Impact of Allele-Specific Expression on Ripening and Quality Characteristics of ABB Banana Fruit
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Analysis of Allele-Specific Expression (ASE) of Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs) in Fen Jiao During Fruit Ripening
2.2. GO and KEGG Enrichment Analyses of ASE Genes in FJ Fruit
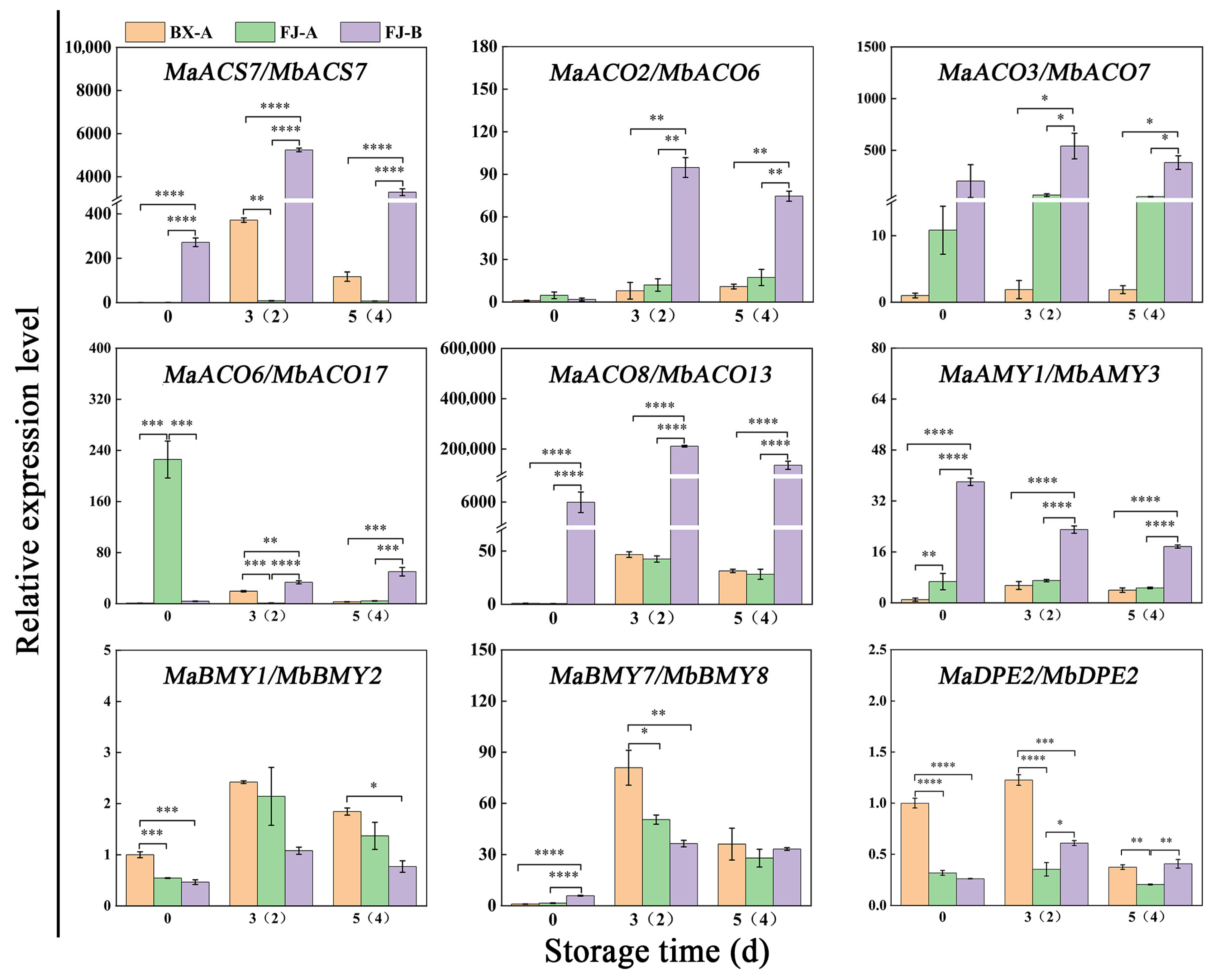
2.3. ASE Genes Involved in Ethylene Biosynthesis During FJ Fruit Ripening
2.4. ASE Genes Associated with Starch Degradation Pathway During FJ Fruit Ripening
2.5. Ase Genes Associated with Cell Wall Degradation Pathway During FJ Fruit Ripening
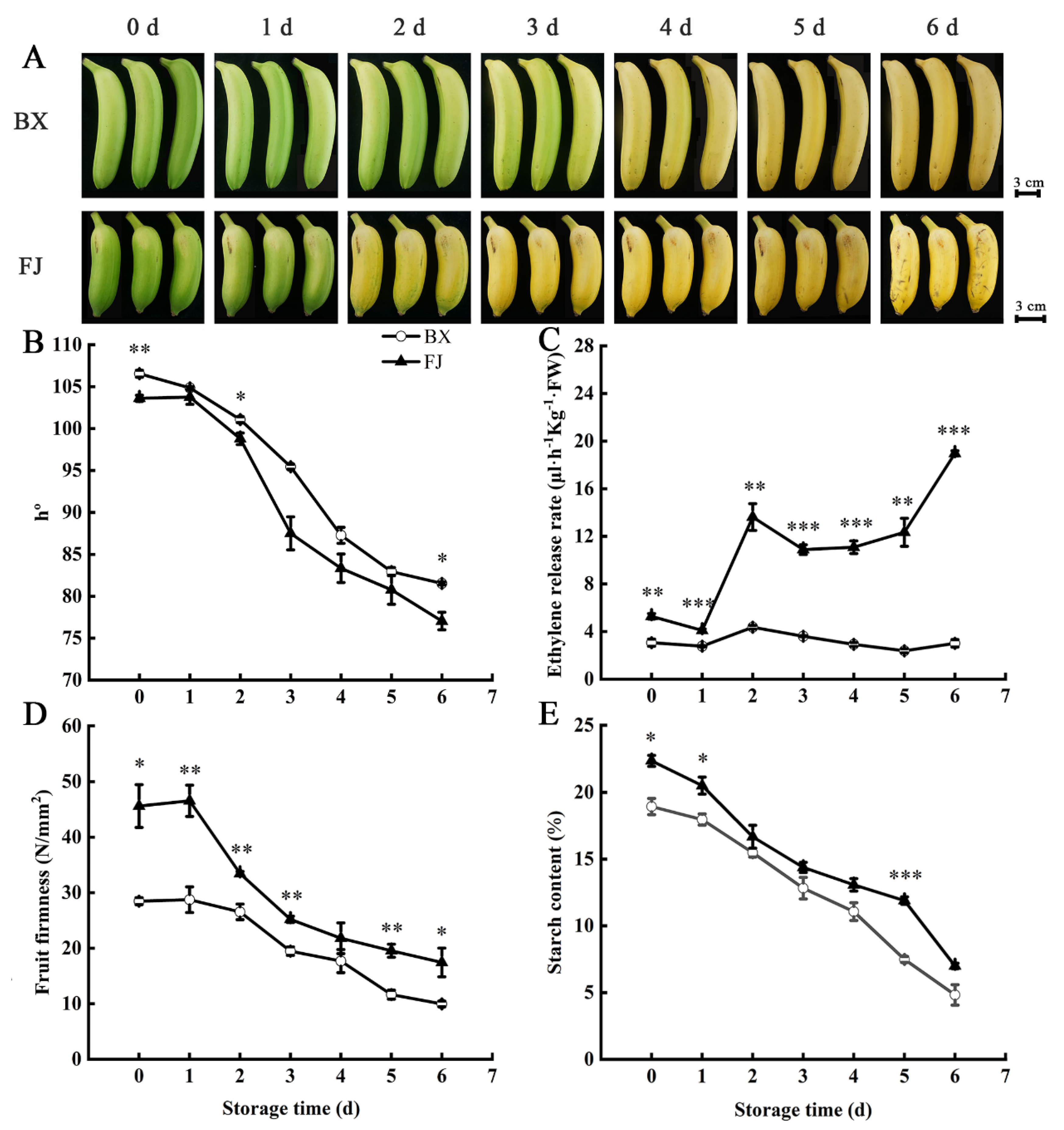
2.6. Changes in Fruit Ripening Parameters in BX and FJ Bananas
2.7. Verification of ASE Using Real-Time qPCR
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material and Treatments
4.2. Assessment of Fruit Ripening Parameters
4.3. Transcriptome and Allele-Specific Expression Analysis
4.4. Allele-Specific qRT-PCR Analysis
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bell, C.G.; Beck, S. Advances in the identification and analysis of allele-specific expression. Genome Med. 2009, 1, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Rupe, M.A.; Zinselmeier, C.; Habben, J.; Bowen, B.A.; Smith, O.S. Allelic variation of gene expression in maize hybrids. Plant Cell 2004, 16, 1707–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Rupe, M.A.; Yang, X.; Crasta, O.; Zinselmeier, C.; Smith, O.S.; Bowen, B. Genome-wide transcript analysis of maize hybrids: Allelic additive gene expression and yield heterosis. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2006, 113, 831–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Springer, N.M.; Stupar, R.M. Allele-specific expression patterns reveal biases and embryo-specific parent-of-origin effects in hybrid maize. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 2391–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, A.J.; Makarevitch, I.; Noshay, J.; Burghardt, L.T.; Hirsch, C.N.; Hirsch, C.D.; Springer, N.M. Natural variation for gene expression responses to abiotic stress in maize. Plant J. 2017, 89, 706–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Borevitz, J.O. Global analysis of allele-specific expression in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genetics 2009, 182, 943–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Ng, D.W.; Zhang, C.; Comai, L.; Ye, W.; Chen, Z.J. Cis- and trans-regulatory divergence between progenitor species determines gene-expression novelty in Arabidopsis allopolyploids. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todesco, M.; Balasubramanian, S.; Hu, T.T.; Traw, M.B.; Horton, M.; Epple, P.; Kuhns, C.; Sureshkumar, S.; Schwartz, C.; Lanz, C.; et al. Natural allelic variation underlying a major fitness trade-off in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature 2010, 465, 632–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Korff, M.; Radovic, S.; Choumane, W.; Stamati, K.; Udupa, S.M.; Grando, S.; Ceccarelli, S.; Mackay, I.; Powell, W.; Baum, M.; et al. Asymmetric allele-specific expression in relation to developmental variation and drought stress in barley hybrids. Plant J. 2009, 59, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ereful, N.C.; Liu, L.; Tsai, E.; Kao, S.; Dixit, S.; Mauleon, R.; Malabanan, K.; Thomson, M.; Laurena, A.; Lee, D.; et al. Analysis of allelic imbalance in rice hybrids under water stress and association of asymmetrically expressed genes with drought-response QTLs. Rice 2016, 9, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Thrimawithana, A.; Ding, T.; Guo, J.; Gleave, A.; Chagne, D.; Ampomah-Dwamena, C.; Ireland, H.S.; Schaffer, R.J.; Luo, Z.; et al. Transposon insertions regulate genome-wide allele-specific expression and underpin flower colour variations in apple (Malus spp.). Plant Biotechnol. J. 2022, 20, 1285–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, J.Y.; Khanna, H.; Kleidon, J.; Hoang, P.; Geijskes, J.; Daniells, J.; Zaplin, E.; Rosenberg, Y.; James, A.; Mlalazi, B.; et al. Golden bananas in the field: Elevated fruit pro-vitamin a from the expression of a single banana transgene. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2017, 15, 520–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmonds, N.W.; Shepherd, K. The taxonomy and origins of the cultivated bananas. J. Linn. Soc. Lond. Bot. 1955, 55, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrier, X.; Bakry, F.; Carreel, F.; Jenny, C.; Horry, J.; Lebot, V.; Hippolyte, I. Combining biological approaches to shed light on the evolution of edible bananas. Ethnobot. Res. Appl. 2009, 7, 199–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Yang, Y.Y.; Wu, C.J.; Kuang, J.F.; Chen, J.Y.; Lu, W.J.; Shan, W. MaMADS1-MaNAC083 transcriptional regulatory cascade regulates ethylene biosynthesis during banana fruit ripening. Hortic. Res. 2023, 10, uhad177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Ma, Z.; Qin, Y.; Li, Y.; Huang, B.; Zhang, X.; Du, L.; Song, J.; Zhang, Z.; Pang, X. Imbalanced expression of stay-green 1 alleles in banana AAB/ABB cultivars prevents high-temperature-induced green ripening as in AAA Cavendish fruit. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2019, 158, 110980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Xing, F.; Xu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Che, J.; Wang, X.; Song, J.; Li, X.; Xiao, J.; Chen, L.L.; et al. Patterns of genome-wide allele-specific expression in hybrid rice and the implications on the genetic basis of heterosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 5653–5658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, E.; Yorukoglu, D.; Zhang, L.; Nyquist, S.K.; Shalek, A.K.; Kellis, M.; Numanagic, I.; Berger, B. Improved haplotype inference by exploiting long-range linking and allelic imbalance in RNA-seq datasets. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junior, A.V.; Nascimento, J.R.O.D.; Lajolo, F.M. Molecular cloning and characterization of an α-amylase occuring in the pulp of ripening bananas and its expression in Pichia pastoris. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 8222–8228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do Nascimento, J.R.O.; Júnior, A.V.; Bassinello, P.Z.; Cordenunsi, B.R.; Mainardi, J.A.; Purgatto, E.; Lajolo, F.M. Beta-amylase expression and starch degradation during banana ripening. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2006, 40, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, G.; Yin, X.; Zhang, A.; Wang, M.; Zhu, Q.; Liu, X.; Xie, X.; Chen, K.; Grierson, D. Ethylene and fruit softening. Food Qual. Saf. 2017, 1, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Miao, H.; Liu, J.; Xu, B.; Yao, X.; Xu, C.; Zhao, S.; Fang, X.; Jia, C.; Wang, J.; et al. Musa balbisiana genome reveals subgenome evolution and functional divergence. Nat. Plants 2019, 5, 810–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botet, R.; Keurentjes, J.J.B. The role of transcriptional regulation in hybrid vigor. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paschold, A.; Jia, Y.; Marcon, C.; Lund, S.; Larson, N.B.; Yeh, C.; Ossowski, S.; Lanz, C.; Nettleton, D.; Schnable, P.S.; et al. Complementation contributes to transcriptome complexity in maize (Zea mays L.) hybrids relative to their inbred parents. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 2445–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Zhu, X.; Elling, A.A.; Chen, L.; Wang, X.; Guo, L.; Liang, M.; He, H.; Zhang, H.; Chen, F.; et al. Global epigenetic and transcriptional trends among two rice subspecies and their reciprocal hybrids. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Jiao, C.; Schwaninger, H.; Chao, C.T.; Ma, Y.; Duan, N.; Khan, A.; Ban, S.; Xu, K.; Cheng, L.; et al. Phased diploid genome assemblies and pan-genomes provide insights into the genetic history of apple domestication. Nat. Genet. 2020, 52, 1423–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, R.; Long, X.; Wang, W.L.; Huang, Y.; Huang, W.X.; Yao, J.Y. Preliminary report on introduction experiment of nine banana cultivars in Guangxi. Guangdong Agric. Sci. 2013, 40, 42–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Cheng, D.; Wang, B.; Khan, I.; Ni, Y. Ethylene control technologies in extending postharvest shelf life of climacteric fruit. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 7308–7319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattyn, J.; Vaughan-Hirsch, J.; Van de Poel, B. The regulation of ethylene biosynthesis: A complex multilevel control circuitry. New Phytol. 2021, 229, 770–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.Y.; Kuang, J.F.; Qi, X.N.; Ye, Y.J.; Wu, Z.X.; Chen, J.Y.; Lu, W.J. A comprehensive investigation of starch degradation process and identification of a transcriptional activator MabHLH6 during banana fruit ripening. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2018, 16, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordenunsi-Lysenko, B.R.; Nascimento, J.R.O.; Castro-Alves, V.C.; Purgatto, E.; Fabi, J.P.; Peroni-Okyta, F.H.G. The starch is (not) just another brick in the wall: The primary metabolism of sugars during banana ripening. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Whistler, R.L.; BeMiller, J.N.; Hamaker, B.R. Banana starch: Production, physicochemical properties, and digestibility—A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2005, 59, 443–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufour, D.; Gibert, O.; Giraldo, A.; Sánchez, T.; Reynes, M.; Pain, J.; González, A.; Fernández, A.; Díaz, A. Differentiation between cooking bananas and dessert bananas. 2. thermal and functional characterization of cultivated colombian musaceae (Musa sp.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 7870–7876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peroni-Okita, F.H.; Cardoso, M.B.; Agopian, R.G.; Louro, R.P.; Nascimento, J.R.; Purgatto, E.; Tavares, M.I.; Lajolo, F.M.; Cordenunsi, B.R. The cold storage of green bananas affects the starch degradation during ripening at higher temperature. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 96, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Huang, S.; Dong, T.; Yang, Q.; Yi, G. Analysis of resistant starch degradation in postharvest ripening of two banana cultivars: Focus on starch structure and amylases. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2016, 119, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, W.; Kuang, J.; Chen, L.; Xie, H.; Peng, H.; Xiao, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, W.; He, Q.; Chen, J.; et al. Molecular characterization of banana NAC transcription factors and their interactions with ethylene signalling component EIL during fruit ripening. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 5171–5187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Song, G.; Liu, Z.; Qu, X.; Chen, R.; Jiang, D.; Sun, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, D. Global epigenomic analysis indicates that epialleles contribute to Allele-specific expression via Allele-specific histone modifications in hybrid rice. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conesa, A.; Gotz, S.; Garcia-Gomez, J.M.; Terol, J.; Talon, M.; Robles, M. Blast2GO: A universal tool for annotation, visualization and analysis in functional genomics research. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 3674–3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, C.Y.; Wilkins, T.A. A modified hot borate method significantly enhance the yield of high-quality RNA from cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Anal. Biochem. 1994, 223, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhong, H.; Kuang, J.; Li, J.; Lu, W.; Chen, J. Validation of reference genes for RT-qPCR studies of gene expression in banana fruit under different experimental conditions. Planta 2011, 234, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


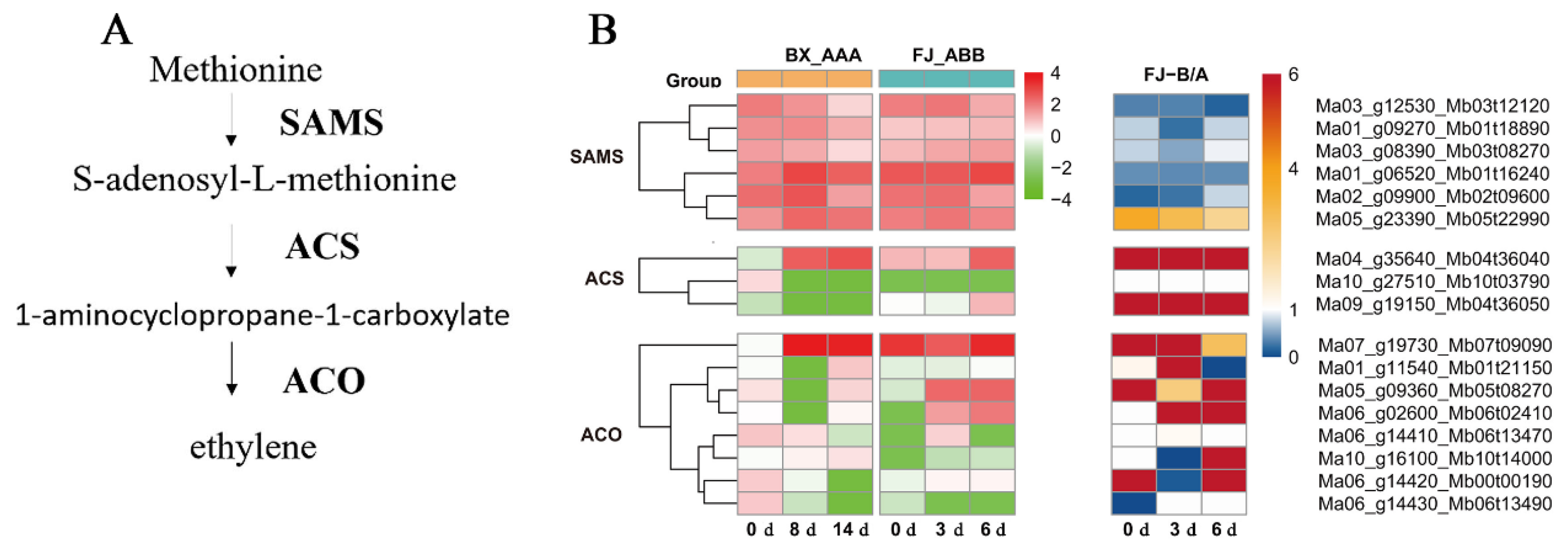
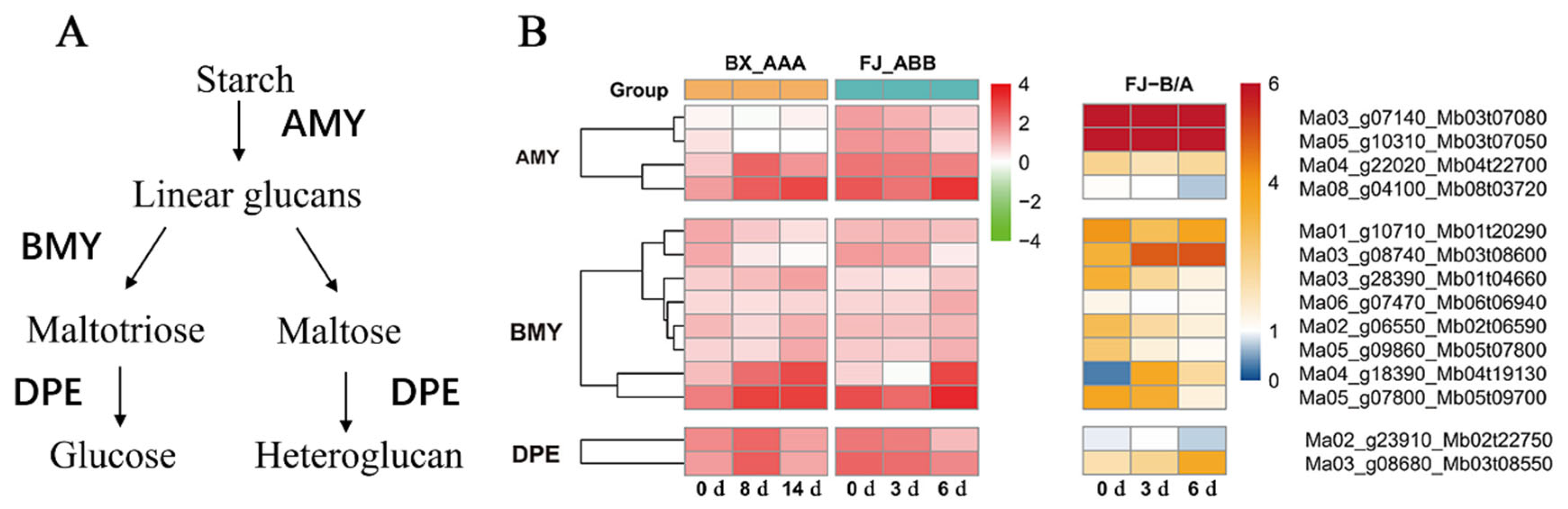
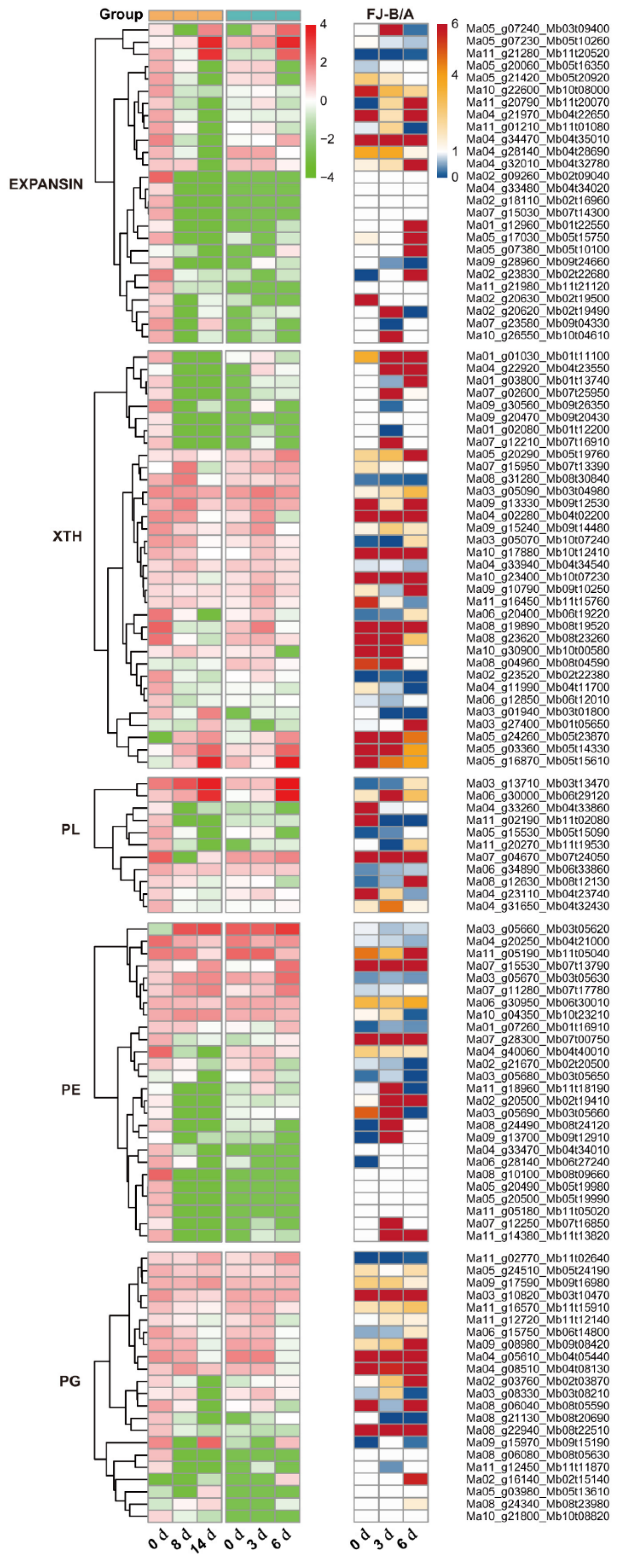
| Gene Name | Number of DEGs | A > B | B > 4A | ASE Ratio (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAMS-3d | 6 | 5 | 0 | 83.33 |
| SAMS-6d | 6 | 5 | 0 | 83.33 |
| ACS-3d | 3 | 0 | 2 | 66.67 |
| ACS-6d | 3 | 0 | 2 | 66.67 |
| ACO-3d | 8 | 2 | 3 | 62.50 |
| ACO-6d | 8 | 1 | 4 | 62.50 |
| Gene Name | Number of DEGs | A > B | B > 4A | ASE Ratio (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AMY-3d | 4 | 0 | 2 | 50 |
| AMY-6d | 4 | 1 | 2 | 75 |
| BMY-3d | 8 | 0 | 1 | 12.5 |
| BMY-6d | 8 | 0 | 1 | 12.5 |
| DPE-3d | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| DPE-6d | 2 | 1 | 0 | 50 |
| Gene Name | Number of DEGs | A > B | B > 4A | ASE Ratio (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EXPANSIN-3d | 26 | 5 | 4 | 34.62 |
| EXPANSIN-6d | 26 | 6 | 8 | 53.85 |
| XTH-3d | 34 | 12 | 14 | 76.47 |
| XTH-6d | 34 | 7 | 12 | 55.88 |
| PL-3d | 11 | 7 | 3 | 90.91 |
| PL-6d | 11 | 3 | 2 | 45.45 |
| PE-3d | 26 | 7 | 9 | 61.54 |
| PE-6d | 26 | 9 | 5 | 53.85 |
| PG-3d | 22 | 5 | 4 | 40.91 |
| PG-6d | 22 | 4 | 8 | 54.55 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fang, F.; Liu, B.; Chen, Q.; Xiao, L.; Deng, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, X.; Pang, X. Impact of Allele-Specific Expression on Ripening and Quality Characteristics of ABB Banana Fruit. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4090. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094090
Fang F, Liu B, Chen Q, Xiao L, Deng Z, Zhang Z, Huang X, Pang X. Impact of Allele-Specific Expression on Ripening and Quality Characteristics of ABB Banana Fruit. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):4090. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094090
Chicago/Turabian StyleFang, Fang, Bin Liu, Qiuzi Chen, Lisi Xiao, Zhuozi Deng, Zhaoqi Zhang, Xuemei Huang, and Xuequn Pang. 2025. "Impact of Allele-Specific Expression on Ripening and Quality Characteristics of ABB Banana Fruit" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 4090. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094090
APA StyleFang, F., Liu, B., Chen, Q., Xiao, L., Deng, Z., Zhang, Z., Huang, X., & Pang, X. (2025). Impact of Allele-Specific Expression on Ripening and Quality Characteristics of ABB Banana Fruit. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 4090. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094090






