Prognostic Value of Erythrogram Indicators and C-Reactive Protein Levels in Predicting Outcomes of Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characteristics and Outcome of Study Participants
2.2. Erythrogram Indicators in the Evaluation of COVID-19
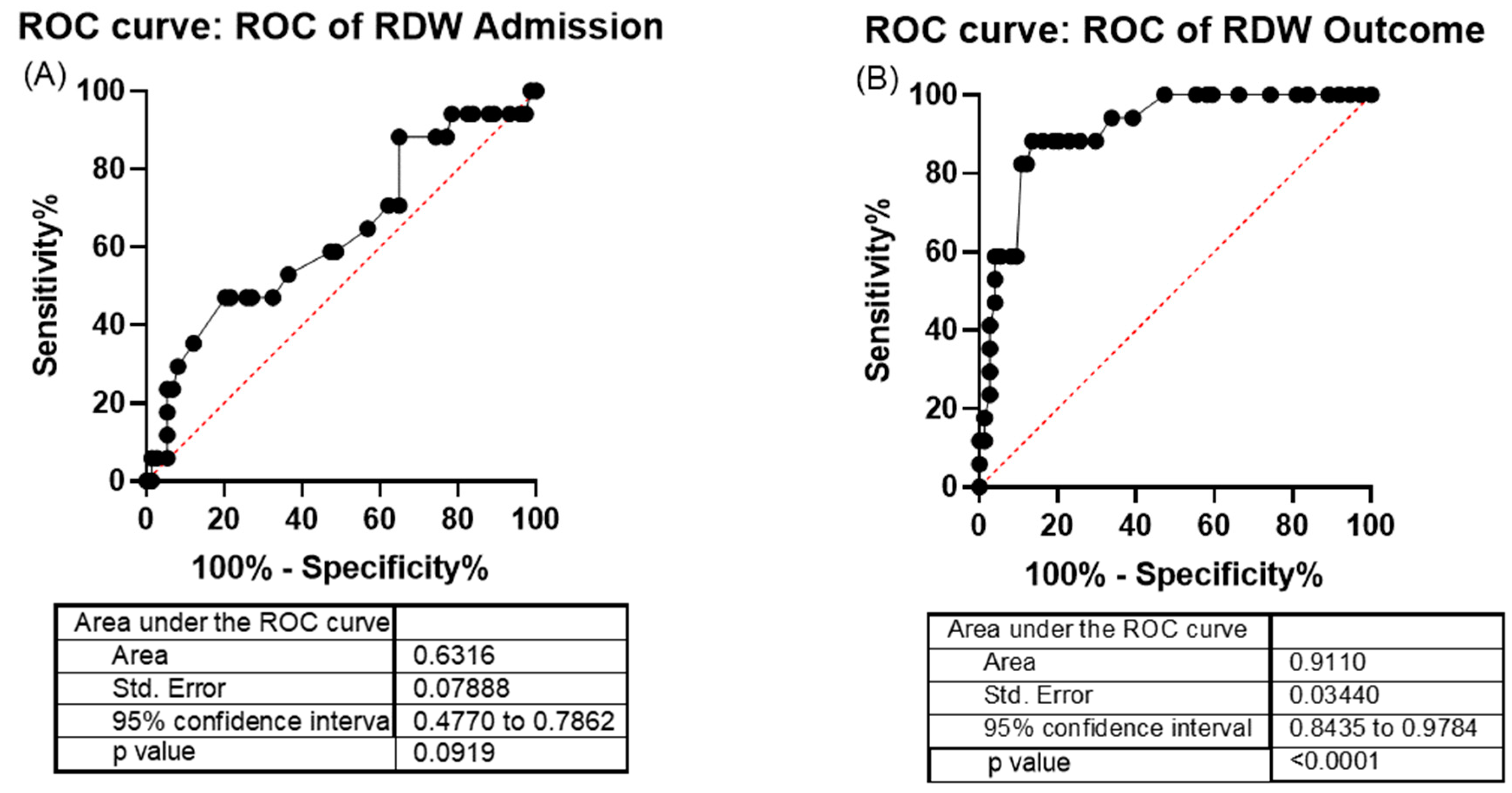
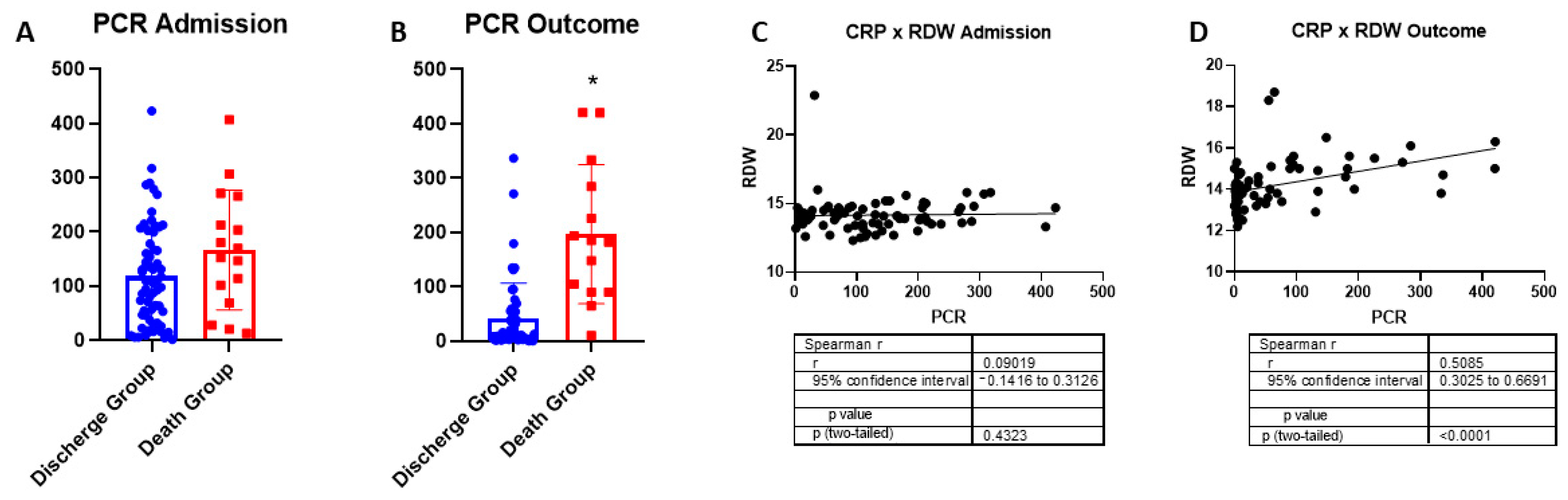
2.3. Red Cell Distribution Width and C-Reactive Protein as COVID-19 Indicators of Severity
3. Discussion
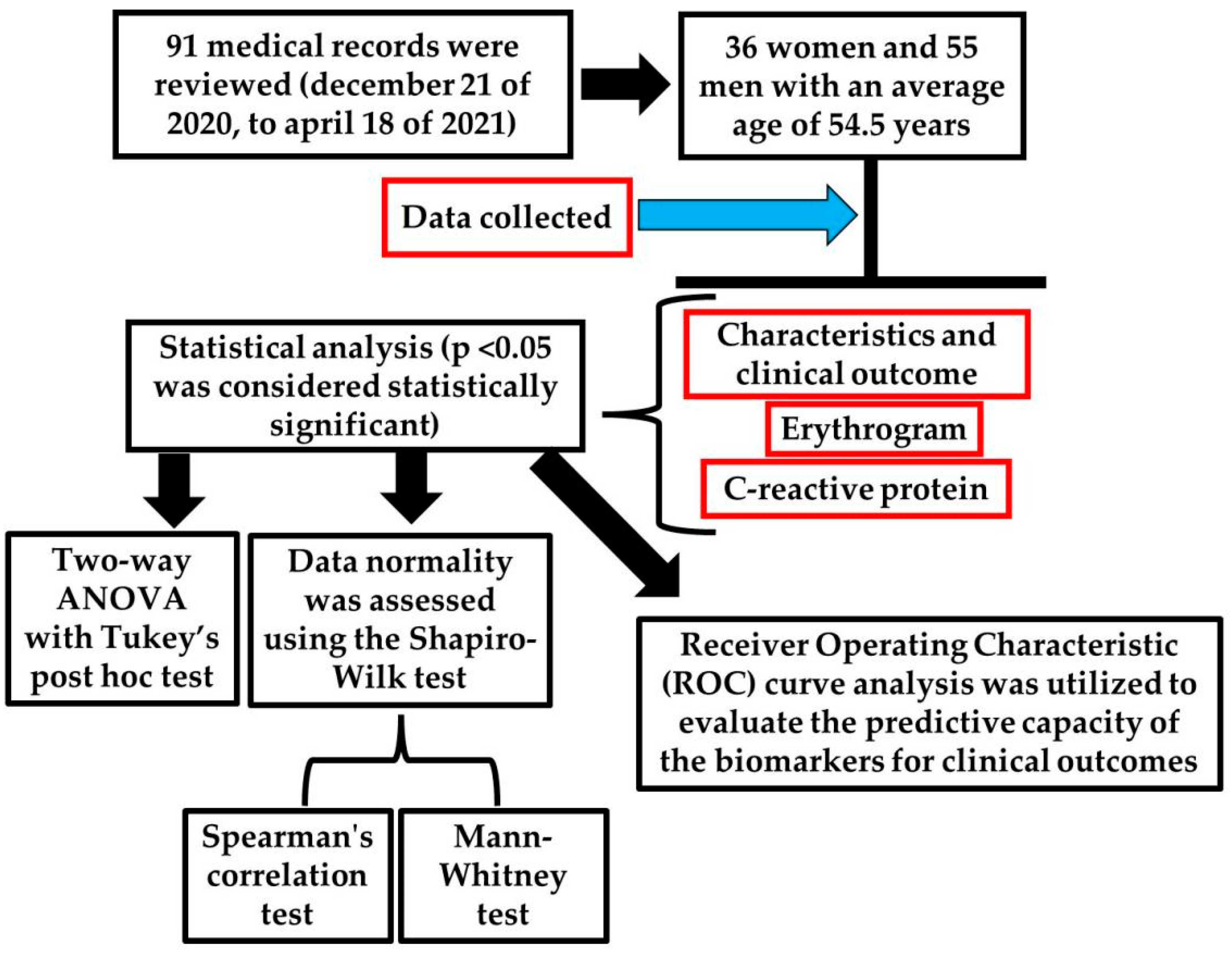
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Design
4.2. Patients Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
4.3. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Briassoulis, G.; Briassoulis, P.; Ilia, S.; Miliaraki, M.; Briassouli, E. The Anti-Oxidative, Anti-Inflammatory, Anti-Apoptotic, and Anti-Necroptotic Role of Zinc in COVID-19 and Sepsis. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayala, J.C.; Grismaldo, A.; Sequeda-Castañeda, L.G.; Aristizábal-Pachón, A.F.; Morales, L. Oxidative Stress in Icu Patients: Ros as Mortality Long-Term Predictor. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farnsworth, C.W.; Roemmich, B.; Prostko, J.; Davis, G.; Murtagh, G.; Jackson, L.; Jacobson, C.; Jeanblanc, N.; Griffiths, T.; Frias, E.; et al. Systemic inflammation is associated with worse outcomes from SARS-CoV-2 infection but not neutralizing antibody. Microbiol. Spectr. 2025, 13, e0245924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Han, X.; Li, C.; Cui, J.; Yuan, X.; Meng, J.; Han, Z.; Han, X.; Chen, W.; Xiong, J.; et al. Clinical Outcomes of Hospitalized Immunocompromised Patients With COVID-19 and the Impact of Hyperinflammation: A Retrospective Cohort Study. J. Inflamm. Res. 2025, 18, 3385–3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maláska, J.; Stašek, J.; Máca, J.; Kutěj, M.; Duška, F.; Kafka, P.; Klementová, O.; Doubravská, L.; Hruda, J.; Fencl, M.; et al. Effects of two different dexamethasone dosing regimens on ventilator-free days and long-term mortality in COVID-19 patients with moderate-to-severe ARDS: The REMED randomized clinical trial. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2024, 29, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Liu, S.; Bian, Y.; Li, L.; Qian, B.; Shen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Abuduaini, A.; Dong, F.; Zhang, X.; et al. Safety and efficacy of oral administrated cepharanthine in non-hospitalized, asymptomatic or mild COVID-19 patients: A Double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial: Author detials. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran Van Hoi, E.; Appelman, B.; Mooijaart, S.; Dalm, V.A.S.H.; Polinder Bos, H.A.; van Heemst, D.; van Raaij, B.F.M.; Noordam, R.; Kuranova, A.; Hoogerwerf, J.J.; et al. The Association of Inflammatory Markers with Frailty and In-Hospital Mortality in Older COVID-19 Patients. Exp. Gerontol. 2024, 195, 112534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastos Mendes, L.F.; Dal-Pizzol, H.R.; Prestes, G.; Saibro Girardi, C.; Santos, L.; Gelain, D.P.; Westphal, G.A.; Walz, R.; Ritter, C.; Dal-Pizzol, F.; et al. Prediction of COVID-19 mortality using machine learning strategies and a large-scale panel of plasma inflammatory proteins: A cohort study. Med. Intensiva (Engl. Ed.) 2025, 3, 502200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Xie, X.; Tu, Z.; Fu, J.; Xu, D.; Zhou, Y. The signal pathways and treatment of cytokine storm in COVID-19. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021, 6, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coradduzza, D.; Medici, S.; Chessa, C.; Zinellu, A.; Madonia, M.; Angius, A.; Carru, C.; De Miglio, M.R. Assessing the Predictive Power of the Hemoglobin/Red Cell Distribution Width Ratio in Cancer: A Systematic Review and Future Directions. Medicina 2023, 59, 2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; She, Y.; Fu, L.; Zhou, R.; Xiang, W.; Luo, L. Association Between Red Cell Distribution Width and Hospital Mortality in Patients with Sepsis. J. Int. Med. Res. 2021, 49, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, N.; Jiang, M.; Wu, C.; He, F. Red Cell Distribution Width at Admission Predicts the Frequency of Acute Kidney Injury and 28-Day Mortality in Patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Shock 2022, 57, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Huang, X.; Yue, S.; Wang, J.; Ye, E.; Huang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Niu, D.; Hou, X.; Wu, J. Association of Red Cell Distribution Width-to-Platelet Ratio and Mortality in Patients with Sepsis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2022, 2022, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.W.; Chun, W.; Lee, H.J.; Min, J.H.; Kim, S.M.; Seo, J.Y.; Ahn, K.S.; Oh, S.R. The Role of Macrophages in the Development of Acute and Chronic Inflammatory Lung Diseases. Cells 2021, 10, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.S.; Chen, Z.Q.; Hu, Y.F.; Chen, J.X.; Xu, W.W.; Shu, J.; Pan, J.Y. Red Blood Cell Distribution Width Is Associated with Mortality Risk in Patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Based on the Berlin Definition: A Propensity Score Matched Cohort Study. Heart Lung 2020, 49, 641–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, W.; Li, R.; Liang, H.; Huang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Li, Y.; Ou, L.; Mao, P.; Liu, X.; Li, Y. Development and Validation of a Clinical Risk Model to Predict the Hospital Mortality in Ventilated Patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: A Population-Based Study. BMC Pulm. Med. 2022, 22, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joosse, H.J.; Van Oirschot, B.A.; Kooijmans, S.A.A.; Hoefer, I.E.; Van Wijk, R.A.H.; Huisman, A.; Van Solinge, W.W.; Haitjema, S. In-vitro and in—Silico Evidence for Oxidative Stress as Drivers for RDW. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 9223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emans, M.E.; Gaillard, C.A.; Pfister, R.; Tanck, M.W.; Boekholdt, S.M.; Wareham, N.J.; Khaw, K.T. Red cell distribution width is associated with physical inactivity and heart failure, independent of established risk factors, inflammation or iron metabolism; the EPIC-Norfolk study. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 168, 3550–3555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foy, B.H.; Carlson, J.C.T.; Reinertsen, E.; Padros, I.V.; Pallares Lopez, R.; Palanques-Tost, E.; Mow, C.; Westover, M.B.; Aguirre, A.D.; Higgins, J.M. Association of Red Blood Cell Distribution Width With Mortality Risk in Hospitalized Adults With SARS-CoV-2 Infection. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e2022058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soma, P.; Bester, J. Pathophysiological Changes in Erythrocytes Contributing to Complications of Inflammation and Coagulation in COVID-19. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 899629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yu, C.-H.; Guo, K.-P.; Huang, C.-Z.; Mo, L.-Y. Prognostic role of red blood cell distribution width in patients with sepsis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Immunol. 2020, 21, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Askar, S.; Deveboynu, S.N.; Er, H.; Askar, T.K.; Hismiogullari, A.A. Changes in pro-inflammatory cytokines and antimicrobial proteins in elderly women with iron deficiency anemia. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 35, 298–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, T.; Cong, Y.; Meng, J.; Qian, H.; Ye, W.; Sun, W.S.; Zhao, J.N.; Bao, N.R. Arachidonic acid causes hidden blood loss-like red blood cell damage through oxidative stress reactions. J. Surg. Res. 2017, 211, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Lu, D.; Zhang, L.; Wang, M. Prognostic value of red blood cell distribution width in sepsis induced cardiomyopathy patients. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 24483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakobyan, S.; Hakobyan, L.; Abroyan, L.; Avetisyan, A.; Avagyan, H.; Bayramyan, N.; Niazyan, L.; Davidyants, M.; Sargsyan, K.; Ghalechyan, T.; et al. Pathology of Red Blood Cells in Patients with SARS-CoV-2. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topaz, G.; Kitay-Cohen, Y.; Peled, L.; Gharra, W.; Kaminer, K.; Eitan, M.; Mahamid, L.; Shilo, L. The Association between Red Cell Distribution Width and Poor Outcomes in Hospitalized Patients with Influenza. J. Crit. Care 2017, 41, 166–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, H.; Cao, X.; Deng, R.; Ye, Y.; Fu, Z.; Gou, L.; Shao, F.; Li, J.; Fu, W.; et al. Red Cell Distribution Width (RDW): A Prognostic Indicator of Severe COVID-19. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owoicho, O.; Tapela, K.; Olwal, C.O.; Djomkam Zune, A.L.; Nganyewo, N.N.; Quaye, O. Red Blood Cell Distribution Width as a Prognostic Biomarker for Viral Infections: Prospects and Challenges. Biomark. Med. 2022, 16, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linssen, J.; Ermens, A.; Berrevoets, M.; Seghezzi, M.; Previtali, G.; van der Sar-van der Brugge, S.; Russcher, H.; Verbon, A.; Gillis, J.; Riedl, J.; et al. A Novel Haemocytometric COVID-19 Prognostic Score Developed and Validated in an Observational Multicentre European Hospital-Based Study. eLife 2020, 9, e63195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, T.; Stefanoni, D.; Dzieciatkowska, M.; Issaian, A.; Nemkov, T.; Hill, R.C.; Francis, R.O.; Hudson, K.E.; Buehler, P.W.; Zimring, J.C.; et al. Evidence of Structural Protein Damage and Membrane Lipid Remodeling in Red Blood Cells from COVID-19 Patients. J. Proteome Res. 2020, 19, 4455–4469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrán-García, J.; Osca-Verdegal, R.; Pallardó, F.V.; Ferreres, J.; Rodríguez, M.; Mulet, S.; Sanchis-Gomar, F.; Carbonell, N.; García-Giménez, J.L. Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in COVID-19-Associated Sepsis: The Potential Role of Anti-Oxidant Therapy in Avoiding Disease Progression. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 2–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalmazzo, L.F.F.; de Almendra Freitas, A.F.; Alves, B.E.; Cardoso, D.K.; de Carvalho, E.F.; Akil, F.; da Cunha Vieira Perini, F.; Pires, K.T.; de Aguiar, L.C.; Moraes, M.C.; et al. Transfusion Profile, Clinical Characteristics, Comorbidities and Outcomes of 3014 Hospitalized Patients Diagnosed with COVID-19 in Brazil. Vox Sang. 2021, 116, 983–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anemia—PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29763170/ (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- Huang, Y.; Tu, M.; Wang, S.; Chen, S.; Zhou, W.; Chen, D.; Zhou, L.; Wang, M.; Zhao, Y.; Zeng, W.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of Laboratory Confirmed Positive Cases of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Wuhan, China: A Retrospective Single Center Analysis. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2020, 36, 101606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suna, S.; Caib, X.; Wang, H.; He, G.; Lin, Y.; Lu, B.; Chen, C.; Pan, Y.; Hu, X. Abnormalities of Peripheral Blood System in Patients with COVID-19 in Wenzhou, China. Clin. Chim. Acta J. 2020, 507, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, B.E.; Chong, V.C.L.; Chan, S.S.W.; Lim, G.H.; Lim, K.G.E.; Tan, G.B.; Mucheli, S.S.; Kuperan, P.; Ong, K.H. Hematologic Parameters in Patients with COVID-19 Infection. Am. J. Hematol. 2020, 95, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellmann-weiler, R.; Lanser, L.; Barket, R.; Rangger, L.; Schapfl, A.; Schaber, M.; Fritsche, G.; Wöll, E.; Weiss, G. Prevalence and Predictive Value of Anemia and Dysregulated Iron Homeostasis in Patients with COVID-19 Infection. J.Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira Júnior, W.V.; de Paula Sabino, A.; Figueiredo, R.C.; Rios, D.R.A. Inflammation and Poor Response to Treatment with Erythropoietin in Chronic Kidney Disease. Braz. J. Nephrol. 2015, 37, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, R.; Kanso, A.; Sedor, J.R. Chronic Kidney Disease and Its Complications. Prim. Care 2008, 35, 329–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yağcı, S.; Serin, E.; Odabaşı, M.S.; Acicbe, Ö.; Zeren, M.İ. The Relationship between Serum Erythropoietin, Hepcidin, and Haptoglobin Levels with Disease Severity and Other Biochemical Values in Patients with COVID-19. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2021, 43, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, L.; Christensen, S.; Lenler-petersen, P.; Johnsen, S.P. Anemia and 90-Day Mortality in COPD Patients Requiring Invasive Mechanical Ventilation. Clin. Epidemiol. 2010, 3, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadre, S.K.; Jhand, A.S.; Abuqayyas, S.; Wang, X.; Guzman, J.; Duggal, A. Effect of Anemia on Mortality in Mechanically Ventilated Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. J. Intensive Care Med. 2017, 35, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polo, T.C.F.; Miot, H.A. Aplicações Da Curva ROC Em Estudos Clínicos e Experimentais. J. Vasc. Bras. 2020, 19, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Failace, R.; Fernandes, F. Hemograma: Manual de Interpretação, 6th ed.; Artmed: Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Nooh, H.A.; Abdellateif, M.S.; Refaat, L.; Kandeel, E.Z.; Bayoumi, A.; Samra, M.; Khafagy, M. The Role of Inflammatory Indices in the Outcome of COVID-19 Cancer Patients. Med. Oncol. 2021, 39, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magri, C.J.; Tian, T.X.; Camilleri, L.; Xuereb, R.; Galea, J.; Fava, S. Red Blood Cell Distribution Width and Myocardial Scar Burden in Coronary Artery Disease. Postgrad. Med. J. 2017, 93, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, K.V.; Semba, R.D.; Ferrucci, L.; Newman, A.B.; Fried, L.P.; Wallace, R.B.; Bandinelli, S.; Phillips, C.S.; Yu, B.; Connelly, S.; et al. Red Cell Distribution Width and Mortality in Older Adults: A Meta-Analysis. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2010, 65A, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.-D.; Ding, M.; Dong, X.; Zhang, J.-J.; Kursat Azkur, A.; Azkur, D.; Gan, H.; Sun, Y.-L.; Fu, W.; Li, W.; et al. Risk Factors for Severe and Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients: A Review. Allergy 2021, 76, 428–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horta-Baas, G.; del Socorro Romero-Figueroa, M. Clinical Utility of Red Blood Cell Distribution Width in Inflammatory and Non-Inflammatory Joint Diseases. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 22, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draxler, A.; Blaschke, A.; Binar, J.; Weber, M.; Haslacher, M.; Bartak, V.; Bragagna, L.; Mare, G.; Maqboul, L.; Klapp, R.; et al. Redox Biology Age-Related Influence on DNA Damage, Proteomic Inflammatory Markers and Oxidative Stress in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients Compared to Healthy Controls. Redox Biol. 2023, 67, 102914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pincemail, J.; Cavalier, E.; Charlier, C.; Bien, J.C.; Brevers, E.; Courtois, A.; Fadeur, M.; Meziane, S.; Goff, C.-L.; Misset, B.; et al. Oxidative Stress Status in COVID-19 Patients Hospitalized in Intensive Care Unit for Severe Pneumonia. A Pilot Study. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Cao, Y.; Si, J.; Li, J.; Cao, K.; Pang, X. Probucol Decreases Homocysteine-Stimulated CRP Production in Rat Aortic Smooth Muscle Cells via Regulating HO-1/NADPH Oxidase/ROS/P38 Pathway. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. (Shanghai) 2021, 53, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-torres, V.; Sánchez-chica, E.; Castejón, R.; Bermejo, A.C.; Mills, P.; Diago-sempere, E.; Rosado, S.; Sancho-lópez, A.; Ruiz-antorán, B.; Fernández-cruz, A. Red Blood Cell Distribution Width as a Marker of Hyperinflammation and Mortality in COVID-19. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2022, 11, 2609–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosmachevskaya, O.V.; Novikova, N.N.; Topunov, A.F.; Blood, R. Carbonyl Stress in Red Blood Cells and Hemoglobin. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedayati-Ch, M.; Ebrahim-Saraie, H.S.; Bakhshi, A. Clinical and Immunological Comparison of COVID-19 Disease between Critical and Non-Critical Courses: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1341168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Andretta, M.E.; Frizzo, M.N.; Goettems-Fiorin, P.B.; Heck, T.G.; Sulzbacher, L.M.; Sulzbacher, M.M.; Ludwig, M.S.; Favero, G.; Rezzani, R.; de Oliveira, V.A. Prognostic Value of Erythrogram Indicators and C-Reactive Protein Levels in Predicting Outcomes of Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4135. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094135
Andretta ME, Frizzo MN, Goettems-Fiorin PB, Heck TG, Sulzbacher LM, Sulzbacher MM, Ludwig MS, Favero G, Rezzani R, de Oliveira VA. Prognostic Value of Erythrogram Indicators and C-Reactive Protein Levels in Predicting Outcomes of Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):4135. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094135
Chicago/Turabian StyleAndretta, Maria Eduarda, Matias Nunes Frizzo, Pauline Brendler Goettems-Fiorin, Thiago Gomes Heck, Lucas Machado Sulzbacher, Maicon Machado Sulzbacher, Mirna Stela Ludwig, Gaia Favero, Rita Rezzani, and Vitor Antunes de Oliveira. 2025. "Prognostic Value of Erythrogram Indicators and C-Reactive Protein Levels in Predicting Outcomes of Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 4135. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094135
APA StyleAndretta, M. E., Frizzo, M. N., Goettems-Fiorin, P. B., Heck, T. G., Sulzbacher, L. M., Sulzbacher, M. M., Ludwig, M. S., Favero, G., Rezzani, R., & de Oliveira, V. A. (2025). Prognostic Value of Erythrogram Indicators and C-Reactive Protein Levels in Predicting Outcomes of Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 4135. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094135








