Paeonol Relieves Chronic Neuropathic Pain by Reducing Communication Between Schwann Cells and Macrophages in the Dorsal Root Ganglia After Injury
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. The Proportion of Macrophages in the DRG Is Increased After Peripheral Nerve Injury
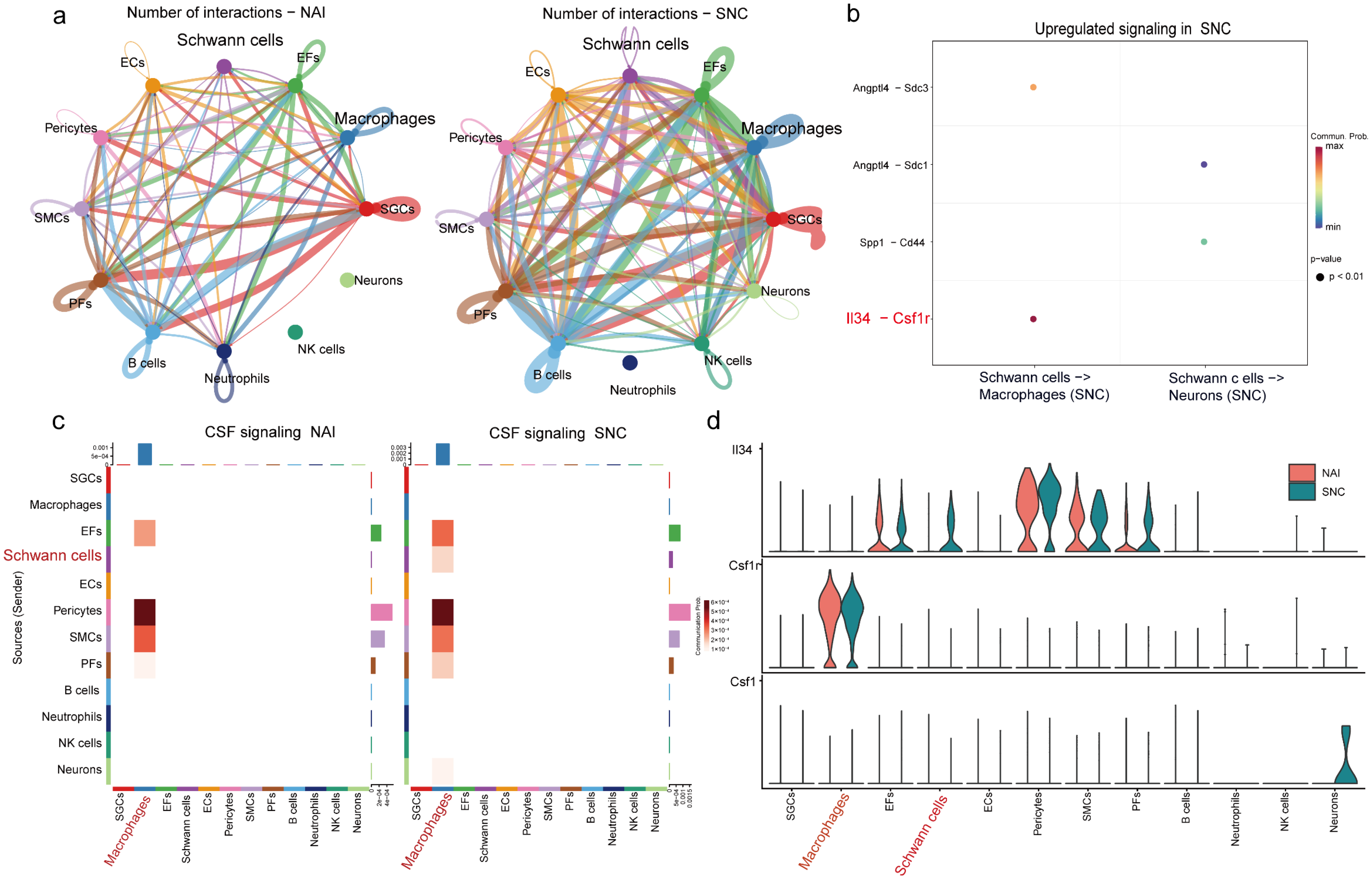
2.2. IL-34 Is Secreted by Schwann Cells and Taken Up by Macrophages in the DRG After Nerve Injury
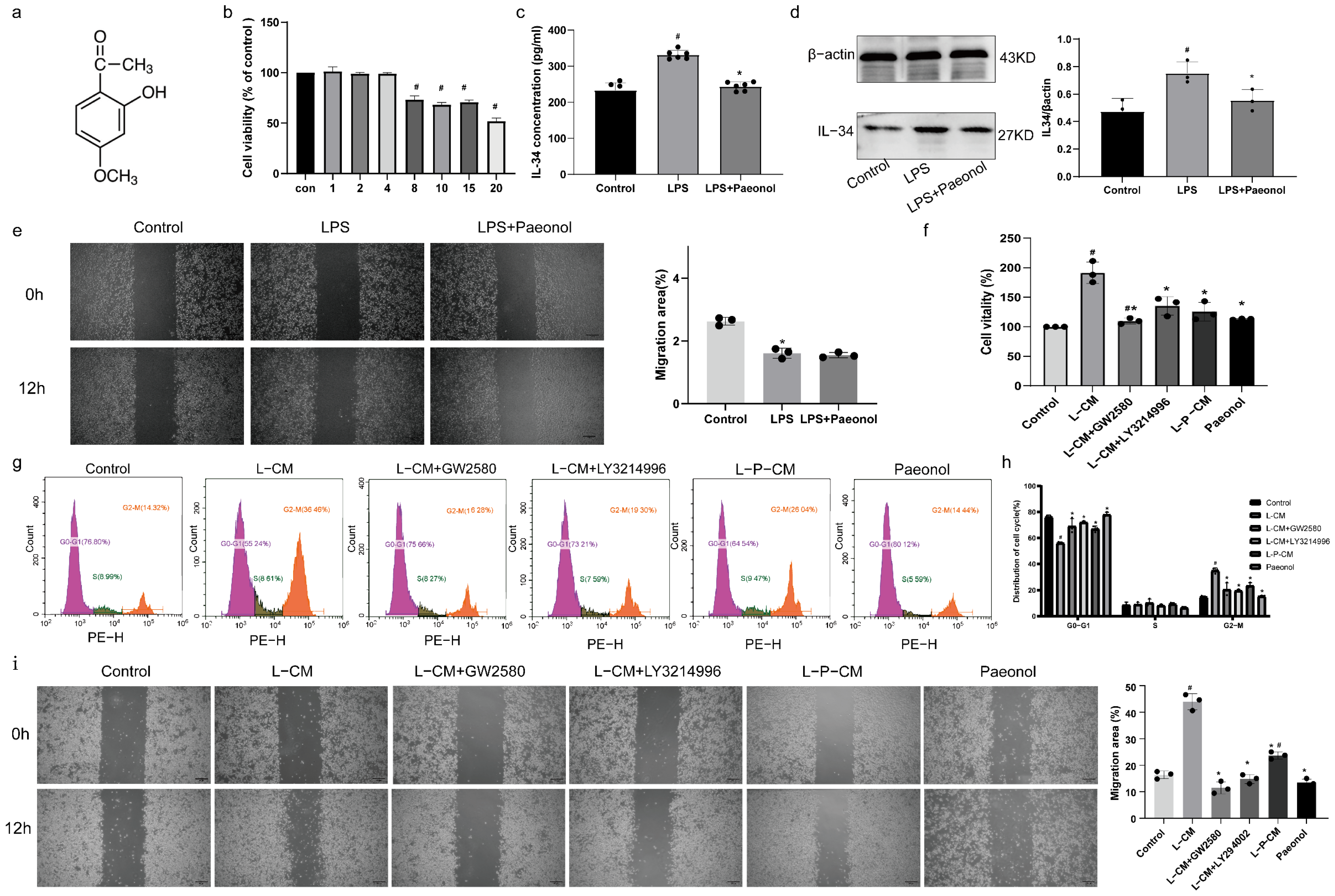
2.3. The Impact of Paeonol on the Viability of RSC96 Cells
2.4. Paeonol Inhibits the Secretion of IL-34 by RSC96 Schwann Cells Stimulated by LPS
2.5. LPS and Paeonol Do Not Affect the Migration Ability of RAW264.7 Cells
2.6. L-P-CM Failed to Trigger the Proliferation of RAW264.7 Cells
2.7. L-P-CM Does Not Notably Promote the Migration of RAW264.7 Cells
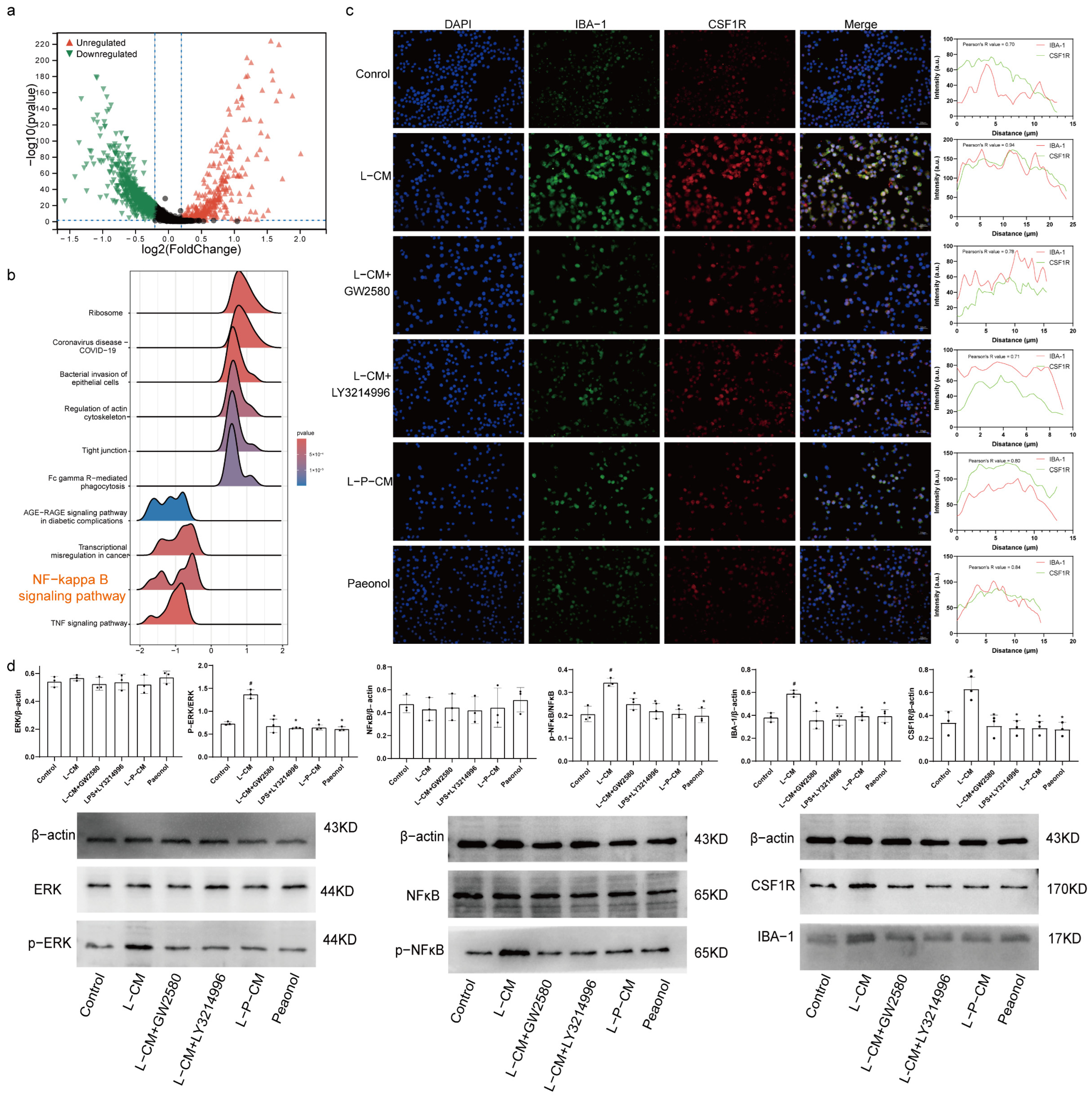
2.8. Immunofluorescence Colocalization Analysis of CSF1R and IBA-1
2.9. L-P-CM Fails to Activate the CSF1R/ERK/NF-κB Pathway in RAW264.7 Cells
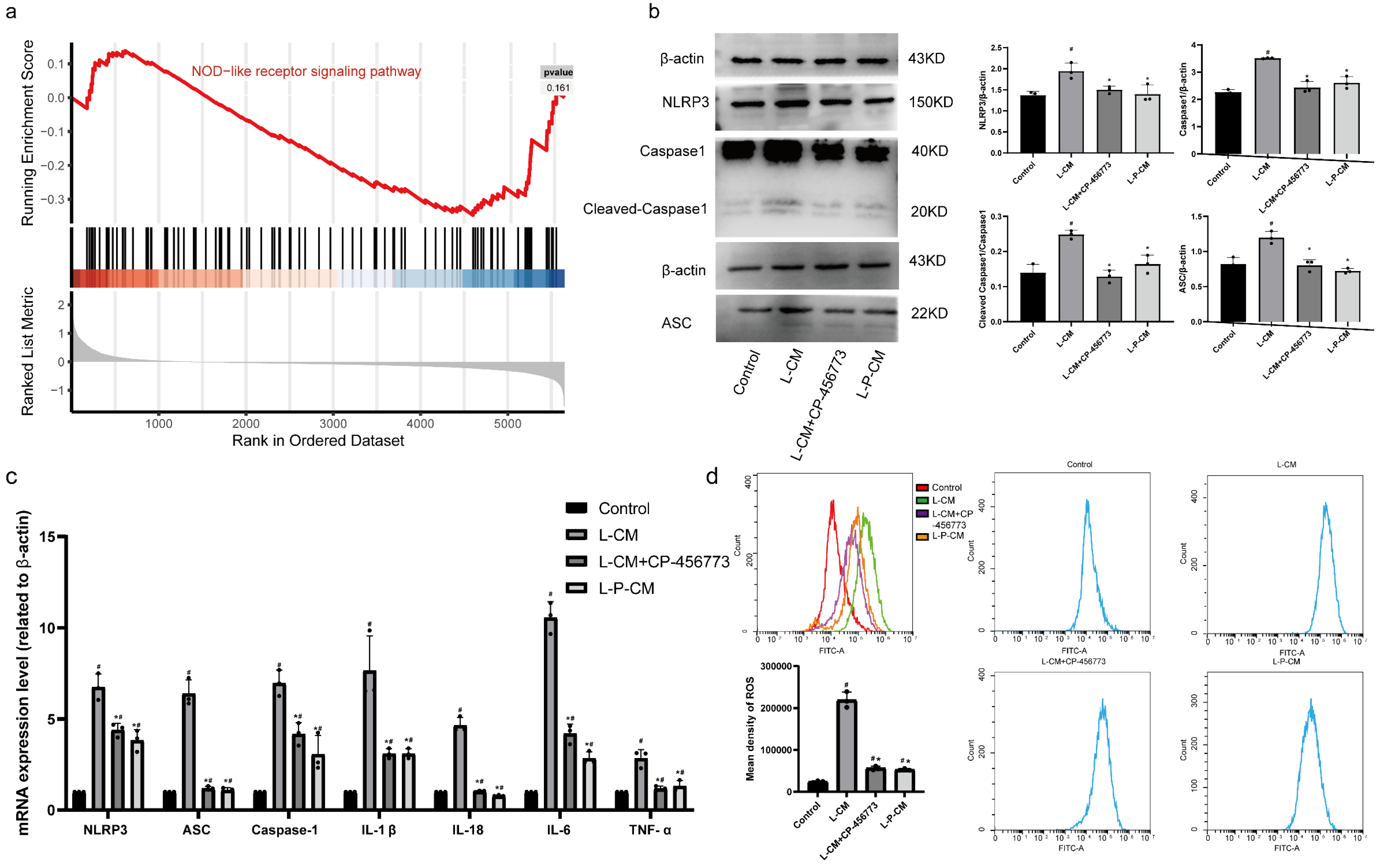
2.10. L-P-CM Significantly Curbs Activation of the NLRP3 Inflammasome in RAW264.7 Cells
2.11. L-P-CM Reduces ROS Production by RAW264.7 Macrophages Induced by NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation In Vitro
2.12. Paeonol Relieves Mechanical Pain and Cold Hyperalgesia in CCI Rats
2.13. Paeonol Reduces Serum Inflammatory Factor Levels in CCI Rats
2.14. Paeonol Reduces Levels of CSF1R, NLRP3, and IBA-1 in the DRG
2.15. Paeonol Curbs Activation of the CSF1R/ERK/NFκB Pathway and the NLRP3 Inflammasome
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Single-Cell Data Quality Control and Annotation
4.3. Differential Gene Analysis of Macrophages
4.4. Analysis of Cell Communication in the DRG
4.5. Cell Culture
4.6. Experimental Grouping of RSC96 Schwann Cells and Preparation of Conditioned Medium
4.7. Experimental Grouping of RAW264.7 Macrophages
4.8. IL-34 Secretion by RSC96 Cells
4.9. Analysis of Cell Viability
4.10. Cell Cycle Analysis via Flow Cytometry
4.11. Macrophage Migration Assay
4.12. Immunofluorescence
4.13. Detection of ROS by Flow Cytometry
4.14. Subjects
4.15. Neuropathic Pain Model
4.16. Behavioral Tests
4.17. H&E Staining
4.18. Measurement of Inflammatory Factor Levels in Rat Serum by ELISA
4.19. Immunohistochemistry
4.20. qRT–PCR Analysis of RAW264.7 Cells
4.21. Western Blotting
4.22. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Definition | Abbreviation |
| Apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD | ASC |
| Angiopoietin-like 4 | Angptl4 |
| Chronic constriction injury | CCI |
| C-C motif chemokine ligand 2 | CCL2 |
| Colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor | CSF1R |
| Dorsal root ganglion | DRG |
| Extracellular signal-regulated kinase | ERK |
| Gene set enrichment analysis | GSEA |
| Interleukin-1 | IL-1 |
| Interleukin-1 beta | IL-1β |
| Interleukin-6 | IL-6 |
| Interleukin-18 | IL-18 |
| Interleukin-34 | IL-34 |
| Lipopolysaccharide | LPS |
| Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes | KEGG |
| Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B | NF-κB |
| NACHT, LRR, and PYD domain–containing protein 3 | NLRP3 |
| Reactive oxygen species | ROS |
| Tumor necrosis factor-α | TNF-α |
References
- National Guideline Centre. National Guideline Centre. National institute for health and care excellence: Guidelines. In Low Back Pain and Sciatica in Over 16s: Assessment and Management; National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE): London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Schaffer, D.; Florin, T.; Eagle, C.; Marschner, I.; Singh, G.; Grobler, M.; Fenn, C.; Schou, M.; Curnow, K.M. Risk of serious NSAID-related gastrointestinal events during long-term exposure: A systematic review. Med. J. Aust. 2006, 185, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanas, A.; Ferrandez, A. Inappropriate prevention of NSAID-induced gastrointestinal events among long-term users in the elderly. Drugs Aging 2007, 24, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyengar, S.; Ossipov, M.H.; Johnson, K.W. The role of calcitonin gene-related peptide in peripheral and central pain mechanisms including migraine. Pain 2017, 158, 543–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.L.; Lopes, A.H.; Guimaraes, R.M.; Cunha, T.M. CXCL1/CXCR2 signaling in pathological pain: Role in peripheral and central sensitization. Neurobiol. Dis. 2017, 105, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Shi, H.; Zhang, D.; Jing, B.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Chang, S.; Gao, L.; Zhao, G. Paeonol alleviates neuropathic pain by modulating microglial M1 and M2 polarization via the RhoA/p38MAPK signaling pathway. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2023, 29, 2666–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Zheng, X.; Fan, Z.; Zhou, H.; Zhu, X.; Wang, G.; Liu, Z. Paeonol alleviates primary dysmenorrhea in mice via activating CB2R in the uterus. Phytomedicine 2020, 68, 153151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.; Zeng, R.; Huang, Q.; Liu, X.; Cao, Z.; Guo, Q. Paeonol inhibits chronic constriction injury-induced astrocytic activation and neuroinflammation in rats via the HDAC/miR-15a pathway. Drug Dev. Res. 2022, 83, 1758–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, M.F.; Malayil, R.; Hanes, M.; Deer, T. Unique Characteristics of the Dorsal Root Ganglion as a Target for Neuromodulation. Pain. Med. 2019, 20 (Suppl. 1), S23–S30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Liu, H.; Hamel, K.A.; Morvan, M.G.; Yu, S.; Leff, J.; Guan, Z.; Braz, J.M.; Basbaum, A.I. Dorsal root ganglion macrophages contribute to both the initiation and persistence of neuropathic pain. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shubayev, V.I.; Angert, M.; Dolkas, J.; Campana, W.M.; Palenscar, K.; Myers, R.R. TNFalpha-induced MMP-9 promotes macrophage recruitment into injured peripheral nerve. Mol. Cell Neurosci. 2006, 31, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trias, E.; Kovacs, M.; King, P.H.; Si, Y.; Kwon, Y.; Varela, V.; Ibarburu, S.; Moura, I.C.; Hermine, O.; Beckman, J.S.; et al. Schwann cells orchestrate peripheral nerve inflammation through the expression of CSF1, IL-34, and SCF in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Glia 2020, 68, 1165–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, G.; Gabay, E.; Tal, M.; Yirmiya, R.; Shavit, Y. Genetic impairment of interleukin-1 signaling attenuates neuropathic pain, autotomy, and spontaneous ectopic neuronal activity, following nerve injury in mice. Pain 2006, 120, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felix, J.; Elegheert, J.; Gutsche, I.; Shkumatov, A.V.; Wen, Y.; Bracke, N.; Pannecoucke, E.; Vandenberghe, I.; Devreese, B.; Svergun, D.I.; et al. Human IL-34 and CSF-1 establish structurally similar extracellular assemblies with their common hematopoietic receptor. Structure 2013, 21, 528–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guilbert, L.J.; Stanley, E.R. Specific interaction of murine colony-stimulating factor with mononuclear phagocytic cells. J. Cell Biol. 1980, 85, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, Y.G.; Jubinsky, P.T.; Sengupta, A.; Yeung, D.C.; Stanley, E.R. Purification of the colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor and demonstration of its tyrosine kinase activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 1268–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, E.R.; Chitu, V. CSF-1 receptor signaling in myeloid cells. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a021857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz, J.; Woolf, C.J. The neuropathic pain triad: Neurons, immune cells and glia. Nat. Neurosci. 2007, 10, 1361–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Gereau, R.W. Acute p38-mediated modulation of tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium channels in mouse sensory neurons by tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaible, H.G. Nociceptive neurons detect cytokines in arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2014, 16, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nashtahosseini, Z.; Eslami, M.; Paraandavaji, E.; Haraj, A.; Dowlat, B.F.; Hosseinzadeh, E.; Oksenych, V.; Naderian, R. Cytokine Signaling in Diabetic Neuropathy: A Key Player in Peripheral Nerve Damage. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, K.A.; Nguyen, K.L.; Gupta, S.; Ricard, J.; Bethea, J.R. TNFR1/p38αMAPK signaling in Nex + supraspinal neurons regulates estrogen-dependent chronic neuropathic pain. Brain Behav. Immun. 2024, 119, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, T.; Zhang, L.; Yang, J.; Zhao, F.; Wang, Y.; Ouyang, Y.; Liu, J. TRAF6 promotes spinal microglial M1 polarization to aggravate neuropathic pain by activating the c-JUN/NF-kB signaling pathway. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2024, 40, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Gong, Q.; He, S.; Peng, J.; Chen, L.; Wang, L.; Chen, P. Analgesic effect of Dahuang Fuzi Decoction in neuropathic pain through inhibiting TNF-α and PI3K-AKT signaling. Front. Neurosci. 2024, 18, 1464477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, Z.; Zhenni, C.; Zifeng, Z.; Bei, J.; Yong, C.; Yixuan, L.; Yuwei, P.; Li, G.; Jiaxu, C.; Guoping, Z. Danggui Sini Decoction normalizes the intestinal microbiota and serum metabolite levels to treat sciatica. Phytomedicine 2024, 132, 155740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Jing, B.; Chen, Z.N.; Li, X.; Shi, H.M.; Zheng, Y.C.; Chang, S.Q.; Gao, L.; Zhao, G.P. Ferulic acid alleviates sciatica by inhibiting neuroinflammation and promoting nerve repair via the TLR4/NF-kappaB pathway. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2023, 29, 1000–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, B.; Zhao, J.J.; Chen, Z.N.; Si, W.M.; Chang, S.Q.; Zheng, Y.C.; Zhuang, Z.F.; Zhao, G.P.; Zhang, D. ( +)-Catechin Alleviates CCI-Induced Neuropathic Pain by Modulating Microglia M1 and M2 Polarization via the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB Signaling Pathway. J. Neuroimmune Pharm. 2025, 20, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Yu, L.; Luo, J.; Huo, R.; Zhu, B. Paeonol induces the apoptosis of the SGC-7901 gastric cancer cell line by downregulating ERBB2 and inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 42, 1473–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, R.R.; Berta, T.; Nedergaard, M. Glia and pain: Is chronic pain a gliopathy? Pain 2013, 154 (Suppl. 1), S10–S28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, K.; Dubner, R. Interactions between the immune and nervous systems in pain. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 1267–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Xue, R.; Hassan, S.; Nguyen, T.M.L.; Wang, T.; Pan, H.; Xu, J.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, W.; Wen, Z. Il34-Csf1r Pathway Regulates the Migration and Colonization of Microglial Precursors. Dev. Cell 2018, 46, 552–563.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, W.; Chen, Z.; Bei, J.; Chang, S.; Zheng, Y.; Gao, L.; Zhao, G.; Li, X.; Zhang, D. Stigmasterol alleviates neuropathic pain by reducing Schwann cell-macrophage cascade in DRG by modulating IL-34/CSF1R. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2024, 30, e14657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, B.; Chen, Z.N.; Si, W.M.; Zhao, J.J.; Zhao, G.P.; Zhang, D. (+)-Catechin Alleviates CCI-Induced Neuropathic Pain in Rats by Modulating the IL34/CSFIR Axis and Attenuating the Schwann Cell-Macrophage Cascade Response in the DRG. Mol. Neurobiol. 2024, 61, 5027–5041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hauenstein, A.V. The NLRP3 inflammasome: Mechanism of action, role in disease and therapies. Mol. Asp. Med. 2020, 76, 100889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, N.; Jeltema, D.; Duan, Y.; He, Y. The NLRP3 inflammasome: An overview of mechanisms of activation and regulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhary, C.; Weinert, B.T.; Nishida, Y.; Verdin, E.; Mann, M. The growing landscape of lysine acetylation links metabolism and cell signalling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 536–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto-Diaz, K.; Vailati-Riboni, M.; Louie, A.Y.; McKim, D.B.; Gaskins, H.R.; Johnson, R.W.; Steelman, A.J. Treatment With the CSF1R Antagonist GW2580, Sensitizes Microglia to Reactive Oxygen Species. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 734349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteras, N.; Kopach, O.; Maiolino, M.; Lariccia, V.; Amoroso, S.; Qamar, S.; Wray, S.; Rusakov, D.A.; Jaganjac, M.; Abramov, A.Y. Mitochondrial ROS control neuronal excitability and cell fate in frontotemporal dementia. Alzheimers Dement. 2022, 18, 318–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Jing, B.; Chen, Z.; Li, X.; Shi, H.; Zheng, Y.; Chang, S.; Zhao, G. Ferulic acid alleviates sciatica by inhibiting peripheral sensitization through the RhoA/p38MAPK signalling pathway. Phytomedicine 2022, 106, 154420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
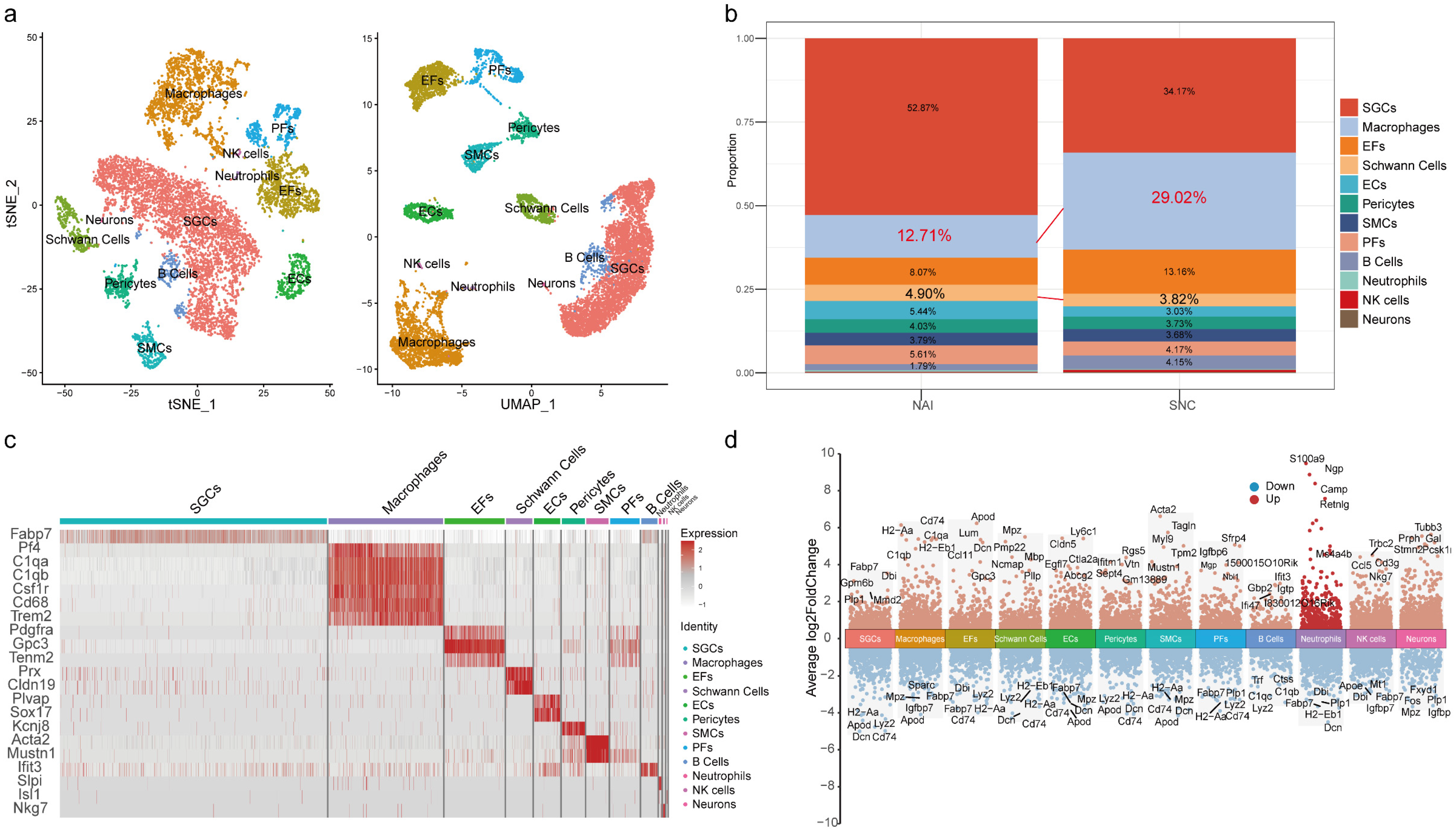

| Cell Types | Markers |
|---|---|
| SGCs | Fabp7 |
| Macrophages | Pf4, C1qa, C1qb, Csf1r, Cd68, Trem2 |
| EFs | Pdgfra |
| Schwann Cells | Prx, Cldn19 |
| ECs | Plvap, Sox17 |
| Pericytes | Kcnj8 |
| SMCs | Acta2, Mustn1 |
| PFs | Gpc3, Tenm2 |
| B Cells | Ifit3 |
| Neutrophils | Slpi |
| NK cells | Nkg7 |
| Neurons | Isl1 |
| Cell Types | Naive | SNC |
|---|---|---|
| SGCs | 52.87% (3282) | 34.17% (1467) |
| Macrophages | 12.71% (789) | 29.02% (1246) |
| EFs | 8.07% (501) | 13.16% (565) |
| Schwann Cells | 4.90% (304) | 3.82% (164) |
| ECs | 5.44% (338) | 3.03% (130) |
| Pericytes | 4.03% (250) | 3.73% (160) |
| SMCs | 3.79% (235) | 3.68% (158) |
| PFs | 5.61% (348) | 4.17% (179) |
| B Cells | 1.79% (111) | 4.15% (178) |
| Neutrophils | 0.53% (33) | 0.21% (9) |
| NK cells | 0.16% (10) | 0.61% (26) |
| Neurons | 0.11% (7) | 0.26% (11) |
| Gene | Forward Primer (5’->3’) | Reverse Primer (5’->3’) |
|---|---|---|
| β actin | CCTAGACTTCGAGCAAGAGA | GGAAGGAAGGCTGGAAGA |
| TNF-α | GCGTGTTCATCCGTTCTCTACC | TACTTCAGCGTCTCGTGTGTTTCT |
| Caspase1 | TGAAAGACAAGCCCAAGGT | GAAGAGCAGAAAAGGAAAAA |
| NLRP3 | CTGTCTCACATCTGCGTGTT | GTCTCCCAAGGCATTTTCT |
| IL-6 | AGTTGCCTTCTTGGGACTGATGT | GGTCTGTTGTGGGTGGTATCCTC |
| IL1β | AGGAGAGACAAGCAACGACA | CTTTTCCATCTTCTTCTTTGGGTAT |
| IL-18 | CTGGCTGTGACCCTATCTG | AAGCATCATCTTCCTTTTGG |
| ASC | AGACATCGGGAGGATTTTAC | GAGCACCACACTCAAGG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Zhuang, Z.; Hao, Y.; Lin, S.; Gu, J.; Chang, S.; Lan, L.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, D. Paeonol Relieves Chronic Neuropathic Pain by Reducing Communication Between Schwann Cells and Macrophages in the Dorsal Root Ganglia After Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3964. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26093964
Li X, Zhuang Z, Hao Y, Lin S, Gu J, Chang S, Lan L, Zhao G, Zhang D. Paeonol Relieves Chronic Neuropathic Pain by Reducing Communication Between Schwann Cells and Macrophages in the Dorsal Root Ganglia After Injury. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):3964. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26093964
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xin, Zifeng Zhuang, Yuting Hao, Shaozi Lin, Junyan Gu, Shiquan Chang, Lin Lan, Guoping Zhao, and Di Zhang. 2025. "Paeonol Relieves Chronic Neuropathic Pain by Reducing Communication Between Schwann Cells and Macrophages in the Dorsal Root Ganglia After Injury" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 3964. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26093964
APA StyleLi, X., Zhuang, Z., Hao, Y., Lin, S., Gu, J., Chang, S., Lan, L., Zhao, G., & Zhang, D. (2025). Paeonol Relieves Chronic Neuropathic Pain by Reducing Communication Between Schwann Cells and Macrophages in the Dorsal Root Ganglia After Injury. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 3964. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26093964





