Dual Disruption of EGFR/PI3K Signaling: IGF2BP2 Targeting Reverses Anti-EGFR Resistance in CAFs-Infiltrated Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
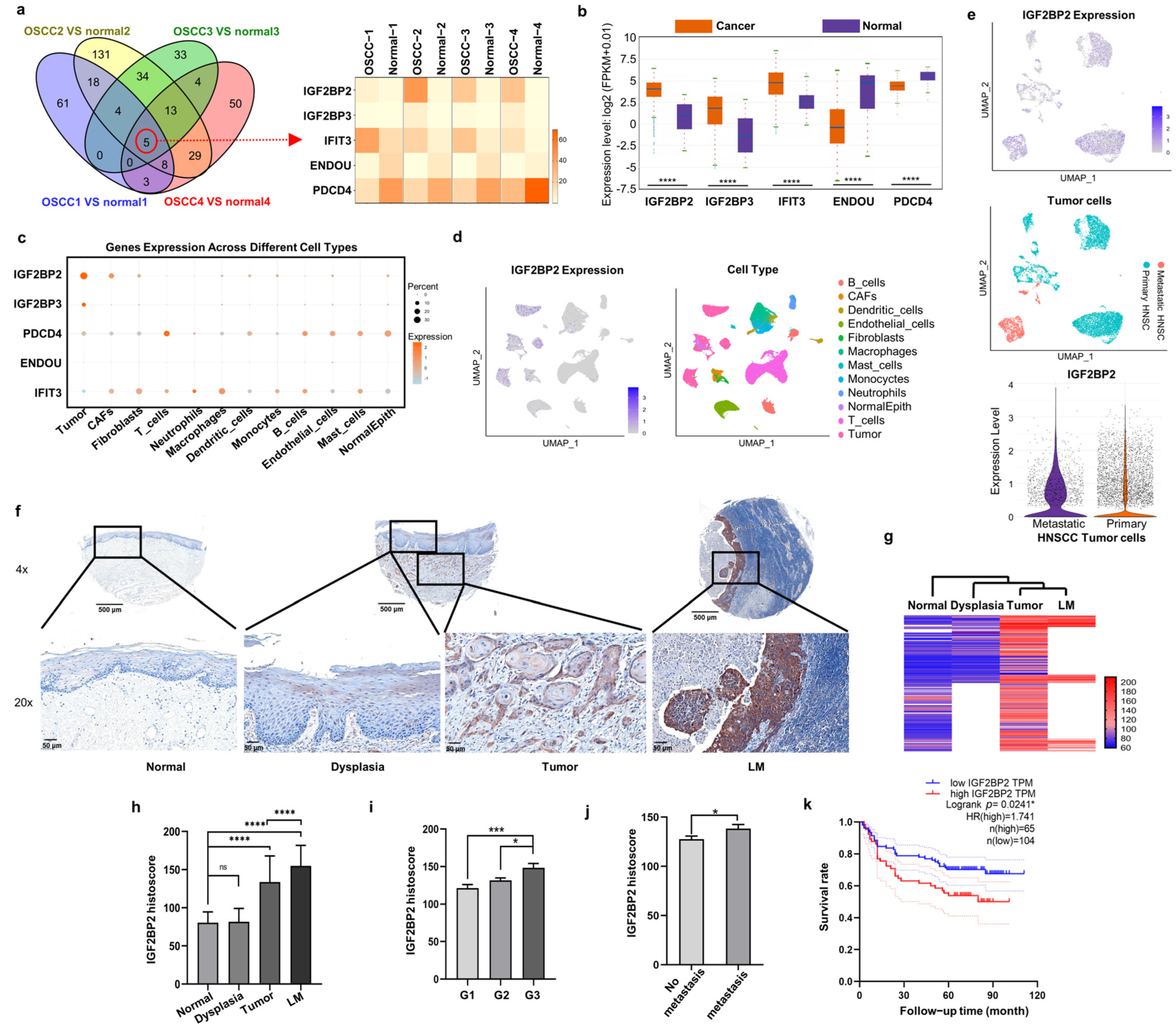
2.1. IGF2BP2 Is the Most Markedly Upregulated RBP in OSCC Cells and CAFs, and Is Associated with Poor Clinical Prognosis
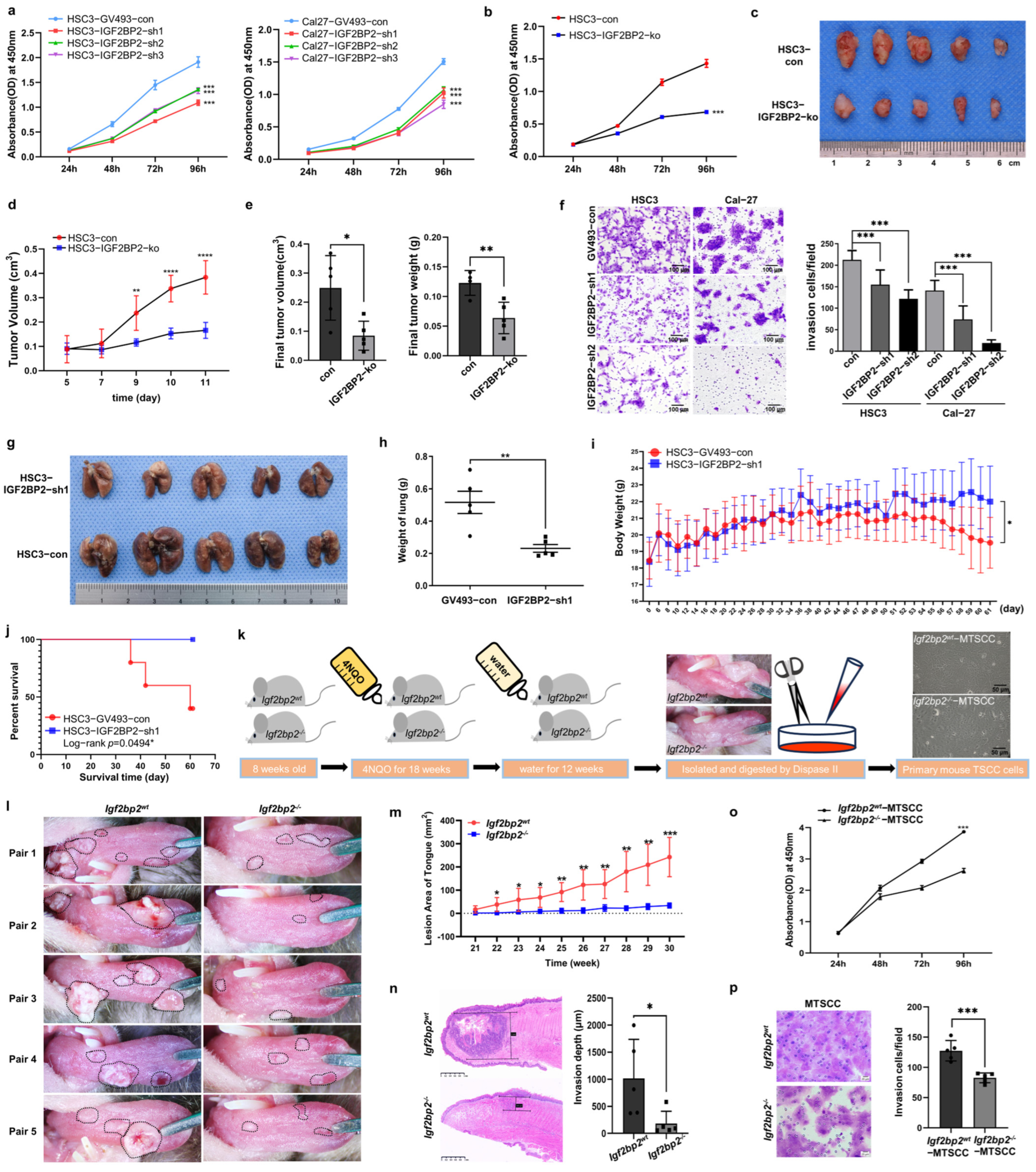
2.2. Impaired IGF2BP2 Expression Inhibits Tumor Progression in OSCC
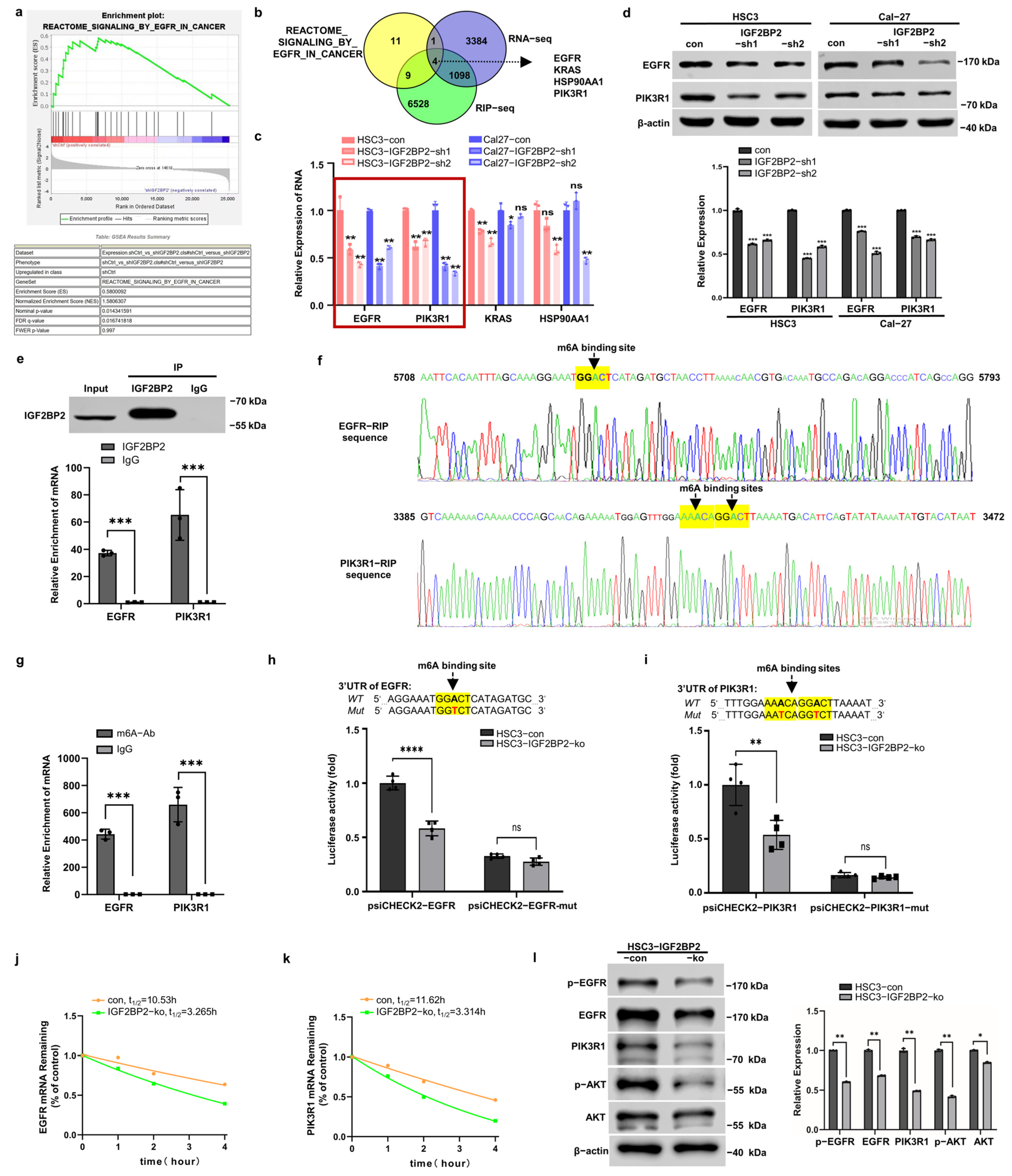
2.3. IGF2BP2 Regulates EGFR and PIK3R1 in an m6A-Dependent Manner
2.4. IGF2BP2 Inhibitor Exhibits Potent Anti-OSCC Efficacy in Both Cetuximab-Sensitive and -Resistant Cells

2.5. CWI1-2 but Not Cetuximab Suppresses EGFR/PI3K/AKT Pathway in CAFs
2.6. CWI1-2 Overcomes CAFs-Mediated Cetuximab Resistance in OSCC
2.7. CWI1-2 Exhibits Promising Anti-Tumor Efficacy in 4NQO-Induced TSCC Mouse Model
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Clinical Samples Collection
4.2. Cell Culture, Plasmid Construction, and Transfection
4.3. RNA Sequencing (RNA-Seq) and RNA Immunoprecipitation Sequencing (RIP-Seq)
4.4. Western Blotting, RT-qPCR, Immunohistochemistry (IHC), and Immunofluorescence (IF) Staining
4.5. CCK-8, Transwell Assay, and Mice Xenografts
4.6. Primary Cell Culture, Purification, and Passage from Human and Mouse TSCC and Adjacent Normal Tissues
4.7. Cell Co-Culture Models
4.8. RNA Stability Assay
4.9. RNA Immunoprecipitation-qPCR (RIP-qPCR) and Methylated RNA Immunoprecipitation-qPCR (MeRIP-qPCR)
4.10. Luciferase Reporter Assay
4.11. Generation of Igf2bp2 Depletion Transgenic Mouse and Tongue SCC (TSCC) Induction
4.12. Single-Cell RNA Sequencing (scRNA-Seq) Data Source and Analysis
4.13. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Kwon, S.C.; Yi, H.; Eichelbaum, K.; Föhr, S.; Fischer, B.; You, K.T.; Castello, A.; Krijgsveld, J.; Hentze, M.W.; Kim, V.N. The RNA-binding protein repertoire of embryonic stem cells. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2013, 20, 1122–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, M.; Díaz-Muñoz, M.D. RNA-binding proteins control gene expression and cell fate in the immune system. Nat. Immunol. 2018, 19, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsafadi, S.; Houy, A.; Battistella, A.; Popova, T.; Wassef, M.; Henry, E.; Tirode, F.; Constantinou, A.; Piperno-Neumann, S.; Roman-Roman, S.; et al. Cancer-associated SF3B1 mutations affect alternative splicing by promoting alternative branchpoint usage. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.; Yu, J.; Han, W.; Fan, X.; Qian, H.; Wei, H.; Tsai, Y.-h.S.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Q.; et al. A splicing isoform of TEAD4 attenuates the Hippo–YAP signalling to inhibit tumour proliferation. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Weng, H.; Sun, W.; Qin, X.; Shi, H.; Wu, H.; Zhao, B.S.; Mesquita, A.; Liu, C.; Yuan, C.L.; et al. Recognition of RNA N6-methyladenosine by IGF2BP proteins enhances mRNA stability and translation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2018, 20, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Q.; Wang, L.; Yu, F.; Gao, H.; Lei, T.; Li, P.; Liu, P.; Zheng, X.; Hu, X.; Chen, Y.; et al. Imp2 regulates GBM progression by activating IGF2/PI3K/Akt pathway. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2015, 16, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlem, C.; Barghash, A.; Puchas, P.; Haybaeck, J.; Kessler, S.M. The Insulin-Like Growth Factor 2 mRNA Binding Protein IMP2/IGF2BP2 is Overexpressed and Correlates with Poor Survival in Pancreatic Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lu, J.-H.; Wu, Q.-N.; Jin, Y.; Wang, D.-S.; Chen, Y.-X.; Liu, J.; Luo, X.-J.; Meng, Q.; Pu, H.-Y.; et al. LncRNA LINRIS stabilizes IGF2BP2 and promotes the aerobic glycolysis in colorectal cancer. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.; Meng, S.; Li, M.; Lin, T.; Chu, S.; Li, Z.; Zheng, J.; Gu, Y.; Bai, J. LINC00460/DHX9/IGF2BP2 complex promotes colorectal cancer proliferation and metastasis by mediating HMGA1 mRNA stability depending on m6A modification. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Xiong, X.; Sun, Y.; Geng, Z.; Chen, X.; Cui, X.; Lv, J.; Ge, L.; Jia, X.; Xu, J. IGF2BP2 promotes ovarian cancer growth and metastasis by upregulating CKAP2L protein expression in an m(6) A-dependent manner. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2023, 37, e23183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Dai, X.; Wu, J.; Wen, K. N6-methyladenosine (m6A) reader IGF2BP2 stabilizes HK2 stability to accelerate the Warburg effect of oral squamous cell carcinoma progression. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 148, 3375–3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, F.; Miu, Y.-Y.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, H.; Lu, X.-L.; Cheng, H.; Zheng, Z.-G. A micro-peptide encoded by HOXB-AS3 promotes the proliferation and viability of oral squamous cell carcinoma cell lines by directly binding with IGF2BP2 to stabilize c-Myc. Oncol. Lett. 2021, 22, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Cai, H.; Hou, C.; Song, F.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Qiu, D.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, F.; Yu, D.; et al. METTL14 inhibits malignant progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma by targeting the autophagy-related gene RB1CC1 in an m6A-IGF2BP2-dependent manner. Clin. Sci. 2023, 137, 1373–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Guo, Y.; Yang, R.; Zhao, N.; Ge, N.; Wang, Y.; Guo, C. m(6)A methyltransferase METTL3 promotes oral squamous cell carcinoma progression through enhancement of IGF2BP2-mediated SLC7A11 mRNA stability. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2021, 11, 5282–5298. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.; Pan, M.; Li, Y.; Lu, T.; Wang, Z.; Liu, C.; Hu, G. RNA N6-methyladenosine reader IGF2BP2 promotes lymphatic metastasis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of head and neck squamous carcinoma cells via stabilizing slug mRNA in an m6A-dependent manner. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. CR 2022, 41, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlessinger, J. Receptor Tyrosine Kinases: Legacy of the First Two Decades. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a008912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, W.; He, J.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, X. Prognostic role of epidermal growth factor receptor in head and neck cancer: A meta-analysis. J. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 108, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, H.-Y.; Liu, Y.-C.; Chen, N.-Y.; Tsai, C.-F.; Wang, Y.-T.; Chen, Y.-J.; Hsu, T.-L.; Yang, P.-C.; Wong, C.-H. Effect of sialylation on EGFR phosphorylation and resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 6955–6960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pidugu, V.K.; Wu, M.-M.; Yen, A.-H.; Pidugu, H.B.; Chang, K.-W.; Liu, C.-J.; Lee, T.-C. IFIT1 and IFIT3 promote oral squamous cell carcinoma metastasis and contribute to the anti-tumor effect of gefitinib via enhancing p-EGFR recycling. Oncogene 2019, 38, 3232–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzawa, K.; Amelio, A.L.; Kasamatsu, A.; Saito, T.; Kita, A.; Fukamachi, M.; Sawai, Y.; Toeda, Y.; Eizuka, K.; Hayashi, F.; et al. Resveratrol Targets Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator Receptor Expression to Overcome Cetuximab-Resistance in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertotti, A.; Papp, E.; Jones, S.; Adleff, V.; Anagnostou, V.; Lupo, B.; Sausen, M.; Phallen, J.; Hruban, C.A.; Tokheim, C.; et al. The genomic landscape of response to EGFR blockade in colorectal cancer. Nature 2015, 526, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garvey, C.M.; Lau, R.; Sanchez, A.; Sun, R.X.; Fong, E.J.; Doche, M.E.; Chen, O.; Jusuf, A.; Lenz, H.J.; Larson, B.; et al. Anti-EGFR Therapy Induces EGF Secretion by Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts to Confer Colorectal Cancer Chemoresistance. Cancers 2020, 12, 1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remsing Rix, L.L.; Sumi, N.J.; Hu, Q.; Desai, B.; Bryant, A.T.; Li, X.; Welsh, E.A.; Fang, B.; Kinose, F.; Kuenzi, B.M.; et al. IGF-binding proteins secreted by cancer-associated fibroblasts induce context-dependent drug sensitization of lung cancer cells. Sci. Signal. 2022, 15, eabj5879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaryouh, H.; De Pauw, I.; Baysal, H.; Peeters, M.; Vermorken, J.B.; Lardon, F.; Wouters, A. Recent insights in the PI3K/Akt pathway as a promising therapeutic target in combination with EGFR-targeting agents to treat head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Med. Res. Rev. 2022, 42, 112–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Liu, B.; Xiong, H.; Wu, F.; Hu, C.; Liu, P. Trans-3,5,4′-trimethoxystilbene reduced gefitinib resistance in NSCLCs via suppressing MAPK/Akt/Bcl-2 pathway by upregulation of miR-345 and miR-498. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 2431–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Y.; Dou, B.; Tan, H.; Feng, Y.; Wang, N.; Wang, D. Tumor microenvironment-driven non-cell-autonomous resistance to antineoplastic treatment. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bejarano, L.; Jordāo, M.J.C.; Joyce, J.A. Therapeutic Targeting of the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 933–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Ni, H.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Xi, T.; Li, X.; Zheng, L. RNA-binding proteins in tumor progression. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-L.; Li, B.; Luo, Y.-X.; Lin, Q.; Liu, S.-R.; Zhang, X.-Q.; Zhou, H.; Yang, J.-H.; Qu, L.-H. Comprehensive Genomic Characterization of RNA-Binding Proteins across Human Cancers. Cell Rep. 2018, 22, 286–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, S.; Ding, Q.; Guo, Y.; Hou, K.; Kan, Y.; Deng, F.; Xu, Q. A pan-cancer landscape of IGF2BPs and their association with prognosis, stemness and tumor immune microenvironment. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1049183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Li, H.; Cai, H.; Liu, W.; Pan, E.; Yu, D.; He, S. Upregulation of IGF2BP2 Promotes Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Progression That Is Related to Cell Proliferation, Metastasis and Tumor-Infiltrating Immune Cells. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 809589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Zhang, X.; Bi, F.; Wang, D.; Zhou, X.; Li, X.; Yang, Q. FTO Inhibits Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Progression by Destabilising SNAI1 mRNA through IGF2BP2. Cancers 2022, 14, 5218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, B.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, Z.; An, F.; Nie, H.; Wang, H.; Yang, C.; Sun, J.; Chen, K.; Zhou, J.; et al. CircEZH2/miR-133b/IGF2BP2 aggravates colorectal cancer progression via enhancing the stability of m6A-modified CREB1 mRNA. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiraishi, Y.; Wada, T.; Nakatani, K.; Negoro, K.; Fujita, S. Immunohistochemical expression of EGFR and p-EGFR in oral squamous cell carcinomas. Pathol. Oncol. Res. POR 2006, 12, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batta, N.; Pandey, M. Mutational spectrum of tobacco associated oral squamous carcinoma and its therapeutic significance. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 17, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, D.S.; Wang, W.; Leong, H.S.; Sew, P.H.; Lau, D.P.; Chong, F.T.; Krisna, S.S.; Lim, T.K.; Iyer, N.G. Tongue carcinoma infrequently harbor common actionable genetic alterations. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, E.D.S.; Nogueira, K.A.B.; Fernandes, L.C.C.; Martins, J.R.P.; Reis, A.V.F.; Neto, J.B.V.; Júnior, I.; Pessoa, C.; Petrilli, R.; Eloy, J.O. EGFR targeting for cancer therapy: Pharmacology and immunoconjugates with drugs and nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 592, 120082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xiong, X.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, W.; Dong, Y.; Li, J.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Wu, H.; et al. Membrane-tethered Notch1 exhibits oncogenic property via activation of EGFR–PI3K–AKT pathway in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 234, 5940–5952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novoplansky, O.; Shnerb, A.B.; Marripati, D.; Jagadeeshan, S.; Abu Shareb, R.; Conde-Lόpez, C.; Zorea, J.; Prasad, M.; Ben Lulu, T.; Yegodayev, K.M.; et al. Activation of the EGFR/PI3K/AKT pathway limits the efficacy of trametinib treatment in head and neck cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2023, 17, 2618–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozaki, M.; Yasui, H.; Ohnishi, Y. Ligand-Independent EGFR Activation by Anchorage-Stimulated Src Promotes Cancer Cell Proliferation and Cetuximab Resistance via ErbB3 Phosphorylation. Cancers 2019, 11, 1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, A.R.; Gomez-Roca, C.A.; Robbrecht, D.G.J.; Verlingue, L.; Italiano, A.; Bauman, J.E.; Steeghs, N.; Prenen, H.; Fayette, J.; Spicer, J.; et al. Phase 1b Study of the Immunocytokine Simlukafusp alfa (FAP-IL2v), in Combination with Cetuximab in Patients with Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2024, 30, 5540–5547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Tian, Z.; Yang, G.; Wang, R.; Wang, C.; Wu, Q.; Wu, Y.; Gao, J.; et al. Clinical utility of PDX cohorts to reveal biomarkers of intrinsic resistance and clonal architecture changes underlying acquired resistance to cetuximab in HNSCC. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picon, H.; Guddati, A.K. Mechanisms of resistance in head and neck cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2020, 10, 2742–2751. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, I.; Gaykalova, D.A. Unveiling the role of PIK3R1 in cancer: A comprehensive review of regulatory signaling and therapeutic implications. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2024, 106–107, 58–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Lin, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, S.; Lan, J.; Lu, N.; Xie, C.; He, S.; Zhang, W. N6-methyladenosine-modified circPLPP4 sustains cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer cells via PIK3R1 upregulation. Mol. Cancer 2024, 23, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, W.; Li, B.; Wang, L.; Xu, Z.; Zeng, A.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; et al. Circular RNA AKT3 upregulates PIK3R1 to enhance cisplatin resistance in gastric cancer via miR-198 suppression. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.-c.; Xu, X.-L.; Li, F.; Gong, B.-g.; Liu, S.; Cui, Y.-q.; Sun, H.-c.; Xu, P.-y.; Zheng, Y.-m.; Jiang, H. Silencing pancreatic adenocarcinoma upregulated factor (PAUF) increases the sensitivity of pancreatic cancer cells to gemcitabine. Tumor Biol. 2015, 37, 7555–7564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stronach, E.A.; Alfraidi, A.; Rama, N.; Datler, C.; Studd, J.B.; Agarwal, R.; Guney, T.G.; Gourley, C.; Hennessy, B.T.; Mills, G.B.; et al. HDAC4-Regulated STAT1 Activation Mediates Platinum Resistance in Ovarian Cancer. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 4412–4422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, J.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, J.; Mao, J.; Zuo, X. CircRHBDD1 augments metabolic rewiring and restricts immunotherapy efficacy via m6A modification in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2022, 24, 755–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parseghian, C.M.; Napolitano, S.; Loree, J.M.; Kopetz, S. Mechanisms of Innate and Acquired Resistance to Anti-EGFR Therapy: A Review of Current Knowledge with a Focus on Rechallenge Therapies. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 6899–6908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.F.; Zhu, M.L.; Liu, M.M.; Xu, Y.T.; Yuan, L.L.; Bian, J.; Xia, Y.Z.; Kong, L.Y. EGFR mutation mediates resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in NSCLC: From molecular mechanisms to clinical research. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 167, 105583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, S.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, R.; Luo, F.; Li, Y.; Dai, L.; Peng, X. Cancer-associated fibroblasts mediate resistance to anti-EGFR therapies in cancer. Pharmacol. Res. 2024, 206, 107304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, A.C.; Ansell, A.; Jerhammar, F.; Lindh, M.B.; Grénman, R.; Munck-Wikland, E.; Östman, A.; Roberg, K. Cancer-associated fibroblasts induce matrix metalloproteinase-mediated cetuximab resistance in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells. Mol. Cancer Res. MCR 2012, 10, 1158–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, H.; Huang, F.; Yu, Z.; Chen, Z.; Prince, E.; Kang, Y.; Zhou, K.; Li, W.; Hu, J.; Fu, C.; et al. The m6A reader IGF2BP2 regulates glutamine metabolism and represents a therapeutic target in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Cell 2022, 40, 1566–1582.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Wu, K.; Liao, S.; Pan, Y.; Sun, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, S.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, J. MicroRNA-transcription factor network analysis reveals miRNAs cooperatively suppress RORA in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncogenesis 2018, 7, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Pan, Y.; Chen, X.; Xia, S.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, J. Inactivation of homeodomain-interacting protein kinase 2 promotes oral squamous cell carcinoma metastasis through inhibition of P53-dependent E-cadherin expression. Cancer Sci. 2021, 112, 117–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Sun, Y.; Li, Y.; Ma, J.; Lv, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, J. A Novel Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cell Line Escapes from Immune Recognition due to Genetic Alterations in HLA Class I Complex. Cells 2022, 12, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bill, R.; Wirapati, P.; Messemaker, M.; Roh, W.; Zitti, B.; Duval, F.; Kiss, M.; Park, J.C.; Saal, T.M.; Hoelzl, J.; et al. CXCL9:SPP1 macrophage polarity identifies a network of cellular programs that control human cancers. Science 2023, 381, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, Y.; Zhu, T.; Nong, S.; Sun, Y.; Li, Y.; Pan, J.; Ma, J.; Zhang, J. Dual Disruption of EGFR/PI3K Signaling: IGF2BP2 Targeting Reverses Anti-EGFR Resistance in CAFs-Infiltrated Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3941. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26093941
Hu Y, Zhu T, Nong S, Sun Y, Li Y, Pan J, Ma J, Zhang J. Dual Disruption of EGFR/PI3K Signaling: IGF2BP2 Targeting Reverses Anti-EGFR Resistance in CAFs-Infiltrated Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):3941. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26093941
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Yaying, Tianshuang Zhu, Sheng Nong, Yanan Sun, Yiwei Li, Junchen Pan, Jiyuan Ma, and Jiali Zhang. 2025. "Dual Disruption of EGFR/PI3K Signaling: IGF2BP2 Targeting Reverses Anti-EGFR Resistance in CAFs-Infiltrated Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 3941. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26093941
APA StyleHu, Y., Zhu, T., Nong, S., Sun, Y., Li, Y., Pan, J., Ma, J., & Zhang, J. (2025). Dual Disruption of EGFR/PI3K Signaling: IGF2BP2 Targeting Reverses Anti-EGFR Resistance in CAFs-Infiltrated Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 3941. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26093941






