Antiviral Activity of Marine Bacterium Paraliobacillus zengyii Against Enterovirus 71 In Vitro and In Vivo
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. P. zengyii Inhibits EV71 Infection In Vitro
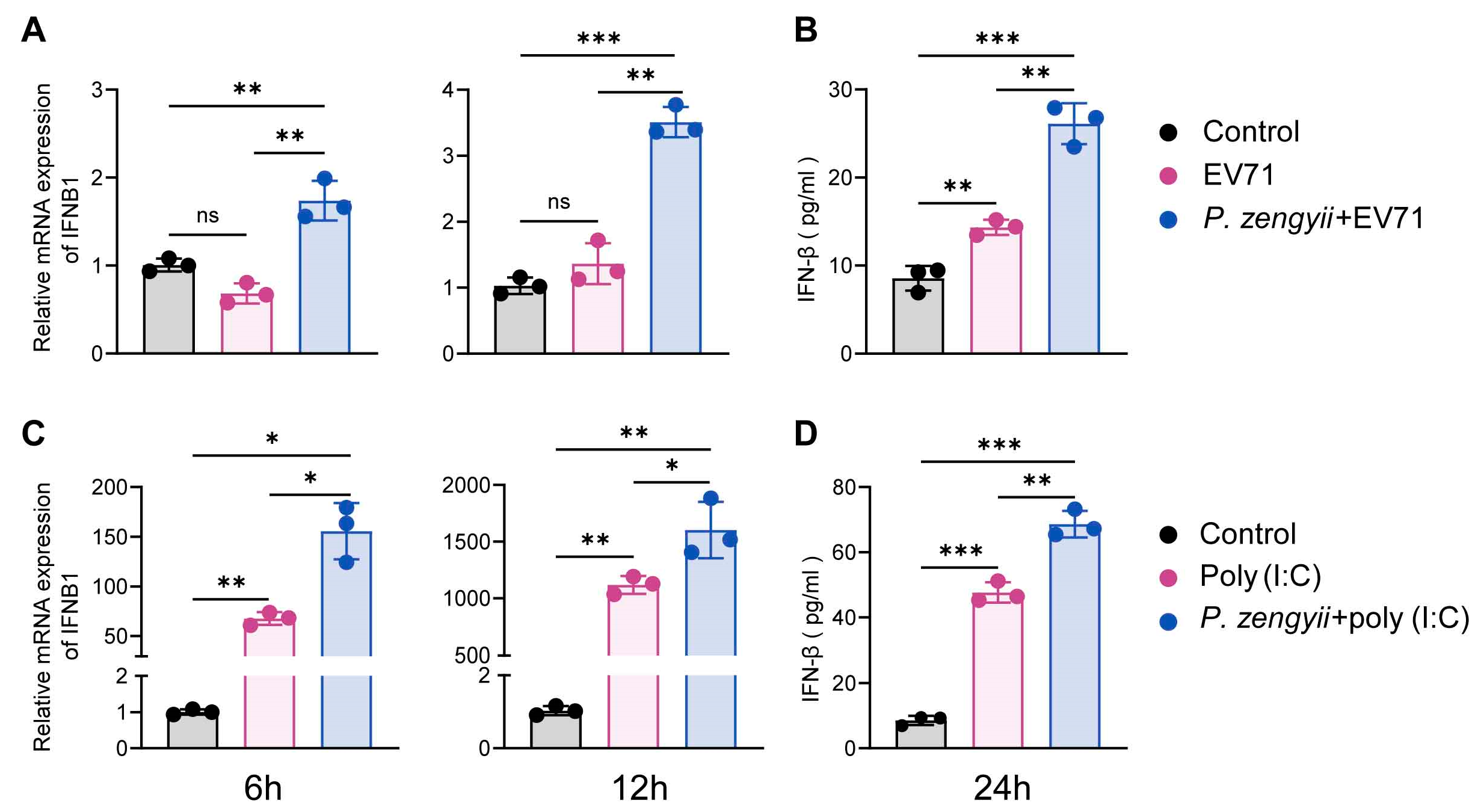
2.2. P. zengyii Induces IFN-I Expression
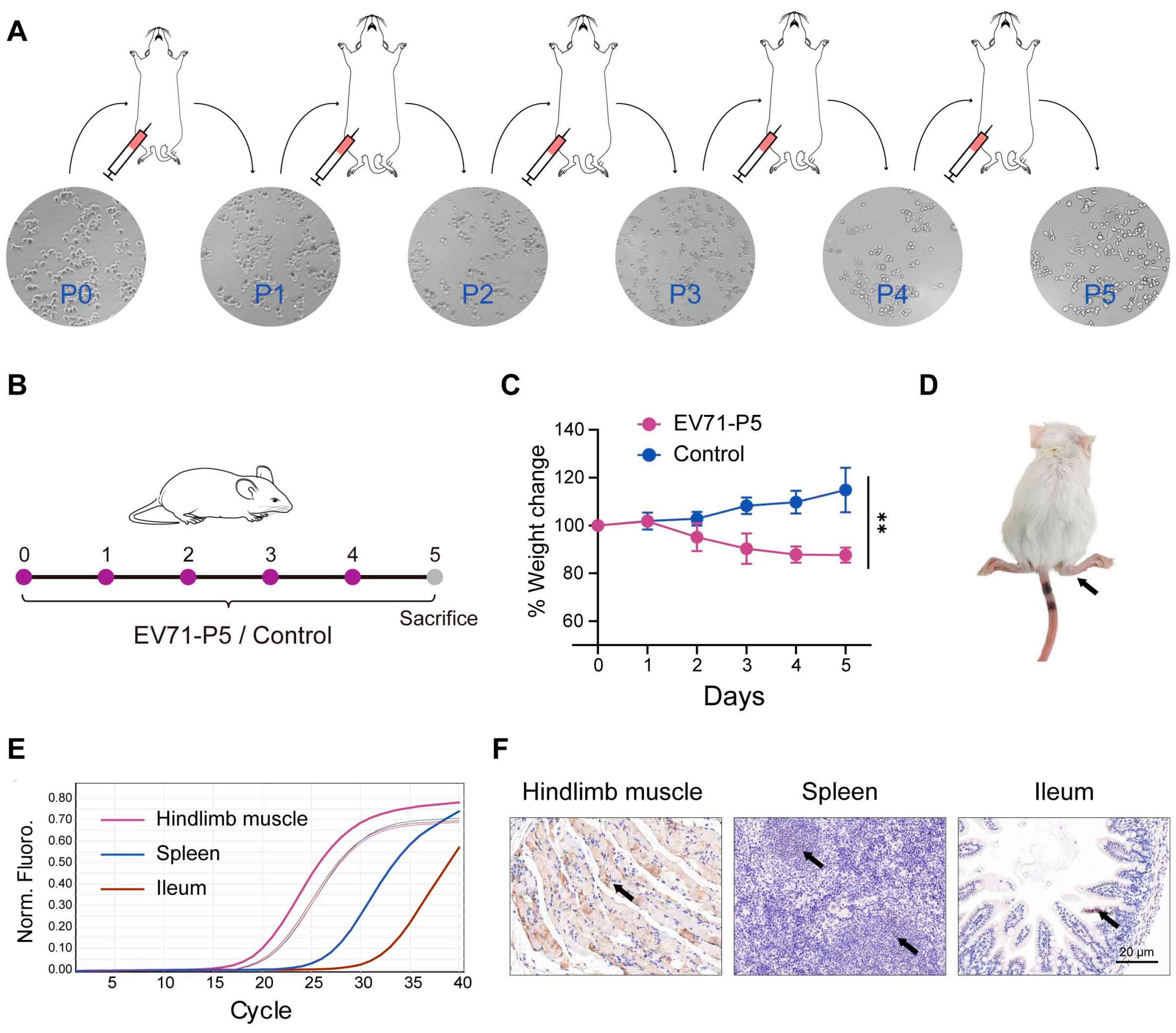
2.3. Establishment of EV71-Infected Mouse Model
2.4. P. zengyii Exhibits Antiviral Activity in EV71-Infected Mice
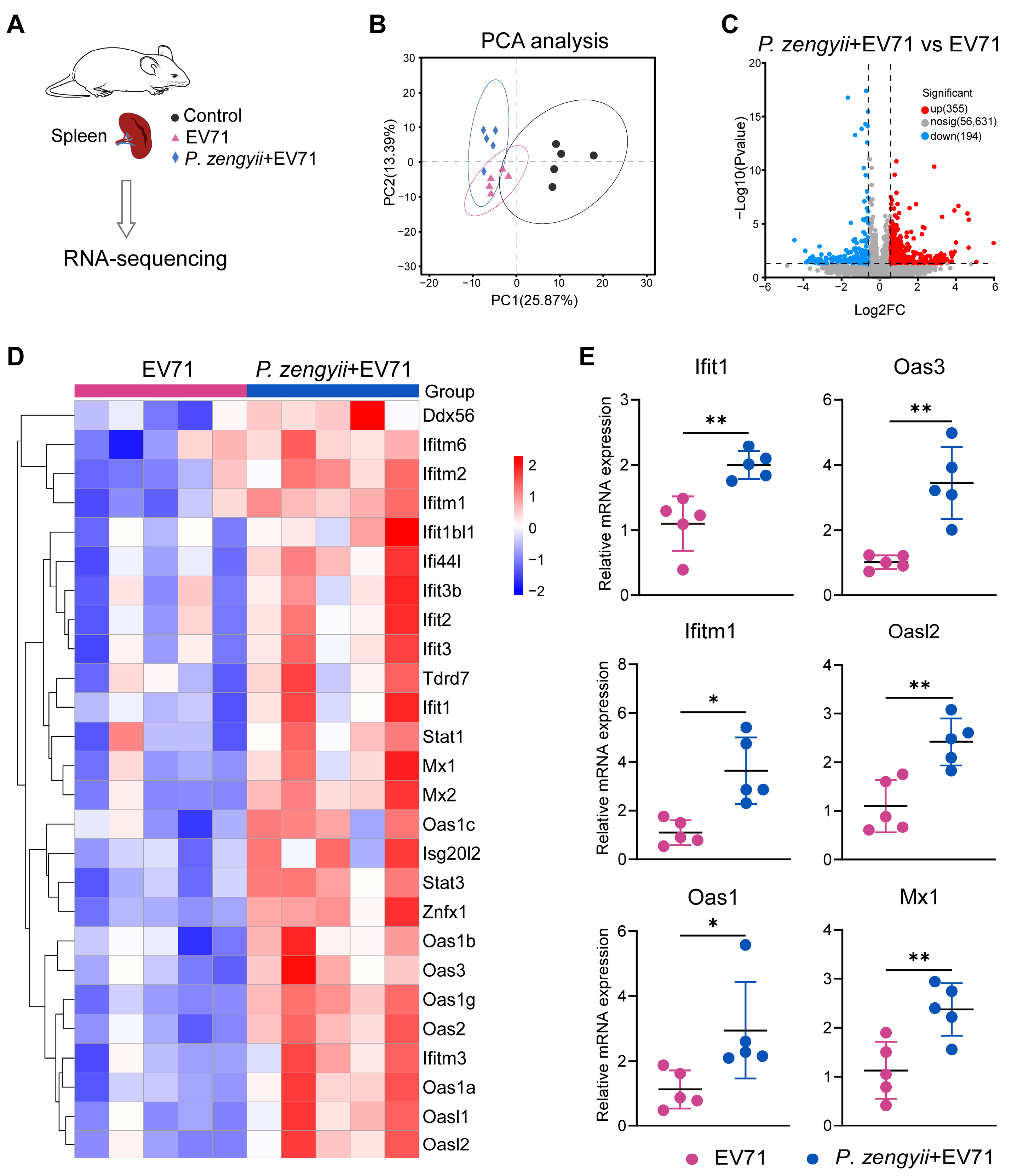
2.5. P. zengyii Enhances ISG Production in Spleens of EV71-Infected Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cells, Viruses, and Bacteria
4.2. Cell Viability Assay
4.3. Antiviral Activity Assays
4.4. Mouse Infection Model
4.5. Experimental Animals
4.6. TCID50 Assay
4.7. RNA Extraction, RT–qPCR, and RNA Sequencing
4.8. Immunofluorescence and Immunohistochemistry Analyses
4.9. Transfection of Poly(I:C) and Detection of IFN-β
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, H.; Song, Z.; Zou, J.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ren, L.; Zhang, X.; Hu, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Yi, Z. An infectious clone of enterovirus 71(EV71) that is capable of infecting neonatal immune competent mice without adaptive mutations. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Zhu, G.; Qiu, F.; Ren, F.; Lin, B.; Zhang, D.; Yang, Q.; Huang, C. PLX8394, a RAF inhibitor, inhibits enterovirus 71 replication by blocking RAF/MEK/ERK signaling. Virol. Sin. 2023, 38, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yip, C.C.; Lau, S.K.; Woo, P.C.; Yuen, K.Y. Human enterovirus 71 epidemics: What’s next? Emerg. Health Threat. J. 2013, 6, 19780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Q.; Meng, J.; Ke, X.; Hu, Q.; Wang, H. 2C Proteins of Enteroviruses Suppress IKKβ Phosphorylation by Recruiting Protein Phosphatase 1. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 5141–5151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, T.; Lewthwaite, P.; Perera, D.; Cardosa, M.J.; McMinn, P.; Ooi, M.H. Virology, epidemiology, pathogenesis, and control of enterovirus 71. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2010, 10, 778–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phyu, W.K.; Ong, K.C.; Wong, K.T. Modelling person-to-person transmission in an Enterovirus A71 orally infected hamster model of hand-foot-and-mouth disease and encephalomyelitis. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2017, 6, e62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pant, N.; Marcotte, H.; Brüssow, H.; Svensson, L.; Hammarström, L. Effective prophylaxis against rotavirus diarrhea using a combination of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG and antibodies. BMC Microbiol. 2007, 7, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toscano, M.; De Grandi, R.; Pastorelli, L.; Vecchi, M.; Drago, L. A consumer’s guide for probiotics: 10 golden rules for a correct use. Dig. Liver Dis. 2017, 49, 1177–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Guo, R.; Ju, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, J.; Xie, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Li, T.; Liu, Z.; Lu, L.; et al. A single bacterium restores the microbiome dysbiosis to protect bones from destruction in a rat model of rheumatoid arthritis. Microbiome 2019, 7, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Peng, L.; Chen, S.; Pu, Y.; Lv, H.; Wei, H.; Wan, C. Lactiplantibacillus plantarum 1201 Inhibits Intestinal Infection of Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica Serovar Typhimurium Strain ATCC 13311 in Mice with High-Fat Diet. Foods 2021, 11, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Jung, K.B.; Kwon, O.; Son, Y.S.; Choi, E.; Yu, W.D.; Son, N.; Jeon, J.H.; Jo, H.; Yang, H.; et al. Limosilactobacillus reuteri DS0384 promotes intestinal epithelial maturation via the postbiotic effect in human intestinal organoids and infant mice. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2121580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Fang, X.; Xu, J.; Gao, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, J.; Meng, Y.; Zhou, W.; Han, X.; Bai, Y.; et al. Bifidobacterium longum alleviates irritable bowel syndrome-related visceral hypersensitivity and microbiota dysbiosis via Paneth cell regulation. Gut Microbes 2020, 12, 1782156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.; He, S.; Yue, K.; Mi, J.; Huang, Y.; Song, L.; Yang, T.; Ren, Z.; Ren, L.; Xu, J. Lactobacillus plantarum GUANKE modulate anti-viral function of dendritic cells in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 134, 112169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumova, O.K.; Fike, A.J.; Thayer, J.L.; Nguyen, L.T.; Mell, J.C.; Pascasio, J.; Stairiker, C.; Leon, L.G.; Katsikis, P.D.; Carey, A.J. Lung transcriptional unresponsiveness and loss of early influenza virus control in infected neonates is prevented by intranasal Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1008072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.-J.; Song, J.-H.; Park, K.-S.; Baek, S.-H.; Lee, E.-S.; Kwon, D.-H. Antiviral activity of yogurt against enterovirus 71 in vero cells. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2010, 19, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, L.Y.; Too, H.K.; Tan, E.L.; Chow, T.K.; Shek, L.P.; Tham, E.H.; Alonso, S. Antiviral activity of Lactobacillus reuteri Protectis against Coxsackievirus A and Enterovirus 71 infection in human skeletal muscle and colon cell lines. Virol. J. 2016, 13, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravi, A.V.; Musthafa, K.S.; Jegathammbal, G.; Kathiresan, K.; Pandian, S.K. Screening and evaluation of probiotics as a biocontrol agent against pathogenic Vibrios in marine aquaculture. Lett Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madison, D.; Schubiger, C.; Lunda, S.; Mueller, R.S.; Langdon, C. A marine probiotic treatment against the bacterial pathogen Vibrio coralliilyticus to improve the performance of Pacific (Crassostrea gigas) and Kumamoto (C. sikamea) oyster larvae. Aquaculture 2022, 560, 738611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eze, O.C.; Berebon, D.P.; Emencheta, S.C.; Evurani, S.A.; Okorie, C.N.; Balcão, V.M.; Vila, M.M.D.C. Therapeutic Potential of Marine Probiotics: A Survey on the Anticancer and Antibacterial Effects of Pseudoalteromonas spp. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Park, J.G.; Moon, K.S.; Jung, S.B.; Kwon, Y.M.; Kang, N.S.; Kim, J.H.; Nam, S.J.; Choi, G.; Baek, Y.B.; et al. Identification and characterization of a marine bacterium extract from Mameliella sp. M20D2D8 with antiviral effects against influenza A and B viruses. Arch. Virol. 2024, 169, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.C.; Lehman, C.W.; Stewart, A.K.; Panny, L.; Bracci, N.; Wright, J.L.C.; Paige, M.; Strangman, W.K.; Kehn-Hall, K. Homoseongomycin, a compound isolated from marine actinomycete bacteria K3-1, is a potent inhibitor of encephalitic alphaviruses. Antivir. Res. 2021, 191, 105087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, M.; Ishizaki, S.; Yamamoto, Y.; Yamasato, K. Paraliobacillus ryukyuensis gen. nov., sp. nov., a new Gram-positive, slightly halophilic, extremely halotolerant, facultative anaerobe isolated from a decomposing marine alga. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 2002, 48, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Yang, J.; Lu, S.; Lai, X.H.; Jin, D.; Pu, J.; Niu, L.; Zhu, W.; Liang, J.; Huang, Y.; et al. Paraliobacillus zengyii sp. nov., a slightly halophilic and extremely halotolerant bacterium isolated from Tibetan antelope faeces. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 1426–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Q.J.; Li, B.J.; Lu, S.M.; Yue, K.; Luo, X.L.; Xu, J.G. Study on the Anti⁃Influenza Virus of Marine Probiotic Paraliobacillus zengyii CGMCC1.16464. Bingduxuebao 2025, 41, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Liu, J.; Lu, N.; Zhang, C. Enterovirus 71 Antagonizes Antiviral Effects of Type III Interferon and Evades the Clearance of Intestinal Intraepithelial Lymphocytes. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 806084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Huang, P.N.; Mwale, P.F.; Wang, W.C.; Leu, S.J.; Tseng, S.N.; Shih, S.R.; Chiang, L.C.; Mao, Y.C.; Tsai, B.Y.; et al. The Bottlenecks of Preparing Virus Particles by Size Exclusion for Antibody Generation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, T.; Nakano, Y.; Onomoto, K.; Yoneyama, M.; Ui-Tei, K. LGP2 virus sensor enhances apoptosis by upregulating apoptosis regulatory genes through TRBP-bound miRNAs during viral infection. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 1494–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, T.; Hall, M.W.; McDonald, D.R.; Newhams, M.M.; Mistry, A.J.; Panoskaltsis-Mortari, A.; Mourani, P.M.; Loftis, L.L.; Weiss, S.L.; Tarquinio, K.M.; et al. RIG-I and TLR4 responses and adverse outcomes in pediatric influenza-related critical illness. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 145, 1673–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Guardeño, J.M.; Apolonia, L.; Betancor, G.; Malim, M.H. Immunoproteasome activation enables human TRIM5α restriction of HIV-1. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 933–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mythrayee, R.; Gayathri, K.V. Survival Strategies of Extremophiles: Physiology and Biochemistry. In Extremophiles for Sustainable Agriculture and Soil Health Improvement; Ranjan, A., Rajput, V.D., Chauhan, A., Prazdnova, E.V.e., Minkina, T., Zargar, S.M., Eds.; Springer Nature Switzerland: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 21–45. [Google Scholar]
- Hui, M.L.; Tan, L.T.; Letchumanan, V.; He, Y.W.; Fang, C.M.; Chan, K.G.; Law, J.W.; Lee, L.H. The Extremophilic Actinobacteria: From Microbes to Medicine. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neifar, M.; Maktouf, S.; Ghorbel, R.; Jaouani, A.; Cherif, A. Extremophiles as source of novel bioactive compounds with industrial potential. In Biotechnology of Bioactive Compounds: Sources and Applications; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 245–267. [Google Scholar]
- El Aichar, F.; Muras, A.; Parga, A.; Otero, A.; Nateche, F. Quorum quenching and anti-biofilm activities of halotolerant Bacillus strains isolated in different environments in Algeria. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 132, 1825–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Fan, X.; Li, D.; Zhao, T.; Wu, D.; Liu, Z.; Long, D.; Li, B.; Huang, X. High Antioxidant Capacity of Lacticaseibacillus paracasei TDM-2 and Pediococcus pentosaceus TCM-3 from Qinghai Tibetan Plateau and Their Function towards Gut Modulation. Foods 2023, 12, 1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, X.; Li, X.; Xie, X.; Lei, J.; Yang, F.; Chen, D. Effects of Probiotic Enterococcus faecium from Yak on the Intestinal Microflora and Metabolomics of Mice with Salmonella Infection. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2024, 16, 1036–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, K.; Koike, S. Cellular receptors for enterovirus A71. J. Biomed. Sci. 2020, 27, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arita, M.; Shimizu, H.; Nagata, N.; Ami, Y.; Suzaki, Y.; Sata, T.; Iwasaki, T.; Miyamura, T. Temperature-sensitive mutants of enterovirus 71 show attenuation in cynomolgus monkeys. J. Gen. Virol. 2005, 86, 1391–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arita, M.; Nagata, N.; Iwata, N.; Ami, Y.; Suzaki, Y.; Mizuta, K.; Iwasaki, T.; Sata, T.; Wakita, T.; Shimizu, H. An attenuated strain of enterovirus 71 belonging to genotype a showed a broad spectrum of antigenicity with attenuated neurovirulence in cynomolgus monkeys. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 9386–9395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, I.; Hagiwara, A. Pathogenicity of a poliomyelitis-like disease in monkeys infected orally with enterovirus 71: A model for human infection. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 1982, 8, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.Q.; Jiang, J.D.; Li, Y.H. Establishment of EV71 animal models with 2-week-old BALB/c mice. Yao Xue Xue Bao 2013, 48, 343–346. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, C.C.; Liou, A.T.; Chang, Y.S.; Wu, S.Y.; Chang, C.S.; Lee, C.K.; Kung, J.T.; Tu, P.H.; Yu, Y.Y.; Lin, C.Y.; et al. Immunodeficient mouse models with different disease profiles by in vivo infection with the same clinical isolate of enterovirus 71. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 12485–12499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, K.; Nagata, N.; Sato, Y.; Ong, K.C.; Wong, K.T.; Yamayoshi, S.; Shimanuki, M.; Shitara, H.; Taya, C.; Koike, S. Transgenic mouse model for the study of enterovirus 71 neuropathogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci USA 2013, 110, 14753–14758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, A.T.; Wu, S.Y.; Liao, C.C.; Chang, Y.S.; Chang, C.S.; Shih, C. A new animal model containing human SCARB2 and lacking stat-1 is highly susceptible to EV71. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, K.C.; Devi, S.; Cardosa, M.J.; Wong, K.T. Formaldehyde-inactivated whole-virus vaccine protects a murine model of enterovirus 71 encephalomyelitis against disease. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 661–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Good, C.; Wells, A.I.; Coyne, C.B. Type III interferon signaling restricts enterovirus 71 infection of goblet cells. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaau4255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.F.; Chou, C.T.; Lei, H.Y.; Liu, C.C.; Wang, S.M.; Yan, J.J.; Su, I.J.; Wang, J.R.; Yeh, T.M.; Chen, S.H.; et al. A mouse-adapted enterovirus 71 strain causes neurological disease in mice after oral infection. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 7916–7924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Zang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ruan, S.; Zheng, X.; Chong, G.; Xu, D.; Yang, Y.; Yang, Y.; et al. Nanofactory for metabolic and chemodynamic therapy: Pro-tumor lactate trapping and anti-tumor ROS transition. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, T.; Chen, S.; Xie, Y.; Shuai, O.; Li, X.; Chen, D.; Su, J.; Jiao, C.; Liang, Y. Hypouricemic Effects of Extracts From Agrocybe aegerita on Hyperuricemia Mice and Virtual Prediction of Bioactives by Molecular Docking. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Zhou, X.; Tian, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W. IFN-β1b induces OAS3 to inhibit EV71 via IFN-β1b/JAK/STAT1 pathway. Virol. Sin. 2022, 37, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.I.; Lin, J.Y.; Chen, S.H. EV71 Infection Induces IFNβ Expression in Neural Cells. Viruses 2019, 11, 1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macpherson, C.; Audy, J.; Mathieu, O.; Tompkins, T.A. Multistrain probiotic modulation of intestinal epithelial cells’ immune response to a double-stranded RNA ligand, poly(i·c). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 1692–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, N.; Gao, H.; He, L.; Liu, Y.; Fan, H.; Xu, Q.; Yang, S. Ginsenoside Rb1 is an immune-stimulatory agent with antiviral activity against enterovirus 71. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 266, 113401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Dai, Y.; Fu, Y.; Wang, K.; Yang, Y.; Li, M.; Xu, W.; Wei, L. Cathelicidin antimicrobial peptides suppress EV71 infection via regulating antiviral response and inhibiting viral binding. Antivir. Res. 2021, 187, 105021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Li, L.; Chen, Y.; Yu, C.; Azevedo, P.; Gong, J.; Yang, C. Bacillus licheniformis PF9 improves barrier function and alleviates inflammatory responses against enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli F4 infection in the porcine intestinal epithelial cells. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2022, 13, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, Y.; Ren, J.; Aballay, A. The transcription factor HLH-26 controls probiotic-mediated protection against intestinal infection through up-regulation of the Wnt/BAR-1 pathway. PLoS Biol. 2022, 20, e3001581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deriu, E.; Liu, J.Z.; Pezeshki, M.; Edwards, R.A.; Ochoa, R.J.; Contreras, H.; Libby, S.J.; Fang, F.C.; Raffatellu, M. Probiotic bacteria reduce salmonella typhimurium intestinal colonization by competing for iron. Cell Host Microbe 2013, 14, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Passage Numbers | P0 | P1 | P2 | P3 | P4 | P5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Virus titers | 1.61 × 108 TCID50/mL | 1.79 × 108 TCID50/mL | 6.40 × 108 TCID50/mL | 1.0 × 109 TCID50/mL | 1.28 × 109 TCID50/mL | 1.79 × 109 TCID50/mL |
| Gene Name 1 | Forward (5′-3′) | Reverse (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| hGAPDH | GACACCCACTCCTCCACCTTT | TTGCTGTAGCCAAATTCGTTGT |
| hIFNB1 | GCCGCATTGACCATCTAT | TAGACATTAGCCAGGAGGTT |
| EV71-VP1 | AAGGTTCCAGCACTCCAAGC | TCTCCAACTAATCCCGCCC |
| mGAPDH | AGGTCGGTGTGAACGGATTTG | TGTAGACCATGTAGTTGAGGTCA |
| mIfItm1 | GACAGCCACCACAATCAACAT | CCCAGGCAGCAGAAGTTCAT |
| mOasl2 | TTGTGCGGAGGATCAGGTACT | TGATGGTGTCGCAGTCTTTGA |
| mMx1 | GACCATAGGGGTCTTGACCAA | AGACTTGCTCTTTCTGAAAAGCC |
| mIfit1 | CTGAGATGTCACTTCACATGGAA | GTGCATCCCCAATGGGTTCT |
| mOas1 | GAAGAGGCTGATGTGTGGCT | TGTCCAGTTCTCTTCTACCTGC |
| mOas3 | GAACAGCAAGGTGGCCTTTG | CCTCAGGAGTCCTTGTGCAG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, Q.; Huangfu, H.; Chen, L.; Jiao, M.; Li, B.; Cao, Z.; Sun, H.; Luo, X.; Xu, J. Antiviral Activity of Marine Bacterium Paraliobacillus zengyii Against Enterovirus 71 In Vitro and In Vivo. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3500. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083500
Fan Q, Huangfu H, Chen L, Jiao M, Li B, Cao Z, Sun H, Luo X, Xu J. Antiviral Activity of Marine Bacterium Paraliobacillus zengyii Against Enterovirus 71 In Vitro and In Vivo. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(8):3500. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083500
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Qianjin, Haoyue Huangfu, Lan Chen, Mengqi Jiao, Beijie Li, Zhijie Cao, Hui Sun, Xuelian Luo, and Jianguo Xu. 2025. "Antiviral Activity of Marine Bacterium Paraliobacillus zengyii Against Enterovirus 71 In Vitro and In Vivo" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 8: 3500. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083500
APA StyleFan, Q., Huangfu, H., Chen, L., Jiao, M., Li, B., Cao, Z., Sun, H., Luo, X., & Xu, J. (2025). Antiviral Activity of Marine Bacterium Paraliobacillus zengyii Against Enterovirus 71 In Vitro and In Vivo. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(8), 3500. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083500







