Optimizing Costs to Collect Local Infauna through Grabs: Effect of Sampling Size and Replication
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Literature Review
2.2. Local Study: Site, Sampling and Taxonomic Identifications
2.3. Statistical Analyses: Literature Review
2.4. Statistical Analyses: Local Study
2.5. Costs
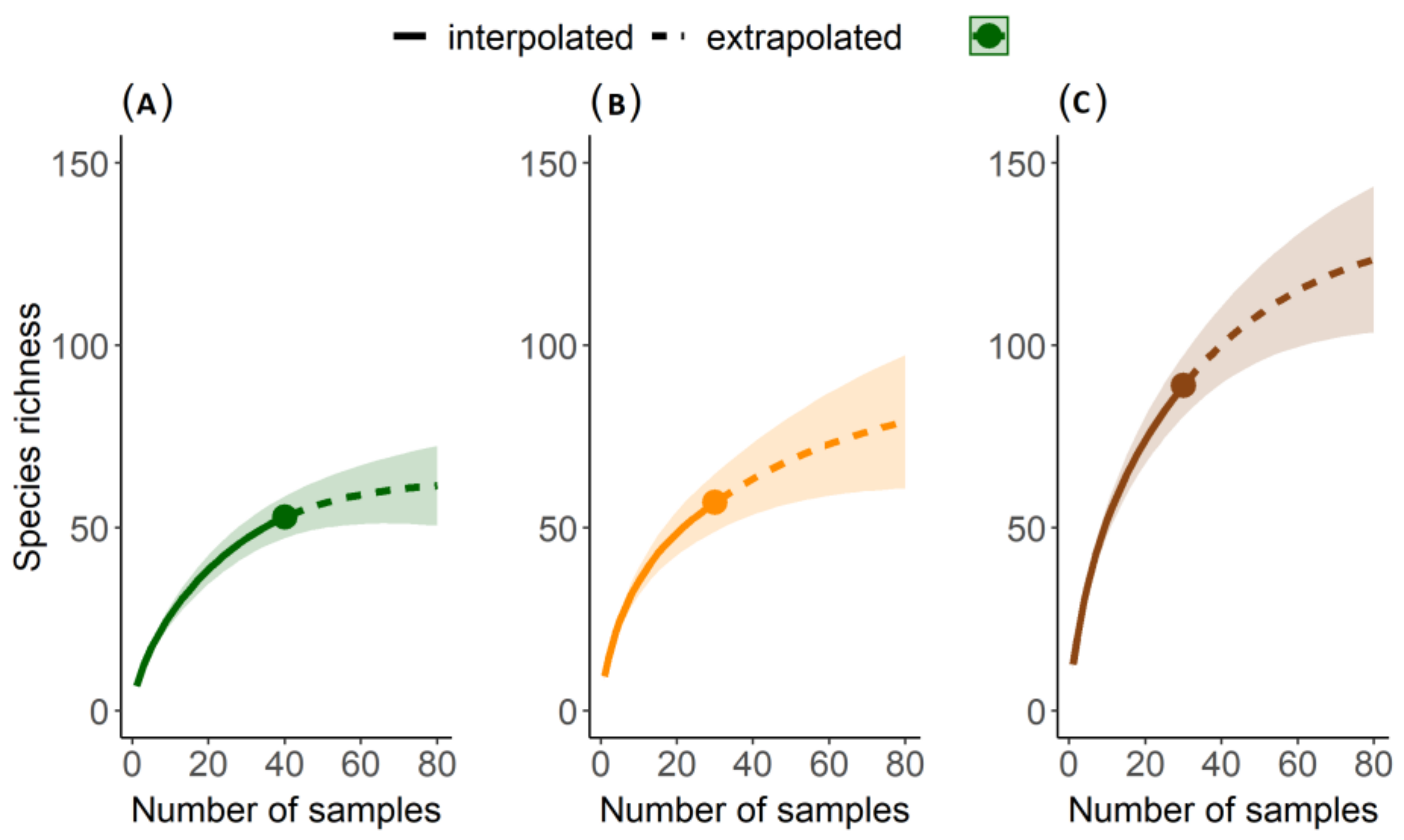
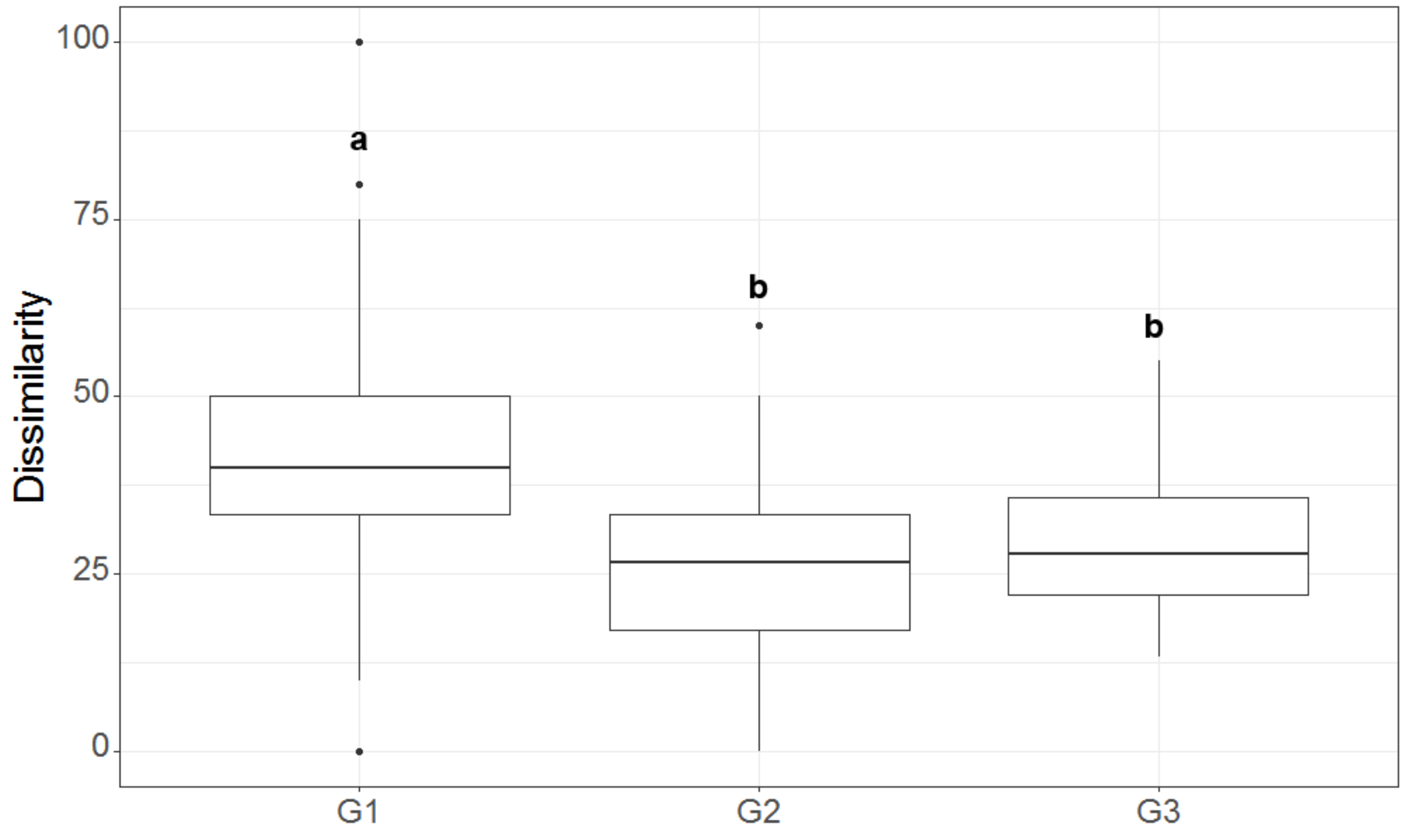
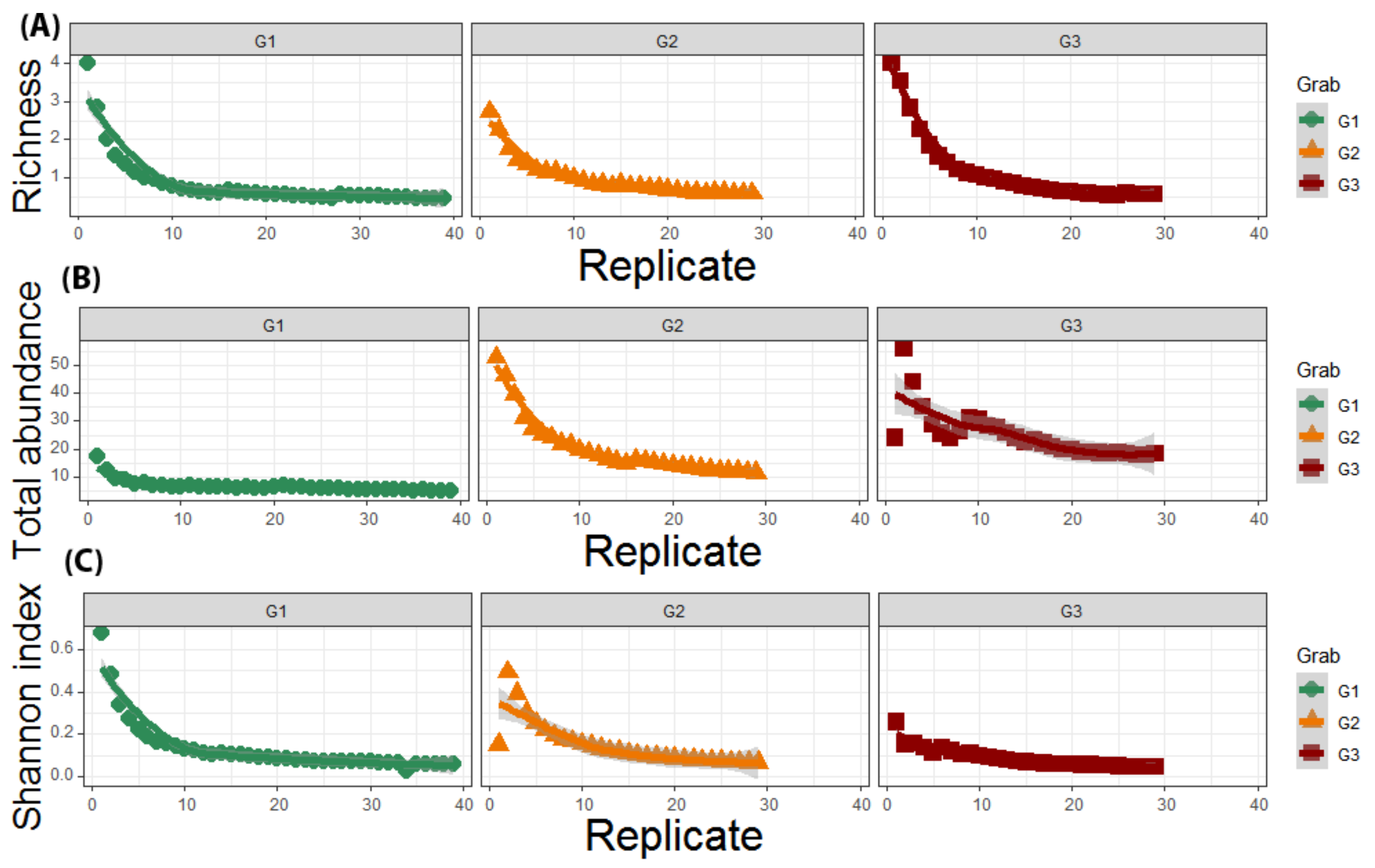
3. Results
3.1. Literature Review
3.2. Local Study
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kingsford, M.; Battershill, C. Studying Temperate Marine Environments: A Handbook for Ecologists; Canterbury University Press: Christchurch, New Zealand, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Quinn, G.P.; Keough, M.J. Experimental Design and Data Analysis for Biologists; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Zabala, J.; Amorim, A.; Tuya, F.; Soler-Onís, E. Benthic dinoflagellates: Testing the reliability of the ‘artificial substrate’ method in the Macaronesian region. Harmful Algae 2019, 87, 101634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, J.A.; Reynolds, J.F. Statistical Ecology: A Primer on Methods and Computing; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Pringle, J.D. Efficiency estimates for various quadrat sizes used in benthic sampling. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1984, 41, 1485–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, J.M.; Keough, M.J. Compositing and subsampling to reduce costs and improve power in benthic infaunal monitoring programs. Estuaries 2002, 25, 1053–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, M.; Schmiegelow, F. Cost-effective sampling design applied to large-scale monitoring of boreal birds. Conserv. Ecol. 2002, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wiegert, R.G. The selection of an optimum quadrat size for sampling the standing crop of grasses and forbs. Ecology 1962, 43, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, P.S.; Lemeshow, S. Sampling of Populations: Methods and Applications; Wiley Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Underwood, A.J.; Chapman, M.G. Design and analysis in benthic surveys. In Methods for the Study of Marine Benthos; Blackwell Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Gotelli, N.J.; Ellison, A.M. A Primer of Ecological Statistics; Sinauer Associates, Inc.: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh, T.C.; Ma, K.H.; Chao, A. iNEXT: An R package for rarefaction and extrapolation of species diversity (Hill numbers). Methods Ecol. Evol. 2016, 7, 1451–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langlois, T.J.; Harvey, E.S.; Fitzpatrick, B.; Mclean, D.L. Cost-efficient sampling of fish assemblages: Comparison of baited video stations and diver video transects. Aquat. Biol. 2010, 9, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bosch, N.E.; Gonçalves, J.M.S.; Erzini, K.; Tuya, F. “How” and “what” matters: Sampling method affects biodiversity estimates of reef fishes. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 7, 4891–4906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Stefano, J. How much power is enough? Against the development of an arbitrary convention for statistical power calculations. Funct. Ecol. 2003, 17, 707–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wigley, R.L. Comparative efficiencies of van Veen and Smith-McIntyre grab samplers as revealed by motion pictures. Ecology 1967, 48, 168–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raz-Guzman, A.; Grizzle, R.E. Techniques for quantitative sampling of infauna and small epifauna in seagrass. In Global Seagrass Research Methods; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherland, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Montagna, P.A.; Baguley, J.G.; Hsiang, C.-Y.; Reuscher, M.G. Comparison of sampling methods for deep-sea infauna. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2017, 15, 166–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thrush, S.F. Spatial patterns in soft-bottom communities. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1991, 6, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holte, B.; Buhl-Mortensen, L. Does grab size influence sampled macrofauna composition? A test conducted on deep-sea communities in the northeast Atlantic. Mar. Environ. Res. 2020, 154, 104867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dauvin, J.C.; Bellan-Santini, D. Illustrated key to Ampelisca species from the north-eastern Atlantic. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 1988, 68, 659–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, S.E.; Barry, J.; Nicholson, M. A comparative study of a 0.1 m2 and 0.25 m2 Hamon grab for sampling macrobenthic fauna from offshore marine gravels. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2006, 86, 1315–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayward, P.J.; Ryland, J.S. The Marine Fauna of the British Isles and North-West Europe. Vol. 1: Introduction and Protozoans to Arthropods; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Núñez, J.; San Marin, G.; Brito, M.C. Syllinae (Polychaeta. Syllidae) de las Islas Canarias. Rev. Acad. Canar. Cienc. 1992, 3, 109–129. [Google Scholar]
- González, J.A. Catálogo de los Crustáceos Decápodos de las Islas Canarias: Gambas, Langostas y Cangrejos; Turquesa: Canary Islands, Spain, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Brito, M.C.; Núñez, J.; Bacallado, J.J.; Ocaña, O. Anélidos Poliquetos de Canarias: Orden Phyllodocida (Chrysopetalidae, Pisionidae, Glyceridae, Sphaerodoridae, Hesionidae y Pilargidae). Monogr. Inst. Canar. Cienc. Mar. 1996, 13, 157–179. [Google Scholar]
- Capaccioni-Azzati, R. Prionospio multibranchiata (Polychaeta, Spionidae), Notomastus aberans y N. formianus (Polychaeta, Capitellidae) en el litoral de la Península Ibérica. Mis. Zool. 1988, 12, 47–56. [Google Scholar]
- Núñez, J.; Pascual, M.; Delgado, J.D.; Brito, M.C. Polychaetous Annelids from the Canary Islands: Family Eunicidae. Vieraea 1998, 26, 47–75. [Google Scholar]
- Corbera, J.; Brito, M.C.; Núñez, J.; Riera, R. Catálogo de los Cumáceos (Crustacea, Malacostraca) de las Islas Canarias. Rev. Acad. Canar. Cienc. 2001, 12, 67–73. [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz, M.; Jimeno, A. Guía lustrada para la identificación de las familias y los géneros de los anfípodos del suborden gammaridea de la península ibérica. Graellsia 2001, 57, 3–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual, M.; Núñez, J.; Brito, M.C.; Riera, R. Ctenodrilidos y cirratulidos (annelida: Polychaeta) asociados a demosponjas litorales de Canarias y Madeira. Rev. Acad. Canar. Cienc. 2002, 4, 49–59. [Google Scholar]
- Moro, L.; Martín, J.L.; Garrido, M.J.; Izquierdo, I. (Eds.) Lista de Especies Marinas de Canarias (Algas, Hongos, Plantas y Animales); Consejería de Política Territorial y Medio Ambiente del Gobierno de Canarias: Canary Islands, Spain, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Riera, R.; Guerra, J.M.; Brito, M.C.; Núñez, J. Estudio de los caprélidos de Lanzarote, Islas Canarias (Crustacea: Amphipoda: Caprellidea). Vieraea 2003, 31, 157–166. [Google Scholar]
- Sanz, M.C.; Riera, R.; Brito, M.C.; Núñez, J. Primera aportación al conocimiento de los tanaidáceos (Malacostraca: Tanaidacea) de las Islas Canarias. Rev. Acad. Canar. Cienc. 2003, 15, 69–76. [Google Scholar]
- Viéitez, J.M.; Alós, C.; Parapar, J.; Besteiro, C.; Moreira, J.; Núñez, J.; Laborada, J.; San Martín, G. Claves para el reconocimiento de familias de poliquetos. Annelida, Polychaeta I. In Fauna Ibérica; Museo Nacional de Ciencias Naturales: Madrid, Spain, 2004; Volume 25. [Google Scholar]
- Núñez, J.; Brito, M.C.; Docoito, J.R. Annelid Polychaetes from Canaries: Catalogue of species, distribution and habitats. Vieraea 2005, 33, 297–321. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, A.M.; Pires, A.; Mendo, S.; Quintino, V. Diopatra neapolitana and Diopatra marocensis from the Portuguese coast: Morphological and genetic comparison. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2009, 85, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, A.; Anadón, N.; Paxton, H. New records of Diopatra marocensis (Annelida: Onuphidae) from northern Spain. Zootaxa 2010, 2691, 67–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moro, L.; Herrera, R.; Ortea, J.; Riera, R.; Bacallado, J.J.; Martín, J. Aportaciones al conocimiento y distribución de los decápodos y estomatópodos (Crustacea: Malacostraca) de las Islas Canarias. Rev. Acad. Canar. Cienc. 2014, 16, 33–82. [Google Scholar]
- Borges, J.P.; Martins, A.M.F.; Ávila, S.P. Checklist of the littoral gastropods (Mollusca Gastropoda) from the Archipelago of the Azores (NE Atlantic). Biodivers. J. 2015, 6, 855–900. [Google Scholar]
- Herrera-Bachiller, A.; Fernández-Álvarez, F.A.; Junoy, J. A Taxonomic Catalogue of the Nemerteans (Phylum Nemertea) of Spain and Portugal. Zool. Sci. 2015, 32, 507–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Esquete, P.; Ramos, E.; Riera, R. New data on the Tanaidacea (Crustacea: Peracarida) from the Canary Islands, with a description of a new species of Apseudopsis. Zootaxa 2016, 4093, 248–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paxton, H.; Arias, A. Unveiling a surprising diversity of the genus Diopatra Audouin & Milne Edwards, 1833 (Annelida: Onuphidae) in the Macaronesian region (eastern North Atlantic) with the description of four new species. Zootaxa 2017, 4, 505–535. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, S.N. Generalized Additive Models: An Introduction with R; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hastie, T.J.; Tibshirani, R.J. Generalized Additive Models; CRC Press: Boca-Raton, FL, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Neuman, U.; Wright, S.; Warton, D.I. Mvabund: An R package for model-based analysis of multivariate abundance data. Meth. Ecol. Evol. 2012, 3, 471–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kindt, R.; Coe, R. Tree Diversity Analysis: A Manual and Software for Common Statistical Methods for Ecological and Biodiversity Studies; World Agroforestry Centre ICRAF: Nairobi, Kenya, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Venables, W.N.; Ripley, B.D. Modern Applied Statistics with S; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Rumohr, H.; Karakassis, I.; Jensen, J.N. Estimating species richness, abundance and diversity with 70 macrobenthic replicates in the Western Baltic Sea. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2001, 214, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gray, J.S. Okologie Mariner Sedimente; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Ellingsen, K.E.; Hewitt, J.E.; Thrush, S.F. Rare species, habitat diversity and functional redundancy in marine benthos. J. Sea Res. 2007, 58, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, J.M. Some Statistical Methods for the Statistical Analysis of Samples of Benthic Invertebrates; The Ferry House Ambleside, Westmorland; Freshwater Biological Association, Scientic Publication: Ambleside, UK, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Andrew, N.L.; Mapstone, B.D. Sampling and the description of spatial pattern in marine ecology. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. 1987, 25, 39–90. [Google Scholar]
- Downing, J.A. Aggregation, transformation, and the design of benthos sampling programs. J. Fish. Res. Board Can. 1987, 36, 1454–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newell, R.C.; Seiderer, L.J.; Robinson, J.E. Animal-sediment relationships in coastal deposits of the eastern English Channel. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2001, 81, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sorting (min) | Identifications (min) | Total (min) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | ||
| G1 | 29.85 | 8.84 | 14.03 | 9.65 | 43.88 |
| G2 | 43.48 | 14.57 | 32.70 | 14.88 | 76.18 |
| G3 | 75.98 | 32.34 | 33.68 | 21.30 | 109.66 |
| Coefficient | Estimate | SE | t Value | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 4.898 | 0.08 | 59.28 | 1 × 10−16 |
| Grab (G2) | −0.089 | 0.11 | −0.77 | 0.4428 |
| Grab (G3) | −0.111 | 0.14 | −0.75 | 0.4538 |
| Richness | 0.049 | 0.001 | 32.1 | 1 × 10−16 |
| Grab (G2) × Richness | 0.002 | 0.002 | 1.34 | 0.1913 |
| Grab (G3) × Richness | −0.007 | 0.002 | −2.84 | 0.009 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Álvarez, L.N.; García-Sanz, S.; Bosch, N.E.; Riera, R.; Tuya, F. Optimizing Costs to Collect Local Infauna through Grabs: Effect of Sampling Size and Replication. Diversity 2020, 12, 410. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12110410
Álvarez LN, García-Sanz S, Bosch NE, Riera R, Tuya F. Optimizing Costs to Collect Local Infauna through Grabs: Effect of Sampling Size and Replication. Diversity. 2020; 12(11):410. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12110410
Chicago/Turabian StyleÁlvarez, Lidia N., Sara García-Sanz, Néstor E. Bosch, Rodrigo Riera, and Fernando Tuya. 2020. "Optimizing Costs to Collect Local Infauna through Grabs: Effect of Sampling Size and Replication" Diversity 12, no. 11: 410. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12110410
APA StyleÁlvarez, L. N., García-Sanz, S., Bosch, N. E., Riera, R., & Tuya, F. (2020). Optimizing Costs to Collect Local Infauna through Grabs: Effect of Sampling Size and Replication. Diversity, 12(11), 410. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12110410







