Transcriptomic Comparison of Rice lncRNAs in Response to Feeding by Brown Planthopper Populations with Different Virulence
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
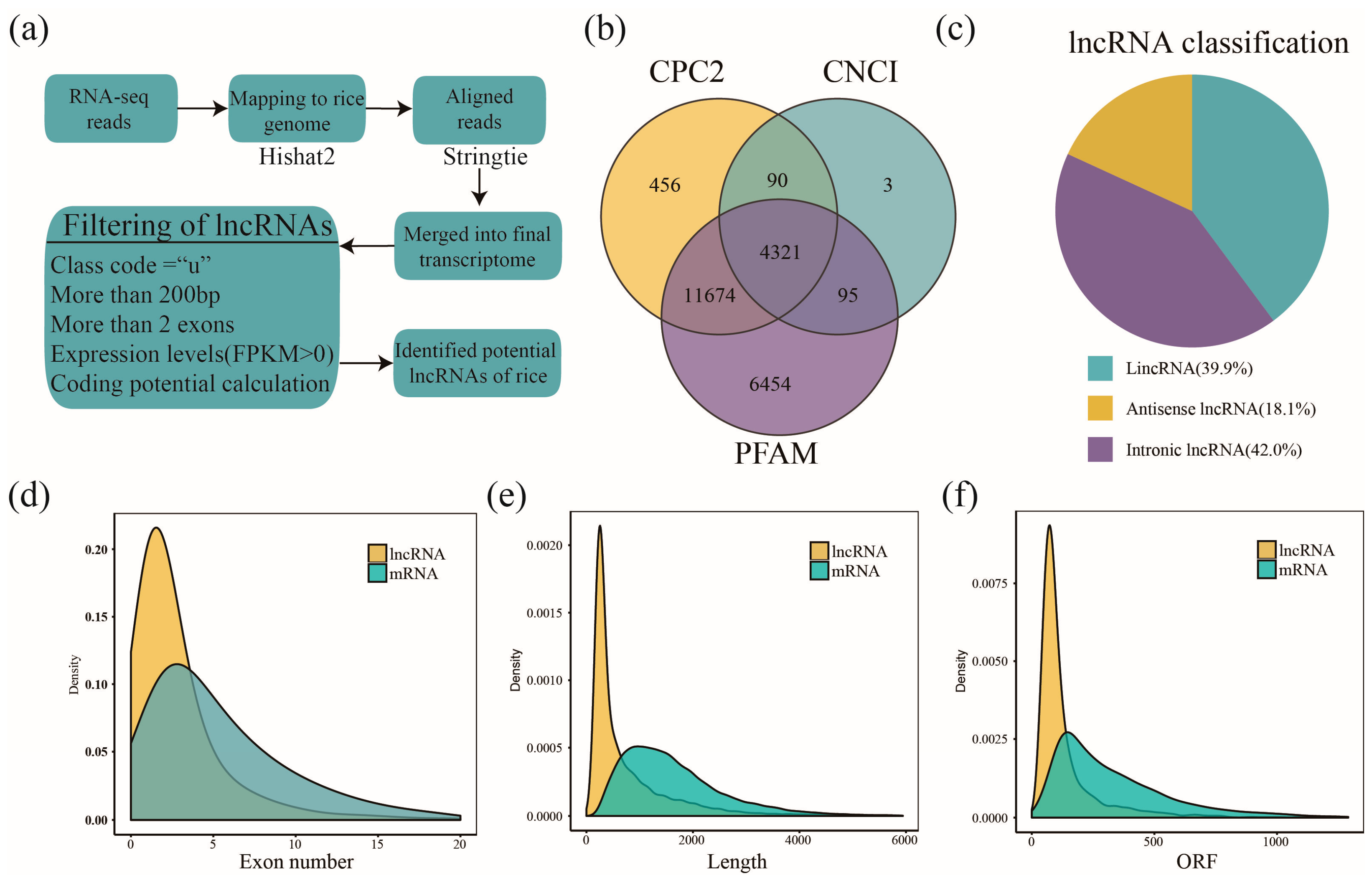
2.1. Genome-Wide Identification of Rice lncRNAs Responsive to BPH Infestation
2.2. Identification of lncRNAs Related to BPH Resistance
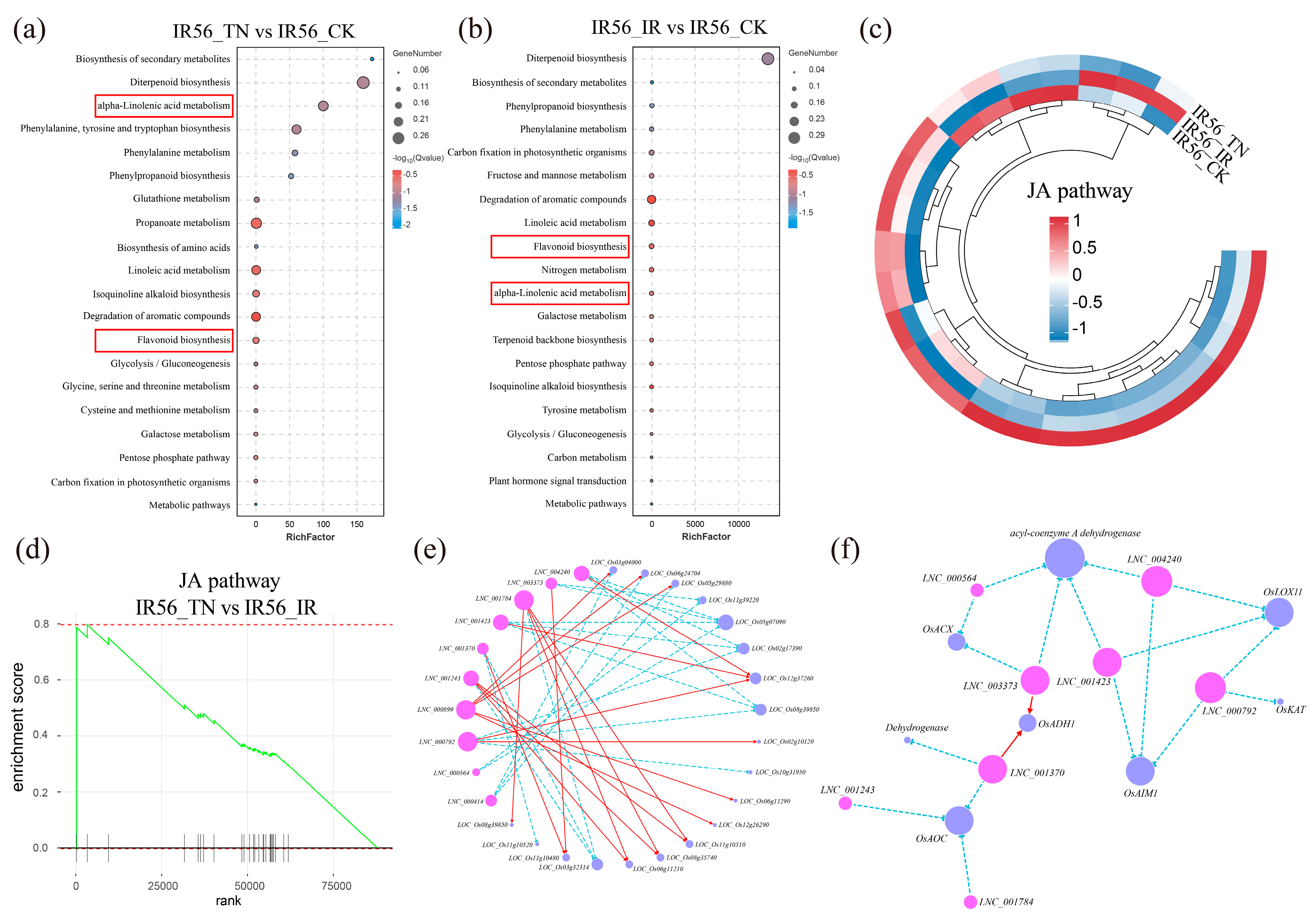
2.3. Identification of Potential Target Genes of lncRNAs and mRNA
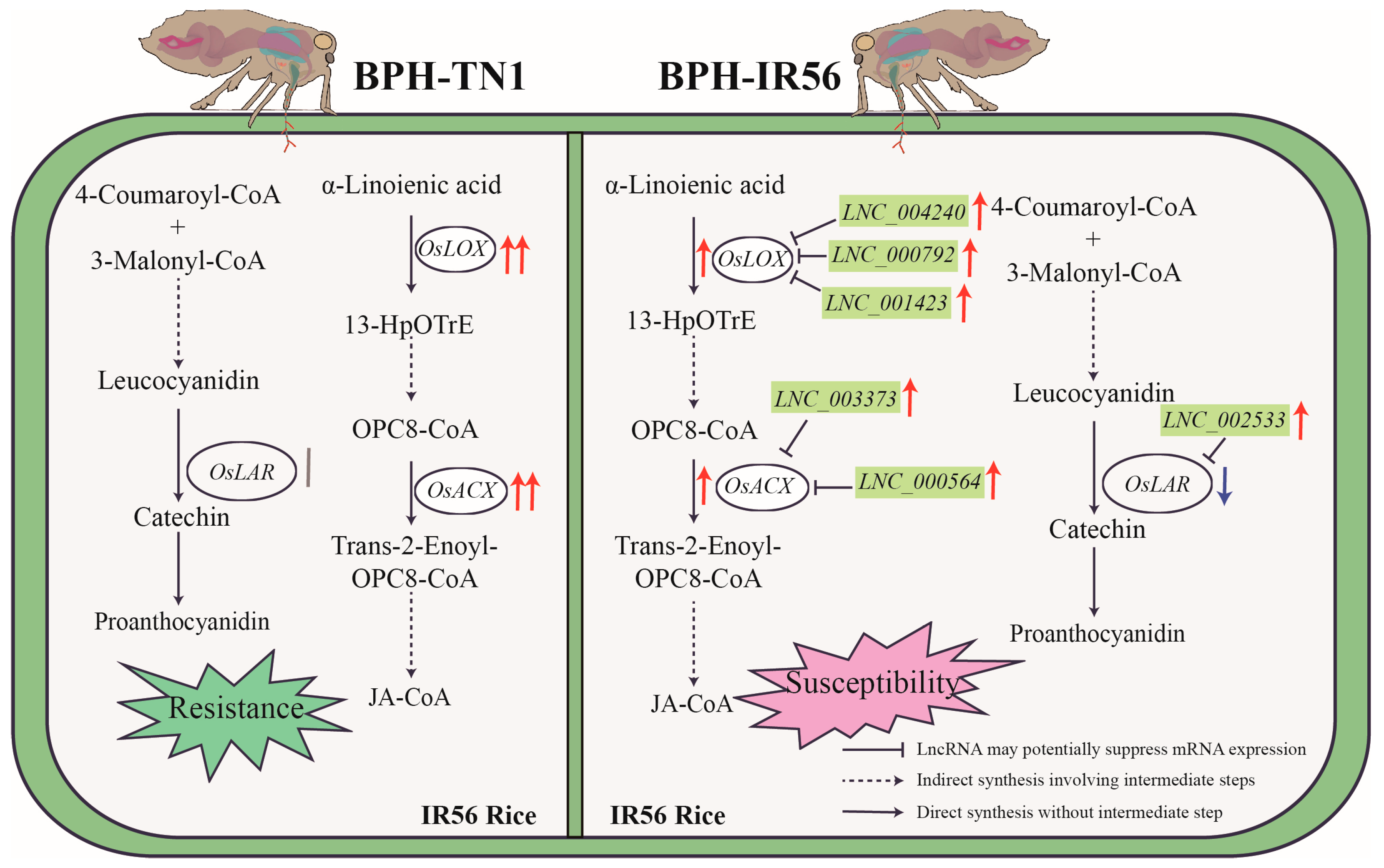
2.4. Validation of the BPH-Feeding Response in IR56-Associated lncRNAs and Their Putative Targets JA Genes
3. Discussion
3.1. Regulation of Rice Defense Against Brown Planthopper by lncRNAs
3.2. Regulation of Secondary Metabolite Synthesis in Rice by lncRNAs
3.3. lncRNAs Regulate the Jasmonic Acid Pathway in Rice After Brown Planthopper Infestation
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
4.2. Insect Materials and Growth Conditions
4.3. Sample Collections and RNA Isolation
4.4. Library Construction and Sequencing
4.5. Identification of lncRNAs
4.6. Differential Expression Analyses of mRNAs and lncRNAs
4.7. KEGG Pathway Analysis and Network Construction
4.8. cDNA Synthesis
4.9. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qPCR) and Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BPH | Brown planthopper |
| lncRNAs | Long noncoding RNAs |
| DElncRNAs | Differentially expressed lncRNAs |
| JA | Jasmonic acid |
| IR56-BPH | Brown planthopper population reared on IR56 rice |
| TN1-BPH | Brown planthopper population reared on TN1 rice |
| IR56-CK | IR56 rice without brown planthopper infestation |
| IR56-IR | IR56 rice without IR56-BPH infestation |
| IR56-TN | IR56 rice without TN1-BPH infestation |
References
- Hu, J.; Xiao, C.; He, Y. Recent progress on the genetics and molecular breeding of brown planthopper resistance in rice. Rice 2016, 9, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jena, K.K.; Kim, S. Current status of brown planthopper (BPH) resistance and genetics. Rice 2010, 3, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T. Evolving ideas about genetics underlying insect virulence to plant resistance in rice-brown planthopper interactions. J. Insect Physiol. 2016, 84, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bottrell, D.G.; Schoenly, K.G. Resurrecting the ghost of green revolutions past: The brown planthopper as a recurring threat to high-yielding rice production in tropical Asia. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2012, 15, 122–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Xiong, S.; Guan, X.; Tang, T.; Zhu, Z.; Zhu, X.; Hu, J.; Wu, J.; Zhang, S. Insight into rice resistance to the brown planthopper: Gene cloning, functional analysis, and breeding applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 13397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, H.; Chen, H.; Liu, Y.; He, J.; Kang, H.; Sun, Z.; Pan, G.; Wang, Q.; Hu, J.; et al. A gene cluster encoding lectin receptor kinases confers broad-spectrum and durable insect resistance in rice. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 33, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; He, J.; Wan, P.; Lai, F.; Sun, Y.; Lin, J.; Fu, Q. Virulence characteristics of Nilaparvata lugens (Stål) reared on resistant rice variety IR56. Chin. J. Rice Sci. 2016, 30, 552–558. [Google Scholar]
- Wierzbicki, A.T.; Blevins, T.; Swiezewski, S. Long noncoding RNAs in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2021, 72, 245–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chekanova, J.A. Long non-coding RNAs and their functions in plants. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2015, 27, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numan, M.; Sun, Y.; Li, G. Exploring the emerging role of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) in plant biology: Functions, mechanisms of action, and future directions. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2024, 212, 108797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahad, M.; Tariq, L.; Muhammad, S.; Wu, L. Underground communication: Long non-coding RNA signaling in the plant rhizosphere. Plant Commun. 2024, 5, 100927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, J.S.; Diloknawarit, P.; Park, B.S.; Chua, N. ELF18-INDUCED LONG NONCODING RNA 1 evicts fibrillarin from mediator subunit to enhance PATHOGENESIS-RELATED GENE 1 (PR1) expression. New Phytol. 2019, 221, 2067–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, J.S.; Sun, H.; Park, B.S.; Huang, C.; Yeh, S.; Jung, C.; Chua, N. ELF18-INDUCED LONG-NONCODING RNA associates with mediator to enhance expression of innate immune response genes in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2017, 29, 1024–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Luan, Y.; Jiang, N.; Bao, H.; Meng, J. Comparative transcriptome analysis between resistant and susceptible tomato allows the identification of lncRNA16397 conferring resistance to Phytophthora infestans by co-expressing glutaredoxin. Plant J. 2017, 89, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Feng, Y.; He, H.; Lian, J.; Yang, Y.; Lei, M.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y. Transcriptional landscape of pathogen-responsive lncRNAs in rice unveils the role of ALEX1 in jasmonate pathway and disease resistance. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Cui, J.; Shi, Y.; Yang, G.; Zhou, X.; Hou, X.; Meng, J.; Luan, Y. Tomato lncRNA23468 functions as a competing endogenous RNA to modulate NBS-LRR genes by decoying miR482b in the tomato-Phytophthora infestans interaction. Hortic. Res. 2019, 6, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, J.; Meng, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, C.; Yang, J.; Luan, Y. The lncRNA39896–miR166b–HDZs module affects tomato resistance to Phytophthora infestans. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2022, 64, 1979–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Chua, N. Long noncoding RNA transcriptome of plants. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2015, 13, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinn, J.L.; Chang, H.Y. Genome Regulation by Long Noncoding RNAs. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2012, 81, 145–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, J.R.; Mhatre, K.J.; Yadav, K.; Yadav, L.S.; Srivastava, S.; Nikalje, G.C. Flavonoids in plant-environment interactions and stress responses. Discov. Plants 2024, 1, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gfeller, A.; Dubugnon, L.; Liechti, R.; Farmer, E.E. Jasmonate biochemical pathway. Sci. Signal. 2010, 3, cm3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, P.Y.; Wang, L.; Lui, A.C.W.; Liu, H.; Takeda-Kimura, Y.; Chen, M.-X.; Zhu, F.-Y.; Zhang, J.; Umezawa, T.; Tobimatsu, Y.; et al. Deficiency in flavonoid biosynthesis genes CHS, CHI, and CHIL alters rice flavonoid and lignin profiles. Plant Physiol. 2021, 188, 1993–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Xiao, M.; Liu, H.; He, H.; Peng, L.; Tao, Q.; Tang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, R.; et al. A plant growth-promoting bacterium supports cadmium detoxification of rice by inducing phenylpropanoid and flavonoid biosynthesis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 484, 136795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y. Genome-wide identification and expression profiles of 13 key structural gene families involved in the biosynthesis of rice flavonoid scaffolds. Genes 2022, 13, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, A.; Tamayo, P.; Mootha, V.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Ebert, B.L.; Gillette, M.A.; Paulovich, A.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Golub, T.R.; Lander, E.S.; et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: A knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15545–15550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marla, S.S.; Singh, V.K. LOX genes in blast fungus (Magnaporthe grisea) resistance in rice. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2012, 12, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, S.-B.; Lee, B.-C.; Lee, D.-E.; Kuk, Y.I.; Lee, A.Y.; Han, O.; Back, K. Molecular characterization of the gene encoding rice allene oxide synthase and its expression. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2002, 66, 2719–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haga, K.; Iino, M. Phytochrome-mediated transcriptional up-regulation of ALLENE OXIDE SYNTHASE in rice seedlings. Plant Cell Physiol. 2004, 45, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.C.; Kim, T.H.; Park, J.H.; Moon, B.Y.; Lee, C.-H.; Cho, S.H. Expression of rice acyl-CoA oxidase isoenzymes in response to wounding. J. Plant Physiol. 2007, 164, 665–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhou, F.; Liu, B.; Feng, D.; He, Y.; Qi, K.; Wang, H.; Wang, J. Comparative characterization, expression pattern and function analysis of the 12-oxo-phytodienoic acid reductase gene family in rice. Plant Cell Rep. 2011, 30, 981–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Guo, Z.; Gu, F.; Ke, S.; Sun, D.; Dong, S.; Liu, W.; Huang, M.; Xiao, W.; Yang, G.; et al. 4-coumarate-CoA ligase-like gene OsAAE3 negatively mediates the rice blast resistance, floret development and lignin biosynthesis. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 7, 2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.Z.; He, S.; Huang, X.Y.; Deng, L.; Wang, G.X. Cloning, molecular characterization and heterologous expression of a glutathione S-transferase gene in rice. Russ. J. Bioorganic Chem. 2011, 37, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.-Y.; Lee, H.-J.; Kong, K.-H. A phi class glutathione S-transferase from Oryza sativa (OsGSTF5): Molecular cloning, expression and biochemical characteristics. BMB Rep. 2007, 40, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, H.; Zhou, Z.; Hua, H.; Ma, W. Comparative transcriptome analysis of defense response of rice to Nilaparvata lugens and Chilo suppressalis infestation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 163, 2270–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zha, W.; Qiu, D.; Guo, J.; Liu, G.; Li, C.; Wu, B.; Li, S.; Chen, J.; Hu, L.; et al. Comprehensive identification and characterization of lncRNAs and circRNAs reveal potential brown planthopper-responsive ceRNA networks in rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1242089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Ma, X.; Zhao, L.; Lai, X.; Chen, J.; Lang, X.; Han, Q.; Wan, X.; Li, C. Comprehensive transcriptomic analysis of three varieties with different brown planthopper-resistance identifies leaf sheath lncRNAs in rice. BMC Plant Biol. 2023, 23, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Fan, H.; Wang, B.; Yuan, F. Research progress on the roles of lncRNAs in plant development and stress responses. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1138901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhu, Q.; Kaufmann, K. Long non-coding RNAs in plants: Emerging modulators of gene activity in development and stress responses. Planta 2020, 252, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zheng, H.; Sui, N. Regulation mechanism of long non-coding RNA in plant response to stress. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 503, 402–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, J.; Misra, P.; Trivedi, P.K.; Pandey, A. Molecular components associated with the regulation of flavonoid biosynthesis. Plant Sci. 2022, 317, 111196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Tan, J.; Zhou, C.; Yang, X.; Yang, F.; Zhang, S.; Sun, S.; Miao, X.; Shi, Z. The OsmiR396–OsGRF8–OsF3H-flavonoid pathway mediates resistance to the brown planthopper in rice (Oryza sativa). Plant Biotechnol. J. 2019, 17, 1657–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Yao, H.; Li, L.; Du, H.; Guo, P.; Wang, D.; Rennenberg, H.; Ma, M. Differentially-expressed genes related to glutathione metabolism and heavy metal transport reveals an adaptive, genotype-specific mechanism to Hg2+ exposure in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Environ. Pollut. 2023, 324, 121340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Liu, M.; Chu, N.; Chen, G.; Wang, P.; Mo, J.; Guo, H.; Xu, J.; Zhou, H. Combined transcriptome and metabolome reveal glutathione metabolism plays a critical role in resistance to salinity in rice landraces HD961. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 952595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, W.; Li, S.; Xu, H.; Chen, J.; Liu, K.; Li, P.; Liu, K.; Yang, G.; Chen, Z.; Shi, S.; et al. Genome-wide identification of long non-coding (lncRNA) in Nilaparvata lugens’s adaptability to resistant rice. PeerJ 2022, 10, e13587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimini, S.; Locato, V.; Giacinti, V.; Molinari, M.; De Gara, L. A multifactorial regulation of glutathione metabolism behind salt tolerance in rice. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, H.; Sun, H.; Liu, R.; Zhang, W.; Shang, L.; Wang, J.; Khassanov, V.; Lyu, D. Construction of drought stress regulation networks in potato based on SMRT and RNA sequencing data. BMC Plant Biol. 2022, 22, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Jin, G.; Liu, M.; Wang, L.; Lou, Y.; Baldwin, I.; Li, R. Multiomic analyses reveal key sectors of jasmonate-mediated defense responses in rice. Plant Cell 2024, 36, 3362–3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, X.; Zu, H.; Zeng, X.; Baldwin, I.T.; Lou, Y.; Li, R. Molecular dissection of rice phytohormone signaling involved in resistance to a piercing-sucking herbivore. New Phytol. 2021, 230, 1639–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christeller, J.T.; Galis, I. α-Linolenic acid concentration and not wounding per se is the key regulator of octadecanoid (oxylipin) pathway activity in rice (Oryza sativa L.) leaves. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 83, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanda, S.; Yuan, S.; Lai, F.; Wang, W.; Fu, Q.; Wan, P. Identification and analysis of miRNAs in IR56 rice in response to BPH infestations of different virulence levels. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanda, S.; Wan, P.; Yuan, S.; Lai, F.; Wang, W.; Fu, Q. Differential responses of OsMPKs in IR56 rice to two BPH populations of different virulence levels. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 4030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. HISAT: A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pertea, M.; Pertea, G.M.; Antonescu, C.M.; Chang, T.-C.; Mendell, J.T.; Salzberg, S.L. StringTie enables improved reconstruction of a transcriptome from RNA-seq reads. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhao, S.; Wei, L.; Gao, G. CPC: Assess the protein-coding potential of transcripts using sequence features and support vector machine. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W345–W349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Luo, H.; Bu, D.; Zhao, G.; Yu, K.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Y.; Chen, R.; Zhao, Y. Utilizing sequence intrinsic composition to classify protein-coding and long non-coding transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.D.; Miller, B.L.; Clements, J.; Bateman, A. iPfam: A database of protein family and domain interactions found in the Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 42, D364–D373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Wang, L.; Han, Y.; He, Q. clusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. OMICS A J. Integr. Biol. 2012, 16, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Luo, C.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, R.; Ling, F.; Xiao, L.; Lin, Y.; Chen, H. Gene expression and plant hormone levels in two contrasting rice genotypes responding to brown planthopper infestation. BMC Plant Biol. 2017, 17, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, K.; Xiao, J.; Liu, F.; Yang, H.; Cai, Y.; Lai, F.; Fu, Q.; Wan, P. Transcriptomic Comparison of Rice lncRNAs in Response to Feeding by Brown Planthopper Populations with Different Virulence. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3486. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083486
Wang Y, Wang X, Zhang K, Xiao J, Liu F, Yang H, Cai Y, Lai F, Fu Q, Wan P. Transcriptomic Comparison of Rice lncRNAs in Response to Feeding by Brown Planthopper Populations with Different Virulence. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(8):3486. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083486
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yaxuan, Xinfeng Wang, Kunjie Zhang, Jing Xiao, Fang Liu, Houhong Yang, Yubiao Cai, Fengxiang Lai, Qiang Fu, and Pinjun Wan. 2025. "Transcriptomic Comparison of Rice lncRNAs in Response to Feeding by Brown Planthopper Populations with Different Virulence" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 8: 3486. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083486
APA StyleWang, Y., Wang, X., Zhang, K., Xiao, J., Liu, F., Yang, H., Cai, Y., Lai, F., Fu, Q., & Wan, P. (2025). Transcriptomic Comparison of Rice lncRNAs in Response to Feeding by Brown Planthopper Populations with Different Virulence. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(8), 3486. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083486





