Advances in Metabolomics: A Comprehensive Review of Type 2 Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease Interactions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Metabolomics
2.1. NMR Spectroscopy
2.2. Mass Spectrometry
2.3. Selection of the Method
3. Applications and Methodological Approaches of Metabolomics in Type 2 Diabetes
3.1. Biomarker Discovery and Risk Prediction in T2D
3.2. Amino Acids and Metabolite Profiles in T2D
3.3. Applications of Metabolomics Risk Assessment in T2D
3.4. Mendelian Randomization Studies in T2D
3.5. Microbiome-Related Metabolites and the Risk of T2D
3.6. Heterogeneity of T2D
3.7. Integrative Profiling and Future Directions in T2D
4. Metabolomics of Cardiovascular Diseases
4.1. Metabolites Associated with CAD
4.2. Mechanisms Linking Metabolites to CAD
4.3. Metabolomic Profiling and Disease Mechanisms in CAD
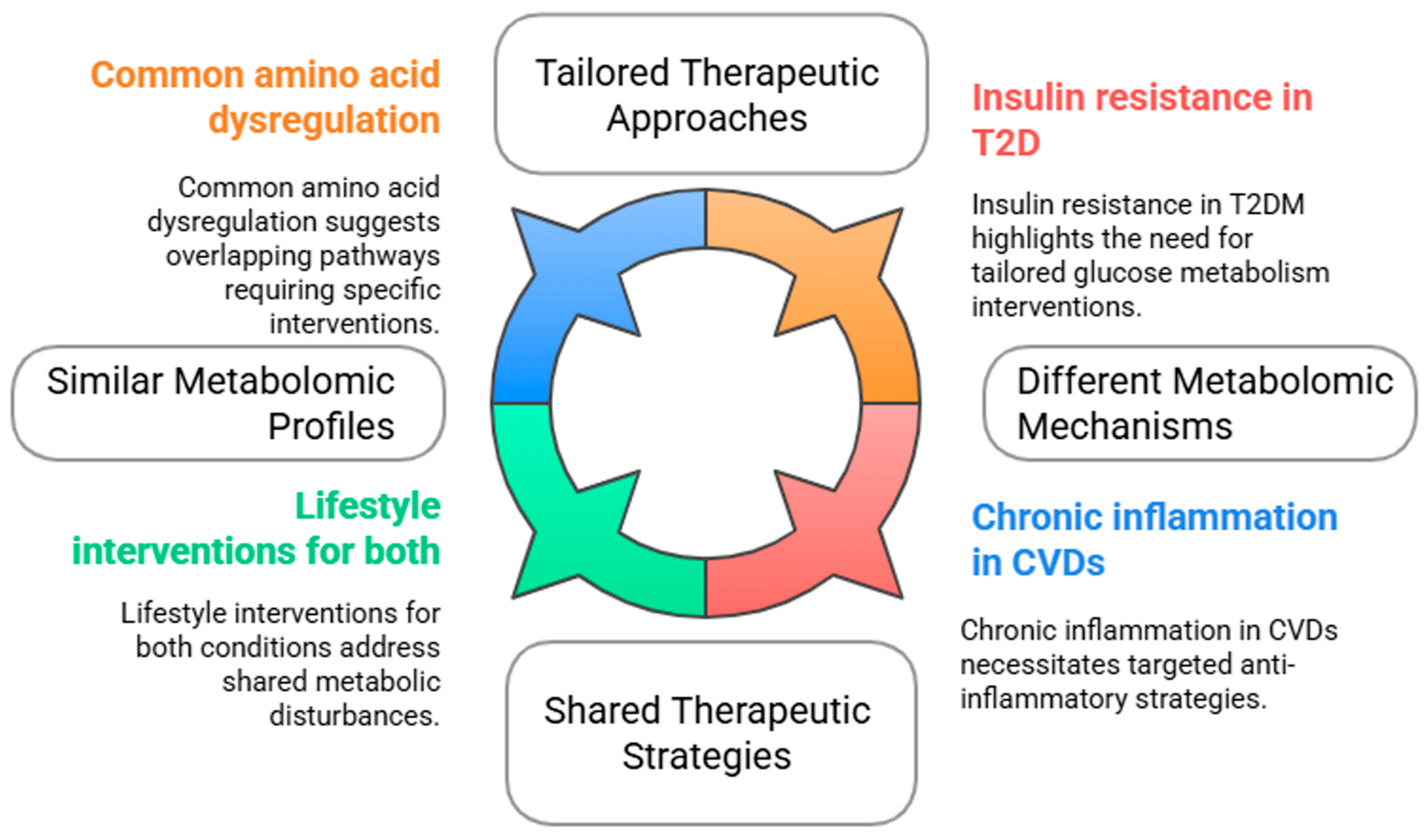
5. Comparative Analysis Between Type 2 Diabetes and Cardiovascular Diseases
6. Microbiota and Cardiovascular Diseases
7. Clinical Implications and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Buergel, T.; Steinfeldt, J.; Ruyoga, G.; Pietzner, M.; Bizzarri, D.; Vojinovic, D.; zu Belzen, J.U.; Loock, L.; Kittner, P.; Christmann, L.; et al. Metabolomic profiles predict individual multidisease outcomes. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 2309–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Urgent Action Needed as Global Diabetes Cases Increase Four-Fold Over Past Decades; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, X.; Chan, L.S.; Bose, D.; Jackson, A.U.; VandeHaar, P.; Locke, A.E.; Fuchsberger, C.; Stringham, H.M.; Welch, R.; Yu, K.; et al. Genome-wide association studies of metabolites in Finnish men identify disease-relevant loci. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Bose, D.; Kwon, A.; Hanks, S.C.; Jackson, A.U.; Stringham, H.M.; Welch, R.; Oravilahti, A.; Silva, L.F.; Locke, A.E.; et al. Integrating transcriptomics, metabolomics, and GWAS helps reveal molecular mechanisms for metabolite levels and disease risk. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2022, 109, 1727–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, R.; Seum, T.; Sha, S.; Trares, K.; Holleczek, B.; Brenner, H.; Schöttker, B. Improving 10-year cardiovascular risk prediction in patients with type 2 diabetes with metabolomics. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2025, 24, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mora-Ortiz, M.; Alcala-Diaz, J.F.; Rangel-Zuñiga, O.A.; Larriva, A.P.A.-D.; Abollo-Jimenez, F.; Luque-Cordoba, D.; Priego-Capote, F.; Malagon, M.M.; Delgado-Lista, J.; Ordovas, J.M.; et al. Metabolomics analysis of type 2 diabetes remission identifies 12 metabolites with predictive capacity: A CORDIOPREV clinical trial study. BMC Med. 2022, 20, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Yang, Z.; Wang, L.; Han, Y.; Peng, C.; Yan, C.; Yan, D. Metabolite biomarkers of type 2 diabetes mellitus and pre-diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2020, 20, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laakso, M. Cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetes: Challenge for treatment and prevention. J. Intern. Med. 2001, 249, 225–235. [Google Scholar]
- Batty, M.; Bennett, M.R.; Yu, E. The role of oxidative stress in atherosclerosis. Cells 2022, 11, 3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Huang, Z.; Liu, B.; Zhang, Y. Metabolomics in cardiovascular diseases. Int. J. Drug Discov. Pharmacol. 2024, 3, 100019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, J.K.; Lindon, J.C.; Holmes, E. Systems biology: Metabonomics. Nature 2008, 455, 1054–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lankinen, M.A.; Nuotio, P.; Kauppinen, S.; Koivu, N.; Tolonen, U.; Malkki-Keinänen, K.; Oravilahti, A.; Kuulasmaa, T.; Uusitupa, M.; Schwab, U.; et al. Effects of genetic risk on incident type 2 diabetes and glycemia: The T2D-GENE lifestyle intervention trial. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2025, 110, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karjalainen, M.K.; Karthikeyan, S.; Oliver-Williams, C.; Sliz, E.; Allara, E.; Fung, W.T.; Surendran, P.; Zhang, W.; Jousilahti, P.; Kristiansson, K.; et al. Genome-wide characterization of circulating metabolic biomarkers. Nature 2024, 628, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauermeister, A.; Mannochio-Russo, H.; Costa-Lotufo, L.V.; Jarmusch, A.K.; Dorrestein, P.C. Mass spectrometry-based metabolomics in microbiome investigation. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 143–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Minno, A.; Gelzo, M.; Caterino, M.; Costanzo, M.; Ruoppolo, M.; Castaldo, G. Challenges in metabolomics-based tests, biomarkers revealed by metabolomic analysis, and the promise of the application of metabolomics in precision medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.; Ivanisevic, J.; Siuzdak, G. Metabolomics: Beyond biomarkers and towards mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 17, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markley, J.L.; Brüschweiler, R.; Edison, A.S.; Eghbalnia, H.R.; Powers, R.; Raftery, D.; Wishart, D.S. The future of NMR-based metabolomics. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2017, 43, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyer, T.; Rübenthaler, J.; Alunni-Fabbroni, M.; Schinner, R.; Weber, S.; Mayerle, J.; Schiffer, E.; Höckner, S.; Malfertheiner, P.; Ricke, J. NMR-based lipid metabolite profiles to predict outcomes in patients undergoing interventional therapy for a Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC): A substudy of the SORAMIC trial. Cancers 2021, 13, 2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anh, N.K.; Thu, N.Q.; Tien, N.T.N.; Long, N.P.; Nguyen, H.T. Advancements in mass spectrometry-based targeted metabolomics and lipidomics: Implications for clinical research. Molecules 2024, 29, 5934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crook, A.A.; Powers, R. Quantitative NMR-based biomedical metabolomics: Current status and applications. Molecules 2020, 25, 5128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emwas, A.H. The strengths and weaknesses of NMR spectroscopy and mass spectrometry with particular focus on metabolomics research. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1277, 161–193. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, D.D.; Powers, R. Beyond the paradigm: Combining mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance for metabolomics. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 2017, 100, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, A.; Kim, W.; Park, J.; Park, Y.; Lee, W.; Lee, S.; Kim, H. Mass spectrometry advancements and applications for biomarker discovery, diagnostic innovations, and personalized medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Akl, N.S.; Khalifa, O.; Ponirakis, G.; Parray, A.; Ramadan, M.; Khan, S.; Chandran, M.; Ayadathil, R.; Elsotouhy, A.; Own, A.; et al. Untargeted metabolomic profiling reveals differentially expressed serum metabolites and pathways in Type 2 diabetes patients with and without cognitive decline: A Cross-Sectional Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triebl, A.; Trötzmüller, M.; Hartler, J.; Stojakovic, T.; Köfeler, H.C. Lipidomics by ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry and its application to complex biological samples. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2017, 1053, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dona, A.C.; Kyriakides, M.; Scott, F.; Shephard, E.A.; Varshavi, D.; Veselkov, K.; Everett, J.R. A guide to the identification of metabolites in NMR-based metabonomics/metabolomics experiments. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2016, 14, 135–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Titkare, N.; Chaturvedi, S.; Borah, S.; Sharma, N. Advances in mass spectrometry for metabolomics: Strategies, challenges, and innovations in disease biomarker discovery. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2024, 38, e6019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izundegui, D.G.; Nayor, M. Metabolomics of type 1 and type 2 diabetes: Insights into risk prediction and mechanisms. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2022, 22, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morze, J.; Wittenbecher, C.; Schwingshackl, L.; Danielewicz, A.; Rynkiewicz, A.; Hu, F.B.; Guasch-Ferré, M. Metabolomics and type 2 diabetes risk: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Diabetes Care 2022, 45, 1013–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.Z.; Gerszten, R.E. Metabolomics and proteomics in type 2 diabetes. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 1613–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laakso, M.; Fernandes-Silva, L. Genetics of type 2 diabetes: Past, present, and future. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arneth, B.; Arneth, R.; Shams, M. Metabolomics of type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shojima, N.; Yamauchi, T. Progress in genetics of type 2 diabetes and diabetic complications. J. Diabetes Investig. 2023, 14, 503–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, R.; Herder, C.; Sha, S.; Peng, L.; Brenner, H.; Schöttker, B. Novel type 2 diabetes prediction score based on traditional risk factors and circulating metabolites: Model derivation and validation in two large cohort studies. eClinicalMedicine 2024, 79, 102971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berisha, V.; Krantsevich, C.; Hahn, P.R.; Hahn, S.; Dasarathy, G.; Turaga, P.; Liss, J. Digital medicine and the curse of dimensionality. NPJ Digit. Med. 2021, 4, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosley, J.D.; Shi, M.; Agamasu, D.; Vaitinadin, N.S.; Murthy, V.L.; Shah, R.V.; Bagheri, M.; Ferguson, J.F. Branched chain amino acids and type 2 diabetes: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization analysis. Obesity 2024, 32, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotta, L.A.; Scott, R.A.; Sharp, S.J.; Burgess, S.; Luan, J.A.; Tillin, T.; Schmidt, A.F.; Imamura, F.; Stewart, I.D.; Perry, J.R.; et al. Genetic predisposition to an impaired metabolism of the branched-chain amino acids and risk of type 2 diabetes: A Mendelian randomisation analysis. PLoS Med. 2016, 13, e1002179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Hu, W.; Yang, Y. Serum metabolomic analysis revealed potential metabolite biomarkers for diabetes mellitus with coronary heart disease. Anal. Methods 2023, 15, 3432–3438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laakso, M. Biomarkers for Type 2 Diabetes. Mol. Metab. 2019, 27, S139–S146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahola-Olli, A.V.; Mustelin, L.; Kalimeri, M.; Kettunen, J.; Jokelainen, J.; Auvinen, J.; Puukka, K.; Havulinna, A.S.; Lehtimäki, T.; Kähönen, M.; et al. Circulating metabolites and the risk of Type 2 Diabetes: A prospective study of 11,896 young adults from four Finnish Cohorts. Diabetologia 2019, 62, 2298–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahendran, Y.; Cederberg, H.; Vangipurapu, J.; Kangas, A.J.; Soininen, P.; Kuusisto, J.; Uusitupa, M.; Ala-Korpela, M.; Laakso, M. Glycerol and fatty acids in serum predict the development of hyperglycemia and type 2 diabetes in Finnish men. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 3732–3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Al Dubayee, M.; Alshahrani, A.; Masood, A.; Benabdelkamel, H.; Zahra, M.; Li, L.; Rahman, A.M.A.; Aljada, A. Distinctive metabolomics patterns associated with insulin resistance and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 609806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.J.; Kwak, S.-Y.; Jo, G.; Song, T.-J.; Shin, M.-J. Serum metabolite profile associated with incident Type 2 Diabetes in Koreans: Findings from the Korean genome and epidemiology study. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Li, J.; Hui, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y. Assessing the causal relationship between metabolic biomarkers and coronary artery disease by Mendelian randomization studies. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 19034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Larsson, S.C. An atlas on risk factors for type 2 diabetes: A wide-angled Mendelian randomisation study. Diabetologia 2020, 63, 2359–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, S.; Merino, J.; Larsson, S.C. Causal factors underlying diabetes risk informed by Mendelian randomisation analysis: Evidence, opportunities and challenges. Diabetologia 2023, 66, 800–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aikens, R.C.; Zhao, W.; Saleheen, D.; Reilly, M.P.; Epstein, S.E.; Tikkanen, E.; Salomaa, V.; Voight, B.F. Systolic blood pressure and risk of type 2 diabetes: A Mendelian randomization study. Diabetes 2017, 66, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, N.M.G.; Borges, M.C.; Hingorani, A.D.; Engmann, J.; Shah, T.; Zhang, X.; Luan, J.; Langenberg, C.; Wong, A.; Kuh, D.; et al. Liver function and risk of type 2 diabetes: Bidirectional Mendelian randomization study. Diabetes 2019, 68, 1681–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.; Sorokin, E.P.; Thomas, E.L.; Sattar, N.; Cule, M.; Bell, J.D.; Yaghootkar, H. Estimating the effect of liver and pancreas volume and fat content on risk of diabetes: A Mendelian randomization study. Diabetes Care 2022, 45, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wainberg, M.; Mahajan, A.; Kundaje, A.; McCarthy, M.I.; Ingelsson, E.; Sinnott-Armstrong, N.; Rivas, M.A. Homogeneity in the association of body mass index with type 2 diabetes across the UK Biobank: A Mendelian randomization study. PLoS Med. 2019, 16, e1002982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, T.; Rask-Andersen, M.; Pan, G.; Höglund, J.; Wadelius, C.; Ek, W.E.; Johansson, Å. Contribution of genetics to visceral adiposity and its relation to cardiovascular and metabolic disease. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1390–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Larsson, S.C. A causal relationship between cigarette smoking and type 2 diabetes mellitus: A Mendelian randomization study. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Tang, J.; Lin, S.; Liu, X.; Li, Y. Mendelian randomization analysis demonstrates the causal effects of IGF family members in diabetes. Front. Med. 2024, 11, 1332162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Sang, Y.; Liu, M.; Wang, Q.; Yang, H.; Li, X. Gut microbiota in health and disease: Advances and future prospects. Med. Comm. 2024, 5, e70012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Goodarzi, M.O. Metabolites linking the gut microbiome with risk for type 2 diabetes. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2020, 2, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, C.; Qi, C.; Zhang, J.; Wang, W.; Meng, X.; Aikepaer, A.; Lin, Y.; Su, C.; Liu, Y.; Feng, X.; et al. When short-chain fatty acids meet type 2 diabetes mellitus: Revealing mechanisms, envisioning therapies. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2025, 233, 116791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Sun, S.; Yan, Y.; Zhou, H.; Liu, Z.; Fu, Q. The role of short-chain fatty acid in metabolic syndrome and its complications: Focusing on immunity and inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1519925. [Google Scholar]
- Navab-Moghadam, F.; Sedighi, M.; Khamseh, M.E.; Alaei-Shahmiri, F.; Talebi, M.; Razavi, S.; Amirmozafari, N. The association of type II diabetes with gut microbiota composition. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 110, 630–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, S.; DeVon, H.A.; Cantor, R.M.; Cupido, A.J.; Pan, C.; Ha, S.M.; Silva, L.F.; Hilser, J.R.; Hartiala, J.; Allayee, H.; et al. Relationships and mendelian randomization of gut microbe-derived metabolites with metabolic syndrome traits in the METSIM Cohort. Metabolites 2024, 14, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abildinova, G.Z.; Benberin, V.V.; Vochshenkova, T.A.; Afshar, A.; Mussin, N.M.; Kaliyev, A.A.; Zhussupova, Z.; Tamadon, A. The gut-brain-metabolic axis: Exploring the role of microbiota in insulin resistance and cognitive function. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1463958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Chen, M.; Zhuang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Qian, Y.; Xu, J.; Fan, J. Genetic associations between gut microbiota and type 2 diabetes mediated by plasma metabolites: A Mendelian randomization study. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1430675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laakso, M.; Kuusisto, J.; Stančáková, A.; Kuulasmaa, T.; Pajukanta, P.; Lusis, A.J.; Collins, F.S.; Mohlke, K.L.; Boehnke, M. The Metabolic Syndrome in Men study: A resource for studies of metabolic and cardiovascular diseases. J. Lipid Res. 2017, 58, 481–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vangipurapu, J.; Silva, L.F.; Kuulasmaa, T.; Smith, U.; Laakso, M. Microbiota-related metabolites and the risk of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 1319–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newgard, C.B. Metabolomics and metabolic diseases: Where do we stand? Cell Metab. 2017, 25, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, C.J.; Adams, S.H. Branched-chain amino acids in metabolic signalling and insulin resistance. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2014, 10, 723–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, M.I. Painting a new picture of personalised medicine for diabetes. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 793–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udler, M.S.; Kim, J.; von Grotthuss, M.; Bonàs-Guarch, S.; Cole, J.B.; Chiou, J.; Anderson, C.D.; Boehnke, M.; Laakso, M.; Atzmon, G.; et al. Type 2 diabetes genetic loci informed by multi-trait associations point to disease mechanisms and subtypes: A soft clustering analysis. PLoS Med. 2018, 15, e1002654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Hatzikotoulas, K.; Southam, L.; Taylor, H.J.; Yin, X.; Lorenz, K.M.; Mandla, R.; Huerta-Chagoya, A.; Melloni, G.E.; Kanoni, S.; et al. Genetic drivers of heterogeneity in type 2 diabetes pathophysiology. Nature 2024, 627, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haffner, S.M.; Lehto, S.; Rönnemaa, T.; Pyörälä, K.; Laakso, M. Mortality from coronary heart disease in subjects with type 2 diabetes and in nondiabetic subjects with and without prior myocardial infarction. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayor, M.; Brown, K.J.; Vasan, R.S. The molecular basis of predicting atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk. Circ. Res. 2021, 128, 287–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Zou, Y.; Cui, J.; Ma, X.; Zhang, L.; Yu, S.; Qiu, L. Analysis of two intestinal bacterial metabolites (trimethylamine N-oxide and phenylacetylglutamine) in human serum samples of patients with T2D and AMI using a liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry method. Clin. Chim. Acta. 2022, 536, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Qin, M.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Chen, X.; Liu, C.; Ma, Q.; Liu, Y.; Lai, W.; Chen, H.; et al. Plasma metabolomics provides new insights into the relationship between metabolites and outcomes and left ventricular remodeling of coronary artery disease. Cell Biosci. 2022, 12, 173. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Z.; Zhong, Y.; Zhou, L.; Xu, P.; Gao, N.; Lu, J.; Yan, X.; Cao, H. Unveiling the microbiota-metabolite-myocardium axis: A novel perspective on cardiovascular health. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1389311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Pan, C.; Cai, Y.; Han, X.; Wang, C.; Ma, J.; Pang, J.; Xu, F.; Wu, S.; Kou, T.; et al. Plasma metabolomics reveals the shared and distinct metabolic disturbances associated with cardiovascular events in coronary artery disease. Nat. Comm. 2024, 15, 5729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Chu, M.; Fu, Z.; Liu, Q.; Liang, J.; Xu, J.; Weng, Z.; Chen, X.; Xu, C.; Gu, A. The association of metabolomic profiles of a healthy lifestyle with heart failure risk in a prospective study. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikegami, R.; Shimizu, I.; Yoshida, Y.; Minamino, T. Metabolomic analysis in heart failure. Circ. J. 2017, 82, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, K.; Forrest, I.S.; Petrazzini, B.O.; Duffy, Á.; Park, J.K.; Malick, W.; Rosenson, R.S.; Rocheleau, G.; Jordan, D.M.; Do, R. Evaluation of a machine learning-based metabolic marker for coronary artery disease in the UK Biobank. Atherosclerosis 2025, 401, 119103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Liu, W.; Jiang, H.; Wu, X.; Zhang, S.; Liu, H. Large-scale comprehensive plasma metabolomic analyses reveal potential biomarkers for the diagnosis of early-stage coronary atherosclerosis. Clin. Chim. Acta. 2024, 562, 119832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Cao, Y.; Jia, L. Lipidomics-based investigation of its impact on the pathogenesis of coronary atherosclerosis: A Mendelian randomization study. Hereditas 2025, 162, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Wu, Y.; Mai, J.; Guo, G.; Meng, J.; Fang, X.; Chen, X.; Liu, C.; Zhong, S. Comprehensive metabolic profiling of inflammation indicated key roles of glycerophospholipid and arginine metabolism in coronary artery disease. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 829425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jauhiainen, R.; Vangipurapu, J.; Laakso, A.; Kuulasmaa, T.; Kuusisto, J.; Laakso, M. The association of 9 amino acids with cardiovascular events in Finnish men in a 12-year follow-up study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 106, 3448–3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliou, A.; Mikros, E.; Karaman, I.; Elliott, F.; Griffin, J.L.; Tzoulaki, I.; Elliott, P. Metabolic phenotyping and cardiovascular disease: An overview of evidence from epidemiological settings. Heart 2021, 107, 1123–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prechtl, L.; Carrard, J.; Gallart-Ayala, H.; Borreggine, R.; Teav, T.; Königstein, K.; Wagner, J.; Knaier, R.; Infanger, D.; Streese, L.; et al. Features urea cycle alterations associated with coronary artery disease. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 25848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omori, K.; Katakami, N.; Yamamoto, Y.; Ninomiya, H.; Takahara, M.; Matsuoka, T.-A.; Bamba, T.; Fukusaki, E.; Shimomura, I. Identification of metabolites associated with onset of CAD in diabetic patients using CE-MS analysis: A pilot study. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2019, 26, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernon, S.T.; Tang, O.; Kim, T.; Chan, A.S.; Kott, K.A.; Park, J.; Hansen, T.; Koay, Y.C.; Grieve, S.M.; O’sullivan, J.F.; et al. Metabolic signatures in coronary artery disease: Results from the BioHEART-CT Study. Cells. 2021, 10, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, K.; Gupta, D.K.; Shu, X.-O.; Lipworth, L.; Zheng, W.; Cai, H.; Cai, Q.; Yu, D. Circulating metabolite profiles and risk of coronary heart disease among racially and geographically diverse populations. Circ. Genom. Precis. Med. 2024, 17, e004437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Feng, G.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, W. Metabolites and coronary heart disease: A two sample Mendelian Randomization. Int. J. Cardiol. Cardiovasc. Risk Prev. 2025, 200365. [Google Scholar]
- Mei, Z.; Xu, L.; Huang, Q.; Lin, C.; Yu, M.; Shali, S.; Wu, H.; Lu, Y.; Wu, R.; Wang, Z.; et al. Metabonomic biomarkers of plaque burden and instability in patients with coronary atherosclerotic disease after moderate lipid-lowering therapy. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2024, 13, e036906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anlar, G.G.; Anwardeen, N.; Al Ashmar, S.; Pedersen, S.; Elrayess, M.A.; Zeidan, A. Metabolomics profiling of stages of coronary artery disease progression. Metabolites 2024, 14, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.; Chen, X.; Yu, C.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, S.; Chen, X.; Chen, K.; Yang, Y.; Ling, W. Gut microbially produced indole-3-propionic acid inhibits atherosclerosis by promoting reverse cholesterol transport and its deficiency is causally related to atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Circ. Res. 2022, 131, 404–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laakso, M.; Fernandes Silva, L. Statins and risk of type 2 diabetes: Mechanism and clinical implications. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1239335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohain, A.T.; Barrington, W.T.; Jordan, D.M.; Beckmann, N.D.; Argmann, C.A.; Houten, S.M.; Charney, A.W.; Ermel, R.; Sukhavasi, K.; Franzen, O.; et al. An integrative multiomic network model links lipid metabolism to glucose regulation in coronary artery disease. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Klaric, L.; Krasauskaite, J.; Khalid, W.; Strachan, M.W.J.; Wilson, J.F.; Price, J.F. Combining serum metabolomic profiles with traditional risk factors improves 10-year cardiovascular risk prediction in people with type 2 diabetes. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2023, 30, 1255–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costanzo, M.; Caterino, M.; Sotgiu, G.; Ruoppolo, M.; Franconi, F.; Campesi, I. Sex differences in the human metabolome. Biol. Sex. Differ. 2022, 13, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Yao, J.; Deng, S.; Balasubramanian, R.; Jiménez, M.C.; Li, J.; Guo, X.; Cruz, D.E.; Gao, Y.; Huang, T.; et al. Differences in metabolomic profiles between black and white women and risk of coronary heart disease: An observational study of women from four US cohorts. Circ. Res. 2022, 131, 601–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhaar, B.J.; Mosterd, C.M.; Collard, D.; Galenkamp, H.; Muller, M.; Rampanelli, E.; van Raalte, D.H.; Nieuwdorp, M.; Born, B.-J.H.v.D. Sex differences in associations of plasma metabolites with blood pressure and heart rate variability: The HELIUS Study. Atherosclerosis 2023, 384, 117147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lew, J.; Sanghavi, M.; Ayers, C.R.; McGuire, D.K.; Omland, T.; Atzler, D.; Gore, M.O.; Neeland, I.; Berry, J.D.; Khera, A.; et al. Sex-based differences in cardiometabolic biomarkers. Circulation 2017, 135, 544–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, Y.; Chen, Z.; Baudier, R.L.; Krousel-Wood, M.; Anderson, A.H.; Fonseca, V.A.; Mauvais-Jarvis, F. Sex differences in the progression of metabolic risk factors in diabetes development. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2222070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freaney, P.M.; Khan, S.S.; Lloyd-Jones, D.M.; Stone, N.J. The role of sex-specific risk factors in the risk assessment of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease for primary prevention in women. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2020, 22, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, Y.; Chen, Z.; Fonseca, V.A.; Mauvais-Jarvis, F. Sex differences in cardiovascular risk Associated with prediabetes and undiagnosed diabetes. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2023, 65, 854–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barovic, M.; Hahn, J.J.; Heinrich, A.; Adhikari, T.; Schwarz, P.; Mirtschink, P.; Funk, A.; Kabisch, S.; Pfeiffer, A.F.; Blüher, M.; et al. Proteomic and metabolomic signatures in prediabetes progressing to diabetes or reversing to normoglycemia within 1 year. Diabetes Care 2025, 48, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, J.E.; Nuthikattu, S.; Milenkovic, D.; Villablanca, A.C. Sex modifies the impact of type 2 diabetes mellitus on the murine whole brain metabolome. Metabolites 2023, 13, 1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loesch, D.P.; Garg, M.; Matelska, D.; Vitsios, D.; Jiang, X.; Ritchie, S.C.; Sun, B.B.; Runz, H.; Whelan, C.D.; Holman, R.R.; et al. Identification of plasma proteomic markers underlying polygenic risk of type 2 diabetes and related comorbidities. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmann, K.N.; Wang, T.J. Biomarkers of cardiovascular diseases: Contributions to risk prediction in individuals with diabetes. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 987–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theofilatos, K.; Stojkovic, S.; Hasman, M.; van der Laan, S.W.; Baig, F.; Barallobre-Barreiro, J.; Schmidt, L.E.; Yin, S.; Yin, X.; Burnap, S.; et al. Proteomic Atlas of Atherosclerosis: The contribution of proteoglycans to sex differences, plaque phenotypes, and outcomes. Circ. Res. 2023, 133, 542–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Li, G.; Viallon, V.; Ferrari, P.; Freisling, H.; Qiao, Y.; Shao, L.; Wu, L.; Ding, Y.; Ke, C. A large study of metabolomics reveals common and distinct metabolic biomarkers for type 2 diabetes, coronary heart disease, and stroke. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2024, kwae167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, J.-E.; He, H.; Qin, M.; Lei, H.; Meng, J.; Liu, C.; Chen, X.; Luo, W.; Zhong, S. Characterizing the metabolic divide: Distinctive metabolites differentiating CAD-T2DM from CAD patients. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2024, 23, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurilshikov, A.; Medina-Gomez, C.; Bacigalupe, R.; Radjabzadeh, D.; Wang, J.; Demirkan, A.; Le Roy, C.I.; Garay, J.A.R.; Finnicum, C.T.; Liu, X.; et al. Large-scale association analyses identify host factors influencing human gut microbiome composition. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, T.V.A.; Hwangbo, H.; Lai, Y.; Hong, S.B.; Choi, Y.-J.; Park, H.-J.; Ban, K. The gut-heart axis: Updated review for the roles of microbiome in cardiovascular health. Korean Circ. J. 2023, 53, 499–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Li, R.; Raes, J.; Arumugam, M.; Burgdorf, K.S.; Manichanh, C.; Nielsen, T.; Pons, N.; Levenez, F.; Yamada, T.; et al. A human gut microbial gene catalogue established by metagenomic sequencing. Nature 2010, 464, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Huda, M.N.; Bennett, B.J. Sequence meets function-microbiota and cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc. Res. 2021, 118, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talmor-Barkan, Y.; Bar, N.; Shaul, A.A.; Shahaf, N.; Godneva, A.; Bussi, Y.; Lotan-Pompan, M.; Weinberger, A.; Shechter, A.; Chezar-Azerrad, C.; et al. Metabolomic and microbiome profiling reveals personalized risk factors for coronary artery disease. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Org, E.; Blum, Y.; Kasela, S.; Mehrabian, M.; Kuusisto, J.; Kangas, A.J.; Soininen, P.; Wang, Z.; Ala-Korpela, M.; Hazen, S.L.; et al. Relationships between gut microbiota, plasma metabolites, and metabolic syndrome traits in the METSIM cohort. Genome Biol. 2017, 18, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhry, U.A.R.; Fortescue, R.; Bowen, L.; Woolford, S.J.; Knights, F.; Cook, D.G.; Harris, T.; Critchley, J. Comparison of mortality in people with type 2 diabetes between different ethnic groups: Systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0314318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Key Findings | Implications | |
|---|---|---|
| Biomarker Discovery and Risk Prediction | Specific metabolites (e.g., BCAAs, aromatic AAs, acylcarnitines, and ceramides) are associated with increased T2D risk, while glycine, glutamine, and indolepropionate are protective. | Enhances the early detection and risk stratification of T2D. Enables more accurate, personalized preventive strategies. |
| Amino Acid and Lipid Metabolism | Alterations in the amino acid and lipid pathways are consistently observed in T2D patients: BCAAs and aromatic AAs are elevated, while glycine is decreased. | Indicates metabolic dysregulation; there is the potential for therapeutic targeting and metabolic pathway modulation. |
| Metabolomics and CVD Risk | Metabolites such as TMAO, phenylacetylglutamine, and acylcarnitines are linked to CAD and heart failure risk. | Facilitates the identification of high-risk individuals and supports targeted interventions for cardiovascular outcomes in T2D patients. |
| Sex Differences | Metabolic and proteomic profiles differ by sex due to hormonal influences (e.g., estrogen and testosterone); women with T2D may face higher CVD risk. | Highlights the need for sex-specific risk assessment and therapeutic approaches. |
| Microbiota-Related Metabolites | Gut microbial metabolites (e.g., SCFAs and indole derivatives) are associated with insulin secretion, resistance, and T2D risk. | Emphasizes the gut–metabolism axis and its relevance in disease progression and treatment design. |
| Genetics and Precision Medicine | GWAS and polygenic risk scores identify clusters of T2D risk related to insulin secretion and resistance. Integration with metabolomics improves prediction. | Supports the implementation of precision medicine through integrated multi-omics profiling. |
| Clinical Challenges | Methodological complexity, lack of standardization, and cost limit metabolomics’ clinical adoption. | Necessitates development of standardized, cost-effective protocols and validation in diverse cohorts. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fernandes Silva, L.; Laakso, M. Advances in Metabolomics: A Comprehensive Review of Type 2 Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease Interactions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3572. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083572
Fernandes Silva L, Laakso M. Advances in Metabolomics: A Comprehensive Review of Type 2 Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease Interactions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(8):3572. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083572
Chicago/Turabian StyleFernandes Silva, Lilian, and Markku Laakso. 2025. "Advances in Metabolomics: A Comprehensive Review of Type 2 Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease Interactions" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 8: 3572. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083572
APA StyleFernandes Silva, L., & Laakso, M. (2025). Advances in Metabolomics: A Comprehensive Review of Type 2 Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease Interactions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(8), 3572. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083572






