Dibromo-Edaravone Induces Anti-Erythroleukemia Effects via the JAK2-STAT3 Signaling Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
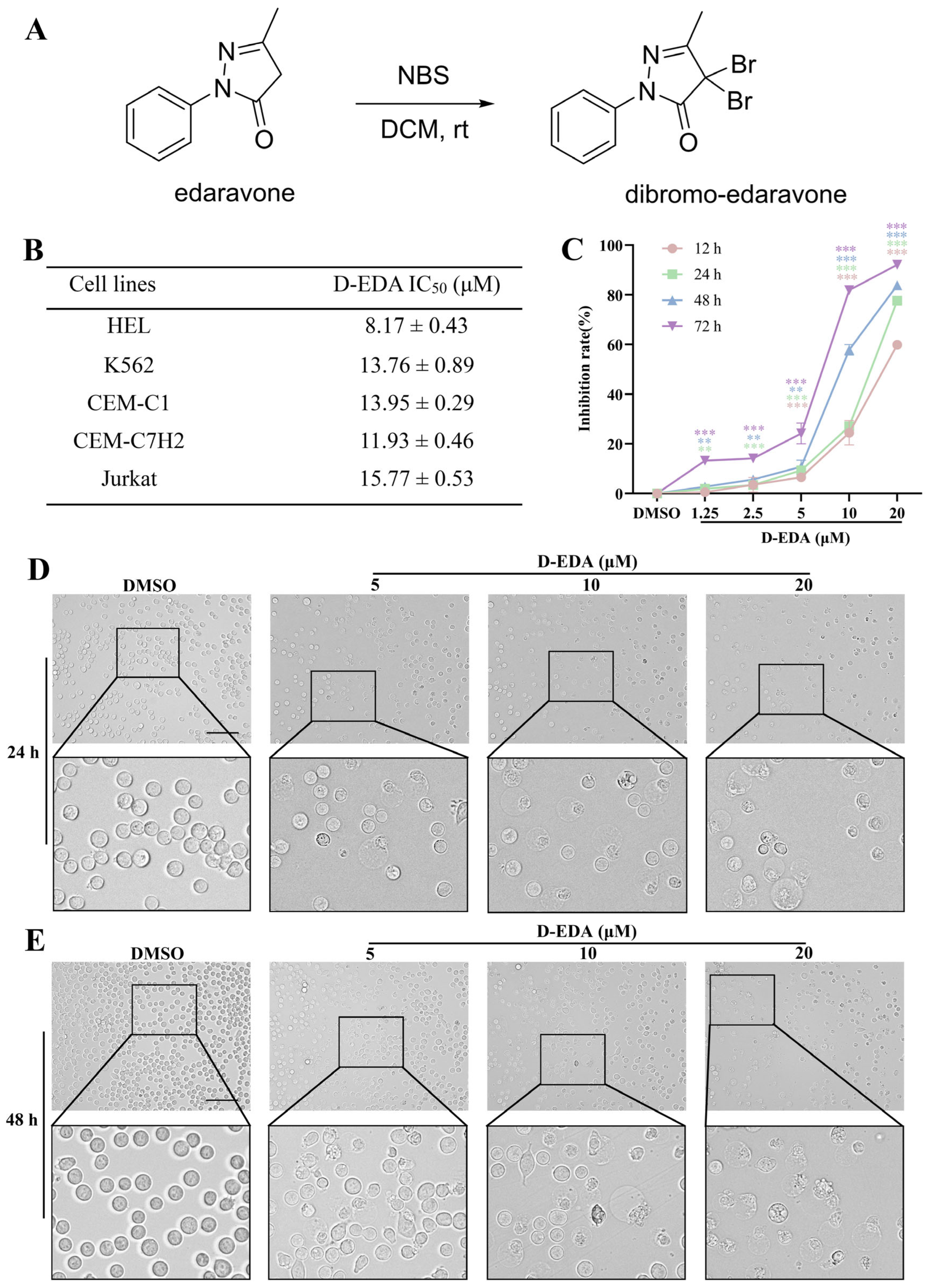
2.1. D-EDA Inhibits the Viability of HEL Cells
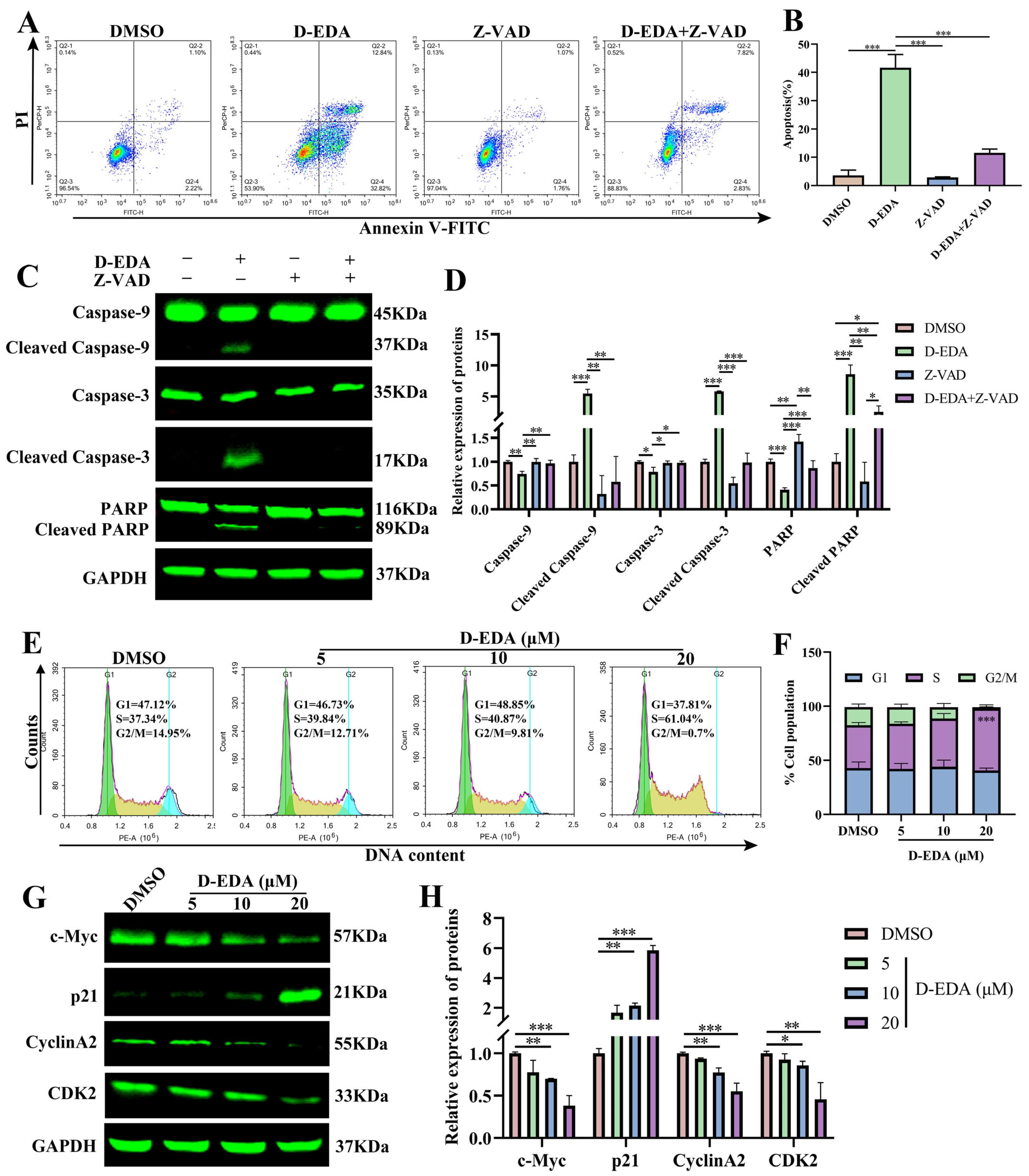
2.2. D-EDA Induces Apoptosis in HEL Cells
2.3. D-EDA Reduces HEL Cells’ MMP and Increases ROS Levels in HEL Cells
2.4. D-EDA Induces Apoptosis by Activating the Caspase Cascade Reaction and Blocking the S Phase Cycle in HEL Cells
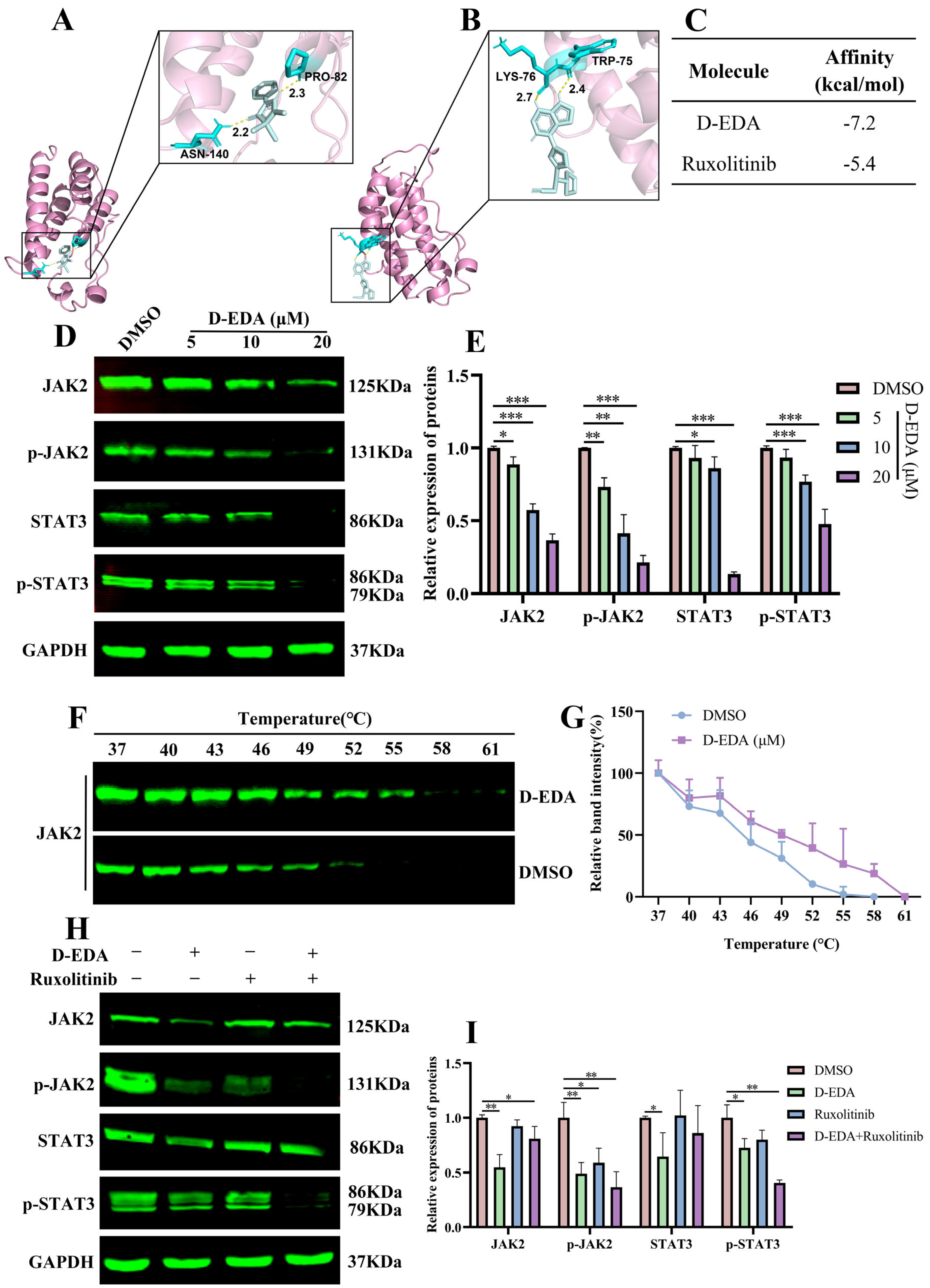
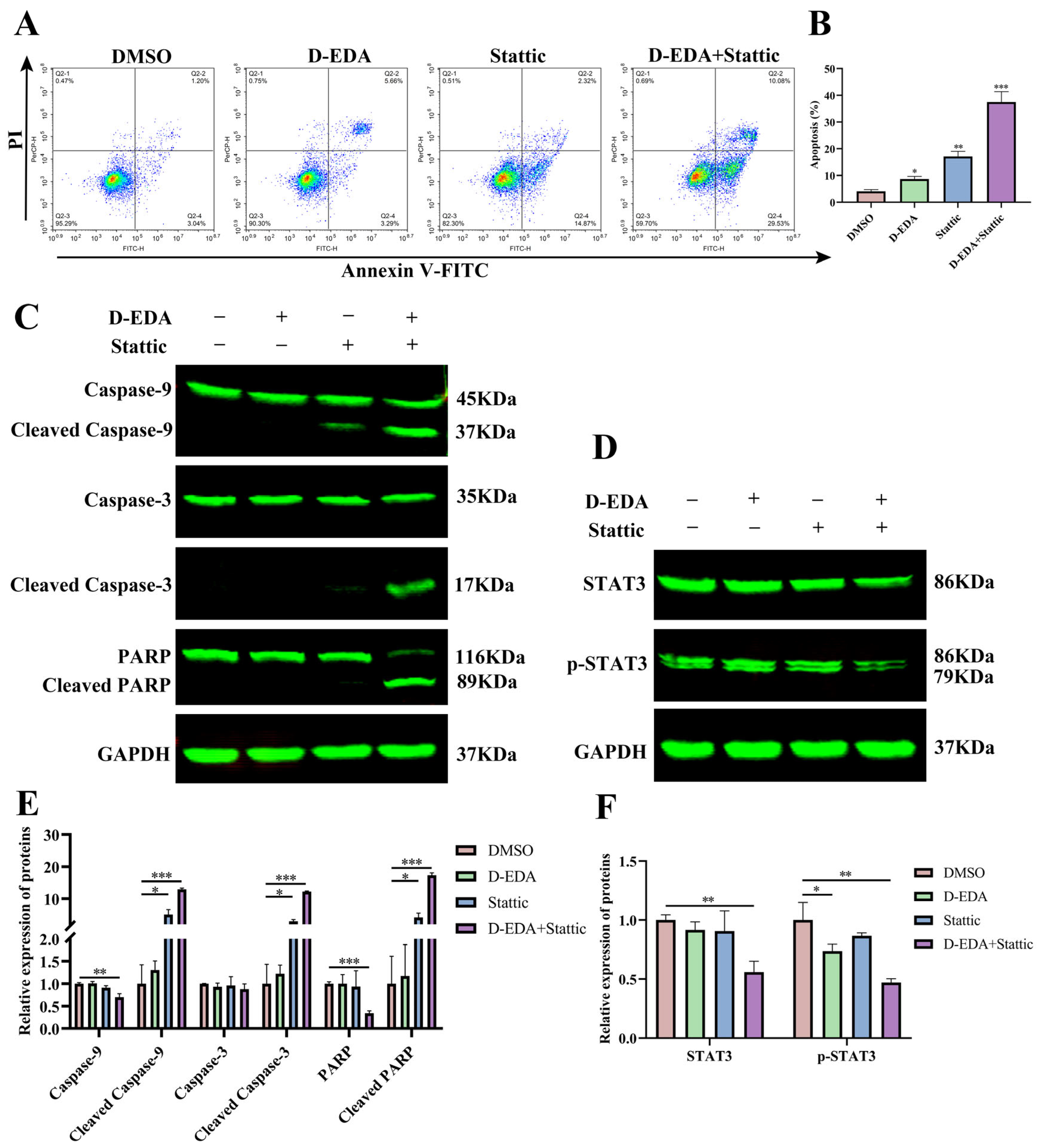
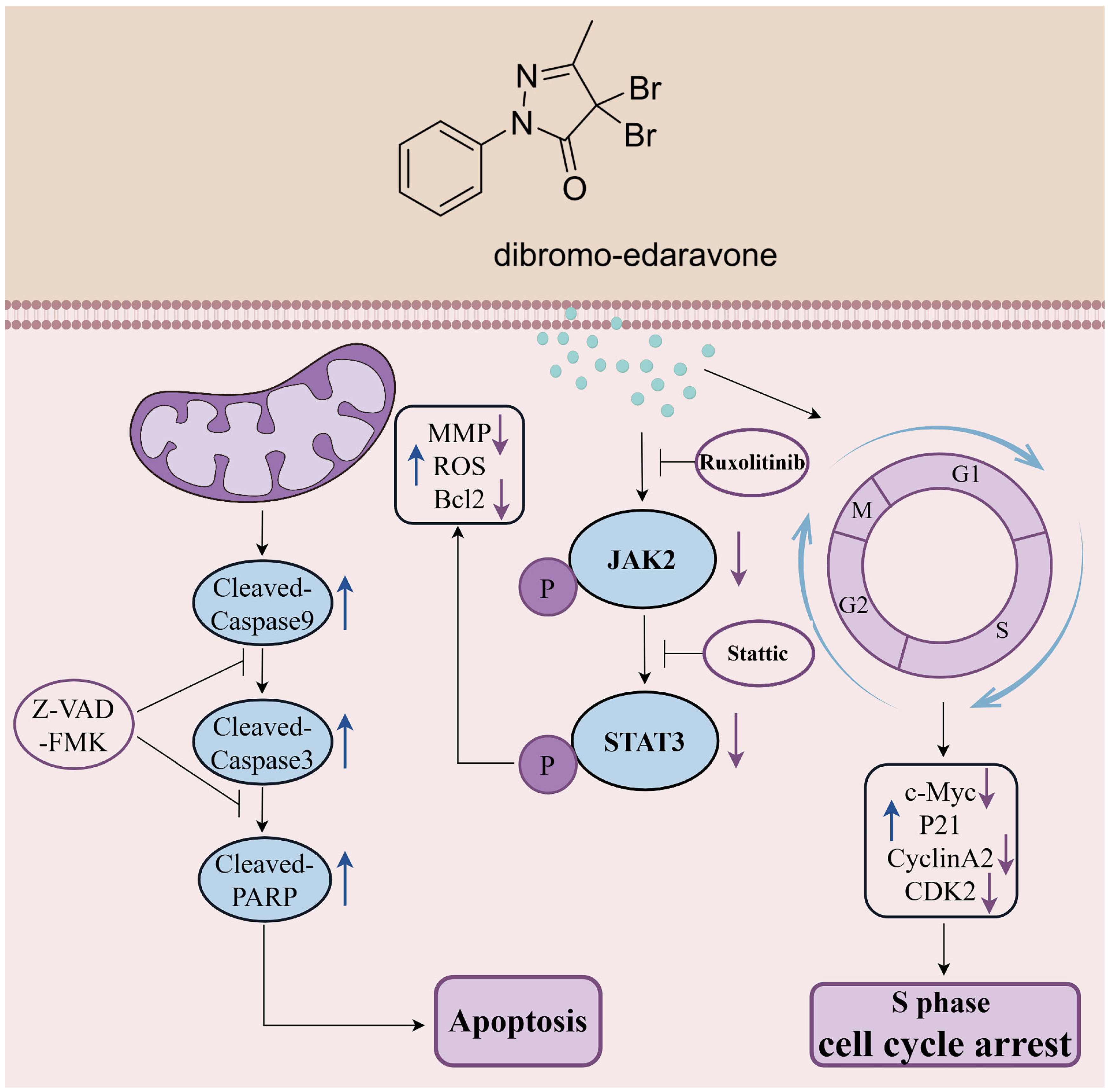
2.5. D-EDA Regulates the JAK2-STAT3 Signaling Pathway in HEL Cells
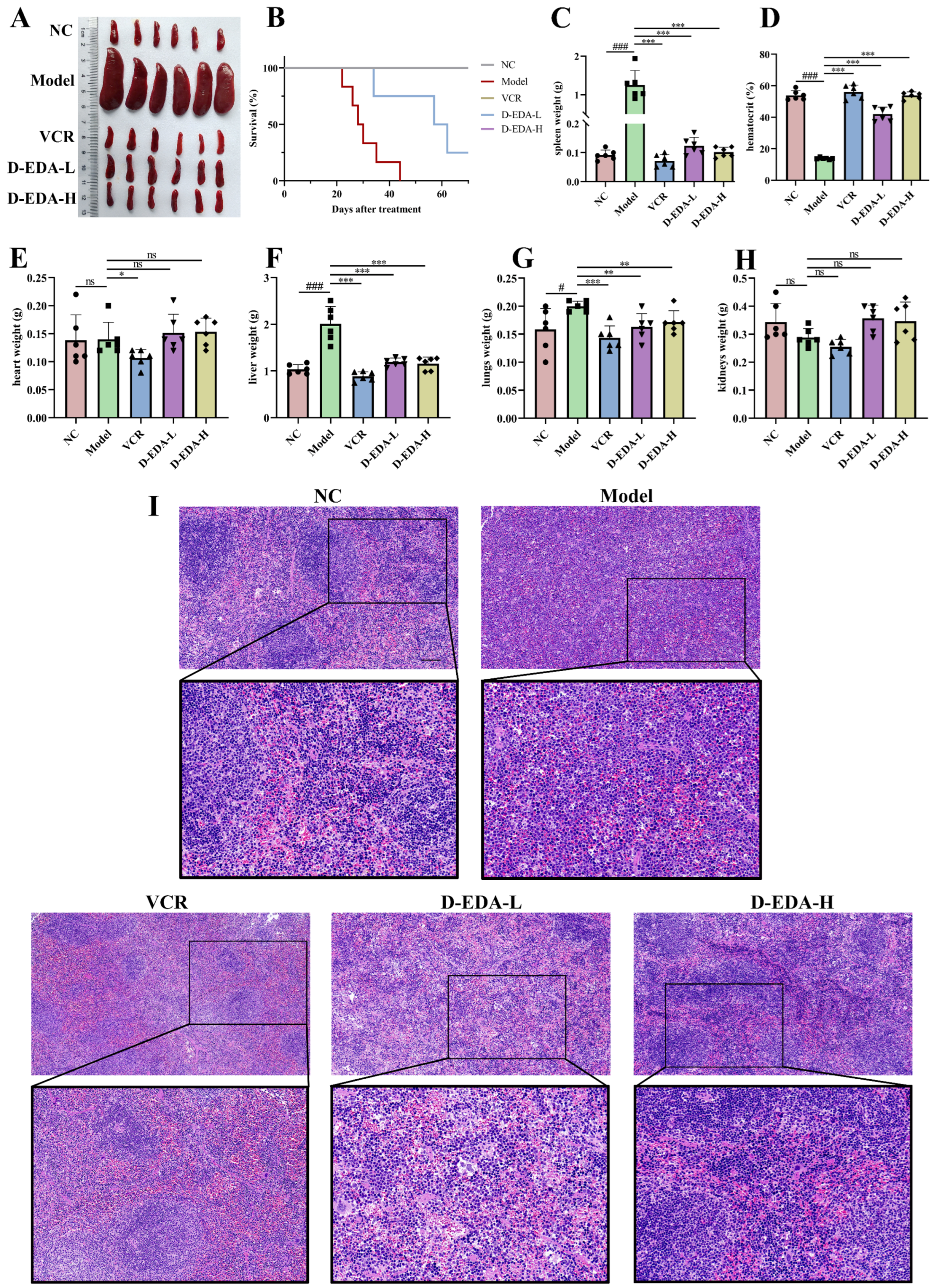
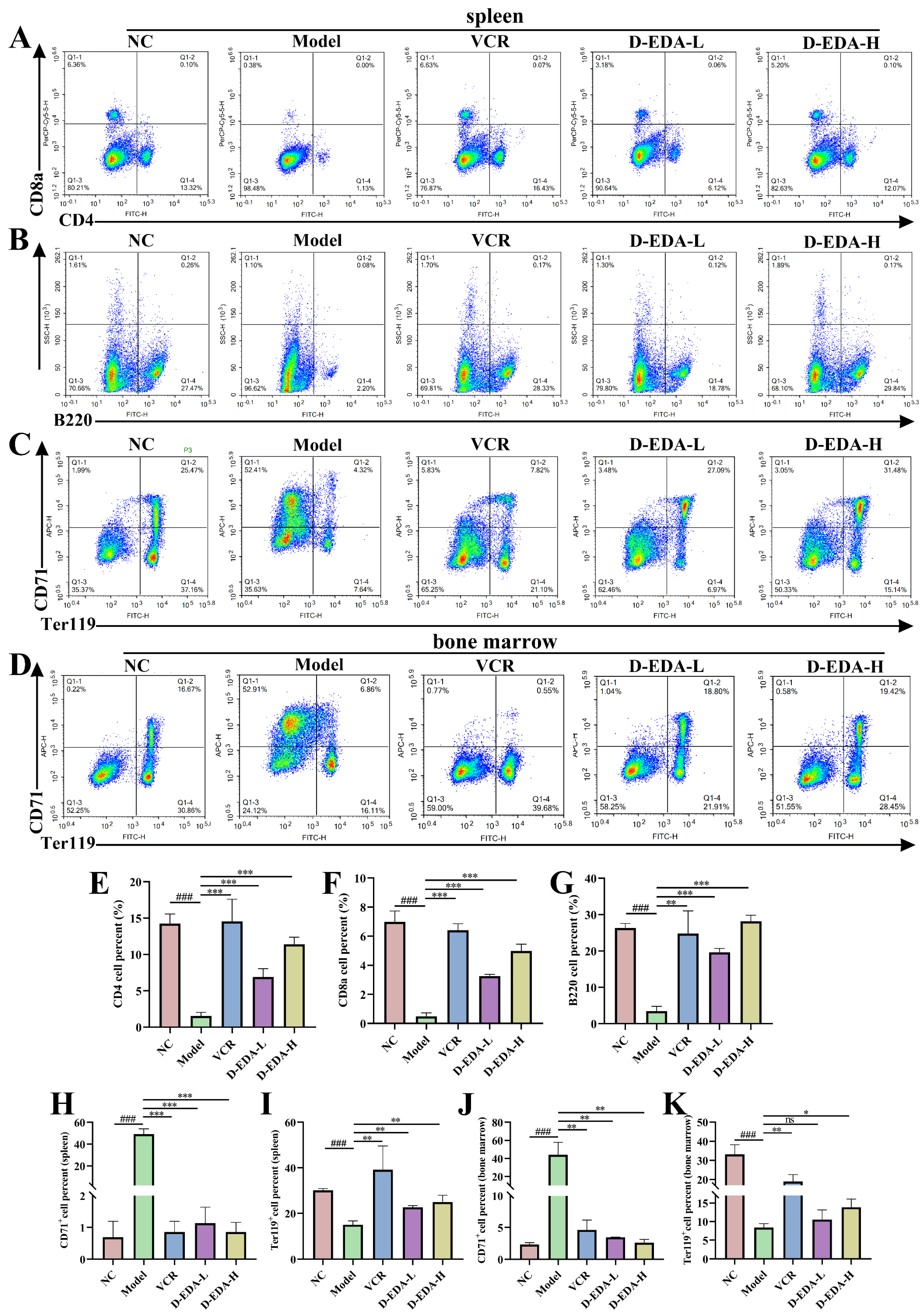
2.6. D-EDA Effectively Treats Mice with Acute Erythroleukemia
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Cell Viability Assays
4.3. Flow Cytometry Analysis of Apoptosis and Cell Cycle
4.4. Hoechst 33258 Staining
4.5. Mitochondrial Membrane Potential (MMP) Assay
4.6. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Assay
4.7. Western Blotting
4.8. Molecular Docking and Inhibitor Treatment
4.9. Cellular Thermal Shift Assay (CETSA)
4.10. In Vivo Experiment
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, N.; Wu, J.; Wang, Q.; Liang, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, G.; Ma, L.; Liu, X.; Zhou, F. Global burden of hematologic malignancies and evolution patterns over the past 30 years. Blood Cancer J. 2023, 13, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, P.; Waldron, N.; Chatzilygeroudi, T.; Naji, N.S.; Karantanos, T. Acute Erythroid Leukemia: From Molecular Biology to Clinical Outcomes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinberg, O.K.; Arber, D.A. Erythroleukemia: An Update. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2021, 23, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, C. A History and Current Understanding of Acute Erythroid Leukemia. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2023, 23, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteley, A.E.; Price, T.T.; Cantelli, G.; Sipkins, D.A. Leukaemia: A model metastatic disease. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2021, 21, 461–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; Li, J.; Wu, J.; Liu, J.; Sun, S. Chemotherapeutics for Acute Erythroid Leukemia: Research, Present and Future. Curr. Mol. Med. 2021, 21, 819–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, H.A.; Takatsuka, T.; Hada, Y.; Umebayashi, R.; Takeuchi, H.; Shikata, K.; Subramanian, V.; Daugherty, A.; Wada, J. Edaravone Attenuated Angiotensin II-Induced Atherosclerosis and Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms in Apolipoprotein E-Deficient Mice. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, M.K. Riluzole and edaravone: A tale of two amyotrophic lateral sclerosis drugs. Med. Res. Rev. 2019, 39, 733–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, R.; Wang, M.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Liu, L.; Wu, Q.; Zhao, J.; Ji, P.; Zhong, L.; Licinio, J.; et al. Edaravone ameliorates depressive and anxiety-like behaviors via Sirt1/Nrf2/HO-1/Gpx4 pathway. J. Neuroinflamm. 2022, 19, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duranti, E.; Cordani, N.; Villa, C. Edaravone: A Novel Possible Drug for Cancer Treatment? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W. Role of JAK/STAT3 Signaling in the Regulation of Metastasis, the Transition of Cancer Stem Cells, and Chemoresistance of Cancer by Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. Cells 2020, 9, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, K.L.; Brockwell, N.K.; Parker, B.S. JAK-STAT Signaling: A Double-Edged Sword of Immune Regulation and Cancer Progression. Cancers 2019, 11, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, C.; Yao, Q.; Gu, X.; Shi, Q.; Yuan, X.; Chu, Q.; Bao, Z.; Lu, J.; Li, L. Evolving cognition of the JAK-STAT signaling pathway: Autoimmune disorders and cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarino, A.V.; Kanno, Y.; O’Shea, J.J. Mechanisms and consequences of Jak–STAT signaling in the immune system. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamilloux, Y.; El Jammal, T.; Vuitton, L.; Gerfaud-Valentin, M.; Kerever, S.; Sève, P. JAK inhibitors for the treatment of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Autoimmun. Rev. 2019, 18, 102390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Li, J.; Fu, M.; Zhao, X.; Wang, W. The JAK/STAT signaling pathway: From bench to clinic. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agashe, R.P.; Lippman, S.M.; Kurzrock, R. JAK: Not Just Another Kinase. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2022, 21, 1757–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venugopal, S.; Bar-Natan, M.; Mascarenhas, J.O. JAKs to STATs: A tantalizing therapeutic target in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood Rev. 2020, 40, 100634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Dong, Q.; Zhang, S.; Feng, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhao, L. Acute myeloid leukemia (AML)-derived mesenchymal stem cells induce chemoresistance and epithelial–mesenchymal transition-like program in AML through IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 signaling. Cancer Sci. 2023, 114, 3287–3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E Sabaawy, H.; Ryan, B.M.; Khiabanian, H.; Pine, S.R. JAK/STAT of all trades: Linking inflammation with cancer development, tumor progression and therapy resistance. Carcinogenesis 2021, 42, 1411–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Ofengeim, D. A guide to cell death pathways. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2024, 25, 379–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Ye, X.; Xiong, Z.; Ihsan, A.; Ares, I.; Martínez, M.; Lopez-Torres, B.; Martínez-Larrañaga, M.-R.; Anadón, A.; Wang, X.; et al. Cancer Metabolism: The Role of ROS in DNA Damage and Induction of Apoptosis in Cancer Cells. Metabolites 2023, 13, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferri, K.F.; Kroemer, G. Mitochondria—The suicide organelles, BioEssays: News and reviews in molecular. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2001, 23, 111–115. [Google Scholar]
- Ayele, T.M.; Muche, Z.T.; Teklemariam, A.B.; Bogale, A.; Abebe, E.C. Role of JAK2/STAT3 Signaling Pathway in the Tumorigenesis, Chemotherapy Resistance, and Treatment of Solid Tumors: A Systemic Review. J. Inflamm. Res. 2022, 15, 1349–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rawashde, F.A.; Al-Sanabra, O.M.; Alqaraleh, M.; Jaradat, A.Q.; Al-Wajeeh, A.S.; Johan, M.F.; Taib, W.R.W.; Ismail, I.; Al-Jamal, H.A.N. Thymoquinone Enhances Apoptosis of K562 Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Cells through Hypomethylation of SHP-1 and Inhibition of JAK/STAT Signaling Pathway. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Z.; Polski, J.M.; Kasyan, A.; Medeiros, L.J. Acute erythroid leukemia. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2010, 134, 1261–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mushtaq, A.; Wu, P.; Naseer, M.M. Recent drug design strategies and identification of key heterocyclic scaffolds for promising anticancer targets. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, 254, 108579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, K.; Strasser, A.; Kayagaki, N.; Dixit, V.M. Cell death. Cell 2024, 187, 235–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketelut-Carneiro, N.; Fitzgerald, K.A. Apoptosis, Pyroptosis, and Necroptosis—Oh My! The Many Ways a Cell Can Die. J. Mol. Biol. 2022, 434, 167378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gielecińska, A.; Kciuk, M.; Yahya, E.-B.; Ainane, T.; Mujwar, S.; Kontek, R. Apoptosis, necroptosis, and pyroptosis as alternative cell death pathways induced by chemotherapeutic agents? Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Rev. Cancer 2023, 1878, 189024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, B.A.; El-Deiry, W.S. Targeting apoptosis in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 395–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertheloot, D.; Latz, E.; Franklin, B.S. Necroptosis, pyroptosis and apoptosis: An intricate game of cell death. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 1106–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Kanneganti, T.-D. From pyroptosis, apoptosis and necroptosis to PANoptosis: A mechanistic compendium of programmed cell death pathways. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 4641–4657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czabotar, P.E.; Garcia-Saez, A.J. Mechanisms of BCL-2 family proteins in mitochondrial apoptosis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2023, 24, 732–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Noorden, C.J. The history of Z-VAD-FMK, a tool for understanding the significance of caspase inhibition. Acta Histochem. 2001, 103, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.K.; Chaudhuri, O. Mechanical regulation of cell-cycle progression and division. Trends Cell Biol. 2022, 32, 773–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligasová, A.; Frydrych, I.; Koberna, K. Basic Methods of Cell Cycle Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzbekov, R.; Prigent, C. A Journey through Time on the Discovery of Cell Cycle Regulation. Cells 2022, 11, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, H.K.; Bertoli, C.; de Bruin, R.A.M. Cell cycle control in cancer. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2022, 23, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Chang, X.; MacIsaac, H.J.; Wen, J.; Zhao, L.; Dai, Z.; Li, J. Phytosphingosine inhibits cell proliferation by damaging DNA in human cell lines. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 256, 114840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.; Jiang, X. p21-Activated kinases as promising therapeutic targets in hematological malignancies. Leukemia 2022, 36, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llombart, V.; Mansour, M.R. Therapeutic targeting of “undruggable” MYC. eBioMedicine 2022, 75, 103756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philips, R.L.; Wang, Y.; Cheon, H.; Kanno, Y.; Gadina, M.; Sartorelli, V.; Horvath, C.M.; Darnell, J.E.; Stark, G.R.; O’shea, J.J. The JAK-STAT pathway at 30: Much learned, much more to do. Cell 2022, 185, 3857–3876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liao, S.; Bennett, S.; Tang, H.; Song, D.; Wood, D.; Zhan, X.; Xu, J. STAT3 and its targeting inhibitors in osteosarcoma. Cell Prolif. 2021, 54, e12974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Tang, H.; Song, C.; Yan, Z.; Liang, Y.; Wang, H. JAK/STAT in leukemia: A clinical update. Mol. Cancer 2024, 23, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasouli, E.S.; Katsantoni, E. JAK-STAT in Early Hematopoiesis and Leukemia. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 669363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- How, J.; Garcia, J.S.; Mullally, A. Biology and therapeutic targeting of molecular mechanisms in MPNs. Blood 2023, 141, 1922–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roskoski, R., Jr. Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors in the treatment of neoplastic and inflammatory disorders. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 183, 106362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.-L.; Chen, H.-Y.; Yen, J.-C.; Yu, S.-J.; Chou, T.-Y.; Yeh, S.-W.; Chuang, H.-Y.; Huang, F.-L. Stattic suppresses p-STAT3 and induces cell death in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Mol. Med. Rep. 2025, 31, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Han, Y.; Duan, H.; Song, W.; Tian, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, G.; Wu, C.; et al. Eleutheroside B alleviates oxidative stress and neuroinflammation by inhibiting the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway in a rat high altitude cerebral edema model. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1506483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-David, Y.; Giddens, E.B.; Bernstein, A. Identification and mapping of a common proviral integration site Fli-1 in erythroleukemia cells induced by Friend murine leukemia virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 1332–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Wang, B.; Mou, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, Q.; Pu, W.; Rao, Q.; Wang, C.; Song, J.; Huang, Y.; et al. Design, Synthesis, and Anti-Leukemic Evaluation of a Series of Dianilinopyrimidines by Regulating the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK and STAT3/c-Myc Pathways. Molecules 2024, 29, 1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Q.; Liu, S.; Wei, X.; Zhao, P.; Tian, F.; Yang, K.; Song, J.; Huang, Y.; Wen, M.; Song, J.; et al. Dibromo-Edaravone Induces Anti-Erythroleukemia Effects via the JAK2-STAT3 Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4000. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094000
Chen Q, Liu S, Wei X, Zhao P, Tian F, Yang K, Song J, Huang Y, Wen M, Song J, et al. Dibromo-Edaravone Induces Anti-Erythroleukemia Effects via the JAK2-STAT3 Signaling Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):4000. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094000
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Qiqing, Sheng Liu, Xuenai Wei, Peng Zhao, Fen Tian, Kang Yang, Jingrui Song, Yubing Huang, Min Wen, Jialei Song, and et al. 2025. "Dibromo-Edaravone Induces Anti-Erythroleukemia Effects via the JAK2-STAT3 Signaling Pathway" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 4000. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094000
APA StyleChen, Q., Liu, S., Wei, X., Zhao, P., Tian, F., Yang, K., Song, J., Huang, Y., Wen, M., Song, J., Jian, Y., & Li, Y. (2025). Dibromo-Edaravone Induces Anti-Erythroleukemia Effects via the JAK2-STAT3 Signaling Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 4000. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094000




