Significant Associations Between Blood Cell Counts and Plasma Cytokines, Chemokines, and Growth Factors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Patient Characteristics
2.2. Correlations Between Platelet Count and Cytokine and Chemokine Levels
2.3. Correlations Between White Blood Cell Count and Cytokine Levels
2.4. Correlations Between Cytokine Levels and Red Blood Cell Count
2.5. Correlations Between Cytokine Levels and the Erythrocyte Volume Fraction
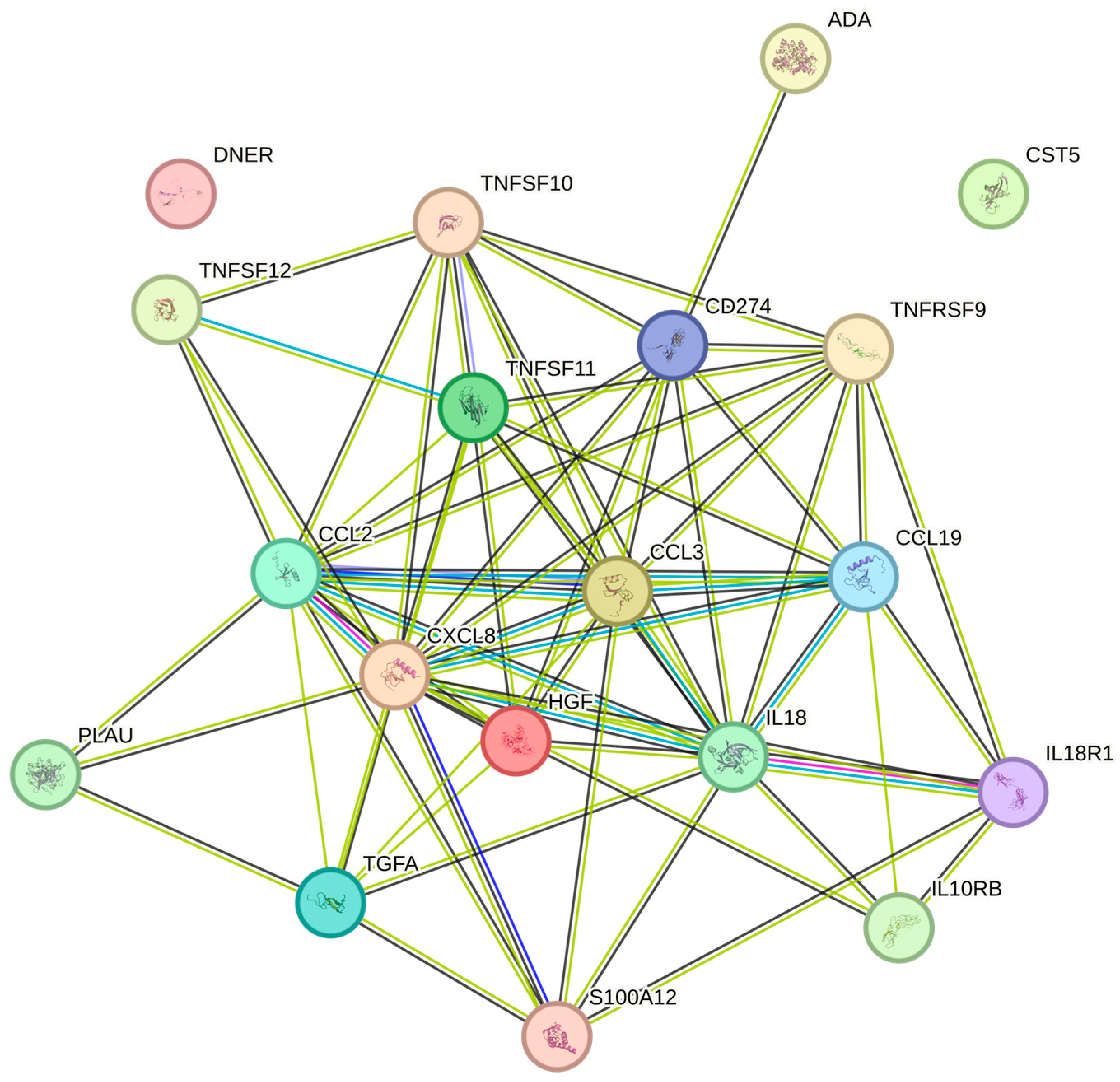
3. Discussion
Limitations
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Population
4.2. Sampling Procedures
4.3. Ethics
4.4. Proximity Extension Assay (PEA)
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hegde, R.; Awan, K.H. Effects of periodontal disease on systemic health. Dis. Mon. 2019, 65, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plachokova, A.S.; Andreu-Sánchez, S.; Noz, M.P.; Fu, J.; Riksen, N.P. Oral Microbiome in Relation to Periodontitis Severity and Systemic Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayani, M.; Pourali, M.; Keivan, M. Possible interaction between visfatin, periodontal infection, and other systemic diseases: A brief review of literature. Eur. J. Dent. 2017, 11, 407–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Chu, D.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; George, J.; Young, H.A.; Liu, G. Cytokines: From Clinical Significance to Quantification. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, e2004433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fajgenbaum, D.C.; June, C.H. Cytokine Storm. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2255–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaffer, U.; Wade, R.G.; Gourlay, T. Cytokines in the systemic inflammatory response syndrome: A review. HSR Proc. Intensive Care Cardiovasc. Anesth. 2010, 2, 161–175. [Google Scholar]
- Brinkmann, V.; Reichard, U.; Goosmann, C.; Fauler, B.; Uhlemann, Y.; Weiss, D.S.; Weinrauch, Y.; Zychlinsky, A. Neutrophil extracellular traps kill bacteria. Science 2004, 303, 1532–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branzk, N.; Lubojemska, A.; Hardison, S.E.; Wang, Q.; Gutierrez, M.G.; Brown, G.D.; Papayannopoulos, V. Neutrophils sense microbe size and selectively release neutrophil extracellular traps in response to large pathogens. Nat. Immunol. 2014, 15, 1017–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, A.; Sakoulas, G.; Nizet, V.; Ulloa, E.R. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps: An Emerging Therapeutic Target to Improve Infectious Disease Outcomes. J. Infect. Dis. 2024, 230, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorch, S.K.; Kubes, P. An emerging role for neutrophil extracellular traps in noninfectious disease. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Kim, S.J.; Lei, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, H.; Huang, H.; Zhang, H.; Tsung, A. Neutrophil extracellular traps in homeostasis and disease. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 235. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, S.; Rizvi, Z.A.; Awasthi, A. Metabolic Checkpoints in Differentiation of Helper T Cells in Tissue Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyette, L.B.; Macedo, C.; Hadi, K.; Elinoff, B.D.; Walters, J.T.; Ramaswami, B.; Chalasani, G.; Taboas, J.M.; Lakkis, F.G.; Metes, D.M. Phenotype, function, and differentiation potential of human monocyte subsets. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Austermann, J.; Roth, J.; Barczyk-Kahlert, K. The Good and the Bad: Monocytes’ and Macrophages’ Diverse Functions in Inflammation. Cells 2022, 11, 1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arango Duque, G.; Descoteaux, A. Macrophage cytokines: Involvement in immunity and infectious diseases. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonelli, A.; Scarpa, E.S.; Magnani, M. Human Red Blood Cells Modulate Cytokine Expression in Monocytes/Macrophages Under Anoxic Conditions. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 632682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karsten, E.; Herbert, B.R. The emerging role of red blood cells in cytokine signalling and modulating immune cells. Blood Rev. 2020, 41, 100644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakogiannis, C.; Sachse, M.; Stamatelopoulos, K.; Stellos, K. Platelet-derived chemokines in inflammation and atherosclerosis. Cytokine 2019, 122, 154157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maouia, A.; Rebetz, J.; Kapur, R.; Semple, J.W. The Immune Nature of Platelets Revisited. Transfus. Med. Rev. 2020, 34, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habets, K.L.; Huizinga, T.W.; Toes, R.E. Platelets and autoimmunity. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 43, 746–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasiadi, A.T.; Arvaniti, V.Z.; Hudson, K.E.; Kriebardis, A.G.; Stathopoulos, C.; D’Alessandro, A.; Spitalnik, S.L.; Tzounakas, V.L. Exploring unconventional attributes of red blood cells and their potential applications in biomedicine. Protein Cell 2024, 15, 315–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.D.; Kar, D.; Akhtar, M.N.; Willard, B.; Roy, D.; Hussain, T.; Rajyaguru, P.I.; Eswarappa, S.M. Evidence for low-level translation in human erythrocytes. Mol. Biol. Cell 2022, 33, br21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczmarski, R.S.; Mufti, G.J. The cytokine receptor superfamily. Blood Rev. 1991, 5, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelso, A. Cytokines and their receptors: An overview. Ther. Drug Monit. 2000, 22, 40–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinarello, C.A. Historical insights into cytokines. Eur. J. Immunol. 2007, 37, S34–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathnayake, N.; Akerman, S.; Klinge, B.; Lundegren, N.; Jansson, H.; Tryselius, Y.; Sorsa, T.; Gustafsson, A. Salivary biomarkers for detection of systemic diseases. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balmasova, I.P.; Lomakin, Y.A.; Babaev, E.A.; Tsarev, V.N.; Gabibov, A.G.; Smirnov, I.V.; Knorre, V.D.; Ovchinnikova, L.A.; Gnuchev, N.V.; Khurs, E.N.; et al. “Shielding” of Cytokine Induction by the Periodontal Microbiome in Patients with Periodontitis Associated with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Acta Naturae 2019, 11, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galhardo, L.F.; Ruivo, G.F.; de Oliveira, L.D.; Parize, G.; Santos, S.; Pallos, D.; Leão, M.V.P. Inflammatory markers in saliva for diagnosis of sepsis of hospitalizes patients. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 50, e13219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, I.L.; Huang, H.C.; Ou-Yang, M.C.; Chen, F.S.; Chung, M.Y.; Chen, C.C. A novel method to detect bacterial infection in premature infants: Using a combination of inflammatory markers in blood and saliva. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2020, 53, 892–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Mandel, H.; Levingston, C.A.; Young, M.R.I. An exploratory approach demonstrating immune skewing and a loss of coordination among cytokines in plasma and saliva of Veterans with combat-related PTSD. Hum. Immunol. 2016, 77, 652–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Majewski, K.; Kraus, O.; Rhein, C.; Lieb, M.; Erim, Y.; Rohleder, N. Acute stress responses of autonomous nervous system, HPA axis, and inflammatory system in posttraumatic stress disorder. Transl. Psychiatry 2023, 13, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assarsson, E.; Lundberg, M.; Holmquist, G.; Björkesten, J.; Thorsen, S.B.; Ekman, D.; Eriksson, A.; Rennel Dickens, E.; Ohlsson, S.; Edfeldt, G.; et al. Homogenous 96-plex PEA immunoassay exhibiting high sensitivity, specificity, and excellent scalability. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, T.M.; Bruce, A.G. Oncostatin M is a member of a cytokine family that includes leukemia-inhibitory factor, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, and interleukin 6. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 8641–8645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacFarlane, M.; Ahmad, M.; Srinivasula, S.M.; Fernandes-Alnemri, T.; Cohen, G.M.; Alnemri, E.S. Identification and molecular cloning of two novel receptors for the cytotoxic ligand TRAIL. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 25417–25420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, Y.; Fujita, S.; Ikemoto, T.; Okada, Y.; Sohmiya, K.; Hoshiga, M.; Ishizaka, N. The relationship of fibroblast growth factors 21 and 23 and α-Klotho with platelet activity measured by platelet volume indices. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2015, 53, 1569–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sosman, J.A.; Verma, A.; Moss, S.; Sorokin, P.; Blend, M.; Bradlow, B.; Chachlani, N.; Cutler, D.; Sabo, R.; Nelson, M.; et al. Interleukin 10-induced thrombocytopenia in normal healthy adult volunteers: Evidence for decreased platelet production. Br. J. Haematol. 2000, 111, 104–111. [Google Scholar]
- Blakytny, R.; Ludlow, A.; Martin, G.E.; Ireland, G.; Lund, L.R.; Ferguson, M.W.; Brunner, G. Latent TGF-beta1 activation by platelets. J. Cell Physiol. 2004, 199, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moscardó, A.; Vallés, J.; Latorre, A.; Jover, R.; Santos, M.T. The histone deacetylase sirtuin 2 is a new player in the regulation of platelet function. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2015, 13, 1335–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senchenkova, E.Y.; Komoto, S.; Russell, J.; Almeida-Paula, L.D.; Yan, L.S.; Zhang, S.; Granger, D.N. Interleukin-6 mediates the platelet abnormalities and thrombogenesis associated with experimental colitis. Am. J. Pathol. 2013, 183, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonmez, O.; Sonmez, M. Role of platelets in immune system and inflammation. Porto Biomed. J. 2017, 2, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leone, G.M.; Mangano, K.; Petralia, M.C.; Nicoletti, F.; Fagone, P. Past, Present and (Foreseeable) Future of Biological Anti-TNF Alpha Therapy. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishimoto, T. Discovery of IL-6 and Development of Anti-IL-6R Antibody. Keio J. Med. 2019, 68, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, D.C.; Crawford, J.; Klippel, Z.; Reiner, M.; Osslund, T.; Fan, E.; Morrow, P.K.; Allcott, K.; Lyman, G.H. A systematic literature review of the efficacy, effectiveness, and safety of filgrastim. Support. Care Cancer 2018, 26, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunn, H.F. Erythropoietin. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2013, 3, a011619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksson, L.B.; Gordh, T.; Karlsten, R.; LoMartire, R.; Thor, A.; Tegelberg, Å. Intravenous S-ketamine’s analgesic efficacy in third molar surgery. A randomized placebo-controlled double-blind clinical trial. Br. J. Pain. 2024, 18, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WMA Declaration of Helsinki—Ethical Principles for Medical Research Involving Human Subjects. Available online: https://www.wma.net/policies-post/wma-declaration-of-helsinki-ethical-principles-for-medical-research-involving-human-subjects/ (accessed on 23 March 2022).
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Methodol.) 2018, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridker, P.M.; Everett, B.M.; Thuren, T.; MacFadyen, J.G.; Chang, W.H.; Ballantyne, C.; Fonseca, F.; Nicolau, J.; Koenig, W.; Anker, S.D.; et al. Antiinflammatory Therapy with Canakinumab for Atherosclerotic Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1119–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Narazaki, M.; Kishimoto, T. IL-6 in inflammation, immunity, and disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a016295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Valid N | Geometric Mean | Minimum | Maximum | Std. Dev. | CV | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight | 165 | 73 | 48 | 111 | 13 | 17 |
| Height | 165 | 171 | 153 | 195 | 8.6 | 5 |
| BMI | 165 | 25 | 15 | 41 | 4.4 | 17 |
| hsCRP | 165 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 10 | 2.0 | 250 |
| Hb | 165 | 137 | 94 | 167 | 12.1 | 9 |
| RBC | 165 | 5 | 4 | 6 | 0.41 | 9 |
| EVF | 165 | 0.41 | 0.14 | 0.48 | 0.04 | 10 |
| Platelets | 165 | 238 | 100 | 430 | 52 | 21 |
| WBC | 165 | 5.7 | 3.4 | 13.1 | 1.8 | 31 |
| Neutrophils | 165 | 3.1 | 0.5 | 9.5 | 1.4 | 42 |
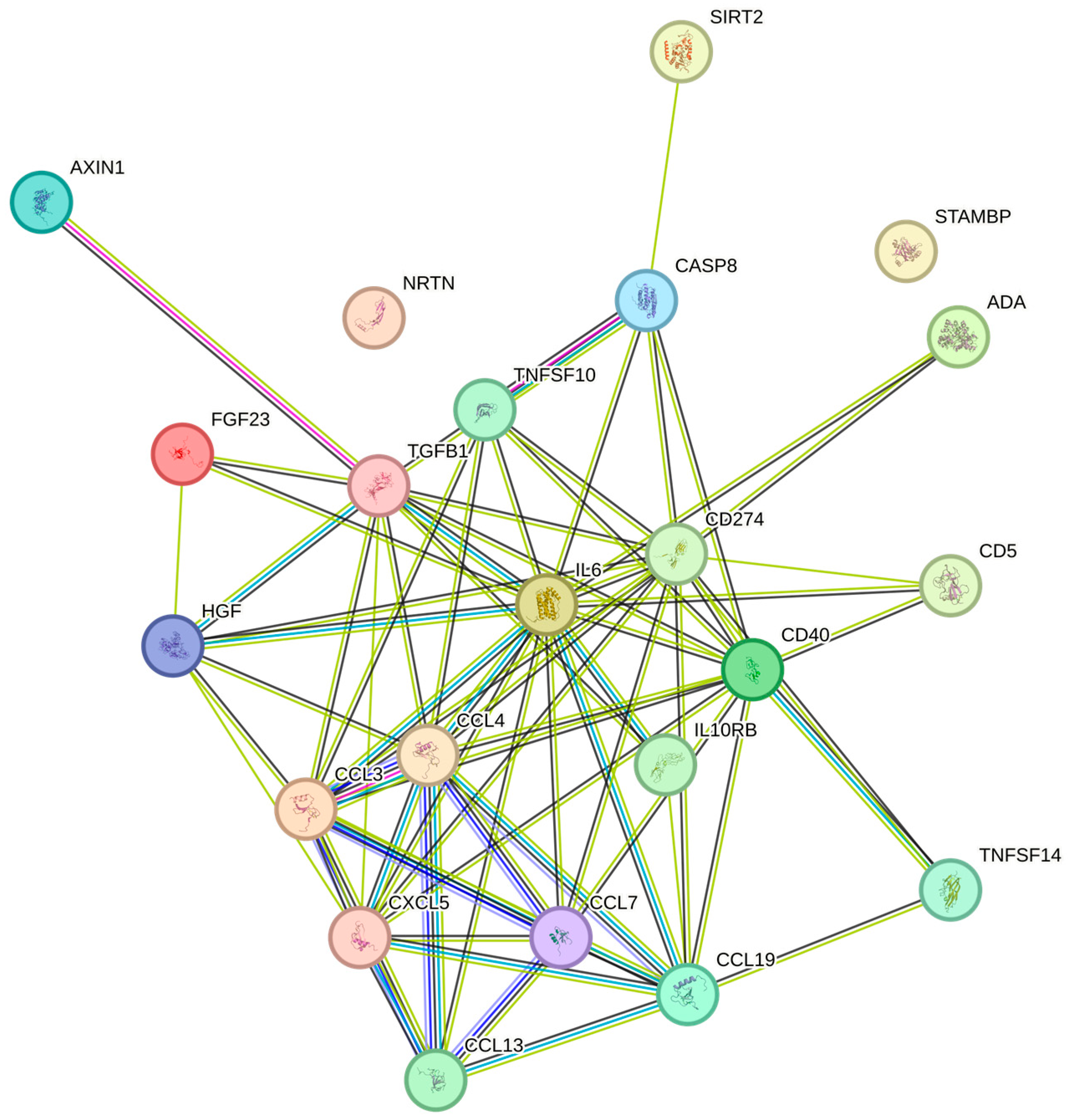
| Blood Cell Marker | Cytokine | UniProt ID | N | Spearman Rank Correlations | Benjamini–Hochberg p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
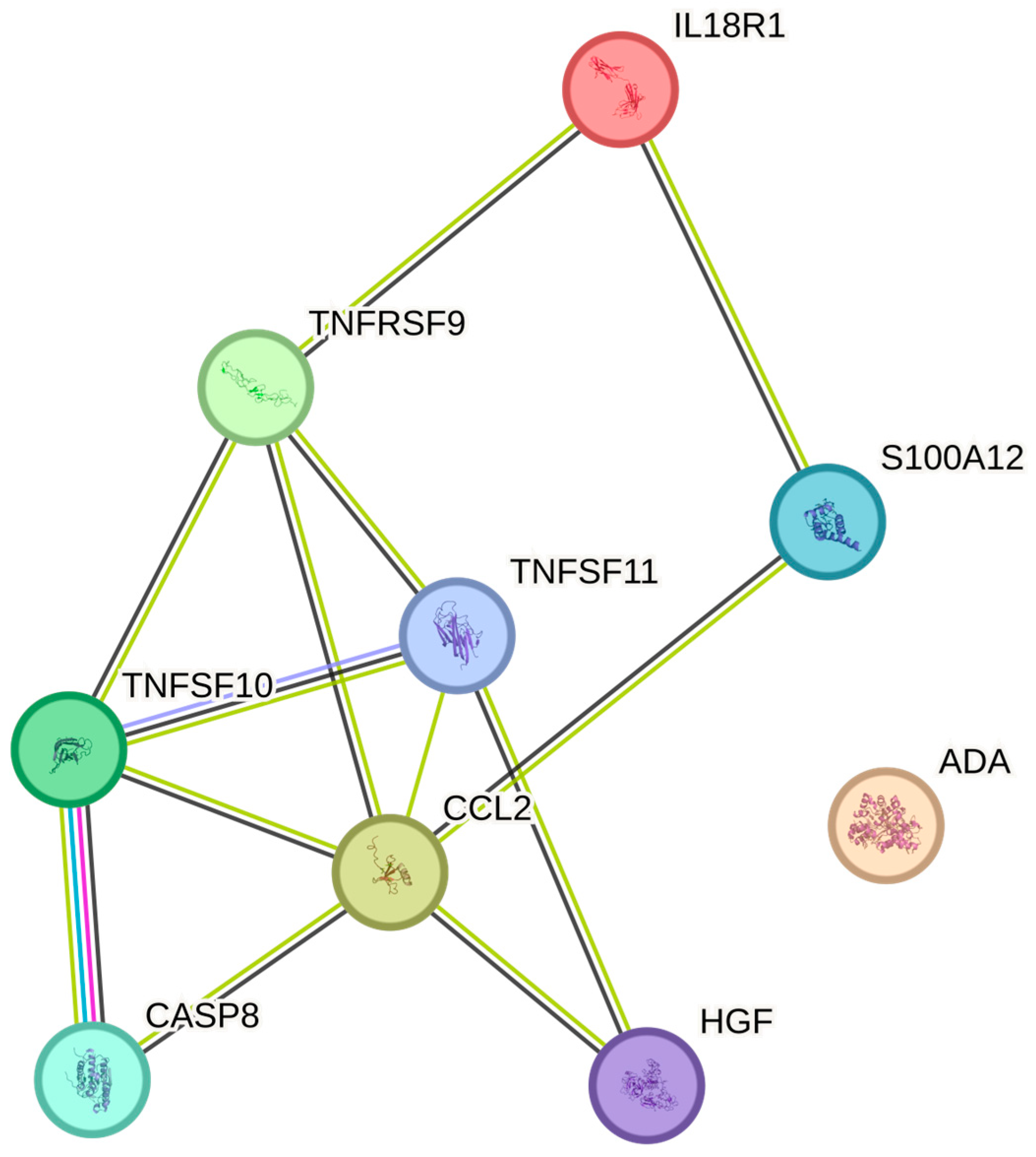
| EVF | TRAIL | P50591 | 165 | 0.349 | 0.001 |
| EVF | MCP-1 | P13500 | 165 | 0.321 | 0.002 |
| EVF | HGF | P14210 | 165 | 0.304 | 0.006 |
| EVF | TNFRSF9 | Q07011 | 165 | 0.259 | 0.022 |
| EVF | ADA | P00813 | 165 | 0.251 | 0.031 |
| EVF | DNER | Q8NFT8 | 165 | 0.236 | 0.046 |
| EVF | CCL19 | Q99731 | 165 | 0.23 | 0.051 |
| EVF | IL-10RB | Q08334 | 165 | 0.229 | 0.051 |
| EVF | IL18 | Q14116 | 165 | 0.228 | 0.051 |
| EVF | TWEAK | O43508 | 165 | 0.224 | 0.053 |
| EVF | CST5 | P28325 | 165 | 0.217 | 0.061 |
| EVF | PD-L1 | Q9NZQ7 | 165 | 0.213 | 0.067 |
| EVF | CCL3 | P10147 | 165 | 0.212 | 0.069 |
| EVF | uPA | P00749 | 165 | 0.211 | 0.069 |
| EVF | EN-RAGE | P80511 | 165 | 0.205 | 0.076 |
| EVF | TRANCE | O14788 | 165 | 0.205 | 0.076 |
| EVF | IL-18R1 | Q13478 | 165 | 0.202 | 0.081 |
| EVF | TGF-alpha | P01135 | 165 | 0.198 | 0.088 |
| EVF | IL8 | P10145 | 165 | 0.196 | 0.092 |
| Hb | TRAIL | P50591 | 165 | 0.337 | 0.001 |
| Hb | MCP-1 | P13500 | 165 | 0.291 | 0.011 |
| Hb | HGF | P14210 | 165 | 0.276 | 0.017 |
| Hb | ADA | P00813 | 165 | 0.233 | 0.049 |
| Hb | DNER | Q8NFT8 | 165 | 0.232 | 0.049 |
| Hb | TNFRSF9 | Q07011 | 165 | 0.229 | 0.051 |
| Hb | IL18 | Q14116 | 165 | 0.205 | 0.076 |
| Hb | uPA | P00749 | 165 | 0.200 | 0.084 |
| Hb | EN-RAGE | P80511 | 165 | 0.199 | 0.087 |
| Hb | TWEAK | O43508 | 165 | 0.196 | 0.092 |
| Hb | TRANCE | O14788 | 165 | 0.193 | 0.099 |
| MCHC | IL-12B | P29460 | 165 | −0.214 | 0.066 |
| MCV | IL-18R1 | Q13478 | 165 | −0.229 | 0.051 |
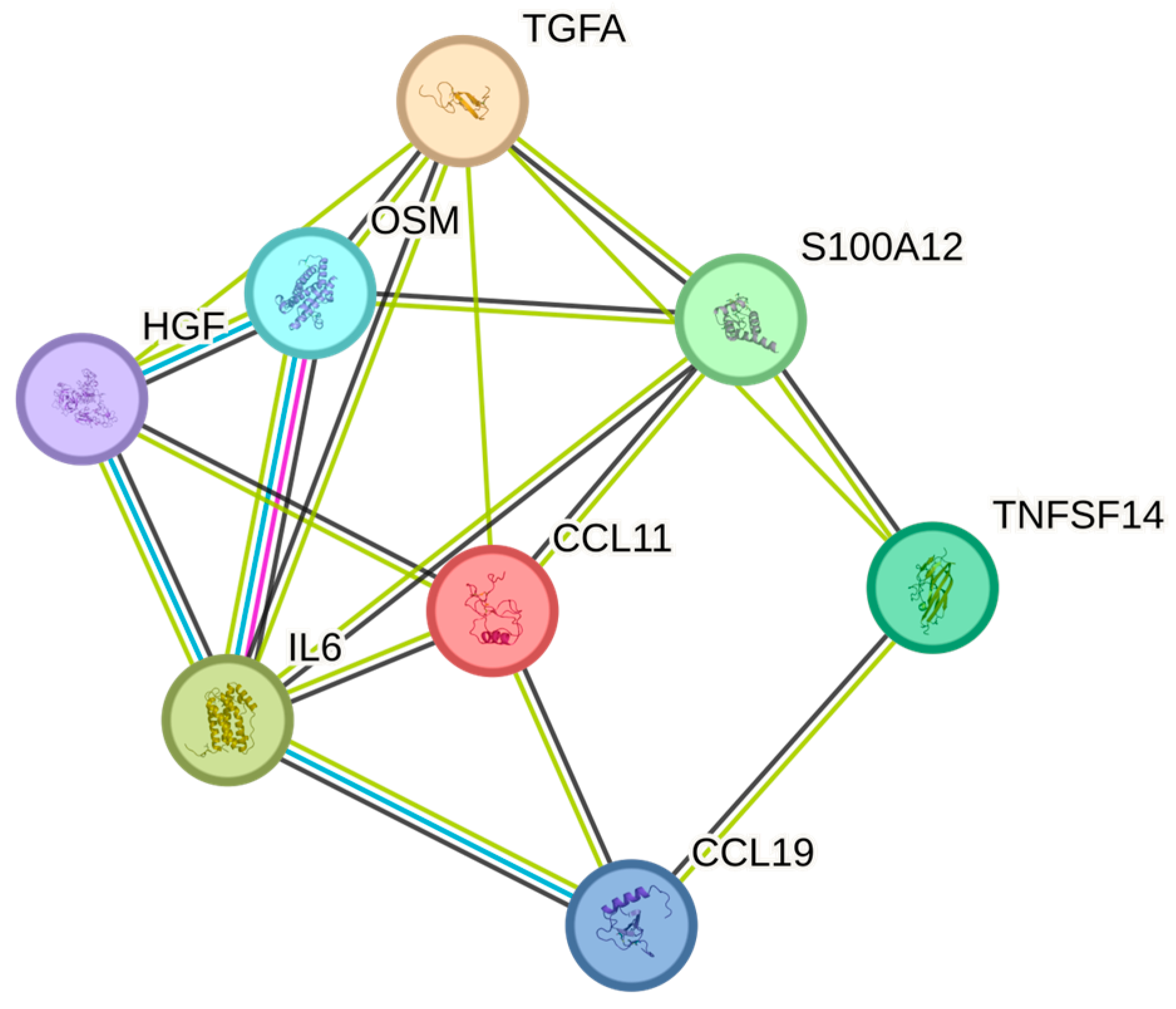
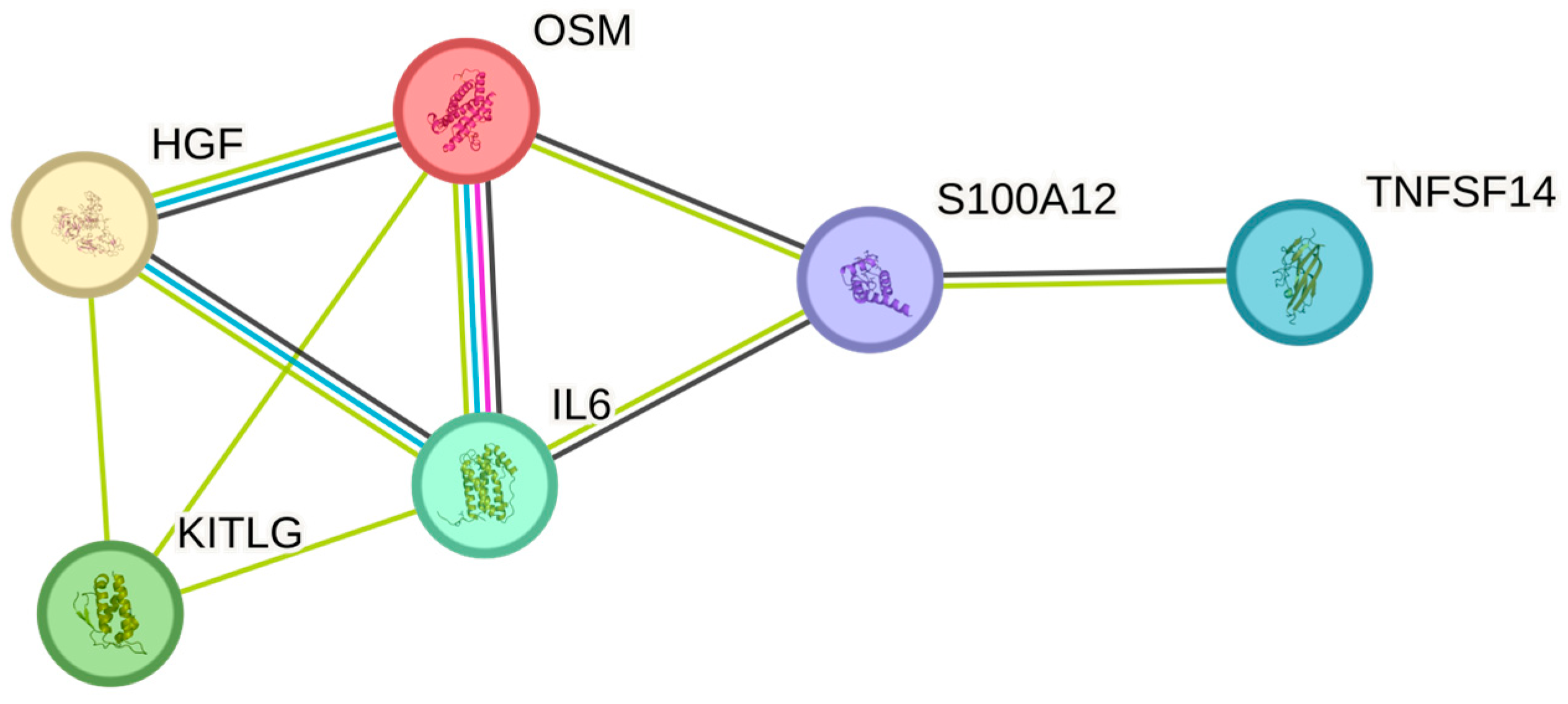
| Neutroph | OSM | P13725 | 165 | 0.505 | 0 |
| Neutroph | IL6 | P05231 | 165 | 0.327 | 0.002 |
| Neutroph | TNFSF14 | O43557 | 165 | 0.241 | 0.040 |
| Neutroph | HGF | P14210 | 165 | 0.232 | 0.049 |
| Neutroph | EN-RAGE | P80511 | 165 | 0.214 | 0.067 |
| Neutroph | SCF | P21583 | 165 | −0.204 | 0.079 |
| Plt | FGF-23 | Q9GZV9 | 165 | 0.282 | 0.016 |
| Plt | IL-10RB | Q08334 | 165 | 0.269 | 0.017 |
| Plt | LAP TGF-beta-1 | P01137 | 165 | 0.269 | 0.017 |
| Plt | CCL19 | Q99731 | 165 | 0.263 | 0.021 |
| Plt | SIRT2 | Q8IXJ6 | 165 | 0.261 | 0.022 |
| Plt | IL6 | P05231 | 165 | 0.26 | 0.022 |
| Plt | VEGFA | P15692 | 165 | 0.257 | 0.024 |
| Plt | AXIN1 | O15169 | 165 | 0.244 | 0.037 |
| Plt | CASP-8 | Q14790 | 165 | 0.239 | 0.042 |
| Plt | CD40 | P25942 | 165 | 0.231 | 0.050 |
| Plt | PD-L1 | Q9NZQ7 | 165 | 0.227 | 0.051 |
| Plt | CXCL5 | P42830 | 165 | 0.227 | 0.051 |
| Plt | MCP-3 | P80098 | 165 | 0.225 | 0.052 |
| Plt | STAMBP | O95630 | 165 | 0.225 | 0.052 |
| Plt | CCL3 | P10147 | 165 | 0.223 | 0.054 |
| Plt | NRTN | Q99748 | 165 | 0.223 | 0.054 |
| Plt | HGF | P14210 | 165 | 0.218 | 0.059 |
| Plt | CD5 | P06127 | 165 | 0.216 | 0.063 |
| Plt | TRAIL | P50591 | 165 | 0.214 | 0.067 |
| Plt | CCL4 | P13236 | 165 | 0.210 | 0.070 |
| Plt | ADA | P00813 | 165 | 0.210 | 0.071 |
| Plt | TNFSF14 | O43557 | 165 | 0.208 | 0.072 |
| Plt | MCP-4 | Q99616 | 165 | 0.193 | 0.099 |
| RBC | TRAIL | P50591 | 165 | 0.277 | 0.017 |
| RBC | IL-18R1 | Q13478 | 165 | 0.270 | 0.017 |
| RBC | HGF | P14210 | 165 | 0.270 | 0.017 |
| RBC | MCP-1 | P13500 | 165 | 0.240 | 0.042 |
| RBC | TRANCE | O14788 | 165 | 0.227 | 0.051 |
| RBC | TNFRSF9 | Q07011 | 165 | 0.224 | 0.053 |
| RBC | ADA | P00813 | 165 | 0.211 | 0.069 |
| RBC | EN-RAGE | P80511 | 165 | 0.209 | 0.071 |
| RBC | CASP-8 | Q14790 | 165 | 0.199 | 0.086 |
| WBC | OSM | P13725 | 165 | 0.463 | 0 |
| WBC | IL6 | P05231 | 165 | 0.325 | 0.002 |
| WBC | HGF | P14210 | 165 | 0.277 | 0.017 |
| WBC | TNFSF14 | O43557 | 165 | 0.265 | 0.020 |
| WBC | EN-RAGE | P80511 | 165 | 0.222 | 0.054 |
| WBC | TGF-alpha | P01135 | 165 | 0.212 | 0.069 |
| WBC | CCL19 | Q99731 | 165 | 0.203 | 0.079 |
| WBC | CCL11 | P51671 | 165 | −0.197 | 0.090 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eriksson, L.B.; Eriksson, M.B.; Gordh, T.; Larsson, A.O. Significant Associations Between Blood Cell Counts and Plasma Cytokines, Chemokines, and Growth Factors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4065. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094065
Eriksson LB, Eriksson MB, Gordh T, Larsson AO. Significant Associations Between Blood Cell Counts and Plasma Cytokines, Chemokines, and Growth Factors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):4065. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094065
Chicago/Turabian StyleEriksson, Lars B., Mats B. Eriksson, Torsten Gordh, and Anders O. Larsson. 2025. "Significant Associations Between Blood Cell Counts and Plasma Cytokines, Chemokines, and Growth Factors" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 4065. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094065
APA StyleEriksson, L. B., Eriksson, M. B., Gordh, T., & Larsson, A. O. (2025). Significant Associations Between Blood Cell Counts and Plasma Cytokines, Chemokines, and Growth Factors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 4065. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094065








