Nitrogen Metabolism at Tillering Stage Differently Affects the Grain Yield and Grain Protein Content in Two Durum Wheat Cultivars
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material and Field Experiment Design
2.2. Agronomic, Productive, and Qualitative Parameters
2.3. Intracellular Inorganic and Organic Nitrogen Pools
2.4. Enzymatic Activities Assay
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
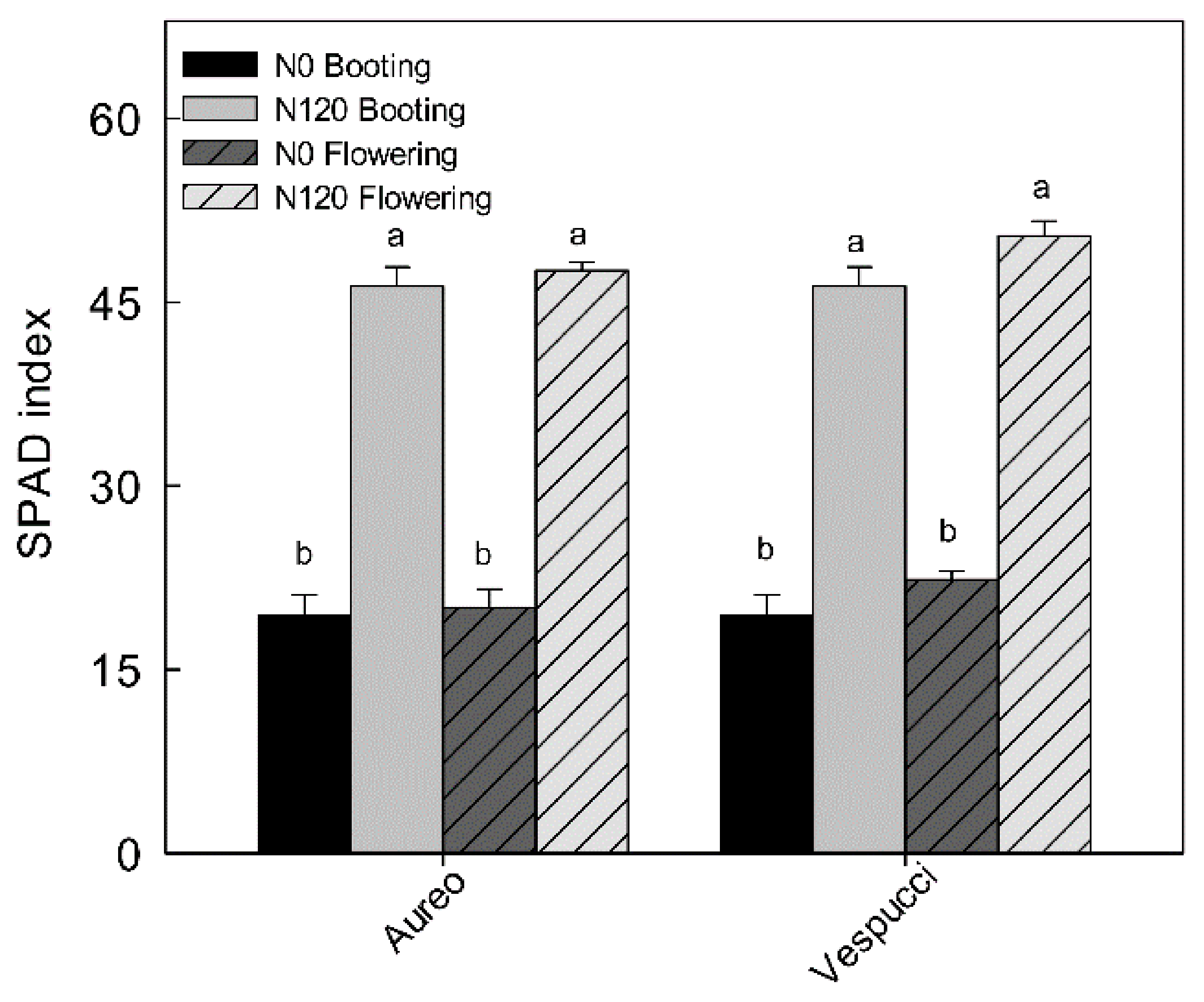
3.1. Effects of Nitrogen Fertilization on Agronomic, Yield, and Qualitative Traits in Two Durum Wheat Cultivars
3.2. Nitrogen Metabolism in Two Wheat Cultivars during Tillering Stage
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kichey, T.; Hirel, B.; Heumez, E.; Dubois, F.; Le Gouis, J. In winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.), post-anthesis nitrogen uptake and remobilisation to the grain correlates with agronomic traits and nitrogen physiological markers. Field Crop. Res. 2007, 102, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krapp, A. Plant nitrogen assimilation and its regulation: A complex puzzle with missing pieces. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2015, 25, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marschner, H. Marschner’s Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Fois, N.; Schlichting, L.; Marchylo, B.; Dexter, J.; Motzo, R.; Giunta, F. Environmental conditions affect semolina quality in durum wheat (Triticum turgidum ssp. durum L.) cultivars with different gluten strength and gluten protein composition. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2011, 91, 2664–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, A.; Singh, N.; Kaur, S.; Katyal, M.; Virdi, A.S.; Kaur, D.; Singh, A.M. Relationship of various flour properties with noodle making characteristics among durum wheat varieties. Food Chem. 2015, 188, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demotes-Mainard, S.; Jeuffroy, M.H. Partitioning of dry matter and nitrogen to the spike throughout the spike growth period in wheat crops subjected to nitrogen deficiency. Field Crop. Res. 2001, 70, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demotes-Mainard, S.; Jeuffroy, M.H. Incorporating radiation and nitrogen nutrition into a model of kernel number in wheat. Crop Sci. 2001, 41, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigro, D.; Gadaleta, A.; Mangini, G.; Colasuonno, P.; Marcotuli, I.; Giancaspro, A.; Giove, S.L.; Simeone, R.; Blanco, A. Candidate genes and genome-wide association study of grain protein content and protein deviation in durum wheat. Planta 2019, 249, 1157–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chope, G.A.; Wan, Y.; Penson, S.P.; Bhandari, D.G.; Powers, S.J.; Shewry, P.R.; Hawkesford, M.J. Effects of genotype, season, and nitrogen nutrition on gene expression and protein accumulation in wheat grain. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 4399–4407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maccaferri, M.; Harris, N.S.; Twardziok, S.O.; Pasam, R.K.; Gundlach, H.; Spannagl, M.; Ormanbekova, D.; Lux, T.; Prade, V.M.; Milner, S.G.; et al. Durum wheat genome highlights past domestication signatures and future improvement targets. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 885–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laidig, F.; Piepho, H.P.; Rentel, D.; Drobek, T.; Meyer, U.; Huesken, A. Breeding progress, environmental variation and correlation of winter wheat yield and quality traits in German official variety trials and on-farm during 1983–2014. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2017, 130, 223–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnett, T.; Conn, V.; Kaiser, B.N. Root based approaches to improving nitrogen use efficiency in plants. Plant Cell Environ. 2009, 32, 1272–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrido-Lestache, E.; López-Bellido, R.J.; López-Bellido, L. Durum wheat quality under Mediterranean conditions as affected by N rate, timing and splitting, N form and S fertilization. Eur. J. Agron. 2005, 23, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuertes-Mendizábal, T.; Aizpurua, A.; González-Moro, M.B.; Estavillo, J.M. Improving wheat breadmaking quality by splitting the N fertilizer rate. Eur. J. Agron. 2010, 33, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercoli, L.; Arduini, I.; Mariotti, M.; Lulli, L.; Masoni, A. Management of sulphur fertiliser to improve durum wheat production and minimise S leaching. Eur. J. Agron. 2012, 38, 74–82. [Google Scholar]
- Moll, R.H.; Kamprath, E.J.; Jackson, W.A. Development of nitrogen efficient prolific hybrids of maize. Crop Sci. 1987, 27, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gouis, J.; Beghin, D.; Heumez, E.; Pluchard, P. Genetic differences for nitrogen uptake and nitrogen utilisation efficiencies in winter wheat. Eur. J. Agron. 2000, 12, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, J.C.; Huggins, D.R.; Jones, S.S. Characterizing nitrogen use efficiency in natural and agricultural ecosystems to improve the performance of cereal crops in low-input and organic agricultural systems. Field Crop. Res. 2008, 107, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giambalvo, D.; Ruisi, P.; Di Miceli, G.; Frenda, A.S.; Amato, G. Nitrogen Use Efficiency and Nitrogen Fertilizer Recovery of Durum Wheat Genotypes as Affected by Interspecific Competition. Agron. J. 2010, 102, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cossani, C.M.; Slafer, G.A.; Savin, R. Nitrogen and water use efficiencies of wheat and barley under a Mediterranean environment in Catalonia. Field Crop. Res. 2012, 128, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Bellido, L.; Lopez-Bellido, R.J.; Lopez-Bellido, F.J. Fertilizer nitrogen efficiency in durum wheat under rainfed Mediterranean conditions: Effect of split application. Agron. J. 2006, 98, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, M.; Morton, J.D.; Lieffering, M.; Bisset, L. The partitioning of nitrate assimilation between root and shoot of a range of temperate cereals and pasture grasses. Ann. Bot. Lond. 1992, 70, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lillo, C. Signalling cascades integrating light-enhanced nitrate metabolism. Biochem. J. 2008, 415, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidari, B.; Matre, P.; Nemie-Feyissa, D.; Meyer, C.; Rognli, O.A.; Moller, S.G.; Lillo, C. Protein phosphatase 2A B55 and A regulatory subunits interact with nitrate reductase and are essential for nitrate reductase activation. Plant Physiol. 2011, 156, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blackwood, G.C.; Hallam, R. Nitrate reductase activity in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) II. The correlation with yield. New Phytol. 1979, 82, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, H.S. Regulation of nitrate reductase activity in higher plants. Phytochemistry 1980, 19, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S. Yield response of uniculm wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) to early and late application of nitrogen: Flag leaf development and senescence. J. Agric. Sci. 2011, 3, 170–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.Q.; Nie, X.L.; Xiao, X.G. Over-Expression of a tobacco nitrate reductase gene in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) increases seed protein content and weight without augmenting nitrogen supplying. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, S.; Guerriero, G.; Vona, V.; Rigano, V.D.; Carfagna, S.; Rigano, C. Glutamate synthase activities and protein changes in relation to nitrogen nutrition in barley: The dependence on different plastidic glucose-6P dehydrogenase isoforms. J. Exp. Bot. 2005, 56, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.C.; Tischner, R.; Gutierrez, R.A.; Hoffman, M.; Xing, X.J.; Chen, M.S.; Coruzzi, G.; Crawford, N.M. Genomic analysis of the nitrate response using a nitrate reductase-null mutant of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2004, 136, 2512–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Sun, Q.J.; Mang, C.F.; Yuan, Y.Z.; Ji, Z.; Lu, B.B. Effect of salt stress on ammonium assimilation enzymes of the roots of rice (Oryza sativa) genotypes differing in salinity resistance. Acta Bot. Sin. 2004, 46, 921–927. [Google Scholar]
- Raymond, J. The evolution of biological carbon and nitrogen cycling—A genomic perspective. Rev. Miner. Geochem. 2005, 59, 211–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabuchi, M.; Abiko, T.; Yamaya, T. Assimilation of ammonium ions and reutilization of nitrogen in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J. Exp. Bot. 2007, 58, 2319–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canovas, F.M.; Avila, C.; Canton, F.R.; Canas, R.A.; de la Torre, F. Ammonium assimilation and amino acid metabolism in conifers. J. Exp. Bot. 2007, 58, 2307–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nigro, D.; Gu, Y.Q.; Huo, N.X.; Marcotuli, I.; Blanco, A.; Gadaleta, A.; Anderson, O.D. Structural analysis of the wheat genes encoding NADH-dependent glutamine-2-oxoglutarate amidotransferases and correlation with grain protein content. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nigro, D.; Blanco, A.; Anderson, O.D.; Gadaleta, A. Characterization of ferredoxin-dependent glutamine-oxoglutarate amidotransferase (Fd-GOGAT) genes and their relationship with grain protein content QTL in wheat. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habash, D.Z.; Bernard, S.; Schondelmaier, J.; Weyen, J.; Quarrie, S.A. The genetics of nitrogen use in hexaploid wheat: N utilisation, development and yield. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2007, 114, 403–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomsen, H.C.; Eriksson, D.; Moller, I.S.; Schjoerring, J.K. Cytosolic glutamine synthetase: A target for improvement of crop nitrogen use efficiency? Trends Plant Sci. 2014, 19, 656–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigro, D.; Fortunato, S.; Giove, S.L.; Paradiso, A.; Gu, Y.Q.; Blanco, A.; de Pinto, M.C.; Gadaleta, A. Glutamine synthetase in durum wheat: Genotypic variation and relationship with grain protein content. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigro, D.; Fortunato, S.; Giove, S.L.; Mangini, G.; Yacoubi, I.; Simeone, R.; Blanco, A.; Gadaleta, A. Allelic variants of glutamine synthetase and glutamate synthase genes in a collection of durum wheat and association with grain protein content. Divers. Basel 2017, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadaleta, A.; Nigro, D.; Marcotuli, I.; Giancaspro, A.; Giove, S.L.; Blanco, A. Isolation and characterization of cytosolic glutamine synthetase (GSe) genes and association with grain protein content in durum wheat. Crop Pasture Sci. 2014, 65, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaranta, F.; Belocchi, A.; Fornara, M.; Mazzon, V.; Cecchini, C.; Nocente, F. Le varietà di grano duro per le semine 2015. L’informatore Agrario. 2015, 33, 5–11. (In Italian) [Google Scholar]
- Quaranta, F.; Belocchi, A.; Cecchini, C.; Mazzon, V.; Fornara, M. Le varietà di grano duro per le semine 2016. L’informatore Agrario. 2016, 33, 25–31. (In Italian) [Google Scholar]
- Violante, P. Methods of Soil Chemical Analyses; Franco Angeli: Milano, Italy, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Varga, B.; Svecnjak, Z. The effect of late-season urea spraying on grain yield and quality of winter wheat genotypes under low and high basal nitrogen fertilization. Field Crop. Res. 2006, 96, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdon, C.P.; Burton, B.A.; Prior, R.L. Sample pretreatment with nitrate reductase and glucose-6-phosphate-dehydrogenase quantitatively reduces nitrate while avoiding interference by NADP+ when the Griess reaction is used to assay for nitrite. Anal. Biochem. 1995, 224, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magné, C.; Larher, F. High sugar content of extracts interferes with colorimetric determination of amino-acids and free proline. Anal. Biochem. 1992, 200, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.X.; Kirkham, M.B. Antioxidant responses to drought in sunflower and sorghum seedlings. New Phytol. 1996, 132, 361–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibon, Y.; Blaesing, O.E.; Hannemann, J.; Carillo, P.; Hohne, M.; Hendriks, J.H.M.; Palacios, N.; Cross, J.; Selbig, J.; Stitt, M. A robot-based platform to measure multiple enzyme activities in Arabidopsis using a set of cycling assays: Comparison of changes of enzyme activities and transcript levels during diurnal cycles and in prolonged darkness. Plant Cell 2004, 16, 3304–3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, M.; Sasaki, Y.; Ida, S.; Morikawa, H. Nitrite reductase gene enrichment improves assimilation of NO(2) in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2001, 126, 731–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, S.; Guerriero, G.; Vona, V.; Rigano, V.D.M.; Carfagna, S.; Rigano, C. Glucose-6P dehydrogenase in Chlorella sorokiniana (211/8k): An enzyme with unusual characteristics. Planta 2006, 223, 796–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Follett, R.H.; Follett, R.F.; Halvorson, A.D. Use of a Chlorophyll Meter to evaluate the nitrogen status of dryland winter-wheat. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant 1992, 23, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartelat, A.; Cerovic, Z.G.; Goulas, Y.; Meyer, S.; Lelarge, C.; Prioul, J.L.; Barbottin, A.; Jeuffroy, M.H.; Gate, P.; Agati, G.; et al. Optically assessed contents of leaf polyphenolics and chlorophyll as indicators of nitrogen deficiency in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Field Crop. Res. 2005, 91, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debaeke, P.; Rouet, P.; Justes, E. Relationship between the normalized SPAD index and the nitrogen nutrition index: Application to durum wheat. J. Plant Nutr. 2006, 29, 75–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, D.L.; Chen, J.; Yu, T.T.; Gao, W.L.; Ling, X.X.; Li, Y.; Peng, S.B.; Huang, J.L. SPAD-based leaf nitrogen estimation is impacted by environmental factors and crop leaf characteristics. Sci. Rep. UK 2015, 5, 13389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nielsen, D.C.; Halvorson, A.D. Nitrogen fertility influence on water-stress and yield of winter-wheat. Agron. J. 1991, 83, 1065–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spano, G.; Di Fonzo, N.; Perrotta, C.; Platani, C.; Ronga, G.; Lawlor, D.W.; Napier, J.A.; Shewry, P.R. Physiological characterization of ‘stay green’ mutants in durum wheat. J. Exp. Bot. 2003, 54, 1415–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masclaux-Daubresse, C.; Reisdorf-Cren, M.; Orsel, M. Leaf nitrogen remobilisation for plant development and grain filling. Plant Biol. 2008, 10, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.F.; Gao, S.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Zhao, X.L.; Liu, X.M.; Xiao, K. Growth traits and nitrogen assimilation-associated physiological parameters of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) under low and high N conditions. J. Integr. Agr. 2015, 14, 1295–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliani, M.M.; Giuzio, L.; De Caro, A.; Flagella, Z. Relationships between nitrogen utilization and grain technological quality in durum wheat: II. Grain yield and quality. Agron. J. 2011, 103, 1668–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, A.; Pasqualone, A.; Troccoli, A.; Di Fonzo, N.; Simeone, R. Detection of grain protein content QTLs across environments in tetraploid wheats. Plant Mol. Biol. 2002, 48, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oury, F.X.; Godin, C. Yield and grain protein concentration in bread wheat: How to use the negative relationship between the two characters to identify favourable genotypes? Euphytica 2007, 157, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, M.C.; Qualset, C.O.; Rains, D.W. Genetic-variation for nitrogen assimilation and translocation in wheat. 2. nitrogen assimilation in relation to grain-yield and protein. Crop Sci. 1985, 25, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaghan, J.M.; Snape, J.W.; Chojecki, A.J.S.; Kettlewell, P.S. The use of grain protein deviation for identifying wheat cultivars with high grain protein concentration and yield. Euphytica 2001, 122, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido-Lestache, E.; Lopez-Bellido, R.J.; Lopez-Bellido, L. Effect of N rate, timing and splitting and N type on bread-making quality in hard red spring wheat under rainfed Mediterranean conditions. Field Crop. Res. 2004, 85, 213–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galieni, A.; Stagnari, F.; Visioli, G.; Marmiroli, N.; Speca, S.; Angelozzi, G.; D’Egidio, S.; Pisante, M. Nitrogen fertilisation of durum wheat: A case study in Mediterranean area during transition to conservation agriculture. Ital. J. Agron. 2016, 11, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slafer, G.A. Genetic basis of yield as viewed from a crop physiologist’s perspective. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2003, 142, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marti, J.; Bort, J.; Slafer, G.A.; Araus, J.L. Can wheat yield be assessed by early measurements of Normalized Difference Vegetation Index? Ann. Appl. Biol. 2007, 150, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palta, J.A.; Fillery, I.R.P. N application increases pre-anthesis contribution of dry matter to grain yield in wheat grown on a duplex soil. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 1995, 46, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masclaux-Daubresse, C.; Daniel-Vedele, F.; Dechorgnat, J.; Chardon, F.; Gaufichon, L.; Suzuki, A. Nitrogen uptake, assimilation and remobilization in plants: Challenges for sustainable and productive agriculture. Ann. Bot. Lond. 2010, 105, 1141–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, G.; Asthir, B.; Bains, N.S.; Farooq, M. Nitrogen nutrition, its assimilation and remobilization in diverse wheat genotypes. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2015, 17, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foyer, C.H.; Noctor, G. Photosynthetic nitrogen assimilation: Inter-pathway control and signalling. In Photosyntetic Nitrogen Assimilation and Associated Carbon and Respiratory Metabolism; Foyer, C.H., Noctor, G., Eds.; Kluwer: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Andrews, M.; Raven, J.A.; Lea, P.J. Do plants need nitrate? The mechanisms by which nitrogen form affects plants. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2013, 163, 174–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lothier, J.; Gaufichon, L.; Sormani, R.; Lemaitre, T.; Azzopardi, M.; Morin, H.; Chardon, F.; Reisdorf-Cren, M.; Avice, J.C.; Masclaux-Daubresse, C. The cytosolic glutamine synthetase GLN1;2 plays a role in the control of plant growth and ammonium homeostasis in Arabidopsis rosettes when nitrate supply is not limiting. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 1375–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hachiya, T.; Watanabe, C.K.; Fujimoto, M.; Ishikawa, T.; Takahara, K.; Kawai-Yamada, M.; Uchimiya, H.; Uesono, Y.; Terashima, I.; Noguchi, K. Nitrate addition alleviates ammonium toxicity without lessening ammonium accumulation, organic acid depletion and inorganic cation depletion in Arabidopsis thaliana shoots. Plant Cell Physiol. 2012, 53, 577–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oaks, A. Primary nitrogen assimilation in higher-plants and its regulation. Can. J. Bot. 1994, 72, 739–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, W.H. Nitrate reductase structure, function and regulation: Bridging the gap between biochemistry and physiology. Ann. Rev. Plant. Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 1999, 50, 277–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balotf, S.; Kavoosi, G.; Kholdebarin, B. Nitrate reductase, nitrite reductase, glutamine synthetase, and glutamate synthase expression and activity in response to different nitrogen sources in nitrogen-starved wheat seedlings. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2016, 63, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makino, A.; Mae, T.; Ohira, K. Photosynthesis and ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase oxygenase in rice leaves from emergence through senescence-quantitative-analysis by carboxylation oxygenation and regeneration of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate. Planta 1985, 166, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hageman, J.; Robinson, C.; Smeekens, S.; Weisbeek, P. A Thylakoid Processing Protease Is Required for Complete Maturation of the Lumen Protein Plastocyanin. Nature 1986, 324, 567–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawlor, D.W.; Kontturi, M.; Young, A.T. Photosynthesis by flag leaves of wheat in relation to protein, ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase activity and nitrogen supply. J. Exp. Bot. 1989, 40, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornley, J.H.M. Acclimation of photosynthesis to light and canopy nitrogen distribution: An interpretation. Ann. Bot. Lond. 2004, 93, 473–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjana, S.U.; Umar, S.; Abrol, Y.P.; Iqbal, M. Modulation of Nitrogen-Utilization Efficiency in Wheat Genotypes Differing in Nitrate Reductase Activity. J. Plant Nutr. 2011, 34, 920–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheible, W.R.; GonzalezFontes, A.; Lauerer, M.; MullerRober, B.; Caboche, M.; Stitt, M. Nitrate acts as a signal to induce organic acid metabolism and repress starch metabolism in tobacco. Plant Cell 1997, 9, 783–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, V.; Khetarpal, S.; Das, R.; Abrol, Y.P. Nitrate assimilation in contrasting wheat genotypes. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2011, 17, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berwal, M.K.; Chugh, L.K.; Kumar, R. Possibility of using leaf in vivo nitrate reductase activity as a biochemical marker for predicting grain protein content of pearl millet. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2015, 4, 630–634. [Google Scholar]
- Bertin, P.; Gallais, A. Genetic variation for nitrogen use efficiency in a set of recombinant maize inbred lines I. Agrophysiological results. Maydica 2000, 45, 53–66. [Google Scholar]
- Gallais, A.; Coque, M. Genetic Variation and Selection for Nitrogen Use Efficiency in Maize: A Synthesis. Maydica 2005, 50, 531–547. [Google Scholar]




| Genotypes and Treatment | Aerial Biomass (g/m2) | Plant Height (cm) | Number of Culms (n°/m2) | Number of Spikes (n°/m2) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aureo | N0 | 409b ± 58 | 68.3b ± 1.7 | 318.0b ± 10 | 292.4b ± 1.8 |
| N120 | 1473a ± 49 | 80.7a,b ± 1.7 | 500.8a ± 3.8 | 465.2a ± 3.4 | |
| Vespucci | N0 | 337b ± 43 | 64.3b ± 3.4 | 316.7b ± 10.3 | 288.6b ± 2.1 |
| N120 | 1678a ± 44 | 90.0a ± 2.9 | 482.6a ± 14.4 | 454.5a ± 10.9 | |
| Cultivars and Treatment | Thousand Kernels Weight (g) | Hectolitre Weight (g/hl) | Grain Yield (g/m2) | Grain Protein Content (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aureo | N0 | 43.0c ± 1.1 | 78.3b ± 1.3 | 152c ± 26 | 11.4b ± 0.1 |
| N120 | 45.6b ± 1.3 | 81.3a,b ± 2.3 | 642b ± 38 | 14.2a ± 1.3 | |
| Vespucci | N0 | 45.7b ± 1.7 | 79.3b ± 2.3 | 144c ± 21 | 10.8b ± 0.2 |
| N120 | 51.3a ± 1.9 | 83.3a ± 2.3 | 773a ± 38 | 12.1b ± 0.3 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fortunato, S.; Nigro, D.; Paradiso, A.; Cucci, G.; Lacolla, G.; Trani, R.; Agrimi, G.; Blanco, A.; de Pinto, M.C.; Gadaleta, A. Nitrogen Metabolism at Tillering Stage Differently Affects the Grain Yield and Grain Protein Content in Two Durum Wheat Cultivars. Diversity 2019, 11, 186. https://doi.org/10.3390/d11100186
Fortunato S, Nigro D, Paradiso A, Cucci G, Lacolla G, Trani R, Agrimi G, Blanco A, de Pinto MC, Gadaleta A. Nitrogen Metabolism at Tillering Stage Differently Affects the Grain Yield and Grain Protein Content in Two Durum Wheat Cultivars. Diversity. 2019; 11(10):186. https://doi.org/10.3390/d11100186
Chicago/Turabian StyleFortunato, Stefania, Domenica Nigro, Annalisa Paradiso, Giovanna Cucci, Giovanni Lacolla, Roberta Trani, Gennaro Agrimi, Antonio Blanco, Maria Concetta de Pinto, and Agata Gadaleta. 2019. "Nitrogen Metabolism at Tillering Stage Differently Affects the Grain Yield and Grain Protein Content in Two Durum Wheat Cultivars" Diversity 11, no. 10: 186. https://doi.org/10.3390/d11100186
APA StyleFortunato, S., Nigro, D., Paradiso, A., Cucci, G., Lacolla, G., Trani, R., Agrimi, G., Blanco, A., de Pinto, M. C., & Gadaleta, A. (2019). Nitrogen Metabolism at Tillering Stage Differently Affects the Grain Yield and Grain Protein Content in Two Durum Wheat Cultivars. Diversity, 11(10), 186. https://doi.org/10.3390/d11100186









