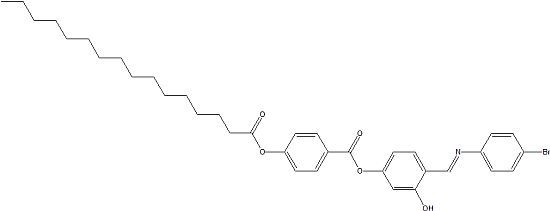
4-{[(4-Bromophenyl)imino]methyl}-3-hydroxyphenyl 4-(Hexadecanoyloxy)benzoate
Abstract
:Experimental
Supplementary materials
Supplementary File 1Supplementary File 2Supplementary File 3Acknowledgements
References
- Yuksel, F.; Atilla, D.; Ahsen, V. Synthesis and characterization of liquid-crystalline asymmetric phthalocyanines. Polyhedron 2007, 26, 4551–4556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.Y.; Meng, F.B.; Tian, M.; Xiao, W.Q. Side-chain liquid-crystalline polysiloxanes containing ionic mesogens and cholesterol ester groups. React. Funct. Polym. 2007, 66, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelker, H; Scheurle, B. Liquid-crystalline (nematic) phase with a particularly loq solidification point. Angew. Chem. Int. Edn. 1969, 8, 884–885. [Google Scholar]
- Eran, B.E.; Nesrullajev, A.; Canli, N.Y. Characterization and investigation of the mesogenic, thermo-morphological and thermotropic properties of new chiral (S)-5-octyloxy-2-[{4-(2-methylbuthoxy)phenylimino(methyl)phenol liquid crystalline compound. Mat. Chem. Phys. 2008, 111, 555–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra, M.; Vergara, J.; Zuniga, C.; Soto, E.; Sierra, T.; Serrano, J.L. New chiral Schiff’s bases with a 1,3,4-thiadizole ring in the mesogenic core: Synthesis, mesomorphic. Liq. Cryst. 2004, 32, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, A.K.; Varia, C.C. Azomesogens with polar chloro, nitro and phenolic –OH substituents. Liq. Cryst. 2008, 35, 1271–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vora, R.; Prajapati, A.K.; Kevat, J. Effect of terminal branching on mesomorphism. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2001, 357, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, S.T.; Ong, L.K.; Ong, S.T.; Yeap, G.Y.; Wong, J.P.W.; Koh, T.M.; Lin, H.C. Synthesis and mesomorphic properties of new Schiff base esters with different alkyl chains. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2009, 20, 767–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, S.T.; Lee, T.L.; Lee, S.L.; Yeap, G.Y.; Win, Y.F.; Ong, S.T. Mesomorphic behavior of new azomethine liquid crystals having terminal bromo substituent. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2012, 23, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeap, G.Y.; Ha, S.T.; Boey, P.L.; Mahmood, W.A.K.; Ito, M.M.; Youhei, Y. Synthesis and characterization of some new mesogenic Schiff base esters N-[4-(4-n-hexadecanoyloxybenzoyloxy)benzylidene]-4-substituted anilines. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2006, 452, 73–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Ha, S.-T.; Yeap, G.-Y.; Boey, P.-L. 4-{[(4-Bromophenyl)imino]methyl}-3-hydroxyphenyl 4-(Hexadecanoyloxy)benzoate. Molbank 2012, 2012, M755. https://doi.org/10.3390/M755
Ha S-T, Yeap G-Y, Boey P-L. 4-{[(4-Bromophenyl)imino]methyl}-3-hydroxyphenyl 4-(Hexadecanoyloxy)benzoate. Molbank. 2012; 2012(2):M755. https://doi.org/10.3390/M755
Chicago/Turabian StyleHa, Sie-Tiong, Guan-Yeow Yeap, and Peng-Lim Boey. 2012. "4-{[(4-Bromophenyl)imino]methyl}-3-hydroxyphenyl 4-(Hexadecanoyloxy)benzoate" Molbank 2012, no. 2: M755. https://doi.org/10.3390/M755
APA StyleHa, S. -T., Yeap, G. -Y., & Boey, P. -L. (2012). 4-{[(4-Bromophenyl)imino]methyl}-3-hydroxyphenyl 4-(Hexadecanoyloxy)benzoate. Molbank, 2012(2), M755. https://doi.org/10.3390/M755