Synergistic Effects of Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 and Platelet-Derived Growth Factor-BB in Tendon Healing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
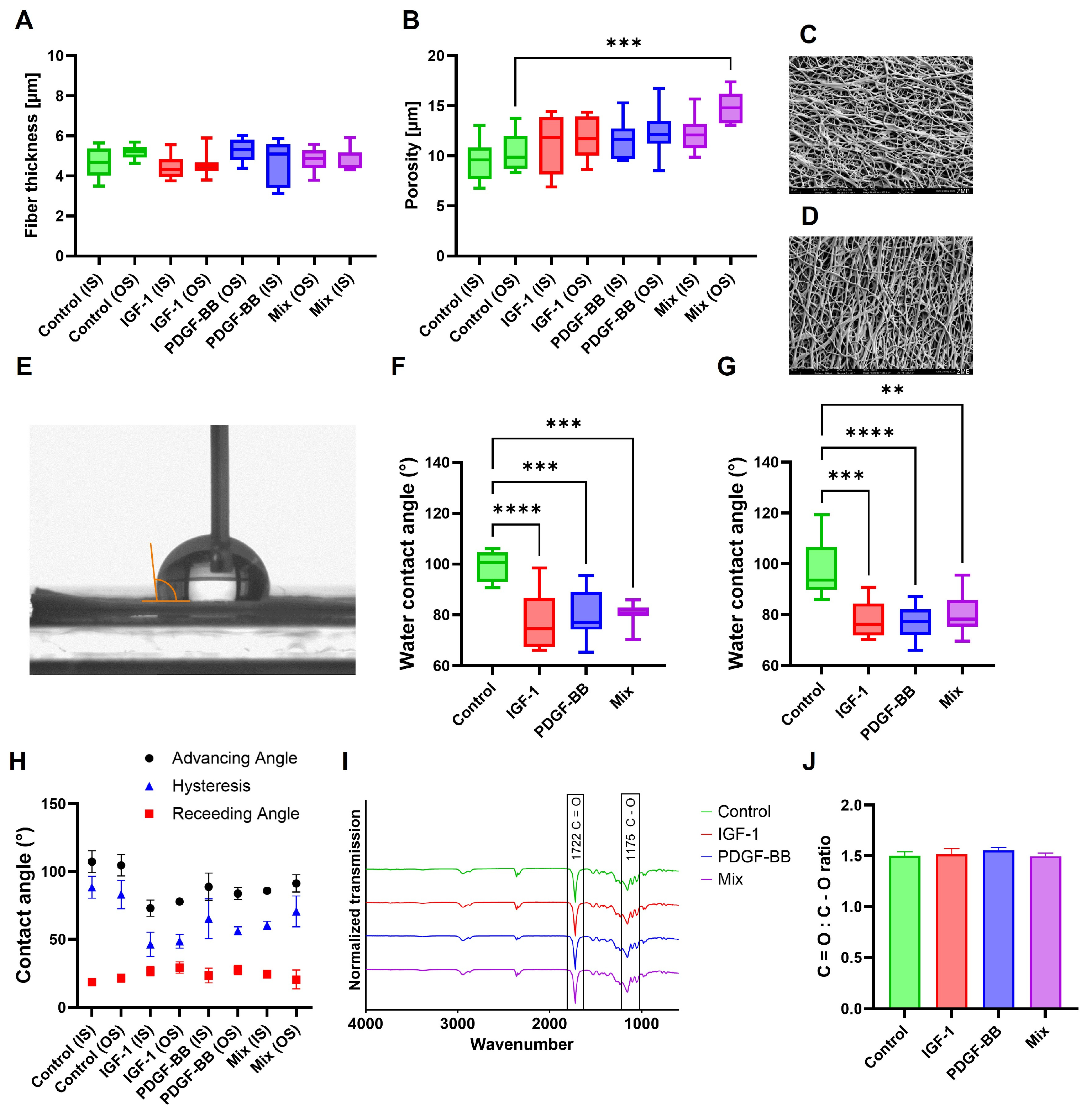
2.1. Charcterization of DP Scaffolds
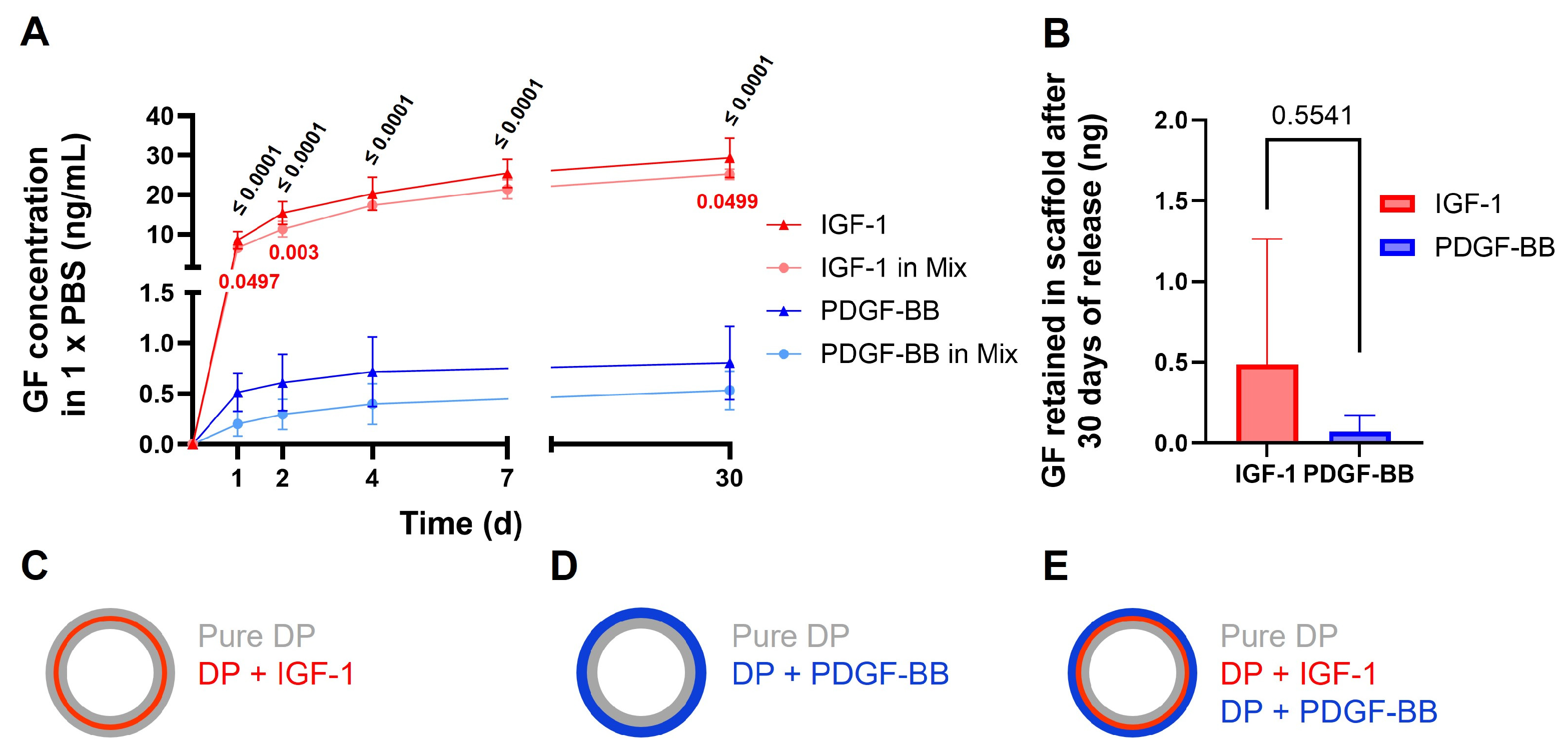
2.2. Release of GF from Scaffolds
2.3. Gene Expression Analysis
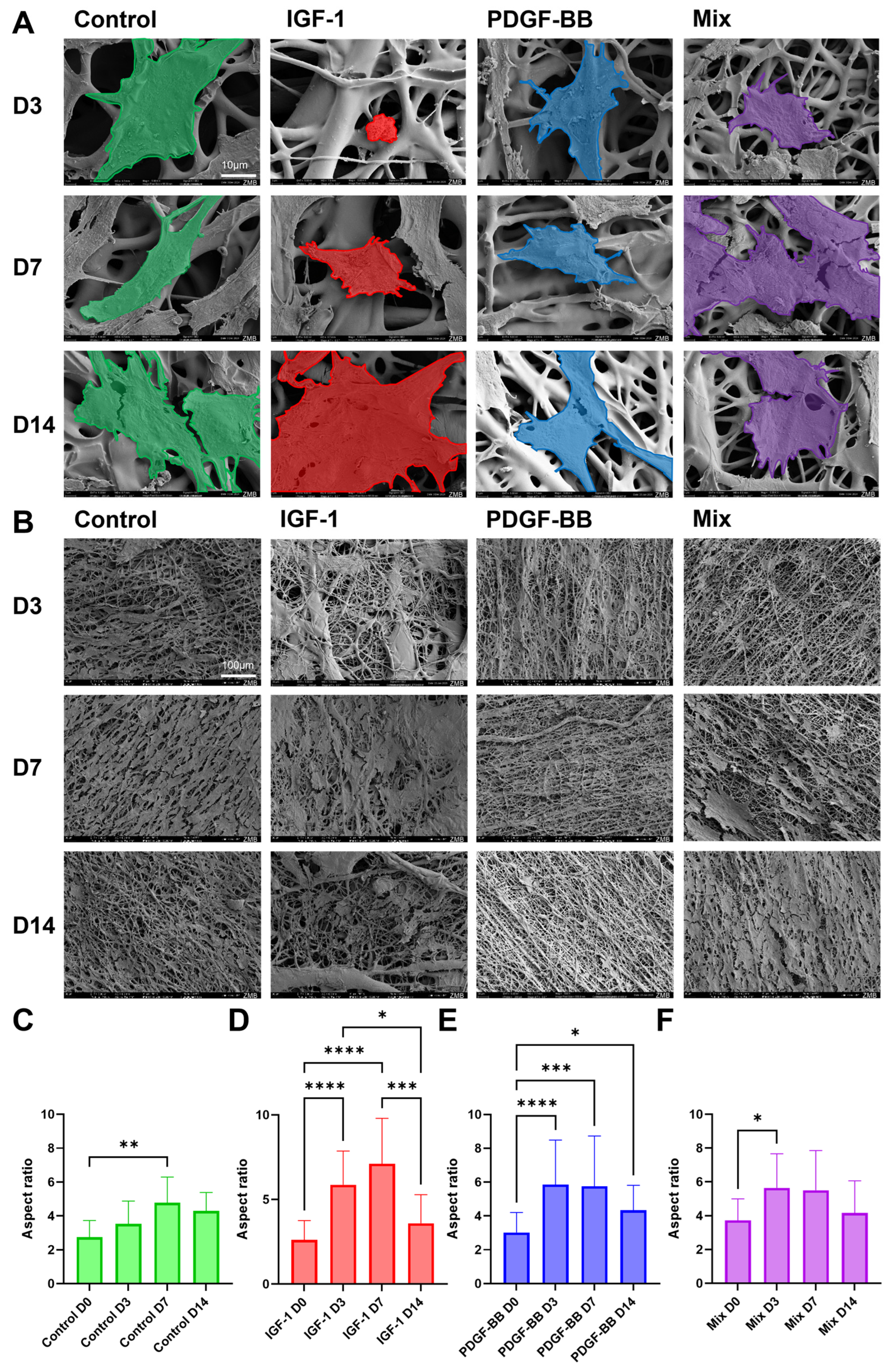
2.4. Cell Seeding on Scaffolds
2.5. Aspect Ratio
2.6. Metabolic Analysis with Seahorse
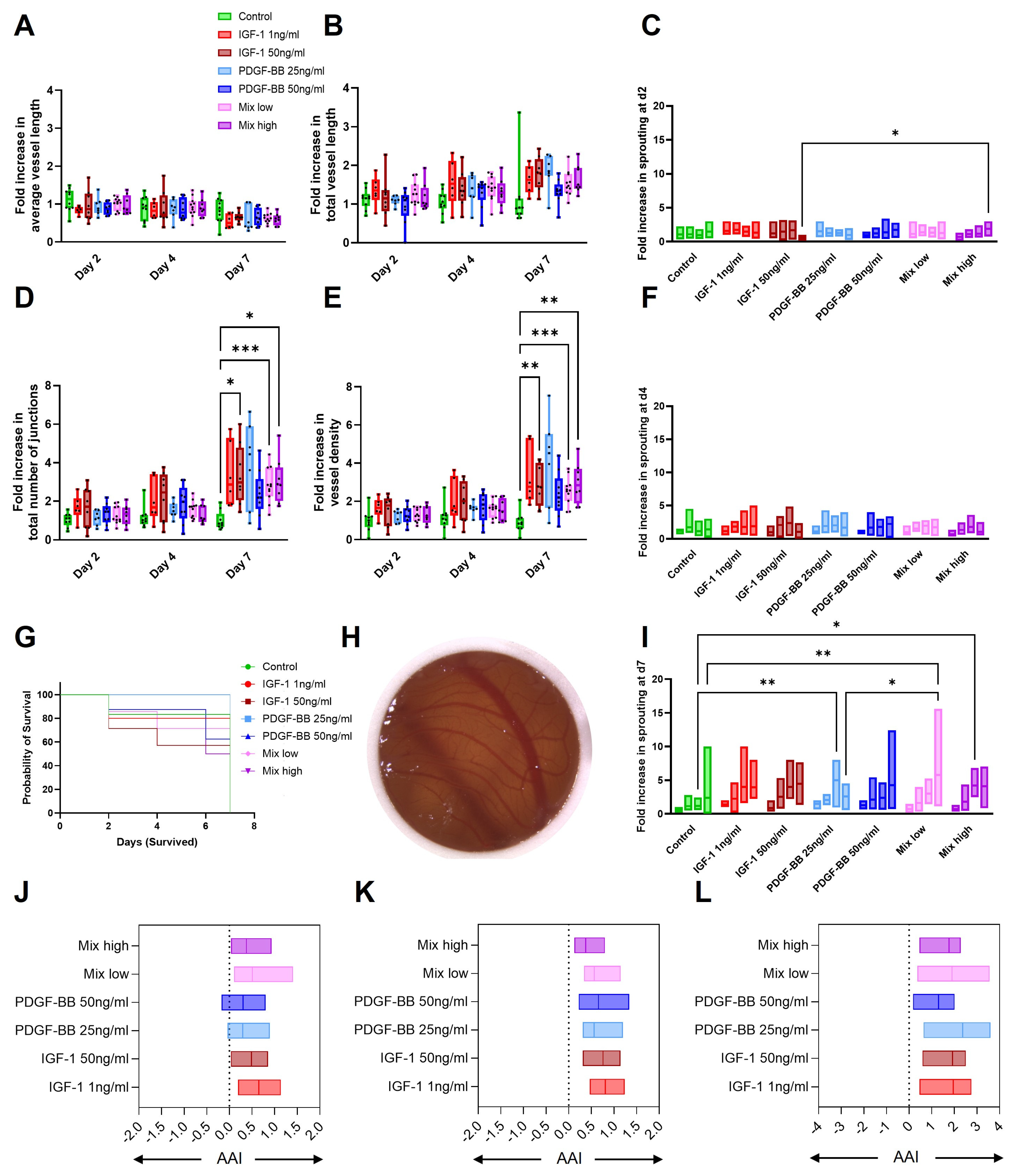
2.7. CAM Assay
2.8. In Vivo Mechanical Testing
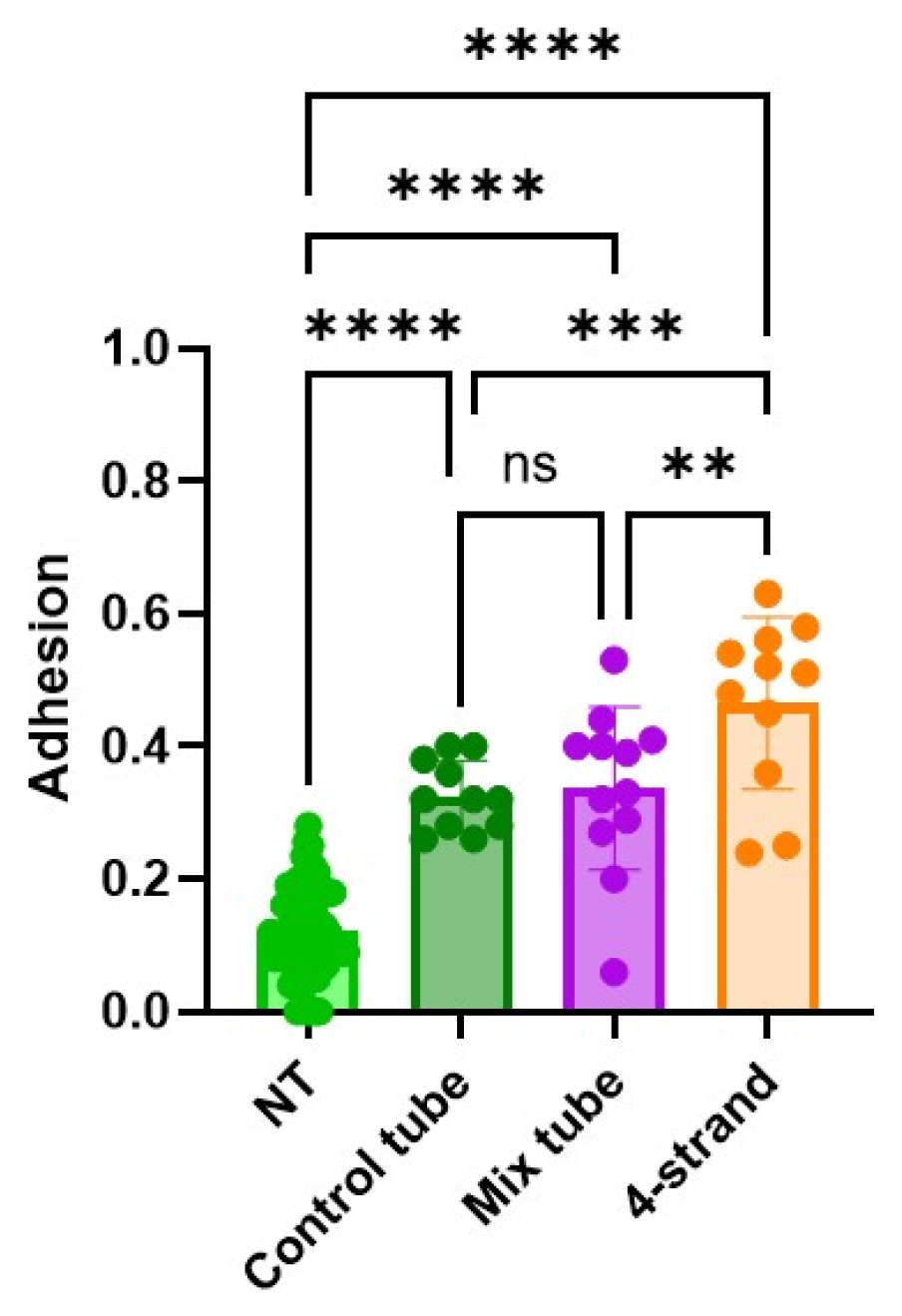
2.9. Adhesion
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Synthesis of DegraPol® (DP)
4.2. Scaffold Production and Incorporation of GFs
4.3. SEM Fiber and Pore Size Analysis
4.4. WCA Evaluation
4.5. FTIR Analysis
4.6. Release and Lipase Assay
4.7. Cell Culture (Including Image Capture, Aspect Ratio, AB, and qPCR)
4.8. Cell Seeding on Different Scaffolds
4.9. Seahorse
4.10. CAM
4.11. In Vivo Experiments: Biomechanics and Adhesion Extent
4.12. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leong, N.L.; Kator, J.L.; Clemens, T.L.; James, A.; Enamoto-Iwamoto, M.; Jiang, J. Tendon and Ligament Healing and Current Approaches to Tendon and Ligament Regeneration. J. Orthop. Res. 2020, 38, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Liu, S.; Fan, C. Applications of functionally-adapted hydrogels in tendon repair. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1135090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Jiang, L.; Lyu, K.; Lu, J.; Long, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, T.; Li, S. A Promising Candidate in Tendon Healing Events—PDGF-BB. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, X.; Peng, Y.; Zhu, B.; Guo, S.; Wang, C.; Wang, D.; Li, S. Transforming growth factor-β signalling pathway in tendon healing. Growth Factors 2022, 40, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, M.; Li, W.; Ni, X.; Sui, Y.; Li, H.; Chen, X.; Lu, Y.; Jiang, M.; Wang, C. Growth factors in the treatment of Achilles tendon injury. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1250533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hope, M.; Saxby, T.S. Tendon healing. Foot Ankle Clin. 2007, 12, 553–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molloy, T.; Wang, Y.; Murrell, G. The roles of growth factors in tendon and ligament healing. Sports Med. 2003, 33, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, T.; Zhang, T.; Ju, W.; Chen, X.; Heng, B.C.; Shen, W.; Yin, Z. Biomimetic strategies for tendon/ligament-to-bone interface regeneration. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 2491–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nourissat, G.; Berenbaum, F.; Duprez, D. Tendon injury: From biology to tendon repair. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2015, 11, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montaseri, A.; Busch, F.; Mobasheri, A.; Buhrmann, C.; Aldinger, C.; Rad, J.S.; Shakibaei, M. IGF-1 and PDGF-bb Suppress IL-1β-Induced Cartilage Degradation through Down-Regulation of NF-κB Signaling: Involvement of Src/PI-3K/AKT Pathway. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yang, T.; Ding, L.; Ye, X.; Wu, L. Platelet-derived growth factor AA-modified electrospun fibers promote tendon healing. J. Biomater. Appl. 2023, 37, 1018–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.-J.; Chen, L.; Wu, S.-K.; Wu, Y.-J.; Pang, Q.-J. rhPDGF-BB combined with ADSCs in the treatment of Achilles tendinitis via miR-363/PI3 K/Akt pathway. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 438, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, S.A.; Todorov, A.; Heisterbach, P.E.; Martin, I.; Majewski, M. Tendon healing: An overview of physiology, biology, and pathology of tendon healing and systematic review of state of the art in tendon bioengineering. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2015, 23, 2097–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evrova, O.; Buschmann, J. In vitro and in vivo effects of PDGF-BB delivery strategies on tendon healing: A review. Eur. Cell Mater. 2017, 34, 15–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, C.A.; Loebig, T.G.; Anderson, D.D.; DeMeo, P.J.; Campbell, P.G. Insulin-like growth factor I accelerates functional recovery from Achilles tendon injury in a rat model. Am. J. Sports Med. 1999, 27, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, U.G.; Lamberti, A.; Petrillo, S.; Maffulli, N.; Denaro, V. Scaffolds in Tendon Tissue Engineering. Stem Cells Int. 2012, 2012, 517165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmerling, K.A.; McQuilling, J.P.; Staples, M.C.; Mowry, K.C. Tenocyte cell density, migration, and extracellular matrix deposition with amniotic suspension allograft. J. Orthop. Res. 2019, 37, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalski, P.S.; Bhattacharya, C.; Afewerki, S.; Langer, R. Smart Biomaterials: Recent Advances and Future Directions. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 4, 3809–3817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Yoon, J.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Park, K.; Kim, S.E. Long-term local PDGF delivery using porous microspheres modified with heparin for tendon healing of rotator cuff tendinitis in a rabbit model. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 209, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, S.H.; Grande, D.A.; Hee, C.K.; Kestler, H.K.; Roden, C.M.; Shah, N.V.; Razzano, P.; Dines, D.M.; Chahine, N.O.; Dines, J.S. Effect of recombinant human platelet-derived growth factor-BB-coated sutures on Achilles tendon healing in a rat model: A histological and biomechanical study. J. Tissue Eng. 2012, 3, 204173141245357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Yao, L.; Li, M.; Zhang, X.; Weng, B.; Zhu, W.; Ni, R.; Chen, K.; Yi, L.; Zhao, J.; et al. Enhancement of Tendon Repair Using Tendon-Derived Stem Cells in Small Intestinal Submucosa via M2 Macrophage Polarization. Cells 2022, 11, 2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evrova, O.; Houska, J.; Welti, M.; Bonavoglia, E.; Calcagni, M.; Giovanoli, P.; Vogel, V.; Buschmann, J. Bioactive, Elastic, and Biodegradable Emulsion Electrospun DegraPol Tube Delivering PDGF-BB for Tendon Rupture Repair. Macromol. Biosci. 2016, 16, 1048–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rieber, J.; Meier-Bürgisser, G.; Miescher, I.; Weber, F.E.; Wolint, P.; Yao, Y.; Ongini, E.; Milionis, A.; Snedeker, J.G.; Calcagni, M.; et al. Bioactive and Elastic Emulsion Electrospun DegraPol Tubes Delivering IGF-1 for Tendon Rupture Repair. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolint, P.; Hofmann, S.; Von Atzigen, J.; Böni, R.; Miescher, I.; Giovanoli, P.; Calcagni, M.; Emmert, M.Y.; Buschmann, J. Standardization to Characterize the Complexity of Vessel Network Using the Aortic Ring Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 26, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Maffulli, N. Biology of tendon injury: Healing, modeling and remodeling. J. Musculoskelet. Neuronal Interact. 2006, 6, 181–190. [Google Scholar]
- Docheva, D.; Muller, S.A.; Majewski, M.; Evans, C.H. Biologics for tendon repair. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2015, 84, 222–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, C.M.; Vartivarian, M. Achilles Tendon Rupture Repair: Simple to Complex. Clin. Podiatr. Med. Sur. 2023, 40, 75–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze-Tanzil, G.G.; Delgado Cáceres, M.; Stange, R.; Wildemann, B.; Docheva, D. Tendon healing: A concise review on cellular and molecular mechanisms with a particular focus on the Achilles tendon. Bone Jt. Res. 2022, 11, 561–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parekh, S.G.; Aran, F.S.; Mithani, S.; Chopra, A. Achilles: Failed Acute Repair. Foot Ankle Clin. 2022, 27, 415–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chartier, C.; Elhawary, H.; Baradaran, A.; Vorstenbosch, J.; Xu, L.; Efanov, J.I. Tendon: Principles of Healing and Repair. Semin. Plast. Surg. 2021, 35, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miescher, I.; Schaffner, N.; Rieber, J.; Bürgisser, G.M.; Ongini, E.; Yang, Y.; Milionis, A.; Vogel, V.; Snedeker, J.G.; Calcagni, M.; et al. Hyaluronic acid/PEO electrospun tube reduces tendon adhesion to levels comparable to native tendons—An in vitro and in vivo study. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 273, 133193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evrova, O.; Burgisser, G.M.; Ebnother, C.; Adathala, A.; Calcagni, M.; Bachmann, E.; Snedeker, J.G.; Scalera, C.; Giovanoli, P.; Vogel, V.; et al. Elastic and surgeon friendly electrospun tubes delivering PDGF-BB positively impact tendon rupture healing in a rabbit Achilles tendon model. Biomaterials 2020, 232, 119722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, M.A.; Wu, C.; Pham, B.V.; Chong, A.K.S.; Pham, H.M.; Chang, J. Tissue Engineering of Flexor Tendons: Optimization of Tenocyte Proliferation Using Growth Factor Supplementation. Tissue Eng. 2006, 12, 1937–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herchenhan, A.; Bayer, M.L.; Eliasson, P.; Magnusson, S.P.; Kjaer, M. Insulin-like growth factor I enhances collagen synthesis in engineered human tendon tissue. Growth Horm. IGF Res. 2015, 25, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsiapalis, D.; Kearns, S.; Kelly, J.L.; Zeugolis, D.I. Growth factor and macromolecular crowding supplementation in human tenocyte culture. Biomater. Biosyst. 2021, 1, 100009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durgam, S.S.; Stewart, A.A.; Pondenis, H.C.; Gutierrez-Nibeyro, S.M.; Evans, R.B.; Stewart, M.C. Comparison of equine tendon- and bone marrow–derived cells cultured on tendon matrix with or without insulin-like growth factor-I supplementation. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2012, 73, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Fukui, M.; Taketani, S.; Kako, A.; Kunieda, S.; Kakudo, N. Predominant control of PDGF/PDGF receptor signaling in the migration and proliferation of human adipose-derived stem cells under culture conditions with a combination of growth factors. Exp. Ther. Med. 2024, 27, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evrova, O.; Kellenberger, D.; Calcagni, M.; Vogel, V.; Buschmann, J. Supporting Cell-Based Tendon Therapy: Effect of PDGF-BB and Ascorbic Acid on Rabbit Achilles Tenocytes in Vitro. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier Burgisser, G.; Evrova, O.; Calcagni, M.; Scalera, C.; Giovanoli, P.; Buschmann, J. Impact of PDGF-BB on cellular distribution and extracellular matrix in the healing rabbit Achilles tendon three weeks post-operation. FEBS Open Bio 2020, 10, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laron, Z. Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1): A growth hormone. Mol. Pathol. 2001, 54, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.; Won, Y.-Y. Phenomenology of the Initial Burst Release of Drugs from PLGA Microparticles. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 6053–6062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulotta, L.V.; Rodeo, S.A. Growth Factors for Rotator Cuff Repair. Clin. Sports Med. 2009, 28, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhmetova, A.; Heinz, A. Electrospinning Proteins for Wound Healing Purposes: Opportunities and Challenges. Pharmaceutics 2020, 13, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eral, H.B.; ’T Mannetje, D.J.C.M.; Oh, J.M. Contact angle hysteresis: A review of fundamentals and applications. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2013, 291, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Korschelt, K.; Viel, M.; Wiesmann, N.; Kappl, M.; Brieger, J.; Landfester, K.; Thérien-Aubin, H.; Tremel, W. Nanozymes in Nanofibrous Mats with Haloperoxidase-like Activity To Combat Biofouling. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 44722–44730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teimouri, R.; Abnous, K.; Taghdisi, S.M.; Ramezani, M.; Alibolandi, M. Surface modifications of scaffolds for bone regeneration. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 24, 7938–7973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suamte, L.; Tirkey, A.; Barman, J.; Jayasekhar Babu, P. Various manufacturing methods and ideal properties of scaffolds for tissue engineering applications. Smart Mater. Manuf. 2023, 1, 100011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Xiong, S.; Liu, M.; Yang, H.; Wei, P.; Yi, F.; Ouyang, M.; Xi, H.; Long, Z.; Liu, Y.; et al. Study on the influence of scaffold morphology and structure on osteogenic performance. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1127162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, B.; Kuboki, Y.; Welti, M.; Uhlschmid, G.; Neuenschwander, P.; Suter, U. DegraPol-foam: A degradable and highly porous polyesterurethane foam as a new substrate for bone formation. Artif. Organs 2000, 24, 939–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asefnejad, A.; Khorasani, M.T.; Behnamghader, A.; Farsadzadeh, B.; Bonakdar, S. Manufacturing of biodegradable polyurethane scaffolds based on polycaprolactone using a phase separation method: Physical properties and in vitro assay. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 2375–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnes, M.E.; Gonyea, C.R.; Coburn, J.M.; Pins, G.D. A biomimetic approach to modulating the sustained release of fibroblast growth factor 2 from fibrin microthread scaffolds. Explor. BioMat-X 2024, 1, 58–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asiri, A.; Saidin, S.; Sani, M.H.; Al-Ashwal, R.H. Epidermal and fibroblast growth factors incorporated polyvinyl alcohol electrospun nanofibers as biological dressing scaffold. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chew, S.Y.; Wen, J.; Yim, E.K.F.; Leong, K.W. Sustained Release of Proteins from Electrospun Biodegradable Fibers. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 2017–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Hadjiargyrou, M. Induction of Cell Migration In Vitro by an Electrospun PDGF-BB/PLGA/PEG-PLA Nanofibrous Scaffold. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2011, 7, 823–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, T.; Shi, Y.; Zhou, B.; Wang, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, G.; Mo, X.; Wang, W.; Wu, J.; Liu, W. Type I collagen and fibromodulin enhance the tenogenic phenotype of hASCs and their potential for tendon regeneration. NPJ Regen. Med. 2023, 8, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Kaufman, P.D. Ki-67: More than a proliferation marker. Chromosoma 2018, 127, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uxa, S.; Castillo-Binder, P.; Kohler, R.; Stangner, K.; Müller, G.A.; Engeland, K. Ki-67 gene expression. Cell Death Differ. 2021, 28, 3357–3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Alberton, P.; Caceres, M.D.; Volkmer, E.; Schieker, M.; Docheva, D. Tenomodulin is essential for prevention of adipocyte accumulation and fibrovascular scar formation during early tendon healing. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, C.A. Role of mTORC1 in mechanically induced increases in translation and skeletal muscle mass. J. Appl. Physiol. 2019, 127, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simcox, J.; Lamming, D.W. The central moTOR of metabolism. Dev. Cell 2022, 57, 691–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miescher, I.; Rieber, J.; Calcagni, M.; Buschmann, J. In Vitro and In Vivo Effects of IGF-1 Delivery Strategies on Tendon Healing: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caliari, S.R.; Harley, B.A. Composite growth factor supplementation strategies to enhance tenocyte bioactivity in aligned collagen-GAG scaffolds. Tissue Eng. Part A 2013, 19, 1100–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musson David, S. Lactoferrin and parathyroid hormone are not harmful to primary tenocytes in vitro, but PDGF may be. Muscles Ligaments Tendons J. 2017, 7, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banes, A.J.; Tsuzaki, M.; Hu, P.; Brigman, B.; Brown, T.; Almekinders, L.; Lawrence, W.T.; Fischer, T. PDGF-BB, IGF-I and mechanical load stimulate DNA synthesis in avian tendon fibroblasts in vitro. J. Biomech. 1995, 28, 1505–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farnebo, S.; Farnebo, L.; Kim, M.; Woon, C.; Pham, H.; Chang, J. Optimized Repopulation of Tendon Hydrogel. HAND 2017, 12, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bürgisser, G.M.; Evrova, O.; Heuberger, D.M.; Wolint, P.; Rieber, J.; Miescher, I.; Schüpbach, R.A.; Giovanoli, P.; Calcagni, M.; Buschmann, J. Electrospun tube reduces adhesion in rabbit Achilles tendon 12 weeks post-surgery without PAR-2 overexpression. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 23293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thankam, F.G.; Chandra, I.S.; Kovilam, A.N.; Diaz, C.G.; Volberding, B.T.; Dilisio, M.F.; Radwan, M.M.; Gross, R.M.; Agrawal, D.K. Amplification of Mitochondrial Activity in the Healing Response Following Rotator Cuff Tendon Injury. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, B.; Cao, S.; Dong, Y.; Cao, L.; Guo, S. Adipose-derived stem cells regulate metabolic homeostasis and delay aging by promoting mitophagy. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elstrom, R.L.; Bauer, D.E.; Buzzai, M.; Karnauskas, R.; Harris, M.H.; Plas, D.R.; Zhuang, H.; Cinalli, R.M.; Alavi, A.; Rudin, C.M.; et al. Akt Stimulates Aerobic Glycolysis in Cancer Cells. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 3892–3899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sádaba, M.C.; Martín-Estal, I.; Puche, J.E.; Castilla-Cortázar, I. Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) therapy: Mitochondrial dysfunction and diseases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Basis Dis. 2016, 1862, 1267–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Frederick, D.T.; Wu, L.; Wei, Z.; Krepler, C.; Srinivasan, S.; Chae, Y.C.; Xu, X.; Choi, H.; Dimwamwa, E.; et al. Targeting mitochondrial biogenesis to overcome drug resistance to MAPK inhibitors. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 1834–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, Y.C.; Vaira, V.; Caino, M.C.; Tang, H.-Y.; Seo, J.H.; Kossenkov, A.V.; Ottobrini, L.; Martelli, C.; Lucignani, G.; Bertolini, I.; et al. Mitochondrial Akt Regulation of Hypoxic Tumor Reprogramming. Cancer Cell 2016, 30, 257–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajoria, B.; Zhang, X.; Yee, D. IGF-1 Stimulates Glycolytic ATP Production in MCF-7L Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yin, Y.; Li, W.; Zhao, X.; Yu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Qin, Z.; Wang, Q.; Wang, K.; Lu, W.; et al. Over-Expression of PDGFR-β Promotes PDGF-Induced Proliferation, Migration, and Angiogenesis of EPCs through PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moench, R.; Grimmig, T.; Kannen, V.; Tripathi, S.; Faber, M.; Moll, E.-M.; Chandraker, A.; Lissner, R.; Germer, C.-T.; Waaga-Gasser, A.M.; et al. Exclusive inhibition of PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling is not sufficient to prevent PDGF-mediated effects on glycolysis and proliferation in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 68749–68767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novosyadlyy, R.; Dudas, J.; Pannem, R.; Ramadori, G.; Scharf, J.-G. Crosstalk between PDGF and IGF-I receptors in rat liver myofibroblasts: Implication for liver fibrogenesis. Lab. Investig. 2006, 86, 710–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliceiri, B.P. Integrin and Growth Factor Receptor Crosstalk. Circ. Res. 2001, 89, 1104–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiratori, R.; Furuichi, K.; Yamaguchi, M.; Miyazaki, N.; Aoki, H.; Chibana, H.; Ito, K.; Aoki, S. Glycolytic suppression dramatically changes the intracellular metabolic profile of multiple cancer cell lines in a mitochondrial metabolism-dependent manner. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vander Heiden, M.G.; Cantley, L.C.; Thompson, C.B. Understanding the Warburg Effect: The Metabolic Requirements of Cell Proliferation. Science 2009, 324, 1029–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberti, M.V.; Locasale, J.W. The Warburg Effect: How Does it Benefit Cancer Cells? Trends Biochem. Sci. 2016, 41, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deberardinis, R.J.; Lum, J.J.; Hatzivassiliou, G.; Thompson, C.B. The Biology of Cancer: Metabolic Reprogramming Fuels Cell Growth and Proliferation. Cell Metab. 2008, 7, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribatti, D. The chick embryo chorioallantoic membrane (CAM) assay. Reprod. Toxicol. 2017, 70, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerra, A.; Belinha, J.; Mangir, N.; MacNeil, S.; Natal Jorge, R. Simulation of the process of angiogenesis: Quantification and assessment of vascular patterning in the chicken chorioallantoic membrane. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 136, 104647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laschke, M.W.; Gu, Y.; Menger, M.D. Replacement in angiogenesis research: Studying mechanisms of blood vessel development by animal-free in vitro, in vivo and in silico approaches. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 981161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellström, M.; Kalén, M.; Lindahl, P.; Abramsson, A.; Betsholtz, C. Role of PDGF-B and PDGFR-β in recruitment of vascular smooth muscle cells and pericytes during embryonic blood vessel formation in the mouse. Development 1999, 126, 3047–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilting, J.; Christ, B.; Weich, H. The effects of growth factors on the day 13 chorioallantoic membrane (CAM): A study of VEGF165 and PDGF-BB. Anat. Embryol. 1992, 186, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Zhang, Q.; Shao, X.; Zhang, T.; Xue, C.; Shi, S.; Zhao, D.; Lin, Y. IGF-1 promotes angiogenesis in endothelial cells/adipose-derived stem cells co-culture system with activation of PI-3K/Akt signal pathway. Cell Prolif. 2017, 50, e12390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heldin, C.-H.; Westermark, B. Mechanism of Action and In Vivo Role of Platelet-Derived Growth Factor. Physiol. Rev. 1999, 79, 1283–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Hu, F.; Li, J.; Chen, L.; Mao, Y.-F.; Li, Q.-B.; Nie, C.-Y.; Lin, C.; Xiao, J. IGF-1 inhibits inflammation and accelerates angiogenesis via Ras/PI3K/IKK/NF-κB signaling pathways to promote wound healing. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 200, 106847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicosia, R.F.; Nicosia, S.V.; Smith, M. Vascular endothelial growth factor, platelet-derived growth factor, and insulin-like growth factor-1 promote rat aortic angiogenesis in vitro. Am. J. Pathol. 1994, 145, 1023–1029. [Google Scholar]
- Reinmuth, N.; Fan, F.; Liu, W.; Parikh, A.A.; Stoeltzing, O.; Jung, Y.D.; Bucana, C.D.; Radinsky, R.; Gallick, G.E.; Ellis, L.M. Impact of Insulin-Like Growth Factor Receptor-I Function on Angiogenesis, Growth, and Metastasis of Colon Cancer. Lab. Investig. 2002, 82, 1377–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bir, S.C.; Esaki, J.; Marui, A.; Yamahara, K.; Tsubota, H.; Ikeda, T.; Sakata, R. Angiogenic properties of sustained release platelet-rich plasma: Characterization in-vitro and in the ischemic hind limb of the mouse. J. Vasc. Surg. 2009, 50, 870–879.e872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, R.; Bråkenhielm, E.; Pawliuk, R.; Wariaro, D.; Post, M.J.; Wahlberg, E.; Leboulch, P.; Cao, Y. Angiogenic synergism, vascular stability and improvement of hind-limb ischemia by a combination of PDGF-BB and FGF-2. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 604–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellon, R.; Hamdi, H.K.; Sacerio, I.; Aoki, A.M.; Cristina Kenney, M.; Ljubimov, A.V. Effects of Angiogenic Growth Factor Combinations on Retinal Endothelial Cells. Exp. Eye Res. 2002, 74, 523–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, K.M.; Kanczler, J.M.; Oreffo, R.O. Evolving applications of the egg: Chorioallantoic membrane assay and ex vivo organotypic culture of materials for bone tissue engineering. J. Tissue Eng. 2020, 11, 204173142094273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetik, R.M.; Yabanoglu Ciftci, S.; Arica, B.; Baysal, I.; Akarca Dizakar, S.O.; Erbay Elibol, F.K.; Gencer, A.; Demir, T.; Ayvaz, M. Evaluation of the Effects of Transforming Growth Factor-Beta 3 (TGF-β3) Loaded Nanoparticles on Healing in a Rat Achilles Tendon Injury Model. Am. J. Sports Med. 2022, 50, 1066–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galatz, L.M.; Gerstenfeld, L.; Heber-Katz, E.; Rodeo, S.A. Tendon regeneration and scar formation: The concept of scarless healing. J. Orthop. Res. 2015, 33, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titan, A.L.; Foster, D.S.; Chang, J.; Longaker, M.T. Flexor Tendon: Development, Healing, Adhesion Formation, and Contributing Growth Factors. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2019, 144, 639e–647e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Xu, Y.; Li, R.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Yang, L.; Cui, W.; Wang, L. Synergistic Biofilter Tube for Promoting Scarless Tendon Regeneration. Nano Lett. 2024, 24, 7381–7388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier Bürgisser, G.; Calcagni, M.; Bachmann, E.; Fessel, G.; Snedeker, J.G.; Giovanoli, P.; Buschmann, J. Rabbit Achilles tendon full transection model—Wound healing, adhesion formation and biomechanics at 3, 6 and 12 weeks post-surgery. Biol. Open 2016, 5, 1324–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigozzi, S.; Müller, R.; Snedeker, J.G. Local strain measurement reveals a varied regional dependence of tensile tendon mechanics on glycosaminoglycan content. J. Biomech. 2009, 42, 1547–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergari, C.; Pourcelot, P.; Holden, L.; Ravary-Plumioën, B.; Laugier, P.; Mitton, D.; Crevier-Denoix, N. A Linear Laser Scanner to Measure Cross-Sectional Shape and Area of Biological Specimens During Mechanical Testing. J. Biomech. Eng. 2010, 132, 105001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fessel, G.; Cadby, J.; Wunderli, S.; van Weeren, R.; Snedeker, J.G. Dose- and time-dependent effects of genipin crosslinking on cell viability and tissue mechanics—Toward clinical application for tendon repair. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 1897–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, V.; Nourbakhsh, A.; Capo, J.; Cottrell, J.A.; Meyenhofer, M.; O’Connor, J.P. Effects of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on flexor tendon adhesion. J. Hand Surg. Am. 2010, 35, 941–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Gene | mRNA ID (NCBI Reference Sequence) | Amplicon Size (bp) | Forward Primer Sequence (3′ → 5′) | Reverse Primer Sequence (5′ → 3′) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18s rRNA | NR_033238.1 | 176 | GGAACTGAGGCCATGATTAAG | CGGAACTACGACGGTATCTG |
| Col1A1 | XM_008271783.1 | 271 | CTGGTGAATCTGGACGTGAG | TGTCTCACCCTTGTCACCAC |
| Tenomodulin | NM_001109818.1 | 239 | GCAGTTTCCGAGTTACAAGAC | CGACGGCAGTAAATACAACAG |
| Ki67 | XM_008251084.2 | 283 | CACATCCAGCAGTGAAACGG | GTGTTAGCAGTACCTGAAGTC |
| MTROC 1 | XM_088251668.2 | 117 | GTTTGTCGCGGACGTTTAAG | AGGAAAGGCATGACAAAGGC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rieber, J.; Wolint, P.; Meier-Bürgisser, G.; Ongini, E.; Giovanoli, P.; Calcagni, M.; Snedeker, J.G.; Buschmann, J. Synergistic Effects of Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 and Platelet-Derived Growth Factor-BB in Tendon Healing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4039. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094039
Rieber J, Wolint P, Meier-Bürgisser G, Ongini E, Giovanoli P, Calcagni M, Snedeker JG, Buschmann J. Synergistic Effects of Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 and Platelet-Derived Growth Factor-BB in Tendon Healing. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):4039. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094039
Chicago/Turabian StyleRieber, Julia, Petra Wolint, Gabriella Meier-Bürgisser, Esteban Ongini, Pietro Giovanoli, Maurizio Calcagni, Jess G. Snedeker, and Johanna Buschmann. 2025. "Synergistic Effects of Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 and Platelet-Derived Growth Factor-BB in Tendon Healing" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 4039. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094039
APA StyleRieber, J., Wolint, P., Meier-Bürgisser, G., Ongini, E., Giovanoli, P., Calcagni, M., Snedeker, J. G., & Buschmann, J. (2025). Synergistic Effects of Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 and Platelet-Derived Growth Factor-BB in Tendon Healing. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 4039. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094039






