Diversity and Structure of Parrotfish Assemblages across the Northern Great Barrier Reef
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
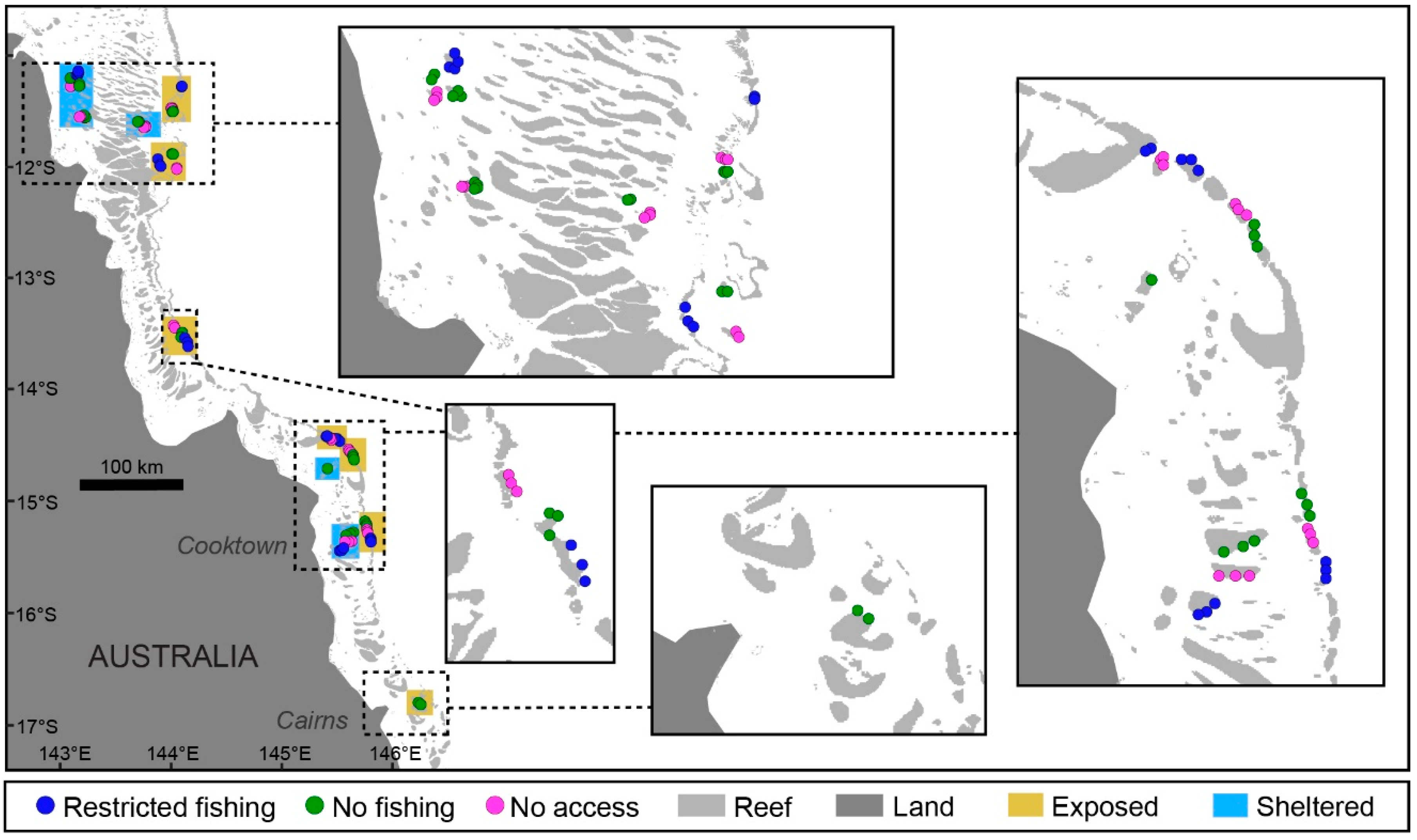
2.1. Study Location
2.2. Population Surveys of Study Species
2.3. Estimating Reef Structural Properties
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Abundance and Biomass
3.2. Cross-Shelf Assemblage Structure
3.3. Patterns of Diversity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tittensor, D.P.; Mora, C.; Jetz, W.; Lotze, H.K.; Ricard, D.; Berghe, E.V.; Worm, B. Global patterns and predictors of marine biodiversity across taxa. Nature 2010, 466, 1098–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mora, C.; Chittaro, P.M.; Sale, P.F.; Kritzer, J.P.; Ludsin, S.A. Patterns and processes in reef fish diversity. Nature 2003, 421, 933–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Floeter, S.R.; Guimarães, R.Z.P.; Rocha, L.A.; Ferreira, C.E.; Rangel, C.A.; Gasparini, J.L. Geographic variation in reef-fish assemblages along the Brazilian coast. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2001, 10, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong-Seng, K.; Mannering, T.D.; Pratchett, M.S.; Bellwood, D.R.; Graham, N.A.J. The influence of coral reef benthic condition on associated fish assemblages. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, N.A.J.; Nash, K.L. The importance of structural complexity in coral reef ecosystems. Coral Reefs 2013, 32, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellwood, D.R.; Wainwright, P.C. The history and biogeography of fishes on coral reefs. In Coral Reef Fishes: Dynamics and Diversity in a Complex Ecosystem; Sale, P.F., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2002; pp. 5–32. ISBN 0-12-615185-7. [Google Scholar]
- Hixon, M.A.; Beets, J.P. Predation, prey refuges, and the structure of coral-reef fish assemblages. Ecol. Monogr. 1993, 63, 77–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedlander, A.M.; DeMartini, E.E. Contrasts in density, size, and biomass of reef fishes between the northwestern and the main Hawaiian islands: The effects of fishing down apex predators. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2002, 230, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabricius, K.; De’ath, G.; McCook, L.; Turak, E.; Williams, D.M. Changes in algal, coral and fish assemblages along water quality gradients on the inshore Great Barrier Reef. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 51, 384–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, K.D.; Raubenheimer, D.; Choat, J.H. Nutritional ecology of marine herbivorous fishes: Ten years on. Funct. Ecol. 2009, 23, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustaka, M.; Langlois, T.J.; McLean, D.; Bond, T.; Fisher, R.; Fearns, P.; Dorji, P.; Evans, R.D. The effects of suspended sediment on coral reef fish assemblages and feeding guilds of north-west Australia. Coral Reefs 2018, 37, 659–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russ, G. Distribution and abundance of herbivorous grazing fishes in the central Great Barrier Reef. I: Levels of variability across the entire continental shelf. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1984, 20, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gust, N. Scarid biomass on the northern Great Barrier Reef: The influence of exposure, depth and substrata. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2002, 64, 353–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, B.M.; Houk, P.; Russ, G.R.; Choat, J.H. Life histories predict vulnerability to overexploitation in parrotfishes. Coral Reefs 2014, 33, 869–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGehee, M.A. Correspondence between assemblages of coral reef fishes and gradients of water motion, depth, and substrate size off Puerto Rico. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1994, 105, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.M.; Hatcher, A.I. Structure of fish communities on outer slopes of inshore, mid-shelf and outer shelf reefs of the Great Barrier Reef. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1983, 10, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, B.M.; Lindfield, S.J.; Choat, J.H. Hierarchical and scale-dependent effects of fishing pressure and environment on the structure and size distribution of parrotfish communities. Ecography 2015, 38, 520–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roff, G.; Bejarano, S.; Priest, M.; Marshell, A.; Chollett, I.; Steneck, R.S.; Doropoulos, C.; Golbuu, Y.; Mumby, P.J. Seascapes as drivers of herbivore assemblages in coral reef ecosystems. Ecol. Monogr. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiens, J.A. Spatial scaling in ecology. Funct. Ecol. 1989, 3, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith, S.A.; Baird, A.H.; Hughes, T.P.; Madin, J.S.; Connolly, S.R. Faunal breaks and species composition of Indo-Pacific corals: The role of plate tectonics, environment and habitat distribution. Proc. R. Soc. B 2013, 280, 20130818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sale, P.F. Appropriate spatial scales for studies of reef-fish ecology. Aust. J. Ecol. 1998, 23, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellin, C.; Bradshaw, C.J.A.; Meekan, M.G.; Caley, M.J. Environmental and spatial predictors of species richness and abundance in coral reef fishes. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2010, 19, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, G.R.V.; Ehrlich, A.H.; Ehrlich, P.R.; Roughgarden, J.D.; Russell, B.C.; Talbot, F.H. The community structure of coral reef fishes. Am. Nat. 1981, 117, 476–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.M. Patterns in the distribution of fish communities across the central Great Barrier Reef. Coral Reefs 1982, 1, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russ, G. Distribution and abundance of herbivorous grazing fishes in the central Great Barrier Reef. II: Patterns of zonation of mid-shelf and outershelf reefs. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1984, 20, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, C.M.; Shepherd, A.R.D.; Ormond, R.F.G. Large-scale variation in assemblage structure of Red Sea butterflyfishes and angelfishes. J. Biogeogr. 1992, 19, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gust, N.; Choat, J.H.; McCormick, M.I. Spatial variability in reef fish distribution, abundance, size and biomass: A multi scale analysis. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2001, 214, 237–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoey, A.S.; Bellwood, D.R. Cross-shelf variation in the role of parrotfishes on the Great Barrier Reef. Coral Reefs 2008, 27, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russ, G.R.; Cheal, A.J.; Dolman, A.M.; Emslie, M.J.; Evans, R.D.; Miller, I.; Sweatman, H.; Williamson, D.H. Rapid increase in fish numbers follows creation of world’s largest marine reserve network. Curr. Biol. 2008, 18, R514–R515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCook, L.J.; Ayling, T.; Cappo, M.; Choat, J.H.; Evans, R.D.; De Freitas, D.M.; Heupel, M.; Hughes, T.P.; Jones, G.P.; Mapstone, B.; et al. Adaptive management of the Great Barrier Reef: A globally significant demonstration of the benefits of networks of marine reserves. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 18278–18285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Robbins, W.D.; Hisano, M.; Connolly, S.R.; Choat, J.H. Ongoing collapse of coral-reef shark populations. Curr. Biol. 2006, 16, 2314–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellwood, D.R.; Choat, J.H. A functional analysis of grazing in parrotfishes (family Scaridae): The ecological implications. Environ. Biol. Fishes 1990, 28, 189–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellwood, D.R. Direct estimate of bioerosion by two parrotfish species, Chlorurus gibbus and C. sordidus, on the Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Mar. Biol. 1995, 121, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gust, N.; Choat, J.H.; Ackerman, J.L. Demographic plasticity in tropical reef fishes. Mar. Biol. 2002, 140, 1039–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, B.M.; Brandl, S.J.; Kapur, M.; Robbins, W.D.; Johnson, G.; Huveneers, C.; Renaud, P.; Choat, J.H. Bottom-up processes mediated by social systems drive demographic traits of coral-reef fishes. Ecology 2018, 99, 642–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russ, G.R.; Questel, S.A.; Rizzari, J.R.; Alcala, A.C. The parrotfish-coral relationship: Refuting the ubiquity of a prevailing paradigm. Mar. Biol. 2015, 162, 2029–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Questel, S.L.; Russ, G.R. No-take marine reserve effects on parrotfish and parrotfish-benthos interactions. In The Biology and Ecology of Parrotfishes; Hoey, A.S., Bonaldo, R.M., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 329–354. ISBN 13:978-1-4822-2401-6. [Google Scholar]
- Day, J.C. Zoning—Lessons from the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2002, 45, 139–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, E.S.; Goetze, J.; McLaren, B.; Langlois, T.; Shortis, M.R. Influence of range, angle of view, image resolution and image compression on underwater stereo-video measurements: High-definition and broadcast-resolution video cameras compared. Mar. Technol. Soc. J. 2010, 29, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, B.M. Drivers of protogynous sex change differ across spatial scales. Proc. R. Soc. B 2014, 281, 20132423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, P. VEGAN, a package of R functions for community ecology. J. Veg. Sci. 2003, 14, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Wollenberg, A.L. Redundancy analysis: An alternative for canonical correlation analysis. Psychometria 1977, 42, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2018; Available online: http://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 28 December 2018).
- Allen, B.; Kon, M.; Bar-Yam, Y. A new phylogenetic diversity measure generalizing the Shannon Index and its application to Phyllostomid Bats. Am. Nat. 2009, 174, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcon, E.; Hérault, B. entropart: An R package to measure and partition diversity. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 67, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choat, J.H.; Klanten, O.S.; Van Herwerden, L.; Robertson, D.R.; Clements, K.D. Patterns and processes in the evolutionary history of parrotfishes (Family Labridae). Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2012, 107, 529–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burnham, K.P.; Anderson, D.R. Model Selection and Multimodel Inference: A Practical Information-Theoretic Approach, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 149–203. ISBN 0-387-95364-7. [Google Scholar]
- Cheal, A.; Emslie, M.; Miller, I.; Sweatman, H. The distribution of herbivorous fishes on the Great Barrier Reef. Mar. Biol. 2012, 159, 1143–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellwood, D.R.; Choat, J.H. A description of the juvenile phase colour patterns of 24 parrotfish species (family Scaridae) from the Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Rec. Aust. Mus. 1989, 41, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellwood, D.R.; Choat, J.H. Dangerous demographics: The lack of juvenile humphead parrotfishes Bolbometopon muricatum on the Great Barrier Reef. Coral Reefs 2011, 30, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, R.J.; Almany, G.R.; Brown, C.J.; Pita, J.; Peterson, N.A.; Choat, J.H. Logging degrades nursery habitat for an iconic coral reef fish. Biol. Conserv. 2017, 210, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, K.D.; German, D.P.; Piché, J.; Tribollet, A.; Choat, J.H. Integrating ecological roles and trophic diversification on coral reefs: Multiple lines of evidence identify parrotfishes as microphages. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2017, 120, 729–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, K.D.; Choat, J.H. Nutritional ecology of parrotfishes (Scarinae, Labridae). In The Biology and Ecology of Parrotfishes; Hoey, A.S., Bonaldo, R.M., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 43–68. ISBN 13:978-1-4822-2401-6. [Google Scholar]
- Marcus, M.A.; Amini, S.; Stifler, C.A.; Sun, C.; Tamura, N.; Bechtel, H.A.; Parkinson, D.Y.; Barnard, H.S.; Zhang, X.X.X.; Chua, J.Q.I.; et al. Parrotfish teeth: Stiff biominerals whose microstructure makes them tough and abrasion-resistant to bite stony corals. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 11856–11865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crossman, D.J.; Choat, J.H.; Clements, K.D.; Hardy, T.; McConochie, J. Detritus as food for grazing fishes on coral reefs. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2001, 46, 1596–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tribollet, A.; Golubic, S. Cross-shelf differences in the pattern and pace of bioerosion of experimental carbonate substrates exposed for 3 years on the northern Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Coral Reefs 2005, 24, 422–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tribollet, A. Dissolution of dead corals by euendolithic microorganisms across the northern Great Barrier Reef. Microb. Ecol. 2008, 55, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madin, J.S.; Connolly, S.R. Ecological consequences of major hydrodynamic disturbances on coral reefs. Nature 2006, 444, 477–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, T.P.; Kerry, J.T.; Simpson, T. Large-scale bleaching of corals on the Great Barrier Reef. Ecology 2018, 99, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzari, J.R.; Bergseth, B.J.; Frisch, A.J. Impact of conservation areas on trophic interactions between apex predators and herbivores on coral reefs. Conserv. Biol. 2015, 29, 418–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casey, J.M.; Baird, A.H.; Brandl, S.J.; Hoogenboom, M.O.; Rizzari, J.R.; Frisch, A.J.; Mirbach, C.E.; Connolly, S.R. A test of trophic cascade theory: Fish and benthic assemblages across a predator density gradient on coral reefs. Oecologia 2017, 183, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emslie, M.J.; Logan, M.; Williamson, D.H.; Ayling, A.M.; MacNeil, M.A.; Ceccarelli, D.; Cheal, A.J.; Evans, R.D.; Johns, K.A.; Jonker, M.J.; et al. Expectations and outcomes of reserve network performance following re-zoning of the Great Barrier Reef Marin Park. Curr. Biol. 2015, 25, 983–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almany, G.R. Priority effects in coral reef fish communities of the Great Barrier Reef. Ecology 2004, 85, 2872–2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbins, W.D.; Renaud, P. Foraging mode of the grey reef shark, Carcharhinus amblyrhynchos, under two different scenarios. Coral Reefs 2016, 35, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMartini, E.E.; Friedlander, A.M.; Sandin, S.A.; Sala, E. Differences in fish-assemblage structure between fished and unfished atolls in the northern Line Islands, central Pacific. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2008, 365, 199–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hughes, T.P.; Kerry, J.T.; Baird, A.H.; Connolly, S.R.; Dietzel, A.; Eakin, C.M.; Heron, S.F.; Hoey, A.S.; Hoogenboom, M.O.; Liu, G.; et al. Global warming transforms coral reef assemblages. Nature 2018, 556, 492–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| (a) Abundance | |||||
| Model or Subset | Variance Explained (%) | df | F | Significance Level | |
| Global model | 43.6 | 11,70 | 6.7 | *** | |
| Geography | (total) | 36.9 | 2,79 | 24.7 | *** |
| (independent) | 9.1 | 2,70 | 6.9 | ** | |
| Biophysical | (total) | 34.2 | 6,75 | 8.0 | *** |
| (independent) | 6.5 | 6,70 | 2.5 | ** | |
| Management/Predatory | (total) | 7.6 | 2,79 | 4.3 | * |
| (independent) | 0.5 | 3,70 | 1.1 | NS | |
| (b) Biomass | |||||
| Model or Subset | Variance Explained (%) | df | F | Significance Level | |
| Global model | 29.8 | 11,70 | 4.1 | *** | |
| Geography | (total) | 26.0 | 2,79 | 15.2 | *** |
| (independent) | 5.8 | 2,70 | 4.0 | ** | |
| Biophysical | (total) | 23.7 | 6,75 | 5.2 | *** |
| (independent) | 3.3 | 6,70 | 1.7 | ** | |
| Management/Predatory | (total) | 6.3 | 2,79 | 3.7 | * |
| (independent) | 0.4 | 3,70 | 1.1 | NS | |
| (a) Species richness | |||||
| Variable | numDF | denDF | F | P | Response |
| Intercept | 1 | 50 | 513.5 | <0.0001 | |
| Shelf position | 1 | 29 | 7.3 | 0.0116 | Figure 4a |
| Latitude | 1 | 50 | 8.8 | 0.0046 | Figure 4d |
| (b) Abundance-weighted phylogenetic diversity | |||||
| Variable | numDF | denDF | F | P | Response |
| Intercept | 1 | 49 | 854.9 | <0.0001 | |
| Shelf position | 1 | 29 | 7.4 | 0.0108 | Figure 4b |
| Latitude | 1 | 49 | 20.2 | <0.0001 | Figure 4e |
| Predator biomass | 1 | 49 | 17.9 | 0.0001 | Figure 4g |
| (c) Biomass-weighted phylogenetic diversity | |||||
| Variable | numDF | denDF | F | P | Response |
| Intercept | 1 | 50 | 576.0 | <0.0001 | |
| Shelf position | 1 | 29 | 17.5 | <0.0001 | Figure 4c |
| Sea surface temp | 1 | 50 | 18.0 | <0.0001 | Figure 4f |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Johnson, G.B.; Taylor, B.M.; Robbins, W.D.; Franklin, E.C.; Toonen, R.; Bowen, B.; Choat, J.H. Diversity and Structure of Parrotfish Assemblages across the Northern Great Barrier Reef. Diversity 2019, 11, 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/d11010014
Johnson GB, Taylor BM, Robbins WD, Franklin EC, Toonen R, Bowen B, Choat JH. Diversity and Structure of Parrotfish Assemblages across the Northern Great Barrier Reef. Diversity. 2019; 11(1):14. https://doi.org/10.3390/d11010014
Chicago/Turabian StyleJohnson, Garrett B., Brett M. Taylor, William D. Robbins, Erik C. Franklin, Rob Toonen, Brian Bowen, and J. Howard Choat. 2019. "Diversity and Structure of Parrotfish Assemblages across the Northern Great Barrier Reef" Diversity 11, no. 1: 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/d11010014
APA StyleJohnson, G. B., Taylor, B. M., Robbins, W. D., Franklin, E. C., Toonen, R., Bowen, B., & Choat, J. H. (2019). Diversity and Structure of Parrotfish Assemblages across the Northern Great Barrier Reef. Diversity, 11(1), 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/d11010014





