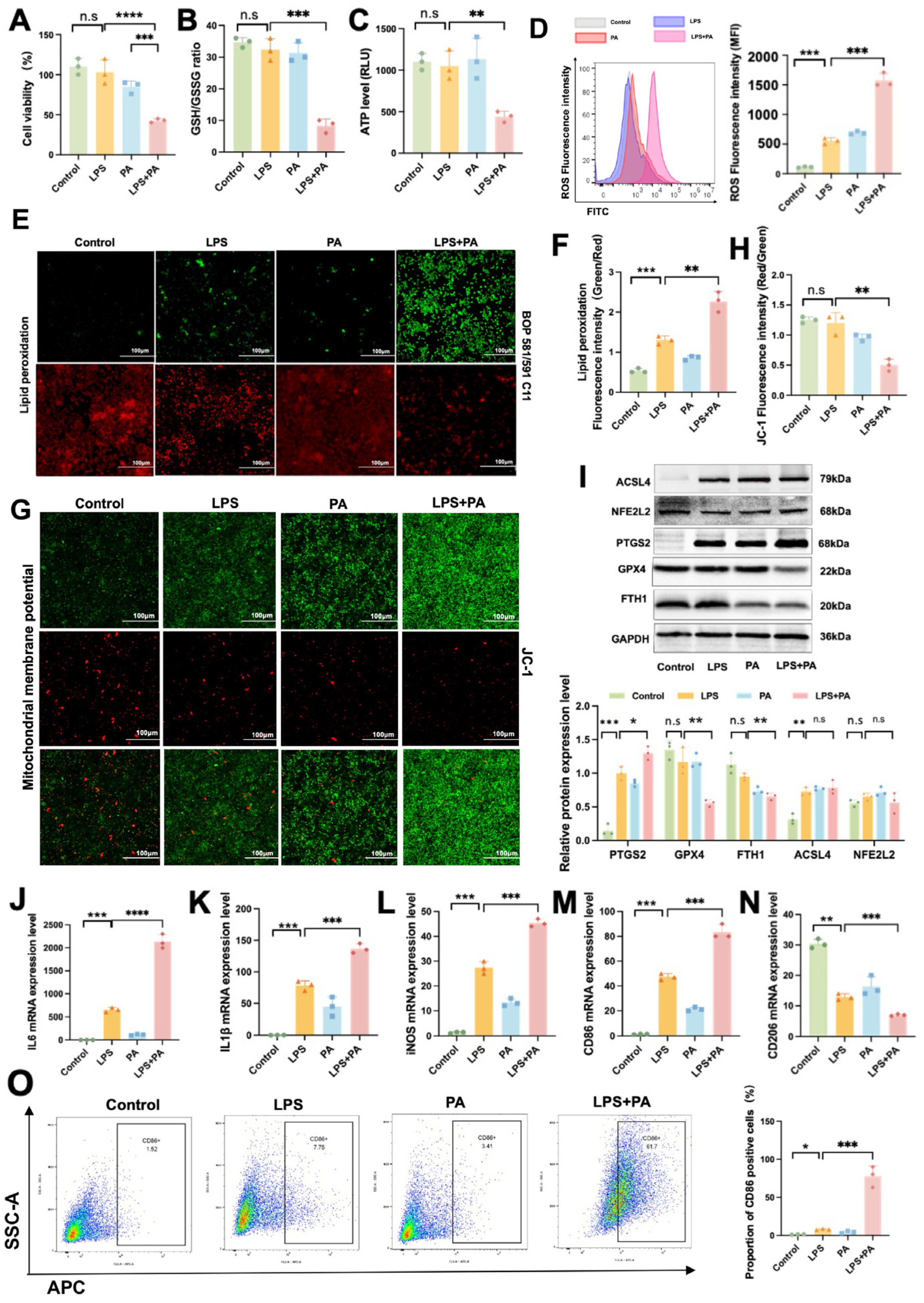
2.7. In Vitro Validation of Ferroptosis and Inflammatory Responses in ATMs During Obesity-Related SAP
2.8. Lip-1 Alleviates Ferroptosis and Inflammation in ATMs in Obesity-Related SAP
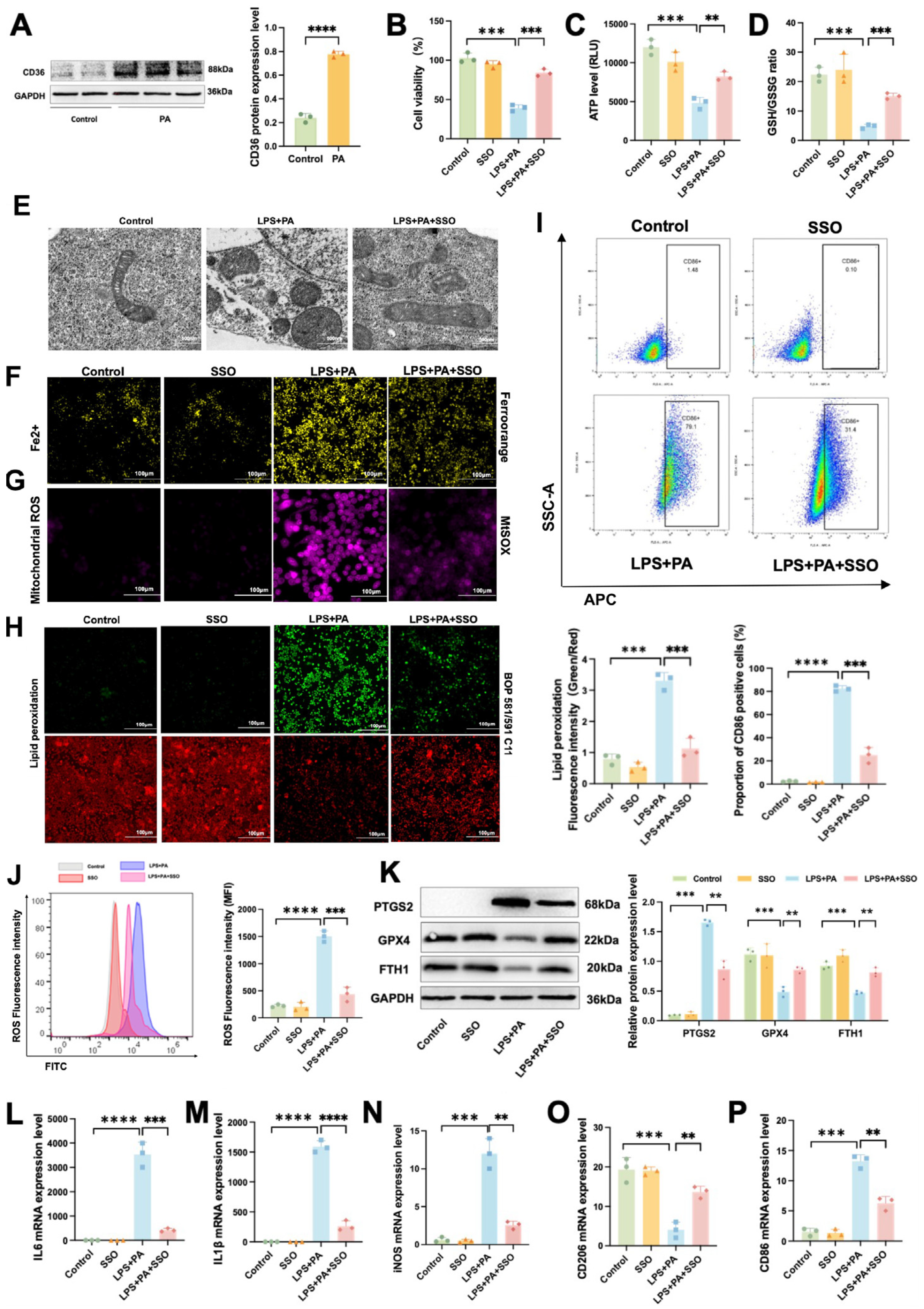
2.9. CD36 Induces Inflammation by Promoting Ferroptosis in ATMs in Obesity-Related SAP
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Experimental Animals
3.2. Animal Grouping and Treatment
3.3. Enzyme Activities and Proinflammatory Cytokine Detection
3.4. Serum Triglycerides and Free Fatty Acids Levels Detection
3.5. Hematoxylin-Eosin Staining
3.6. Immunofluorescence Staining
3.7. Measurement of Oxidative Stress Indicators
3.8. Tissue Ferrous Ions (Fe2+) Level Assay
3.9. Cell Culture and Treatment
3.10. Cell Viability Assay
3.11. Lipid Peroxidation Assay
3.12. Intracellular Iron Assay
3.13. Mitochondrial ROS Assay
3.14. Mitochondrial Membrane Potential Assay
3.15. Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) Level Detection
3.16. Flow Cytometry
3.17. Transmission Electron Microscopy
3.18. Western Blot Assay (WB)
3.19. Real-Time Quantitative PCR Analysis
3.20. Statistical Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lankisch, P.G.; Apte, M.; Banks, P.A. Acute pancreatitis. Lancet 2015, 386, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradley, E.L., 3rd. A clinically based classification system for acute pancreatitis. Summary of the International Symposium on Acute Pancreatitis, Atlanta, Ga, September 11 through 13, 1992. Arch. Surg. 1993, 128, 586–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gapp, J.; Hall, A.G.; Walters, R.W.; Jahann, D.; Kassim, T.; Reddymasu, S. Trends and Outcomes of Hospitalizations Related to Acute Pancreatitis: Epidemiology From 2001 to 2014 in the United States. Pancreas 2019, 48, 548–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuire, S.P.; Keller, S.; Maatman, T.K.; Lewellen, K.A.; Ceppa, E.P.; House, M.G.; Nakeeb, A.; Nguyen, T.K.; Quigley, S.N.; Schmidt, C.M.; et al. Obesity Worsens Local and Systemic Complications of Necrotizing Pancreatitis and Prolongs Disease Course. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2022, 26, 2128–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeets, X.J.N.M.; Knoester, I.; Grooteman, K.V.; Singh, V.K.; Banks, P.A.; Papachristou, G.I.; Duarte-Rojo, A.; Robles-Díaz, G.; Kievit, W.; Besselink, M.G.H.; et al. The association between obesity and outcomes in acute pancreatitis: An individual patient data meta-analysis. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 31, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Sun, H.; Chen, L.; Yu, H.; Shi, L.; Xia, W.; Sun, X.; Yang, Y.; Huang, H. Novel anthropometric indicators of visceral obesity predict the severity of hyperlipidemic acute pancreatitis. Lipids Health Dis. 2024, 23, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdivielso, P.; Ramírez-Bueno, A.; Ewald, N. Current knowledge of hypertriglyceridemic pancreatitis. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2014, 25, 689–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, S.J.; Lemberg, K.M.; Lamprecht, M.R.; Skouta, R.; Zaitsev, E.M.; Gleason, C.E.; Patel, D.N.; Bauer, A.J.; Cantley, A.M.; Yang, W.S.; et al. Ferroptosis: An iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell 2012, 149, 1060–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Y.; Yang, Y.; Ren, N.; Xu, H.; Cheng, C.; Lu, D.-m.; Wang, Q.; Yao, X.; Ma, W. Jinwu Jiangu capsule attenuates rheumatoid arthritis via the SLC7A11/GSH/GPX4 pathway in M1 macrophages. Phytomedicine Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2024, 135, 156232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Guo, N.; Xu, H.; Li, Y.; Sun, T.; Jiang, X.; Fu, D.; You, T.; Diao, S.; Huang, Y.; et al. Caveolin-1 ameliorates hepatic injury in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by inhibiting ferroptosis via the NOX4/ROS/GPX4 pathway. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2024, 2024, 116594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, A.; Li, Z.; Gao, Y.; Hu, F.; Han, S.; Liu, F.; Liu, Z.; Chen, J.; Yuan, C.; Zhou, C. Isobicyclogermacrenal ameliorates hippocampal ferroptosis involvement in neurochemical disruptions and neuroinflammation induced by sleep deprivation in rats. Phytomedicine Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2024, 136, 156306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Huoshen, W.; Bai, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, B.; Guan, Y.; Luo, P. Uncovering the molecular networks of ferroptosis in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes and its complications: A multi-omics investigation. Mol. Med. 2024, 30, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Kang, R.; Kroemer, G.; Tang, D. Ferroptosis in infection, inflammation, and immunity. J. Exp. Med. 2021, 218, e20210518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.-W.; Liu, J.; Zou, B.; Li, C.; Zeh, H.J.; Kang, R.; Kroemer, G.; Huang, J.; Tang, D. Trypsin-Mediated Sensitization to Ferroptosis Increases the Severity of Pancreatitis in Mice. Cell Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 13, 483–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.-T.; Zhou, Y.; Han, P.; Ren, H.-b. Ferroptosis inhibition attenuates inflammatory response in mice with acute hypertriglyceridemic pancreatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 29, 2294–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caslin, H.L.; Bhanot, M.; Bolus, W.R.; Hasty, A.H. Adipose tissue macrophages: Unique polarization and bioenergetics in obesity. Immunol. Rev. 2020, 295, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, M.; Samdal Steinskog, E.S.; Wiig, H. Adipose tissue macrophages: The inflammatory link between obesity and cancer? Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2015, 19, 527–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinetti-Gbaguidi, G.; Colin, S.; Staels, B. Macrophage subsets in atherosclerosis. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2015, 12, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisberg, S.P.; McCann, D.; Desai, M.; Rosenbaum, M.; Leibel, R.L.; Ferrante, A.W., Jr. Obesity is associated with macrophage accumulation in adipose tissue. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 1796–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Zhang, L.; Fu, Q.; Zhang, B.; Chen, J. Plasma Exosomes Aggravate Acute Pancreatitis by Promoting M1 Polarization of Adipose Tissue Macrophages in Obesity-Related Severe Acute Pancreatitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2023, 68, 3660–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Xiao, L.; Liu, L.; Ye, L.; Su, P.; Bi, E.; Wang, Q.; Yang, M.; Qian, J.; Yi, Q. CD36-mediated ferroptosis dampens intratumoral CD8+ T cell effector function and impairs their antitumor ability. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 1001–1012.e1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepino, M.Y.; Kuda, O.; Samovski, D.; Abumrad, N.A. Structure-function of CD36 and importance of fatty acid signal transduction in fat metabolism. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2014, 34, 281–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ma, Y.; Yang, L.-y.; Zhao, D. MicroRNA-20a-5p Ameliorates Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease via Inhibiting the Expression of CD36. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 596329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Li, Z.; Wei, Z.; Li, J.; Bian, Y.-f. Kaempferol regulating macrophage foaming and atherosclerosis through piezo1-mediated MAPK/NF-κB and Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. J. Adv. Res. 2024, 24, 2090–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, T.-f.; Liu, Z.; Cao, P.; Zheng, S.; Guo, W.; Wang, T.-X.; Chen, Y.; Duan, Y.; Li, Q.; Liao, C.; et al. Fisetin treatment alleviates kidney injury in mice with diabetes-exacerbated atherosclerosis through inhibiting CD36/fibrosis pathway. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2023, 44, 2065–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, W.; Cui, X.; Guo, T.; Liu, N.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Shang, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; et al. ALOX15 Aggravates Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease in Mice with Type 2 Diabetes via Activating the PPARγ/CD36 Axis. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2025, 4, 1546–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Luo, X.; Chen, J.; Zhou, B.; Yang, M.; Liu, R.; Liu, D.; Gu, H.F.; Zhu, Z.; Zheng, H.; et al. Osteoprotegerin Promotes Liver Steatosis by Targeting the ERK–PPAR-γ–CD36 Pathway. Diabetes 2019, 68, 1902–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joffin, N.; Gliniak, C.M.; Funcke, J.-B.; Paschoal, V.A.; Crewe, C.; Chen, S.; Gordillo, R.; Kusminski, C.M.; Oh, D.Y.; Geldenhuys, W.J.; et al. Adipose tissue macrophages exert systemic metabolic control by manipulating local iron concentrations. Nat. Metab. 2022, 4, 1474–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-N.; Tang, Y.; He, Z.; Ma, H.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Q.-Q.; Pan, D.; Zhu, C.; Qian, S.-W.; et al. Slit3 secreted from M2-like macrophages increases sympathetic activity and thermogenesis in adipose tissue. Nat. Metab. 2021, 3, 1536–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kylänpää, L.; Rakonczay, Z.; O’reilly, D. The Clinical Course of Acute Pancreatitis and the Inflammatory Mediators That Drive It. Int. J. Inflamm. 2012, 2012, 360685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, P.; Singh, V.P. Organ Failure Due to Systemic Injury in Acute Pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 2008–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devani, K.; Charilaou, P.; Radadiya, D.; Brahmbhatt, B.; Young, M.F.; Reddy, C.M. Acute pancreatitis: Trends in outcomes and the role of acute kidney injury in mortality- A propensity-matched analysis. Pancreatol. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Pancreatol. IAP 2018, 18, 870–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, K.; Huang, L.; Deng, B.; Chen, C.; Zhao, K.; Wang, W. Ganoderic Acid A Alleviates Severe Acute Pancreatitis by Modulating Gut Homeostasis and Inhibiting TLR4-NLRP3 Signaling. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 73, 1563–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eşrefoğlu, M. Experimental and clinical evidence of antioxidant therapy in acute pancreatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 5533–5541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pădureanu, V.; Florescu, D.N.; Pădureanu, R.; Ghenea, A.E.; Gheonea, D.I.; Oancea, C.N. Role of antioxidants and oxidative stress in the evolution of acute pancreatitis (Review). Exp. Ther. Med. 2022, 23, 11120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.H.; Kim, H. Oxidative stress and inflammatory signaling in cerulein pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 17324–17329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, Y.-F.; Kang, H.-X.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.-m.; Ren, H.-Y.; Zhu, L.; Chen, H.; Yuan, L.; Su, H.; Wan, M.-H.; et al. Effect of Sheng-jiang powder on multiple-organ inflammatory injury in acute pancreatitis in rats fed a high-fat diet. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 683–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Mikhael, M.R.; Xu, D.; Li, Y.; Soe-Lin, S.; Ning, B.; Li, W.; Nie, G.; Zhao, Y.; Ponka, P. Lysosomal proteolysis is the primary degradation pathway for cytosolic ferritin and cytosolic ferritin degradation is necessary for iron exit. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2010, 13, 999–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, J.C.; Pellecchia, M. Ironing Out Cell Death Mechanisms. Cell 2012, 149, 963–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera, G.; Pizzimenti, S.; Ciamporcero, E.S.; Daga, M.; Ullio, C.; Arcaro, A.; Cetrangolo, G.P.; Ferretti, C.; Dianzani, C.; Lepore, A.; et al. Role of 4-hydroxynonenal-protein adducts in human diseases. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2015, 22, 1681–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimita, W.; Petrov, M.S. Iron Metabolism and the Exocrine Pancreas. Clin. Chim. Acta Int. J. Clin. Chem. 2020, 511, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Li, C.; Jiang, P.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, D. Inhibition of Ferroptosis Attenuates Acute Kidney Injury in Rats with Severe Acute Pancreatitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2020, 66, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, X.; Xu, M.; Liu, L.; Meng, N.; Lei, Y.; Feng, Y.; Tang, G. Liproxstatin-1 attenuates acute hypertriglyceridemic pancreatitis through inhibiting ferroptosis in rats. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 9548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Chaudhary, O.; Rodríguez-Morales, P.; Sun, X.; Chen, D.; Zappasodi, R.; Xu, Z.; Pinto, A.F.M.; Williams, A.E.; Schulze, I.; et al. Uptake of oxidized lipids by the scavenger receptor CD36 promotes lipid peroxidation and dysfunction in CD8+ T cells in tumors. Immunity 2021, 54, 1561–1577.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Cui, W.; Silverstein, R.L. CD36, a signaling receptor and fatty acid transporter that regulates immune cell metabolism and fate. J. Exp. Med. 2022, 219, e20211314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Li, M.; Mo, T.; Xu, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, L. mTORC2 knockdown mediates lipid metabolism to alleviate hyperlipidemic pancreatitis through PPARα. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2024, 38, e23802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Li, M.; Zheng, S.; Wang, X.; Sun, J.; Li, C.; Shi, W.; et al. CD36-mediated uptake of oxidized LDL induces double-negative regulatory T cell ferroptosis in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. Metab. Clin. Exp. 2024, 2024, 156127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, P.-F.; Luo, W.; Fu, D.; Shen, W.-Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, S.; Dai, R.-P. CD36-mediated ferroptosis destabilizes CD4+ T cell homeostasis in acute Stanford type-A aortic dissection. Cell Death Dis. 2024, 15, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, M.; Huang, W.; Chen, W.; Zhao, Y.; Schulte, M.L.; Volberding, P.; Gerbec, Z.; Zimmermann, M.T.; Zeighami, A.; et al. Mitochondrial Metabolic Reprogramming by CD36 Signaling Drives Macrophage Inflammatory Responses. Circ. Res. 2019, 125, 1087–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Gene | Forward Primer (5′→3′) | Reverse Primer (5′→3′) |
|---|---|---|
| IL-6 | TAGTCCTTCCTACCCCAATTTCC | TTGGTCCTTAGCCACTCCTTC |
| IL-1β | GCAACTGTTCCTGAACTCAACT | ATCTTTTGGGGTCCGTCAACT |
| TNF-α | CCCTCACATCAGATCATCTTCT | GCTACGACGTGGGCTACAG |
| iNOS | GTTCTCAGCCCAACAATACAAGA | GTGGACGGGTCGATGTCAC |
| CD86 | CTGGAAACGGAGACAGATACAC | TTAGGTGACTTTGGTCTCCGTT |
| CD206 | CTCTGTTCAGCTATTGGACGC | CGGAATTTCTGGGATTCAGCT |
| GAPDH | AGGTCGGTGTGAACGGATTTG | TGTAGACCATGTATGAGGTCA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, R.; Ling, X.; Guo, X.; Ding, Z. CD36 Induces Inflammation by Promoting Ferroptosis in Pancreas, Epididymal Adipose Tissue, and Adipose Tissue Macrophages in Obesity-Related Severe Acute Pancreatitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3482. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083482
Zhang R, Ling X, Guo X, Ding Z. CD36 Induces Inflammation by Promoting Ferroptosis in Pancreas, Epididymal Adipose Tissue, and Adipose Tissue Macrophages in Obesity-Related Severe Acute Pancreatitis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(8):3482. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083482
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Ruoyi, Xin Ling, Xianwen Guo, and Zhen Ding. 2025. "CD36 Induces Inflammation by Promoting Ferroptosis in Pancreas, Epididymal Adipose Tissue, and Adipose Tissue Macrophages in Obesity-Related Severe Acute Pancreatitis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 8: 3482. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083482
APA StyleZhang, R., Ling, X., Guo, X., & Ding, Z. (2025). CD36 Induces Inflammation by Promoting Ferroptosis in Pancreas, Epididymal Adipose Tissue, and Adipose Tissue Macrophages in Obesity-Related Severe Acute Pancreatitis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(8), 3482. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083482






