Tumor-Educated Platelets in Urological Tumors: A Novel Biosource in Liquid Biopsy
Abstract
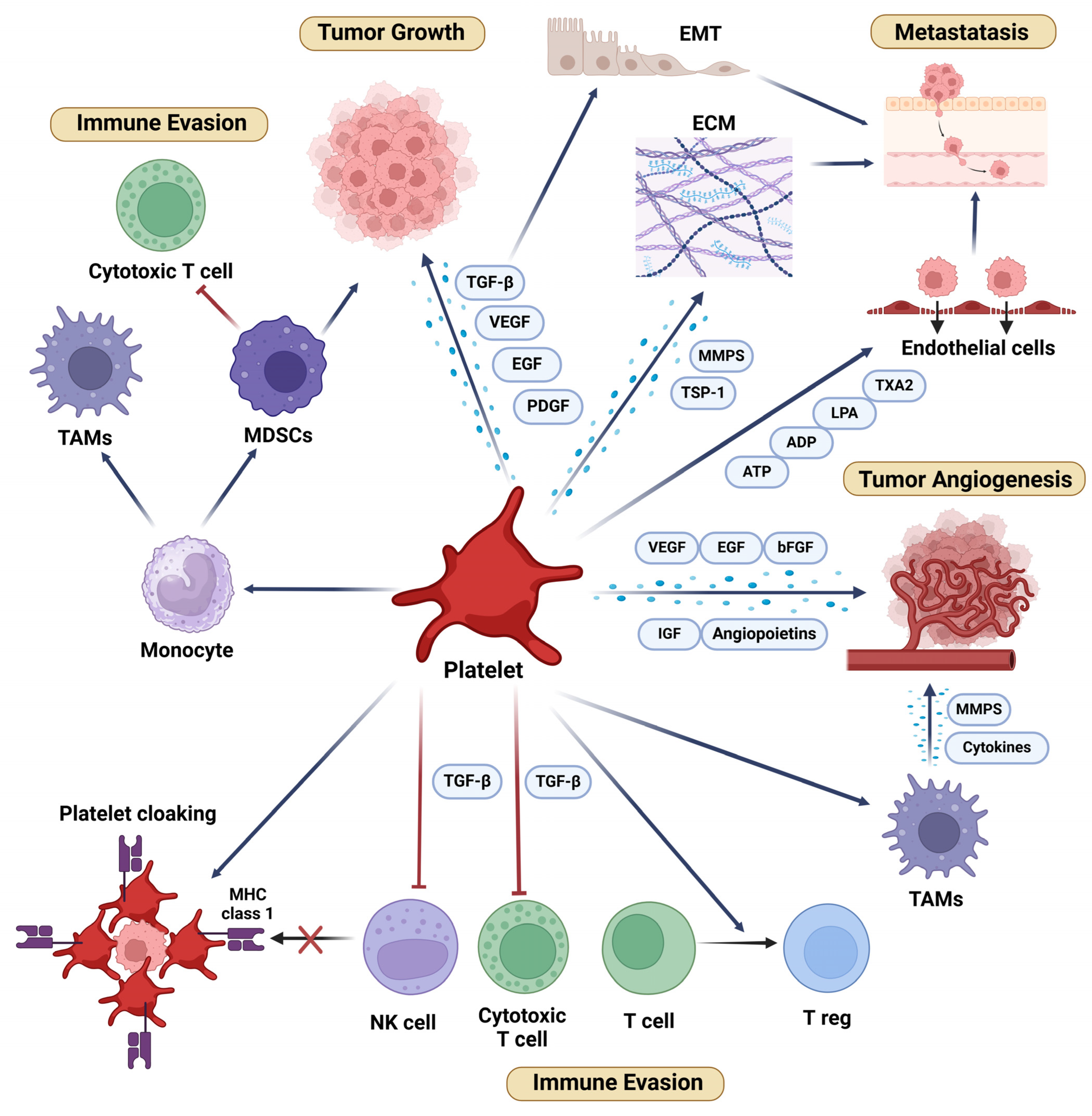
1. The Role of Platelets in Cancer: An Overview
1.1. Platelets in Tumor Growth and Progression
1.2. Platelets in Tumor Angiogenesis
1.3. Platelets and Immune Evasion in Cancer
1.4. Platelets in Cancer Metastasis
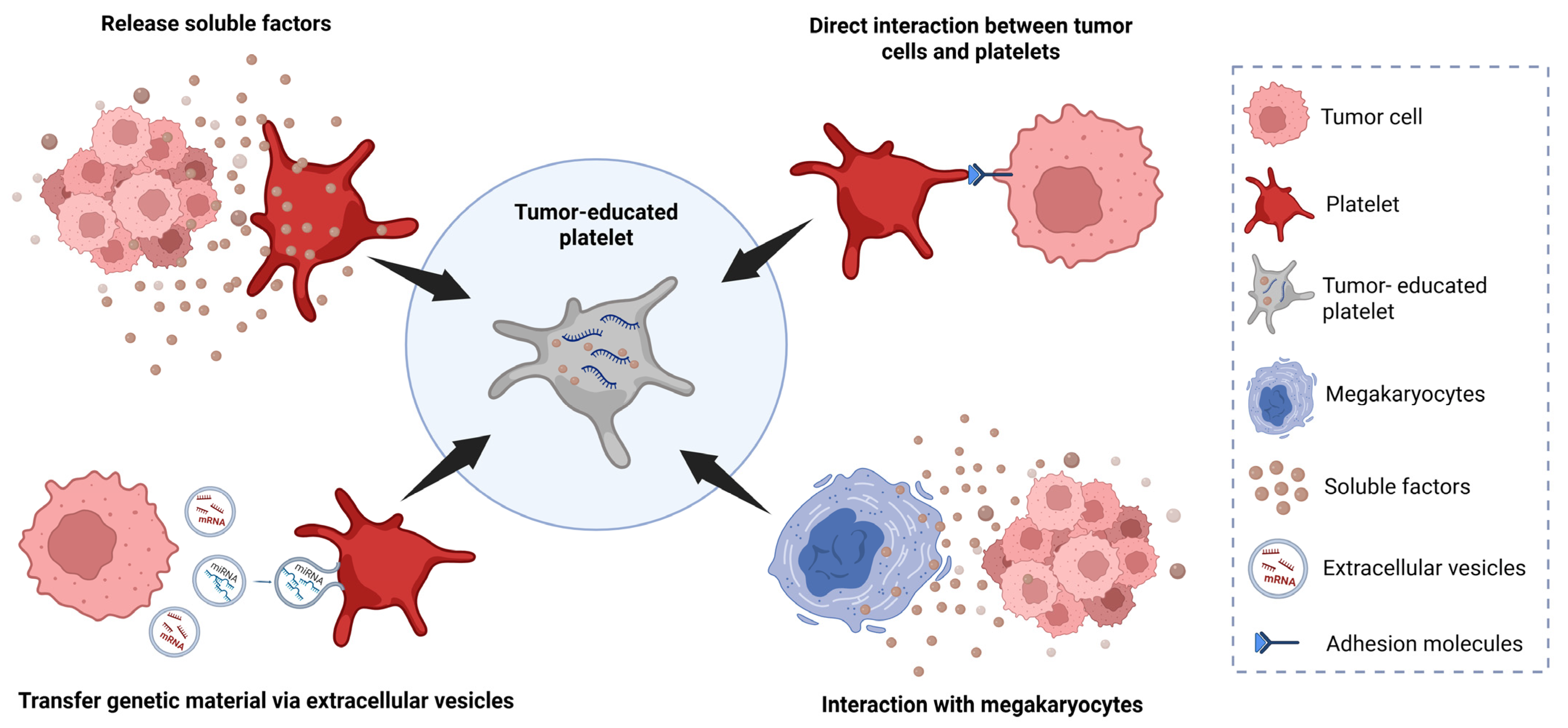
2. Tumor-Educated Platelets
2.1. TEPs as Blood-Sourced Biomarkers for Solid Tumors
2.2. TEPs and Prostate Cancer
2.3. TEPs and Kidney Cancer
2.4. TEPs and Bladder Cancer
3. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALK | Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase |
| AUC | Area Under the Curve |
| bFGF | Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor |
| CD40L | CD40 Ligand |
| CTCs | Circulating Tumor Cells |
| ctDNA | Circulating Tumor DNA |
| EGF | Epidermal Growth Factor |
| EGFR | Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor |
| EGFRvIII | Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Variant III |
| EML4 | Echinoderm Microtubule Associated Protein-Like 4 |
| EMT | Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition |
| EVs | Extracellular Vesicles |
| EZH2 | Enhancer of Zeste Homolog 2 |
| GARP | TGFβ Docking Receptor Glycoprotein A Repetitions Predominant |
| G-CSF | Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor |
| GM-CSF | Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor |
| GPIIb/IIIa | Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| KRAS | Kirsten Rat Sarcoma Virus |
| MALAT1 | Metastasis Associated Lung Adenocarcinoma Transcript 1 |
| MDSCs | Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells |
| MHC | Major Histocompatibility Complex |
| MIBC | Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer |
| mCRPC | Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer |
| MMPs | Metalloproteinases |
| NK Cells | Natural Killer Cells |
| NSCLC | Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer |
| OS | Overall Survival |
| PCA3 | Prostate Cancer Antigen 3 |
| PDGF | Platelet-Derived Growth Factor |
| PD-L1 | Programmed Death Ligand 1 |
| PIK3CA | Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-Bisphosphate 3-Kinase, Catalytic Subunit Alpha |
| PFS | Progression-Free Survival |
| PSA | Prostate-Specific Antigen |
| PSMA | Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen |
| RCC | Renal Cell Carcinoma |
| TAMs | Tumor-Associated Macrophages |
| TEPs | Tumor-Educated Platelets |
| TGF-β | Transforming Growth Factor-Beta |
| TIMP1 | TIMP Metallopeptidase Inhibitor 1 |
| TME | Tumor Microenvironment |
| Tregs | Regulatory T Cells |
| TSP-1 | Thrombospondin-1 |
| VEGF | Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor |
References
- Menter, D.G.; Tucker, S.C.; Kopetz, S.; Sood, A.K.; Crissman, J.D.; Honn, K.V. Platelets and cancer: A casual or causal relationship: Revisited. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2014, 33, 231–269. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jain, S.; Harris, J.; Ware, J. Platelets: Linking hemostasis and cancer. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2010, 30, 2362–2367. [Google Scholar]
- Connolly, G.C.; Phipps, R.P.; Francis, C.W. Platelets and cancer-associated thrombosis. Semin. Oncol. 2014, 41, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Lu, Z.; Wu, S.; Chu, T.; Li, B.; Qi, F.; Zhao, Y.; Nie, G. The dynamic role of platelets in cancer progression and their therapeutic implications. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2024, 24, 72–87. [Google Scholar]
- Pinedo, H.M.; Verheul, H.M.; D’Amato, R.J.; Folkman, J. Involvement of platelets in tumour angiogenesis? Lancet 1998, 352, 1775–1777. [Google Scholar]
- Baj-Krzyworzeka, M.; Majka, M.; Pratico, D.; Ratajczak, J.; Vilaire, G.; Kijowski, J.; Reca, R.; Janowska-Wieczorek, A.; Ratajczak, M.Z. Platelet-derived microparticles stimulate proliferation, survival, adhesion, and chemotaxis of hematopoietic cells. Exp. Hematol. 2002, 30, 450–459. [Google Scholar]
- Labelle, M.; Begum, S.; Hynes, R.O. Direct signaling between platelets and cancer cells induces an epithelial-mesenchymal-like transition and promotes metastasis. Cancer Cell 2011, 20, 576–590. [Google Scholar]
- Bothina, S.M.I.W.B.; Iman, M.; Maha, M.S.; Mamdouh, R.; Faiza, M.E. Platelet and neutrophil cross-talk-mediating cancer growth and metastasis in patients with urinary bladder cancer. J. Arab. Soc. Med. Res. 2012, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, Z.; Tian, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, S. The critical role of platelet in cancer progression and metastasis. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2023, 28, 385. [Google Scholar]
- Nierodzik, M.L.; Karpatkin, S. Thrombin induces tumor growth, metastasis, and angiogenesis: Evidence for a thrombin-regulated dormant tumor phenotype. Cancer Cell 2006, 10, 355–362. [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar]
- Klement, G.L.; Yip, T.T.; Cassiola, F.; Kikuchi, L.; Cervi, D.; Podust, V.; Italiano, J.E.; Wheatley, E.; Abou-Slaybi, A.; Bender, E.; et al. Platelets actively sequester angiogenesis regulators. Blood 2009, 113, 2835–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabrkhany, S.; Griffioen, A.W.; Oude Egbrink, M.G. The role of blood platelets in tumor angiogenesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1815, 189–196. [Google Scholar]
- Wojtukiewicz, M.Z.; Sierko, E.; Hempel, D.; Tucker, S.C.; Honn, K.V. Platelets and cancer angiogenesis nexus. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2017, 36, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- O’Byrne, K.J.; Dobbs, N. Vascular endothelial growth factor platelet counts, and prognosis in renal cancer. Lancet 1999, 353, 1494–1495. [Google Scholar]
- Cumpanas, A.A.; Cimpean, A.M.; Ferician, O.; Ceausu, R.A.; Sarb, S.; Barbos, V.; Dema, A.; Raica, M. The Involvement of PDGF-B/PDGFRbeta Axis in the Resistance to Antiangiogenic and Antivascular Therapy in Renal Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2016, 36, 2291–2295. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guillaume, Z.; Auvray, M.; Vano, Y.; Oudard, S.; Helley, D.; Mauge, L. Renal Carcinoma and Angiogenesis: Therapeutic Target and Biomarkers of Response in Current Therapies. Cancers 2022, 14, 6167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, J.A.; Pollard, J.W. Microenvironmental regulation of metastasis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 239–252. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, L.Q.; Du, W.L.; Cai, M.H.; Yao, J.Y.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Mou, X.Z. The roles of tumor-associated macrophages in tumor angiogenesis and metastasis. Cell Immunol. 2020, 353, 104119. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Z.; Yang, Y.; Meng, Z.; Qin, L. Effects of the interactions between platelets with other cells in tumor growth and progression. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1165989. [Google Scholar]
- Tuerhong, N.; Yang, Y.; Wang, C.; Huang, P.; Li, Q. Interactions between platelets and the cancer immune microenvironment. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2024, 199, 104380. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Okazaki, M.; Yamaguchi, T.; Tajima, H.; Fushida, S.; Ohta, T. Platelet adherence to cancer cells promotes escape from innate immune surveillance in cancer metastasis. Int. J. Oncol. 2020, 57, 980–988. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Placke, T.; Kopp, H.G.; Salih, H.R. The wolf in sheep’s clothing: Platelet-derived “pseudo self” impairs cancer cell “missing self” recognition by NK cells. Oncoimmunology 2012, 1, 557–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Li, T.; Jiang, R.; Yang, X.; Guo, H.; Yang, R. Targeting MHC-I molecules for cancer: Function, mechanism, and therapeutic prospects. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 194. [Google Scholar]
- Zaslavsky, A.B.; Adams, M.P.; Cao, X.; Maj, T.; Choi, J.E.; Stangl-Kremser, J.; Patel, S.; Putelo, A.; Lee, S.K.; Nallandhighal, S.; et al. Platelet PD-L1 suppresses anti-cancer immune cell activity in PD-L1 negative tumors. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19296. [Google Scholar]
- Lutz, M.S.; Klimovich, B.; Maurer, S.; Heitmann, J.S.; Marklin, M.; Zekri, L.; Jung, G.; Salih, H.R.; Hinterleitner, C. Platelets subvert antitumor efficacy of T cell-recruiting bispecific antibodies. J. Immunother. Cancer 2022, 10, e003655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopp, H.G.; Placke, T.; Salih, H.R. Platelet-derived transforming growth factor-beta down-regulates NKG2D thereby inhibiting natural killer cell antitumor reactivity. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 7775–7783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, D.Q.; Andersson, J.; Wang, R.; Ramsey, H.; Unutmaz, D.; Shevach, E.M. GARP (LRRC32) is essential for the surface expression of latent TGF-beta on platelets and activated FOXP3+ regulatory T cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 13445–13450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachidi, S.; Metelli, A.; Riesenberg, B.; Wu, B.X.; Nelson, M.H.; Wallace, C.; Paulos, C.M.; Rubinstein, M.P.; Garrett-Mayer, E.; Hennig, M.; et al. Platelets subvert T cell immunity against cancer via GARP-TGFbeta axis. Sci. Immunol. 2017, 2, eaai7911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmer, N.; Krebs, F.K.; Zimmer, S.; Mitzel-Rink, H.; Kumm, E.J.; Jurk, K.; Grabbe, S.; Loquai, C.; Tuettenberg, A. Platelet-Derived GARP Induces Peripheral Regulatory T Cells-Potential Impact on T Cell Suppression in Patients with Melanoma-Associated Thrombocytosis. Cancers 2020, 12, 3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servais, L.; Wera, O.; Epoh, J.D.; Delierneux, C.; Bouznad, N.; Rahmouni, S.; Mazzucchelli, G.; Baiwir, D.; Delvenne, P.; Lancellotti, P.; et al. Platelets contribute to the initiation of colitis-associated cancer by promoting immunosuppression. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 16, 762–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatogai, K.; Sweis, R.F. The Tumor Microenvironment of Bladder Cancer. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1296, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Welch, D.R.; Hurst, D.R. Defining the Hallmarks of Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 3011–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlesinger, M. Role of platelets and platelet receptors in cancer metastasis. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, K.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Teng, F.; He, Y.; Cheng, J.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Xie, Y.; Guo, D.; et al. The role of platelets in the regulation of tumor growth and metastasis: The mechanisms and targeted therapy. MedComm 2023, 4, e350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, Y.; Lake, R.; Faraji, F.; Sperger, J.; Martin, P.; Gilliard, C.; Ku, K.P.; Rodems, T.; Niles, D.; Tillman, H.; et al. Platelets Promote Metastasis via Binding Tumor CD97 Leading to Bidirectional Signaling that Coordinates Transendothelial Migration. Cell Rep. 2018, 23, 808–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezei, T.; Bode, I.; Tenke, P.; Josa, V.; Merkel, K.; Szilasi, Z.; Tordai, A.; Mathe, D.; Baranyai, Z. The Correlation Between Platelet Count and Survival in Prostate Cancer. Res. Rep. Urol. 2022, 14, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garofano, K.; Rashid, K.; Smith, M.; Brantner, C.; Suwunnakorn, S.; Diemert, D.; Gordon, O.; Horvath, A.; Khan, S.; Popratiloff, A.; et al. Prostate cancer cell-platelet bidirectional signaling promotes calcium mobilization, invasion and apoptotic resistance via distinct receptor-ligand pairs. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessenbrock, K.; Plaks, V.; Werb, Z. Matrix metalloproteinases: Regulators of the tumor microenvironment. Cell 2010, 141, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.; Esemuede, N.; Sumpio, B.E.; Gahtan, V. Thrombospondin-1 induces matrix metalloproteinase-2 activation in vascular smooth muscle cells. J. Vasc. Surg. 2003, 38, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaren, K.M. Immunohistochemical localisation of thrombospondin in human megakaryocytes and platelets. J. Clin. Pathol. 1983, 36, 197–199. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Best, M.G.; Sol, N.; Kooi, I.; Tannous, J.; Westerman, B.A.; Rustenburg, F.; Schellen, P.; Verschueren, H.; Post, E.; Koster, J.; et al. RNA-Seq of Tumor-Educated Platelets Enables Blood-Based Pan-Cancer, Multiclass, and Molecular Pathway Cancer Diagnostics. Cancer Cell 2015, 28, 666–676. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Najafi, S.; Asemani, Y.; Majidpoor, J.; Mahmoudi, R.; Aghaei-Zarch, S.M.; Mortezaee, K. Tumor-educated platelets. Clin. Chim. Acta 2024, 552, 117690. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roweth, H.G.; Battinelli, E.M. Lessons to learn from tumor-educated platelets. Blood 2021, 137, 3174–3180. [Google Scholar]
- D’Ambrosi, S.; Nilsson, R.J.; Wurdinger, T. Platelets and tumor-associated RNA transfer. Blood 2021, 137, 3181–3191. [Google Scholar]
- Varkey, J.; Nicolaides, T. Tumor-Educated Platelets: A Review of Current and Potential Applications in Solid Tumors. Cureus 2021, 13, e19189. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, H.; Xiong, J.; Wang, J.; Huang, Y. Application of tumor-educated platelets as new fluid biopsy markers in various tumors. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2023, 25, 114–125. [Google Scholar]
- Wurdinger, T.; In ’t Veld, S.; Best, M.G. Platelet RNA as Pan-Tumor Biomarker for Cancer Detection. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 1371–1373. [Google Scholar]
- Joosse, S.A.; Pantel, K. Tumor-Educated Platelets as Liquid Biopsy in Cancer Patients. Cancer Cell 2015, 28, 552–554. [Google Scholar]
- Connal, S.; Cameron, J.M.; Sala, A.; Brennan, P.M.; Palmer, D.S.; Palmer, J.D.; Perlow, H.; Baker, M.J. Liquid biopsies: The future of cancer early detection. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 118. [Google Scholar]
- In ’t Veld, S.; Wurdinger, T. Tumor-educated platelets. Blood 2019, 133, 2359–2364. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Calverley, D.C.; Phang, T.L.; Choudhury, Q.G.; Gao, B.; Oton, A.B.; Weyant, M.J.; Geraci, M.W. Significant downregulation of platelet gene expression in metastatic lung cancer. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2010, 3, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, R.J.A.; Balaj, L.; Hulleman, E.; van Rijn, S.; Pegtel, D.M.; Walraven, M.; Widmark, A.; Gerritsen, W.R.; Verheul, H.M.; Vandertop, W.P.; et al. Blood platelets contain tumor-derived RNA biomarkers. Blood 2011, 118, 3680–3683. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, R.J.A.; Karachaliou, N.; Berenguer, J.; Gimenez-Capitan, A.; Schellen, P.; Teixido, C.; Tannous, J.; Kuiper, J.L.; Drees, E.; Grabowska, M.; et al. Rearranged EML4-ALK fusion transcripts sequester in circulating blood platelets and enable blood-based crizotinib response monitoring in non-small-cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 1066–1075. [Google Scholar]
- Sol, N.; In ’t Veld, S.; Vancura, A.; Tjerkstra, M.; Leurs, C.; Rustenburg, F.; Schellen, P.; Verschueren, H.; Post, E.; Zwaan, K.; et al. Tumor-Educated Platelet RNA for the Detection and (Pseudo) progression Monitoring of Glioblastoma. Cell Rep. Med. 2020, 1, 100101. [Google Scholar]
- Heinhuis, K.M.; In ’t Veld, S.; Dwarshuis, G.; van den Broek, D.; Sol, N.; Best, M.G.; Coevorden, F.V.; Haas, R.L.; Beijnen, J.H.; van Houdt, W.J.; et al. RNA-Sequencing of Tumor-Educated Platelets, a Novel Biomarker for Blood-Based Sarcoma Diagnostics. Cancers 2020, 12, 1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wei, X.; Wu, B.; Su, J.; Tan, W.; Yang, K. Tumor-educated platelet miR-34c-3p and miR-18a-5p as potential liquid biopsy biomarkers for nasopharyngeal carcinoma diagnosis. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 3351–3360. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Jiang, Q.; Li, D.Z.; Zhou, X.; Yu, D.S.; Zhong, J. TIMP1 mRNA in tumor-educated platelets is diagnostic biomarker for colorectal cancer. Aging 2019, 11, 8998–9012. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.; Wang, N.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Sun, S.; Yu, H.; Lin, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wang, H.; Wu, X.; et al. PD-L1 mRNA derived from tumor-educated platelets as a potential immunotherapy biomarker in non-small cell lung cancer. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2024, 13, 345–354. [Google Scholar]
- Hanze, J.; Jakubowski, P.; Heers, H.; Hegele, A.; Timmesfeld, N.; Hofmann, R.; Olbert, P.J. Assessing blood platelets as RNA biomarker source for prostate cancer. Biomarkers 2016, 21, 653–659. [Google Scholar]
- GJG, S.; Arkani, M.; Post, E.; Antunes-Ferreira, M.; D’Ambrosi, S.; Vessies, D.C.; Vermunt, L.; Vancura, A.; Muller, M.; Niemeijer, A.L.N.; et al. Detection and localization of early- and late-stage cancers using platelet RNA. Cancer Cell 2022, 40, 999–1009.e6. [Google Scholar]
- Tjon-Kon-Fat, L.A.; Lundholm, M.; Schroder, M.; Wurdinger, T.; Thellenberg-Karlsson, C.; Widmark, A.; Wikstrom, P.; Nilsson, R.J.A. Platelets harbor prostate cancer biomarkers and the ability to predict therapeutic response to abiraterone in castration resistant patients. Prostate 2018, 78, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xiao, R.; Liu, C.; Zhang, B.; Ma, L. Tumor-Educated Platelets as a Promising Biomarker for Blood-Based Detection of Renal Cell Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 844520. [Google Scholar]
- Hinsenveld, F.J.; Noordman, B.J.; Boormans, J.L.; Voortman, J.; van Leenders, G.J.L.H.; van der Pas, S.L.; van Beek, S.C.; Oprea-Lager, D.E.; Vis, A.N. Prediction of pathological response following neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer: The PRE-PREVENCYS trial. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 1161. [Google Scholar]
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar]
- Sartor, O.; de Bono, J.S. Metastatic Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 645–657. [Google Scholar]
- Miquelestorena-Standley, E.; Jourdan, M.L.; Collin, C.; Bouvier, C.; Larousserie, F.; Aubert, S.; Gomez-Brouchet, A.; Guinebretiere, J.M.; Tallegas, M.; Brulin, B.; et al. Effect of decalcification protocols on immunohistochemistry and molecular analyses of bone samples. Mod. Pathol. 2020, 33, 1505–1517. [Google Scholar]
- Boerrigter, E.; Groen, L.N.; Van Erp, N.P.; Verhaegh, G.W.; Schalken, J.A. Clinical utility of emerging biomarkers in prostate cancer liquid biopsies. Expert. Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2020, 20, 219–230. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, A.; Conteduca, V.; Zoubeidi, A.; Beltran, H. Biological Evolution of Castration-resistant Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. Focus 2019, 5, 147–154. [Google Scholar]
- Rose, T.L.; Kim, W.Y. Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Review. JAMA 2024, 332, 1001–1010. [Google Scholar]
- Young, M.; Jackson-Spence, F.; Beltran, L.; Day, E.; Suarez, C.; Bex, A.; Powles, T.; Szabados, B. Renal cell carcinoma. Lancet 2024, 404, 476–491. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zieren, R.C.; Zondervan, P.J.; Pienta, K.J.; Bex, A.; de Reijke, T.M.; Bins, A.D. Diagnostic liquid biopsy biomarkers in renal cell cancer. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2024, 21, 133–157. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Machaalani, M.; Eid, M.; Semaan, K.; El Hajj Chehade, R.; Nawfal, R.; Baca, S.C.; Choueiri, T.K. Liquid biopsy in renal cell carcinoma. Oncologist 2024, 29, 821–823. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Heng, D.Y.; Xie, W.; Regan, M.M.; Warren, M.A.; Golshayan, A.R.; Sahi, C.; Eigl, B.J.; Ruether, J.D.; Cheng, T.; North, S.; et al. Prognostic factors for overall survival in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with vascular endothelial growth factor-targeted agents: Results from a large, multicenter study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 5794–5799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sole, K. Thrombocytosis predicts mortality in patients with renal cell carcinoma. Nat. Clin. Pract. Urol. 2006, 3, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Gaborieau, V.; Niman, S.M.; Mukeria, A.; Liu, X.; Maremanda, K.P.; Takakura, A.; Zaridze, D.; Freedman, M.L.; Xie, W.; et al. Plasma Kidney Injury Molecule-1 for Preoperative Prediction of Renal Cell Carcinoma Versus Benign Renal Masses, and Association With Clinical Outcomes. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, 2691–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Puligandla, M.; Halbert, B.; Haas, N.B.; Flaherty, K.T.; Uzzo, R.G.; Dutcher, J.P.; DiPaola, R.S.; Sabbisetti, V.; Bhatt, R.S. Plasma KIM-1 Is Associated with Recurrence Risk after Nephrectomy for Localized Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Trial of the ECOG-ACRIN Research Group (E2805). Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 3397–3403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albiges, L.; Bex, A.; Suárez, C.; Uzzo, R.; Tang, X.; Assaf, Z.J.; Dubey, S.; Goluboff, E.; Carter, C.; Banchereau, R.; et al. Circulating kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1) biomarker analysis in IMmotion010: A randomized phase 3 study of adjuvant (adj) atezolizumab (atezo) vs placebo (pbo) in patients (pts) with renal cell carcinoma (RCC) at increased risk of recurrence after resection. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, 4506. [Google Scholar]
- Jubber, I.; Ong, S.; Bukavina, L.; Black, P.C.; Comperat, E.; Kamat, A.M.; Kiemeney, L.; Lawrentschuk, N.; Lerner, S.P.; Meeks, J.J.; et al. Epidemiology of Bladder Cancer in 2023: A Systematic Review of Risk Factors. Eur. Urol. 2023, 84, 176–190. [Google Scholar]
- Babjuk, M.; Burger, M.; Compérat, E.M.; Gontero, P.; Mostafid, A.H.; Palou, J.; van Rhijn, B.W.; Rouprêt, M.; Shariat, S.F.; Sylvester, R.; et al. European Association of Urology Guidelines on Non-muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer (Ta, T1, and Carcinoma in Situ). Eur. Urol. 2022, 81, 75–94. [Google Scholar]
- Kamat, A.M.; Hahn, N.M.; Efstathiou, J.A.; Lerner, S.P.; Malmstrom, P.U.; Choi, W.; Guo, C.C.; Lotan, Y.; Kassouf, W. Bladder cancer. Lancet 2016, 388, 2796–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Porras, V.R.; Pardo, J.C.; Etxaniz, O.; Font, A. Neoadjuvant therapy for muscle-invasive bladder cancer: Current clinical scenario, future perspectives, and unsolved questions. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2022, 178, 103795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powles, T.; Catto, J.W.; Galsky, M.D.; Al-Ahmadie, H.; Meeks, J.J.; Nishiyama, H.; Vu, T.Q.; Antonuzzo, L.; Wiechno, P.; Atduev, V.; et al. Perioperative Durvalumab with Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Operable Bladder Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 391, 1773–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossman, H.B.; Natale, R.B.; Tangen, C.M.; Speights, V.O.; Vogelzang, N.J.; Trump, D.L.; deVere White, R.W.; Sarosdy, M.F.; Wood, D.P., Jr.; Raghavan, D.; et al. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy plus cystectomy compared with cystectomy alone for locally advanced bladder cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witjes, J.A.; Bruins, H.M.; Carrión, A.; Cathomas, R.; Compérat, E.; Efstathiou, J.A.; Fietkau, R.; Gakis, G.; Lorch, A.; Martini, A.; et al. European Association of Urology Guidelines on Muscle-invasive and Metastatic Bladder Cancer: Summary of the 2023 Guidelines. Eur. Urol. 2024, 85, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crocetto, F.; Barone, B.; Ferro, M.; Busetto, G.M.; La Civita, E.; Buonerba, C.; Di Lorenzo, G.; Terracciano, D.; Schalken, J.A. Liquid biopsy in bladder cancer: State of the art and future perspectives. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2022, 170, 103577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xin, K.; Pan, S.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, X.; Liu, B.; Xu, Z.; Chen, X. Blood-based liquid biopsy: Insights into early detection, prediction, and treatment monitoring of bladder cancer. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2023, 28, 28. [Google Scholar]
- Crupi, E.; de Padua, T.C.; Marandino, L.; Raggi, D.; Dyrskjot, L.; Spiess, P.E.; Sonpavde, G.P.; Kamat, A.M.; Necchi, A. Circulating tumor DNA as a Predictive and Prognostic Biomarker in the Perioperative Treatment of Muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer: A Systematic Review. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2024, 7, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Qi, W.; Li, J.; Xia, Y.; Ding, P.; Guo, D.; Shi, B.; Jiang, X. Prognostic and predictive role of circulating tumor DNA detection in patients with muscle invasive bladder cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Cell Int. 2025, 25, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakatani, T.; Sumiyoshi, T.; Kita, Y.; Takada, H.; Nakamura, K.; Hamada, A.; Murakami, K.; Sano, T.; Goto, T.; Sawada, A.; et al. Clinical Utility of Serial Circulating Tumor DNA Analysis as a Minimally Invasive Biomarker in Advanced Urothelial Cancer. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2025, 9, e2400472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellmunt, J.; Russell, B.M.; Szabados, B.; Valderrama, B.P.; Nadal, R. Current and Future Role of Circulating DNA in the Diagnosis and Management of Urothelial Carcinoma. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book. 2025, 45, e471912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellmunt, J.; Hussain, M.; Gschwend, J.E.; Albers, P.; Oudard, S.; Castellano, D.; Daneshmand, S.; Nishiyama, H.; Majchrowicz, M.; Degaonkar, V.; et al. Adjuvant atezolizumab versus observation in muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma (IMvigor010): A multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 525–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powles, T.; Assaf, Z.J.; Davarpanah, N.; Banchereau, R.; Szabados, B.E.; Yuen, K.C.; Grivas, P.; Hussain, M.; Oudard, S.; Gschwend, J.E.; et al. ctDNA guiding adjuvant immunotherapy in urothelial carcinoma. Nature 2021, 595, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powles, T.; Assaf, Z.J.; Degaonkar, V.; Grivas, P.; Hussain, M.; Oudard, S.; Gschwend, J.E.; Albers, P.; Castellano, D.; Nishiyama, H.; et al. Updated Overall Survival by Circulating Tumor DNA Status from the Phase 3 IMvigor010 Trial: Adjuvant Atezolizumab Versus Observation in Muscle-invasive Urothelial Carcinoma. Eur. Urol. 2024, 85, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powles, T.; Chang, W.Y.-H.; Yamamoto, Y.; Muñoz-Langa, J.; Reyes, F.; Peer, A.; Yu, E.Y.; Cohen, G.; Lorch, A.; Bavle, A.; et al. Quantitative circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) assessment in patients (pts) with advanced urothelial carcinoma (UC) treated with pembrolizumab (pembro) or platinum-based chemotherapy (chemo) from the phase 3 KEYNOTE-361 trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42 (Suppl. 16), 4518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best, M.G.; Sol, N.; In ’t Veld, S.; Vancura, A.; Muller, M.; Niemeijer, A.N.; Fejes, A.V.; Tjon Kon Fat, L.A.; Huis In ’t Veld, A.E.; Leurs, C.; et al. Swarm Intelligence-Enhanced Detection of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Using Tumor-Educated Platelets. Cancer Cell 2017, 32, 238–252 e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Prostate Cancer | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study Reference | Objective of TEP Analysis | Gene Expression Signature | Method of Analysis | Nº Cases/Controls | Key Findings | Clinical Implications |
| [53] | Detection of tumoral RNA in platelets | PCA3 | RT-PCR | 12 patients/10 controls | PCA3 RNA detected in prostate cancer patients | Potential for prostate cancer detection |
| [60] | Early tumor detection | PCA3, MALAT1, EZH2, AMACR PSGR, PSA, PSMA, TRPM8 | RT-PCR | 31 patients/29 controls | No significant differences between cases and controls | TEPs may not be suitable for early tumor detection |
| [61] | Tumor detection and tumor origin identification | Broad pan-cancer RNA | ThromboSeq (RNA-seq) | 35 patients | Detected tumor in 92% (AUC = 0.98), improved with higher stage; origin identified in >80% | High potential for detecting advanced prostate cancer |
| [62] | Prediction of response to therapy | KLK2, KLK3, FOLH1, NPY | Digital PCR | 50 patients/15 controls | A three-gene panel (KLK3, NPY, FOLH1) identified resistance to abiraterone therapy | Predictive/prognostic tool for mCRPC patients |
| Kidney Cancer | ||||||
| Study Reference | Objective of TEP Analysis | Gene Expression Signature | Method of Analysis | Nº Cases/Controls | Key Findings | Clinical Implications |
| [63] | Diagnostic | 68-gene panel | RNA-seq | 24 patients/25 controls | Diagnostic accuracy of 95.9% (AUC: 0.988) | Significant potential for RCC blood-based screening |
| [61] | Tumor detection and tumor origin identification | Broad pan-cancer RNA | ThromboSeq (RNA-seq) | 28 patients | Detection accuracy of 66% (AUC = 0.87); tumor origin identified in >80% | Demonstrated potential for liquid biopsy though limited renal-specific data |
| Bladder Cancer | ||||||
| Study Reference | Objective of TEP Analysis | Gene Expression Signature | Method of Analysis | Nº Cases/Controls | Key Findings | Clinical Implications |
| [61] | Tumor detection and tumor origin identification | Broad pan-cancer RNA | ThromboSeq (RNA-seq) | 28 patients | Detection accuracy of 89% (AUC 0.99); tumor origin identified in >80% | Demonstrated potential for liquid biopsy though limited bladder-specific data |
| [64] | Predict pathological response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy | Not specified | WES on tissue samples, followed by qPCR on liquid biopsy | 150 patients | No results | Potential for bladder preservation by avoiding unnecessary cystectomies |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Figols, M.; Chekhun, S.; Fernández-Saorin, M.; Pérez-Criado, I.; Bautista, A.; Font, A.; Ruiz de Porras, V. Tumor-Educated Platelets in Urological Tumors: A Novel Biosource in Liquid Biopsy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3595. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083595
Figols M, Chekhun S, Fernández-Saorin M, Pérez-Criado I, Bautista A, Font A, Ruiz de Porras V. Tumor-Educated Platelets in Urological Tumors: A Novel Biosource in Liquid Biopsy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(8):3595. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083595
Chicago/Turabian StyleFigols, Mariona, Sviatoslav Chekhun, Maria Fernández-Saorin, Ignacio Pérez-Criado, Ana Bautista, Albert Font, and Vicenç Ruiz de Porras. 2025. "Tumor-Educated Platelets in Urological Tumors: A Novel Biosource in Liquid Biopsy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 8: 3595. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083595
APA StyleFigols, M., Chekhun, S., Fernández-Saorin, M., Pérez-Criado, I., Bautista, A., Font, A., & Ruiz de Porras, V. (2025). Tumor-Educated Platelets in Urological Tumors: A Novel Biosource in Liquid Biopsy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(8), 3595. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083595








