Therapeutic Effects of Hemerocallis citrina Baroni Extract on Animal Models of Neurodegenerative Diseases Through Serotonin and HLH-30/TFEB-Dependent Mechanisms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
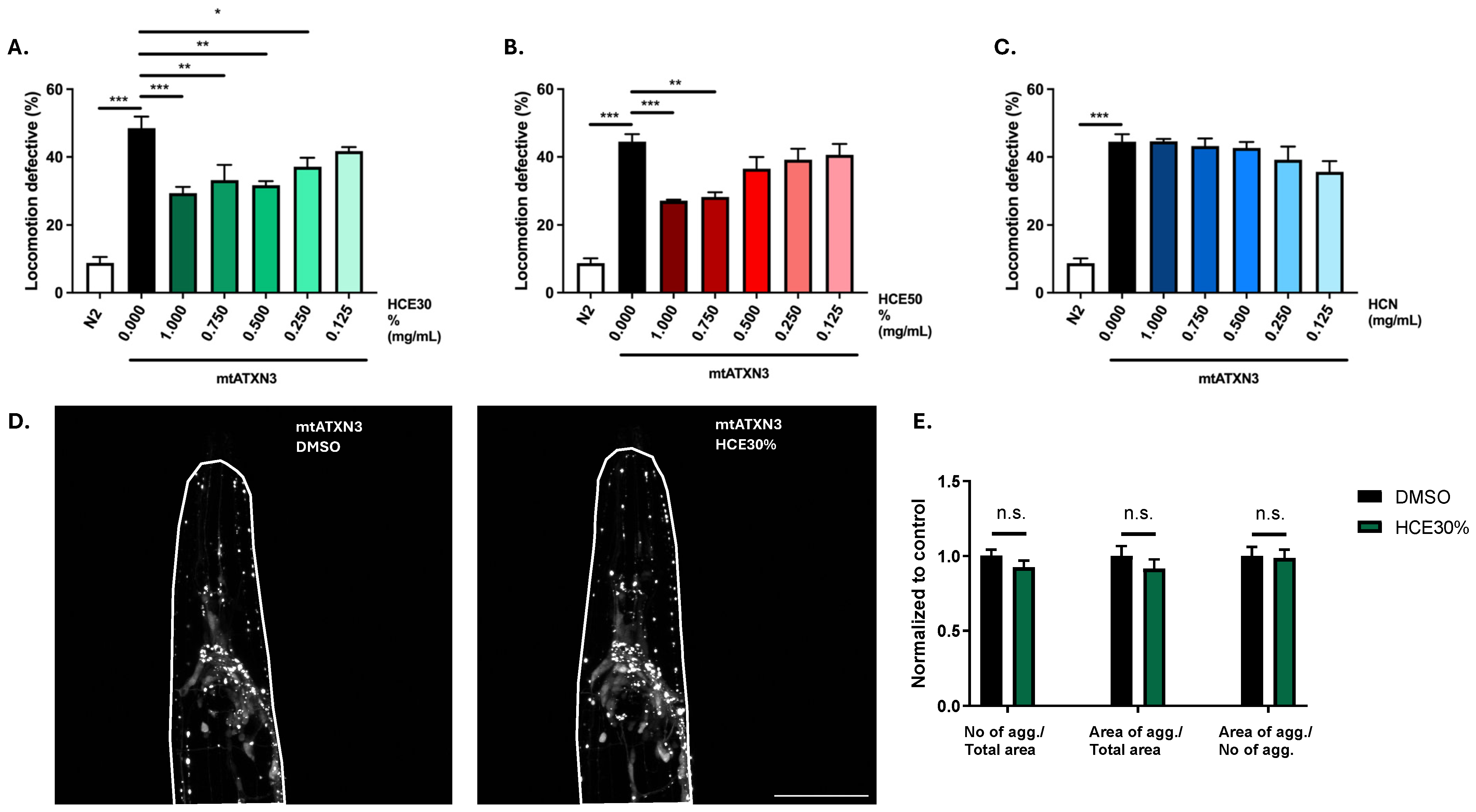
2.1. H. citrina Baroni Ethanolic Extracts Ameliorate Motor Deficits in the Model of MJD/SCA3, Independently of Effects on mATXN3 Neuronal Aggregation
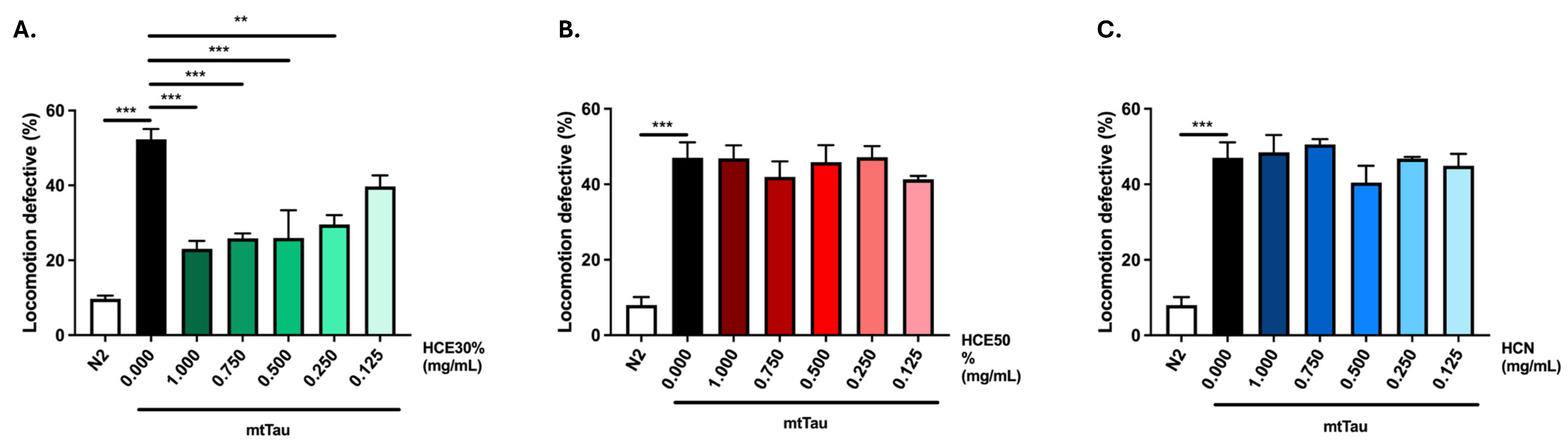
2.2. H. citrina Baroni Ethanolic Extract Ameliorates Motor Deficits in a Model of FTDP-17
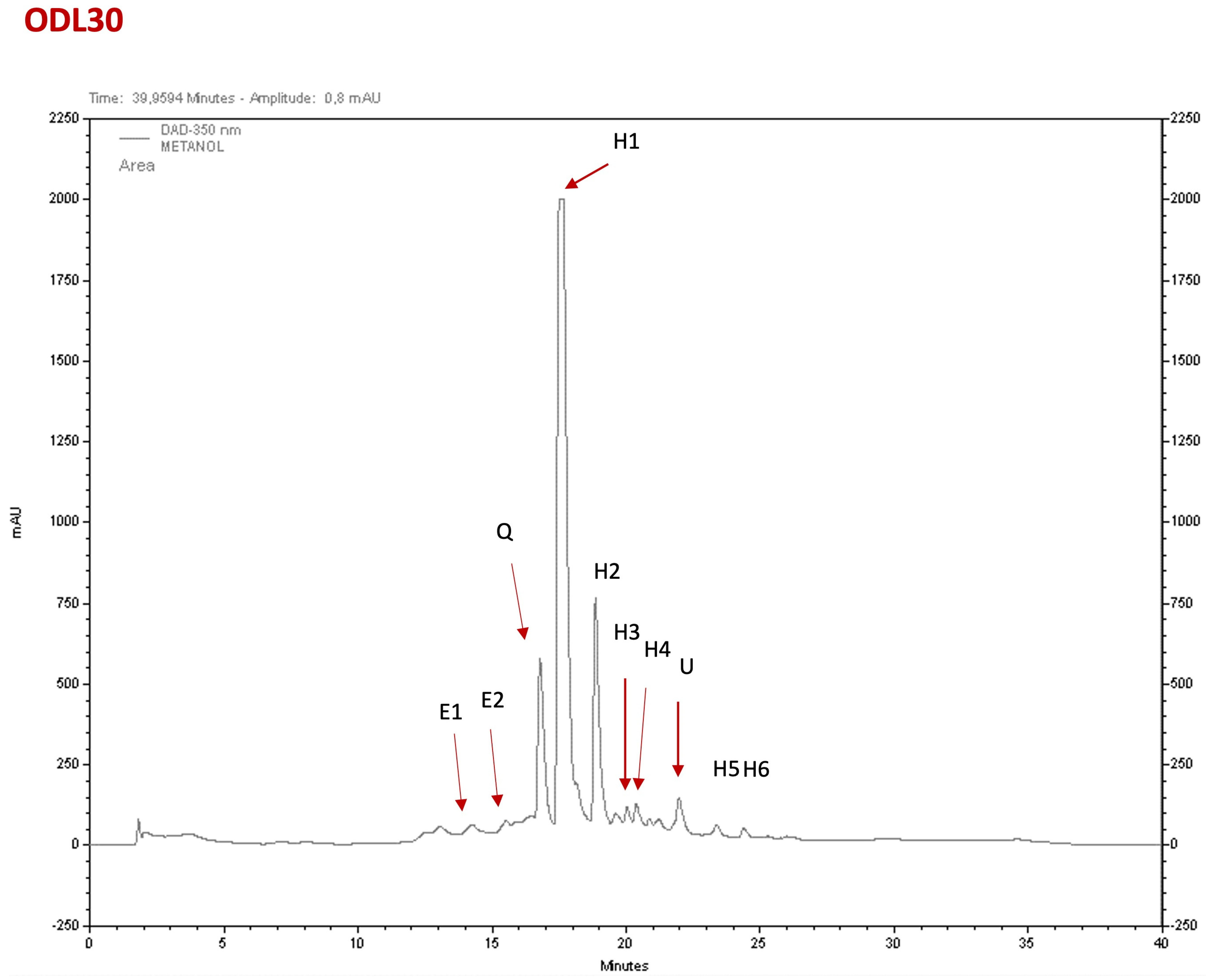
2.3. Phytochemical Composition of the Extracts
2.4. HCE Effect Was Dependent on Serotonergic but Not Dopaminergic Signaling in the MJD/SCA3 Model
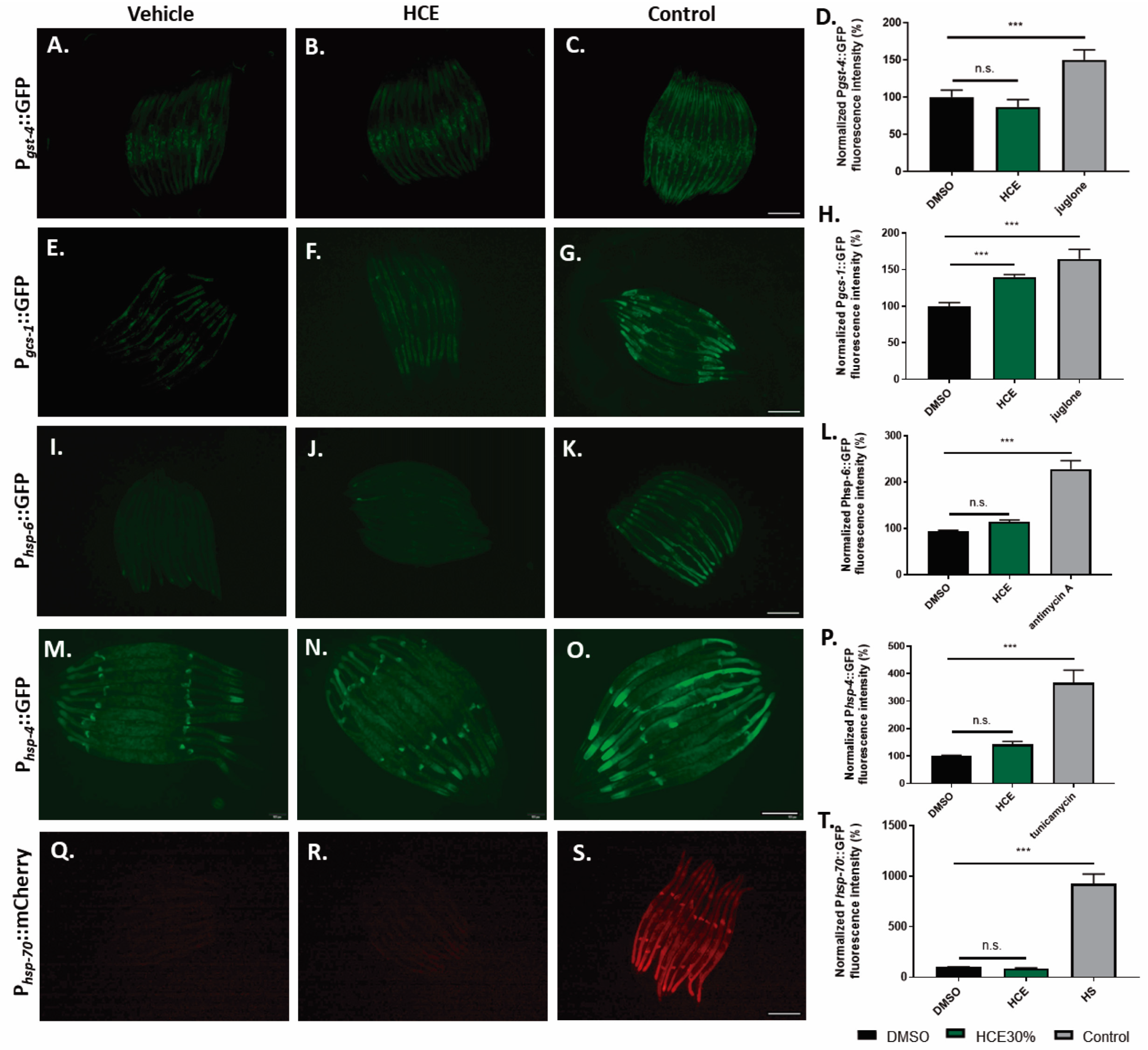
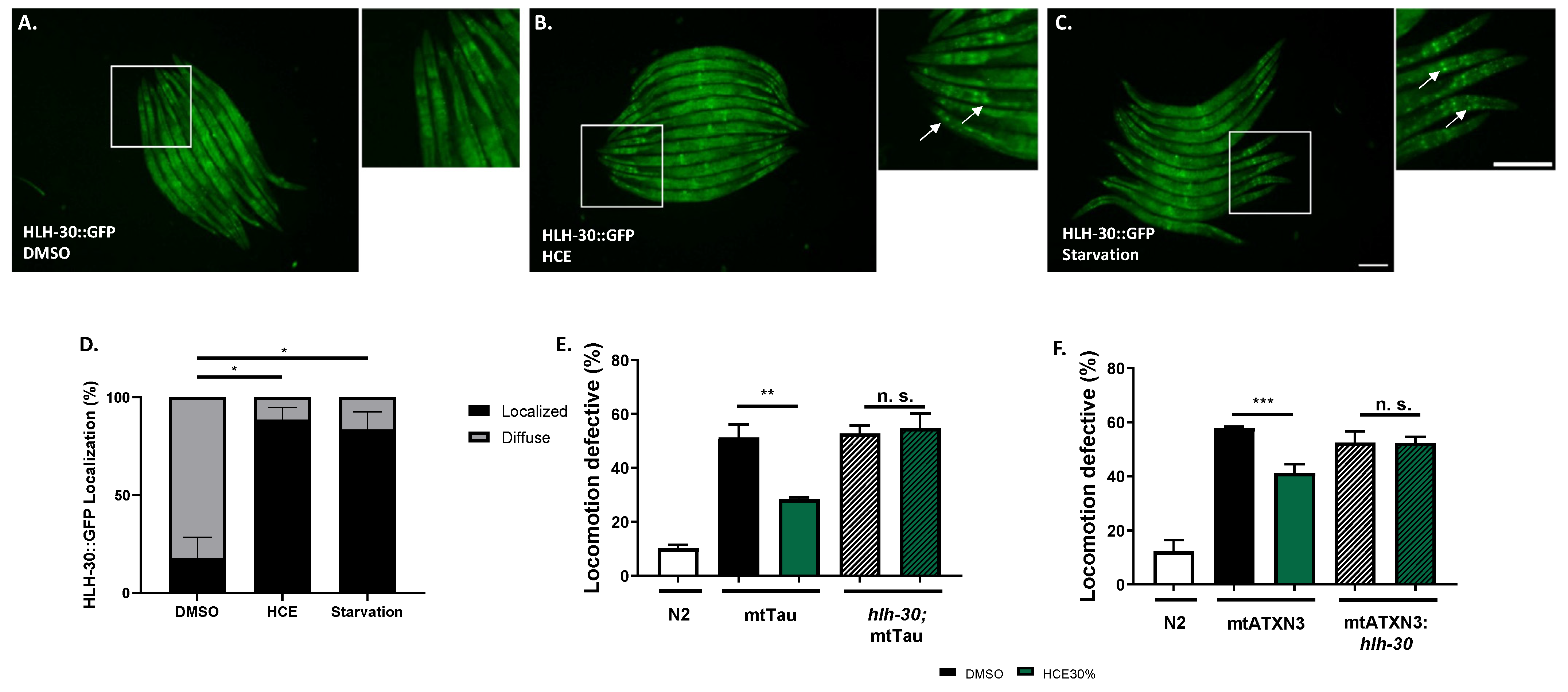
2.5. HCE Treatment Promotes HLH-30/TFEB Nuclear Translocation
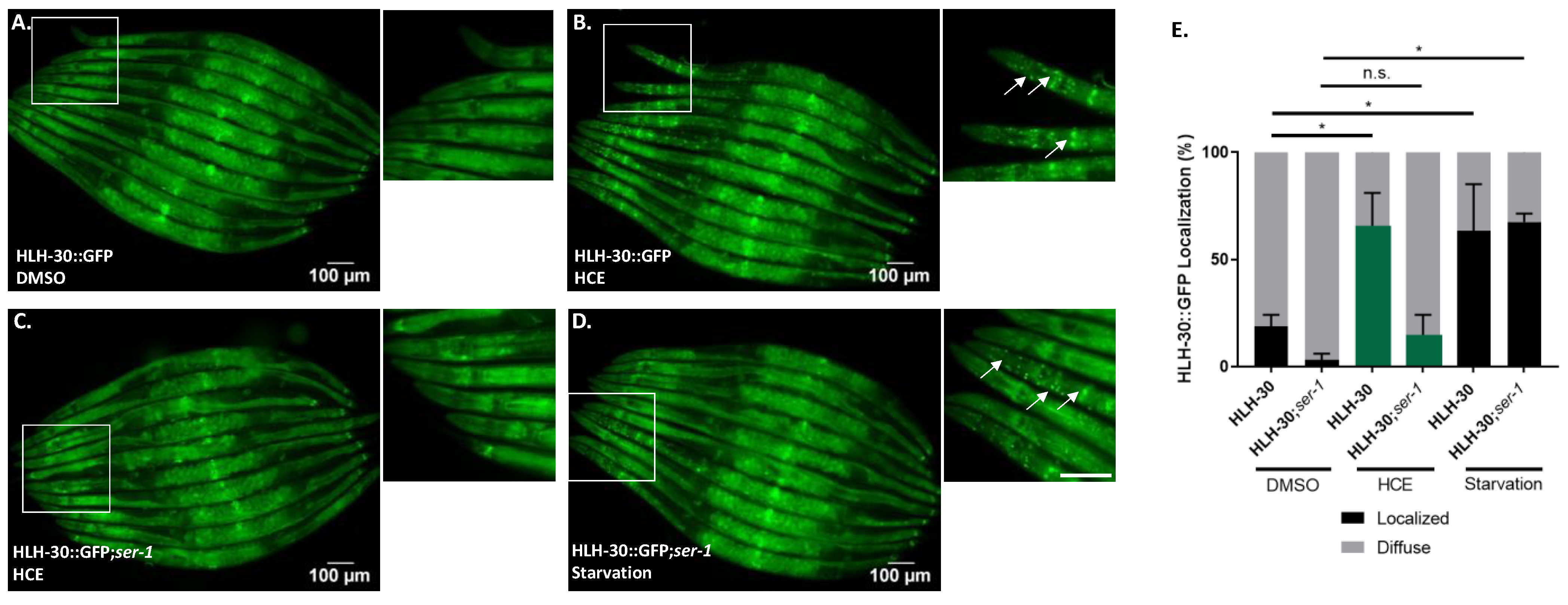
2.6. HLH-30/TFEB Activation by HCE Treatment Requires Serotonergic Signaling
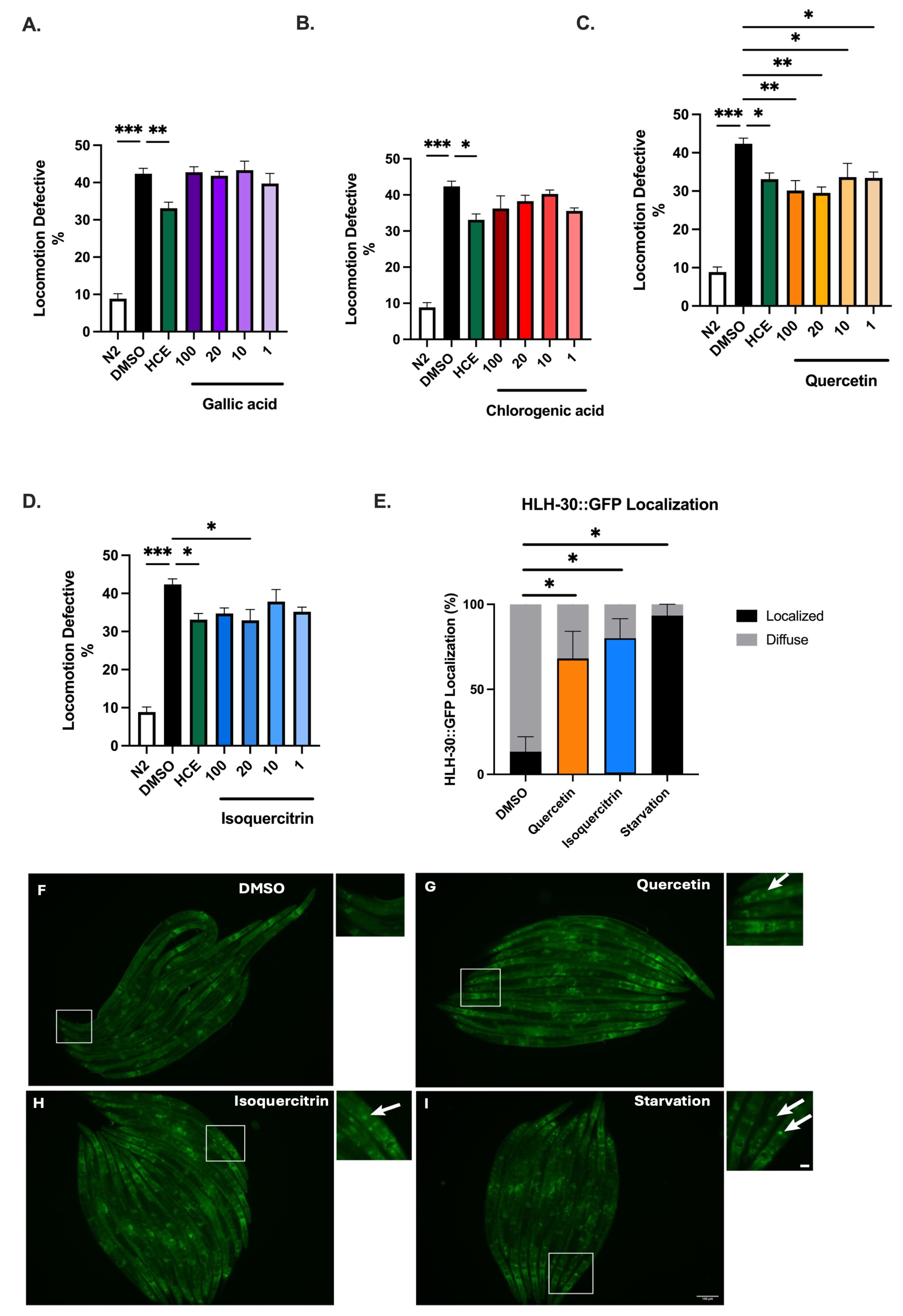
2.7. HCE Effects May Be Mediated by Quercetin or Its Glucoside Derivatives
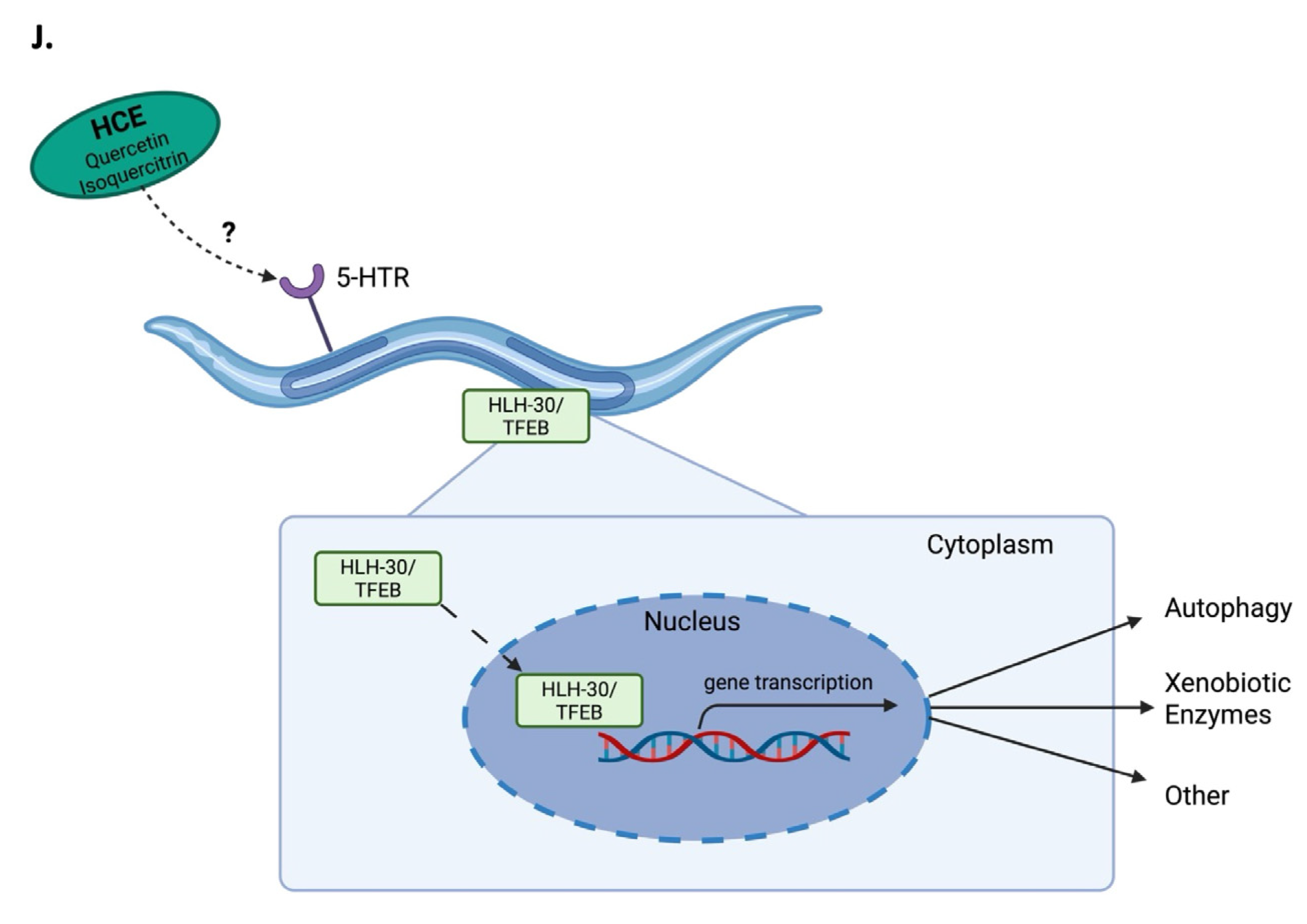
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Extract Preparation
4.2. Phytochemical Analysis
4.3. Nematode Strains and Maintenance
4.4. Nematode Treatments
4.5. Extract Toxicity Assay
4.6. Motility Assay
4.7. Mutant Ataxin-3 Neuronal Aggregation Assay
4.8. Transcriptional Reporter Strains
4.9. Lipid Droplet Staining
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ATXN3 | Ataxin-3 |
| CFP | Cyan Fluorescent Protein |
| DMSO | Dimethyl Sulfoxide |
| FITC | Fluorescein Isothiocyanate |
| GCS-1 | Gamma-glutamyl Cysteine Synthetase 1 |
| GFP | Green Fluorescent Protein |
| GST-4 | Glutathione S-Transferase 4 |
| HCE | Hemerocallis citrina ethanolic Extract |
| HCN | Hemerocallis citrina N-butanol extract |
| HLH | Helix-Loop-Helix |
| HPLC-DAD | High-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Diode Array Detector |
| HSR | Heat Shock Response |
| MAPT | Microtubule Associated Protein Tau |
| MiT/TFE | Microphthalmia/Transcription Factor E |
| MJD | Machado–Joseph Disease |
| mtATXN3 | Mutant Ataxin-3 |
| mtTau | Mutant Tau |
| NDs | Neurodegenerative Diseases |
| NGM | Nematode Growth Media |
| SCA3 | Spinocerebellar Ataxia type 3 |
| SEM | Standard Error of the Mean |
| SERT | Serotonin Transporter |
| TFEB | Transcription Factor EB |
| UPRER | Unfolded Protein Response of the Endoplasmic Reticulum |
| UPRmt | Unfolded Protein Response of the mitochondria |
References
- Soto, C.; Pritzkow, S. Protein Misfolding, Aggregation, and Conformational Strains in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 1332–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansson, O. Biomarkers for Neurodegenerative Diseases. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 954–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyler, S.E.B.; Tyler, L.D.K. Pathways to Healing: Plants with Therapeutic Potential for Neurodegenerative Diseases. IBRO Neurosci. Rep. 2023, 14, 210–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pohl, F.; Teixeira-Castro, A.; Costa, M.D.; Lindsay, V.; Fiúza-Fernandes, J.; Goua, M.; Bermano, G.; Russell, W.; Maciel, P.; Kong Thoo Lin, P. GST-4-Dependent Suppression of Neurodegeneration in C. elegans Models of Parkinson’s and Machado-Joseph Disease by Rapeseed Pomace Extract Supplementation. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilasboas-Campos, D.; Costa, M.D.; Teixeira-Castro, A.; Rios, R.; Silva, F.G.; Bessa, C.; Dias, A.C.P.; Maciel, P. Neurotherapeutic Effect of Hyptis Spp. Leaf Extracts in Caenorhabditis elegans Models of Tauopathy and Polyglutamine Disease: Role of the Glutathione Redox Cycle. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 162, 202–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.; Liu, Y.-J.; Wang, Y.-B.; Yi, L.-T. Role for Monoaminergic Systems in the Antidepressant-like Effect of Ethanol Extracts from Hemerocallis citrina. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 139, 780–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Lin, J.; Gan, A.; Sun, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, M.; Wan, M.; Yan, T.; Jia, Y. Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of the Components in Flowers of Hemerocallis citrina Baroni by UHPLC–Q-TOF-MS/MS and UHPLC–QQQ-MS/MS and Evaluation of Their Antioxidant Activities. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 120, 105329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Yang, F.-F.; Liu, C.-Y.; Liu, X.-M.; Pan, R.-L.; Chang, Q.; Zhang, Z.-S.; Liao, Y.-H. Effects of Phenolic Constituents of Daylily Flowers on Corticosterone- and Glutamate-Treated PC12 Cells. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöls, L.; Bauer, P.; Schmidt, T.; Schulte, T.; Riess, O. Autosomal Dominant Cerebellar Ataxias: Clinical Features, Genetics, and Pathogenesis. Lancet Neurol. 2004, 3, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira-Castro, A.; Jalles, A.; Esteves, S.; Kang, S.; da Silva Santos, L.; Silva-Fernandes, A.; Neto, M.F.; Brielmann, R.M.; Bessa, C.; Duarte-Silva, S.; et al. Serotonergic Signalling Suppresses Ataxin 3 Aggregation and Neurotoxicity in Animal Models of Machado-Joseph Disease. Brain 2015, 138, 3221–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, Y.; Okamoto, T.; Taniwaki, M.; Aizawa, M.; Inoue, M.; Katayama, S.; Kawakami, H.; Nakamura, S.; Nishimura, M.; Akiguchi, I.; et al. CAG Expansions in a Novel Gene for Machado-Joseph Disease at Chromosome 14q32.1. Nat. Genet. 1994, 8, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraemer, B.C.; Zhang, B.; Leverenz, J.B.; Thomas, J.H.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Schellenberg, G.D. Neurodegeneration and Defective Neurotransmission in a Caenorhabditis elegans Model of Tauopathy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 9980–9985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spillantini, M.G.; Bird, T.D.; Ghetti, B. Frontotemporal Dementia and Parkinsonism Linked to Chromosome 17: A New Group of Tauopathies. Brain Pathol. 1998, 8, 387–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira-Castro, A.; Ailion, M.; Jalles, A.; Brignull, H.R.; Vilaça, J.L.; Dias, N.; Rodrigues, P.; Oliveira, J.F.; Neves-Carvalho, A.; Morimoto, R.I.; et al. Neuron-Specific Proteotoxicity of Mutant Ataxin-3 in C. Elegans: Rescue by the DAF-16 and HSF-1 Pathways. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2011, 20, 2996–3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, M.R.M.; Felgueiras, M.L.; Cunha, A.; Chicau, G.; Ferreres, F.; Dias, A.C.P. Differential Phenolic Production in Leaves of Vitis Vinifera Cv. Alvarinho Affected with Esca Disease. Plant Physiol. Biochem. PPB 2017, 112, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Tang, X.; Liu, F.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, G.; Ren, F.; Leng, X. Antidepressant-like Effects of the Hydroalcoholic Extracts of Hemerocallis Citrina and Its Potential Active Components. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 14, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.d.C.; Ashraf, N.S.; Fischer, S.; Yang, Y.; Schapka, E.; Joshi, G.; McQuade, T.J.; Dharia, R.M.; Dulchavsky, M.; Ouyang, M.; et al. Unbiased Screen Identifies Aripiprazole as a Modulator of Abundance of the Polyglutamine Disease Protein, Ataxin-3. Brain 2016, 139, 2891–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalles, A.; Vieira, C.; Pereira-Sousa, J.; Vilasboas-Campos, D.; Mota, A.F.; Vasconcelos, S.; Ferreira-Lomba, B.; Costa, M.D.; Da Silva, J.D.; Maciel, P.; et al. Aripiprazole Offsets Mutant ATXN3-Induced Motor Dysfunction by Targeting Dopamine D2 and Serotonin 1A and 2A Receptors in C. Elegans. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olde, B.; McCombie, W.R. Molecular Cloning and Functional Expression of a Serotonin Receptor fromCaenorhabditis Elegans. J. Mol. Neurosci. 1997, 8, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranganathan, R.; Sawin, E.R.; Trent, C.; Horvitz, H.R. Mutations in the Caenorhabditis Elegans Serotonin Reuptake Transporter MOD-5 Reveal Serotonin-Dependent and -Independent Activities of Fluoxetine. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 5871–5884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapierre, L.R.; De Magalhaes Filho, C.D.; McQuary, P.R.; Chu, C.-C.; Visvikis, O.; Chang, J.T.; Gelino, S.; Ong, B.; Davis, A.E.; Irazoqui, J.E.; et al. The TFEB Orthologue HLH-30 Regulates Autophagy and Modulates Longevity in Caenorhabditis Elegans. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leiser, S.F.; Miller, H.; Rossner, R.; Fletcher, M.; Leonard, A.; Primitivo, M.; Rintala, N.; Ramos, F.J.; Miller, D.L.; Kaeberlein, M. Cell Nonautonomous Activation of Flavin-Containing Monooxygenase Promotes Longevity and Health Span. Science 2015, 350, 1375–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visvikis, O.; Ihuegbu, N.; Labed, S.A.; Luhachack, L.G.; Alves, A.-M.F.; Wollenberg, A.C.; Stuart, L.M.; Stormo, G.D.; Irazoqui, J.E. Innate Host Defense Requires TFEB-Mediated Transcription of Cytoprotective and Antimicrobial Genes. Immunity 2014, 40, 896–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswamy, D.; Gonzalez, X.; Labed, S.A.; Irazoqui, J.E. C. elegans Orphan Nuclear Receptor NHR-42 Represses Innate Immunity and Promotes Lipid Loss Downstream of HLH-30/TFEB. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1094145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Li, F.; Zhou, T.; Wang, G.; Li, Z. Caenorhabditis Elegans as a Useful Model for Studying Aging Mutations. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 554994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dag, U.; Nwabudike, I.; Kang, D.; Gomes, M.A.; Kim, J.; Atanas, A.A.; Bueno, E.; Estrem, C.; Pugliese, S.; Wang, Z.; et al. Dissecting the Functional Organization of the C. Elegans Serotonergic System at Whole-Brain Scale. Cell 2023, 186, 2574–2592.e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodir, S.A.; Ali, E.; El-Domiaty, H. Rutin Exerts Antidepressant Effect in a Rat Model of Diabetes. Menoufia Med. J. 2023, 36, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Seol, H.-S.; Eom, S.; Lee, J.; Kim, C.; Park, J.-H.; Kim, T.-H.; Lee, J.H. Hydroxy Pentacyclic Triterpene Acid, Kaempferol, Inhibits the Human 5-Hydroxytryptamine Type 3A Receptor Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotelli, A.E.; Aguilar, C.F.; Pelzer, L.E. Structural Basis of the Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Quercetin: Inhibition of the 5-Hydroxytryptamine Type 2 Receptor. Eur. Biophys. J. 2009, 38, 865–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Chen, H.; Li, H.; Tang, Y.; Yang, L.; Cao, S.; Qin, D. Antidepressant Potential of Chlorogenic Acid-Enriched Extract from Eucommia Ulmoides Oliver Bark with Neuron Protection and Promotion of Serotonin Release through Enhancing Synapsin I Expression. Molecules 2016, 21, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira-Sousa, J.; Ferreira-Lomba, B.; Bellver-Sanchis, A.; Vilasboas-Campos, D.; Fernandes, J.H.; Costa, M.D.; Varney, M.A.; Newman-Tancredi, A.; Maciel, P.; Teixeira-Castro, A. Identification of the 5-HT1A Serotonin Receptor as a Novel Therapeutic Target in a C. Elegans Model of Machado-Joseph Disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2021, 152, 105278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martini-Stoica, H.; Xu, Y.; Ballabio, A.; Zheng, H. The Autophagy–Lysosomal Pathway in Neurodegeneration: A TFEB Perspective. Trends Neurosci. 2016, 39, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decressac, M.; Mattsson, B.; Weikop, P.; Lundblad, M.; Jakobsson, J.; Björklund, A. TFEB-Mediated Autophagy Rescues Midbrain Dopamine Neurons from α-Synuclein Toxicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E1817–E1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.-X.; Liu, J.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Li, M. Transcription Factor EB: An Emerging Drug Target for Neurodegenerative Disorders. Drug Discov. Today 2021, 26, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wang, R.; Xu, S.; Lakshmana, M.K. Transcription Factor EB Is Selectively Reduced in the Nuclear Fractions of Alzheimer’s and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Brains. Neurosci. J. 2016, 2016, 4732837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuervo, A.M. Preventing Lysosomal Fat Indigestion. Nat. Cell Biol. 2013, 15, 565–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Rourke, E.J.; Ruvkun, G. MXL-3 and HLH-30 Transcriptionally Link Lipolysis and Autophagy to Nutrient Availability. Nat. Cell Biol. 2013, 15, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Settembre, C.; De Cegli, R.; Mansueto, G.; Saha, P.K.; Vetrini, F.; Visvikis, O.; Huynh, T.; Carissimo, A.; Palmer, D.; Jürgen Klisch, T.; et al. TFEB Controls Cellular Lipid Metabolism through a Starvation-Induced Autoregulatory Loop. Nat. Cell Biol. 2013, 15, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.Q.; Ryan, C.J.; Bonal, D.M.; Mills, J.; Lapierre, L.R. Neuronal HLH-30/TFEB Modulates Peripheral Mitochondrial Fragmentation to Improve Thermoresistance in Caenorhabditis Elegans. Aging Cell 2023, 22, e13741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamoli, M.; Rane, A.; Foulger, A.; Chinta, S.J.; Shahmirzadi, A.A.; Kumsta, C.; Nambiar, D.K.; Hall, D.; Holcom, A.; Angeli, S.; et al. A Drug-like Molecule Engages Nuclear Hormone Receptor DAF-12/FXR to Regulate Mitophagy and Extend Lifespan. Nat. Aging 2023, 3, 1529–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.S.; Bhat, A.; Howington, M.B.; Schaller, M.L.; Cox, R.L.; Huang, S.; Beydoun, S.; Miller, H.A.; Tuckowski, A.M.; Mecano, J.; et al. FMO Rewires Metabolism to Promote Longevity through Tryptophan and One Carbon Metabolism in C. elegans. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Howington, M.B.; Dobry, C.J.; Evans, C.R.; Leiser, S.F. Flavin-Containing Monooxygenases Are Conserved Regulators of Stress Resistance and Metabolism. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 630188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Lu, J.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Gao, F.; Dai, Z.; Xu, S.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; et al. Revealing the Mechanism of Hemerocallis Citrina Baroni in Depression Treatment Through Integrated Network Pharmacology and Transcriptomic Analysis. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, R.; Luo, J.; Kim Chung, S.; Xu, B. Anti-Depression Molecular Mechanism Elucidation of the Phytochemicals in Edible Flower of Hemerocallis Citrina Baroni. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 12, 10164–10180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmieri, M.; Pal, R.; Nelvagal, H.R.; Lotfi, P.; Stinnett, G.R.; Seymour, M.L.; Chaudhury, A.; Bajaj, L.; Bondar, V.V.; Bremner, L.; et al. mTORC1-Independent TFEB Activation via Akt Inhibition Promotes Cellular Clearance in Neurodegenerative Storage Diseases. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, S. The genetics of caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics 1974, 77, 71–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voisine, C.; Varma, H.; Walker, N.; Bates, E.A.; Stockwell, B.R.; Hart, A.C. Identification of Potential Therapeutic Drugs for Huntington’s Disease Using Caenorhabditis Elegans. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gidalevitz, T.; Ben-Zvi, A.; Ho, K.H.; Brignull, H.R.; Morimoto, R.I. Progressive Disruption of Cellular Protein Folding in Models of Polyglutamine Diseases. Science 2006, 311, 1471–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira-Castro, A.; Dias, N.; Rodrigues, P.; Oliveira, J.F.; Rodrigues, N.F.; Maciel, P.; Vilaça, J.L. An Image Processing Application for Quantification of Protein Aggregates in Caenorhabditis elegans. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Practical Applications of Computational Biology & Bioinformatics (PACBB 2011), Salamanca, Spain, 6–8 April 2011; Rocha, M.P., Rodríguez, J.M.C., Fdez-Riverola, F., Valencia, A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 31–38. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fernandes, J.H.; Costa, M.D.; Vilasboas-Campos, D.; Ferreira-Lomba, B.; Pereira-Sousa, J.; Wang, Q.; Teixeira-Castro, A.; Liu, X.; Wang, F.; Dias, A.C.P.; et al. Therapeutic Effects of Hemerocallis citrina Baroni Extract on Animal Models of Neurodegenerative Diseases Through Serotonin and HLH-30/TFEB-Dependent Mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4145. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094145
Fernandes JH, Costa MD, Vilasboas-Campos D, Ferreira-Lomba B, Pereira-Sousa J, Wang Q, Teixeira-Castro A, Liu X, Wang F, Dias ACP, et al. Therapeutic Effects of Hemerocallis citrina Baroni Extract on Animal Models of Neurodegenerative Diseases Through Serotonin and HLH-30/TFEB-Dependent Mechanisms. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):4145. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094145
Chicago/Turabian StyleFernandes, Jorge H., Marta Daniela Costa, Daniela Vilasboas-Campos, Bruna Ferreira-Lomba, Joana Pereira-Sousa, Qiong Wang, Andreia Teixeira-Castro, Xinmin Liu, Fengzhong Wang, Alberto C. P. Dias, and et al. 2025. "Therapeutic Effects of Hemerocallis citrina Baroni Extract on Animal Models of Neurodegenerative Diseases Through Serotonin and HLH-30/TFEB-Dependent Mechanisms" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 4145. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094145
APA StyleFernandes, J. H., Costa, M. D., Vilasboas-Campos, D., Ferreira-Lomba, B., Pereira-Sousa, J., Wang, Q., Teixeira-Castro, A., Liu, X., Wang, F., Dias, A. C. P., & Maciel, P. (2025). Therapeutic Effects of Hemerocallis citrina Baroni Extract on Animal Models of Neurodegenerative Diseases Through Serotonin and HLH-30/TFEB-Dependent Mechanisms. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 4145. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094145










