Conditional Overexpression of Neuritin in Supporting Cell Protects Cochlear Hair Cell and Delays Age-Related Hearing Loss by Enhancing Autophagy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
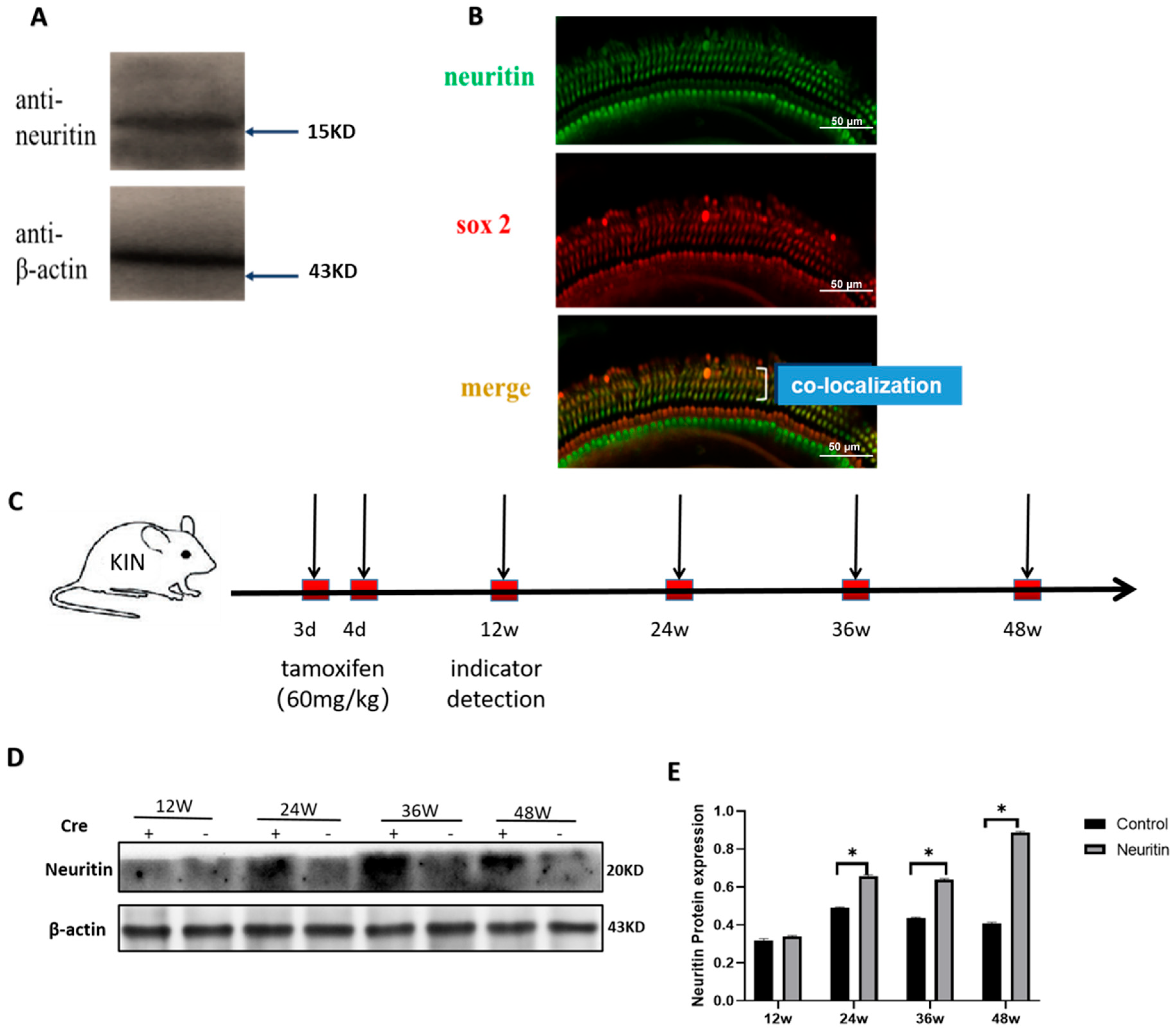
2.1. The Expression of Neuritin in the Cochlea of Wild-Type and Neuritin Knock-In Mice
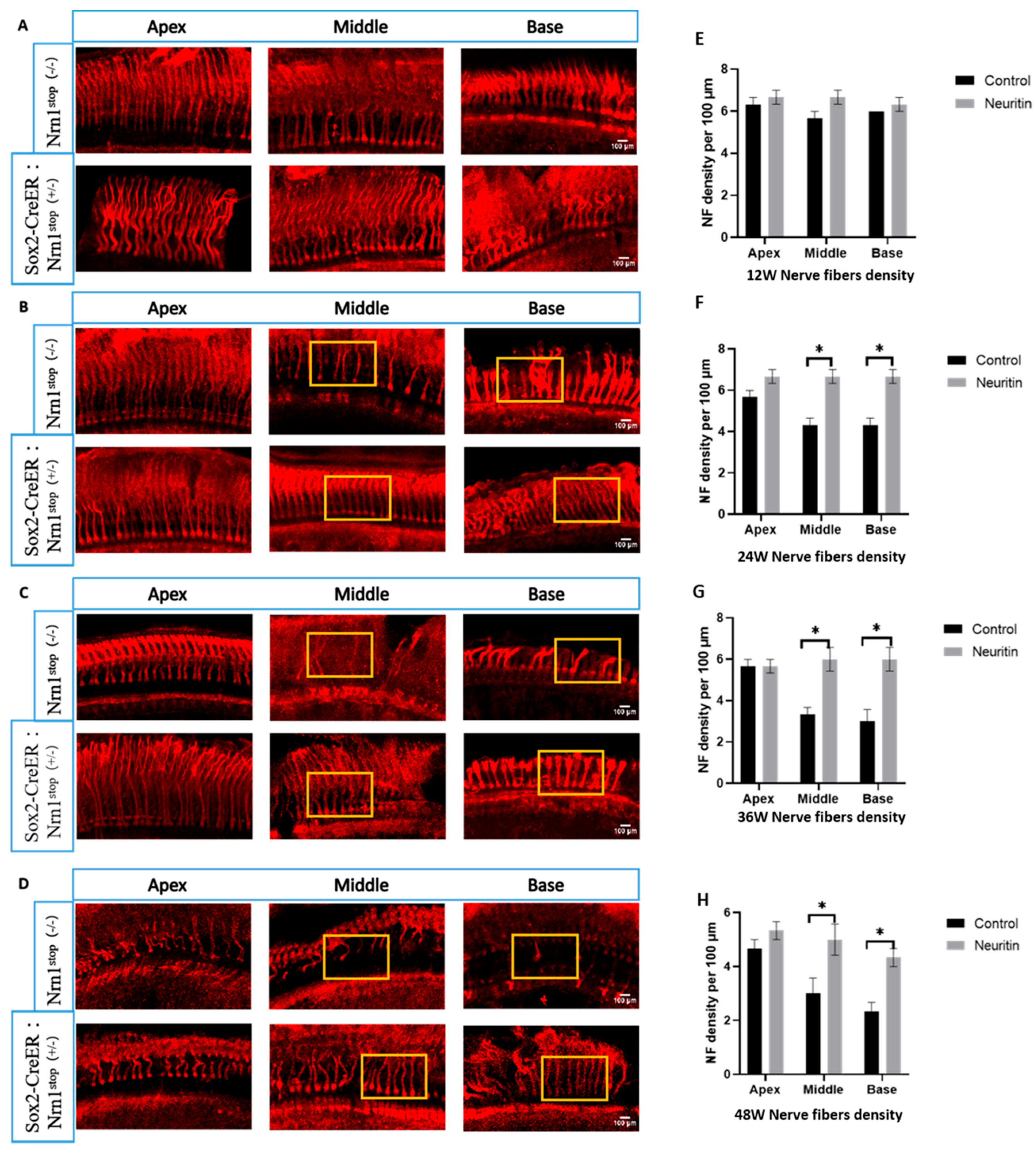
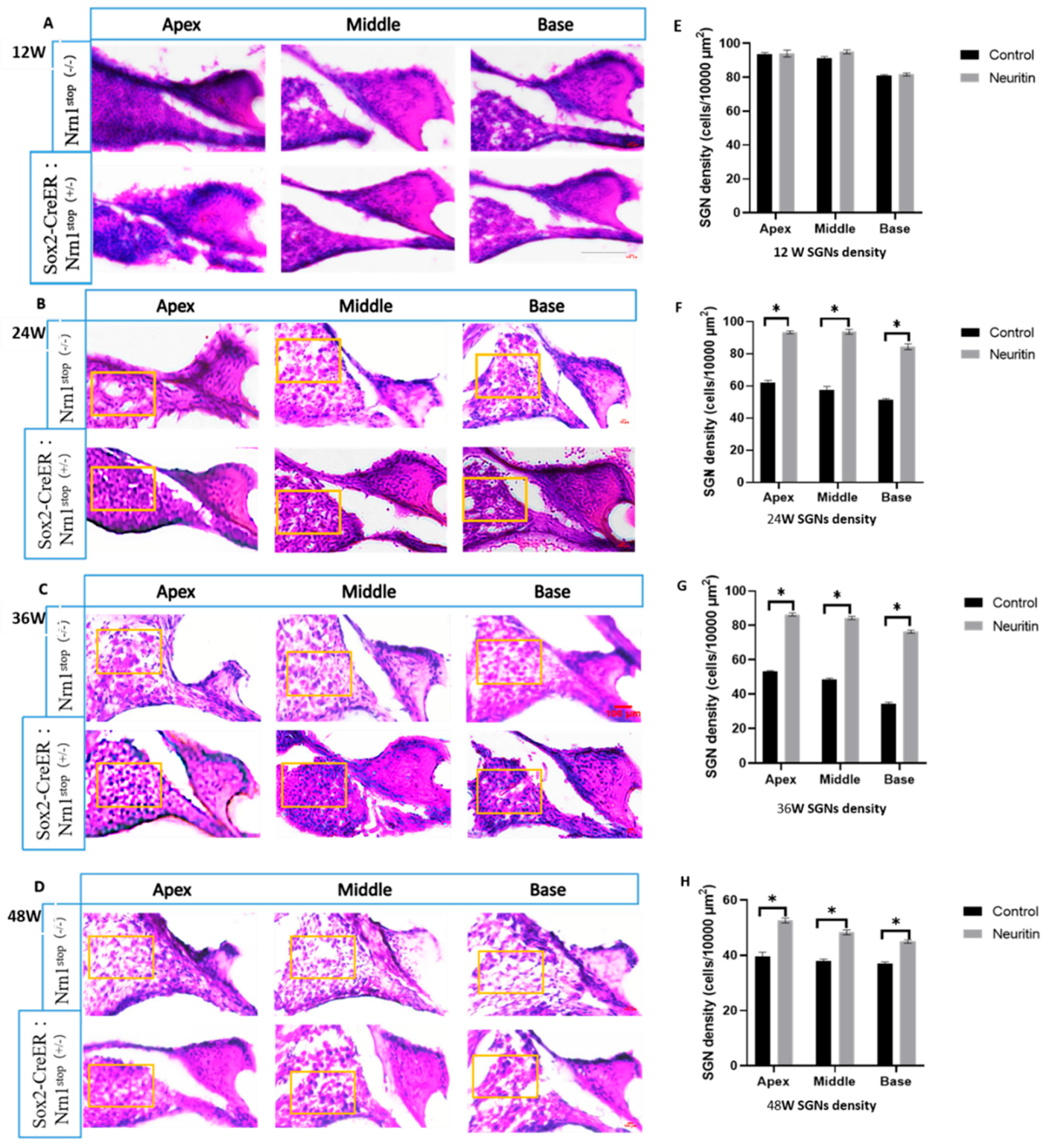
2.2. Conditional Overexpression of Neuritin Protects Against Damages in Cochlear Hair Cells, Nerve Fibers, and Spiral Ganglion Neurons (SGNs) Caused by Aging
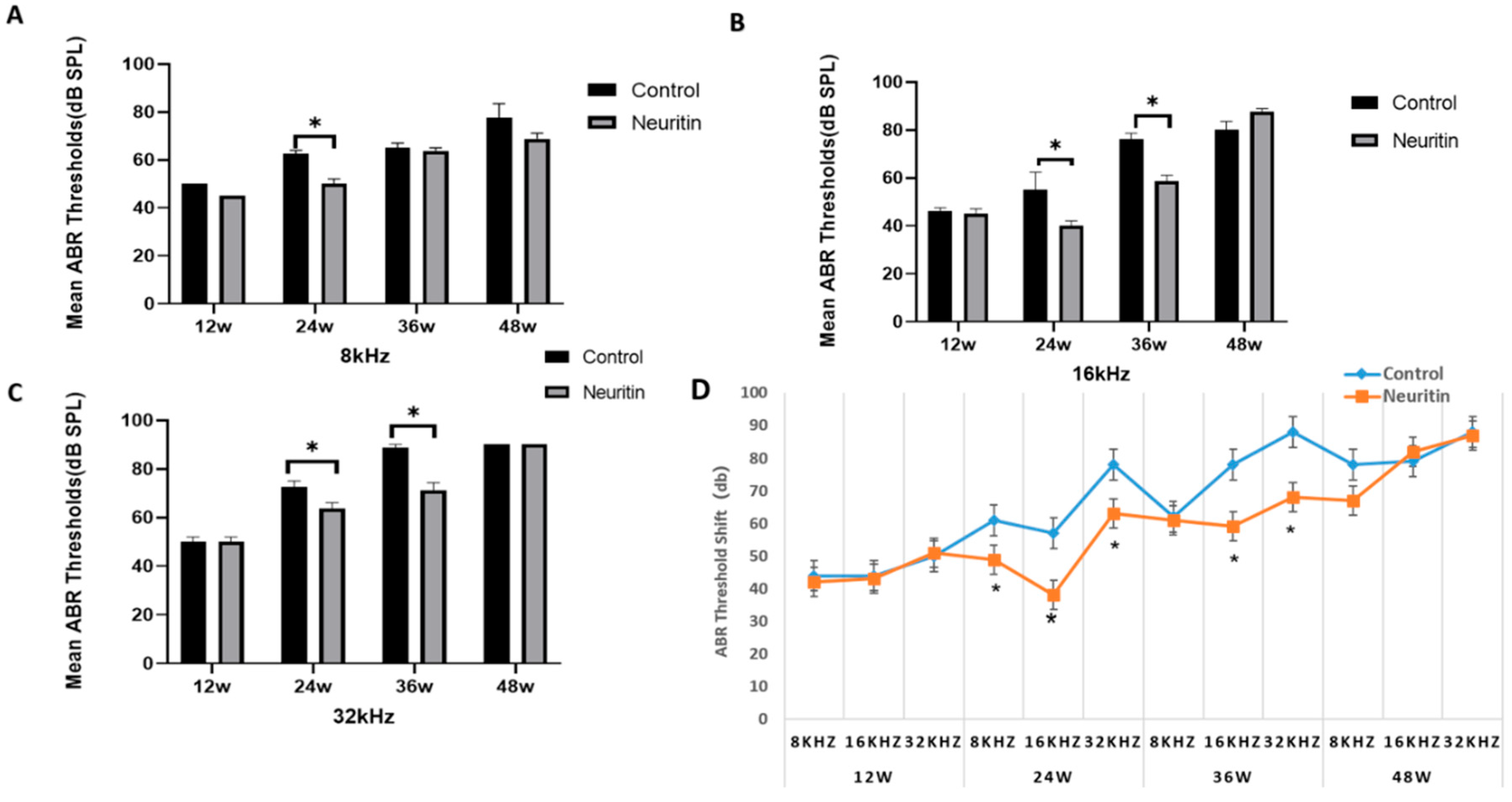
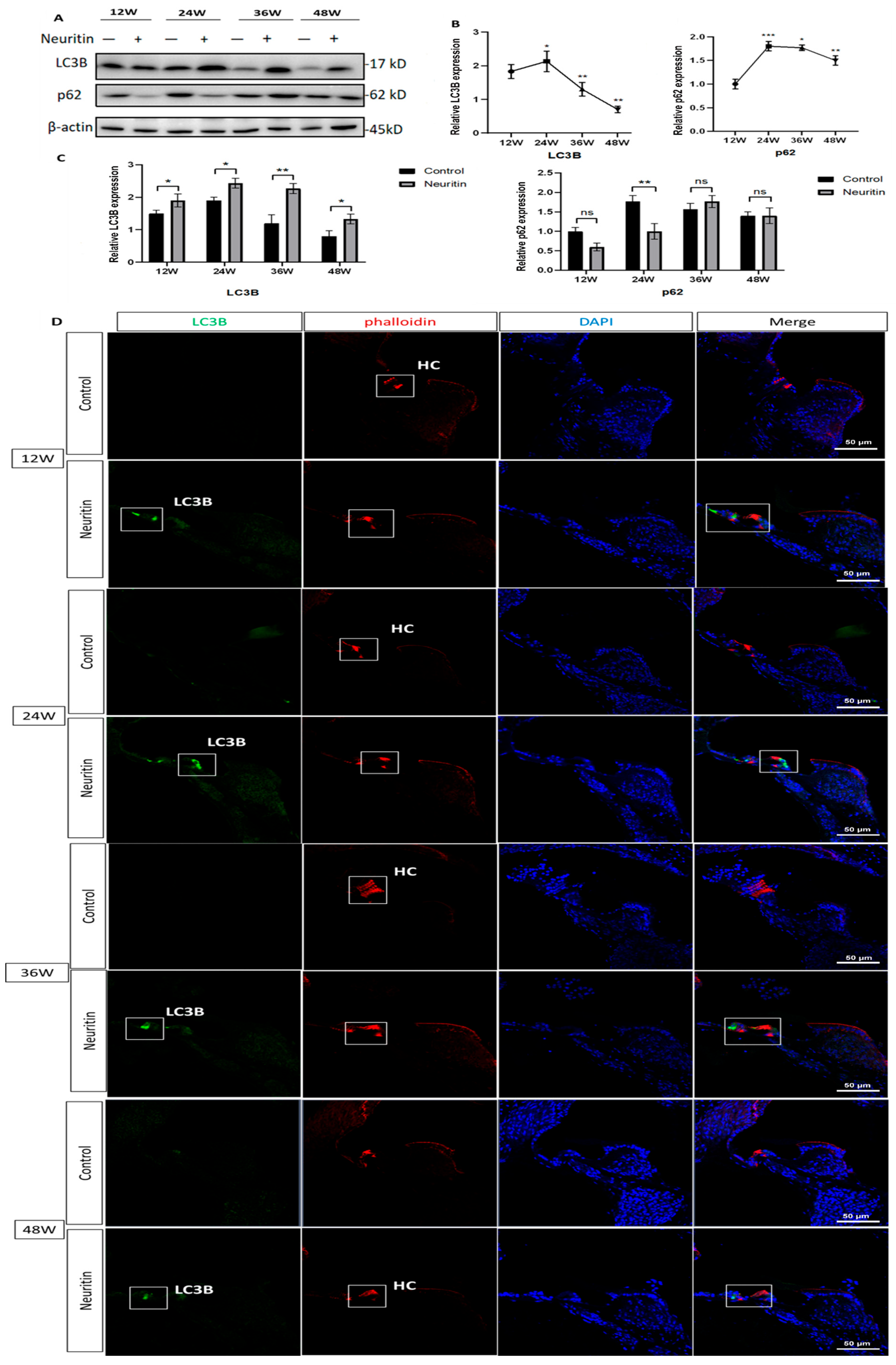
2.3. Conditional Overexpression of Neuritin Restores Aging-Associated Hearing Loss and Enhances Autophagic Influx in the Cochlea of the Mice
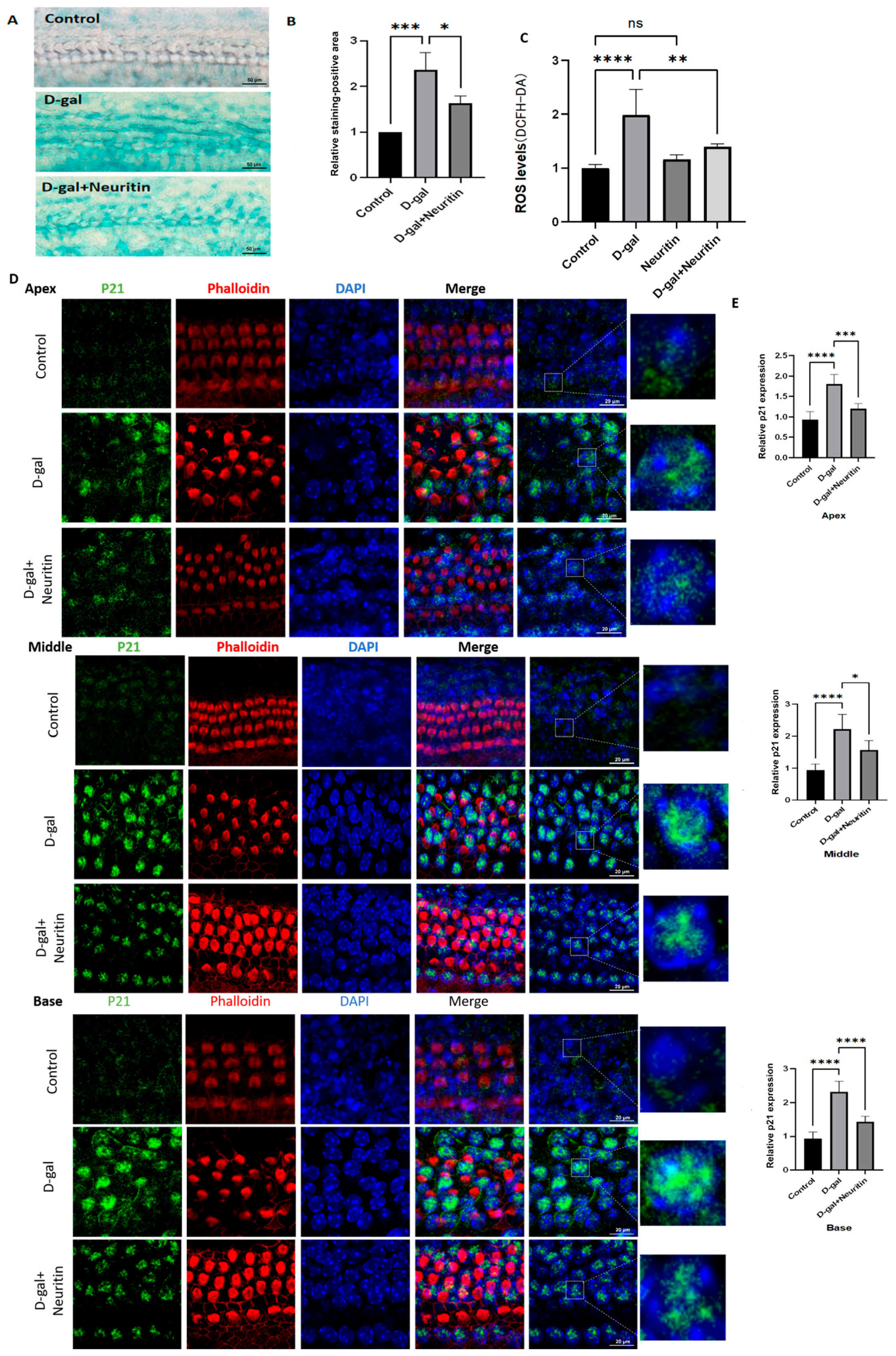
2.4. D-Gal Induced Senescence in Cultured Mouse Cochlear Basilar Membranes (CBMs)
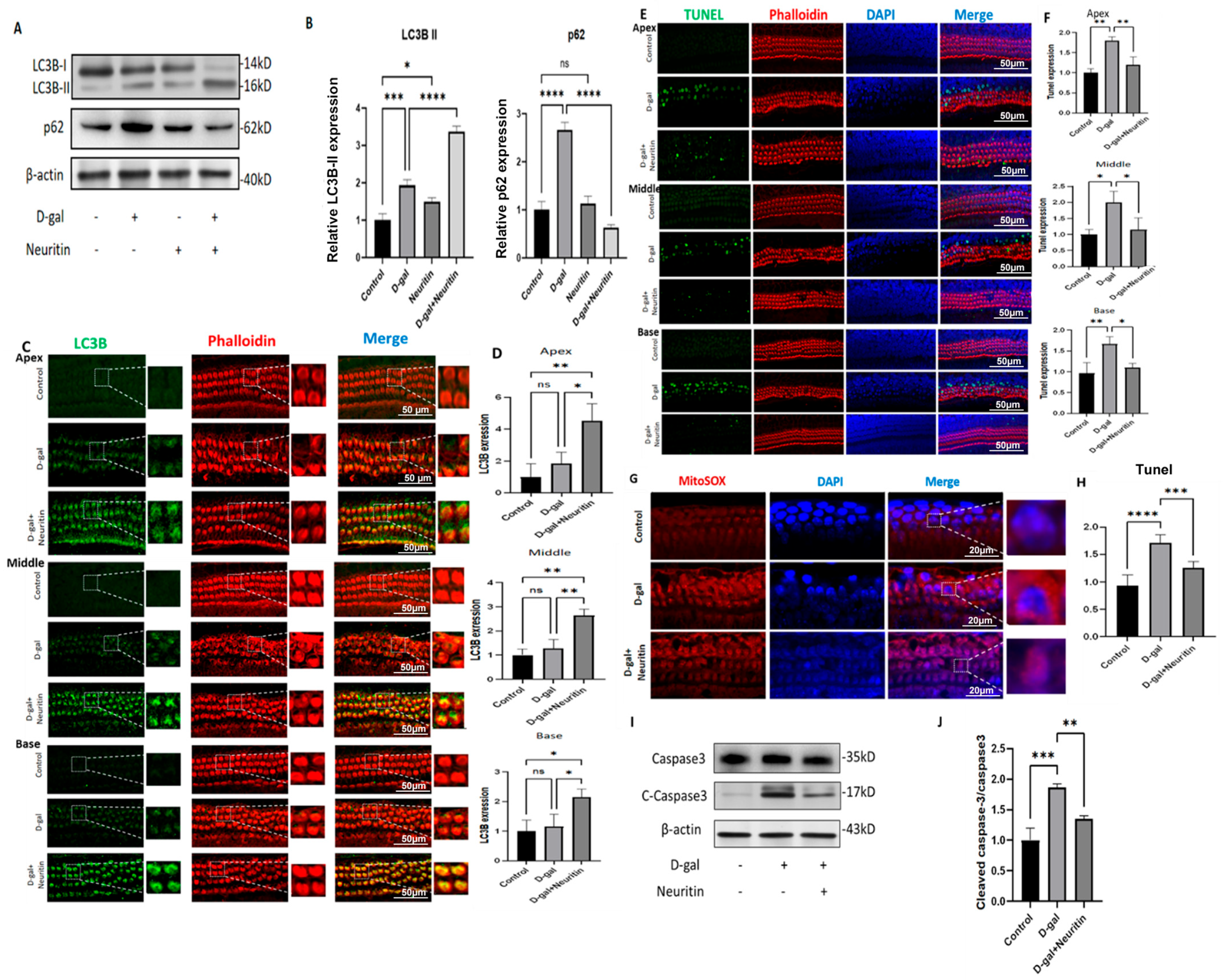
2.5. Neuritin Administration Mitigates d-Galactose-Induced Senescence, ROS Production, and Cellular Apoptosis, Enhancing Autophagic Influx in Cultured Neonatal Mouse Cochlear Basilar Membranes (CBMs)
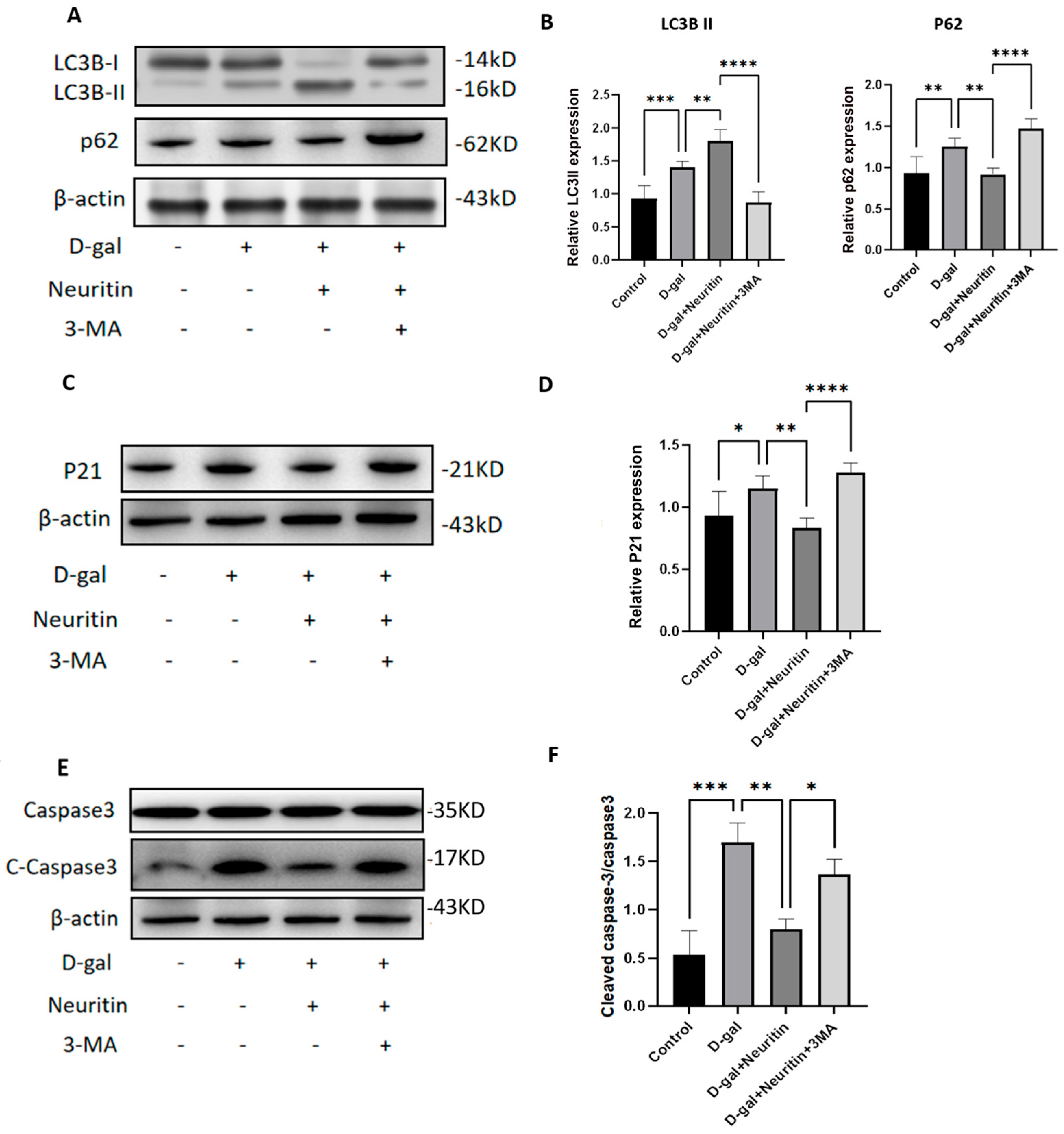
2.6. The Protective Effects of Neuritin on d-Galactose-Induced Senescence Damages Were Weakened by Administration of Autophagy Inhibitor 3-MA
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Ethical Assessment
4.2. Generation of Sox2CreER/+ Neuritinstop/+ Mice and PCR Genotyping
4.3. In Vivo Knock-In of Neuritin in Sox2+ SCs in the Mouse Cochlea
4.4. Preparation and Treatment of Cultured Cochlear Basilar Membranes (CBMs)
4.5. Auditory Brainstem Response (ABR) Test
4.6. Immunostaining and Image Acquisition
4.7. Cryosections
4.8. Western Blot Analysis
4.9. Senescence-Associated β-Galactosidase (SA-β-Gal) Activity Staining
4.10. Detection of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) and Mitochondrial Fluorescent Probe Staining Analysis
4.11. TUNEL Assay
4.12. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, F.R. Age-Related Hearing Loss. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 1505–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, L.L.; Tucci, D.L. Hearing Loss in Adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2465–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Giffen, K.P.; Chen, L.; Henderson, H.J.; Cao, T.A.; Kozeny, G.A.; Beisel, K.W.; Li, Y.; He, D.Z. Molecular and Cytological Profiling of Biological Aging of Mouse Cochlear Inner and Outer Hair Cells. Cell Rep. 2022, 39, 110665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Cheng, Z.; Gong, N.; Xu, Z.; Jin, C.; Wu, H.; Tao, Y. Neural Presbycusis at Ultra-High Frequency in Aged Common Marmosets and Rhesus Monkeys. Aging 2021, 13, 12587–12606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Man, J.; Chen, H.; Zhang, T.; Yin, X.; Yang, X.; Lu, M. Global, Regional, and National Burden of Age-Related Hearing Loss from 1990 to 2019. Aging 2021, 13, 25944–25959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, B.S.; Tucci, D.L. Addressing the Global Burden of Hearing Loss. Lancet 2021, 397, 945–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, N.S.; Altan, A.; Deal, J.A.; Yeh, C.; Kravetz, A.D.; Wallhagen, M.; Lin, F.R. Trends in Health Care Costs and Utilization Associated with Untreated Hearing Loss over 10 Years. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2019, 145, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loughrey, D.G.; Kelly, M.E.; Kelley, G.A.; Brennan, S.; Lawlor, B.A. Association of Age-Related Hearing Loss with Cognitive Function, Cognitive Impairment, and Dementia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2018, 144, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Yang, Y. Hearing loss promotes Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Aging 2024, 4, 443–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.R.; Ferrucci, L. Hearing Loss and Falls among Older Adults in the United States. Arch. Intern. Med. 2012, 172, 369–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, D.; Li, C.M.; Chiu, M.S.; Themann, C.L.; Petersen, H.; Jonasson, F.; Jonsson, P.V.; Sverrisdottir, J.E.; Garcia, M.; Harris, T.B.; et al. Impairments in Hearing and Vision Impact on Mortality in Older People: The Ages-Reykjavik Study. Age Ageing 2014, 43, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilder, A.G.M.; Su, M.P.; Blackshaw, H.; Lustig, L.; Staecker, H.; Lenarz, T.; Safieddine, S.; Gomes-Santos, C.S.; Holme, R.; Warnecke, A. Hearing Protection, Restoration, and Regeneration: An Overview of Emerging Therapeutics for Inner Ear and Central Hearing Disorders. Otol. Neurotol. 2019, 40, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Zhao, X.L.; Chai, R.J.; Fan, J.A. Progress on Mechanisms of Age-Related Hearing Loss. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1253574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, J.Q.; Xiong, H.; Lin, P.L.; Lai, L.; Yang, H.D.; Liu, Y.M.; Huang, Q.H.; Chen, S.J.; Ye, Y.Y.; Sun, Y.F.; et al. Activation of Mir-34a Impairs Autophagic Flux and Promotes Cochlear Cell Death Via Repressing: Implications for Age-Related Hearing Loss. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, W.J.T.; Song, L. Role of Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Oxidative Stress in Sensorineural Hearing Loss. Hear. Res. 2023, 434, 108783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, D.J.; Ha, S.; Choi, J.S.; Lee, S.H.; Park, J.E.; Seo, Y.J. Induced Short-Term Hearing Loss Due to Stimulation of Age-Related Factors by Intermittent Hypoxia, High-Fat Diet, and Galactose Injection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.D.; Pan, Y.; Wang, H.; Ding, R.; Zou, T.Y.; Guo, D.Y.; Shen, Y.L.; Ji, P.L.; Huang, W.Y.; Wen, Q.; et al. Excessive Processing and Acetylation of Opa1 Aggravate Age-Related Hearing Loss Via the Dysregulation of Mitochondrial Dynamics. Aging Cell 2024, 23, e14091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okur, M.N.; Sahbaz, B.D.; Kimura, R.; Manor, U.; Patel, J.; Park, J.H.; Andrade, L.; Puligilla, C.; Croteau, D.L.; Bohr, V.A. Long-Term Nad Plus Supplementation Prevents the Progression of Age-Related Hearing Loss in Mice. Aging Cell 2023, 22, e13909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Si, Y.; Huang, X.; Lin, X.; Lu, L.; Wu, C.; Guan, X.; Liang, Y. Vitamin C Inhibits Nlrp3 Inflammasome Activation and Delays the Development of Age-Related Hearing Loss in Male C57bl/6 Mice. Neurosci. Lett. 2024, 836, 137897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.W.; Hsu, Y.C. Current Development of Patient-Specific Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells Harbouring Mitochondrial Gene Mutations and Their Applications in the Treatment of Sensorineural Hearing Loss. Hear. Res. 2023, 429, 108689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.H.; Li, M.; Fang, Q.J.; Liao, F.L.; Zou, S.Y.; Wu, X.; Sun, H.Y.; Zhao, X.Y.; Hu, Y.J.; Xu, X.X.; et al. Foxg1 Promotes Aging Inner Ear Hair Cell Survival through Activation of the Autophagy Pathway. Autophagy 2021, 17, 4341–4362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, J.Q.; Xiong, H.; Ou, Y.K.; Yang, H.D.; Xu, Y.D.; Chen, S.J.; Lai, L.; Ye, Y.Y.; Su, Z.W.; Lin, H.; et al. Sirt1 Protects Cochlear Hair Cell and Delays Age-Related Hearing Loss Via Autophagy. Neurobiol. Aging 2019, 80, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salam, S.A.; Mostafa, F.; Alnamshan, M.M.; Elshewemi, S.S.; Sorour, J.M. Thymoquinone Ameliorates Age-Related Hearing Loss in C57bl/6j Mice by Modulating Sirt1 Activity and Bak1 Expression. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 143, 112149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.; Chen, S.J.; Lai, L.; Yang, H.D.; Xu, Y.D.; Pang, J.Q.; Su, Z.W.; Lin, H.Q.; Zheng, Y.Q. Modulation of Mir-34a/Sirt1 Signaling Protects Cochlear Hair Cells against Oxidative Stress and Delays Age-Related Hearing Loss through Coordinated Regulation of Mitophagy and Mitochondrial Biogenesis. Neurobiol. Aging 2019, 79, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polanski, J.F.; Cruz, O.L. Evaluation of Antioxidant Treatment in Presbyacusis: Prospective, Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blind, Randomised Trial. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2013, 127, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudian-Sani, M.R.; Jamshidi, M.; Asgharzade, S. Combined Growth Factor and Gene Therapy: An Approach for Hair Cell Regeneration and Hearing Recovery. ORL J. Otorhinolaryngol. Relat. Spec. 2018, 80, 326–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Zhou, J. Neuritin, a Neurotrophic Factor in Nervous System Physiology. Curr. Med. Chem. 2014, 21, 1212–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Li, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, D.; Mei, Y.A. Neuritin Improves the Neurological Functional Recovery after Experimental Intracerebral Hemorrhage in Mice. Neurobiol. Dis. 2021, 156, 105407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Li, X.; Xi, S.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, J.; Shan, L.; Song, X.; Luo, X.; Yang, L.; et al. Exogenous Neuritin Promotes Nerve Regeneration after Acute Spinal Cord Injury in Rats. Hum. Gene Ther. 2016, 27, 544–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, K.; Mao, F.; Li, Q.; Wang, L.; Wei, Z.; Wang, P.; Liao, X.; Xu, M.; Huang, J.; Pan, Z.; et al. Neuritin-Overexpressing Transgenic Mice Demonstrate Enhanced Neuroregeneration Capacity and Improved Spatial Learning and Memory Recovery after Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Aging 2020, 13, 2681–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, G.; Dandan, S.; Haiyan, W.; Shuai, Z.; Xiaopin, S.; Yu, H.; Yi, Y.; Rong, C.; Jin, H.; Xiaoming, S.; et al. Exogenous Neuritin Restores Auditory Following Cochlear Spiral Ganglion Neuron Denervation of Gerbils. Neurosci. Res. 2024, 200, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Sun, X.; Wang, H.; Chen, R.; Yang, Y.; Hu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Gui, F.; Huang, J.; Yang, L.; et al. Conditional Overexpression of Neuritin in Supporting Cells (Scs) Mitigates Hair Cell (Hc) Damage and Induces Hc Regeneration in the Adult Mouse Cochlea after Drug-Induced Ototoxicity. Hear. Res. 2022, 420, 108515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Ye, J.; Kong, W.; Zhang, S.; Zheng, Y. Programmed Cell Death Pathways in Hearing Loss: A Review of Apoptosis, Autophagy and Programmed Necrosis. Cell Prolif. 2020, 53, e12915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ren, K.; Hu, Y.; Liu, B.; He, Y.; Xu, H.; Ma, K.; Tian, W.; Dai, L.; Zhao, D. Neuritin Promotes Autophagic Flux by Inhibiting the Cgas-Sting Pathway to Alleviate Brain Injury after Subarachnoid Haemorrhage. Brain Res. 2024, 1836, 148909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Pan, R.L.; Li, Y.; Hu, Y.Q.; Xv, H.; Zhu, C.; Wang, X.; Yin, J.W.; Ma, K.T.; et al. Neuritin Attenuates Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation/Reoxygenation (Ogd/R)-Induced Neuronal Injury by Promoting Autophagic Flux. Exp. Cell Res. 2021, 407, 112832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, T.; Xie, R.; Huang, S.; Lu, D.; Liu, J. Potential Role of Modulating Autophagy Levels in Sensorineural Hearing Loss. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2024, 222, 116115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeve, G.S.; Ramakrishnan, M.; Kramer, R.; Hevroni, D.; Citri, Y.; Theill, L.E. Neuritin: A Gene Induced by Neural Activity and Neurotrophins That Promotes Neuritogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 2648–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassinotti, L.R.; Ji, L.C.; Borges, B.C.; Cass, N.D.; Desai, A.S.; Kohrman, D.C.; Liberman, M.C.; Corfas, G. Cochlear Neurotrophin-3 Overexpression at Mid-Life Prevents Age-Related Inner Hair Cell Synaptopathy and Slows Age-Related Hearing Loss. Aging Cell 2022, 21, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisina, R.D.; Ding, B.; Zhu, X.; Walton, J.P. Age-Related Hearing Loss: Prevention of Threshold Declines, Cell Loss and Apoptosis in Spiral Ganglion Neurons. Aging 2016, 8, 2081–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, X.; Shan, L.; Zhu, J.; Chen, R.; Li, Y.; Yuan, W.; Yang, L.; Huang, J. Recombinant Hneuritin Promotes Structural and Functional Recovery of Sciatic Nerve Injury in Rats. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.J.; Zhao, Q.R.; Lu, J.M.; Mei, Y.A. Functions and the Related Signaling Pathways of the Neurotrophic Factor Neuritin. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2018, 39, 1414–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roehm, P.C.; Hansen, M.R. Strategies to Preserve or Regenerate Spiral Ganglion Neurons. Curr. Opin. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2005, 13, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, L.; Borges, B.C.; Martel, D.T.; Wu, C.; Liberman, M.C.; Shore, S.E.; Corfas, G. From Hidden Hearing Loss to Supranormal Auditory Processing by Neurotrophin 3-Mediated Modulation of Inner Hair Cell Synapse Density. PLoS Biol. 2024, 22, e3002665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Stohl, J.; Overath, T. Hidden Hearing Loss: Fifteen Years at a Glance. Hear. Res. 2024, 443, 108967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberti, G.; Portelli, D.; Galletti, C. Healthcare Professionals and Noise-Generating Tools: Challenging Assumptions About Hearing Loss Risk. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 6520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, M.; Lv, Q.; Lu, H.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, J. Exogenous Neuritin Treatment Improves Survivability and Functions of Schwann Cells with Improved Outgrowth of Neurons in Rat Diabetic Neuropathy. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 10166–10176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Dong, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yin, J.; Zhu, C.; Wang, X.; Ren, K.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, D. Neuritin Has a Neuroprotective Role in the Rat Model of Acute Ischemia Stroke by Inhibiting Neuronal Apoptosis and Nlrp3 Inflammasome. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2023, 32, 107391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.; Lee, J.; Jung, S.; Lee, Y.; Cho, J.W.; Oh, Y.J. Dysregulated Autophagy Contributes to Caspase-Dependent Neuronal Apoptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsapras, P.; Nezis, I.P. Caspase Involvement in Autophagy. Cell Death Differ. 2017, 24, 1369–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Hua, Q. Cellular Autophagy, the Compelling Roles in Hearing Function and Dysfunction. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2022, 16, 966202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Guan, X.; Zheng, S.; Shi, J.; Wang, X.; Shen, Z.; Chen, Z.; Liao, C.; Zhang, Z. Neuritin Accelerates Schwann Cell Dedifferentiation Via Pi3k/Akt/Mtor Signalling Pathway During Wallerian Degeneration. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2024, 28, e70012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lv, Z.; Liu, Y.; Cao, H.; Yang, J.; Wang, B. Pin1 Protects Hair Cells and Auditory Hei-Oc1 Cells against Senescence by Inhibiting the Pi3k/Akt/Mtor Pathway. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2021, 2021, 9980444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heras-Sandoval, D.; Perez-Rojas, J.M.; Hernandez-Damian, J.; Pedraza-Chaverri, J. The Role of Pi3k/Akt/Mtor Pathway in the Modulation of Autophagy and the Clearance of Protein Aggregates in Neurodegeneration. Cell Signal 2014, 26, 2694–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, J.J.; Zhao, Q.R.; Liu, D.D.; Chow, C.W.; Mei, Y.A. Neuritin up-Regulates Kv4.2 Alpha-Subunit of Potassium Channel Expression and Affects Neuronal Excitability by Regulating the Calcium-Calcineurin-Nfatc4 Signaling Pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 17369–17381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Q.; Chen, Y.; Chen, D.; Zhao, H.; Feng, Y.; Meng, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, H. Calcium Transients on the Er Surface Trigger Liquid-Liquid Phase Separation of Fip200 to Specify Autophagosome Initiation Sites. Cell 2022, 185, 4082–4098.e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurabi, A.; Keithley, E.M.; Housley, G.D.; Ryan, A.F.; Wong, A.C. Cellular Mechanisms of Noise-Induced Hearing Loss. Hear. Res. 2017, 349, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percie du Sert, N.; Hurst, V.; Ahluwalia, A.; Alam, S.; Avey, M.T.; Baker, M.; Browne, W.J.; Clark, A.; Cuthill, I.C.; Dirnagl, U.; et al. The Arrive Guidelines 2.0: Updated Guidelines for Reporting Animal Research. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000410. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Wang, H.; Jaenisch, R. Generating Genetically Modified Mice Using Crispr/Cas-Mediated Genome Engineering. Nat. Protoc. 2014, 9, 1956–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, B.J.; Yamashita, T.; Zuo, J. Sox2-Creer Mice Are Useful for Fate Mapping of Mature, but Not Neonatal, Cochlear Supporting Cells in Hair Cell Regeneration Studies. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, L.; Lu, X.; Cheng, C.; Sun, S.; Li, W.; Zhao, L.; Lai, C.; Zhang, S.; Yu, C.; et al. Characterization of Lgr6+ Cells as an Enriched Population of Hair Cell Progenitors Compared to Lgr5+ Cells for Hair Cell Generation in the Neonatal Mouse Cochlea. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, R.; Kuo, B.; Wang, T.; Liaw, E.J.; Xia, A.; Jan, T.A.; Liu, Z.; Taketo, M.M.; Oghalai, J.S.; Nusse, R.; et al. Wnt Signaling Induces Proliferation of Sensory Precursors in the Postnatal Mouse Cochlea. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 8167–8172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Li, L.; Ni, W.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, S.; Miao, D.; Chai, R.; Li, H. Bmi1 Regulates Auditory Hair Cell Survival by Maintaining Redox Balance. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benkafadar, N.; Francois, F.; Affortit, C.; Casas, F.; Ceccato, J.C.; Menardo, J.; Venail, F.; Malfroy-Camine, B.; Puel, J.L.; Wang, J. Ros-Induced Activation of DNA Damage Responses Drives Senescence-Like State in Postmitotic Cochlear Cells: Implication for Hearing Preservation. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 5950–5969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Lv, S.; Hu, J.; Shi, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Tan, X.; Chen, R.; Hong, Y. Conditional Overexpression of Neuritin in Supporting Cell Protects Cochlear Hair Cell and Delays Age-Related Hearing Loss by Enhancing Autophagy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3709. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083709
Wang S, Lv S, Hu J, Shi Y, Li Y, Zhang J, Tan X, Chen R, Hong Y. Conditional Overexpression of Neuritin in Supporting Cell Protects Cochlear Hair Cell and Delays Age-Related Hearing Loss by Enhancing Autophagy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(8):3709. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083709
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Shanshan, Shaowei Lv, Junhao Hu, Yunfan Shi, Yu Li, Jianyun Zhang, Xiaohua Tan, Rong Chen, and Yu Hong. 2025. "Conditional Overexpression of Neuritin in Supporting Cell Protects Cochlear Hair Cell and Delays Age-Related Hearing Loss by Enhancing Autophagy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 8: 3709. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083709
APA StyleWang, S., Lv, S., Hu, J., Shi, Y., Li, Y., Zhang, J., Tan, X., Chen, R., & Hong, Y. (2025). Conditional Overexpression of Neuritin in Supporting Cell Protects Cochlear Hair Cell and Delays Age-Related Hearing Loss by Enhancing Autophagy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(8), 3709. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083709






