Impact of Escherichia coli and Lipopolysaccharide on the MAPK Signaling Pathway, MMPs, TIMPs, and the uPA System in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
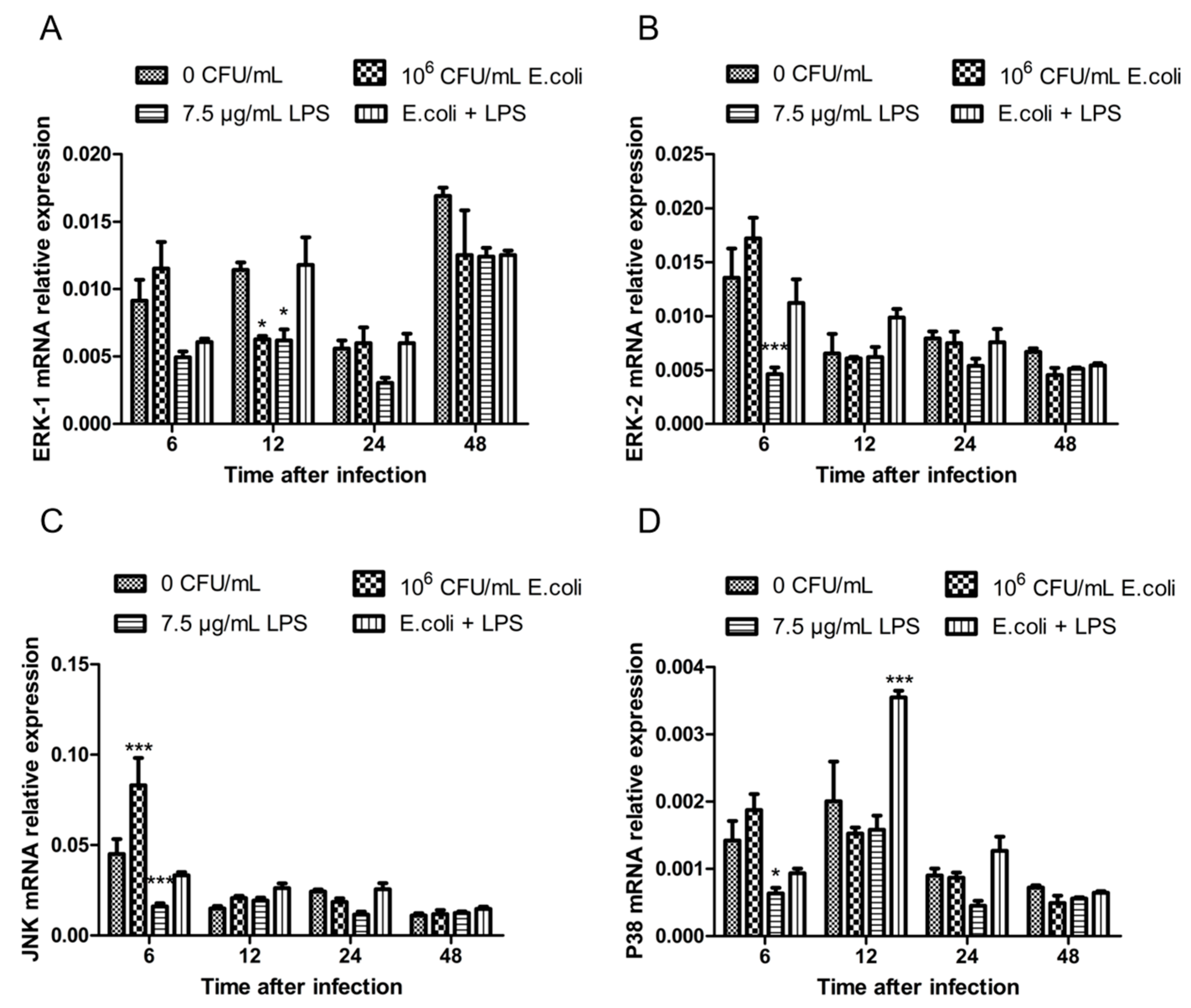
2.1. The Expression of MAPK Genes in BMECs After Treatments with Heat-Inactivated E. coli and LPS
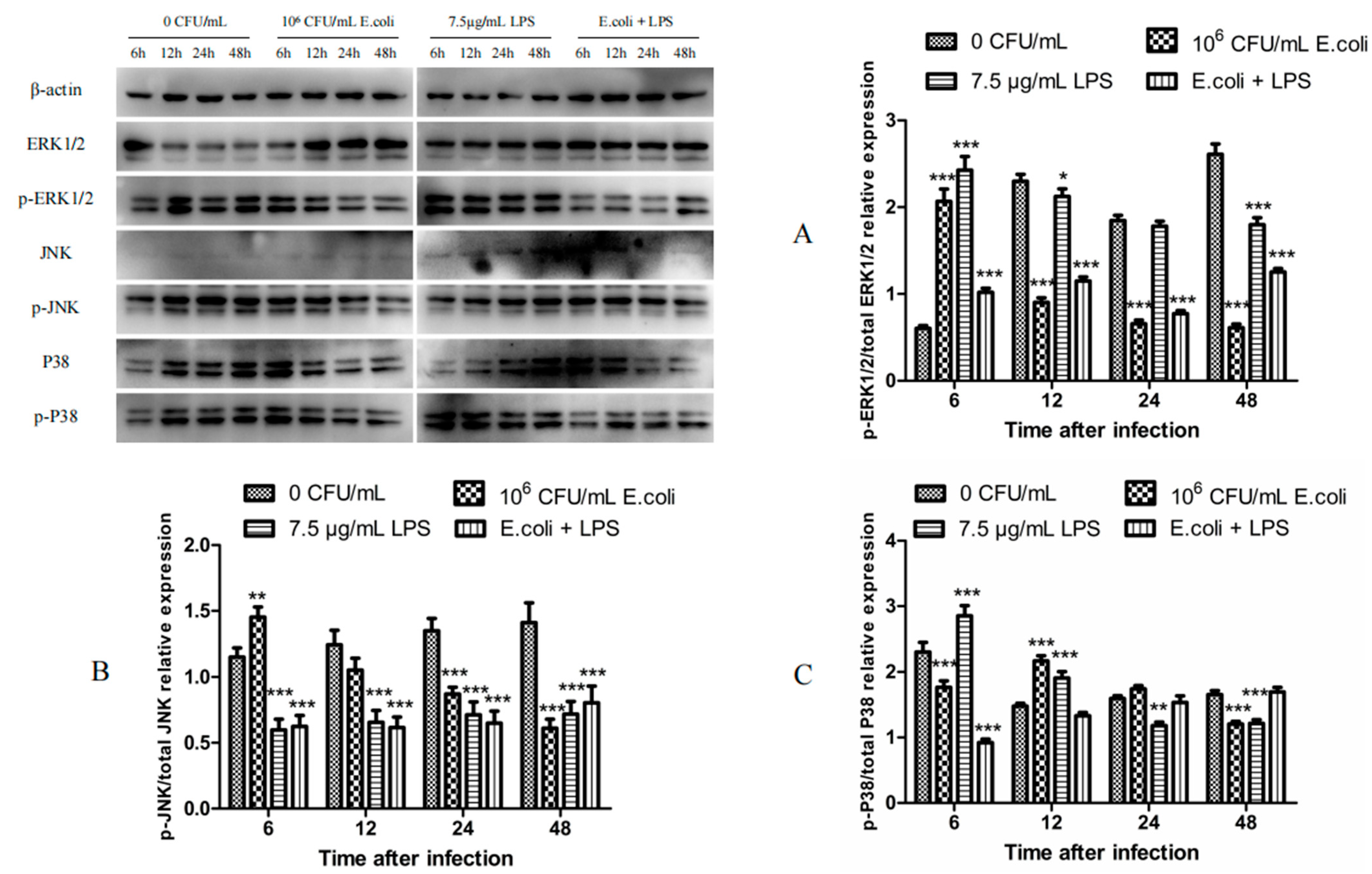
2.2. The Expression of MAPK Proteins in BMECs After Treatments with Heat-Inactivated E. coli and LPS
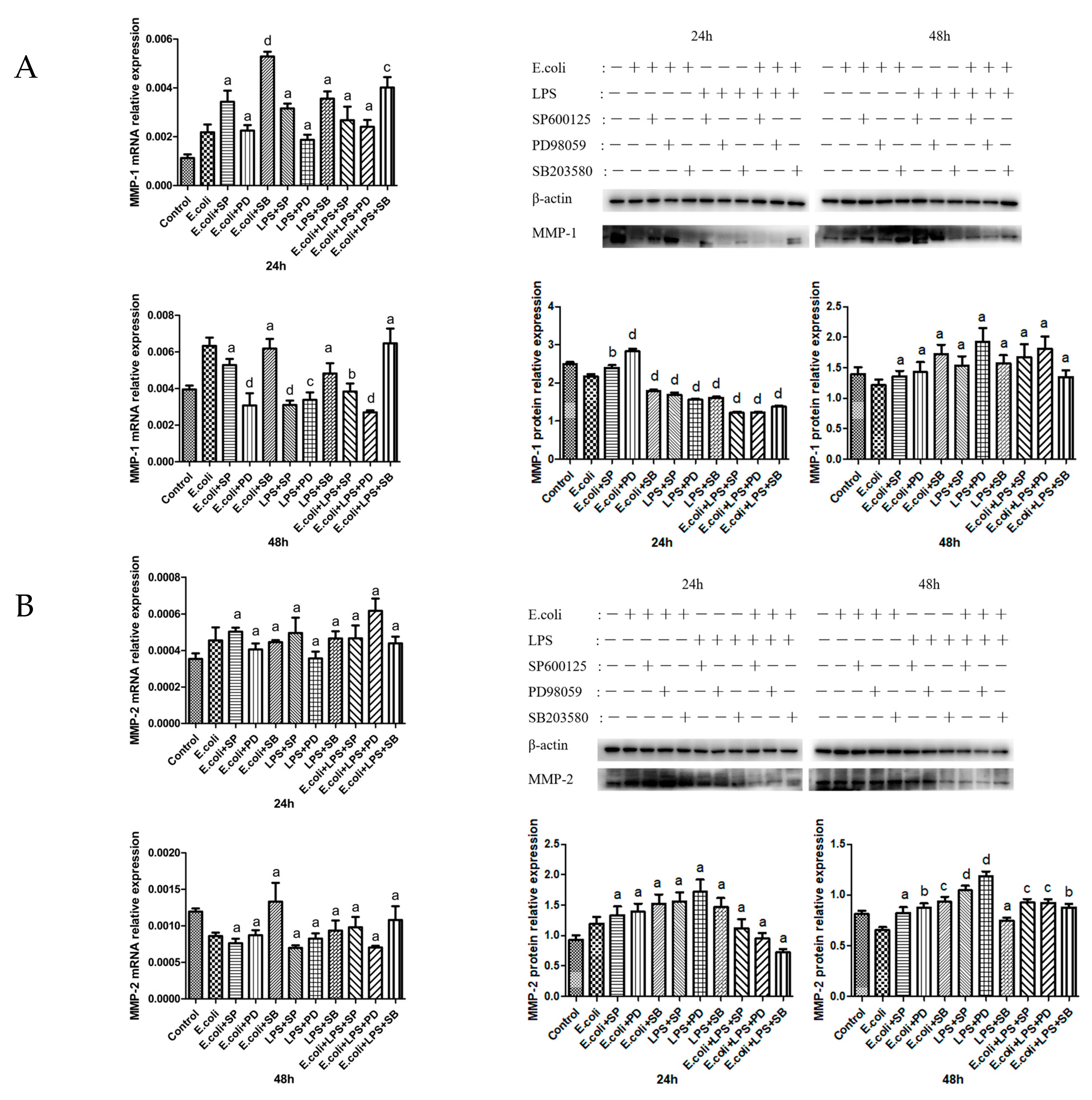
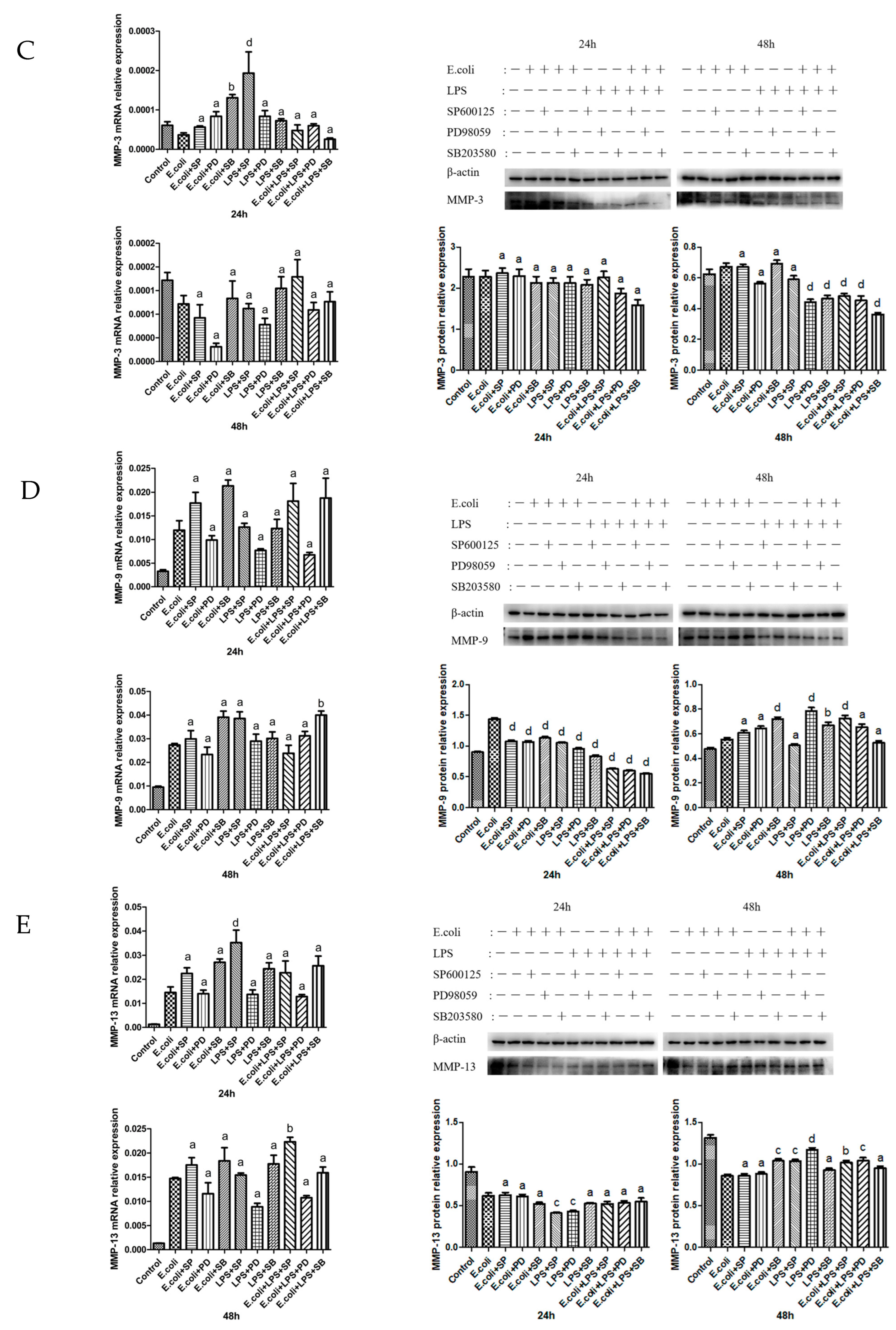
2.3. Effects of MAPK Inhibitors on the Expression of MMPs in BMECs
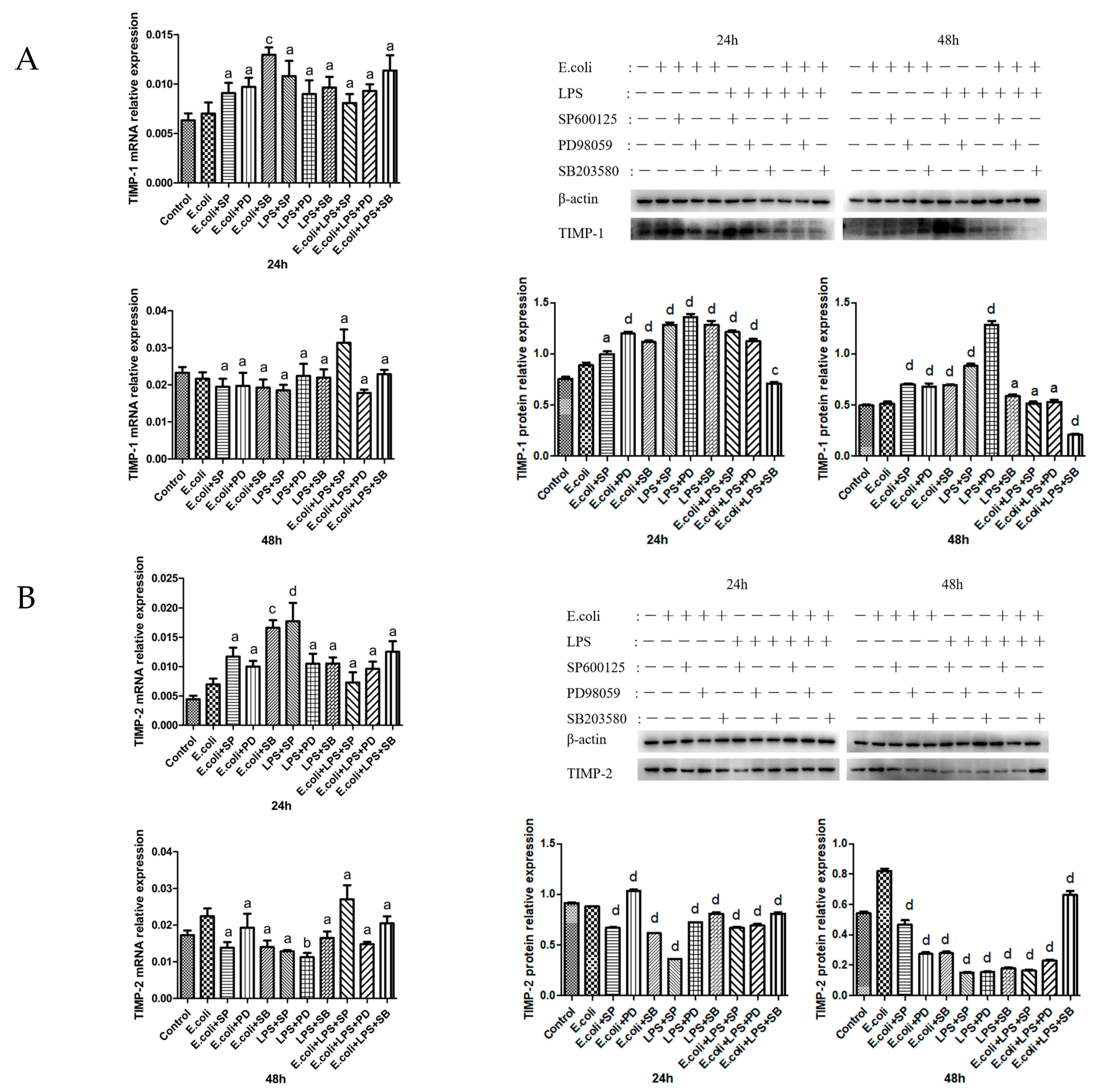
2.4. Effects of MAPK Inhibitors on the Expression of TIMPs in BMECs
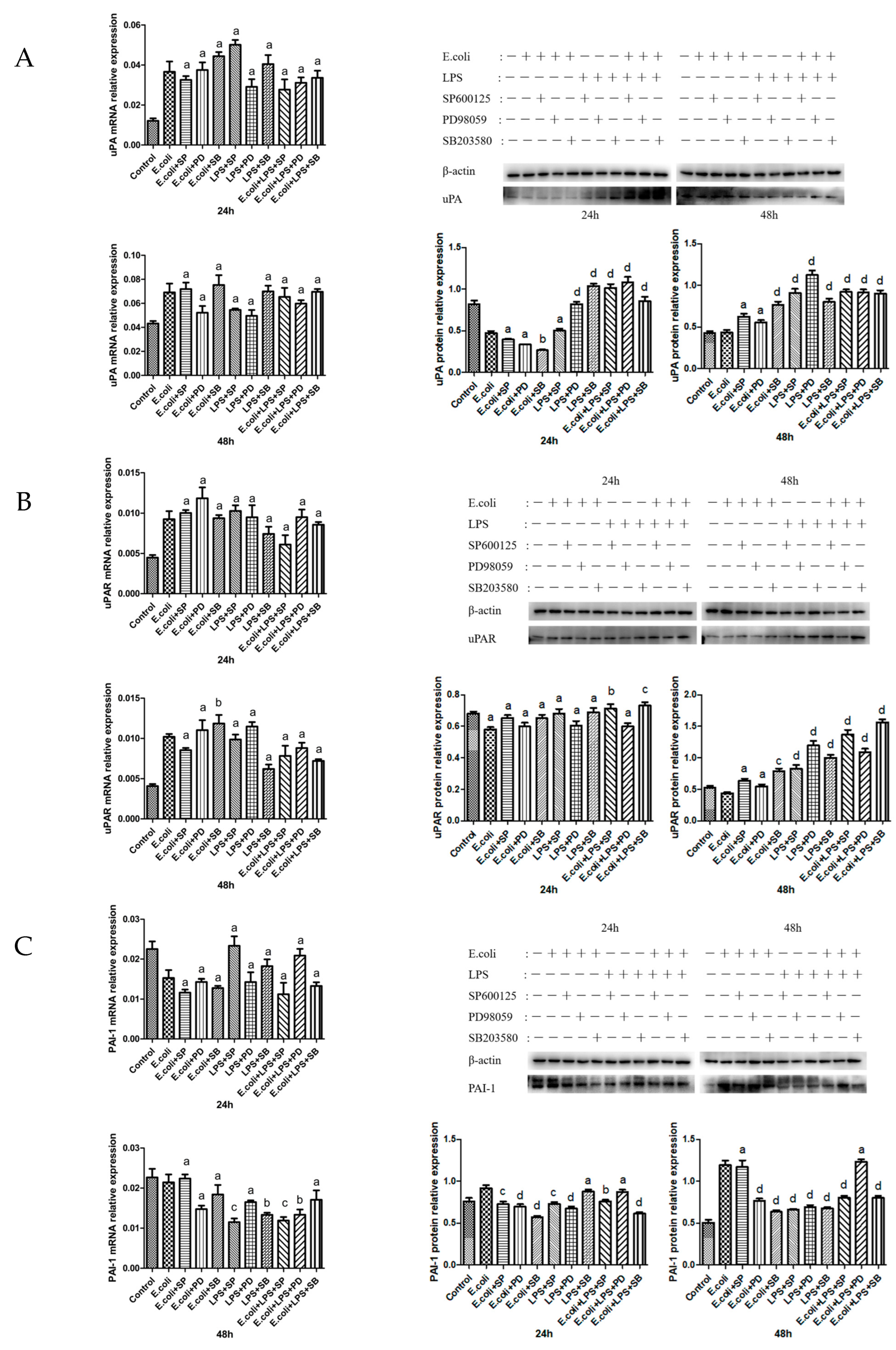
2.5. Effects of MAPK Inhibitors on the Expression of the uPA System in BMECs
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation of Heat-Inactivated E. coli
4.2. Determining the Optimal Dose of LPS
4.3. Cell Treatment
4.4. Total RNA Extraction and RT-qPCR Analysis
4.5. Western Blot Analysis
4.6. Statistical Analysis
4.7. Materials and Reagents
4.8. Laboratory Apparatus
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jeljeli, M.; Riccio, L.G.C.; Doridot, L.; Chêne, C.; Nicco, C.; Chouzenoux, S.; Deletang, Q.; Allanore, Y.; Kavian, N.; Batteux, F. Trained Immunity Modulates Inflammation-Induced Fibrosis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.N.; Han, S.G. Bovine Mastitis: Risk Factors, Therapeutic Strategies, and Alternative Treatments—A Review. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 33, 1699–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, Y.-T.; Yang, J.; Tan, X.; Liu, R.; Zhuang, Y.; Xu, J.-X.; Ren, W.-J. Escherichia Coli and Staphylococcus Aureus Differentially Regulate Nrf2 Pathway in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells: Relation to Distinct Innate Immune Response. Cells 2021, 10, 3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, R.C.; Mercurio, A.M. The Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) and Colorectal Cancer Progression. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2005, 4, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassiouni, W.; Ali, M.A.M.; Schulz, R. Multifunctional Intracellular Matrix Metalloproteinases: Implications in Disease. FEBS J. 2021, 288, 7162–7182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warner, R.B.; Najy, A.J.; Jung, Y.S.; Fridman, R.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.-R.C. Establishment of Structure-Function Relationship of Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinase-1 for Its Interaction with CD63: Implication for Cancer Therapy. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Khalil, R.A. Matrix Metalloproteinases, Vascular Remodeling, and Vascular Disease. Adv. Pharmacol. 2018, 81, 241–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, N.; Hu, M.; Khalil, R.A. Biochemical and Biological Attributes of Matrix Metalloproteinases. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2017, 147, 1–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourboulia, D.; Stetler-Stevenson, W.G. Matrix Metalloproteinases (MMPs) and Tissue Inhibitors of Metalloproteinases (TIMPs): Positive and Negative Regulators in Tumor Cell Adhesion. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2010, 20, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, K.; Sasaki, M.; Matsumoto, M.; Shionoya, H.; Iida, K. Protective Effect of Bacteroides Fragilis LPS on Escherichia Coli LPS-Induced Inflammatory Changes in Human Monocytic Cells and in a Rheumatoid Arthritis Mouse Model. Immunol. Lett. 2021, 233, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral-Pacheco, G.A.; Garza-Veloz, I.; Castruita-De la Rosa, C.; Ramirez-Acuña, J.M.; Perez-Romero, B.A.; Guerrero-Rodriguez, J.F.; Martinez-Avila, N.; Martinez-Fierro, M.L. The Roles of Matrix Metalloproteinases and Their Inhibitors in Human Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logan, R.; Jeffers, A.; Qin, W.; Owens, S.; Chauhan, P.; Komatsu, S.; Ikebe, M.; Idell, S.; Tucker, T.A. TGF-β Regulation of the uPA/uPAR Axis Modulates Mesothelial-Mesenchymal Transition (MesoMT). Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.K.; Vaughan, D.E. PAI-1 in Tissue Fibrosis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2012, 227, 493–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuhrman, B. The Urokinase System in the Pathogenesis of Atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 2012, 222, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, X.; Wang, B.; Nie, Y.; Wen, J.; Wang, Q.; Gu, C. Pirfenidone Suppresses MAPK Signalling Pathway to Reverse Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Renal Fibrosis. Nephrology 2017, 22, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehart, H.; Kumpf, S.; Ittner, A.; Ricci, R. MAPK Signalling in Cellular Metabolism: Stress or Wellness? EMBO Rep. 2010, 11, 834–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kass, L.; Erler, J.T.; Dembo, M.; Weaver, V.M. Mammary Epithelial Cell: Influence of Extracellular Matrix Composition and Organization during Development and Tumorigenesis. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2007, 39, 1987–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaga-Clavellina, V.; Garcia-Lopez, G.; Flores-Pliego, A.; Merchant-Larios, H.; Vadillo-Ortega, F. In Vitro Secretion and Activity Profiles of Matrix Metalloproteinases, MMP-9 and MMP-2, in Human Term Extra-Placental Membranes after Exposure to Escherichia coli. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2011, 9, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreschers, S.; Platen, C.; Ludwig, A.; Gille, C.; Köstlin, N.; Orlikowsky, T.W. Metalloproteinases TACE and MMP-9 Differentially Regulate Death Factors on Adult and Neonatal Monocytes After Infection with Escherichia Coli. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Xie, G.; Ding, F.; Zhou, X. LPS-Induced MMP-9 Expression Is Mediated through the MAPKs-AP-1 Dependent Mechanism in BEAS-2B and U937 Cells. Exp. Lung Res. 2018, 44, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herath, T.D.K.; Wang, Y.; Seneviratne, C.J.; Darveau, R.P.; Wang, C.-Y.; Jin, L. The Expression and Regulation of Matrix Metalloproteinase-3 Is Critically Modulated by Porphyromonas Gingivalis Lipopolysaccharide with Heterogeneous Lipid A Structures in Human Gingival Fibroblasts. BMC Microbiol. 2013, 13, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmood, N.; Mihalcioiu, C.; Rabbani, S.A. Multifaceted Role of the Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator (uPA) and Its Receptor (uPAR): Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Applications. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monção-Ribeiro, L.C.; Cagido, V.R.; Lima-Murad, G.; Santana, P.T.; Riva, D.R.; Borojevic, R.; Zin, W.A.; Cavalcante, M.C.M.; Riça, I.; Brando-Lima, A.C.; et al. Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Lung Injury: Role of P2X7 Receptor. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2011, 179, 314–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Palm, J.; König, J.; Seeland, U.; Rosenkranz, S.; Feiden, W.; Rübe, C.; Rübe, C.E. Matrix-Metallo-Proteinases and Their Tissue Inhibitors in Radiation-Induced Lung Injury. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2007, 83, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossa, C.; Liu, M.; Bronson, P.; Kirkwood, K.L. Transcriptional Activation of MMP-13 by Periodontal Pathogenic LPS Requires P38 MAP Kinase. J. Endotoxin Res. 2007, 13, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maolood, N.; Hardin-Pouzet, H.; Grange-Messent, V. Matrix Metalloproteinases MMP2 and MMP9 Are Upregulated by Noradrenaline in the Mouse Neuroendocrine Hypothalamus. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2008, 27, 1143–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shpigel, N.Y.; Elazar, S.; Rosenshine, I. Mammary Pathogenic Escherichia Coli. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2008, 11, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Dong, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, Z.; Chen, J.; Dong, G. The Synergism of PGN, LTA and LPS in Inducing Transcriptome Changes, Inflammatory Responses and a Decrease in Lactation as Well as the Associated Epigenetic Mechanisms in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells. Toxins 2020, 12, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rockey, D.C.; Bell, P.D.; Hill, J.A. Fibrosis—A Common Pathway to Organ Injury and Failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1138–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madala, S.K.; Schmidt, S.; Davidson, C.; Ikegami, M.; Wert, S.; Hardie, W.D. MEK-ERK Pathway Modulation Ameliorates Pulmonary Fibrosis Associated with Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Activation. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2012, 46, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebe, A.; Masszi, A.; Zulys, M.; Yeung, T.; Speight, P.; Rotstein, O.D.; Nakano, H.; Mucsi, I.; Szászi, K.; Kapus, A. Rac, PAK and P38 Regulate Cell Contact-Dependent Nuclear Translocation of Myocardin-Related Transcription Factor. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The JNK Signaling Pathway in Renal Fibrosis—PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29114233/ (accessed on 27 August 2024).
- Xiao, L.; Du, Y.; Shen, Y.; He, Y.; Zhao, H.; Li, Z. TGF-Beta 1 Induced Fibroblast Proliferation Is Mediated by the FGF-2/ERK Pathway. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed.) 2012, 17, 2667–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, J.N.; Yang, S.H.; Kim, Y.C.; Hwang, J.H.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, D.K.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, D.W.; Hur, D.G.; Oh, Y.K.; et al. Periostin Induces Kidney Fibrosis after Acute Kidney Injury via the P38 MAPK Pathway. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2019, 316, F426–F437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, C.-K.; Tien, Y.-C.; Jine-Yuan Hsieh, D.; Ho, T.-J.; Lai, C.-H.; Yeh, Y.-L.; Hsuan Day, C.; Shen, C.-Y.; Hsu, H.-H.; Lin, J.-Y.; et al. Attenuation of the LPS-Induced, ERK-Mediated Upregulation of Fibrosis-Related Factors FGF-2, uPA, MMP-2, and MMP-9 by Carthamus Tinctorius L in Cardiomyoblasts. Environ. Toxicol. 2017, 32, 754–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, X.; Huang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Lin, X. An Improvement of the 2−ΔΔCT Method for Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction Data Analysis. Biostat. Bioinform. Biomath. 2013, 3, 71–85. [Google Scholar]
| Gene Name | Primer Sequence (5′–3′) | TM (°C) | Product Size/bp |
|---|---|---|---|
| MMP-1 | F: TCAACTCTGGAGCAATGTCACACC | 59.2 | 175 |
| R: ATGAGCGTCTCCTCCGATACCTG | |||
| MMP-2 | F: GACCAGAGCACCATTGAGACCATG | 58.9 | 169 |
| R: GAGCGAAGGCATCATCCACTGTC | |||
| MMP-3 | F: AGAGTCTTCCGATTCTGCTGTTGC | 58.5 | 93 |
| R: GCTCCATGGTGTCTTCCTTGTCC | |||
| MMP-9 | F: GGTGCTGGCTTGCTGCTCTG | 56.7 | 87 |
| R: TTGGTGAGGTTGGTTCGTGGTTC | |||
| MMP-13 | F: CATCCTCAGCAGGTTGAAGCAGAG | 58.2 | 83 |
| R: TCATAGGCGGCATCAATACGGTTG | |||
| TIMP-1 | F: CCTGTTGCTGCTGTGGCTCAC | 58.1 | 91 |
| R: GACGACATCGGAGTTGCAGAAGG | |||
| TIMP-2 | F: ACGAGTGCCTCTGGATGGACTG | 56.6 | 91 |
| R: GAGCCGTCGCTTCTCTTGATGC | |||
| uPA | F: CAGGTCACCAACGCCGAGAAC | 53.8 | 98 |
| R: CTGATGAGGCTGCCACCACAC | |||
| uPAR | F: GCCAACCGCTGCTGCTACTG | 58.6 | 175 |
| R: ACGTTCATCTCATTGCCACCTTCC | |||
| PAI-1 | F: GAGAGCCAGGTTCATCGTCAACG | 57.9 | 199 |
| R: GGTGCTGCCATCGGACTTGTG | |||
| β-actin | F: TCTGGCACCACACCTTCTACAAC | 60.1 | 170 |
| R: GGACAGCACAGCCTGGAT | |||
| ERK1 | F: ACGTCATTGGCATCCGAGACATTC | 57.6 | 192 |
| R: GCACGTTGGCGGAGTGGATATAC | |||
| ERK2 | F: AACCTTCCAACCTGCTGCTCAAC | 57.7 | 182 |
| R: GATGTCGATGGACTTGGTGTAGCC | |||
| JNK | F: ATCTGGTCTGTTGGCTGTATAATGGC | 57.3 | 132 |
| R: CCTGGACATGAAGTCTTGGCTTGG | |||
| P38 | F: GGCTCCTGAGATCATGCTGAACTG | 57.5 | 137 |
| R:TCTGCTGAAGCTGGTTAATATGGTCTG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Liang, J.; Zhang, K.; Su, H.; Wang, D.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, F.; Sun, Z.; Wu, Z.; et al. Impact of Escherichia coli and Lipopolysaccharide on the MAPK Signaling Pathway, MMPs, TIMPs, and the uPA System in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3893. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083893
Zhang Y, Ding Y, Liang J, Zhang K, Su H, Wang D, Zhang M, Zhao F, Sun Z, Wu Z, et al. Impact of Escherichia coli and Lipopolysaccharide on the MAPK Signaling Pathway, MMPs, TIMPs, and the uPA System in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(8):3893. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083893
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yuanyuan, Yulin Ding, Junxi Liang, Kai Zhang, Hong Su, Daqing Wang, Min Zhang, Feifei Zhao, Zhiwei Sun, Zhimin Wu, and et al. 2025. "Impact of Escherichia coli and Lipopolysaccharide on the MAPK Signaling Pathway, MMPs, TIMPs, and the uPA System in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 8: 3893. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083893
APA StyleZhang, Y., Ding, Y., Liang, J., Zhang, K., Su, H., Wang, D., Zhang, M., Zhao, F., Sun, Z., Wu, Z., Wang, F., Cao, G., & Zhang, Y. (2025). Impact of Escherichia coli and Lipopolysaccharide on the MAPK Signaling Pathway, MMPs, TIMPs, and the uPA System in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(8), 3893. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083893






